Pregnant belly kick
Your Baby's Movements During Pregnancy – Health Information Library
Overview
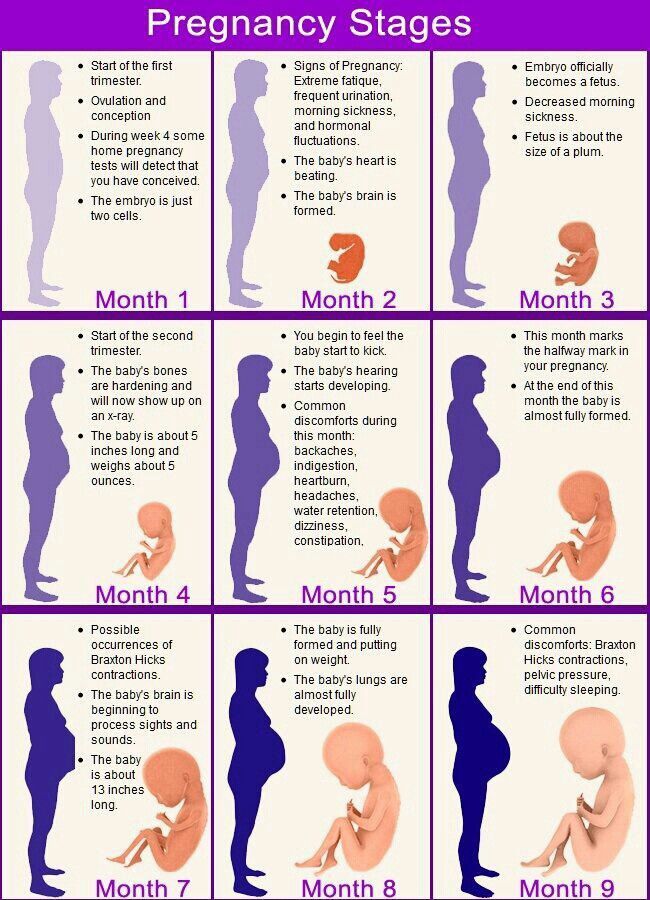
During your pregnancy, you'll feel your baby move. For example, your baby may kick, hiccup, roll, turn, and twist. These movements are common and expected. As your baby grows, these movements will get stronger.
But sometimes you might feel a movement that surprises you. You may wonder what it means. Most pregnant women don't have any serious problems. But it's a good idea to learn about the different kinds of movements. They include:
- Fluttering, butterflies, or bubbles.
-
You'll probably start to feel your baby move sometime between 18 and 22 weeks. At first, these small movements feel like fluttering or "butterflies.
" Some women say that they feel like gas bubbles. These first flutters are sometimes called "quickening."
- Hiccups.
-
Around 21 to 24 weeks, you may start to feel some jerky movements inside your belly. You might even see them on the outside. Repeated jerky movements usually mean that your baby has the hiccups.
Hiccups are perfectly normal. They can last from a minute to an hour. You may feel your baby have hiccups now and then throughout the rest of your pregnancy.
- Kicks, twists, and turns.
-
As your pregnancy goes on, you may feel some changes in your baby's movement. Around 25 to 28 weeks, your baby may start to kick and stretch.
 And you may notice that your baby does less turning and twisting and more squirming or jerking. Around 30 to 32 weeks, your baby turns less and kicks and jabs more.
And you may notice that your baby does less turning and twisting and more squirming or jerking. Around 30 to 32 weeks, your baby turns less and kicks and jabs more. At about 28 weeks, you may feel your baby move from head-down to feet-down, or even sideways.
When and how often babies move
After 18 to 20 weeks, you may notice that your baby moves more at certain times of day. For example, when you are active, you may feel less movement than when you're resting quietly. Believe it or not, babies find the activity and noise of daytime hours to be soothing. So they often sleep during the day and are awake at night.
Starting at about 30 to 32 weeks, you should feel your baby move several times a day. Babies usually sleep 20 to 45 minutes at a time, and then are more active at certain times of day.
By 40 weeks, your baby has grown larger and doesn't have much room to move around. You will probably notice less "big" movement than before.
Call your doctor or midwife right away or seek immediate medical care if you notice that your baby has stopped moving or is moving much less than normal.
