Placenta anterior no previa
Anterior placenta: Effects, pictures, and more
The placenta is an organ that grows in the uterus during pregnancy to supply the fetus with oxygen and nutrients. An anterior placenta is one that attaches to the front of the uterus.
The placenta may attach itself in any of the following positions:
- posterior (at the back of the uterus)
- anterior (at the front of the uterus)
- on the side of the uterus
- fundal (at the top of the uterus)
- low-lying (at the bottom of the uterus and sometimes even over the cervix)
An anterior placenta generally does not affect the pregnancy or health of the fetus. However, it may change how a woman has medical checkups and sometimes increases certain risks. Learn more in this article.
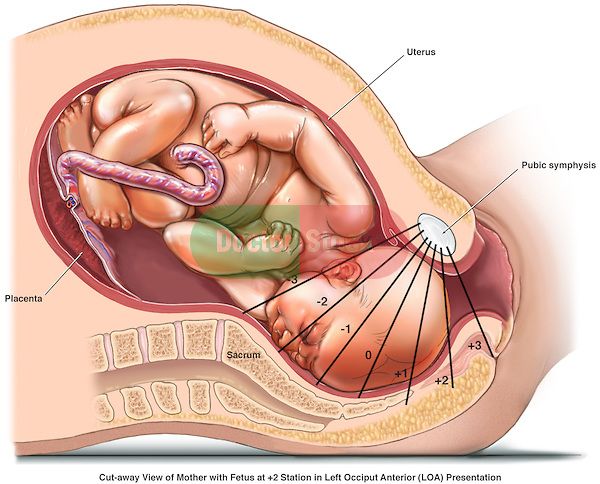
The placenta is an organ that grows in the uterus during pregnancy to nourish the baby with oxygen and nutrients via the umbilical cord. The placenta attaches itself to the wall of the uterus. Anterior placenta is the medical term for a placenta that connects to the front of the uterus.
An anterior placenta will sit between the front of the stomach and the fetus.
Most of the time, a fertilized egg will implant on the back of the uterine wall. When this happens, the placenta generally forms along that wall as well. Doctors refer to this as a posterior placenta.
Sometimes, having an anterior placenta may make it harder for a woman to feel fetal movements. In some cases, it can make it more challenging for an obstetrician to detect a fetal heartbeat.
Generally, the positioning of the placenta does not affect the pregnancy or the fetus unless the placenta blocks the cervix, which is called placenta previa.
A woman with placenta previa may need to stay in the hospital for monitoring, and she is likely to need to give birth via cesarean delivery.
However, an anterior placenta is not likely to affect the pregnancy or its management. The differences in a pregnancy with an anterior placenta are minor. Having an anterior placenta is quite common.
Due to the position of the placenta in front of the baby, a woman with an anterior placenta may not feel fetal movement as strongly as a woman with a posterior placenta, particularly earlier in pregnancy when the fetus is smaller.
In cases where a woman needs an amniocentesis, an anterior placenta may make it slightly more difficult for a doctor to carry out the test.
An amniocentesis is a procedure that takes a sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the baby. A doctor will analyze the fluid for signs of any abnormalities.
They will perform this test by inserting a needle into the uterus via the woman’s abdomen. The location of an anterior placenta at the front of the uterus may make this more challenging.
Share on PinterestA doctor will use an ultrasound to diagnose an anterior placenta.
A doctor can determine the placement of the placenta using an ultrasound, which usually occurs between 18 and 20 weeks of pregnancy.
During this ultrasound, a doctor will examine the fetus and placenta for any abnormalities.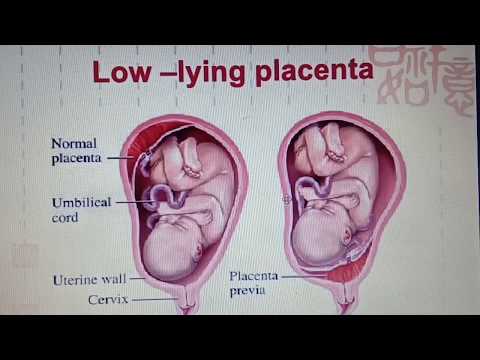
Sometimes, they may recommend additional ultrasounds closer to the delivery date to check the location of the placenta and ensure that it is not covering the cervix.
