How to become a child therapist in canada
How to Become a Child Counselor
Children and adolescents progress through many life changes and challenges in their family, peer groups, schools, and other environments. Treating young clients requires appropriate training, a special level of patience and the ability to connect with both children and their families.
Children and adolescent counselors provide their clients with coping skills to achieve emotional and mental health. The challenges facing their young clients include attention disorders, learning difficulties and behavioral issues, as well as the emotional impact of divorce, death, serious illness, or emotional trauma brought on by child abuse, familial issues or bullying. Teenage clients also present a wide array of concerns such as dealing with peer pressure, eating disorders, self-mutilation, drug abuse, sexual confusion, depression, anxiety and in some cases the early signs of a serious mental illness.
The Family Institute at Northwestern University
infoMaster of Arts in Counseling
Earn a CACREP-accredited master’s in counseling online from top-9 ranked1 Northwestern University.
1U.S. News & World Report: 2022 Best National University Rankings
- CACREP Accredited
- Earn your MA in Counseling from Northwestern in as few as 18 months
- Accelerated full-time, traditional, or part-time tracks available
NYU Steinhardt School of Culture, Education, and Human Development
infoMaster of Arts in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness
Aspiring mental health counselors are prepared to pursue licensure with NYU Steinhardt’s MPCAC-accredited online counseling master’s. Students can earn their degree in as few as 21 mos. GRE not req.
- Prepare to become a mental health counselor
- Accredited by the MPCAC
- As few as 21 months to complete
- GRE not required
Professional and mental health counselors that work with children and adolescent populations are experienced and educated from many different backgrounds. Some may be licensed professional counselors, others clinical mental health counselors or even child psychologists. Child and adolescent counselors may take a holistic approach to treating their clients that may include counseling with the young client’s parent(s) or relevant family members. The counselor evaluates a young client’s frame of mind, while exploring their family dynamic, social circle and schooling to understand how their everyday environment impacts their mental health.
Some may be licensed professional counselors, others clinical mental health counselors or even child psychologists. Child and adolescent counselors may take a holistic approach to treating their clients that may include counseling with the young client’s parent(s) or relevant family members. The counselor evaluates a young client’s frame of mind, while exploring their family dynamic, social circle and schooling to understand how their everyday environment impacts their mental health.
School counselors provide similar support to children but focus more on how their social, personal, and academic development affect their experience with education. School counselors should obtain their master’s degree in school counseling rather than specialize in child and adolescent counseling/therapy. While both careers address the same populations, each approach concerns in a different manner.
Some of the concerns that children and adolescents may present in counseling sessions may include:
Child and adolescent counselors encourage clients to discuss their daily experiences and emotions and help them process their reactions and adjust to major life changes, such as divorce or death. A skilled and successful practitioner will teach their clients to develop skills to change their behavior, cope with life’s challenges, and make good decisions. Often a child and family counselor will coordinate treatment with other practitioners, such as a psychiatrist and/or social worker. As appropriate, they will refer young clients to treatment facilities or community programs.
A skilled and successful practitioner will teach their clients to develop skills to change their behavior, cope with life’s challenges, and make good decisions. Often a child and family counselor will coordinate treatment with other practitioners, such as a psychiatrist and/or social worker. As appropriate, they will refer young clients to treatment facilities or community programs.
Step 1: Complete a bachelor’s degree in a behavioral, social science, psychology field, or another field.
Earning your bachelor’s degree in psychology, social work, or another behavioral field is typically the first step. Some students may enroll in counseling or psychology courses to learn about child development theories, counseling skills, human development, and approaches to child therapy and counseling.
Step 2: Earn a master’s degree in counseling with a focus on child and adolescent development.
Child and adolescent counselors earn their master’s degree in counseling or a related field to fine tune their education with regards to child development theories, counseling techniques with children, review of mental, behavioral, and emotional disorders, educational and psychological testing and measurement, and individual, group, and family therapy.
Step 3: Complete graduate and postgraduate internship experience for certification/licensure requirements.
