Brace for hip dislocation
How to Choose a Hip Brace [Explained by a Nurse]
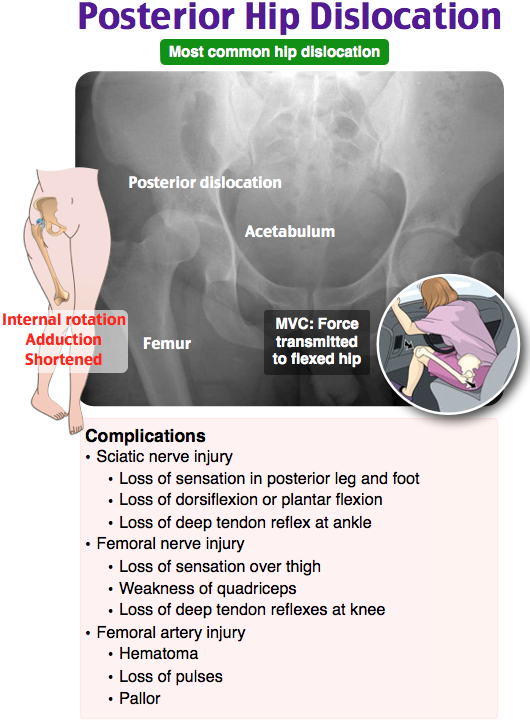
The hip joint is made up of the ball at the end of the thigh bone and the socket in the pelvis. It takes a lot of force to injure this joint, but when it is affected by strains, bursitis, dislocation, fractures, arthritis, or osteoporosis, it can cause pain and severely diminish mobility and range of motion. More than 300,000 seniors are hospitalized each year because of hip fractures, and hip dislocation from trauma is also not uncommon. Supporting the hip with a brace improves stability and mobility and helps users be more comfortable conducting daily life activities.
What is a Hip Brace Used For?
A hip brace promotes healing by keeping the hips level, restricting motion, and holding the thigh bone in the hip socket, and can be used to address a variety of conditions. Certain models can also keep knees and hips separated at a prescribed angle.
Hip Brace After Surgery
Hip replacement surgery, also called total hip arthroplasty, is most commonly used to address pain and limited mobility caused by arthritis. After surgery, certain positions can cause the ball of the hip joint to come out of the socket. Usually after surgery, a hip abduction brace needs to be worn to restrict excessive motion and hold the leg out to the side, which limits the amount you can bend your leg forward and move it across your body. A hip abduction brace is worn outside of clothing. It has two harder pieces, one on the outside of the waist and one on the thigh, each lined with a cushioned pad and each with a strap. The two pieces are connected by a hinged joint on the outside, which is adjusted according to the doctor’s instructions. One strap goes around the waist and the other around the thigh to hold it in place. A hip abduction brace is usually worn 24 hours a day for 2 to 4 weeks following surgery, helping stabilize the joint and allowing the soft tissue in the area to heal as well.
Hip Brace for Dislocation
Most hip dislocations are caused by car accidents or following a hip replacement when the femoral head escapes the socket because of overreaching range of motion, especially in the first three months after surgery.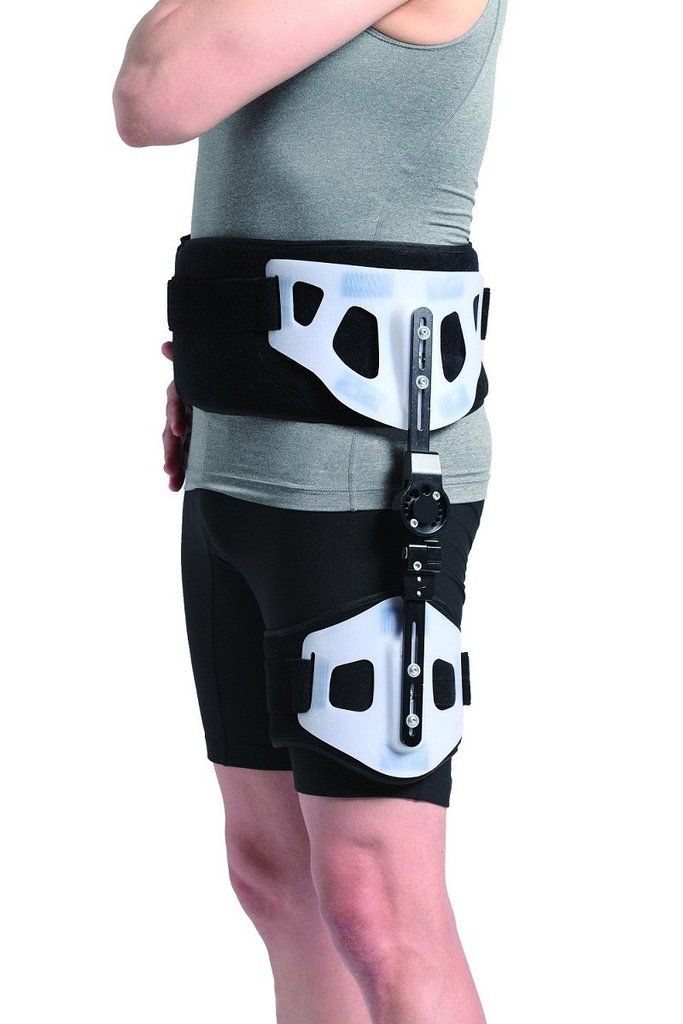 A hip abduction brace is used to prevent the leg from making excessive movements away from the body and eliminate the risk of hyperflexion, where the knee moves toward the chest. It’s worn to stabilize the joint for a few weeks up to a few months after the dislocation. It should always be worn if you are using crutches, and doesn’t need to be worn while sleeping, toileting, showering, laying on your stomach, or while icing your hip. As noted previously, this type of brace is worn outside of clothing. It has a hard piece with a cushioned pad and a strap on the outside of the waist and another on the thigh. The two pieces are connected by an arm joint on the outside, which is adjusted according to the treatment plan. One strap goes around the waist and the other around the thigh to hold it in place.