Although an anterior placenta is not usually a cause for concern, some studies have shown that the placement of a placenta could affect the outcome of the pregnancy.
One study indicated that women with an anterior placenta might have an increased risk of the following complications:
- pregnancy-induced hypertension
- intrauterine growth restriction
- gestational diabetes
- placental abruption
- intrauterine fetal death
There is also some evidence to suggest that women with an anterior placenta have a higher risk of problems after the baby is born.
The placenta can also migrate during pregnancy, meaning that it starts growing in another direction. An anterior placenta may migrate upward and attach itself to the top of the uterus where many of the bigger blood vessels are present.
All pregnant women should see a doctor regularly throughout their pregnancy. While an anterior placenta will not usually cause any issues, other symptoms can indicate a problem with the placenta.
A woman should call her doctor immediately if she notices any of the following symptoms:
- vaginal bleeding
- fast or constant contractions
- severe back pain
- abdominal pain
- decreased fetal movement
- firmness in the uterus
The symptoms of a placental problem tend to begin suddenly, and they are often severe.
An anterior placenta occurs when the placenta grows in the front of the uterine wall. An anterior placenta is not typically a cause for concern. Most of the time, it does not affect the outcome or management of a pregnancy.
It may, however, make it more difficult for a woman to feel fetal movements or for a doctor to find the fetus’s heartbeat.
A woman should consult her doctor regarding any concerns about the pregnancy or signs of problems relating to the placenta.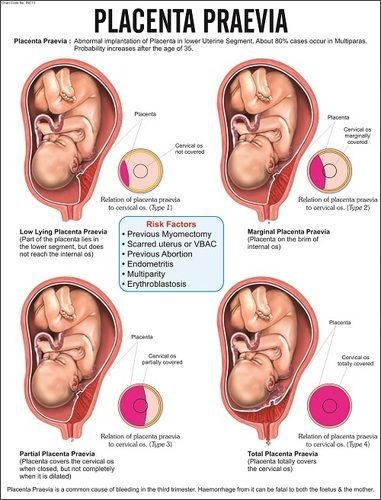 Regular prenatal care can help prevent or manage potential complications.
Regular prenatal care can help prevent or manage potential complications.
Anterior placenta: Effects, pictures, and more
The placenta is an organ that grows in the uterus during pregnancy to supply the fetus with oxygen and nutrients. An anterior placenta is one that attaches to the front of the uterus.
The placenta may attach itself in any of the following positions:
- posterior (at the back of the uterus)
- anterior (at the front of the uterus)
- on the side of the uterus
- fundal (at the top of the uterus)
- low-lying (at the bottom of the uterus and sometimes even over the cervix)
An anterior placenta generally does not affect the pregnancy or health of the fetus. However, it may change how a woman has medical checkups and sometimes increases certain risks. Learn more in this article.