Credits
- Top of the page
-
Next Section:
Related Information
Health Information Library
Where Do You Feel Baby Kicks During Pregnancy?
Once you figure out that it’s not just gas, one of the most exciting parts of pregnancy is feeling all those baby kicks. While they can help you feel connected to your baby, as they get stronger if they land in the wrong place the feeling can be less than pleasant. (Hello, bladder!)
(Hello, bladder!)
On the other hand, if you’re not feeling that many baby kicks, you may become worried about your baby. Is something wrong with them?
As a parent-to-be, the list of questions about baby kicks running through your mind can be endless: What’s normal when it comes to baby kicks? Where should you be feeling your baby kick? How often should your baby be kicking? When should you be worried?
Don’t stress though, we’re here with the answers you need.
Where you’ll feel baby kicks is dependent on a few factors. These include:
- how far along you are in your pregnancy
- the baby’s position in the womb
- the position of the placenta
You’ll feel your baby kick differently as your pregnancy progresses, with fluttery movements below the belly button earlier in pregnancy and stronger movement that can range from up in your ribs to down in your pelvic region later in pregnancy.
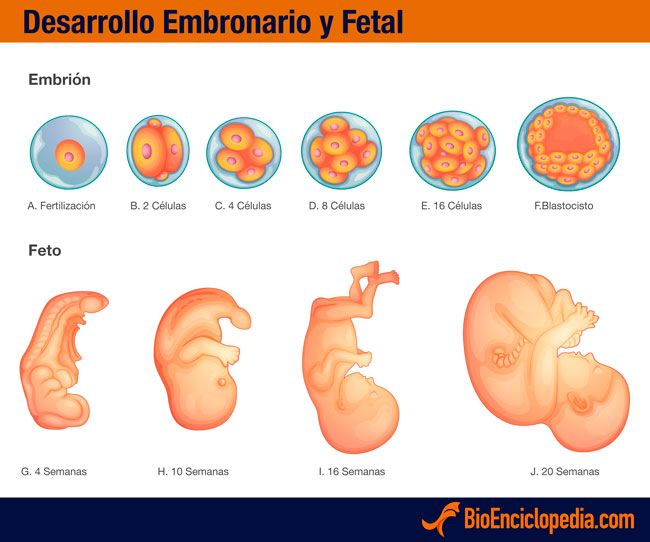
Your baby may make sporadic movements around 9 or 10 weeks, but you probably won’t feel anything in the first trimester. (If your baby happens to be moving around during an early ultrasound, the tech might mention it to you, but otherwise you may never know!)
(If your baby happens to be moving around during an early ultrasound, the tech might mention it to you, but otherwise you may never know!)
By the second trimester, your baby’s movements will become more organized. Some pregnant people can feel their baby kick as early as 13 to 15 weeks into the pregnancy, but closer to 18 weeks is more typical.
Don’t be alarmed if it takes you a bit to feel those first fluttery kicks, known as quickening. Many factors can influence when you first feel them, and kicks are usually felt earlier in subsequent pregnancies, since experienced parents know what to look for.
The person carrying the baby will feel the kicks first, but partners (or others you allow) may feel the baby kicking as early as 20 weeks. Interestingly, pregnant people carrying twins are not likely to feel kicks any sooner than those carrying singletons.
Early movements are typically felt low in the abdomen and described as something similar to a flutter. It may feel like a wave or even a fish swimming. For some, the movement can feel similar to gas or hunger pangs, which can make it tricky to initially identify as kicks.
For some, the movement can feel similar to gas or hunger pangs, which can make it tricky to initially identify as kicks.
Sometimes, it can seem like your baby’s movement is little ticks or pulses. This likely means that they have started hiccupping, which is completely harmless.
By the third trimester when your baby is more cramped and better developed, the movements will likely be stronger and pack more of a punch. You may even notice your belly moving on the outside when your baby kicks!
Your baby’s position in the womb affects how and where you’ll feel kicks. If they’re head down (known as vertex position) then you’ll feel their kicks higher up in your womb. Early in pregnancy this may only be as high as your belly button, but later in pregnancy it may be up in your ribs.