As a crucial aspect of CACREP-accredited counseling degrees, graduate supervised counseling experience allows students to dive into their future licensed role as a child counselor. This experience with postgraduate clinical hours provides crucial insight into work with children postgraduate.
Step 4: Pass any required exams for certification/licensure and apply for licensure.
Some states and/or counseling programs require the passing of a counselor examination for graduation or certification/licensure such as the National Counselor Examination (NCE) and/or the National Clinical Mental Health Counseling Examination (NCMHCE). Check the available licenses and required examinations for counselors in your state through the National Board of Certified Counselors (NBCC).
Step 5: Apply for and earn additional certifications.
In working with children and adolescents, some universities and organizations offer additional certifications, specifically in child psychology, grief counseling, child life, and trauma-informed treatment.
Step 6: Continue your education and stay up to date on child and adolescent counseling trends and changes.
To both maintain state licensure and be relevant in changes and trends, counselors specializing in child and adolescent populations are required to obtain continuing education hours from various formats. The Society for Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology and the American Psychological Association offer ways for child and adolescent counseling professionals to expand their practice and work with children.
Requirements for a state license typically include completion of a counseling master’s degree program from an accredited university, two years of supervised postgraduate clinical experience and a passing score on a state -administered licensing exam. Additionally, practicing counselors may be required to take continuing education to maintain their license. Specific licensure requirements vary by state. See state license requirements.
Child and adolescent counselors work in a variety of settings, including private practice, mental health centers, public and private schools, residential care facilities, outpatient care centers, psychiatric hospitals and more. Counseling children and adolescence may be viewed more as a population/demographic preference for counselor’s, therefore, sessions may occur with marriage and family therapists, licensed professional counselors, clinical social workers, or child psychologists. Counseling with this population can also occur in schools with school counselors or psychologists.
Counseling children and adolescence may be viewed more as a population/demographic preference for counselor’s, therefore, sessions may occur with marriage and family therapists, licensed professional counselors, clinical social workers, or child psychologists. Counseling with this population can also occur in schools with school counselors or psychologists.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment of marriage and family therapists and mental health counselors is projected to grow 23 percent from 2020 to 2030. The BLS also reports that the median annual salary for mental health counselors is about $48,520 and the median salary for marriage and family therapists is about $49,880 as of May 2021.
(Back to Top)
Bellevue University
Master of Science in Clinical Mental Health Counseling
Bellevue, Nebraska
Lock Haven University
Department of Social Work and Counseling
Master of Science in Clinical Mental Health Counseling
Lock Haven, Pennsylvania
Last updated: May 2022
How to Become a Child Therapist
What Does a Child Therapist Do?
Child therapists see children with emotional disturbances from a variety of causes. Some emotional and cognitive problems can stem from physical illness or disability, developmental delays, mental illness, intellectual deficits, trauma, loss, stress, and social difficulties.
Some emotional and cognitive problems can stem from physical illness or disability, developmental delays, mental illness, intellectual deficits, trauma, loss, stress, and social difficulties.
Therapists assess problems of patients from early childhood through adolescence, design interventions to help them, carry out and assess those interventions, report their findings, and coordinate their work with the rest of the health care team.
The duties of child therapists also include assessing cognitive, developmental, emotional, and social status of each child they see. Once an assessment is made the therapist discusses problem areas with the parents and gets an idea of family dynamics as they relate to the child.
Then the therapist composes a care plan for dealing with the child’s problems. He or she might discuss the case with physicians, nurse practitioners, teachers, and other professionals concerned with helping the child. Once a plan for intervention is in effect, the therapist continues to communicate with the child and family, keeping records of the child’s progress.
At long last the child therapist is able to discharge the patient when he or she achieves a satisfactory functional level.
Where Does a Child Therapist Work?
Child therapists can work for school systems, pediatric hospitals, pediatricians, juvenile detention centers, camps for handicapped children, and probation offices. Therapists wanting more independence can work in a solo or group private practice.
Why Do We Need Child Therapists?
Adults aren’t the only ones who can benefit from therapy. Unfortunately, the mental health of children is often overlooked and ignored. Many people think children are always happy, since childhood is regarded as a time of playfulness, bliss, and no responsibility.
