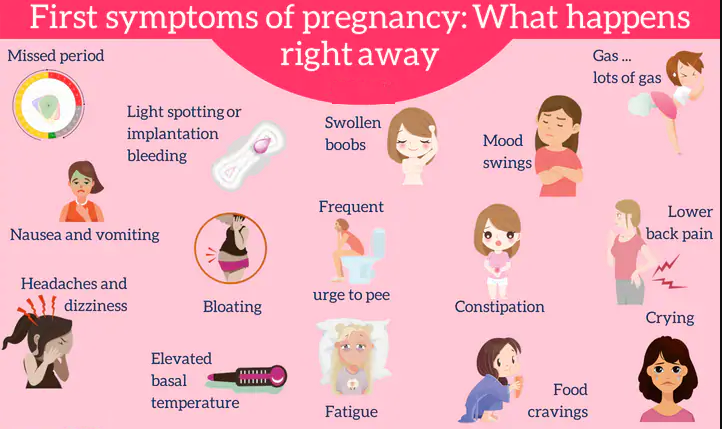
Burping pregnancy symptoms
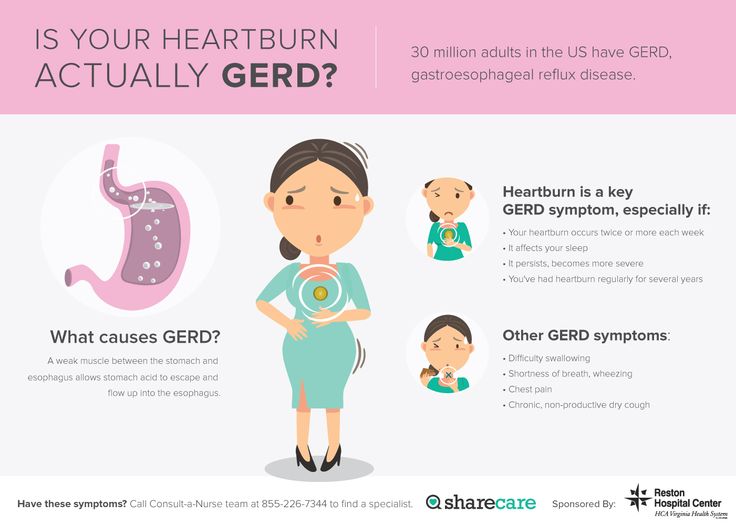
Indigestion and heartburn in pregnancy
Indigestion, also called heartburn or acid reflux, is common in pregnancy. It can be caused by hormonal changes and the growing baby pressing against your stomach.
You can help ease indigestion and heartburn by making changes to your diet and lifestyle, and there are medicines that are safe to take in pregnancy.
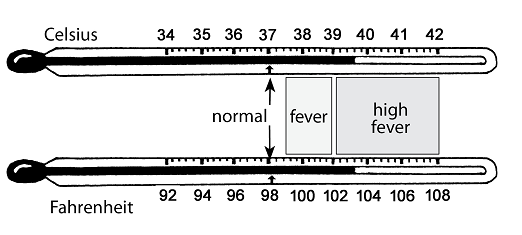
Symptoms of indigestion and heartburn
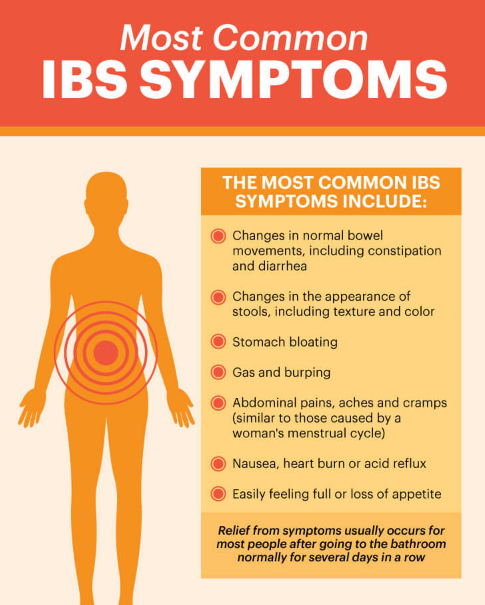
Symptoms of indigestion and heartburn include:
- a burning sensation or pain in the chest
- feeling full, heavy or bloated
- burping or belching
- feeling or being sick
- bringing up food
Symptoms usually come on soon after eating or drinking, but there can sometimes be a delay between eating and developing indigestion.
You can get symptoms at any point during your pregnancy, but they are more common from 27 weeks onwards.
Things you can do to help with indigestion and heartburn
Changes to your diet and lifestyle may be enough to control your symptoms, particularly if they are mild.
Eat healthily
You're more likely to get indigestion if you're very full.
If you're pregnant, it may be tempting to eat more than you would normally, but this may not be good for you or your baby.
Find out more about a healthy diet in pregnancy and foods to avoid.
Change your eating and drinking habits
You may be able to control your indigestion with changes to your eating habits.
It can help to eat small meals often, rather than larger meals 3 times a day, and to not eat within 3 hours of going to bed at night.
Cutting down on drinks containing caffeine, and foods that are rich, spicy or fatty, can also ease symptoms.
Keep upright
Sit up straight when you eat. This will take the pressure off your stomach. Propping your head and shoulders up when you go to bed can stop stomach acid coming up while you sleep.
Stop smoking
Smoking when pregnant can cause indigestion, and can seriously affect the health of you and your unborn baby.
