What does it mean when baby is head down
Symptoms of Baby Turning Head Down
Your baby kicks, squirms, and flips all day (and night!). But what exactly are they doing in there?
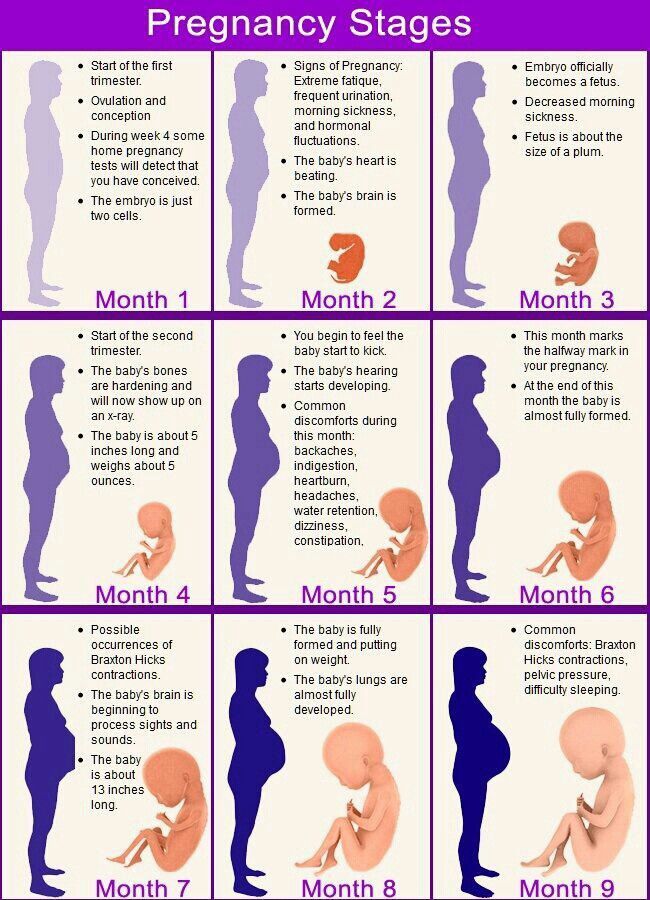
Well, toward the end of your pregnancy, your baby will likely get into a head-down position so that they can begin their descent into the birth canal. The exact timing of when your baby hits this position is individual. And some babies prefer other positions, like breech (head up) or transverse (side lying).
Regardless, some signs can serve as clues about how baby’s relaxing in there. Here’s more about when your baby will move head down, what the options are if they stay head up or in another position, and what to feel for when trying to determine your baby’s position at home.
Related: What Sleeping Position Will Help Turn My Breech Baby?
Most babies tend to shimmy their way into a cephalic (head-first) presentation before birth.
Fast fact
At 28 weeks, around 25 percent of babies are breech (head up), but this number jumps down to just 3 or 4 percent at term.
Your baby may move all over the place in the first and second trimesters. Their position may change wildly early on in the third trimester as well.
However, if you’re between 32 and 36 weeks, you may notice your baby staying put in a head-down position. Your uterus grows to accommodate their size — but there’s only so much room. As time passes, your baby gets bigger and starts to run out of space to move into different positions.
Related: The Third Trimester of Pregnancy: Concerns and Tips
Being head down is just half of the equation when it comes to birth. There’s also the matter of which way your baby is facing.
Why does this make a difference? It comes down to geometry. Your baby’s head must fit through the pelvis on its way into the vaginal canal for delivery. Some positions make this journey easier than others, especially considering how different parts of your baby’s skull are wider and narrower than others.
- Occiput anterior: This position is the most common.
 It means that your baby is head down with their back against your stomach and their chin tucked into their chest.
It means that your baby is head down with their back against your stomach and their chin tucked into their chest. - Occiput posterior: This position means that your baby is head down but facing the opposite direction. In this position, your baby’s back is at your back.
Anterior is the ideal position for an uncomplicated vaginal delivery. When your baby’s chin is tucked, it helps the narrowest part of their head go through the birth canal. Posterior presentation can mean a longer or potentially more difficult delivery, sometimes requiring a vacuum, forceps, or cesarean section.
If your baby is posterior even in early labor, they may still turn throughout the process as contractions move them around in the womb. Some babies completely spin to an anterior position during labor while others are born posterior.
Related: What Your Baby’s Position in the Womb Means
You may not experience any signs that your baby has flipped into a head-down position. There’s really no easy way to tell just by looking at your bump. You need to get in there and feel around. But how?