However, children can also deal with stress and psychological issues, just like adults. Children have specific needs and issues that may require therapy – and this type of therapy is markedly different from traditional adult therapy.
The vastly different approach that is necessary for working with a child in therapy, when compared to working with an adult, begs for the need for an entire subset of child therapy. Children need to be made comfortable in order to open up and share. They often require a playful environment, one that doesn’t even feel like therapy.
Children need to be made comfortable in order to open up and share. They often require a playful environment, one that doesn’t even feel like therapy.
Children look at the world in a completely different way than adults. They also have a different level of understanding of the world around them. Because of this, the approach to therapy for children is much different.
If a child is suffering from some sort of mental health issue or behavioral problem, therapy can help prevent any issues from turning into more long-term issues into adulthood.
Childhood is, in essence, supposed to be a happy time, full of learning, growing, exploring, and laughing. All children deserve that happiness, leading to healthier and happier adulthood.
Related: How to Become a Youth Therapist
What are the Requirements to Become a Child Therapist?
Education
Child therapists are required to have a master’s degree in counseling or social work or a doctoral degree in psychology. Doctoral degree, however, is not mandatory for therapist/counselor licensure.
Doctoral degree, however, is not mandatory for therapist/counselor licensure.
A bachelor’s degree is the first requirement for a child counselor, and most places of employment, as well as state boards, require a master’s level education.
A typical Bachelor or Arts or Bachelor of Science would include basic education, electives, basic psychology, child psychology, developmental psychology, statistics, and a choice of upper division courses specifically related to child therapy.
Some specialized upper division courses might include: early development, adolescent development, disabilities and their emotional impact, development and interpersonal relations, behavioral and emotional childhood problems, perceptual development, cognitive development,play therapy, art therapy, or language development. Some programs allow field studies or research.
Not all universities offer undergraduate programs in childhood therapy, but most offer courses in psychology and counseling. A Bachelor’s degree in a related subject, like child psychology, can be stepping stone toward a graduate degree in child therapy.
A Bachelor’s degree in a related subject, like child psychology, can be stepping stone toward a graduate degree in child therapy.
Students should check catalogs, discuss their goals with faculty and school counselors, and come up with a plan for their education in advance of applying to a university.
Admission to a master’s program requires completion of the bachelor’s degree. Some master’s programs are composed of entirely coursework, while others require original research and a thesis.
Some graduate level courses students might encounter include: hospitalized infant and toddler development, grief and loss, play therapy, crisis intervention, child abuse, family theory, social ecology, and child life, to name a few. Internships allow students to practice child therapy under supervision.
Optional
Doctoral programs require graduate students to design and carry out original research at the level published in the scientific journals.
Students arrange with members of faculty to be their advisors and help them submit research proposals. When proposals are granted, students carry out their proposed studies under the supervision of their advisors and graduate committees.
When proposals are granted, students carry out their proposed studies under the supervision of their advisors and graduate committees.
At the completion of their research, students write a dissertation detailing their work and conclusions they have drawn from it. The last step is to defend their studies before their graduate committees. Once a dissertation is approved, the student officially has his or her PhD.
Licensure
States and territories maintain standards of education and experience that child therapists must live up to in order to receive permission to practice. A license in view of consumers lets them know that their therapist has the necessary qualifications to help them and their families.
State boards of health care and counseling decide upon their own rules, so the necessary qualifications vary from state to state. Students should check with the state government in which they plan to practice to learn which hoops to jump through.
Generally, evidence of the required coursework (i. e. master’s level education) and supervised experience are required, along with a satisfactory score on a test administered by the relevant state board.
e. master’s level education) and supervised experience are required, along with a satisfactory score on a test administered by the relevant state board.
Few if any states license child therapists as a separate specialty but license counselors and psychologists with a broader description. Kansas and Maryland for instance, licenses Licensed Professional Counselors (LPCs) and Licensed Clinical Professional Counselors (LCPCs). Texas and Illinois also license child therapists as LPCs.