When you smoke, the chemicals you inhale can contribute to your indigestion. These chemicals can cause the ring of muscle at the lower end of your gullet to relax, which allows stomach acid to come back up more easily. This is known as acid reflux.
Smoking also increases the risk of:
- your baby being born prematurely (before week 37 of your pregnancy)
- your baby being born with a low birthweight
- sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), or "cot death"
There's lots of help available to stop smoking. Talk to your midwife or call the NHS Smokefree helpline on 0300 123 1044. Find out more about stopping smoking in pregnancy.
Talk to your midwife or call the NHS Smokefree helpline on 0300 123 1044. Find out more about stopping smoking in pregnancy.
Avoid alcohol
Drinking alcohol can cause indigestion. During pregnancy, it can also lead to long-term harm to the baby. It's safest to not drink alcohol at all in pregnancy.
Find out more about alcohol and pregnancy
When to get medical help
See your midwife or GP if you need help managing your symptoms or if changes to your diet and lifestyle do not work. They may recommend medicine to ease your symptoms.
You should also see your midwife or GP if you have any of the following:
- difficulty eating or keeping food down
- weight loss
- stomach pains
Your midwife or GP may ask about your symptoms and examine you by pressing gently on different areas of your chest and stomach to see whether it's painful.
If you're taking prescription medicines
Speak to your GP if you're taking medicine for another condition, such as antidepressants, and you think it may be making your indigestion worse. They may be able to prescribe an alternative medicine.
Never stop taking a prescribed medicine unless you're advised to do so by your GP or another qualified healthcare professional who's responsible for your care.
Medicines for indigestion and heartburn
Medicines for indigestion and heartburn during pregnancy include:
- antacids – to neutralise the acid in your stomach (some are available over the counter from a pharmacist)
- alginates – to relieve indigestion caused by acid reflux by stopping the acid in your stomach coming back up your gullet
You may only need to take antacids and alginates when you start getting symptoms. However, your GP may recommend taking them before symptoms come on – for example, before a meal or before bed.
However, your GP may recommend taking them before symptoms come on – for example, before a meal or before bed.
If you're taking iron supplements as well as antacids, do not take them at the same time. Antacids can stop iron from being absorbed by your body.
If antacids and alginates do not improve your symptoms, your GP may prescribe a medicine to reduce the amount of acid in your stomach. 2 that are widely used in pregnancy and not known to be harmful to an unborn baby are:
- ranitidine – a tablet you take twice a day
- omeprazole – a tablet you take once a day
Causes of indigestion in pregnancy
Symptoms of indigestion come when the acid in your stomach irritates your stomach lining or your gullet. This causes pain and a burning feeling.
When you're pregnant, you're more likely to have indigestion because of:
- hormonal changes
- the growing baby pressing on your stomach
- the muscles between your stomach and gullet relaxing, allowing stomach acid to come back up
You may be more likely to get indigestion in pregnancy if:
- you had indigestion before you were pregnant
- you've been pregnant before
- you're in the later stages of pregnancy
Video: Eating well on a budget
In this video, a dietitian gives advice on how to eat healthily on a budget.
Media last reviewed: 13 January 2021
Media review due: 13 January 2024
Causes & How to Avoid
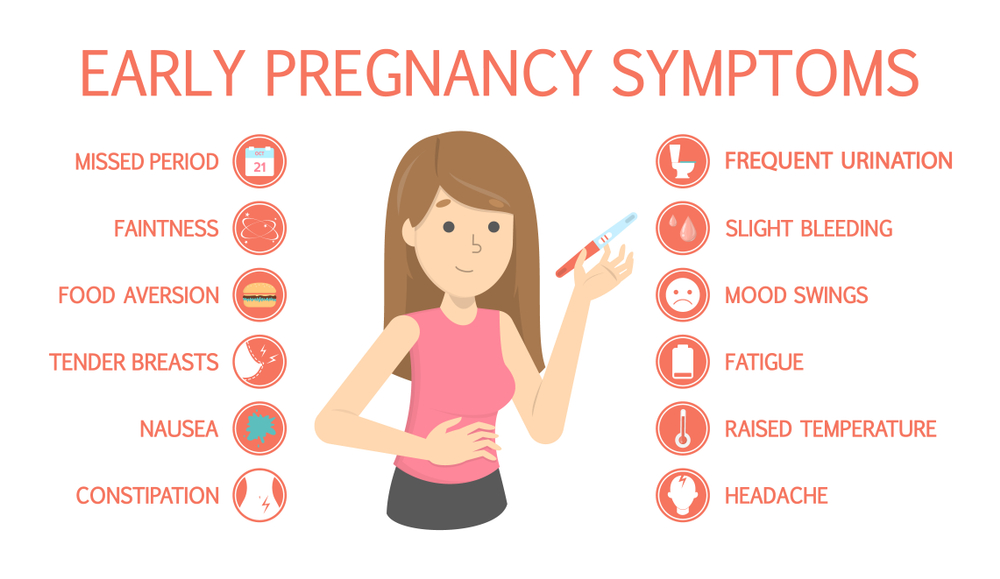
If you are constantly burping during pregnancy, then you might wonder if it is one of the unwanted symptoms of pregnancy. You must be well-acquainted with the other common pregnancy symptoms such as morning sickness, back pain, breathlessness, fatigue, etc. But what about burping? Is it common to burp frequently during pregnancy? Read on to find out!
Is It Common to Burp During Pregnancy?