A hip abduction brace is used to prevent the leg from making excessive movements away from the body and eliminate the risk of hyperflexion, where the knee moves toward the chest. It’s worn to stabilize the joint for a few weeks up to a few months after the dislocation. It should always be worn if you are using crutches, and doesn’t need to be worn while sleeping, toileting, showering, laying on your stomach, or while icing your hip. As noted previously, this type of brace is worn outside of clothing. It has a hard piece with a cushioned pad and a strap on the outside of the waist and another on the thigh. The two pieces are connected by an arm joint on the outside, which is adjusted according to the treatment plan. One strap goes around the waist and the other around the thigh to hold it in place.
Hip Brace for Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease and is the most common form of hip arthritis.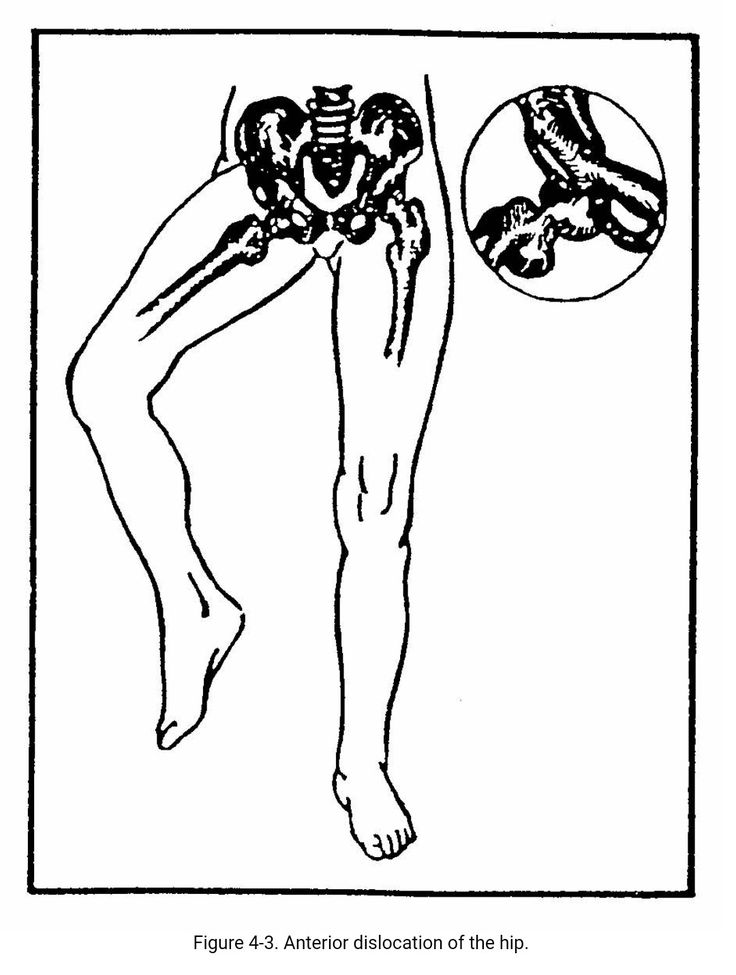 It breaks down cartilage from wear and tear, getting worse as we age, causing painful inflammation. Bracing for osteoarthritis of the hip is commonly known as offloading or unloading. The joint is stabilized through compression to keep it correctly aligned while dispersing the weight bearing load. These braces can reduce the compressive joint reaction force, decreasing the internal rotation and abduction to relieve pain. The compression also helps increase blood flow and decrease swelling. These braces are usually lightweight and can be worn under your clothes while performing everyday activities. They may be prescribed for activities or for 24-hour-a-day wear, depending on your situation. They are often slipped on the thigh and wrap around the waist. For sacroiliac pain, a belt that limits the movement of the Si joint does not have a leg component, and instead is a stretchy wrap worn snuggly around the hips.
It breaks down cartilage from wear and tear, getting worse as we age, causing painful inflammation. Bracing for osteoarthritis of the hip is commonly known as offloading or unloading. The joint is stabilized through compression to keep it correctly aligned while dispersing the weight bearing load. These braces can reduce the compressive joint reaction force, decreasing the internal rotation and abduction to relieve pain. The compression also helps increase blood flow and decrease swelling. These braces are usually lightweight and can be worn under your clothes while performing everyday activities. They may be prescribed for activities or for 24-hour-a-day wear, depending on your situation. They are often slipped on the thigh and wrap around the waist. For sacroiliac pain, a belt that limits the movement of the Si joint does not have a leg component, and instead is a stretchy wrap worn snuggly around the hips. In addition, these braces are often part of pre-surgery treatment for people who are having hip replacements.
In addition, these braces are often part of pre-surgery treatment for people who are having hip replacements.
Hip Brace for Sciatica
Sciatica causes radiating pain along the sciatic nerve, which goes from the lower back through the hips and bottom then down each leg. It most commonly occurs when a herniated disk, bone spur, or spinal stenosis compresses the sciatic nerve causing inflammation, pain, and numbness. A hip or lumbar brace with groin support can be worn over the lower back as needed for short amounts of time to help stabilize and support the area. These are worn under clothing, made of breathable material, and are adjustable for an appropriate fit.
Hip Brace for Sports
Hip pain and instability can be caused by sports and other physically strenuous activities. In these cases, a small amount of support and compression can provide relief from pain and discomfort by providing stability, correcting alignment, and ensuring proper joint positioning. Hip braces for sports range from lightweight neoprene hip wraps to thigh sleeves with a waist wrap to more substantial pieces with external hinged thigh bracing. Some wraps can be worn during exercise to provide compression to help torn or strained hip flexor muscles or decrease pain from sciatica, but most of the time they are worn after exercise to provide a bit of compression and support during muscle recovery.
Hip braces for sports range from lightweight neoprene hip wraps to thigh sleeves with a waist wrap to more substantial pieces with external hinged thigh bracing. Some wraps can be worn during exercise to provide compression to help torn or strained hip flexor muscles or decrease pain from sciatica, but most of the time they are worn after exercise to provide a bit of compression and support during muscle recovery.