California, licenses child therapists as Licensed Professional Clinical Counselors (LPCC). New York on the other hand licenses these therapists as ‘Licensed Mental Health Counselor’.
Florida licenses psychologists and school psychologists. In Florida, candidates must pass the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology and the Florida Laws and Rules examination.
Graduates need to look up the specific licensure requirements in their own states and check back periodically for new developments.
What are the Qualities of a Good Child Therapist?
Listed below are the qualities of a good child therapist:
- Have a “Soft Spot” for Children: A good child therapist must love, or deeply like children. In fact, they must enjoy being around children, and watching them grow, develop, and mature.
- Understand Child Development: A credible child therapist should have a sound understanding of the developmental stages of children. He or she must also be highly familiar with common age-related issues and concerns. Furthermore, it is important that a good child therapist be knowledgeable of child-appropriate treatment approaches.
- Be Willing to Consult with Other Professionals: A good child therapist must also be willing to consult with other professionals (i.e. teachers, social workers, therapists, childcare workers, psychologists, physicians, counselors, etc.). If a child is “acting out” at home, he or she is probably doing the same thing at school, daycare, etc.
 ; therefore, it is important to work with professionals in those areas. It is also imperative to work with physicians, especially if the child is taking psychotropic medications. A willingness to collaborate with medical and educational professionals can promote the child’s success, both at home and away from home.
; therefore, it is important to work with professionals in those areas. It is also imperative to work with physicians, especially if the child is taking psychotropic medications. A willingness to collaborate with medical and educational professionals can promote the child’s success, both at home and away from home.
- Encourage Parental Participation: Lastly, a good child therapist must encourage parental participation. In other words, he or she must actively encourage parents, to become involved in what is happening with their child. A child therapist should also maintain communication with parents on a regular basis. This communication should consist of: progress reports, parenting style suggestions, and ways to improve the child’s behaviors at home, and at school.
What Skills are Required for a Child Therapist?
Child therapists must have excellent interpersonal skills for dealing with not only the patient but adults who affect the child. He or she must be able to communicate a positive, caring attitude, and actively listen to the patient, his family, and others concerned with the case.
He or she must be able to communicate a positive, caring attitude, and actively listen to the patient, his family, and others concerned with the case.
Therapists must have good writing skills for documenting cases. Child therapists in private practice need business and accounting skills.
What is the Job Outlook for Child Therapists?
The future looks bright for aspiring professionals in all health care fields. The Affordable Health Care Act puts help within reach of families regardless of socioeconomic status. The current high level of divorce puts stresses on families and children.
By the year 2031 it is estimated that 12 percent more mental health counselors will be needed than were needed in 2021, resulting in 77,500 new employments.
What is the Salary for a Child Therapist?
As of August 2022, according to ZipRecruiter, the average hourly salary throughout the country for child therapists is $32 and the average annual income is $67,087. Experienced child therapists earn well over $100,000 per year.
Salaries vary from state to state and among various employment settings. Child therapists working in Nebraska, New York and California earn the highest average annual salary of $97,409, $84,078 and $80,778 respectively.
While Child therapists working in Texas, Connecticut and Wyoming on average earn $74,719, $76,261 and $78,535 per year respectively.
Related Reading
- Child Social Work Careers
- How to Become a Child Psychologist
- How to Get a Degree in Child Psychology
- What Can You Do With a Counseling Psychology Degree?
- What Can You Do With a Child Psychology Degree?
More Resources
- Association of Educational Therapists
- ACAChild | Association for Child and Adolescent Counseling
- Division 53—Society of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology
Immigrate to Canada as a Physician or Specialist - Complete Guide
Physicians are one of the most sought after jobs in Canada. Every year, thousands of foreigners immigrate to Canada as doctors.
Every year, thousands of foreigners immigrate to Canada as doctors.
As an experienced doctor, you could earn up to $312,000 a year, and as a specialist, even more, not to mention the crazy and lucrative benefits that all Canadian citizens and permanent residents are entitled to, such as free medical care, initial and secondary education for you and your family, as well as excellent work benefits.
