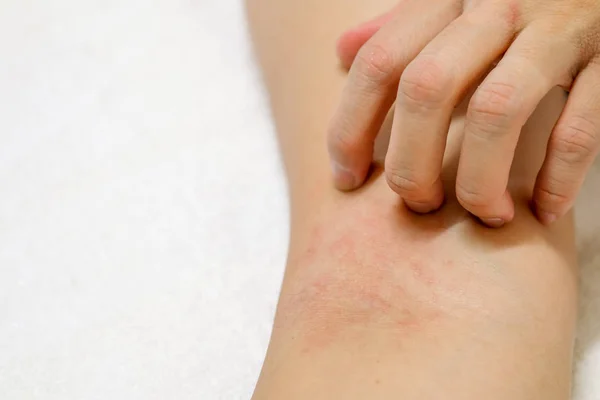
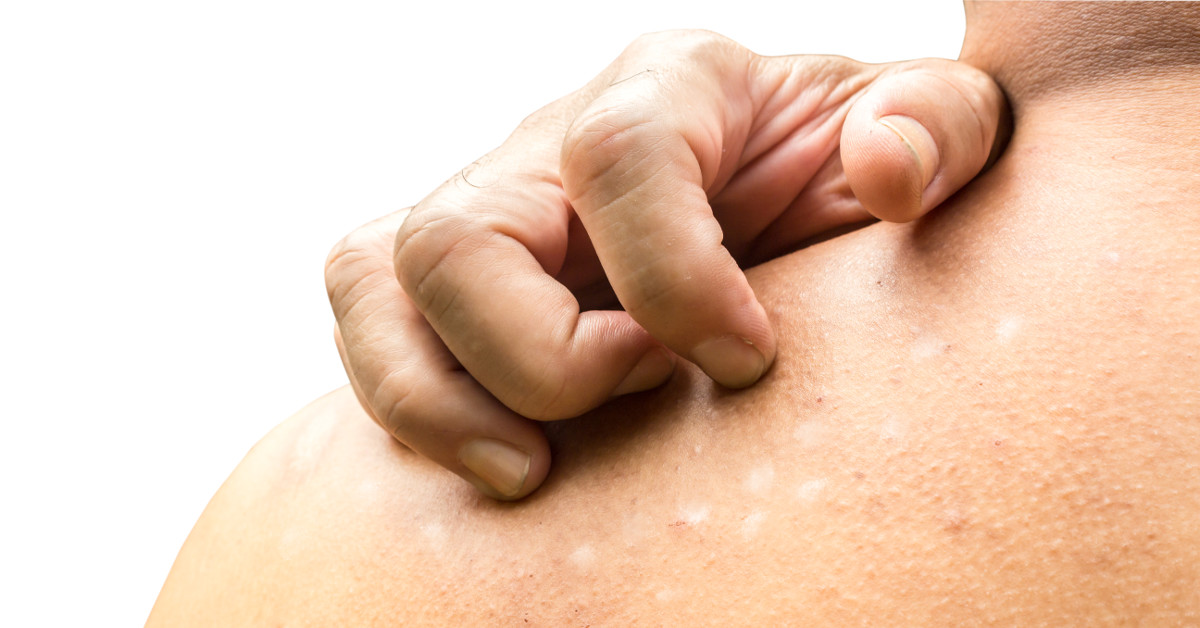
Circle rash on back
Circular rash: Causes and diagnosis
The most common cause of a circular rash on the skin is ringworm, but other issues can also leave this distinctive mark.
A doctor diagnoses the cause of a rash after examining it and asking about symptoms. They may recommend oral medication, a topical cream, or strategies for avoiding triggers.
In this article, learn more about the issues that can cause this rash and how to treat them.
Despite its name, ringworm is a fungal skin infection — it is not caused by a worm or any other parasite.
The infection got its name because it causes a rash that is usually circular, with a thin raised ring around the edge that may look like a worm.
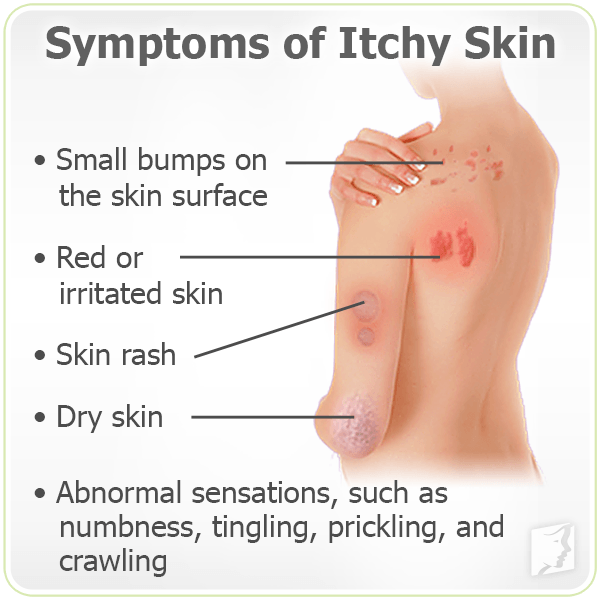
Symptoms
The circular rash may initially measure a few centimeters across, and it can grow without treatment. It may look like a round, flat patch, and the middle of the rash tends to heal first.
On lighter skin, a ringworm rash is red or pink, and on darker skin, it is silver or brown.
The skin around the rash may be dry or scaly, and the rash can be extremely itchy.
Ringworm can appear on any part of the body, and the rash may not be ring-shaped if it appears on the scalp, soles of the feet, palms, groin, or nails. Athlete’s foot and jock itch are types of ringworm.
Ringworm is infectious and can pass from one person to another through close contact.
How long is ringworm contagious for? Find out here.
Treatment
Treatment involves antifungal cream or gel. A person should:
- Use the medication for 2–4 weeks, even after the symptoms go away.