What Are The Types of Hip Braces?
Hip Abduction Brace
An abduction brace is the most popular type of hip brace, and it’s worn outside at least one layer of clothes. The waist section is slid under the user’s waist while the leg is carefully lifted into the thigh section. The straps from the waist and thigh sections are fastened and adjusted to maintain proper alignment, and the hinged bracing limits the movement of the hip joint.
Pros
- Promotes healing of the soft tissues around the hip
- Allows user to get out of bed and move around while recovering
- Highly adjustable for a customized individual fit
Cons
- Potential for pressure sores where the brace rests
- Does not completely restrict movement, so re-injury is possible without user compliance
Best: TLC Hip Abduction Brace
Bilateral Hip Brace
Also called a double hip brace, a bilateral hip brace supports both the left and right leg and hip. This brace can be used before and after surgery, for anterior and posterior hip dysplasia, hip revisions, and mild to moderate osteoarthritis in the hip. This design provides flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction. These braces are sometimes hard sided and sometimes soft sided, with thigh sleeves and straps for both legs connected to the section that wraps around the waist.
This brace can be used before and after surgery, for anterior and posterior hip dysplasia, hip revisions, and mild to moderate osteoarthritis in the hip. This design provides flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction. These braces are sometimes hard sided and sometimes soft sided, with thigh sleeves and straps for both legs connected to the section that wraps around the waist.
Pros
- Delivers off-loading with stabilization of hip joints
- Reduces muscles contracture while supporting the hips
- Controlling range of motion and hip immobilization can effectively stop joint degeneration and reduce pain
Cons
- Not always easy to get a perfect fit
- Prescriptions are often required for shipping to residential addresses
Best: Newport 4 Hip Orthosis
Hip Compression Wrap
Compression is one of the best treatments for overuse injuries and can help muscles recover faster through increased circulation to an area. These hip compression wraps are also known as hip and groin compression wraps, and they range in price from $25 to $100. Although it’s not necessary to pay the highest price to get a quality product, the lowest end of the range are not made as well and are not as durable as those priced in the middle of the range.
These hip compression wraps are also known as hip and groin compression wraps, and they range in price from $25 to $100. Although it’s not necessary to pay the highest price to get a quality product, the lowest end of the range are not made as well and are not as durable as those priced in the middle of the range.
Pros
- Lightweight and can be comfortably worn for extended periods of time
- Provides warmth and compression
- Isolates and supports thigh muscles and joints
- Speeds healing
Cons
- When universally sized, they don’t come come preformed, presized, or prefitted
- Can be difficult for an individual to achieve optimum compression and correct fit
Best: Groin Muscle Strain Compression Brace
Sacroiliac (SI) Belt
Also known as a hip support belt, a sacroiliac belt is worn snugly around the hips to address pelvic, lower back, and leg pain from an inflamed or hyper-mobile sacroiliac (SI) joint. Since these are worn continuously for weeks, the most comfortable options are lightweight and breathable while providing maximum support. This type of support belt can be worn under or over clothes.
Since these are worn continuously for weeks, the most comfortable options are lightweight and breathable while providing maximum support. This type of support belt can be worn under or over clothes.
Pros
- Improved functional performance and posture and reduction of joint inflammation
- Easy to wear and can be worn under clothing where it can’t be sen
- Many styles available including a wide range of sizes so it is easy to find a good fit
Cons
- Has to be worn constantly to get relief
- SI belt is not appropriate in all cases of hip pain, including some arthritic conditions
Best: Bauerfeind SacroLoc Back Support
Hip Abduction Orthosis
When you need knee support coupled with hip stabilization, an expandable hip abduction orthosis splint separates the hips and knees gradually, using abductor muscle resistance for support. This kind of brace treats non-fixed contractures of the hip and knee while addressing hip or knee scissoring, joint destabilization, post surgery or injury trauma, wound management, range of motion, and ability to perform activities of daily living.
Pros
- Gradually separates the knees and hips during recovery
- Highly adjustable to meet changing therapeutic needs during healing process
- Uses the body’s own muscle resistance
Cons
- Can cause pressure areas or skin irritations
- Limits hip movement, making sitting upright awkward and difficult to get used to
Best: Mechanical Hip and Knee Abductor Orthosis
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Do hip braces help with sciatica?
A: Hip braces that deliver compression are used to help torn or strained hip flexor muscles and reduce the pain of sciatica.
Q: What is the difference between orthosis and brace?
A: An orthosis is an externally applied device that is designed and fitted to the body to control biomechanical alignment. A brace is a type of orthosis. Other types of orthoses are splints.
Q: Is there a brace for hip pain?
A: One of the benefits of all the braces featured in this article is that they address underlying factors that contribute to hip pain. Hip pain caused by mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis can benefit from an offloading brace that distributes weight and stabilizes the hip. Hip pain from dislocation, surgery, or injury can be addressed through a hip abduction brace that keeps the hips level, restricts motion, and maintains the position of the thigh bone in the socket. Braces offering targeted compression increase blood flow to soothe pain and decrease swelling and inflammation.
Hip pain caused by mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis can benefit from an offloading brace that distributes weight and stabilizes the hip. Hip pain from dislocation, surgery, or injury can be addressed through a hip abduction brace that keeps the hips level, restricts motion, and maintains the position of the thigh bone in the socket. Braces offering targeted compression increase blood flow to soothe pain and decrease swelling and inflammation.
Q: What does a hip brace do?
A: A hip brace supports your hip and keeps your leg in the correct position to reduce the risk of pain, injury, or dislocation while still allowing you to get up and move around. If soft tissues have been damaged, a hip brace also allows them to heal. By keeping a wearer’s leg out to the side a bit, a hip brace limits how much a leg can be bent forward and moved across the body, preventing dislocation.
Q: What are the alternatives to a hip brace?
A: Bed rest, a therapeutic regimen alternating between heat and cold packs, and surgery are alternatives to wearing a hip brace.
Q: What kind of brace is used for a hip dislocation after a hip replacement?