There’s really no easy way to tell just by looking at your bump. You need to get in there and feel around. But how?
Fortunately, your doctor or midwife is trained to feel for your baby’s position using what are called Leopold’s maneuvers.
With this technique, your provider will feel for what part of your baby is presenting in the pelvis, then for your baby’s back, and then for what part of your baby is in your fundus (up high, near your rib cage). They’ll also feel around for your baby’s cephalic prominence, which simply means which way your baby is facing.
With a head-down presentation:
- baby’s head would be in your pelvis
- baby’s back position would depend on whether baby is anterior/posterior, but generally baby will have either their back to your belly (anterior) or your back (posterior)
- baby’s bottom/legs would be in your fundus
All these findings can also be confirmed via ultrasound to give you the clearest picture.
But how can you figure out your baby’s position at home? Pay close attention to the shapes in your belly, as well as the different movements you feel.
Your baby may be head down if you can:
- feel their head low down in your belly
- feel their bottom or legs above your belly button
- feel larger movements — bottom or legs — higher up toward your rib cage
- feel smaller movements — hands or elbows — low down in your pelvis
- feel hiccups on the lower part of your belly, meaning that their chest is likely lower than their legs
- hear their heartbeat (using an at-home doppler or fetoscope) on the lower part of your belly, meaning that their chest is likely lower than their legs
Belly mapping
It can be difficult to read the different lumps and bumps you feel on your stomach. With practice, you may start to understand what you’re feeling. You might even try belly mapping — a process to estimate baby’s position. It was created by Gaily Tully, certified professional midwife and author of SpinningBabies.com.
To use this technique, wait until you are at least 30 weeks pregnant. You may even want to try belly mapping following a prenatal appointment so your doctor can give you some guidance on baby’s position.
You may even want to try belly mapping following a prenatal appointment so your doctor can give you some guidance on baby’s position.
Lie down in bed or on the couch. Using a washable marker or finger paint, gently mark where you feel your baby’s head (it feels like a small bowling ball). The arms and hands are likely near the head, and their tiny movements give them away.
Then feel for the back, butt, and legs, as well as larger movements. You may find it helpful to use a baby doll to play with different possible positions. You can then lightly draw or paint your baby on your stomach to help you visualize how they’re lying.
Related: Can You Give Birth with Baby in the Vertex Position?
If you’re in late pregnancy and have concerns about your baby’s positioning, ask your doctor about it at your next prenatal appointment. Chances are that your healthcare provider is making a note of your baby’s position as well.
If your baby is breech or in some other position besides head down, there are several options for delivery. Factors at play here include:
Factors at play here include:
- whether your baby stays in a certain position as you reach term
- any other pregnancy complications you might have
- when you end up going into labor naturally
Wait-and-see approach
Again, your baby’s position isn’t usually a big concern until you reach between 32 and 36 weeks in your pregnancy. Before that point, the fluid in the uterus gives your baby plenty of space to move around. As you get closer to delivery and your baby hasn’t settled head down, they start to run out of room to make the switch.
Your doctor can monitor your baby’s position at your prenatal appointments by feeling your belly for where their head, back, and buttocks are. To confirm, you may also have an ultrasound or pelvic exam.
External cephalic version (ECV)
External cephalic version (ECV) is a procedure during which your doctor tries to move your baby into a head-down position to increase the chance you’ll have a vaginal birth. This is done in a setting in which baby can be monitored and you can have an emergency cesarean section (C-section) if needed.
This is done in a setting in which baby can be monitored and you can have an emergency cesarean section (C-section) if needed.
Your provider uses their hands to manually turn the baby head down. If you’ve reached 36 weeks and your baby still isn’t head down, your doctor may suggest an ECV.
The success rate of this procedure is around 58 percent. While that’s not a super impressive statistic, ECV may be worth a try if delivering vaginally is important to you.
It’s also worth noting that some babies that are flipped return to a breech position. You can have a repeat ECV, but space runs out the closer you get to birth, so it may be more difficult the second time.
Cesarean delivery (C-section)
A C-section is another option for delivering babies who aren’t head down. It involves major surgery that you may schedule ahead of time (if you know your baby isn’t head down) or that can be performed in the event you go into labor naturally.
