How to get rid of gas while pregnant
8 best home remedies for gas during pregnancy
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission Here’s our process.
Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Read more about our vetting process.Many women experience gas during pregnancy. It usually goes away on its own, but home remedies can help ease discomfort and reduce the quantity of gas.
Raised levels of the hormone progesterone relax the intestines during pregnancy. This relaxation slows digestion, making constipation more likely and often leading to bloating, belching, and flatulence.
A woman may also experience more gas during the later stages of pregnancy, when the growing fetus places additional pressure on the abdominal cavity.
While it is impossible to prevent gas during pregnancy, several safe home remedies can reduce gas and relieve discomfort. Many of these prevent constipation, which significantly contributes to gas.
Share on PinterestHigher levels of progesterone during pregnancy can slow digestion and cause gas.The United States National Academy of Medicine, formerly the Institute of Medicine, recommend that pregnant women drink around 10 cups, or 2.3 liters, of water a day.
Drinking water before or after a meal helps the stomach digest food. Any undigested food passes into the small intestines, where bacteria break it down, producing gas in the process. Staying hydrated can, therefore, help reduce the buildup of gas.
Any undigested food passes into the small intestines, where bacteria break it down, producing gas in the process. Staying hydrated can, therefore, help reduce the buildup of gas.
Hydration can also prevent constipation, another cause of gas. When a person is dehydrated, their stool becomes dry and hard. Drinking plenty of water keeps stool soft, helping it pass more easily through the colon.
Also, it is best to sip slowly, rather than gulp. People are more likely to swallow air when they gulp, which can contribute to gas.
Some people experience gas when they drink beverages containing the following ingredients:
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a gas in a wide range of drinks, including:
- cola and other sodas
- carbonated energy drinks
- sparkling (fizzy) waters, including tonic water
People get rid of most of this gas through belching, but carbon dioxide can also cause flatulence.
The added sugars or artificial sweeteners in many carbonated drinks can also contribute to intestinal gas.
Fructose
Fructose is a natural sugar that occurs in most fruits. Manufacturers often add fructose to a variety of desserts and drinks.
Some people are unable to digest fructose. In this case, the sugar can ferment in the large intestine, causing gas and bloating. The medical term for this digestive disorder is fructose malabsorption.
Sorbitol
Sorbitol is a low-calorie sugar substitute. However, the body is unable to digest sorbitol. Some people experience abdominal pain, bloating, and gas as a result.
During pregnancy, many women choose to eat a more healthful diet. Many healthful foods are rich in fiber, and adding them to the diet can increase the amount of gas in the short term.
Some high-fiber foods also contain complex carbohydrates called oligosaccharides. When bacteria in the gut break down oligosaccharides, they produce nitrogen gas. Some people are more sensitive to this effect than others.
Foods that contain oligosaccharides include:
- beans
- whole grains
- cabbage
- cauliflower
- Brussels sprouts
- asparagus
Keeping a food diary can help to show whether any foods are contributing to the severity of gas.
Share on PinterestIt is important to drink plenty of fluids when adopting a high-fiber diet.
Although high-fiber foods can increase gas in the short term, over time they help to reduce constipation, which is a major cause of intestinal gas.
Fiber achieves this by drawing in water and softening stool. This eases its passage through the intestines, speeding digestion and giving gas less time to build up.
If a person is switching to a high-fiber diet, the following strategies can help prevent temporary increases in gas:
- raising the fiber intake gradually over a period of months
- eating only small portions of high-fiber foods to allow sufficient time for digestion
- chewing food thoroughly so that it is easier for the stomach to digest
- drinking plenty of fluids, ensuring that there is enough water to soften fibrous stools
Fiber supplements can help relieve gas by reducing constipation.
A 2015 systematic review found that pregnant women who took these supplements had more frequent bowel movements and better stool consistency than those who did not. The authors noted that confirming these findings will require more research. Speak to a doctor before taking any supplements while pregnant or breastfeeding.
The authors noted that confirming these findings will require more research. Speak to a doctor before taking any supplements while pregnant or breastfeeding.
Fiber supplements are available to purchase online.
Research suggests that exercise can speed up digestion and relieve constipation.