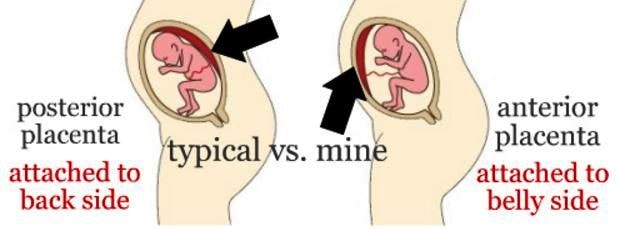
The placenta is an organ that grows in the uterus during pregnancy to nourish the baby with oxygen and nutrients via the umbilical cord.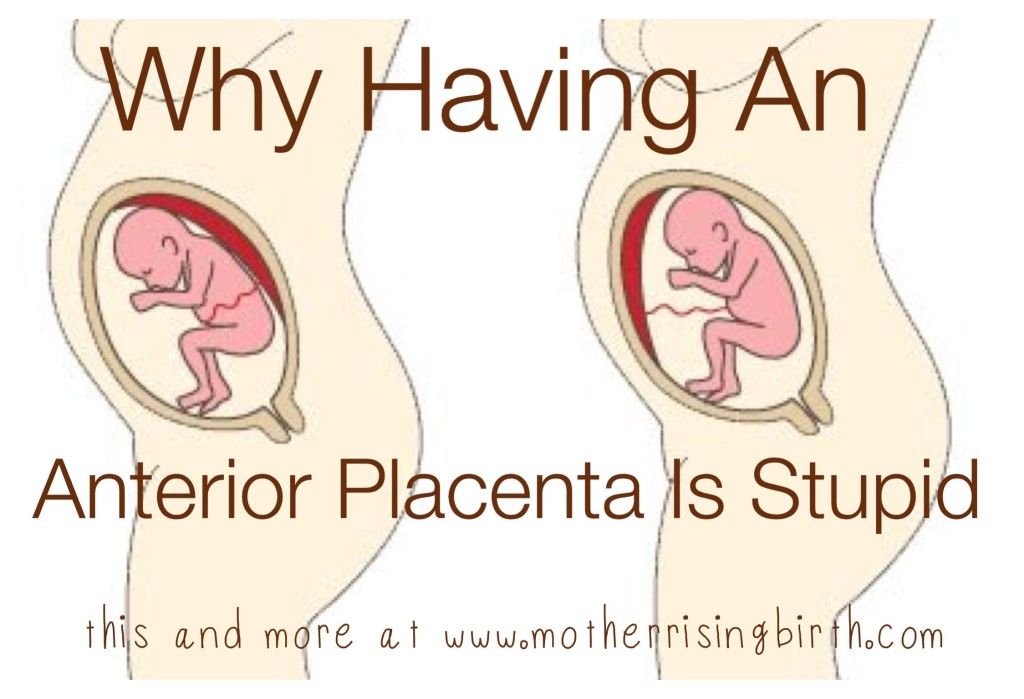 The placenta attaches itself to the wall of the uterus. Anterior placenta is the medical term for a placenta that connects to the front of the uterus.
The placenta attaches itself to the wall of the uterus. Anterior placenta is the medical term for a placenta that connects to the front of the uterus.
An anterior placenta will sit between the front of the stomach and the fetus.
Most of the time, a fertilized egg will implant on the back of the uterine wall. When this happens, the placenta generally forms along that wall as well. Doctors refer to this as a posterior placenta.
Sometimes, having an anterior placenta may make it harder for a woman to feel fetal movements. In some cases, it can make it more challenging for an obstetrician to detect a fetal heartbeat.
Generally, the positioning of the placenta does not affect the pregnancy or the fetus unless the placenta blocks the cervix, which is called placenta previa.
A woman with placenta previa may need to stay in the hospital for monitoring, and she is likely to need to give birth via cesarean delivery.
However, an anterior placenta is not likely to affect the pregnancy or its management.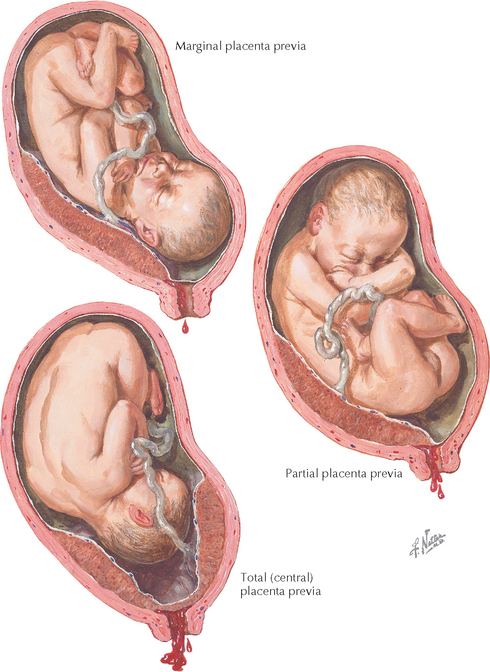 The differences in a pregnancy with an anterior placenta are minor. Having an anterior placenta is quite common.