On this page, you will find everything you need to know about moving to Canada as a doctor, including general and specific immigration requirements for doctors in Canada, as well as the various positions you can fill as an overseas doctor in Canada .
In this article
- Who are doctors or doctors in Canada?
- Job Description / Responsibilities of Physicians in Canada under NOC Code 3111
- Job Description / Responsibilities of Physicians in Canada under NOC Code 3112
- Sample NOC 3111
- NOC 3112
- Physician Immigration Requirements
- General Requirements to Canada as a Physician
- Canada as a Doctor
- Pathways to Canada Immigration as a Doctor or Specialist
- Steps to Canada as a Doctor
- Frequently Asked Questions
Who are doctors or doctors in Canada?
Can doctors immigrate to Canada? Absolutely yes! As previously stated, there are several jobs that you can fill as a doctor in Canada. It is also noteworthy that there are different doctors. Therefore, it will be necessary to discuss who is a doctor and what different doctors do.
It is also noteworthy that there are different doctors. Therefore, it will be necessary to discuss who is a doctor and what different doctors do.
The most common medical specializations are clinicians, surgeons and medical specialists. Clinical medicine specialists diagnose and treat diseases and psychological or mental disorders. They also act as consultants to other physicians.
Clinical medicine professionals usually work in private practice or hospitals, while laboratory medicine and surgery professionals usually work in hospitals. Residents trained as medical specialists are also included in this group of units.
Since you are planning to immigrate to Canada as a doctor, you need to understand the NOC code for this position. In Canada, the National Occupational Classification (NOC) Code is the system used by the Government of Canada to classify various positions. Using this structure, similar vacancies are classified together. Each is given a unique set of digits which becomes the NOC code.
There are several NOCs in Canada for various physician positions. All professions fall between NOC 3111 and 3112. Other NOC codes include physicians who become administrators, politicians and managers. There are also specific NOC codes for dentists, ophthalmologists, veterinarians, etc.
Job Description / Responsibilities of Doctors in Canada under NOC Code 3111
Before migrating to Canada as a doctor, you must know your job description and responsibilities that you will take on when you resume work.
For physicians under NOC 3111, this group includes specialists in clinical medicine, surgery and laboratory medicine.
Job Responsibilities of Clinical Medicine Specialists
- Diagnose and treat diseases, physiological or mental disorders.
- Order laboratory tests, x-rays and other diagnostic procedures
- Administer drugs and treatments and refer patients for surgery
- Act as a consultant to other physicians
- May conduct medical research
Job responsibilities of laboratory medicine specialists
- To study the nature, causes and development of human diseases, as well as structural and functional changes caused by diseases.

- Conducting microscopic and chemical analyzes of laboratory samples and specimens.
- Supervise laboratory activities
- Act as a consultant to other physicians
Responsibilities of surgeons
- Assess patients' illnesses or disorders to select appropriate surgical procedures.
- Perform and supervise surgical procedures to correct physical abnormalities and deficiencies and to repair injuries
- Act as a consultant to other physicians
Job Description / Responsibilities of Physicians in Canada under NOC Code 3112
Under NOC 3112, physicians include family physicians, who are usually in private practice. Their main duties are:
- Examine patients and collect their history, ordering laboratory tests, X-rays and other diagnostic procedures. They also consult with other medical practitioners to assess patients' physical and mental health.
- Prescribe and administer drugs and treatments
- Perform and assist in routine surgery
- Provide emergency care
- Provide emergency care
- Vaccinate patients to prevent and treat diseases
- Have children and provide prenatal and postnatal care
- Advise patients and their families on health issues, including health promotion, disease and accident prevention.

- Advice and support to patients and their families on a wide range of health and lifestyle issues.
- Perform a patient advocacy role
- Coordinate or manage primary health care
- Provide ongoing patient care
- Monitor home care services
- Finally, they report births, deaths, infectious and other diseases to government agencies.