A 2012 study of 49 healthy adults found that moderate and high levels of physical activity improved colon transit in females, but not males.
Colon transit is the amount of time it takes for stool to pass through the large intestine.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that healthy pregnant women get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, per week. It is best to divide this activity over multiple days.
The CDC also recommend that women who do high-intensity aerobic activity, such as running, ask their doctors how to adjust their exercise regimes during pregnancy.
Clothes that are tight around the waist can put added pressure on the abdomen, which may increase the buildup of gas.
Wearing loose-fitting maternal wear in the later stages of pregnancy can help to alleviate this problem.
Share on PinterestMeditation and yoga can aid relaxation during pregnancy.
Some people experience worse gas when they are stressed.
This may be because people tend to gulp down air when they are anxious. Stress-related gas can also be a symptom of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
IBS is a gastrointestinal disorder that causes abdominal pain and changes in bowel habits. Other symptoms can include:
- bloating
- gas
- cramping
- constipation
- diarrhea
Although the exact cause of IBS is unknown, research suggests that stress can trigger symptoms.
Women who experience stress-induced gas during pregnancy may benefit from stress-management and relaxation therapies, such as meditation and yoga.
A 2016 review of evidence suggests that yoga can be a safe and effective treatment for people with IBS symptoms, though the researchers note that further high-quality studies are needed.
A pregnant woman may feel discomfort from gas and bloating, but these symptoms rarely affect the baby.
However, consult a doctor if gas accompanies:
- severe abdominal pain lasting longer than 30 minutes
- constipation lasting longer than 1 week
- diarrhea lasting longer than 2 days
- black or bloody stools
- nausea and vomiting
These symptoms can indicate a more serious underlying issue, so a doctor’s evaluation is important.
Increased gas during pregnancy is common. While it can be uncomfortable and even painful, it is rarely a cause for concern.
Certain lifestyle and dietary changes can help, including drinking plenty of fluids, keeping a food diary, and exercising regularly. Many of these remedies focus on preventing constipation, which is a significant cause of gas.
See a doctor if painful and persistent episodes of gas, or other concerning symptoms, occur during pregnancy.
6 positions to relieve pregnancy gas
Bodily changes during pregnancy can slow down digestion and cause gas, which can lead to pain. However, there are several yoga poses and body positions to help relieve gas during pregnancy.
However, there are several yoga poses and body positions to help relieve gas during pregnancy.
If a person has gas, they may experience:
- burping
- passing gas, or “farting”
- pain in the stomach
- bloating
- distention, or increased size, of the stomach
Changing hormones due to pregnancy can trigger bloating. In a pregnant person, trapped gas does not affect the fetus, and there are many ways to relieve the pain associated with gas.
This article explores different yoga poses and body positions a person can try to relieve gas during pregnancy.
Pregnant people should always check with a doctor before attempting new stretches or types of physical activity.
Child’s Pose can help the stomach move in a way that could help trapped gas move through the digestive tract.
- Start on all fours with the legs together or apart.
- Move the hands forward and move the body backward as far as possible to move the buttocks towards the heels.

- Position the forehead as close as possible to the ground.
- Hold for 30 seconds to 5 minutes.
The stomach should gently rest on the mat or legs if possible.
When a person twists their body, it can help put pressure on their core and alleviate trapped gas.
Standing twist
- Stand upright with the feet shoulder-width apart. If necessary, hold on to a wall or ledge for stability.
- Keeping the feet planted firmly on the floor, gently twist the torso.
Seated twist
- Sit upright with the legs stretched in front of the body.
- Keeping the buttocks planted firmly on the floor, gently twist the torso.
Share on Pinterest
In a forward fold, the stomach should rest gently on the legs or mat if possible.
A person can assume this position with the legs apart if it feels more comfortable.
- Sit upright with the legs straight out in front of the body.
- Slowly and gently bend forward with the upper torso from the hips, keeping the legs straight.

Share on PinterestKohei Hara/Getty Images
Squats can help relieve gas by shifting pressure throughout the stomach, allowing it to move through the body. This can cause a person to pass the gas.
People can also hold on to something for stability, such as a wall or a ledge if needed.
People can also use a block under their buttocks as a seat for support.