Among the numerous symptoms of pregnancy, you may not have heard of burping but it is rather common. If you are burping more than usual during pregnancy, it is because of your pregnancy hormones. The hormonal changes in your body can increase the proportion of gas in the stomach and the intestine. As your eating habits change, you may also experience morning sickness and excess saliva. The stress of pregnancy can also put the body in a different zone altogether, making burping as an unintended consequence of it.
Causes of Burping While Pregnant
The frequency of sour burps during pregnancy is generally high. The main cause of burping is the hormone progesterone, which is secreted during pregnancy. This hormone relaxes the lower oesophagal sphincter, letting the acid to enter the oesophagus easily, which further leads to acidity and burping. Slow digestion process and intestinal movements also aggravate the problem.
Some Other Symptoms Associated With Burping
If you are constantly burping during pregnancy, you may also notice some other symptoms too such as –
- You may feel full and that feeling of fullness reaches your throat
- You may feel bloated
- You will have nausea accompanied by instances of heartburn
Most of these signs are strongest in the initial months of pregnancy, which is when the burps tend to be at their highest frequency, too.
How to Stop Burping While Pregnant
Burping at night during pregnancy can disturb your sleep and you might wake up the next day on the wrong side of the bed. If burping is keeping you awake, there are ways to prevent it. Read on to know how you can keep your pregnancy burps in check and reduce their frequencies to a bare minimum.
If burping is keeping you awake, there are ways to prevent it. Read on to know how you can keep your pregnancy burps in check and reduce their frequencies to a bare minimum.
1. Sleep Properly
While pregnant, it is important that you get a deep sleep and for that, you must sleep in the right posture. Maintaining the right posture while sleeping can help lower the tendency to burp at night. Lie down on your left side, either by bending your legs or tucking them together. Such a position is conducive to digestion and can help your stomach process the food easily at night and prevent the formation of gas.
2. Exercise Regularly
You don’t need to run around and lift weights during pregnancy; performing light exercises regularly can go a long way in keeping your digestive system in a proper condition. When you indulge in physical activity, it will release various chemicals in your body, which will stimulate different parts of your body and enhance their working. Simple activities such as washing utensils or drying clothes can also do the trick!
Simple activities such as washing utensils or drying clothes can also do the trick!
3. Stay Calm
Your physical well-being, particularly, gastrointestinal health depends significantly on your mental health. Any presence of tension or anxiety can disturb the balance of chemicals in the stomach, causing indigestion or increased production of gases. Hence, it is important that you do some light exercises or practice meditation or simple yoga. It will help maintain mental peace and keep your body functioning in an optimal condition.
4. Stop Smoking and Drinking
If you smoke or drink, it is about time to stop if you are pregnant. Smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol should be instinctively avoided once you find out that you are pregnant or even when you are trying to get pregnant. Drinking and smoking can affect your health as well as your baby’s health, so they are best avoided. Furthermore, smoking and drinking increase the chances of swallowing air along with it, which can lead to burping. So, it is best to avoid them.
So, it is best to avoid them.
5. Swallow Liquids Slowly
Swallowing liquids slowly can lower the frequency of burps during pregnancy. Many people are into the habit of drinking directly from a bottle but it is wrong. Drinking water through a bottle without it touching your mouth can increase your chances of taking in more air with the liquid that stays trapped in the stomach. Whenever you drink water, drink it from a cup or glass, slowly and gradually, while sitting straight.
6. Chew Your Food Slowly
While pregnant, try and enjoy your meals. The stress of pregnancy could cause you to eat your food quickly and swallow it rapidly, which will increase the chances of indigestion and the formation of gas. So, eat your food slowly and do not talk while eating. Also, take a light stroll after you are done to stimulate the digestion process.
7. Do Not Drink Aerated Beverages
The chances of burping increase when you gulp down your favourite carbonated drinks. Aerated beverages contain carbon dioxide and caffeine in high amount, which is not healthy for a pregnant woman. So coffee, tea, cola drinks, etc., are best avoided during pregnancy. You can drink water and fresh juices to keep yourself hydrated. If you want to drink tea, opt for herbal teas as they can relax your body and provide various health benefits to you.
Aerated beverages contain carbon dioxide and caffeine in high amount, which is not healthy for a pregnant woman. So coffee, tea, cola drinks, etc., are best avoided during pregnancy. You can drink water and fresh juices to keep yourself hydrated. If you want to drink tea, opt for herbal teas as they can relax your body and provide various health benefits to you.
8. Avoid Eating Gassy Foods
Even if you take all the precautions to reduce the intake of air or other reasons for burping, there are certain food items that will result in an increased production of gas. This is due to the nature of their constitution. Cabbage, asparagus, broccoli and even various sugar-free products contain substances that lead to the formation of gas within the body. Fried products are next in line and their overconsumption could lead to heartburn. So, keep their consumption to a minimum.
9. Have Small But Frequent Meals
A lot of food consumed in one go can increase the load on the stomach and increase the chances of indigestion or slow down the digestive processes. All of these work in tandem in creating gas within your body and increasing the burping frequency. Switch the traditional three-meal structure to a six-meal one. This will keep you full and curb unwanted cravings, and reduce the chances of experiencing the unwanted effects of indigestion.
All of these work in tandem in creating gas within your body and increasing the burping frequency. Switch the traditional three-meal structure to a six-meal one. This will keep you full and curb unwanted cravings, and reduce the chances of experiencing the unwanted effects of indigestion.
10. Take Antacids
Antacids can provide relief from burping too, so you can take them if you don’t feel better after trying other remedies. However, take them under medical supervision.