Around 85 percent of breech babies are born via C-section. While this surgery is routine, it involves some risks, including:
While this surgery is routine, it involves some risks, including:
- infection
- postpartum hemorrhage
- blood clots
- issues with future pregnancies, like a risk of placenta previa or uterine rupture
Vaginal birth
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists explains that some women may be candidates for a vaginal birth even if their babies are breech. This possibility is determined on a case-by-case basis and involves a review of your medical history and weighing the benefits of vaginal delivery versus the risks of C-section.
If you choose to go this route, you’ll need to follow any specific guidelines set up by your hospital or birth center.
Related: Midwives Are Growing in Popularity: Here’s What You Need to Know
Your baby moves a lot throughout your pregnancy. As you get closer to your due date, they’ll likely settle into a head-down position as they get ready for birth.
If you have concerns about your baby’s position, don’t hesitate to bring them up at your next prenatal appointment. Your healthcare provider is also keeping tabs on whether baby is head down and can help guide you with options for repositioning or an alternate birth plan, if necessary. You’ve got this, mama!
Your healthcare provider is also keeping tabs on whether baby is head down and can help guide you with options for repositioning or an alternate birth plan, if necessary. You’ve got this, mama!
Symptoms of Baby Turning Head Down
Your baby kicks, squirms, and flips all day (and night!). But what exactly are they doing in there?
Well, toward the end of your pregnancy, your baby will likely get into a head-down position so that they can begin their descent into the birth canal. The exact timing of when your baby hits this position is individual. And some babies prefer other positions, like breech (head up) or transverse (side lying).
Regardless, some signs can serve as clues about how baby’s relaxing in there. Here’s more about when your baby will move head down, what the options are if they stay head up or in another position, and what to feel for when trying to determine your baby’s position at home.
Related: What Sleeping Position Will Help Turn My Breech Baby?
Most babies tend to shimmy their way into a cephalic (head-first) presentation before birth.
Fast fact
At 28 weeks, around 25 percent of babies are breech (head up), but this number jumps down to just 3 or 4 percent at term.
Your baby may move all over the place in the first and second trimesters. Their position may change wildly early on in the third trimester as well.
However, if you’re between 32 and 36 weeks, you may notice your baby staying put in a head-down position. Your uterus grows to accommodate their size — but there’s only so much room. As time passes, your baby gets bigger and starts to run out of space to move into different positions.
Related: The Third Trimester of Pregnancy: Concerns and Tips
Being head down is just half of the equation when it comes to birth. There’s also the matter of which way your baby is facing.
Why does this make a difference? It comes down to geometry. Your baby’s head must fit through the pelvis on its way into the vaginal canal for delivery. Some positions make this journey easier than others, especially considering how different parts of your baby’s skull are wider and narrower than others.
- Occiput anterior: This position is the most common. It means that your baby is head down with their back against your stomach and their chin tucked into their chest.
- Occiput posterior: This position means that your baby is head down but facing the opposite direction. In this position, your baby’s back is at your back.
Anterior is the ideal position for an uncomplicated vaginal delivery. When your baby’s chin is tucked, it helps the narrowest part of their head go through the birth canal. Posterior presentation can mean a longer or potentially more difficult delivery, sometimes requiring a vacuum, forceps, or cesarean section.
If your baby is posterior even in early labor, they may still turn throughout the process as contractions move them around in the womb. Some babies completely spin to an anterior position during labor while others are born posterior.
Related: What Your Baby’s Position in the Womb Means
You may not experience any signs that your baby has flipped into a head-down position. There’s really no easy way to tell just by looking at your bump. You need to get in there and feel around. But how?
There’s really no easy way to tell just by looking at your bump. You need to get in there and feel around. But how?
Fortunately, your doctor or midwife is trained to feel for your baby’s position using what are called Leopold’s maneuvers.
With this technique, your provider will feel for what part of your baby is presenting in the pelvis, then for your baby’s back, and then for what part of your baby is in your fundus (up high, near your rib cage). They’ll also feel around for your baby’s cephalic prominence, which simply means which way your baby is facing.
With a head-down presentation:
- baby’s head would be in your pelvis
- baby’s back position would depend on whether baby is anterior/posterior, but generally baby will have either their back to your belly (anterior) or your back (posterior)
- baby’s bottom/legs would be in your fundus
All these findings can also be confirmed via ultrasound to give you the clearest picture.
But how can you figure out your baby’s position at home? Pay close attention to the shapes in your belly, as well as the different movements you feel.