- Stand with the feet as far apart as feels comfortable.
- With the feet facing slightly outwards, bend the knees in line with the toes.
- Keep the weight on the heels and squat down gently.
Share on Pinterest
Some people refer to the Knee to Chest Pose as the Wind-Relieving pose.
A pregnant person should not hold this or any position that involves lying on the back for extended periods.
- Lie on the back, clasping the knees.
- Slowly pull the knees up towards the chest as far as possible.
- Tuck the chin to the chest.
Share on Pinterest
Happy Baby Pose can be an effective way of relieving trapped gas.
However, again, a pregnant person should avoid lying on their back for an extended period.
- Lie on the back.
- Lift the knees up towards the sides of the body as far as possible.
- Hold the feet with the hands if possible, or use a yoga strap.
- Relax the back on the floor.
A 2016 review suggests that yoga may be a safe and beneficial treatment option for people experiencing symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. However, this study also involved non-pregnant people, which may have led to unreliable results.
It also states that further research would be necessary to recommend it fully, given the flaws in study methods.
Yoga is a suitable way for a person to remain active during pregnancy, but only when using modified exercises for those who are pregnant.
For example, individuals should avoid standing still or lying on their back for long periods, as it may lead to a drop in blood pressure.
Pregnant people should also avoid overheating, as it can increase the risk of congenital disabilities. This may mean avoiding certain styles of yoga, such as Bikram or hot yoga.
This may mean avoiding certain styles of yoga, such as Bikram or hot yoga.
Along with moving the body into different positions, there are other techniques to help relieve pregnancy gas.
Medications
A person should speak to their doctor before taking over-the-counter medications to ensure they will not affect the fetus. One example of these medicines is simethicone, or simeticone.
Food and drink
Certain foods can help settle stomachs and relieve gas.
According to a 2015 study, ginger could help ease symptoms of stomach pain and bloating. In the experiment, participants taking a ginger and artichoke supplement experienced a greater improvement in indigestion symptoms than those receiving a placebo.
A person can eat ginger in food or drink it in ginger tea.
A person should also make sure that they stay hydrated to try to combat bloating and gas.
Find out more about how food can affect pregnancy gas here.
Exercise
Where possible, people can also take part in physical activity to alleviate the symptoms of gas.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that a pregnant person participates in at least 150 minutes of exercise spread over several days each week where possible. This can be as simple as brisk walking.
Learn more about exercising during pregnancy here.
If a person wishes to prevent developing gas, they should avoid the following:
- Carbonated drinks: One of the main ingredients in fizzy drinks is carbon dioxide, which causes a person to experience gas.
- Certain foods: Some foods can increase the likelihood of developing gas, such as:
- fried or fatty foods
- cabbage
- cauliflower
- beans
- dairy products
People who are pregnant should also avoid taking Alka Seltzer. Aspirin, one of the ingredients in Alka Seltzer, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). The Food & Drug Administration (FDA) state that people should talk with a doctor before taking NSAIDs at or after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Learn more about home remedies that can help reduce gas in pregnancy here.
A pregnant person should contact their doctor immediately if they have any of the following symptoms alongside gas:
- regular, contraction-like pain or severe pain every 5–10 minutes
- nausea
- vomiting
- bloody stools
- diarrhea
When performing yoga, a pregnant person should contact a doctor immediately if they experience any of the following:
- blood or fluid from the vagina
- dizziness
- chest pain
- headache
- weakness
- calf pain or swelling
- regular, contraction-like pain
Pregnancy gas can be an irritating symptom, but it is harmless. There are many ways of moving the body to help relieve the condition. In addition, alternative methods, such as medications or dietary adjustments, may also help prevent or treat it.
Before engaging in any exercise routine, people should discuss it with their healthcare provider to confirm it is suitable for them and their pregnancy.
Bloating and Pregnancy - Espumizan®
Contents
- Introduction
- Causes
- How to deal with bloating?
- Helpful tips for expectant mother
- Treatment with Espumizan ®
Bloating during pregnancy
Pregnancy is an important and responsible period in a woman's life. After all, along with the fact that her body is being rebuilt for the birth of a new life, the baby from the very beginning must receive all the necessary substances for future development. However, during pregnancy, such an unpleasant phenomenon as bloating can occur. According to one study, symptoms of bloating were observed in 49% of cases in pregnant women.