A: A hip abduction brace is usually prescribed after a hip replacement to restrict motion and limit how much you can bend your leg and move it across your body. It includes two padded harder pieces, one on the outside of the waist and one on the thigh, each with a strap used to hold the brace in place. A hip abduction brace is usually worn on the outside of clothing 24 hours a day for 2 to 4 weeks following surgery.
Q: Does insurance pay for a hip brace?
A: Hip braces are often covered by insurance if they are determined to be medically necessary. Hip replacement surgery creates a medical necessity for a hip brace while on crutches to prevent movement that could damage the joint. Consult with your insurance provider for more information.
Q: What is hip loading?
A: Hip loading refers to the force put on the hip joint during activity. Hip loads and accompanying internal hip abduction movement inform treatment and therapy for hip pain.
Final Thoughts
Hip pain is not uncommon, and can be an indicator of underlying conditions that can cause acute or chronic discomfort. By using a hip brace, you can support and stabilize the hip to support mobility and contribute to comfortably undertaking daily life activities.
Thank you for your time reading this article with tips on choosing the best hip brace for your needs! Visit Caregiver University for more information including buying guides and product reviews.
Author:
Amanda Marten, MSN, APRN, FNP-C
Amanda is a certified family nurse practitioner and freelance health writer. With eight years of nursing experience, she has worked in a variety of specialties including urgent care, post-surgical, intensive care, and travel nursing. She is passionate about patient education and strives to make a positive impact on her patients’ well-being.
Meet all of our experts here!
Hip abduction braces | Hip braces | Types of orthotics | Orthotics | Immediate access to the leading types of orthotics
Hip abduction bracesHip abduction braces are used to prevent excessive hip flexion and to abduct the hip (positions the leg away from the midline of the body).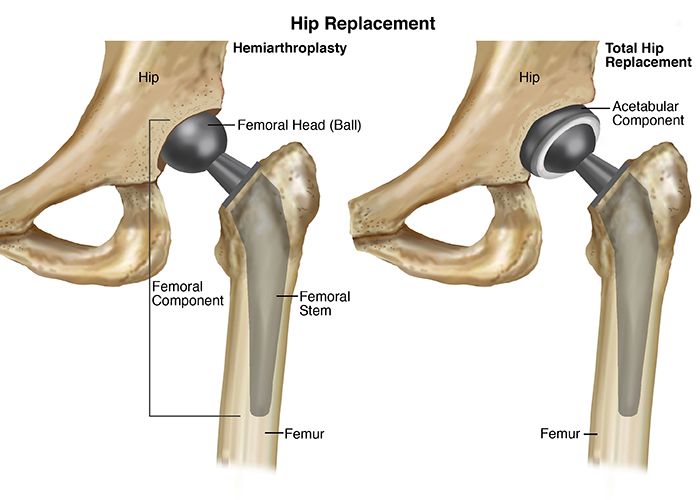 These braces are used following a hip dislocation to provide stability to the injured joint or as a preventative measure if a patient is at risk of hip dislocations. Hip abduction braces can also be used as an offloading brace due to the adjustment of joint angle which occurs during use.
These braces are used following a hip dislocation to provide stability to the injured joint or as a preventative measure if a patient is at risk of hip dislocations. Hip abduction braces can also be used as an offloading brace due to the adjustment of joint angle which occurs during use.
There are many indications for using a hip abduction brace. These include:
- Risk of hip dislocation/ joint instability
- Post dislocation care
- Hip pain
If you are unsure if you would be suitable for a hip abduction brace please contact us to discuss.
What conditions are hip abduction braces often used for?Hip abduction braces are often used for the following conditions:
- Hip dysplasia
- Postoperative care
- Arthritis of the hip
- Inoperable hip abnormalities
This list of conditions is not exhaustive.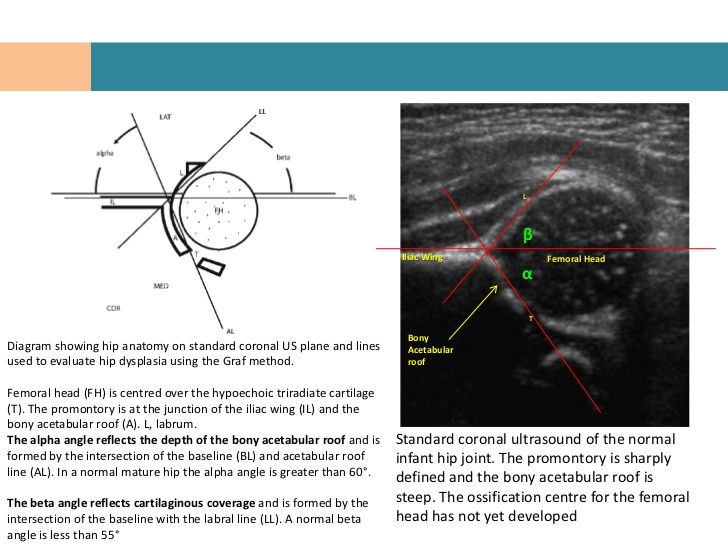 If you are unsure if you would be suitable for a hip abduction brace please contact us to discuss.
If you are unsure if you would be suitable for a hip abduction brace please contact us to discuss.
There are many benefits that come from using a hip abduction brace. These include:
- Adjustable devices able to provide individualised support
- Prevention leg migration
- Aids with posture
- Improves leg positioning
- Reduce pain
- Improve mobility
- Improve joint stability
There are many benefits using a hip abduction brace to find out more please contact us to discuss.
What types of hip abduction braces are available?There is a large range of hip abduction braces available including:
- Dynacox Evolution
- Newport
- Hiptric
The Dynacox Evolution is a modular brace which has a large range of adjustability.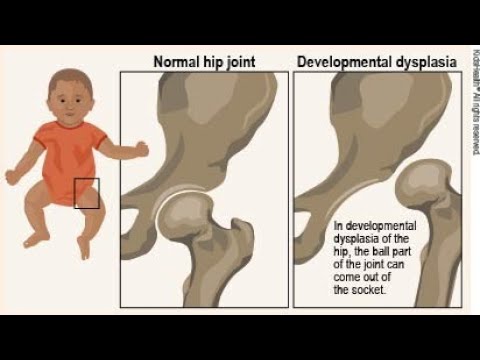 The brace provides support through the use of both an orthosis and a bandage. This combination provides compression of the pelvis, control of the range of motion a the hip joint (in particular flexion) and containment of the hip joint thus preventing further dislocation.
