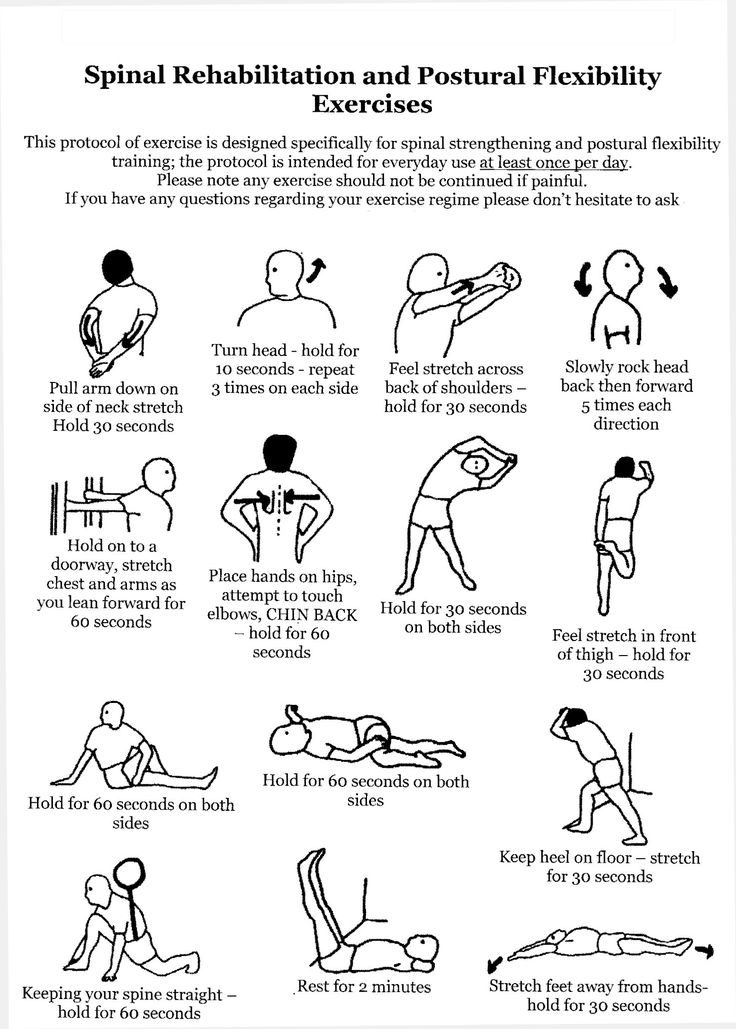
How to gain guardianship of a child
How to Establish Guardianship of a Child FAQs
For anyone interested in learning how to establish guardianship of a child, there are so many concerns accompanying such an important process. First of all, you'll want to get an understanding of the legal process required to get started, not to mention the factors considered by the court.
Read on for answers to common questions about establishing guardianship of a child.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What's the procedure for establishing guardianship of a child?
- Can I appoint a legal guardian for my own children?
- Do I need to explain my choice of legal guardian for my children?
- What if the parents of the child don't consent? Can I still establish guardianship of the child?
- How burdensome are the responsibilities of a legal guardianship?
- Discuss your concerns about how to establish guardianship of a child with an attorney.
What's the procedure for establishing guardianship of a child?
You can establish guardianship of a child by filing papers in court. Initially, file a petition stating your interest in obtaining guardianship along with a filing fee. You'll also want to file a letter of consent from the child's parents if that is possible.
Once you've filed your petition, the court may set up interviews with you and possibly the child, the child's parents (if they're available), and anyone else who may have an interest. In some cases, the court may order a home visit or inspection. Also, a criminal background check of the would-be guardian is usually conducted.
Once the judge has approved your guardianship petition, they'll give you an order to establish guardianship. Be sure to check your local government's website for instructions. Some of these sites may even have forms you can download, fill out, and file with the court.
Can I appoint a legal guardian for my own children?
Yes, and doing so is good planning. In case of the unfortunate event that you become unable to raise your children, you should establish guardianship for them. One way to handle designating someone as your child's guardian is to do so in your will.
One way to handle designating someone as your child's guardian is to do so in your will.
Choose someone you trust and add a clause to your will that you want that person to raise your children if you ever become incapable of doing so. Reasons for the inability to raise your child could include death or incapacitation.