Why can a woman experience bloating during pregnancy?
Unfortunately, for most pregnant women, stomach cramps and bloating are part of this special time. What are the reasons for this state of affairs? Pregnancy brings with it many changes. The level of hormones that help the child grow dramatically increases. One of the unfortunate effects of rising hormone levels is a feeling of bloating caused by excess gas.
In the early stages of pregnancy, hormones, preparing a woman for future motherhood, are produced and released in large quantities. This contributes to the growth of the inner lining of the uterus, which supplies the baby with the necessary nutrients. However, the hormones progesterone and estrogen also have other effects. Progesterone relaxes the muscles, slowing down digestion. Therefore, food is poorly digested, and as a result, excessive gas formation occurs. Elevated estrogen levels can have a similar effect and also lead to water retention, causing pain and bloating.
During late pregnancy, the uterus grows and changes shape and position. Its movement can affect other organs, causing constipation and excess gas, causing bloating.
How to deal with bloating during pregnancy?
What measures can be taken to prevent bloating during pregnancy? Below you will find some simple tips.
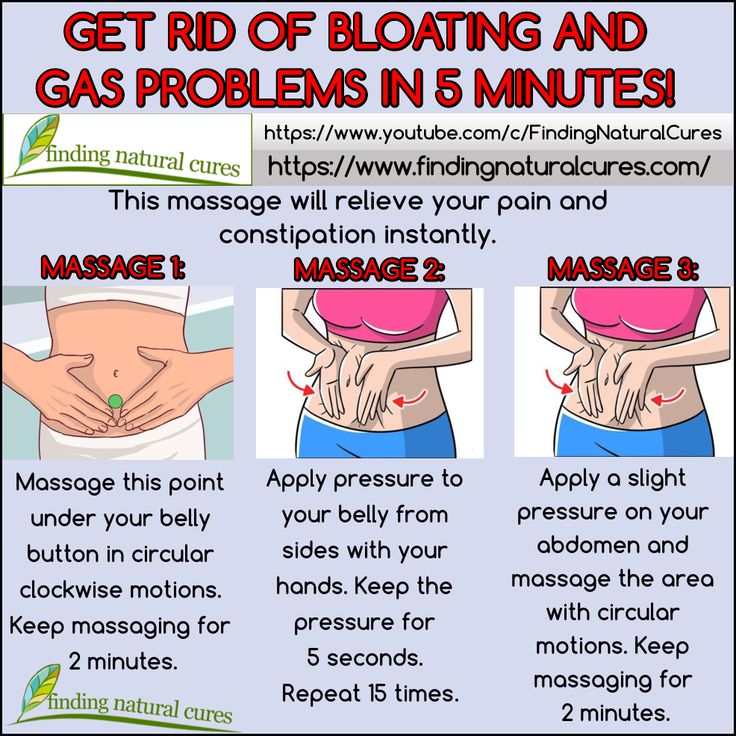
Adjust power supply . It is better to switch to fractional eating - more often and in smaller portions. In order to avoid flatulence, try to limit the consumption of black bread, legumes, cabbage. That is, those products that cause increased gas formation. Improvement of well-being contributes to drinking plain water (which is always useful).
A a slight increase in physical activity also helps to improve digestion and remove accumulated gases.
However, if bloating continues to bother you, you can try Espumizan ® . Espumizan ® is an assistant for bloating. The active substance simethicone, "collapsing" gas bubbles in the body, relieves the symptoms of flatulence. In addition, Espumizan ® can be used not only in pregnant women, but also in lactating women, since the active substance acts only in the intestinal lumen and is not absorbed into the body.
In addition, Espumizan ® can be used not only in pregnant women, but also in lactating women, since the active substance acts only in the intestinal lumen and is not absorbed into the body.
Proper nutrition
water consumption
moderate physical activity
Useful tips for a future mother
Pregnancy is an important period in a woman's life. After all, it is then that the health and intellectual potential of the future baby are laid. That is why it is so important to maintain a healthy lifestyle during this period and visit your obstetrician - gynecologist, who will monitor your pregnancy and make recommendations if necessary. What exactly refers to the right way of life?