- Keep the skin as clean and dry as possible.
- Wash the hands after touching the rash to keep it from spreading to other parts of the body.
The risk of developing ringworm is higher in warm, humid weather. To reduce the chances:
- Always shower after exercise.
- Change clothes daily.
- Do not share towels or brushes.
- Take any pet that develops bare patches of fur or other ringworm symptoms to the vet.
Learn about home remedies for ringworm here.
After a tick bite, a circular rash may develop at the site. This is an early symptom of Lyme disease.
Symptoms
The circular rash can appear days or weeks after the bite, and it may have a distinctive bull’s eye appearance.
On lighter skin, a person may see three circles surrounding the bite: a red circle closest to the bite, then a lighter ring, then another red ring. On darker skin, the appearance can be different — check for a raised ring around the bite.
The rash usually expands over time. It can cause pain, burning, or itching, and it may be warm to the touch.
A tick may bite any part of the body, and it may favor exposed or warm areas. These bites are common in the lower leg, armpit, groin, and back.
About half of the people who contract Lyme disease have flu symptoms, which usually appear before the rash.
Treatment
Receiving treatment early on is crucial. At an initial stage, a course of antibiotics can cure Lyme disease.
Check the skin for tick bites after being outdoors. Remove a tick right away, without squeezing it, and be sure to remove the tick entirely.
Learn more about the Lyme disease rash here.
Contact dermatitis is an allergic skin reaction.
Symptoms
The skin will darken or redden and may feel itchy or dry. Contact dermatitis can also cause the skin to swell or blister.
The size of the rash depends on how much skin has come into contact with the allergen.
The rash may be circular if the object triggering the reaction is round. For example, if a person has a nickel allergy, wearing a nickel watch may cause a round rash to form on the wrist.
Treatment
The most effective way to combat contact dermatitis is to identify and avoid contact with the allergen or irritant.
It can help to use products designed for sensitive skin and to check labels of soaps and personal care products carefully for common allergens and irritants.
Over-the-counter creams can help reduce swelling and irritation.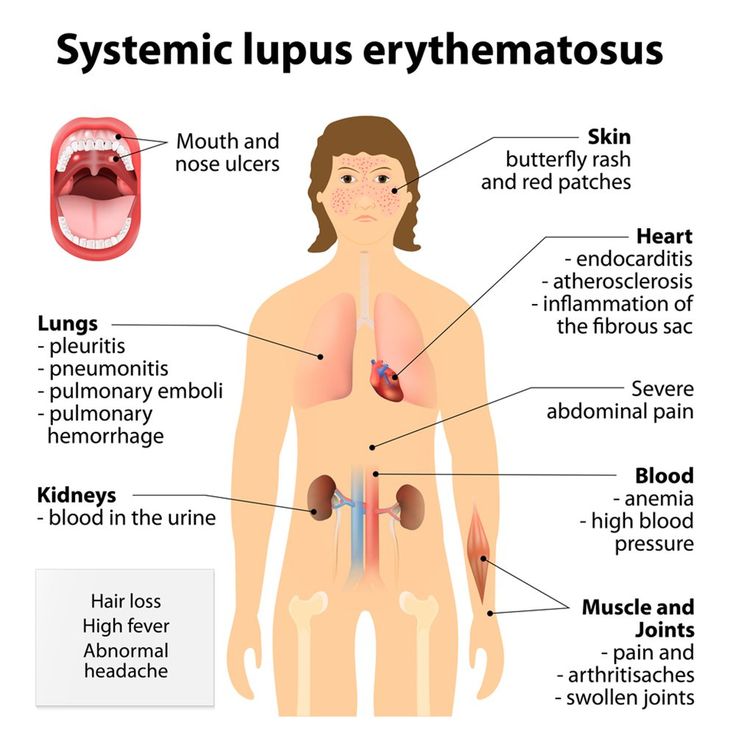
Learn more about contact dermatitis here.
Hives are a reaction to temperature, food, medication, viral infections, and other triggers.
Symptoms
Hives form when the skin swells into welts. These are red or skin-colored bumps or patches that may itch or burn.
Hives can develop on any part of the body, and they may appear and disappear quickly. In some people, hives or patches of hives may be circular and resemble bug bites.
Treatment
Antihistamines can reduce swelling and prevent hives if they result from contact with an allergen.
If hot weather is a trigger for hives, wear loose clothing, and use sunscreen. Also, it may help to dampen the skin with a wet washcloth.
Learn more treatments for hives here.
Granuloma annulare is rare. It causes bumps to form a circular or ring-shaped rash.
The rash most often appears on the hands, arms, or feet. Less commonly, it can spread across the body, or smaller patches can join to form larger ones.
Symptoms
The causes are still unclear, but granuloma annulare can develop after skin damage or a viral infection.
Granuloma annulare causes no symptoms beyond the rash, and it is not contagious.
Treatment
The condition usually disappears without treatment, but it can last for years. Steroid injections or creams may help the body heal.
If any circular rash lasts for a long time, causes significant discomfort, or affects the face or throat, a person should see a doctor.
If ringworm doesn’t go away after 2 weeks of treatment, see a doctor.
If it affects the scalp, however, it is a good idea to consult a doctor or pharmacist right away. Also, anyone who has a weakened immune system should see a doctor if they have ringworm.
If an allergic reaction is severe or the cause is unclear, seek professional guidance.
Always see a doctor about a tick bite, unless the tick was safely removed within 36 hours of the bite.