In your will, name one person as guardian and one person as an alternate. Indicating an alternate is important in case the first person you indicate can't fulfill the position for any reason. Do this for each of your children.
You can even indicate more than one guardian and more than one alternate for any one of your children. Keep in mind, however, that this has the potential to create problems should the co-guardians ever disagree. Appointing a married couple often works well. Be sure to name both members of the couple. Doing so ensures that they have legal custody to make decisions for your child.
But keep in mind the drawbacks unique to designating a guardian in a will. The designation of a guardian in your will may not be honored under some circumstances. For example, in some states, when one parent dies, the other parent automatically gets custody unless they're proven unfit. In such a case, a probate court may refer the case to a family court with jurisdiction to determine custody issues. This might happen if your co-parent were to contest the guardianship designation in your will.
The designation of a guardian in your will may not be honored under some circumstances. For example, in some states, when one parent dies, the other parent automatically gets custody unless they're proven unfit. In such a case, a probate court may refer the case to a family court with jurisdiction to determine custody issues. This might happen if your co-parent were to contest the guardianship designation in your will.
When choosing a legal guardian, keep in mind that by law, the designated person must be:
- An adult
- Physically able to fulfill the responsibilities of a guardianship
- Have ample time to care for your child or children
- Able to afford to raise your children, using their own income or with assets you leave for your child's or children's care
Do I need to explain my choice of legal guardian?
It's always a good idea to leave a letter of explanation for any judge that may question the choice you make concerning the person you designate as your child's guardian. Judges use the "best interests of the child" standard, and a judge will likely want to know why you feel the designated person serves those interests. Judges consider the following:
Judges use the "best interests of the child" standard, and a judge will likely want to know why you feel the designated person serves those interests. Judges consider the following:
- The child's preference
- Who can best fulfill the child's needs, stability, and continuous care
- The relationship between the child and the potential legal guardian
- The moral character, fitness, and conduct of the potential guardian
What if the parents of the child don't consent? Can I still establish guardianship of the child?
Generally, guardianship is only granted if:
- Both parents consent to the guardianship unless only one is available to do so
- The parents have abandoned the child
- A judge finds it would be in the child's best interests to remove the child from the parent's custody
And in cases where the parents object, you may still be able to obtain guardianship. In most cases, this involves proving the parents are unfit.
Besides the parents, the child's other family members also have rights when it comes to how you obtain guardianship. The other family members must be notified, and they also have the option to object. Although you don't need consent from all the child's relatives, their objections could create issues in your application process and the process in general. If this happens, be sure to promptly consult an attorney. And even if you obtain guardianship despite their objections, you may find yourself in a tense relationship with the other family members.
How burdensome are the responsibilities of legal guardianship?
It's not an easy task to be a minor's legal guardian. There are many responsibilities, including financial obligations and time with the child. If the biological parents are still living and still have rights to the child, such as physical child custody or visitation, then they're financially responsible for the child.
In most cases, you're taking on all the responsibilities of a parent when you become a guardian. Before taking on this role, consider the following questions:
Before taking on this role, consider the following questions:
- Do I want the continuous responsibilities of legal guardianship?
- Am I ready to accept full liability for the child's actions?
- Do I want to act as the legal parent of this child for the entirety of the guardianship?
- Will the parents support my guardianship, or will they be hostile?
- How will guardianship affect my own family, health, job, and life overall?
Becoming the legal guardian of a child is a huge responsibility with a lot to consider. Think carefully about the questions above and plan accordingly. Also, keep in mind that, generally speaking, the parent(s) may revoke the guardianship at any time.
Discuss Your Concerns About Guardianship of a Child with an Attorney
Are you applying for guardianship? Are you feeling confused as you navigate how complicated the process can be? A great first step is contacting an experienced family law attorney who can help you map out your plans for establishing guardianship. Get started today by finding a family law attorney near you.
Get started today by finding a family law attorney near you.
Getting guardianship of a child
What is guardianship?
Usually, only a parent of a child has the authority to make decisions about the care of a child or property belonging to a child. Sometimes, a parent cannot or will not make decisions for their child. When this happens, a person that is not the parent can become the legal guardian of the child.
Legal guardianship lets someone that is not a parent make decisions for a child, just as a parent would. The person with authority to make decisions about a child's care or property is called the child's guardian. The guardian does not have to be related to the child.