The brace provides support through the use of both an orthosis and a bandage. This combination provides compression of the pelvis, control of the range of motion a the hip joint (in particular flexion) and containment of the hip joint thus preventing further dislocation.
The Newport 3 Hip System is designed for users who require a high level of support and control of their hip joint. This is due to the large range of adjustability within the brace in all directions of motion. The Newport 3 Hip System uses a unique fastening system which enables easy donning and doffing.
HiptricThe Hiptric brace is suitable for those with any level of instability of the hip joint. It has a low profile design so can be easily worn underneath clothing if desired. The Hiptric works by applying an abduction force to the affected side via a series of pads, a waist and a thigh band. The device also has a range of motion restriction which enables the device to be used throughout rehabilitation.
A classic hip adbuction brace that can be used on children for sitting and standing.The brace is minimalistic and effective in reduce hip dislocations for numerous conditions.
DMO Night Time Positioning ShortsLyrca shorts are forgiving enough for children to tolerate wearing them at night. The shorts have an element of rigidity either side of the legs running above the hips to hold the legs in an abducted position preventing hip dislocations.
What is the process to be receive a hip abduction brace?The process to receive a hip abduction brace would be:
- Assessment
- Measuring
- Fitting
- Review
Hip abduction braces available in a range of stock sizes and also have some adjustability within sizes. Your orthotist will therefore need to undertake a full assessment to select the correct device and size suitable for your needs. The assessment will involve looking at your range of movement at your hip joint, discussing your needs and wants from the orthoses as well as taking a series of measurements. Once your orthotist has selected an appropriate device you will be advised upon wearing instructions.
Once your orthotist has selected an appropriate device you will be advised upon wearing instructions.
To get in touch or arrange an appointment, you can call us at 0330 088 3949 or email [email protected].
Send us a message...Hip dysplasia - clinic "Family Doctor".
“Your child has hip dysplasia” - very often this phrase from the mouth of an orthopedic doctor causes a state close to emotional shock in the parents of the baby. But is everything so gloomy and scary, and what kind of pathology is this?
Dysplasia - this term means a violation of the formation of any organ or body system. In this material we will talk about hip dysplasia.
Hip dysplasia is understood as a violation of the formation of the hip joint, which captures all the elements that make up the joint: the bone and cartilage base, the ligamentous-capsular apparatus and the muscle component. This definition is quite broad and includes the physiological immaturity of the hip joint, preluxation, subluxation and dislocation of the hip.
This definition is quite broad and includes the physiological immaturity of the hip joint, preluxation, subluxation and dislocation of the hip.
Physiological immaturity consists in the incomplete formation of the joint components without violating the congruence (correct matching) of the articular surfaces of the bones and, as a rule, requires minimal treatment or only dynamic observation, and it is this form of hip joint pathology that is mainly assigned the diagnosis of "dysplasia", although this is not entirely correct. terminologically. With pronounced immaturity of the hip joint, treatment is necessary to create favorable conditions for the proper maturation of the joint components.
Predislocation of the hip is already a pathology of the joint associated with the lack of stability of the femoral head in another component of the hip joint - the acetabulum and already requires close attention. In the absence of adequate treatment, hip predislocation can lead to the development of joint deformity (arthrosis), which leads to pain and impaired joint mobility, and can also lead to hip dislocation after the start of walking.
Dislocation of the hip is the most severe form of the pathology of the development of the hip joint, which consists in the almost complete discrepancy between the articular surfaces of the femoral head and the acetabulum. Such a malformation of the joint requires maximum efforts for a thorough diagnosis and active and prompt treatment. Late diagnosis or inadequate treatment leads to gross impairment of the hip joint mobility and, ultimately, leads to disability.
Now we understand why so much attention is paid to hip dysplasia by pediatricians and orthopedists. Why is it the hip joint that is most susceptible to these misfortunes?
The fact is that the hip joint, due to its anatomical and physiological characteristics, is the most loaded joint in our body, and a failure in one of its constituent components leads to dysfunction of the joint and, ultimately, to a deterioration in the quality of life of the patient. That is why the diagnosis of hip dysplasia can so often be heard from the lips of an orthopedist, although one cannot but recognize the fact of some overdiagnosis of this pathology, but given the severity of the consequences in the absence of treatment, this is still justified.
According to statistics, the incidence of hip dysplasia is 4-6 cases per 1000 newborns, in girls it occurs 6-7 times more often. Unilateral lesion predominates over bilateral (more often the left hip joint is affected). There is inheritance from mother to daughter. Quite a lot of factors leading to impaired intrauterine joint formation have been noted, among them are breech presentation of the fetus, narrowness of the uterus, oligohydramnios, toxic and biological (primarily viral diseases of the mother during pregnancy) factors and much more.
When and by what methods can and should hip dysplasia be diagnosed? Can a mother herself suspect the presence of hip dysplasia in a child and, if so, with what methods? The answer to this question depends on the severity of the joint injury. Let's try to answer this question by tying the timing and methods of diagnosis to the age of the baby.
When conducting ultrasound diagnostics during pregnancy, it is possible to diagnose only gross violations - subluxation and dislocation of the hip, that is, those changes in which the articular surface of the femoral head does not correspond to the surface of the acetabulum of the child's pelvis.
In the first 7-10 days of a child's life, an examination can reveal a “click symptom” or “slipping symptom” - dislocation and reduction of the hip in the joint. These symptoms are revealed in a child as follows: in the supine position, the legs are bent at the knee and hip joints at an angle of 90 degrees. The thumbs are located on the inner surface of the child's thighs, the index and middle fingers on the outer. With careful abduction and traction of the hips, the femoral head is set into the acetabulum with a characteristic click.