Your baby may be head down if you can:
- feel their head low down in your belly
- feel their bottom or legs above your belly button
- feel larger movements — bottom or legs — higher up toward your rib cage
- feel smaller movements — hands or elbows — low down in your pelvis
- feel hiccups on the lower part of your belly, meaning that their chest is likely lower than their legs
- hear their heartbeat (using an at-home doppler or fetoscope) on the lower part of your belly, meaning that their chest is likely lower than their legs
Belly mapping
It can be difficult to read the different lumps and bumps you feel on your stomach. With practice, you may start to understand what you’re feeling. You might even try belly mapping — a process to estimate baby’s position. It was created by Gaily Tully, certified professional midwife and author of SpinningBabies.com.
To use this technique, wait until you are at least 30 weeks pregnant. You may even want to try belly mapping following a prenatal appointment so your doctor can give you some guidance on baby’s position.
You may even want to try belly mapping following a prenatal appointment so your doctor can give you some guidance on baby’s position.
Lie down in bed or on the couch. Using a washable marker or finger paint, gently mark where you feel your baby’s head (it feels like a small bowling ball). The arms and hands are likely near the head, and their tiny movements give them away.
Then feel for the back, butt, and legs, as well as larger movements. You may find it helpful to use a baby doll to play with different possible positions. You can then lightly draw or paint your baby on your stomach to help you visualize how they’re lying.
Related: Can You Give Birth with Baby in the Vertex Position?
If you’re in late pregnancy and have concerns about your baby’s positioning, ask your doctor about it at your next prenatal appointment. Chances are that your healthcare provider is making a note of your baby’s position as well.
If your baby is breech or in some other position besides head down, there are several options for delivery. Factors at play here include:
Factors at play here include:
- whether your baby stays in a certain position as you reach term
- any other pregnancy complications you might have
- when you end up going into labor naturally
Wait-and-see approach
Again, your baby’s position isn’t usually a big concern until you reach between 32 and 36 weeks in your pregnancy. Before that point, the fluid in the uterus gives your baby plenty of space to move around. As you get closer to delivery and your baby hasn’t settled head down, they start to run out of room to make the switch.
Your doctor can monitor your baby’s position at your prenatal appointments by feeling your belly for where their head, back, and buttocks are. To confirm, you may also have an ultrasound or pelvic exam.
External cephalic version (ECV)
External cephalic version (ECV) is a procedure during which your doctor tries to move your baby into a head-down position to increase the chance you’ll have a vaginal birth. This is done in a setting in which baby can be monitored and you can have an emergency cesarean section (C-section) if needed.
This is done in a setting in which baby can be monitored and you can have an emergency cesarean section (C-section) if needed.
Your provider uses their hands to manually turn the baby head down. If you’ve reached 36 weeks and your baby still isn’t head down, your doctor may suggest an ECV.
The success rate of this procedure is around 58 percent. While that’s not a super impressive statistic, ECV may be worth a try if delivering vaginally is important to you.
It’s also worth noting that some babies that are flipped return to a breech position. You can have a repeat ECV, but space runs out the closer you get to birth, so it may be more difficult the second time.
Cesarean delivery (C-section)
A C-section is another option for delivering babies who aren’t head down. It involves major surgery that you may schedule ahead of time (if you know your baby isn’t head down) or that can be performed in the event you go into labor naturally.
Around 85 percent of breech babies are born via C-section. While this surgery is routine, it involves some risks, including:
While this surgery is routine, it involves some risks, including:
- infection
- postpartum hemorrhage
- blood clots
- issues with future pregnancies, like a risk of placenta previa or uterine rupture
Vaginal birth
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists explains that some women may be candidates for a vaginal birth even if their babies are breech. This possibility is determined on a case-by-case basis and involves a review of your medical history and weighing the benefits of vaginal delivery versus the risks of C-section.
If you choose to go this route, you’ll need to follow any specific guidelines set up by your hospital or birth center.
Related: Midwives Are Growing in Popularity: Here’s What You Need to Know
Your baby moves a lot throughout your pregnancy. As you get closer to your due date, they’ll likely settle into a head-down position as they get ready for birth.
If you have concerns about your baby’s position, don’t hesitate to bring them up at your next prenatal appointment. Your healthcare provider is also keeping tabs on whether baby is head down and can help guide you with options for repositioning or an alternate birth plan, if necessary. You’ve got this, mama!
Your healthcare provider is also keeping tabs on whether baby is head down and can help guide you with options for repositioning or an alternate birth plan, if necessary. You’ve got this, mama!