Who can be a guardian?
To become a guardian in Illinois, a person must:
- Be at least 18 years old,
- Be a resident of the United States (some courts will appoint undocumented immigrants),
- Be of sound mind,
- Not be legally disabled, and
- Not have a felony conviction that involved harm or threat to a child.

A person's blindness cannot by itself prevent them from becoming a guardian.
What types of guardianship are there?
There are 3 different types of guardianship:
- Plenary guardian (long-term),
- Standby guardian, and
- Short-term guardian (no need to go to court).
Plenary guardian
A plenary guardian is a long-term, permanent guardian. Once someone is appointed a plenary guardian, they cannot give up the responsibility, unless a judge rules that:
- A parent can care for the child again, or
- Someone else is willing to become the guardian.
The guardianship ends automatically when the child turns 18.
To become a plenary guardian, there must be a court case where the judge approves the guardianship. The court can appoint a guardian only if any of the following are true:
- The parents are deceased,
- The parents are unable or unwilling to make daily decisions for the child,
- The parents voluntarily leave the child with another adult and does not return,
- The parents agree to the guardianship, or
- The parents are detained, arrested, removed, or deported because of immigration issues.
Standby guardian
A standby guardian is a person who will take over as guardian when a parent or legal guardian can no longer care for a child. This may happen when a parent or guardian gets sick, dies, or lives apart from the child for an extended period of time.
A parent or guardian must designate the standby guardian. This must be done in writing. A designation can be a simple document such as the Designation of Standby Guardian form. It must be signed and witnessed by at least 2 people who are at least 18 years old. A witness cannot also be the person trying to be the standby guardian. A parent may also designate a standby guardian in their will.
The standby guardian will not have any duties or authority to care for a child until any of the following things happen:
- The parent or legal guardian dies,
- The parent or legal guardian gives consent,
- The parent or legal guardian can no longer make or carry out day-to-day child care decisions for the child, or
- The parent or legal guardian is detained, arrested, removed, or deported because of immigration issues.

When one of these happens, the standby guardian automatically has the authority to act as full guardian for up to 60 days. Within those 60 days, the standby guardian must go to court to apply for further authority to act as the standby guardian. Or they can petition for plenary guardianship, or appoint someone else to be a guardian before the 60 day period ends.
Standby guardianship could be a useful safety plan for immigrant parents who are undocumented. For example, if a parent is afraid that they will be detained or deported, they can designate a standby guardian who will have authority to care for the child when the parent is unable to do so.
Some parents who are undocumented do not want to ask a judge to appoint a standby guardian because they are afraid to go to court. Or, they are afraid that the judge will ask about their immigration status. Immigration status is not necessarily a part of guardianship law in Illinois, but some judges do ask about it.
Immigration status is not necessarily a part of guardianship law in Illinois, but some judges do ask about it.
Short-term guardian
A short-term guardian is responsible for the child for one year or less. The parent or guardian picks the short-term guardian. The parent or guardian does not need to go to court, but the agreement must be in writing.
The agreement must be signed and witnessed by at least 2 people who are at least 18 years old. A witness cannot also be the person trying to be the short-term guardian.
The written agreement should state the exact date the guardianship ends. It usually can't last for more than one year. However, if the guardianship started because the parents were detained, arrested, removed, or deported because of immigration issues, it can be renewed for another year.
The agreement can also state that the guardianship ends if an event happens. For example, if the parent returns from active military duty. A parent or guardian can end the short-term guardianship at any time, even before the end date stated on the written agreement.
A parent or guardian can end the short-term guardianship at any time, even before the end date stated on the written agreement.
The short-term guardian does not have to be related to the child. Only one short-term guardian can exist at any one time.
If the child has assets, such as property or money, a short-term guardian will not have control over these. For a guardian to control these assets on the child's behalf, a plenary guardianship is needed. The exception is that a short term guardian can apply for and receive government benefits on behalf of the child.
What can a guardian decide?
A guardianship can be of the person, and make personal care decisions, or of the estate, and make decisions about property. Guardianship can be of the person, of the estate, or both, depending on the situation.
Guardianship of the person
A guardian of the person has broad power to make decisions for the child's care. A guardian of the person is responsible for physical custody of the child and must provide food, shelter, education and ordinary medical care. A guardian of the person can consent to marriage, enlistment in the armed forces, and medical treatment. A guardian of the person can also represent the child in legal proceedings.