Seek urgent medical care if a rash:
- covers the entire body
- occurs with a fever
- is painful
- begins to blister
- occurs with difficulty breathing
A doctor, such as a dermatologist, will consider accompanying symptoms and any contact with allergens or irritants when diagnosing a circular rash.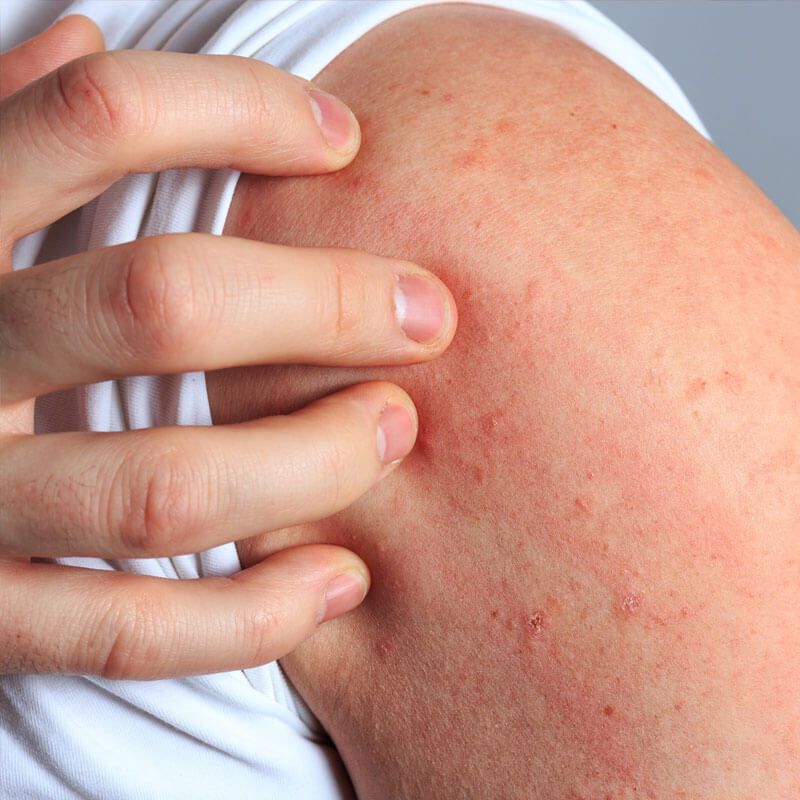
Allergists can test for triggers of skin reactions, which are often pet hair or medication.
They may test the skin, blood, or urine, but they commonly perform patch tests. This involves placing strips containing small amounts of allergens on the back. The doctor then removes the strips after 48 hours to check for an allergic reaction.
Keeping track of foods, drinks, medications, physical activities, and symptoms in a diary can help a person identify what might be triggering a reaction.
The size and shape of a circular rash and the symptoms it accompanies can each point to the cause.
A person can treat mild cases of ringworm, hives, and contact dermatitis with home care and over-the-counter products. However, if a circular rash is severe or may result from a tick bite, see a doctor.
It is also important for a person to receive professional care if they have had an allergic reaction without an obvious cause.
Anyone with a persistent rash or other skin problems may benefit from seeing a dermatologist.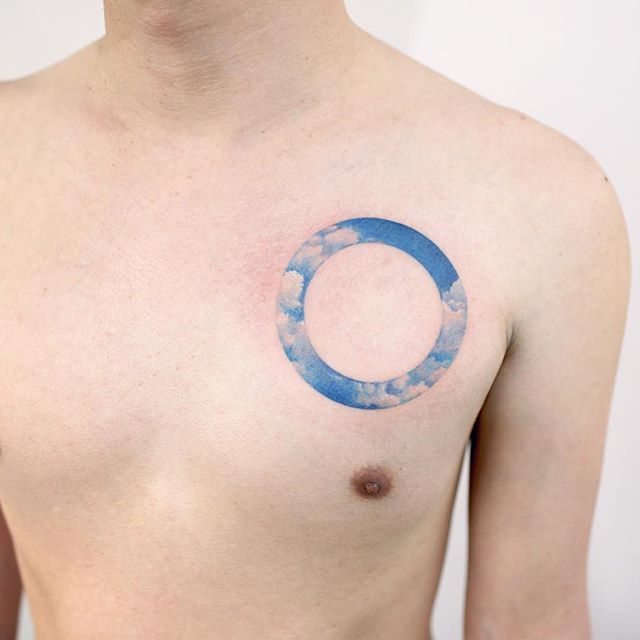
Circular rash: Causes and diagnosis
The most common cause of a circular rash on the skin is ringworm, but other issues can also leave this distinctive mark.
A doctor diagnoses the cause of a rash after examining it and asking about symptoms. They may recommend oral medication, a topical cream, or strategies for avoiding triggers.
In this article, learn more about the issues that can cause this rash and how to treat them.
Despite its name, ringworm is a fungal skin infection — it is not caused by a worm or any other parasite.
The infection got its name because it causes a rash that is usually circular, with a thin raised ring around the edge that may look like a worm.
Symptoms
The circular rash may initially measure a few centimeters across, and it can grow without treatment. It may look like a round, flat patch, and the middle of the rash tends to heal first.
On lighter skin, a ringworm rash is red or pink, and on darker skin, it is silver or brown.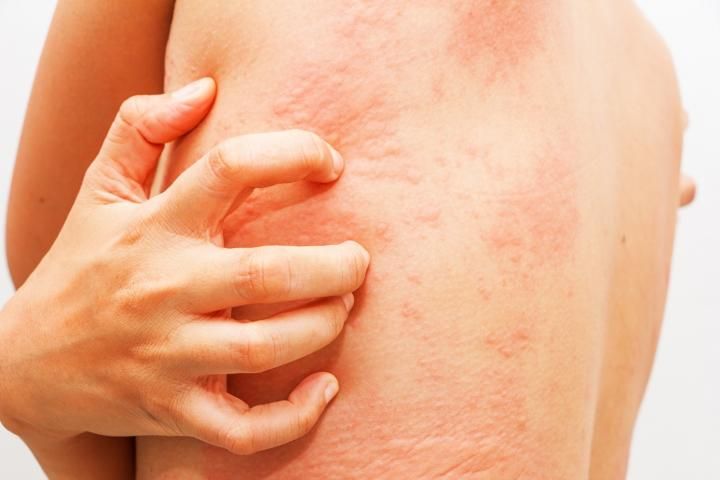
The skin around the rash may be dry or scaly, and the rash can be extremely itchy.