If they’re breech, with their feet dangling down, you’ll feel kicks lower in your abdomen and it may even feel like they’re kicking their way out of your cervix or dancing on your bladder later in pregnancy.
If they’re transverse, laying across your abdomen, you’ll likely feel more kicks on the right or left side, depending on which way they’re facing.
You’ll also feel movements besides kicks — you may feel pressure from the baby’s head or back pressed against your belly. You may be able to feel a swooping sensation when they turn or roll in the womb.
The timing and strength of the movements that you feel may be affected by the placement of the placenta.
If the placenta is positioned on the front of the uterus (known as an anterior placenta) it may act as a cushion between the outside of your belly and the baby’s movements inside. You may not feel movement until later during your pregnancy and when you do feel movement it may not be as strong.
Frequency of baby kicks and movement will change at different stages of your pregnancy.
Just because you can begin to feel the kicks in the second trimester, doesn’t mean you should expect to feel them all day long or even every day. Your baby is still small, so there’s more room for them to flip and roll without you feeling it!
Your baby is still small, so there’s more room for them to flip and roll without you feeling it!
As your baby becomes larger, you may notice rhythms to their movement. They may tend to be more active in the morning or evening depending on their sleep cycle.
In fact, your daytime movement may lull your baby to sleep, so it’s not unusual for them to decide to start kicking when you lie down to get ready to go to bed.
In the later months of your pregnancy, your doctor may suggest counting the number of baby kicks you feel as a way to check in on your baby’s health.
While some doctors suggest just a general awareness of changes to fetal movement, other providers suggest using a more formal counting method starting at about 28 weeks. One example of such a count is timing how long it takes to feel 10 kicks.
If you’re trying to do a formal kick count, some good rules of thumb are:
- Do kick counts at the same time of day.
- Make sure to note the frequency and type of movement.

- Count at a time of day when your baby is frequently active and your distractions are at a minimum (e.g., early evening).
If you’re not feeling much movement and trying to encourage some from your baby, you can try:
- Talking or playing music. By about 25 weeks, your baby may begin to respond to familiar voices with a kick or two.
- Eating or drinking something. The sugar from a little orange juice may get your baby moving again!
If you’re not feeling a lot of movement, it can be comforting to remember that a lack of movement doesn’t necessarily mean there is a problem. Your baby may just be enjoying a nice long nap or be in a position where it’s hard to feel them.
If movement becomes noticeably less or completely absent, you’ll probably want to reach out to your medical provider.
As a general rule of thumb, you should call your doctor if you don’t feel 10 movements in a 2- to 3-hour window during the third trimester, but you can always call them and request monitoring if you feel something is off.
Every pregnancy and baby is different. The amount of kicks you feel and how they feel will differ not only from person to person, but from pregnancy to pregnancy. You may have one baby you rarely felt moving and another who loved to constantly push the boundaries of the womb (literally!).
It’s important to be aware of the amount of kicking you are feeling, especially later in your pregnancy. If you are feeling a marked decrease or movements stop all together, you’ll probably want to reach out to your medical provider, so they can monitor and assess the baby’s health.
While it’s different for everyone, feeling kicks and movements are a special way to feel connected with your baby.
what to do if you hit your stomach?
Pregnancy is a time of joyful expectation and, at the same time, excitement. And one of the hot topics for all pregnant women is what happens if you hit your stomach or fall on it? None of us is immune from falls and bruises under the usual circumstances, and when our body, as happens with a future mother, rapidly changes its usual dimensions, this probability only increases. She stumbled, hurt herself, fell, did not fit into a corner or an opening - these and other life situations, so familiar and not riveting our attention in everyday reality, suddenly begin to seem dangerous for the expectant mother, who strives with all her might to take care and protect her unborn baby . So what to do if such a nuisance did occur?
She stumbled, hurt herself, fell, did not fit into a corner or an opening - these and other life situations, so familiar and not riveting our attention in everyday reality, suddenly begin to seem dangerous for the expectant mother, who strives with all her might to take care and protect her unborn baby . So what to do if such a nuisance did occur?