Guardianship of the estate
A guardian of the estate can only make decisions about the child's money and property. Also, the guardian of the estate can only spend or use the money and property for the benefit of the child.
What is a Guardian ad litem (GAL)?
A guardian ad litem, or a GAL, is someone a judge names to look into the facts of a case. Although it has the word "guardian" in the name, the GAL is not a guardian that can make decisions for the child. A GAL can recommend what would be in the child's best interests. But they cannot make any decisions for the child like a regular guardian. The GAL gives the judge their opinion about who should care for the child. The judge thinks about the GAL's opinion and then makes a final decision.
A GAL can recommend what would be in the child's best interests. But they cannot make any decisions for the child like a regular guardian. The GAL gives the judge their opinion about who should care for the child. The judge thinks about the GAL's opinion and then makes a final decision.
We arrange custody of a child with living parents
Children are the most unprotected category of people in society. Sometimes it is they who need protection more than adults. In life, there are situations in which fathers and mothers do not show the necessary care for their children. There are solutions to this problem in the legislation. One solution to the problem is guardianship.
Free consultation on family issues specialist Sergey Borisovich Volkov REQUEST A CALL
WHEN DO YOU NEED GUARDIANSHIP FOR MINORS?
Guardianship of a minor is issued in the event that the father and mother do not fully fulfill their obligations to the child. To obtain the status of a guardian for a child who has parents, the law establishes the following.
To obtain the status of a guardian for a child who has parents, the law establishes the following.
- This can be both a physical and mental disorder, in which there is no full-fledged care for the child.
- Field of activity related to permanent and unlimited business trips.
- The territory of residence of the father and mother is in another city or country.
- Lack of opportunity to provide your own child with things necessary for life, growth and development.
- The desire of parents to give up their child on a voluntary basis.
The Family Code still contains reasons related to the return of the father and mother of the child. Parents have not reached the 16-year return, and the relationship is not registered according to the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation.
WHO CAN BECOME A GUARDIAN, WHAT REQUIREMENTS DO THE LAW
- Legal legislation puts the interests of the child at the head.
 That is why a prerequisite for the life of the baby and his social development is to improve the standard of living and his environment before the change of guardianship. A complete list of requirements is specified in article 146 of the Family Code
That is why a prerequisite for the life of the baby and his social development is to improve the standard of living and his environment before the change of guardianship. A complete list of requirements is specified in article 146 of the Family Code - The guardian must have full legal capacity. This means that the guardian must have a legal form of legal action and it is he who is absolutely responsible for the execution of any action related to the field of jurisprudence.
- It is unacceptable to have criminal or administrative punishment, as well as cases of deprivation of parental rights from a person who wants to become a guardian and take care of a child.
A person who is ready to take responsibility for a minor citizen will not be appointed as a guardian if he has a chronic drug or alcohol addiction (a mandatory medical examination of candidates for guardianship is carried out). And also people with the first group of disability are not allowed to guardianship.
HOW TO GET GUARDIANCY OVER A CHILD
The legal legislation of the Russian Federation provides for only two main possibilities for obtaining custody of a child:
- - the presence of written consent from the biological parents
- - availability of documents indicating the deprivation of legal parents of their parental rights
WHAT CHILDREN ARE ALLOWED TO GET CUSTODIANS
- Before the age of 14 of the minor.
- In case of deprivation of the father and mother of the rights to the child, then until the age of 18, and in exceptional situations up to 23 years.
- When there is a temporary lack of opportunities for full-fledged child care.
Guardianship for a certain period of time is issued in the following cases:
- The father and mother officially terminated their marriage.
- A person who has not reached the age of majority attends an educational institution located far from the place of residence
- An unfavorable economic situation in the family or one of the parents has a serious physical or mental deviation.

GUARDIANSHIP OF A SICK CHILD WITH A DISABILITY
The process for obtaining guardianship of a minor with a disability is very different from that of a child without a disability. All this is due to the fact that disabled children are more defenseless. According to the law, disability is considered to be physical and mental disabilities.
- A person who wants to become a guardian of a child with a disability must go through the most difficult procedure.
- Proper comprehensive medical examination.
- Written parental consent is required. If this consent is not provided by the guardian, the registration process is very complicated.