Ringworm can appear on any part of the body, and the rash may not be ring-shaped if it appears on the scalp, soles of the feet, palms, groin, or nails. Athlete’s foot and jock itch are types of ringworm.
Ringworm is infectious and can pass from one person to another through close contact.
How long is ringworm contagious for? Find out here.
Treatment
Treatment involves antifungal cream or gel. A person should:
- Use the medication for 2–4 weeks, even after the symptoms go away.
- Keep the skin as clean and dry as possible.
- Wash the hands after touching the rash to keep it from spreading to other parts of the body.
The risk of developing ringworm is higher in warm, humid weather. To reduce the chances:
- Always shower after exercise.
- Change clothes daily.
- Do not share towels or brushes.
- Take any pet that develops bare patches of fur or other ringworm symptoms to the vet.

Learn about home remedies for ringworm here.
After a tick bite, a circular rash may develop at the site. This is an early symptom of Lyme disease.
Symptoms
The circular rash can appear days or weeks after the bite, and it may have a distinctive bull’s eye appearance.
On lighter skin, a person may see three circles surrounding the bite: a red circle closest to the bite, then a lighter ring, then another red ring. On darker skin, the appearance can be different — check for a raised ring around the bite.
The rash usually expands over time. It can cause pain, burning, or itching, and it may be warm to the touch.
A tick may bite any part of the body, and it may favor exposed or warm areas. These bites are common in the lower leg, armpit, groin, and back.
About half of the people who contract Lyme disease have flu symptoms, which usually appear before the rash.
Treatment
Receiving treatment early on is crucial. At an initial stage, a course of antibiotics can cure Lyme disease.
Check the skin for tick bites after being outdoors. Remove a tick right away, without squeezing it, and be sure to remove the tick entirely.
Learn more about the Lyme disease rash here.
Contact dermatitis is an allergic skin reaction.
Symptoms
The skin will darken or redden and may feel itchy or dry. Contact dermatitis can also cause the skin to swell or blister.
The size of the rash depends on how much skin has come into contact with the allergen.
The rash may be circular if the object triggering the reaction is round. For example, if a person has a nickel allergy, wearing a nickel watch may cause a round rash to form on the wrist.
Treatment
The most effective way to combat contact dermatitis is to identify and avoid contact with the allergen or irritant.
It can help to use products designed for sensitive skin and to check labels of soaps and personal care products carefully for common allergens and irritants.
Over-the-counter creams can help reduce swelling and irritation.
Learn more about contact dermatitis here.
Hives are a reaction to temperature, food, medication, viral infections, and other triggers.
Symptoms
Hives form when the skin swells into welts. These are red or skin-colored bumps or patches that may itch or burn.
Hives can develop on any part of the body, and they may appear and disappear quickly. In some people, hives or patches of hives may be circular and resemble bug bites.
Treatment
Antihistamines can reduce swelling and prevent hives if they result from contact with an allergen.
If hot weather is a trigger for hives, wear loose clothing, and use sunscreen. Also, it may help to dampen the skin with a wet washcloth.
Learn more treatments for hives here.
Granuloma annulare is rare. It causes bumps to form a circular or ring-shaped rash.
The rash most often appears on the hands, arms, or feet. Less commonly, it can spread across the body, or smaller patches can join to form larger ones.
Symptoms
The causes are still unclear, but granuloma annulare can develop after skin damage or a viral infection.
Granuloma annulare causes no symptoms beyond the rash, and it is not contagious.
Treatment
The condition usually disappears without treatment, but it can last for years. Steroid injections or creams may help the body heal.
If any circular rash lasts for a long time, causes significant discomfort, or affects the face or throat, a person should see a doctor.
If ringworm doesn’t go away after 2 weeks of treatment, see a doctor.
If it affects the scalp, however, it is a good idea to consult a doctor or pharmacist right away. Also, anyone who has a weakened immune system should see a doctor if they have ringworm.
If an allergic reaction is severe or the cause is unclear, seek professional guidance.
Always see a doctor about a tick bite, unless the tick was safely removed within 36 hours of the bite.
Seek urgent medical care if a rash:
- covers the entire body
- occurs with a fever
- is painful
- begins to blister
- occurs with difficulty breathing
A doctor, such as a dermatologist, will consider accompanying symptoms and any contact with allergens or irritants when diagnosing a circular rash.
Allergists can test for triggers of skin reactions, which are often pet hair or medication.
They may test the skin, blood, or urine, but they commonly perform patch tests. This involves placing strips containing small amounts of allergens on the back. The doctor then removes the strips after 48 hours to check for an allergic reaction.
Keeping track of foods, drinks, medications, physical activities, and symptoms in a diary can help a person identify what might be triggering a reaction.
The size and shape of a circular rash and the symptoms it accompanies can each point to the cause.
A person can treat mild cases of ringworm, hives, and contact dermatitis with home care and over-the-counter products. However, if a circular rash is severe or may result from a tick bite, see a doctor.
It is also important for a person to receive professional care if they have had an allergic reaction without an obvious cause.
Anyone with a persistent rash or other skin problems may benefit from seeing a dermatologist.
Erythema annulare: symptoms, treatment, diagnosis of the disease
Dermatovenereologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
Experience 10 years
Make an appointment
Erythema annulare is a multiform lesion of the skin, a characteristic feature of which is the appearance of ring-shaped spots and rashes on the skin. The color of the skin of the affected areas changes and becomes red, hot pink or bluish. Depending on the causes of the disease, edema, local fever and other manifestations of the disease can be observed. A change in skin color occurs due to the expansion of the lumen of the blood capillaries penetrating the connective tissue, and the blood stagnation associated with it.