A little bit of anatomy: protection for the baby perfectly designed by nature
For starters, don't panic! After all, the calm state of the mother in itself has a positive effect on her entire body and hormonal background - and, therefore, on the baby. Of course, during pregnancy it is worth avoiding any traumatic situations in every possible way, but if something has already happened, it is worth remembering: just as we try to take care of our children, nature has already taken care of us. The expectant mother has already incorporated the protection of the baby from any kind of negligence. First of all, the amniotic sac, consisting of dense connective tissue, which forms a kind of sac filled with amniotic fluid, the amount of which during pregnancy ranges from 0.5 to 1 liter, saves the baby from mechanical damage. In addition to him, the child is protected by the elastic muscles of the uterus and the walls of the abdominal cavity, and in the early stages it is also protected by the pelvic bones. Therefore, before the fifth month of pregnancy, it is almost impossible to harm the baby when falling. It is not until the fifth month that the uterus enlarges enough to leave the safe space between the pelvic bones.
First of all, the amniotic sac, consisting of dense connective tissue, which forms a kind of sac filled with amniotic fluid, the amount of which during pregnancy ranges from 0.5 to 1 liter, saves the baby from mechanical damage. In addition to him, the child is protected by the elastic muscles of the uterus and the walls of the abdominal cavity, and in the early stages it is also protected by the pelvic bones. Therefore, before the fifth month of pregnancy, it is almost impossible to harm the baby when falling. It is not until the fifth month that the uterus enlarges enough to leave the safe space between the pelvic bones.
Abdominal trauma and gestational age
If the blow is aimed directly at the stomach, then even in the early stages certain problems may arise. Note that accidental falls and injuries to the abdomen that are the result of a pregnant woman's clumsiness usually do not harm the fetus. For something really bad to happen, there must be a certain force of impact or its very specific focus - right on the pregnant uterus. The unpleasant thing is that the consequences of an impact can be delayed in time. And the risk of adverse effects increases with the duration of pregnancy. The higher the bottom of the uterus (as its upper part is called), the more “open” it is for outside influences. And if in the middle of pregnancy the baby is small and most of the internal space is occupied by water, protecting the baby from any blow, then by the end of the term the baby is already clearly outlined inside the pregnant belly, and the small amount of water in comparison with its mass no longer protects it so much from adverse external factors.
The unpleasant thing is that the consequences of an impact can be delayed in time. And the risk of adverse effects increases with the duration of pregnancy. The higher the bottom of the uterus (as its upper part is called), the more “open” it is for outside influences. And if in the middle of pregnancy the baby is small and most of the internal space is occupied by water, protecting the baby from any blow, then by the end of the term the baby is already clearly outlined inside the pregnant belly, and the small amount of water in comparison with its mass no longer protects it so much from adverse external factors.
What are warning signs and when to see a doctor
First of all, look for any unusual vaginal discharge - especially bloody or watery, which can be one of the signs of water breakage. Pharmacies sell water leakage tests, it is useful to have one with you just in case. Any pain in the lower abdomen or in the lower back should also alert. Spasms or sharp contractions of the uterus can also be considered an alarm. Pay attention to the presence of dizziness, darkening in the eyes, clouding of consciousness, sudden weakness. All this may be the result of internal bleeding (for example, with placental abruption), as a result of which blood pressure drops sharply, which cannot but affect the well-being of the expectant mother.
Spasms or sharp contractions of the uterus can also be considered an alarm. Pay attention to the presence of dizziness, darkening in the eyes, clouding of consciousness, sudden weakness. All this may be the result of internal bleeding (for example, with placental abruption), as a result of which blood pressure drops sharply, which cannot but affect the well-being of the expectant mother.
If you do not feel any changes in your health, nothing hurts anywhere, the baby behaves as usual, then you should not worry. However, be sure to schedule a visit to the gynecologist to rule out any hidden problems that can only be revealed with the help of special studies.
First aid for abdominal injuries during pregnancy
First of all, you should assess your condition and the presumed condition of the child. If the injury is not accompanied by bleeding, pain, increased number of uterine contractions, you can lie down and follow the baby's behavior - has it changed compared to the usual one? Did he become less active if he was already moving? It is important to remember that in such a situation one should not lie on the stomach, because in this position the enlarged uterus can compress the inferior vena cava (this is true mainly in the middle of pregnancy), as well as on the back - for the same reason (in the later stages, when the mass uterus reaches significant values).