GET A PRICE
0010
Relatives, especially grandmothers, have priority in matters of guardianship. And all because grandmothers, like no one else, can replace a mother for a child.
Although relatives have the first priority when applying for guardianship, the package of documents for guardianship remains unchanged. Of course, the desire of the persons in respect of whom guardianship is issued is taken into account in accordance with the law, but as practice shows, children with a great desire remain to live with close relatives.
Of course, the desire of the persons in respect of whom guardianship is issued is taken into account in accordance with the law, but as practice shows, children with a great desire remain to live with close relatives.
RIGHTS AND OBLIGATIONS OF THE GUARDIAN
The Family Code is the document regulating the main processes related to guardianship and guardianship, and in disputable situations it is necessary to refer to the federal normative act (law).
A person who has taken custody of a minor is obliged:
- The guardian is obliged to provide his ward with housing, clothing and food.
- The guardian takes care of the health of his or her ward and takes measures for treatment in case of symptoms indicating illness.
- The guardian is obliged to provide the minor with all conditions for comprehensive development, provide an opportunity for education.
- The guardian must meet the needs of the child until the age of 16.
- The guardian must have a common residence with the ward until he reaches the age of 16 years.
- When changing the place of residence, the person who has issued guardianship is obliged to notify the guardianship authorities about this.
- The guardian is obliged to own and use the property of the ward with the written permission of the authorized bodies.
- The funds of a minor are spent only on his needs. The guardian submits an annual report for the money of his ward.
A person who has taken custody of a minor has the right:
- A person who has taken custody of a minor has the right to use the things of a minor until the age of 14, and with the permission of the child up to 16 years of age. A person in respect of whom guardianship has been issued begins to participate in legal transactions on his own, only when he reaches the established age.
- The person who has issued guardianship independently establishes the methods of the educational process of the ward, but the guardianship authorities have the right to express their opinion.

- The guardian receives money for the child he has taken into custody.
- If the person who has issued guardianship has a decreased financial condition, or health problems begin, he has the right to cancel guardianship in the relevant authorities.
WHAT DOCUMENTS DO YOU NEED?
Due to the fact that when formalizing guardianship, guardianship authorities entrust the life and health of a minor child, this process is rather laborious and requires a large amount of materials, which reflect the maximum information about the guardian. Documents related to the materials required for registration of guardianship:
- Identity document (passport).
- A complete and consistent account of the life of the person who draws up guardianship (autobiography). The autobiography reflects information about education, places of residence and places of work. Providing false information may result in liability, up to criminal liability.

- Certificates indicating the financial condition of the guardian. In the case when a person has more than one source of income, information on all is required.
- Standard statement of the competent authorities to which the person holding guardianship expresses his desire.
- Written consent is required under the condition that the parents have rights to the child.
- Pension certificate. Required for grandparents if they decide to become guardians of their grandson.
- A document (certificate) certifying the fact that the person formalizing guardianship has no criminal record.
PROCEDURE AND NUANCES OF THE PROCEDURE
The state guardianship authorities are responsible for documenting guardianship in our country. A citizen who wants to take a child to himself must collect a complete package of these documents and together with him apply to the guardianship authorities at the place of residence. It is there that all the necessary checks will be carried out and the person will be able to obtain a legal document on guardianship.
It is there that all the necessary checks will be carried out and the person will be able to obtain a legal document on guardianship.
Having received all the necessary documents, the guardianship authorities are obliged to form an independent commission of guardianship department employees at the candidate's place of residence. The final goal of the commission is to draw up a special. act. The commission is obliged to leave within three days at the place of residence of a person who is ready to become a guardian. On the fact of the actions performed, an act is drawn up on checking the living conditions in which the child will be.
If the commission makes a positive decision on this act, then the guardianship department inspector must verify the authenticity of all previously submitted documents. After 10 working days, employees of the guardianship department are required to notify the person who submitted the application about their decisions in writing.
If the issue is successfully resolved, a guardianship order is issued. This legal document will be valid for two years.
This legal document will be valid for two years.
A child who has reached the age of 10 years at the time of legal guardianship has the right to make his own final decision on the appointment of a guardian. Obligatory only in case of full consent of the child is it possible to complete the guardianship procedure.
How do I get guardianship of a child, elderly or disabled person?
What is guardianship?