The differences in a pregnancy with an anterior placenta are minor. Having an anterior placenta is quite common.
Due to the position of the placenta in front of the baby, a woman with an anterior placenta may not feel fetal movement as strongly as a woman with a posterior placenta, particularly earlier in pregnancy when the fetus is smaller.
In cases where a woman needs an amniocentesis, an anterior placenta may make it slightly more difficult for a doctor to carry out the test.
An amniocentesis is a procedure that takes a sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the baby. A doctor will analyze the fluid for signs of any abnormalities.
They will perform this test by inserting a needle into the uterus via the woman’s abdomen. The location of an anterior placenta at the front of the uterus may make this more challenging.
Share on PinterestA doctor will use an ultrasound to diagnose an anterior placenta.
A doctor can determine the placement of the placenta using an ultrasound, which usually occurs between 18 and 20 weeks of pregnancy.
During this ultrasound, a doctor will examine the fetus and placenta for any abnormalities.
Sometimes, they may recommend additional ultrasounds closer to the delivery date to check the location of the placenta and ensure that it is not covering the cervix.
Although an anterior placenta is not usually a cause for concern, some studies have shown that the placement of a placenta could affect the outcome of the pregnancy.
One study indicated that women with an anterior placenta might have an increased risk of the following complications:
- pregnancy-induced hypertension
- intrauterine growth restriction
- gestational diabetes
- placental abruption
- intrauterine fetal death
There is also some evidence to suggest that women with an anterior placenta have a higher risk of problems after the baby is born.
The placenta can also migrate during pregnancy, meaning that it starts growing in another direction. An anterior placenta may migrate upward and attach itself to the top of the uterus where many of the bigger blood vessels are present.
All pregnant women should see a doctor regularly throughout their pregnancy. While an anterior placenta will not usually cause any issues, other symptoms can indicate a problem with the placenta.
A woman should call her doctor immediately if she notices any of the following symptoms:
- vaginal bleeding
- fast or constant contractions
- severe back pain
- abdominal pain
- decreased fetal movement
- firmness in the uterus
The symptoms of a placental problem tend to begin suddenly, and they are often severe.
An anterior placenta occurs when the placenta grows in the front of the uterine wall. An anterior placenta is not typically a cause for concern. Most of the time, it does not affect the outcome or management of a pregnancy.
It may, however, make it more difficult for a woman to feel fetal movements or for a doctor to find the fetus’s heartbeat.
A woman should consult her doctor regarding any concerns about the pregnancy or signs of problems relating to the placenta.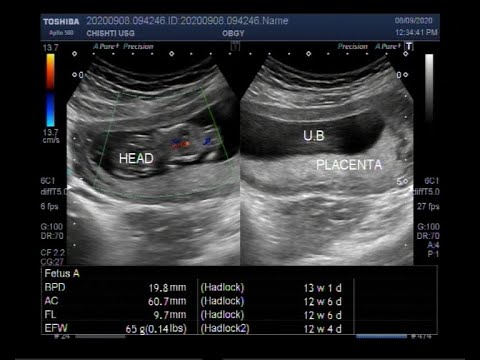 Regular prenatal care can help prevent or manage potential complications.
Regular prenatal care can help prevent or manage potential complications.