If something causes concern, it is best to call an ambulance immediately. If the state of strong anxiety does not cause, you can go to the doctor yourself - he will arrange a preventive examination, and you can definitely feel calmer. The doctor should examine you and evaluate the condition of the baby, as well as make sure that the placenta is functioning properly. The type of diagnosis used by the doctor will also depend on how far along the pregnancy is.
Remember that your excessive anxiety will provoke the release of adrenaline into the blood, which, in turn, will cause an increase in heart rate and pressure, while the uterus will not receive proper blood supply, because all the blood in such situations is directed to ensure the vital activity of the most important organs - brain and lungs. Therefore, your first task in any scenario will be to calm down as much as possible. This is really important for you and for your child.
How to reduce the risk of abdominal injury during pregnancy
It is possible to take measures to prevent falls and bruises of the abdomen during pregnancy in advance. It is important to wear suitable clothing and footwear. Clothing should not restrict movement, and shoes should have high or unstable heels. Always hold on to something when moving through unsafe spaces such as public transport. Choose a level road where there is a minimum of chances for trips, slips, etc. Do not lift heavy; when carrying anything, try to make sure that you can see the space in front of you as much as possible.
It is important to wear suitable clothing and footwear. Clothing should not restrict movement, and shoes should have high or unstable heels. Always hold on to something when moving through unsafe spaces such as public transport. Choose a level road where there is a minimum of chances for trips, slips, etc. Do not lift heavy; when carrying anything, try to make sure that you can see the space in front of you as much as possible.
During pregnancy, you should try to be as careful as possible, not to expose yourself to unnecessary risks, because during this period you are responsible not only for your life. Visit the doctor in a timely manner to always be sure that everything is in order with your baby. Have an easy pregnancy!
You can explain all your questions regarding pregnancy on our forum
February
Roads get slippery during the off-season. And expectant mothers should be especially careful: after all, the worst thing for them is not so much the possibility of getting hurt themselves, but rather disturbing the one who lives in the tummy.
Natural protection
“Slipped”, “hurt”, “collided with someone” - forums for expectant mothers are literally full of anxious questions “what will happen now?” and “did I harm the baby?”. Today we will try to find out what gynecologists think about this, and how well the baby is protected in his temporary home.
Of course, a fall is a very unpleasant event during pregnancy. And the expectant mother needs to beware of situations associated with any injuries in every possible way. Indeed, in some cases, falls and injuries do lead to very sad consequences. However, in reality, it is difficult to find at least one pregnant woman who has not once collided with someone or inadvertently hit something on her stomach for all nine months. That is why the special protection of the baby in the mother's stomach is laid down by nature.
The amniotic sac, the membranes of which consist of dense connective tissue and amniotic fluid, the amount of which varies from 0.5 to 1 liter, depending on the duration of pregnancy, saves the baby from mechanical damage. In addition, the baby is protected by the elastic muscles of the uterus, the walls of the abdominal cavity, and in the early stages also the bones of the pelvis. Therefore, it is almost impossible to damage it when dropped. Only by the fifth month of pregnancy, the uterus increases so much that it goes beyond the border protected by the pelvic bones, which increases the likelihood of mechanical damage. However, this does not mean at all that the natural protection of the baby is one hundred percent, and the fall excludes the possibility of serious consequences, such as a miscarriage or the onset of premature birth. The consequences of the clumsiness of the expectant mother can be delayed in time and rather unpleasant. However, they occur only in those rare cases when a direct traumatic effect is directly on the pregnant uterus (falling directly on the stomach, car accident, accident), and the risk of adverse effects is directly proportional to the gestational age.
In addition, the baby is protected by the elastic muscles of the uterus, the walls of the abdominal cavity, and in the early stages also the bones of the pelvis. Therefore, it is almost impossible to damage it when dropped. Only by the fifth month of pregnancy, the uterus increases so much that it goes beyond the border protected by the pelvic bones, which increases the likelihood of mechanical damage. However, this does not mean at all that the natural protection of the baby is one hundred percent, and the fall excludes the possibility of serious consequences, such as a miscarriage or the onset of premature birth. The consequences of the clumsiness of the expectant mother can be delayed in time and rather unpleasant. However, they occur only in those rare cases when a direct traumatic effect is directly on the pregnant uterus (falling directly on the stomach, car accident, accident), and the risk of adverse effects is directly proportional to the gestational age.