After the 2nd - 3rd week of a child's life, limitation of hip abduction comes to the fore in the diagnosis of hip dysplasia. To identify it, the legs of the child bent at the knee and hip joints in the supine position are bred without violence. Normally, it is possible to spread the hips to an angle of 85-90 degrees to the surface. With increased muscle tone and spasm of the muscles adducting the thigh, abduction can be limited to an angle of about 70 degrees, but such a restriction of hip abduction can also be caused by impaired joint formation.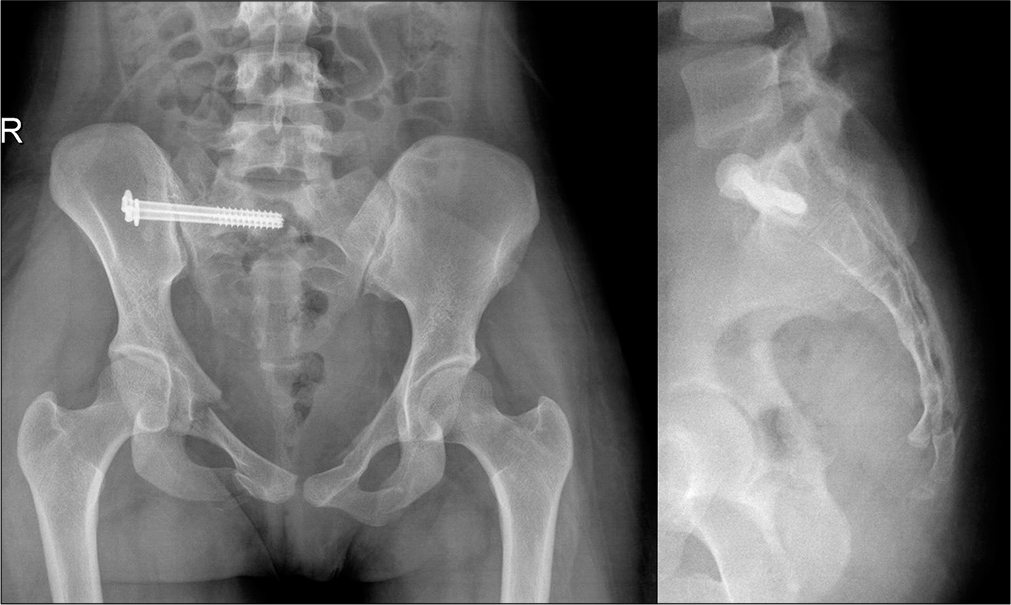 Limitation of hip abduction on one side in most cases is a sign of pathology from the hip joint.
Limitation of hip abduction on one side in most cases is a sign of pathology from the hip joint.
In favor of the pathology of the hip joint, symptoms such as shortening of one limb, turn of the foot on the side of the lesion outward from the middle position (external rotation of the foot) also speak.
The most widely known in parents (so to speak, "mommy symptom") - the asymmetry of the subgluteal folds - is not absolute and can be caused by many factors, but its importance in the diagnosis of hip dysplasia should not be underestimated, since this is the most common question that is addressed to orthopedic doctor.
To confirm the diagnosis of hip dysplasia and control the dynamics of treatment, ultrasound diagnostics are currently widely used. The positive aspects of this method of examination include painlessness, non-invasiveness, relative safety and a sharp increase in recent availability. Also, with the help of an ultrasound examination of the joint, minimal changes in the structure of the hip joint can be detected. But, unfortunately, this examination method does not always give accurate results (its reliability is about 85-90%. Nevertheless, to date, ultrasound diagnostics is the main method of screening for the diagnosis of hip dysplasia.
But, unfortunately, this examination method does not always give accurate results (its reliability is about 85-90%. Nevertheless, to date, ultrasound diagnostics is the main method of screening for the diagnosis of hip dysplasia.
In the case when the clinical picture differs from the data of the ultrasound examination or in case of late diagnosis of the pathology of the hip joint, the X-ray method is used. With a correctly performed radiograph, the picture of the structure of the joint and the position of the femoral head in the joint become completely clear. But due to the rather large radiation exposure during radiography, this examination method is used as rarely as possible.
In children older than a year, the main symptom is lameness on the affected side when walking or a "duck" gait with a bilateral process. Diagnosis at this age is belated. The clinical picture in this case almost always requires confirmation by x-ray, since it is necessary to accurately determine the relative position of the joint components.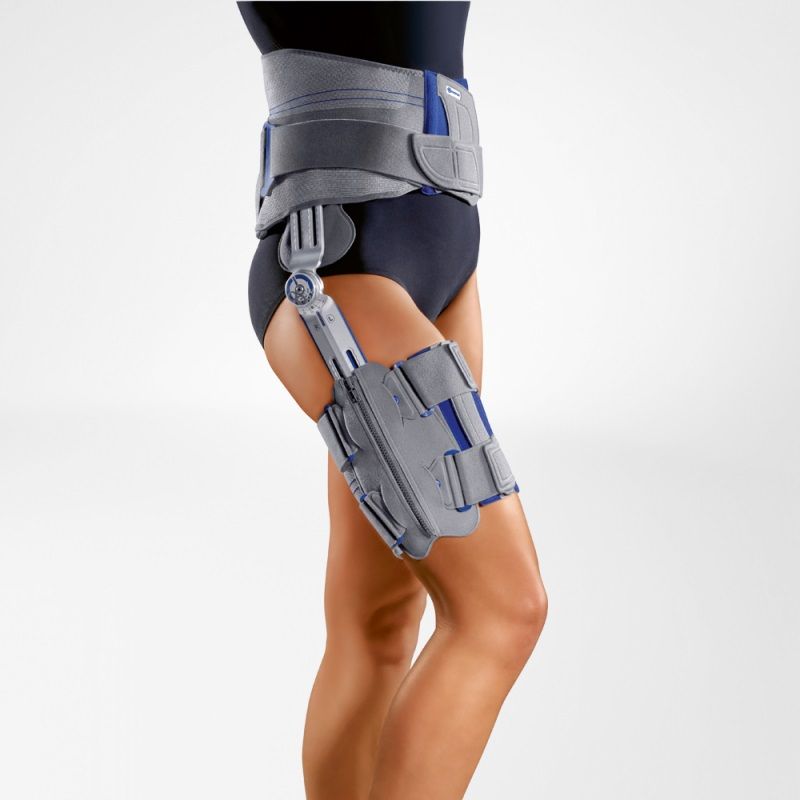
And so, the child was diagnosed with hip dysplasia, what to do next and how to help the baby?