The question is asked by Maria, - a question-answer from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Maria:
23.10.2014
Good afternoon, dear doctor! I ask you to answer a few questions to which no one can give me a definite answer. Honestly, I was going to ask one question, but in the process it turned out that everything and everywhere hurts me :-). I hope that your experience and qualified answers will help me figure it out. Thanks in advance. Maria. 1. At my 15th week of pregnancy, ultrasound showed placenta previa, the placenta is located on the back wall of the uterus. Please tell me what causes placenta previa (from a lack of vitamins, from carrying weights or from fate)? I would also like to know if it is possible to somehow help the placenta rise up, maybe there are some exercises or do you need to sleep in a certain position? 2. Please tell me how to behave during pregnancy, if the temperature has risen, which pills can be taken, and which are contraindicated during pregnancy? (I would like to know how to behave at different temperatures, for example: 37, 2; 38; more than 38 degrees) What are the criteria that you can still tolerate taking medication so as not to harm the child, and when is it necessary to start taking medication so as not to harm the child? 3.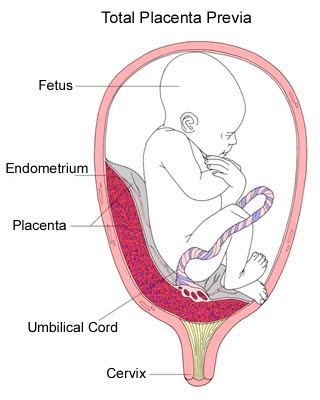 At each visit, the doctor says that I have an increased tone of the uterus. Can you please explain how it can be corrected? 4. What to do if before pregnancy the pressure was 120/75, and now (during pregnancy) it has dropped to 100 (95)/50? The fact is that at the same time I constantly knock at the temples and have a headache.
At each visit, the doctor says that I have an increased tone of the uterus. Can you please explain how it can be corrected? 4. What to do if before pregnancy the pressure was 120/75, and now (during pregnancy) it has dropped to 100 (95)/50? The fact is that at the same time I constantly knock at the temples and have a headache.
Clinic "Mother and Child" Kuntsevo:
01/26/2021
1. Placenta previa may be caused by previous inflammatory diseases of the uterus (for example, as a result of abortions) or hormonal deficiency. There are no special exercises and medications to "improve" the location of the placenta. With the growth of pregnancy, the placenta can "rise", this requires ultrasound control. If placenta previa persists at the time of delivery, then delivery is carried out by caesarean section. 2. The use of antipyretic drugs during pregnancy depends on the cause that caused the temperature, therefore, in such situations, the doctor can prescribe treatment after examination and test results.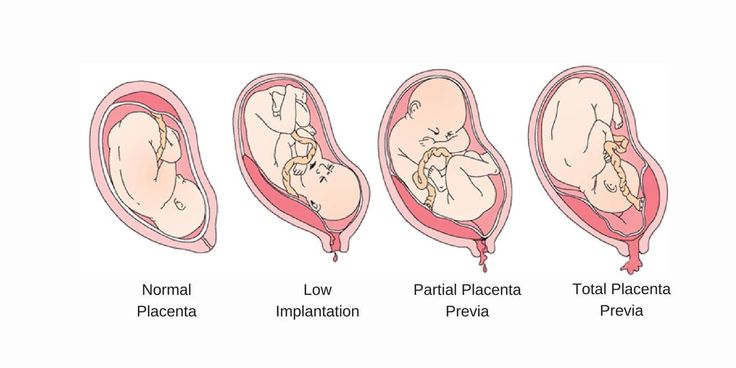 Paracetamol is not contraindicated during pregnancy at high temperature (above 37.8-38.0 gr.) 3. An increased tone of the uterus may indicate the phenomena of a threat of termination of pregnancy, therefore it is better for you to observe physical and sexual rest, it will not be superfluous to take sedative herbs (persen) Magne B6 (10 days), for pain, take antispasmodics (no-shpa, suppositories with papaverine into the rectum). If the threat phenomena persist for a long time or according to ultrasound there is a shortening of the cervix, then the question of hospitalization for more intensive treatment may arise. 4. During pregnancy, blood pressure numbers normally decrease somewhat. With low blood pressure numbers, hot sweet tea or coffee helps well. The intake of drugs must be coordinated with the doctor who guides you through pregnancy.