When to Consult a Doctor
You don’t need to consult a doctor if you are burping more often than usual for a day or two. It could be a one-off incident because of a particular food that you ate. Make sure that your diet continues of everything nutritious and you should be fine. However, if this problem of burping is getting beyond control and you experience heartburn and indigestion, you should consult your doctor. She will guide you the best! She might suggest a few options to calm you down and even check for any other conditions that might be causing it.
Burping in pregnancy is very common but we know it can be troublesome. However, the problem should resolve on its own. You can follow the above-mentioned tips to prevent yourself from burping. These tips should help keep you in the pink of health throughout your pregnancy.
Also Read: Constipation in Pregnancy
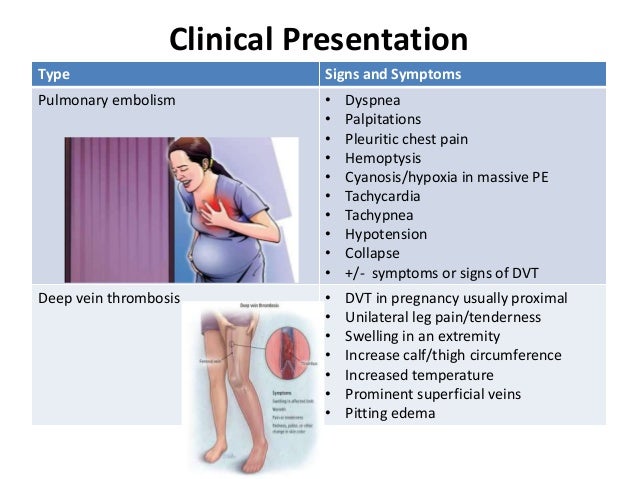
Belching during pregnancy - causes, diagnosis and treatment
Belching during pregnancy is the release of gastric gases in a pregnant woman with a characteristic sound, which occurs due to contraction of the smooth muscles of the stomach with an open cardiac sphincter. The symptom is more often caused by physiological causes: hormonal changes, errors in diet, physical inactivity, but may also indicate the presence of a disease. To identify the root cause of erection during gestation, safe studies are prescribed - ultrasound, tests, pH-metry. To reduce belching, non-drug methods, prokinetics, and sedatives are used.
Causes of belching during pregnancy
During normal pregnancy
The release of a small amount of air through the oral cavity is a physiological process that is observed in absolutely healthy people. During the bearing of a child in a woman's body, changes occur in various organs and systems that can affect the frequency of belching. Physiological erection is characterized by belching of air with a specific sound, while the pregnant woman does not feel an unpleasant odor or taste in her mouth. The following factors contribute to the frequent release of gastric gases during pregnancy:
- Hormonal changes . From the first trimester, a woman has an increased synthesis of progesterone, which is necessary for normal gestation and a decrease in uterine tone. The hormone also affects the smooth muscles of the stomach and esophagus, causing them to relax excessively. Due to the stretching of the organs, an accumulation of gases occurs, provoking a reflex opening of the cardiac sphincter, a spasm of the pylorus and the release of air.
- Uterine growth . A significant increase in the volume of the uterus is detected in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, which is accompanied by a displacement of neighboring organs. The stomach is pushed back to the diaphragm, compressed, as a result of which its contractile activity and coordination of the work of muscle sphincters are disturbed. This leads to frequent burping. Also, women note shortness of breath associated with insufficient expansion of the lungs.
- Reduced physical activity . At late gestational periods, it becomes difficult for a pregnant woman to do her usual work, so women often lead a hypodynamic lifestyle. The reduction in physical activity provokes hypotension of the muscles of the stomach and intestines, slow progress of the chyme through the alimentary canal. Belching occurs as a reflex act due to overstretching of the walls of the digestive tract, sometimes combined with heaviness in the stomach after eating.
- Aerophagy . Swallowing air while eating is a common cause of erections during pregnancy. This condition develops when talking while eating, insufficient chewing of food, snacking in a hurry. Due to the excess amount of air that has entered the stomach, the walls of the organ are overstretched, followed by a sharp contraction. This is manifested by prolonged erection with characteristic sounds, a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium.
- Use of certain foods . Failure to follow the recommendations of a gynecologist on nutrition during pregnancy can lead to belching. The symptom is often provoked by the use of fresh fruits and berries, black bread, legumes. The mechanism of development is associated with increased gas formation, which, against the background of a slowdown in gastric motility, causes flatulence and erection of gastric gases. Belching is also provoked by the use of chewing gum.
- Autonomic innervation changes .
 During pregnancy, a restructuring of all body systems, including the autonomic nervous system, occurs. The regulation of gastrointestinal motility is mainly realized through the parasympathetic fibers of the vagus nerve, with a change in neuro-reflex interactions, mild dyspeptic disorders are possible. Belching of gastric gases occurs at different times of the day, regardless of food intake.
During pregnancy, a restructuring of all body systems, including the autonomic nervous system, occurs. The regulation of gastrointestinal motility is mainly realized through the parasympathetic fibers of the vagus nerve, with a change in neuro-reflex interactions, mild dyspeptic disorders are possible. Belching of gastric gases occurs at different times of the day, regardless of food intake.
Specific pathologies of pregnancy
Dyspeptic disorders are one of the manifestations of specific diseases of the gestational period. These conditions have different etiologies and mechanisms of development; they can be caused by an immunological conflict, pathological visceral impulses from the uterus, and serious dysfunctions of the peripheral nerve plexuses. A sharp deterioration in the condition of a woman and the appearance of atypical symptoms are indications for seeking qualified help. Belching is observed in such pathological conditions as:
- Pregnancy cholestasis .