Treatment of hip dysplasia should be started as early as possible. The goal of the treatment is to center the femoral head in the joint and create conditions for the formation of the entire acetabulum. Early, most gentle, but systematic treatment allows you to completely restore the anatomy and function of the underdeveloped hip joint.
The centering of the hip in the joint in the early stages of treatment is achieved by wide swaddling - two diapers are placed between the divorced hips of the child and fixed with a third. In severe degrees of hip dysplasia, special splints are used to center the femoral head (Pavlik's stirrups, Freik's pillow, etc.). When using these tires, parents may have questions and difficulties in caring for their baby, here are some tips to help you and your baby adjust during this period:
1. Only a baby diaper (disposable or gauze) should be under the stirrups or pillow.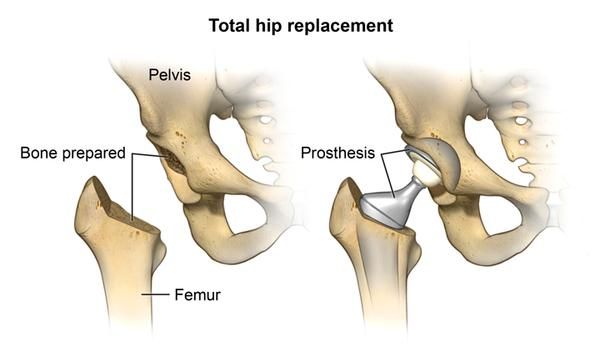 If you prefer to use gauze diapers, wear oilcloth panties that have zippers on the sides.
If you prefer to use gauze diapers, wear oilcloth panties that have zippers on the sides.
2. When changing a diaper, do not lift the child by the legs, but put your hand under the buttocks.
3. The vests can be changed without removing the stirrups: unfasten the shoulder straps from the chest strap and remove the vest over your head.
Over the tires you can wear loose pants, suits, dresses.
4. During the splint period, bathing the child is less frequent, so it is necessary to examine the skin under the straps, under the knees and around the neck 2-3 times a day to make sure there are no signs of inflammation (redness) of the skin. During this period, it is necessary to wipe the baby's skin with a soft cloth soaked in warm water. When carrying out water procedures, you can unfasten one foot part of the stirrup, but do not remove it, and keep the leg in a bent and retracted position.
5. It is also necessary to monitor the hygienic condition of the tire itself, it must always remain dry, avoid getting powders and lotions under the belts, this can cause inflammation on the baby's skin.
6. When feeding, be especially careful to ensure that the baby's hips do not come together.
The wearing of these devices (orthoses) is long-term - from 3 months to a year, and it is extremely important for the parents of a child who has been diagnosed with hip dysplasia to be patient and not be cowardly during the treatment period and meticulously follow the doctor's prescriptions.
After centering the femoral head, they begin massage and therapeutic exercises aimed at creating the correct ratio of the articular surfaces. We can recommend some exercises that are easy to do at home.
1. In the position of the child lying on his back, we bend the child's legs at the knee and hip joints as much as possible, and then fully straighten them.
2. In the previous starting position, we bend the child's legs at the knee and hip joints at a right angle, moderately spread the hips and, giving a moderate load along the axis of the hips, perform rotational movements with the hips.
3. In the position of the child lying on his back, we breed the legs of the child bent at the knee and hip joints as much as possible to the surface of the table.
All exercises are performed 8-10 times 3-4 times a day.
Also during this period, physiotherapy (paraffin baths, electrophoresis with calcium and phosphorus preparations) is used to improve the nutrition of the joint components and complex orthopedic massage.
In cases of late diagnosis of hip dysplasia or in the absence of adequate treatment in the early stages, treatment is carried out by long-term staged plastering, as well as surgical treatment, but in these cases there are no standard treatment regimens and patient care tactics are developed individually.
After treatment of hip dysplasia, the child should be kept in the dispensary with an orthopedist for a long time - from 3 to 5 years until the end of growth. If necessary, control radiographs are performed once every 2 years to monitor the correct development of the joint.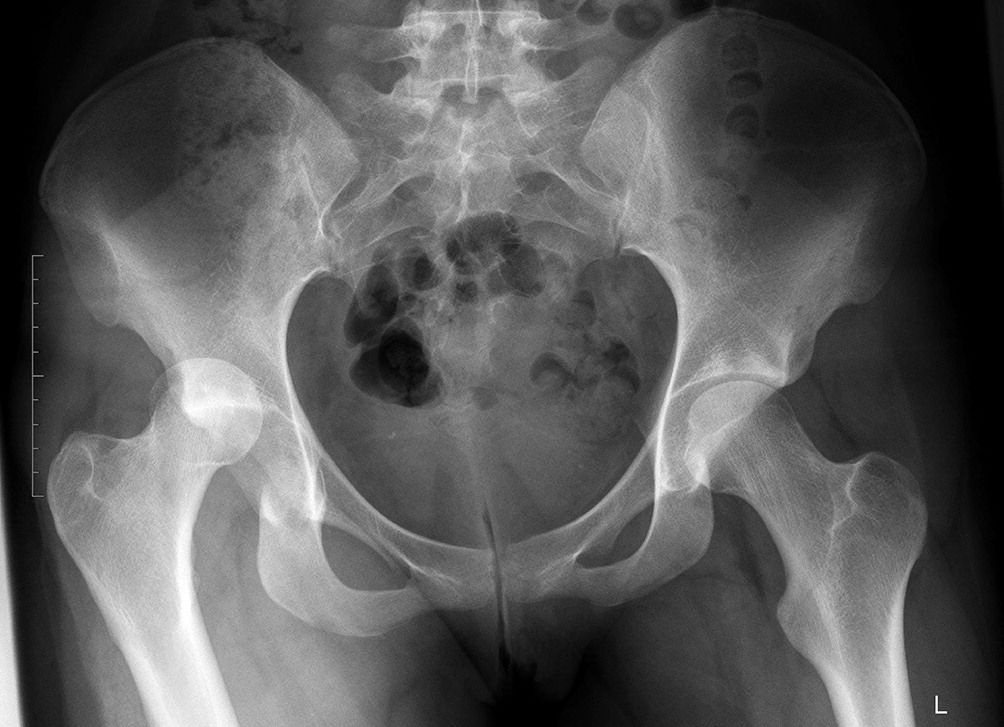 Also, restrictions on the load on the joint are often imposed. For children treated for hip dysplasia, it is desirable to visit specialized orthopedic groups in preschool institutions.