What exactly refers to the right way of life?
- Try to avoid exercise
- Throughout pregnancy, obstetrician-gynecologists recommend taking folic acid and iodine at a dose of 220-250 mcg per day . This is due to the fact that our country is an unfavorable region in terms of iodine supply. Iodine, as is known, ensures the formation of the intellectual potential of the child and reduces the risk of such formidable complications of pregnancy as miscarriage and stillbirth. Why is it so important to provide a sufficient amount of iodine to the body of a pregnant woman, you can find out here .
If you are interested in knowing how the baby's body develops throughout pregnancy, you can download pregnancy calendar here .
Nutritionally, it is important to eat right and regularly: consume food with sufficient energy content with an optimal content of protein, vitamins and minerals, with the obligatory inclusion of meat, fish, legumes, nuts, fruits and whole grains in the diet. If some fruits, legumes and cereals make you bloated, then Espumizan can come to the rescue ® , which, by "collapsing" gas bubbles, relieves the symptoms of flatulence. Espumizan ® can be used in pregnant women, as the active substance is completely inert. It acts only in the intestinal lumen, is not absorbed into the blood and does not affect the body of either the expectant mother or the baby.
If some fruits, legumes and cereals make you bloated, then Espumizan can come to the rescue ® , which, by "collapsing" gas bubbles, relieves the symptoms of flatulence. Espumizan ® can be used in pregnant women, as the active substance is completely inert. It acts only in the intestinal lumen, is not absorbed into the blood and does not affect the body of either the expectant mother or the baby.
Espumizan ® – help with bloating!
Espumizan ® can help manage bloating.
The active ingredient in simethicone has been shown to reduce symptoms of flatulence within 30 minutes of ingestion. In addition to capsules and drops, the Espumizan ® line includes an instant form of granules - Espumizan ® extra. Since the granules dissolve faster than other solid drug forms (tablets or capsules), Espumizan ® Extra can help manage the symptoms of flatulence even faster.
Espumizan ® is a wide range of drugs with a variety of formulations for different needs.
Espumizan ® is presented in 3 forms: Espumizan ® in drops, in capsules and in granules. The variety of forms is very convenient, as it gives the patient a choice.
Espumizan ® capsules are attractive because the small capsules are easy to swallow. This form has shown its effect in the treatment of flatulence and was included in the official recommendations for the qualitative preparation of patients for ultrasound (ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs) by the Russian Association of Ultrasound Diagnostics in Medicine (RASUDM). You can learn more about this here .
For those who prefer to deal with problems as quickly as possible, and also gravitate towards convenience and innovation, there is a form of Espumizan ® extra. Espumizan ® extra contains 3 times more active ingredient than 1 capsule. Thanks to this, a single dose is 1 sachet and is especially suitable for people with severe flatulence. The fast-dissolving granule form provides faster action compared to other solid dosage forms (tablets and capsules). And the small bags in which Espumizan 9 is packed0017 ® extra, make the reception comfortable and, if necessary, invisible to others. Agree, this is very convenient, especially if such a delicate problem as flatulence caught you in a public place.
Thanks to this, a single dose is 1 sachet and is especially suitable for people with severe flatulence. The fast-dissolving granule form provides faster action compared to other solid dosage forms (tablets and capsules). And the small bags in which Espumizan 9 is packed0017 ® extra, make the reception comfortable and, if necessary, invisible to others. Agree, this is very convenient, especially if such a delicate problem as flatulence caught you in a public place.
For those who prefer the form of drops (liquid forms), there is Espumisan ® L, 1 ml (or 25 drops) of which contains the same amount of active ingredient as 1 capsule of Espumisan ® . The bottle of Espumizan ® L is equipped with a measuring cap, which makes it easy to measure the exact number of drops.
Espumizan ® is primarily a high safety profile. It can be used even in pregnant and lactating women.
Simethicone is an inert substance that acts only in the intestinal lumen and is then excreted unchanged from the body. It is not absorbed into the bloodstream and does not have any negative effect on the body, so it is approved for use even in pregnant or lactating mothers.