 Idiopathic bile stasis, according to various sources, affects 0.1-2% of pregnant women. It is believed that cholestasis is caused by increased synthesis of cholesterol and a violation of the colloidal balance of bile under the influence of estrogens. The disorder is manifested by intense itching of the skin, which is combined with jaundice, dark urine, dyspeptic disorders (eructation, nausea, flatulence).
Idiopathic bile stasis, according to various sources, affects 0.1-2% of pregnant women. It is believed that cholestasis is caused by increased synthesis of cholesterol and a violation of the colloidal balance of bile under the influence of estrogens. The disorder is manifested by intense itching of the skin, which is combined with jaundice, dark urine, dyspeptic disorders (eructation, nausea, flatulence). - Toxicosis . Belching during pregnancy is one of the symptoms of early toxicosis, which is detected in 50-60% of patients, starting from the 5th week of gestation. With a mild degree, the general condition of the pregnant woman is not disturbed, she is worried about nausea, salivation, and erection. Moderate and severe forms of the disease are characterized by repeated vomiting up to 20 times a day, up to the impossibility of enteral nutrition, dehydration.
- Intestinal atony . Difficulties with bowel movements are common, affecting about 60% of women during pregnancy.
 Constipation of pregnant women has neurogenic and hormonal prerequisites, the situation is aggravated by the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the intestines. Belching occurs reflexively in response to stagnation of feces, stretching of the intestinal walls, and a decrease in peristaltic activity. With intestinal atony, gastric gases have a fetid odor.
Constipation of pregnant women has neurogenic and hormonal prerequisites, the situation is aggravated by the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the intestines. Belching occurs reflexively in response to stagnation of feces, stretching of the intestinal walls, and a decrease in peristaltic activity. With intestinal atony, gastric gases have a fetid odor.
Other diseases of the digestive system
Belching during pregnancy may occur against the background of concomitant pathology of the digestive system, which is aggravated during gestation. The manifestation of chronic diseases during the period of bearing a child is caused by the influence of sex hormones, an increased load on the digestive system, and a violation of homeostasis reactions. With organic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, erection is usually accompanied by other symptoms (pain, stool instability), which requires a visit to a specialist. Lead to the development of belching:
- GERD.
 The appearance of reflux of aggressive gastric contents is associated with a decrease in the sensitivity of receptors to histamine, a slowdown in gallstone motility and an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. Symptoms are aggravated in the second or third trimester of pregnancy: women complain of acid erection, heartburn, periodic chest pains that appear after diet errors, being in a horizontal position.
The appearance of reflux of aggressive gastric contents is associated with a decrease in the sensitivity of receptors to histamine, a slowdown in gallstone motility and an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. Symptoms are aggravated in the second or third trimester of pregnancy: women complain of acid erection, heartburn, periodic chest pains that appear after diet errors, being in a horizontal position. - Chronic gastritis . If a woman had chronic inflammation of the stomach before pregnancy, then the probability of exacerbation is more than 75%. The severity of symptoms depends on the variant of gastritis. In a hyperacid state, there are pains in the epigastric region, sour eructation, stool disorders with a predominance of diarrhea. With reduced acidity, pregnant women complain of erection with a rotten smell, a feeling of heaviness and fullness of the stomach after eating.
- Chronic pancreatitis . Pregnant women are characterized by a decrease in the synthesis of digestive enzymes and a violation of their activation in the lumen of the duodenum, partial obstruction of the pancreatic ducts, so chronic pancreatitis is exacerbated in 1/3 of patients.
 For the disease, dyspeptic disorders are typical - nausea and periodic vomiting, belching, an increase in the volume of feces and the appearance of particles of undigested food in them.
For the disease, dyspeptic disorders are typical - nausea and periodic vomiting, belching, an increase in the volume of feces and the appearance of particles of undigested food in them. - Irritable bowel syndrome . In pregnant women, the symptoms of functional pathologies of the digestive tract may be aggravated. This is due to changes in autonomic innervation and a special psycho-emotional state of a woman, predisposing to dysregulation of intestinal motility. The disorder is manifested by polymorphic symptoms, which quickly arise and disappear. The condition often worsens with stress.
- Crohn's disease . This inflammatory bowel disease is classified as rare. According to statistics, in women, the disease often manifests itself during pregnancy. Crohn's disease is caused by immunological disorders, which are often triggered by an increase in estrogen levels. Belching is combined with pain in the abdomen (especially in the right iliac region), instability of the stool, nausea, and other dyspeptic symptoms.

Examination
The appearance of belching during pregnancy often indicates a specific gestational pathology or an exacerbation of a chronic gastrointestinal disease against the background of hormonal changes. The examination is prescribed by a gastroenterologist with the obligatory participation of an obstetrician-gynecologist in the diagnosis and selection of therapy. All patients are shown a comprehensive examination using laboratory and instrumental methods that do not pose a danger to either the mother or the fetus. For diagnostic purposes, the following are used:
- Ultrasound . Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is the main instrumental diagnostic method, since this study is absolutely harmless to the child. Sonography reveals signs of inflammatory processes and morphological changes in the gastrointestinal tract. The study is not informative enough in late pregnancy due to a significant increase in the uterus.
- Intragastric pH .
 The occurrence of acid eructation during gestation usually occurs against the background of impaired secretion of hydrochloric acid, therefore a 24-hour measurement of acidity in the stomach is recommended. Additionally, pH-metry of the esophagus is performed - a decrease in the level of less than 4 indicates gastroesophageal reflux.