Paracetamol is not contraindicated during pregnancy at high temperature (above 37.8-38.0 gr.) 3. An increased tone of the uterus may indicate the phenomena of a threat of termination of pregnancy, therefore it is better for you to observe physical and sexual rest, it will not be superfluous to take sedative herbs (persen) Magne B6 (10 days), for pain, take antispasmodics (no-shpa, suppositories with papaverine into the rectum). If the threat phenomena persist for a long time or according to ultrasound there is a shortening of the cervix, then the question of hospitalization for more intensive treatment may arise. 4. During pregnancy, blood pressure numbers normally decrease somewhat. With low blood pressure numbers, hot sweet tea or coffee helps well. The intake of drugs must be coordinated with the doctor who guides you through pregnancy.
Low placenta
Home / Gynecologist / Low placenta
Placenta is a temporary organ that is formed in the body of a pregnant woman in order to maintain a connection between her body and the fetus. She filters the blood , which the unborn baby feeds on, cleansing it of toxins and other harmful substances.
She filters the blood , which the unborn baby feeds on, cleansing it of toxins and other harmful substances.
This pathology can be very dangerous in some cases, while in others it goes away without any treatment and does not bring problems.
Types of location of the placenta
Usually the placenta is attached to the back wall of the uterus closer to its bottom . It is worth noting that the uterus is an inverted vessel, and its bottom is located on top. This is the best option for the location of the placenta. However, this does not always work out. In some cases, the placenta is attached to the anterior wall. Which is also not a pathology.
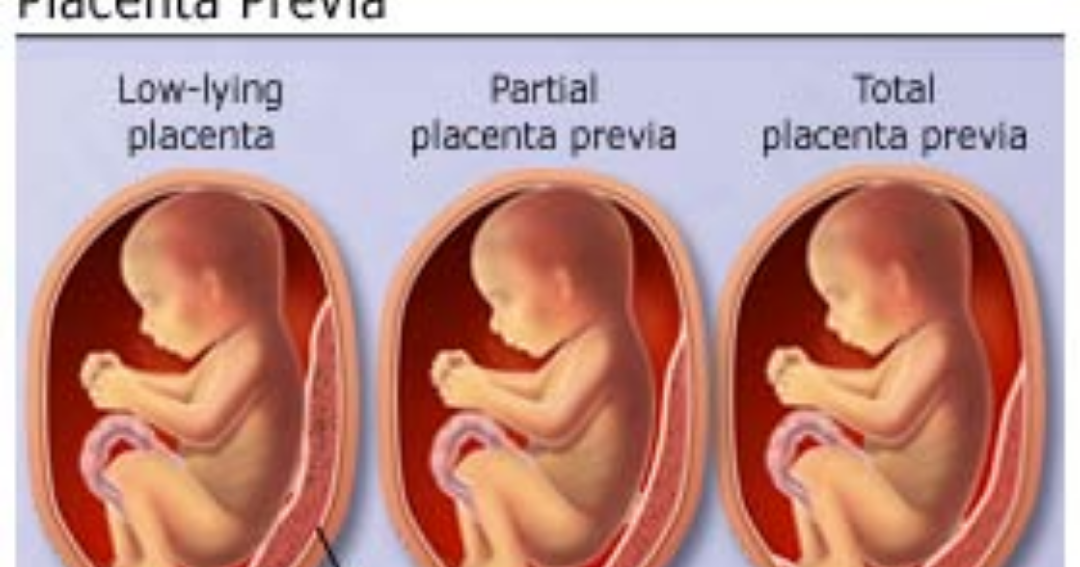
Low placenta during pregnancy is much more dangerous. If the placenta is located low, it is subjected to stronger pressure from the fetus, and even with any external influence, the risk is damage to the placenta or its detachment increases. In addition, in the later stages, an actively moving baby can also damage the placenta, or squeeze the umbilical cord.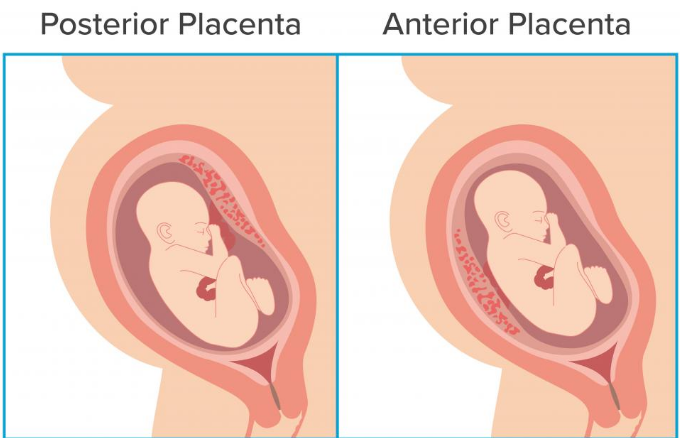
A placenta is said to be low when there is less than 6 cm between its lower edge and the os of the uterus. The anterior wall has a greater tendency to stretch, and migration is also characteristic of it, however, the direction of migration is opposite: usually the placenta moves in the opposite direction, down to the cervix.
An even more complex and dangerous pathology of the location of the placenta is its partial or complete presentation . Previa is a condition when the placenta partially or completely obscures the cervix of the uterus.