HOW TO MAKE A FALL
If you fall or hit your stomach hard, you should pay close attention to how you feel. You should not immediately rise to your feet: sit or lie down for a few minutes, not paying attention to the reaction of passers-by. Come to your senses and don't panic. Panic will not help in this situation.
You should not immediately rise to your feet: sit or lie down for a few minutes, not paying attention to the reaction of passers-by. Come to your senses and don't panic. Panic will not help in this situation.
If you experience any pain, dizziness, or vaginal discharge, water breaks, and contractions begin, call an ambulance or call for help immediately.
WHAT TO WARN FOR:
The appearance of bloody discharge from the vagina (this symptom may indicate placental abruption).
Water from the genital tract (possibly injured fetal bladder).
Feeling of sharp pain in the lower abdomen, lower back or uterine cramps.
THE DOCTOR WILL HELP
If you do not feel any changes, nothing hurts and the baby moves in its previous mode: you should not call your friends and listen to dubious “horror stories”. It is better to pay a visit to the gynecologist who is observing you and to exclude all “what if something is wrong” completely. The doctor will listen to the baby's heartbeat, if necessary, prescribe ultrasound, dopplerography and cardiotocography to make sure that everything is fine with your little one.
But first of all, it is worth treating possible abrasions on the arms or legs that may appear during a fall. Such actions will exclude the possibility of infection in your body.
Medical Consultant of the Independent Laboratory INVITRO Nona Hovsepyan
Injuries, falls during pregnancy can be not only due to an accident, collision with something or someone, but also due to certain changes occurring in the body of the expectant mother. The fact is that the changed general hormonal background during pregnancy affects the redistribution of blood flow, when part of the blood flow is directed to nourish the unborn baby and the growing uterus. This condition can lead to a decrease in blood pressure, which in turn is often accompanied by hypoxia (lack of oxygen). This explains the frequent fainting in pregnant women. Particularly careful should be those women who, even before pregnancy, had low blood pressure and had frequent fainting.
Weakness, fatigue, frequent dizziness, leading to falls, can occur with anemia (decreased hemoglobin level), this is one of the common pathological conditions of pregnancy.
Therefore, the elimination of somatic (organic) causes of falling during pregnancy significantly reduces the risk of various injuries, bruises during pregnancy.
9 tips for a future mother
1. Going for a walk, always take your husband or girlfriend with you, do not walk alone.
2. On stairs and escalators, hold on to the handrails. If you are afraid of turnstiles in the subway - enter through the "luggage" passage.
3. Climbing up and down the stairs, hold on to the railing and put your foot on the whole foot.
4. Refuse to wear shoes with heels and high wedges.
5. When walking, do not keep your hands in your pockets.
6. Choose bags with long shoulder straps so that your hands are always free.
7. On a questionable and slippery surface, move in small steps on slightly bent legs.
8. Learn to group: press your head to your chest and try to fall sideways, on your hip.
9. If you still fell, do not jump up sharply, it is better to recover for a few seconds and only then gradually rise. And don't be afraid to ask for help from those around you.
And don't be afraid to ask for help from those around you.
FIRST AID
The place of injury and (or) damage to the skin (wounds or abrasions) should be washed with running water and treated with hydrogen peroxide or brilliant green. It should be remembered that it is impossible to treat the wound itself with iodine, as it has a cauterizing effect, as a result of which healing is slower. After applying a weak bandage, something cold can be applied to the site of injury. It is better, of course, if it is ice, but you can use a piece of meat from the freezer or a plastic bottle with cold water.
In severe pain, you can take an anesthetic - of course, if the pain is not localized in the lower abdomen, but in the area of damage. As an anesthetic drug, you can use a baralgin tablet.
In addition to the physical consequences of falls and bruises, the expectant mother may be worried about stress. And stress, as you know, is accompanied by the release of adrenaline into the blood, which affects all organs and systems of the body: the number of heartbeats increases, blood vessels narrow, centralization of blood flow occurs, i.