The occurrence of acid eructation during gestation usually occurs against the background of impaired secretion of hydrochloric acid, therefore a 24-hour measurement of acidity in the stomach is recommended. Additionally, pH-metry of the esophagus is performed - a decrease in the level of less than 4 indicates gastroesophageal reflux. - Breath test . To exclude gastrointestinal pathology against the background of H. Pylori infection, a non-invasive respiratory study is prescribed, based on the ability of the bacterium to break down urea in the stomach. The method sometimes gives false-negative results, therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a specific fecal antigen in the blood is additionally determined.
- Laboratory blood tests . All patients are shown a standard biochemical blood test, which allows you to detect signs of protein-energy deficiency, detect problems in the functioning of the hepatobiliary system. According to the indications, it is recommended to study the blood plasma for the level of gastrin and pepsinogen, the determination of the main hormones.
- Endoscopy . EGDS is used for gestation according to strict indications, in cases where belching is accompanied by other dyspeptic disorders. The study allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, visualize inflammatory foci. The endoscopic method is highly informative in assessing the contractile function of muscle sphincters.
The list of mandatory examination methods also includes a coprogram that detects specific changes in feces during inflammation, fermentopathy, maldigestion and malabsorption, analysis for helminth eggs, Gregersen's test for occult blood. If inflammatory bowel disease is suspected, pregnant women should be especially careful with sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy.
Diet needs to be reviewed during pregnancy
Symptomatic treatment
In most cases, belching during pregnancy is physiologically understandable and does not require special treatment.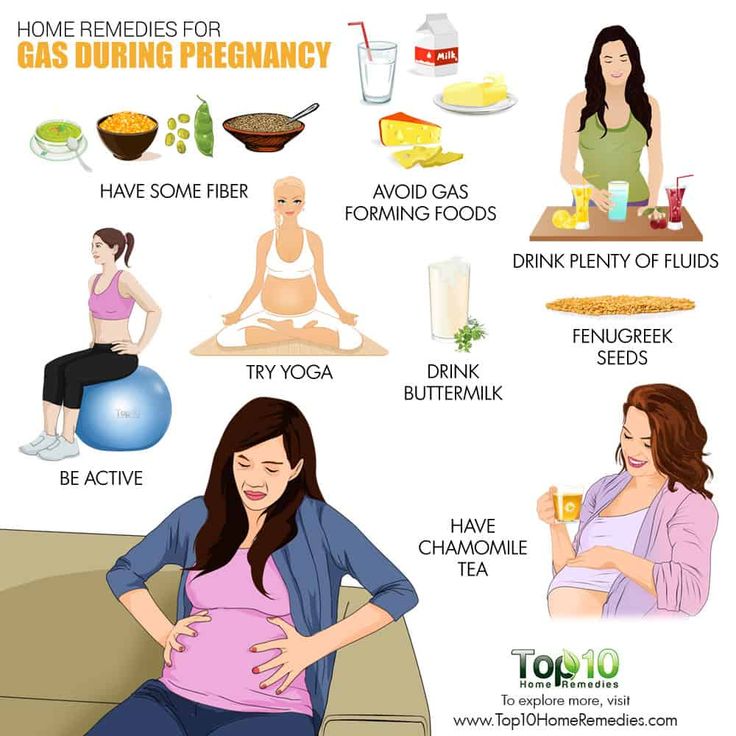 To reduce the frequency of erection, women are advised to adjust their eating habits: eat fractionally, in small portions, do not talk while eating, exclude foods that increase gas formation from the diet. Pregnant women should avoid sharp torso bending, it is undesirable to take a horizontal position immediately after eating.
To reduce the frequency of erection, women are advised to adjust their eating habits: eat fractionally, in small portions, do not talk while eating, exclude foods that increase gas formation from the diet. Pregnant women should avoid sharp torso bending, it is undesirable to take a horizontal position immediately after eating.
If belching bothers a woman very often or is accompanied by pain in the abdomen, stool disorders, other signs of dyspepsia, this may indicate the development of a disease of the digestive organs. In this situation, it is necessary to visit a gastroenterologist as soon as possible. Until an accurate diagnosis is established, it is allowed to take medications that are allowed during pregnancy - prokinetics, mild sedatives that help reduce unpleasant symptoms, but do not harm the baby's body.
Belching during pregnancy - causes, diagnosis and treatment
Belching during pregnancy is the release of gastric gases in a pregnant woman with a characteristic sound, which occurs due to contraction of the smooth muscles of the stomach with an open cardiac sphincter. The symptom is more often caused by physiological causes: hormonal changes, errors in diet, physical inactivity, but may also indicate the presence of a disease. To identify the root cause of erection during gestation, safe studies are prescribed - ultrasound, tests, pH-metry. To reduce belching, non-drug methods, prokinetics, and sedatives are used.
The symptom is more often caused by physiological causes: hormonal changes, errors in diet, physical inactivity, but may also indicate the presence of a disease. To identify the root cause of erection during gestation, safe studies are prescribed - ultrasound, tests, pH-metry. To reduce belching, non-drug methods, prokinetics, and sedatives are used.
Causes of belching during pregnancy
During normal pregnancy
The release of a small amount of air through the oral cavity is a physiological process that is observed in absolutely healthy people. During the bearing of a child in a woman's body, changes occur in various organs and systems that can affect the frequency of belching. Physiological erection is characterized by belching of air with a specific sound, while the pregnant woman does not feel an unpleasant odor or taste in her mouth. The following factors contribute to the frequent release of gastric gases during pregnancy:
- Hormonal changes .