Sample NOC 3111 Physician Jobs
Immigrating to Canada as a physician opens up several job options for you. Physician job types under NOC Code 3111 include the following:
Clinical Specialists
- Anesthesiologist
- Cardiologist
- Clinical immunologist-allergist
- Dermatologist
- Diagnostic Radiologist
- Emergency doctor
- endocrinologist
- gastroenterologist
- Geriatrician
- Hematologist
- Nephrologist
- neurologist
- Oncologist
- Orthopedist
- Pediatrician
- Physiotherapist
- Pneumologist
- Psychiatrist
- Radiation Oncologist
- Respirologist
- Rheumatologist
Laboratory medicine specialists
- Anatomy pathologist
- General pathologist
- Hematopathologist
- Biochemist
- Medical microbiologist
- Neurologist
Surgeons
- Cardiac surgeon
- Chief Surgeon
- Neurosurgeon
- Obstetrician-gynecologist
- Ophthalmologist
- Orthopedic Surgeon
- Otorhinolaryngologist
- Pediatric surgeon
- Plastic surgery
- Thoracic surgeon
- Urologist
- Vascular surgeon
Physician exemptions under NOC 3111
Some positions are not included in NOC 3111 and therefore are not recognized by physicians belonging to this group. They are:
They are:
- Physicians of the Primary Health Care Alliance (3124)
- Chiropractors (3122)
- General practitioners and family doctors (3112)
- Health care managers (0311)
- Other occupational health diagnostics and treatment (3125)
Sample vacancies for a doctor according to NOC code 3112
- Family doctor
- General Practitioner (GP)
- Medical Doctor
- Resident, general practice
NOC 3112 Physician Exemptions
- Primary Health Care Alliance Physicians (3124)
- Chiropractors (3122)
- General practitioners and family doctors (3112)
- Health care managers (0311)
- Medical Specialists (3111)
Immigrate to Canada as a customs consignor and other broker
Requirements to immigrate to Canada as a doctor
Immigrating to Canada as a doctor requires you to follow the correct procedures and meet certain requirements. The requirements for working as a doctor in Canada can be divided into general and specific.
General requirements are common to all physician positions, while specific requirements may vary from one job description to another.
General requirements to immigrate to Canada as a doctor
Age
To immigrate to Canada as a doctor or specialist, you must be between 18 and 35 years of age.
Training
First, you need a Bachelor of Science (BSc) degree to work as a doctor in Canada. If you are planning to immigrate to Quebec, you must complete a college program and one year of pre-medical studies at a university.
For example, if you are moving to Canada from South Africa as a doctor, you must have a bachelor's degree from a recognized university in South Africa with transcripts showing this.
You must then graduate from an approved medical school where you specialize in a specific area of medicine that must be listed.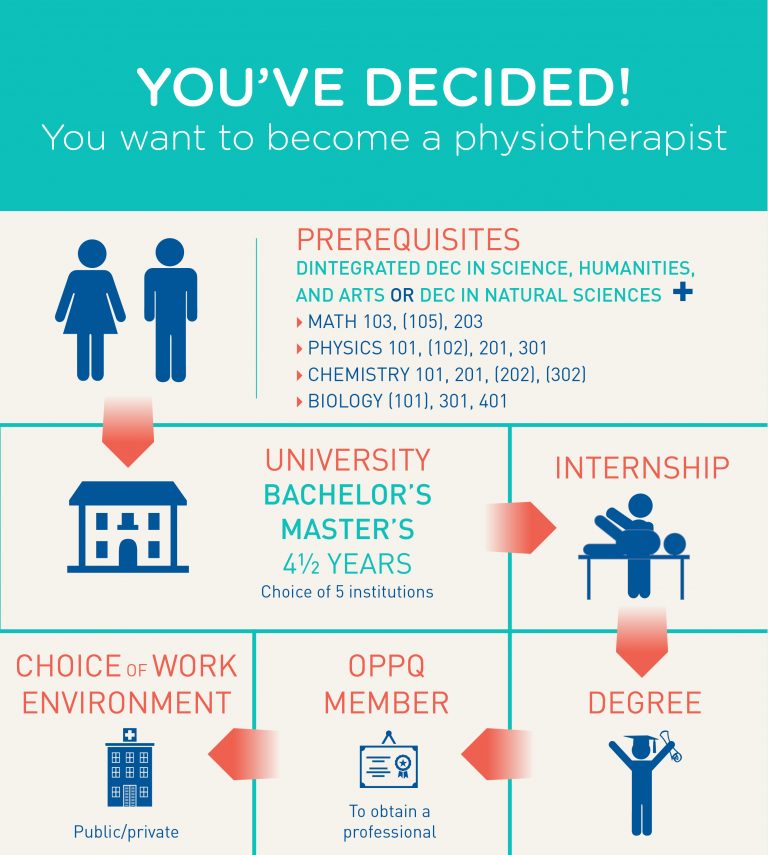
Work Experience
Depending on the immigration path you will be applying for, you may or may not need previous work experience to immigrate to Canada as a doctor.