Also, restrictions on the load on the joint are often imposed. For children treated for hip dysplasia, it is desirable to visit specialized orthopedic groups in preschool institutions.
In severe degrees of hip dysplasia, functional disorders are, as a rule, lifelong in nature, even with timely and properly conducted treatment.
So what do the parents of the baby need to do in order to recognize hip dysplasia in time and, if this diagnosis was made to the child, to prevent serious complications?
First of all, it is necessary to show the child to the orthopedist in time. The recommended terms of examination by an orthopedist are 1 month, 3 months, 6 months and 1 year.
If the orthopedist nevertheless made a diagnosis of hip dysplasia, then the effectiveness of treatment by 50 percent depends on the correct and timely fulfillment by the child's parents of the doctor's prescriptions. It is important to remember that the sooner treatment is started, the better the results and the less chance of severe complications.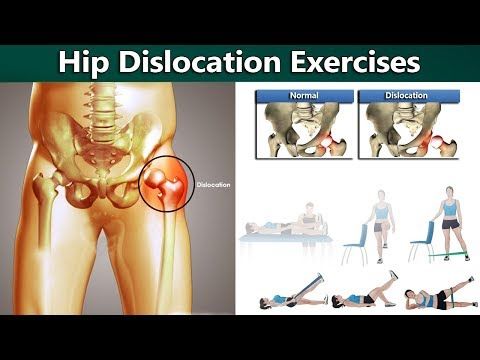 With early diagnosis of hip dysplasia and correct and timely treatment, a positive result is achieved in 96-98% of cases. You should not be AFRAID of this diagnosis, but it is necessary to treat the child, he needs your help and care!
With early diagnosis of hip dysplasia and correct and timely treatment, a positive result is achieved in 96-98% of cases. You should not be AFRAID of this diagnosis, but it is necessary to treat the child, he needs your help and care!
I hope this material helped you understand what kind of incomprehensible and frightening diagnosis it is - hip dysplasia, and it became clear to you how to deal with this pathology.
We recommend that you seek advice from the orthopedists of the Family Doctor clinic by calling the contact center in Moscow +7 (495) 775 75 66, or through the online appointment form.
Athletics
Athletics > Bandages > Bandages for children FOSTA
Select size
- M
- S
- XS
Quantity:
- Description
- Characteristics
- Certificates
Name: bandage for children (Perinka Frejka with straps)
Product description: bandage for children is made of combined materials.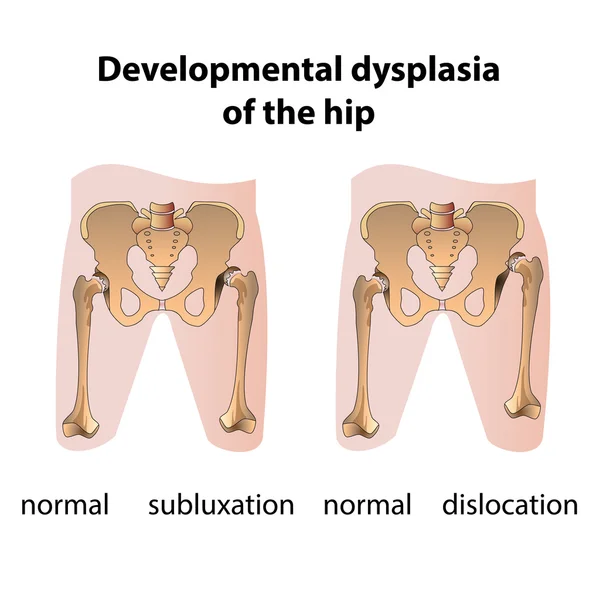 The product is made of a mesh material with six stiffening ribs, which provide the product with elasticity and shape retention during operation. The product is used only on the recommendation of a doctor for congenital dislocation of the hip or hip dysplasia. The straps provide a secure fixation of the bandage on the child's body. Before use, a doctor's consultation is necessary.
The product is made of a mesh material with six stiffening ribs, which provide the product with elasticity and shape retention during operation. The product is used only on the recommendation of a doctor for congenital dislocation of the hip or hip dysplasia. The straps provide a secure fixation of the bandage on the child's body. Before use, a doctor's consultation is necessary.
Degree of fixation:
- medium
Composition:
- polymer material - 96%
- elastic rubber - 3%
- polystyrene - 1%
Colour:
- white
Indications for use:
- hip dysplasia
- congenital dislocation of the hip.
Application result:
- hip flexion and abduction fixation
Application:
It is recommended to wear lying down, on a diaper, directly on the body or on cotton underwear.
Mode and terms of wearing:
- determined by the attending physician
Care instructions:
- wash in warm water (35°C)
- use high quality detergents
- hand wash, do not machine wash
- do not tumble dry
- do not bleach
- do not iron
- dry flat, away from heaters
- Do not dry clean.
Sizes:
| Age (months) | 3-6 | 6-12 | 12-24 |
| 6 | XS | S | M |
Related product:
- orthopedic pillow
- Base: mesh fabric
- Stiffeners: polymer material
- Fastener: velcro
Permits: registration certificate No. ФСЗ 2007/00326 dated October 25, 2007.