 From the first trimester, a woman has an increased synthesis of progesterone, which is necessary for normal gestation and a decrease in uterine tone. The hormone also affects the smooth muscles of the stomach and esophagus, causing them to relax excessively. Due to the stretching of the organs, an accumulation of gases occurs, provoking a reflex opening of the cardiac sphincter, a spasm of the pylorus and the release of air.
From the first trimester, a woman has an increased synthesis of progesterone, which is necessary for normal gestation and a decrease in uterine tone. The hormone also affects the smooth muscles of the stomach and esophagus, causing them to relax excessively. Due to the stretching of the organs, an accumulation of gases occurs, provoking a reflex opening of the cardiac sphincter, a spasm of the pylorus and the release of air. - Uterine growth . A significant increase in the volume of the uterus is detected in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, which is accompanied by a displacement of neighboring organs. The stomach is pushed back to the diaphragm, compressed, as a result of which its contractile activity and coordination of the work of muscle sphincters are disturbed. This leads to frequent burping. Also, women note shortness of breath associated with insufficient expansion of the lungs.
- Reduced physical activity . At late gestational periods, it becomes difficult for a pregnant woman to do her usual work, so women often lead a hypodynamic lifestyle.
 The reduction in physical activity provokes hypotension of the muscles of the stomach and intestines, slow progress of the chyme through the alimentary canal. Belching occurs as a reflex act due to overstretching of the walls of the digestive tract, sometimes combined with heaviness in the stomach after eating.
The reduction in physical activity provokes hypotension of the muscles of the stomach and intestines, slow progress of the chyme through the alimentary canal. Belching occurs as a reflex act due to overstretching of the walls of the digestive tract, sometimes combined with heaviness in the stomach after eating. - Aerophagy . Swallowing air while eating is a common cause of erections during pregnancy. This condition develops when talking while eating, insufficient chewing of food, snacking in a hurry. Due to the excess amount of air that has entered the stomach, the walls of the organ are overstretched, followed by a sharp contraction. This is manifested by prolonged erection with characteristic sounds, a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium.
- Use of certain foods . Failure to follow the recommendations of a gynecologist on nutrition during pregnancy can lead to belching. The symptom is often provoked by the use of fresh fruits and berries, black bread, legumes.
 The mechanism of development is associated with increased gas formation, which, against the background of a slowdown in gastric motility, causes flatulence and erection of gastric gases. Belching is also provoked by the use of chewing gum.
The mechanism of development is associated with increased gas formation, which, against the background of a slowdown in gastric motility, causes flatulence and erection of gastric gases. Belching is also provoked by the use of chewing gum. - Autonomic innervation changes . During pregnancy, a restructuring of all body systems, including the autonomic nervous system, occurs. The regulation of gastrointestinal motility is mainly realized through the parasympathetic fibers of the vagus nerve, with a change in neuro-reflex interactions, mild dyspeptic disorders are possible. Belching of gastric gases occurs at different times of the day, regardless of food intake.
Specific pathologies of pregnancy
Dyspeptic disorders are one of the manifestations of specific diseases of the gestational period. These conditions have different etiologies and mechanisms of development; they can be caused by an immunological conflict, pathological visceral impulses from the uterus, and serious dysfunctions of the peripheral nerve plexuses. A sharp deterioration in the condition of a woman and the appearance of atypical symptoms are indications for seeking qualified help. Belching is observed in such pathological conditions as:
A sharp deterioration in the condition of a woman and the appearance of atypical symptoms are indications for seeking qualified help. Belching is observed in such pathological conditions as:
- Pregnancy cholestasis . Idiopathic bile stasis, according to various sources, affects 0.1-2% of pregnant women. It is believed that cholestasis is caused by increased synthesis of cholesterol and a violation of the colloidal balance of bile under the influence of estrogens. The disorder is manifested by intense itching of the skin, which is combined with jaundice, dark urine, dyspeptic disorders (eructation, nausea, flatulence).
- Toxicosis . Belching during pregnancy is one of the symptoms of early toxicosis, which is detected in 50-60% of patients, starting from the 5th week of gestation. With a mild degree, the general condition of the pregnant woman is not disturbed, she is worried about nausea, salivation, and erection. Moderate and severe forms of the disease are characterized by repeated vomiting up to 20 times a day, up to the impossibility of enteral nutrition, dehydration.
- Intestinal atony . Difficulties with bowel movements are common, affecting about 60% of women during pregnancy. Constipation of pregnant women has neurogenic and hormonal prerequisites, the situation is aggravated by the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the intestines. Belching occurs reflexively in response to stagnation of feces, stretching of the intestinal walls, and a decrease in peristaltic activity. With intestinal atony, gastric gases have a fetid odor.
Other diseases of the digestive system
Belching during pregnancy may occur against the background of concomitant pathology of the digestive system, which is aggravated during gestation. The manifestation of chronic diseases during the period of bearing a child is caused by the influence of sex hormones, an increased load on the digestive system, and a violation of homeostasis reactions. With organic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, erection is usually accompanied by other symptoms (pain, stool instability), which requires a visit to a specialist. Lead to the development of belching:
Lead to the development of belching:
- GERD. The appearance of reflux of aggressive gastric contents is associated with a decrease in the sensitivity of receptors to histamine, a slowdown in gallstone motility and an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. Symptoms are aggravated in the second or third trimester of pregnancy: women complain of acid erection, heartburn, periodic chest pains that appear after diet errors, being in a horizontal position.