Varieties of pathology
Doctors distinguish several types of annular erythema, depending on the causes of the disease:
- Darya centrifugal erythema - most often affecting middle-aged men, less often - children and the elderly, related to infectious-allergic manifestations;
- migratory - a disease of an infectious nature resulting from the bite of a tick infected with Borrelia;
- rheumatic, or annular erythema, is one of the symptoms that accompany rheumatism, characteristic of children and adolescents.
According to external signs, ring erythema can occur:
- in scaly form - with desquamation of dead skin along the edges or the entire surface of the spots;
- in vesicular form - with the appearance of small fluid-filled vesicles along the edge or the entire surface of the spots;
- in a garland-like form - with the mildest course, which is characterized by pale pink spots arranged in chains or garlands and disappearing after a few days;
- in microgarland-like form - with small spots, up to 1 cm in diameter, sometimes accompanied by peeling or blistering, with a long course.
The medical literature also mentions other, very rare types of annular erythema - telangiectatic, purpuric or indurated.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of the disease is the appearance on the skin of characteristic rashes in the form of irregular rings with a bright border raised above the surface of the skin. With centrifugal erythema of Dardieu, they appear, as a rule, on areas of the skin, usually covered with clothing - on the back, abdomen and chest, forearms. Erythema annulare after a midge bite is a single spot that spreads from the site of infection, and in its final form it can reach 20-25 cm in diameter. The spots may be accompanied by itching or burning. In the rheumatic form of the pathology, there are no unpleasant sensations.
With centrifugal erythema of Dardieu, they appear, as a rule, on areas of the skin, usually covered with clothing - on the back, abdomen and chest, forearms. Erythema annulare after a midge bite is a single spot that spreads from the site of infection, and in its final form it can reach 20-25 cm in diameter. The spots may be accompanied by itching or burning. In the rheumatic form of the pathology, there are no unpleasant sensations.
Causes of disease
There are many diseases and conditions that can cause erythema annulare, since it is not an independent disease and always occurs against the background of some pathological process. Skin manifestations most often develop against the background of:
- accumulation of toxins in the body;
- rheumatism;
- fungal, viral or bacterial infections;
- chronic inflammatory diseases;
- endocrine gland dysfunctions;
- tuberculosis;
- borreliosis;
- reduce the protective function of the immune system;
- allergic reaction;
- cancer;
- helminthic infestation;
- taking certain medications.

In addition, in many cases, Darier's annular erythema occurs for no apparent reason in perfectly healthy people.
Diagnostics
When erythema annulare appears, the diagnosis is based on dermatological examination data and history taking. The main task of the examination is to determine the cause that caused pathological changes in the skin. For this, the patient is prescribed:
- skin scraping test for fungus;
- clinical blood test;
- testing for treponematosis;
- skin biopsy for histological analysis;
- serological examination of blood;
- allergy tests.
Based on the results obtained, specific studies can be prescribed to determine the state of certain organs and identify the underlying disease.
Treatment
The main principle of the treatment of erythema annulare is to stop the action of the factor that provokes the pathology. Depending on the results of the diagnosis, the patient may be prescribed drugs for oral administration:
- antibiotics, antivirals for the treatment of infection;
- antiallergic and hyposensitizing agents;
- cytostatics;
- deworming agents;
- glucocorticoids.

In addition, external agents may be useful - antihistamine, steroid or zinc-containing ointments to reduce discomfort and reduce symptoms. With erythema annulare, clinical recommendations may include limiting certain foods that cause an allergic reaction: confectionery, mushrooms, nuts, canned food, smoked meats, citrus fruits, etc. You should be prepared for the fact that the treatment process will last several months, as well as the possibility relapses.
Diagnostics and treatment of annular erythema in Moscow
The clinic of JSC "Medicina" conducts effective diagnostics and treatment of erythema annulare in Moscow. We have a powerful laboratory and diagnostic base that allows us to perform the most modern and informative types of analyzes and diagnostic procedures. Consultations are conducted by experienced doctors of the highest category. Make an appointment online or by phone at a convenient time for you.
Questions and answers
Which doctor treats erythema annulare?
If you suspect an annular erythema, you should immediately contact a dermatologist who will conduct an appropriate diagnosis and prescribe treatment based on its results. In the future, you may need to consult an allergist, rheumatologist, oncologist or other specialists, depending on the cause that caused the appearance of red spots on the skin.
In the future, you may need to consult an allergist, rheumatologist, oncologist or other specialists, depending on the cause that caused the appearance of red spots on the skin.
Ring erythema - is it contagious?
No, this pathology is not transmitted to other people even in cases where it is caused by an infectious disease.
How dangerous is erythema annulare?
By itself, ring erythema does not pose a great danger. With timely started adequate treatment, the patient is guaranteed to recover. However, it should not be neglected: if left untreated, the disease becomes chronic with constant relapses. Skin manifestations indicate the presence of health problems, therefore, when they appear, it is necessary to contact a qualified dermatologist without delay.
Erythema annulare. What is erythema annulare?