Low fetal presentation - medical center "YOUR DOCTOR" Shakhty
Gynecology
At first they are connected with how the baby will develop, and then more terrible experiences appear. As a rule, they are associated with preterm birth, most of all fear causes a low presentation of the fetus.
Symptoms
The most common and main symptom is abdominal pain. As a rule, such pains do not let the girl go for a long time. With a low presentation, bleeding may occur. Due to bleeding, the fetus is subjected to oxygen starvation. This is very dangerous, as it harms the development of the baby.
However, it is worth noting that some are not aware that the fetus is in a low position. This is due to the fact that not every woman has symptoms.
This diagnosis can be made by a doctor during an ultrasound, as all possible risks become clearly visible there.
Consequences
When a girl is diagnosed with low fetal presentation, she must be warned about all the possible consequences that may occur.
Most often there is a risk of early labor. However, they are not only associated with this diagnosis, so their onset can be prevented.
In order to prevent the onset of preterm labor, a woman needs to go to the hospital. This is done in order to competently approach the solution of this problem, and to prevent all possible risks in a timely manner.
Another consequence of this diagnosis is frequent urination. This problem worsens the condition. To prevent it, it is necessary to reduce the amount of liquid that the girl consumes.
Also, low presentation can lead to the formation of hemorrhoids. This is due to the fact that the baby's head is pressing hard. In order to prevent the occurrence of this disease, it is worth eating right, as well as not doing heavy physical exertion.
Tips
Girls with this diagnosis should be constantly monitored by their doctor. And also report any deterioration or new symptoms to the doctor so that he can provide timely assistance.
An antenatal band is available to help reduce the risk of preterm labor. With the help of such a device, it is possible to reduce the pressure that is exerted by the head, which helps to avoid premature opening of the uterus.
Regular follow-up with specialists is necessary to prevent all possible consequences and receive effective treatment in the hospital. Thanks to this, the woman will be able to maintain her own health and the health of the child.
More related articles
Ovarian cancer: causes, symptoms, treatment
Ovarian cancer is one or more malignant neoplasms located inside the ovaries. In terms of its prevalence, the disease occupies the second position among oncological diseases of the reproductive system.
Gynecology
How contagious is thrush? How to get rid of "annoying" disease?
There is a huge amount of microbes, bacteria and similar "inhabitants" in our body. They may not show up for years. However, if immunity is only slightly inferior, the result will be disease.
Gynecology
Bacterial vaginitis. Causes, symptoms, treatment
In recent years, more and more women are turning to the doctor specifically for various bacterial vaginitis.
Why exactly does this happen and how can one suspect the presence of bacterial vaginitis in oneself?
Gynecology
About the first signs of a stroke.
About the first signs of a stroke.Login to site
Login:
Password:
To remember me
Forgot your password?
Registration
A request to confirm registration will be sent to the e-mail specified in the form.
Request to complete the questionnaire: "Do you know about stroke?" and watch the video "BLOW" about stroke.
Stroke: Symptoms, first signs and first aid
There is not a second to lose when there is a threat of a stroke: the patient's life and the possibility of further recovery depend on how quickly assistance is provided to the patient.
Vascular diseases of the brain are an urgent medical and social problem. Every year, strokes affect about 6 million people worldwide and claim more than 4 million lives.
Relentless statistics also show that the majority of stroke patients become disabled, unable to do without outside help (stroke ranks first among all existing causes of disability). Such depressing figures are an indication that few will be able to avoid a stroke: sooner or later, this terrible disease overtakes either the person himself, or one of his relatives or immediate environment.
Terrible cerebrovascular disease - stroke, or it is also called "brain stroke", includes a whole group of diseases caused by acute violation of cerebral circulation, which leads to damage to brain tissue and disruption of its functions.
Stroke is a disease of the brain caused by blockage (ischemia) or rupture (hemorrhage - hemorrhage) of a vessel that feeds part of the brain, or hemorrhage into the membranes of the brain. Thus, there are two types of stroke: hemorrhagic stroke (rupture of the vessel and hemorrhage) and ischemic stroke (blockage of the vessel).
KEY SYMPTOMS OF A STROKE
How can you tell if a person has a stroke? How to behave in this situation?
There are seven main first signs that you should definitely remember (they will all be sudden):
| 1. Distortion of the face (numbness of the lips or half of the face). If possible, ask the person to smile if this is difficult and one corner of the mouth is turned down, a sign of a developing stroke "on the face." 2. Speech disorder: sudden difficulties with articulation or listening to speech - a person is not able to clearly pronounce the simplest sentences. |