- Chronic gastritis . If a woman had chronic inflammation of the stomach before pregnancy, then the probability of exacerbation is more than 75%. The severity of symptoms depends on the variant of gastritis. In a hyperacid state, there are pains in the epigastric region, sour eructation, stool disorders with a predominance of diarrhea. With reduced acidity, pregnant women complain of erection with a rotten smell, a feeling of heaviness and fullness of the stomach after eating.
- Chronic pancreatitis .
 Pregnant women are characterized by a decrease in the synthesis of digestive enzymes and a violation of their activation in the lumen of the duodenum, partial obstruction of the pancreatic ducts, so chronic pancreatitis is exacerbated in 1/3 of patients. For the disease, dyspeptic disorders are typical - nausea and periodic vomiting, belching, an increase in the volume of feces and the appearance of particles of undigested food in them.
Pregnant women are characterized by a decrease in the synthesis of digestive enzymes and a violation of their activation in the lumen of the duodenum, partial obstruction of the pancreatic ducts, so chronic pancreatitis is exacerbated in 1/3 of patients. For the disease, dyspeptic disorders are typical - nausea and periodic vomiting, belching, an increase in the volume of feces and the appearance of particles of undigested food in them. - Irritable bowel syndrome . In pregnant women, the symptoms of functional pathologies of the digestive tract may be aggravated. This is due to changes in autonomic innervation and a special psycho-emotional state of a woman, predisposing to dysregulation of intestinal motility. The disorder is manifested by polymorphic symptoms, which quickly arise and disappear. The condition often worsens with stress.
- Crohn's disease . This inflammatory bowel disease is classified as rare. According to statistics, in women, the disease often manifests itself during pregnancy.
 Crohn's disease is caused by immunological disorders, which are often triggered by an increase in estrogen levels. Belching is combined with pain in the abdomen (especially in the right iliac region), instability of the stool, nausea, and other dyspeptic symptoms.
Crohn's disease is caused by immunological disorders, which are often triggered by an increase in estrogen levels. Belching is combined with pain in the abdomen (especially in the right iliac region), instability of the stool, nausea, and other dyspeptic symptoms.
Examination
The appearance of belching during pregnancy often indicates a specific gestational pathology or an exacerbation of a chronic gastrointestinal disease against the background of hormonal changes. The examination is prescribed by a gastroenterologist with the obligatory participation of an obstetrician-gynecologist in the diagnosis and selection of therapy. All patients are shown a comprehensive examination using laboratory and instrumental methods that do not pose a danger to either the mother or the fetus. For diagnostic purposes, the following are used:
- Ultrasound . Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is the main instrumental diagnostic method, since this study is absolutely harmless to the child.
 Sonography reveals signs of inflammatory processes and morphological changes in the gastrointestinal tract. The study is not informative enough in late pregnancy due to a significant increase in the uterus.
Sonography reveals signs of inflammatory processes and morphological changes in the gastrointestinal tract. The study is not informative enough in late pregnancy due to a significant increase in the uterus. - Intragastric pH . The occurrence of acid eructation during gestation usually occurs against the background of impaired secretion of hydrochloric acid, therefore a 24-hour measurement of acidity in the stomach is recommended. Additionally, pH-metry of the esophagus is performed - a decrease in the level of less than 4 indicates gastroesophageal reflux.
- Breath test . To exclude gastrointestinal pathology against the background of H. Pylori infection, a non-invasive respiratory study is prescribed, based on the ability of the bacterium to break down urea in the stomach. The method sometimes gives false-negative results, therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a specific fecal antigen in the blood is additionally determined.
- Laboratory blood tests .
 All patients are shown a standard biochemical blood test, which allows you to detect signs of protein-energy deficiency, detect problems in the functioning of the hepatobiliary system. According to the indications, it is recommended to study the blood plasma for the level of gastrin and pepsinogen, the determination of the main hormones.
All patients are shown a standard biochemical blood test, which allows you to detect signs of protein-energy deficiency, detect problems in the functioning of the hepatobiliary system. According to the indications, it is recommended to study the blood plasma for the level of gastrin and pepsinogen, the determination of the main hormones. - Endoscopy . EGDS is used for gestation according to strict indications, in cases where belching is accompanied by other dyspeptic disorders. The study allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, visualize inflammatory foci. The endoscopic method is highly informative in assessing the contractile function of muscle sphincters.
The list of mandatory examination methods also includes a coprogram that detects specific changes in feces during inflammation, fermentopathy, maldigestion and malabsorption, analysis for helminth eggs, Gregersen's test for occult blood. If inflammatory bowel disease is suspected, pregnant women should be especially careful with sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy.
Diet needs to be reviewed during pregnancy
Symptomatic treatment
In most cases, belching during pregnancy is physiologically understandable and does not require special treatment. To reduce the frequency of erection, women are advised to adjust their eating habits: eat fractionally, in small portions, do not talk while eating, exclude foods that increase gas formation from the diet. Pregnant women should avoid sharp torso bending, it is undesirable to take a horizontal position immediately after eating.
If belching bothers a woman very often or is accompanied by pain in the abdomen, stool disorders, other signs of dyspepsia, this may indicate the development of a disease of the digestive organs. In this situation, it is necessary to visit a gastroenterologist as soon as possible. Until an accurate diagnosis is established, it is allowed to take medications that are allowed during pregnancy - prokinetics, mild sedatives that help reduce unpleasant symptoms, but do not harm the baby's body.