Causes of low placenta
Many causes of low placenta are due to internal factors - diseases during pregnancy and the condition of the female genital organs . They can be:
- damage to the mucous membrane of the uterus;
- inflammatory processes;
- infections;
- previous abortions;
- miscarriages in the past;
- caesarean section;
- various gynecological operations;
- pathology of the structure, development, functioning of the uterus;
- multiple pregnancy;
- unhealthy lifestyle: active smoking, excessive alcohol consumption;
- previous diseases of the uterus: endometritis, fibroids;
- parity - many births in the past;
- the woman's age is over 35 years.
Curettage of the uterus in the past is the main cause of this pathology. Damage to the mucosa prevents the fetal egg from gaining a foothold in the upper segment of this organ, and it remains below, at the neck.
Symptoms of low placenta
The danger of this pathology is that it practically does not manifest itself. Usually, signs that not everything is in order with the placenta are the result of already running and irreversible processes - for example, its detachment. It can be:
- drawing pains, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- spotting with a low location of the placenta is an alarm signal that it is necessary to call an ambulance;
- freezing of the fetus in the womb for a long time, or, conversely, its too violent activity - this is caused by hypoxia;
- on ultrasound with such a pathology in 50% of cases is the wrong presentation of the fetus;
- in 30% of cases, women suffer from severe toxicosis.
A pregnant woman herself cannot suspect that she has a low placenta. This can only be seen on planned ultrasounds, which must be passed by everyone. After an ultrasound examination, they can not only clarify or refute the diagnosis, but also determine the type of pathology.
Treatment and prevention of low placentation
Management of pregnancy with low placentation is always very careful. A woman will have to undergo ultrasound many times, limit physical activity and stop sexual activity. For a long time, increased uterine tone can provoke detachment of an improperly located placenta, from there bleeding, and possible death of the fetus as a result of acute hypoxia, if placental abruption is large. Bleeding can even provoke a gynecological examination of the cervix, therefore, for no particular reason, doctors try not to conduct examinations on the chair.
Listen to the doctors and hope for the best. Many women give birth on their own or by caesarean section of healthy babies with low placenta previa.