IMPORTANT
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment.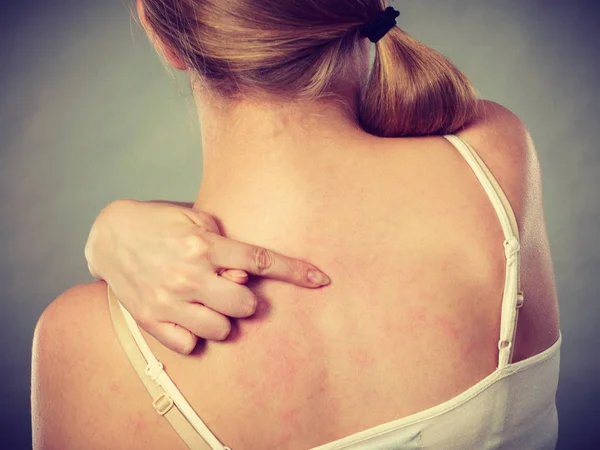 In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Erythema annulare is a skin lesion of various etiologies, manifested by erythematous rashes of various (most often annular) forms on the skin of the trunk, lower and upper extremities. It is characterized by a long course, difficult to treat. Diagnosis of erythema annulare is based on the study of history, examination data and the results of various serological studies conducted to exclude infectious diseases. There is no etiotropic treatment, usually desensitizing therapy is carried out, antibiotics and vitamin preparations are used. In some cases, the rash disappears when the provoking pathology is eliminated.
- Causes of erythema annulare
- Symptoms of ring-shaped dermatosis
- Diagnosis of erythema annulare
- Treatment of erythema annulare
- Prognosis and prevention of erythema annulare
- Treatment prices
General
Erythema annulare (persistent annular erythema, Darier's erythema, long-term erythema) is a group of skin diseases with similar manifestations - the formation of ring-shaped and shapeless erythematous rashes. One of the forms of this state at 1916 was described by the French dermatologist J. Darier, at the moment it is called annular centrifugal erythema Darier. In addition to this type of disease, there are several other types of pathology that differ in age of development, etiology and clinical manifestations. Various types of erythema annulare can occur in children, adolescents, or the elderly. Most varieties of erythema are equally often diagnosed in men and women, Darier's erythema is several times more common in males.
One of the forms of this state at 1916 was described by the French dermatologist J. Darier, at the moment it is called annular centrifugal erythema Darier. In addition to this type of disease, there are several other types of pathology that differ in age of development, etiology and clinical manifestations. Various types of erythema annulare can occur in children, adolescents, or the elderly. Most varieties of erythema are equally often diagnosed in men and women, Darier's erythema is several times more common in males.
erythema annulare
Causes of erythema annulare
The etiology and pathogenesis of erythema annulare in many cases remain unclear, there is only an assumption about the influence of certain factors. The rheumatic form of the pathology is due to rheumatic damage to the joints, but the cause of skin manifestations has not yet been established. Erythema migrans annulare, more commonly seen in children and adolescents, is likely associated with various viral and bacterial infections.
The etiology of Darier's annular erythema raises the greatest number of questions. The development of this form of the disease, presumably, may be due to a fungal infection of the skin, autoimmune processes and the intake of certain drugs. In addition, Darier's erythema often occurs against the background of various helminthiases, which also testifies in favor of the autoimmune nature of the disease. Many cases of the appearance of annular erythema on the background of tonsillitis, other inflammatory processes, endocrine disorders and hormonal disorders have been described. Oncologists note that sometimes erythema annulare is part of the paraneoplastic syndrome. Thus, this condition is a special form of reactive dermatosis of various etiologies.
Symptoms of ring-shaped dermatosis
In addition to highlighting the forms of annular erythema listed above (rheumatic, migrating, Darier), in practical dermatology there is a classification based on the characteristics of the clinical course, which, in general terms, differs in the nature of the rashes, duration and other characteristics.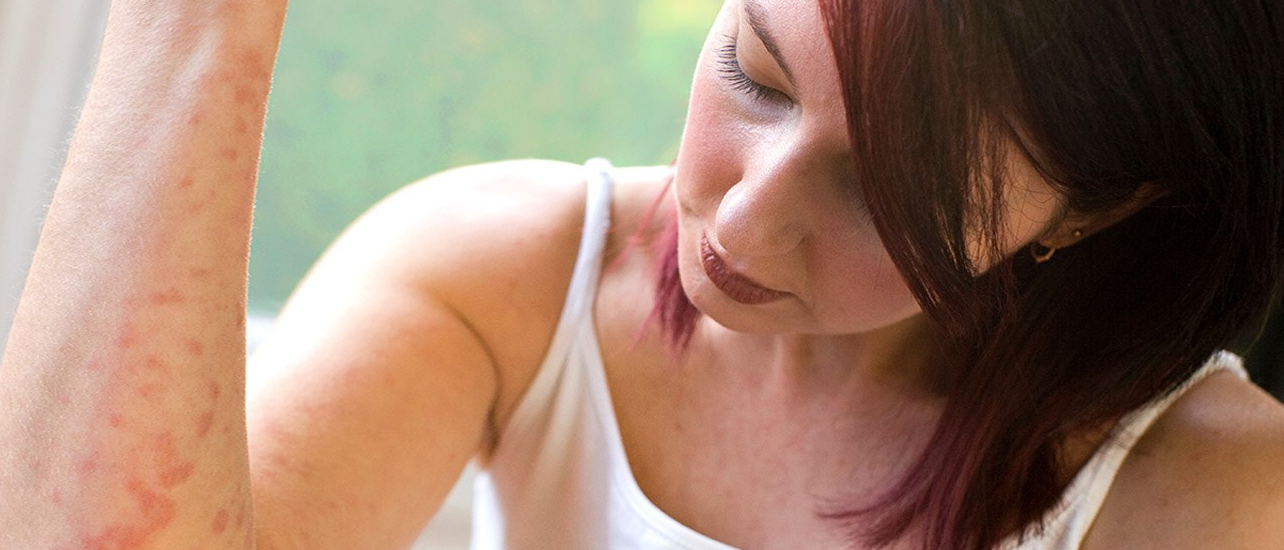 Currently, there are four clinical forms of erythema annulare. The first symptom of all forms is the formation of red spots on the surface of the skin, sometimes with itching. In the subsequent course of each form acquires its own characteristic features.