It is not absorbed into the bloodstream and does not have any negative effect on the body, so it is approved for use even in pregnant or lactating mothers.
Contains no lactose, which is especially important for the elderly. The fact is that with age, the activity of the enzyme that breaks down lactose decreases. Therefore, when using drugs with the addition of lactose as a preservative, such a side effect as discomfort and bloating is possible.
Espumizan ® can be taken by people with diabetes as it does not contain sugar.
When the stomach is swollen with gas - Espumizan ® take immediately!
Espumizan
®capsules
The drug can help relieve the symptoms of bloating that occur after a heavy meal and fatty foods, during stress or during menstruation.
Learn more
Espumizan ® - different forms for different needs
-
Espumizan
® extra granules 125 mgLearn more
• An innovative formulation in instant granules to relieve flatulence in any situation.

• Do not drink water. -
Espumizan
® L 30 ml vialLearn more
• Easy-to-take liquid form with measuring cap for counting drops.
-
Espumizan
® baby 30 and 50 ml bottleLearn more
• Specially formulated for the treatment of colic in children.
• From the first weeks of life.
Flatulence during pregnancy | Motilegaz®
Many expectant mothers experience ailments associated with changes in their body. One of the problems at all stages of pregnancy is excessive gas formation (flatulence), causing bloating and discomfort 1 .
Why bloating occurs during pregnancy
The main cause of increased gas production during pregnancy is changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract of the expectant mother 1, 2 . From the moment of fertilization of the egg, the woman's body completely rebuilds its work in order to ensure the preservation of the pregnancy and the development of the baby.
From the moment of fertilization of the egg, the woman's body completely rebuilds its work in order to ensure the preservation of the pregnancy and the development of the baby.
One of the changes is a slowdown in the motor function of the intestine, which is responsible for the movement of food 1 .
The increase in progesterone levels during pregnancy plays a leading role in the restructuring of the digestive tract 2 . Thus, the woman's body reduces premature contractile activity of the uterus and prevents the threat of interruption 3 . This is due to the property of the hormone to reduce the activity of smooth muscles. The fact is that progesterone acts on the smooth muscles of not only the uterus, but also other organs - the gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract. This leads to a drop in the tone and motor activity of the intestine 2, 4 . As a result, the accumulation of food in the intestines causes an increased formation of gases. Flatulence is often accompanied by bloating, belching, a woman may develop a tendency to constipation 4 . In this case, constipation becomes another factor that is responsible for increased gas formation and bloating 2, 4 .
Flatulence is often accompanied by bloating, belching, a woman may develop a tendency to constipation 4 . In this case, constipation becomes another factor that is responsible for increased gas formation and bloating 2, 4 .
It is the increase in progesterone levels that is the main cause of flatulence during pregnancy in the 1st trimester. The manifestations of flatulence in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy may be aggravated by additional factors 1 .
Among them are 2, 4 :
- Lack of physical activity.
- Unbalanced diet.
- The pressure exerted by the growing uterus on the stomach and intestines.
- Continued rise in progesterone levels.
In addition, in the late stages of pregnancy, blood circulation in the vessels of the small pelvis is noticeably disturbed. Experts note that this also affects the work of the digestive tract. Its peristalsis is significantly slowed down, which leads to increased fermentation processes in the intestines and excessive formation of gases 1 . At this time, the likelihood of constipation increases. According to some reports, 30-40% of pregnant women suffer from them 5 .
At this time, the likelihood of constipation increases. According to some reports, 30-40% of pregnant women suffer from them 5 .
Symptoms of flatulence during pregnancy
Symptoms of flatulence in pregnancy are associated with excessive formation of gases in the intestines, usually accompanying constipation. Bloating during the first trimester of pregnancy, according to various sources, is indicated by 49 to 66% of women 1 . Main manifestations of this disorder 6 :
- Subjective sensation of excess gas in the intestines.
- Feeling of bloating without obvious visible bloating.
- Full feeling.
- Discomfort in the stomach.
As a rule, bloating is not dangerous for the health of the pregnant woman and the baby, but pain can cause concern for the expectant mother.