In Russia, citizens who need guardianship include minors, that is, children under 14, as well as persons recognized by the court as incompetent. We are talking about people who, due to a mental disorder, cannot understand the meaning of their actions or control them. This is stated by the Federal Law "On guardianship and guardianship". Based on the document, citizens appointed by the guardianship and guardianship authority "are the legal representatives of the wards, and perform on their behalf and in their interests all legally significant actions. "
"
Guardianship is aimed at protecting the interests of the listed categories of citizens, as well as the very possibility of declaring a citizen incompetent in a judicial proceeding. This was also emphasized by the Constitutional Court in the framework of Resolution No. 15-P dated June 27, 2012 “On the case of checking the constitutionality of paragraphs 1 and 2 of Article 29, paragraph 2 of Article 31 and Article 32 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in connection with the complaint of citizen I.B. Business".
How is guardianship different from guardianship?
In addition to guardianship, there is also guardianship, under which adolescents aged 14 to 18 years old, as well as persons with limited legal capacity, can fall. Such people cannot be fully responsible for their actions. This category has more rights than minors and the incapacitated. For example, they can independently perform small household transactions and actions provided for by law (dispose of their own income, etc. ). However, in other cases, they are obliged to assist the trustee.
). However, in other cases, they are obliged to assist the trustee.
It turns out that the guardian has more rights and obligations than the trustee, in connection with which he bears a great responsibility.
Who can become a guardian or custodian?
The main requirement for a candidate is full legal capacity. And since it comes from the age of 18, the guardian must be of age. The law also establishes a list of restrictions. Guardianship cannot be issued by persons:
- deprived of parental rights;
- having an unexpunged or outstanding conviction for an intentional crime against life or health;
- who did not agree to become a guardian.
When it comes to guardianship of young children (under 14), additional restrictions are set. Future guardians must undergo special psychological, pedagogical and legal training, as well as prove that they are in a bisexual marriage. Those who have registered a same-sex marriage in the territory of another state will not be able to arrange guardianship.
Registration of custody of a child
This process is supervised by the guardianship and guardianship authorities. To find out all the details of the procedure, you must contact the district office. The state is interested in ensuring that children are not left unattended, are not placed in orphanages and boarding schools, and therefore, most likely, those who wish to arrange guardianship will be met halfway and will be helped in every possible way.
The candidate needs to write an application, collect documents confirming, among other things, the passage of special training, and in case of a positive answer, sign an agreement.
How can I get guardianship of an elderly incapacitated person?
The algorithm is the same as for children - the guardianship and guardianship authority will also deal with the issue of guardianship. However, there are also differences. Thus, custody of an elderly or adult person does not always involve the joint residence of the guardian and his ward. This issue is decided individually, but cohabitation, of course, is welcome. It is much easier for a guardian to fulfill his duties and provide supervision, especially when it comes to a pensioner who, most likely, has a sufficient number of health problems.
This issue is decided individually, but cohabitation, of course, is welcome. It is much easier for a guardian to fulfill his duties and provide supervision, especially when it comes to a pensioner who, most likely, has a sufficient number of health problems.
If cohabitation is intended, consent must be obtained from all family members of the guardian living in the same dwelling, including children aged 10 and over.
How to get paid guardianship?
There are two types of guardianship:
- free of charge;
- paid.
In the first case, nothing is paid to the guardian. Paid guardianship can have quite flexible conditions, which are fixed by the contract. In accordance with Article 16 of the Federal Law “On Custody and Custody”, remuneration can also be paid at the expense of third parties, from the income from the property of the ward (no more than 5% and only if he is already an adult), as well as from the budget .
Features of the legal status
The guardian has an unlimited range of powers - he represents the interests of the ward in any relationship, no matter what is discussed. Moreover, this rule applies even when registering custody of a minor with living parents. If the ward is a child, then the guardian acts as a father or mother. However, in some cases notification of guardianship authorities is required. They can also establish restrictions on the actions of the guardian or, conversely, oblige him to perform any actions. All this is recorded in the act on the appointment of a guardian or custodian, or in an agreement on the implementation of guardianship or guardianship.
What documents are required for registration of guardianship?
- Written statement of consent to the establishment of guardianship.
- Documents of the guardian: proof of identity, proof of income, no criminal record, state of health (medical certificate in the form established for persons wishing to obtain guardianship), marital status and the right to use the living quarters.