Currently, there are four clinical forms of erythema annulare. The first symptom of all forms is the formation of red spots on the surface of the skin, sometimes with itching. In the subsequent course of each form acquires its own characteristic features.
Scaly annular erythema often develops with helminthiasis and paraneoplastic syndrome. The area of redness begins to peel off over time, in the center a slight pigmentation of the skin is revealed, the redness becomes less pronounced. The growth of education continues along the periphery, the size of pathological foci reaches 15-20 centimeters. Changes in the central part are weakly expressed, which, in combination with peripheral growth, leads to the appearance of characteristic formations of a bizarre shape. The duration of the existence of the focus can be several months, after the resolution of the rashes, the skin remains pigmented. Often new spots and areas of annular erythema are formed, with a long-term recurrent course of the disease, bizarre patterns from areas of erythema and areas of hyperpigmentation are revealed on the patient's body.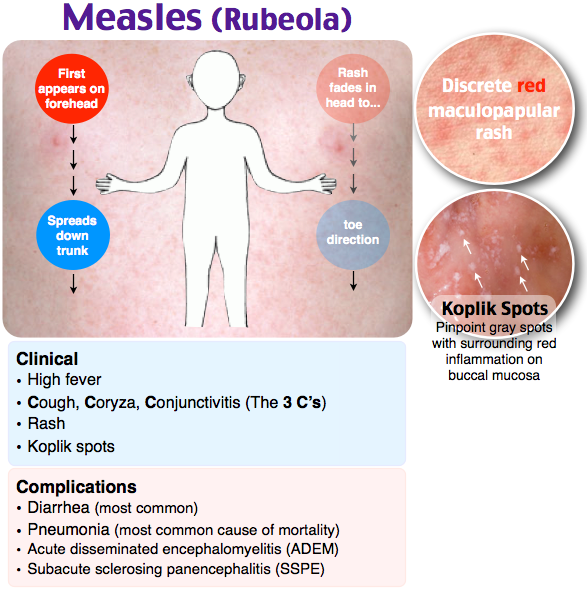
Vesicular annular erythema has an unclear etiology, usually occurs against the background of reduced immunity and endocrine disorders. Even at the stage of a red spot, small vesicles filled with serous fluid appear along the edges of the focus. In the future, as with scaly annular erythema, there is a peripheral growth of the pathological focus with the formation of a hyperpigmentation area in the center. In the process of growth, small vesicles constantly form and disappear along the edges of the focus. The course of this form of annular erythema is chronic, relapsing, the rashes may disappear after a few weeks or months, giving way to the development of new foci.
Erythema simplex occurs when you are allergic to food or medicines. It is the mildest variant of the disease, characterized by a fairly rapid transformation of spots into ring-shaped structures. Peeling of the skin or the formation of vesicles does not occur, redness becomes the only manifestation of the disease. Ring-shaped structures resolve without a trace after a few days or even hours after formation.
Ring-shaped structures resolve without a trace after a few days or even hours after formation.
Persistent annular erythema has an unclear etiology, accompanied by the formation of small spots and rings with a diameter of up to 1 centimeter. Sometimes vesicles or areas of peeling appear in the affected area. Characterized by a long course.
The literature also describes such forms of annular erythema as telangiectatic, indurated and purpuric. Due to the low prevalence (less than a hundred cases), some dermatologists believe that these forms of erythema annulare do not exist, and the described changes are other skin diseases with the formation of ring-shaped structures. The question of the validity of such an opinion remains debatable today.
Diagnosis of erythema annulare
The diagnosis of erythema annulare is based on the history and dermatological findings. In controversial cases, a skin biopsy is performed in the area of \u200b\u200bpathological foci.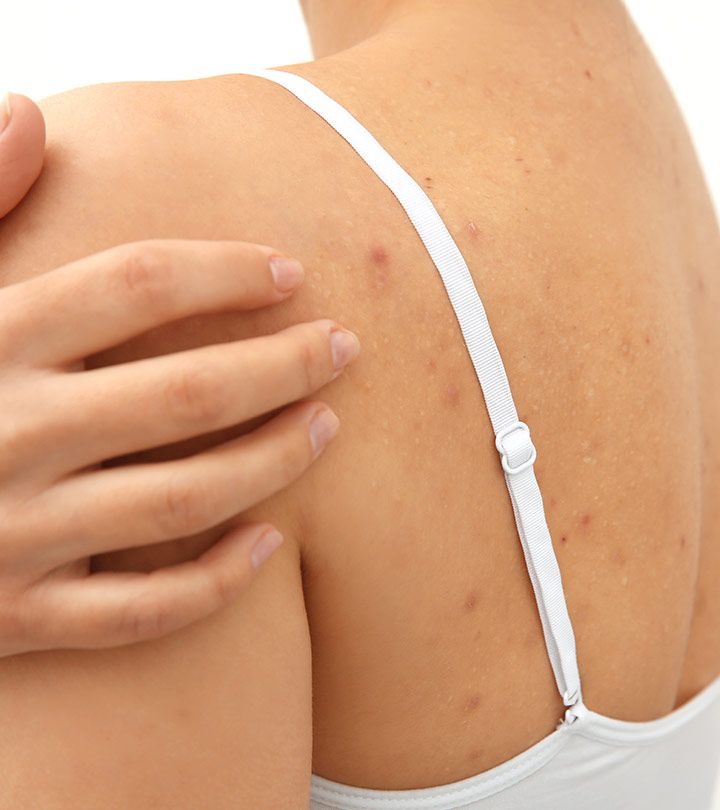 When examined by a dermatologist, erythematous rashes of various shapes and sizes are determined, often in the form of bizarre closed lines and stripes. Depending on the form of erythema annulare, along with reddening of the skin, peeling, the formation of papules or vesicles can be observed.