In case of pain of any nature (aching, stabbing, cramping) in the lower abdomen, including accompanied by discharge, it is important to immediately consult a specialist 5 .
How to Reduce Gas During Pregnancy
Medication options during pregnancy are limited. To prevent increased gas formation, it is worth first considering the available non-drug methods aimed at preventing and treating constipation, as well as reducing gas formation.
However, it is important to remember that in case of any comorbidities or concerns, a specialist should be consulted for advice and recommendations 5 .
Diet correction
Expectant mother needs to reconsider nutrition — in many respects, it is a balanced diet that is the key to the health of both herself and her baby 4 . In addition, compliance with general recommendations on nutrition for constipation and fermentation processes in the intestines will help prevent bloating and flatulence during pregnancy 4, 6 :
- Make sure your diet is optimal in protein, vitamins and minerals 5 .
- Be sure to include meat, fish, nuts, and fruits, vegetables, and whole grains that are rich in dietary fiber 3, 4 .

Drinking regimen
If you are prone to constipation and flatulence during pregnancy, it is important to follow the recommendations for drinking regimen 7 . Monitor fluid intake - unless there are special contraindications (for diseases of the kidneys, heart), most pregnant women require at least 300 ml of additional fluid intake per day 7 . On average, it is recommended to drink 8-10 glasses of water 7 . Water helps digest food and also prevents constipation 7 .
Physical activity
In the absence of complaints and contraindications for a pregnant woman, it is important to maintain a feasible level of physical activity 5 . It is known that its reduction can increase the risk of constipation in expectant mothers, which in turn increases the risk of developing bloating. 2
- Try to walk in the fresh air.
- Do Pregnancy Exercise for 20-30 minutes daily.
How to Get Rid of Gas During Pregnancy
If increased fiber intake, fluid intake, and exercise do not help with flatulence, it is important to see a pregnancy care professional. It will help to choose a drug, taking into account its tolerability, the absence of adverse effects on the fetus, the condition of the woman and possible risks 2 .
One of the drugs that help reduce the manifestations of bloating and flatulence is the over-the-counter drug Motilegaz® Forte - a drug whose active ingredient is simethicone 8 . Simethicone is a chemically inert substance that does not enter into chemical reactions and is not absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, but is excreted from the body unchanged 7 .
The action of simethicone is based on its physical properties. A thin film of this substance is distributed on the surface of the foam bubbles in the intestines and destroys them, releasing gas, which is then excreted naturally * 7 .
Before using Motilegaz® Forte, you should always consult with your doctor. The specialist will assess the possible risks, weigh the expected benefits of using the drug for the expectant mother and make an informed decision 8 .
The article is for informational purposes and is not a recommendation or instruction for use. If you have any questions about the use of the drug Motilegaz® Forte, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
Literature
- 1. Johnson P., Mount K., Graziano S. Functional bowel disorders in pregnancy: effect on quality of life, evaluation and management // Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica, 2014. No. 93(9) . PP. 874–879. URL: https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/aogs.12434 (accessed 11/26/2022).
- 2. Shi, W., Xu, X., Zhang, Y., Guo, S., Wang, J., & Wang, J. Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Functional Constipation in Pregnant Women // PLOS ONE. No. 10(7).
 URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4514689/ (date of access: 11/26/2022).
URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4514689/ (date of access: 11/26/2022). - 3. Obstetrics: national guidance / ed. E.K. Ailamazyan, V.I. Kulakova, V.E. Radzinsky, G.M. Savelyeva. 2nd ed. Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2009.
- 4. Trottier M., Erebara A., Bozzo P. Treating constipation during pregnancy. Canadian Family Physician. 2012. Aug No. 58(8). pp. 836-838. URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3418980/ (accessed 09/18/2022).
- 5. Normal pregnancy (clinical recommendations) // Obstetrics and gynecology: News. Opinions. Learning. 2020. No. 4 (30). URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/normalnaya-beremennost-klinicheskie-re... (Date of access: 18.09.2022).
- 6. Cangemi D.J., Lacy B.E. A Practical Approach to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Abdominal Bloating and Distension // Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2022. No. 18(2). pp. 75–84. URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9053509/ (accessed 11/26/2022).
- 7.