When examined by a dermatologist, erythematous rashes of various shapes and sizes are determined, often in the form of bizarre closed lines and stripes. Depending on the form of erythema annulare, along with reddening of the skin, peeling, the formation of papules or vesicles can be observed.
When studying the patient's history, diseases that provoked the development of this form of reactive dermatosis are often detected. Possible helminthic invasion, skin mycoses, malignant neoplasms, inflammation of the elements of the oral cavity and upper respiratory tract. In the absence of these diseases, the patient may be assigned laboratory and instrumental studies to assess the condition of various organs and systems and determine the causes of the development of erythema annulare. Particular attention should be paid to the possibility of oncological lesions, since erythema annulare is sometimes a manifestation of paraneoplastic syndrome.
Changes in the general blood test in erythema annulare are nonspecific and, in general, contribute to the establishment of the nature of the provoking factor.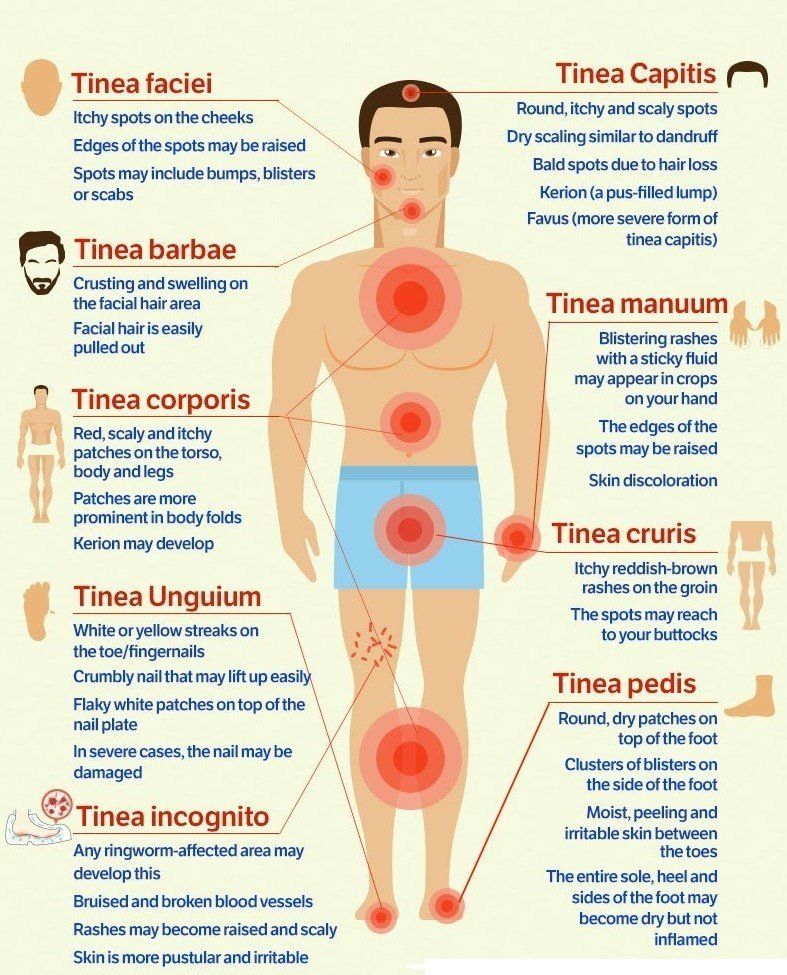 For example, eosinophilia may indicate a helminthic invasion or allergy, leukocytosis - an acute or chronic inflammation. Quite often, with annular erythema, dysproteinemia is detected - a violation of the ratio between individual fractions of plasma proteins. Histological examination of the skin usually reveals an unchanged epidermis with edema and marked leukocyte infiltration of the dermis. Histoimmunofluorescent analysis confirms the accumulation of class G immunoglobulins at the basement membrane of the epidermis. The differential diagnosis of erythema annulare is with seborrheic eczema, granuloma annulare, and syphilitic roseola.
For example, eosinophilia may indicate a helminthic invasion or allergy, leukocytosis - an acute or chronic inflammation. Quite often, with annular erythema, dysproteinemia is detected - a violation of the ratio between individual fractions of plasma proteins. Histological examination of the skin usually reveals an unchanged epidermis with edema and marked leukocyte infiltration of the dermis. Histoimmunofluorescent analysis confirms the accumulation of class G immunoglobulins at the basement membrane of the epidermis. The differential diagnosis of erythema annulare is with seborrheic eczema, granuloma annulare, and syphilitic roseola.
Treatment of erythema annulare
There is no etiotropic treatment for erythema annulare, but successful treatment of the underlying disease can significantly reduce the manifestations of this condition. Depending on the identified pathology, skin mycoses, tonsillitis and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are treated. If necessary, carry out sanitation of the oral cavity. In the process of treating the underlying disease, antibiotics, antihelminthics and other drugs are used. In the presence of a malignant neoplasm, the treatment plan is determined depending on the location, extent and type of neoplasia.
If necessary, carry out sanitation of the oral cavity. In the process of treating the underlying disease, antibiotics, antihelminthics and other drugs are used. In the presence of a malignant neoplasm, the treatment plan is determined depending on the location, extent and type of neoplasia.
Along with the treatment of the underlying disease in erythema annulare, desensitizing therapy is carried out. Use antihistamines (cetirizine, chloropyramine), calcium chloride and sodium thiosulfate. To normalize metabolism, patients are prescribed vitamin therapy, especially vitamins C, A and E. Patients are shown a hypoallergenic diet with an increase in the amount of carbohydrates in the diet. In severe cases, corticosteroids (prednisolone) are used to reduce inflammation. Antipruritic ointments are applied topically, and if vesicles are present, antiseptics are used to prevent secondary infection.
Prediction and prevention of erythema annulare
In general, the prognosis is favorable.