Evidence of proficiency in English or French
The province or territory to which you wish to immigrate will determine in which language you prove proficiency in those languages. The generally accepted way to demonstrate fluency in these languages is to take language tests.
Whether it's English or French, you can take several acceptable language tests in order to immigrate to Canada as a doctor.
There are certain immigration options that require you to achieve a certain CRS score in order to be eligible to immigrate to Canada as a doctor. CRS stands for Comprehensive Ranking System and is a popular scoring method used by some immigration programs in Canada.
Special requirements for immigrating to Canada as a doctor
Some professions require special certifications for foreign educated professionals to successfully immigrate to Canada.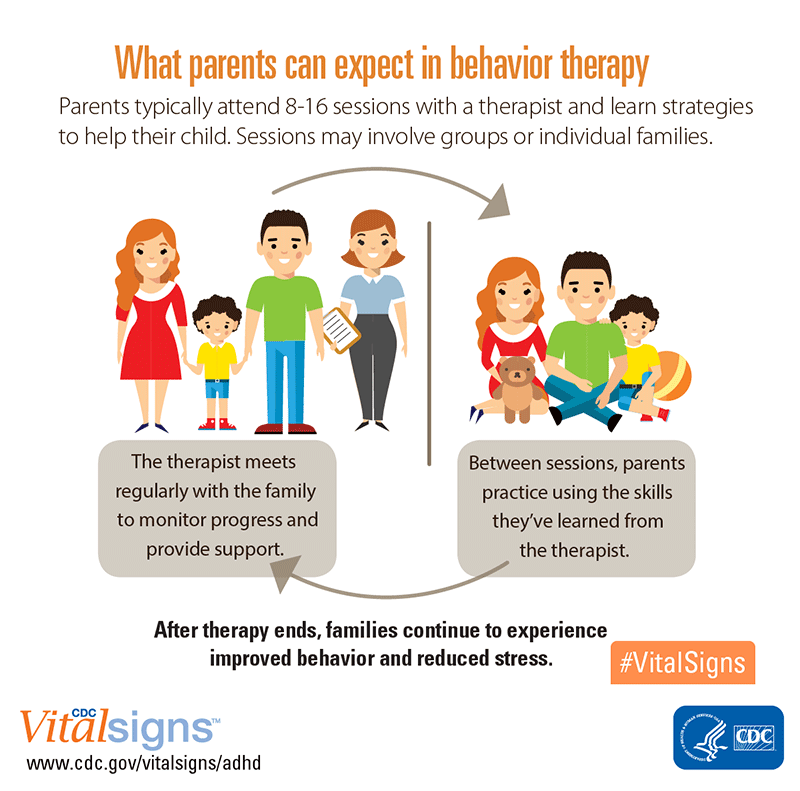 Physicians and medical specialists are two such professions.
Physicians and medical specialists are two such professions.
To work as a doctor in Canada, you must pass the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada certification exams. It is important to note that it is best to obtain a license from the licensing authority of the province or territory in which you will be working.
Specialist physicians may require two to five years of specialized residency training in the specific niche of their chosen food.
To find out more about the specific requirements for the specific profession you have chosen to specialize in medicine, you can visit the Government of Canada website for NOC codes and job descriptions and search for your profession using the NOC code.
Ways to immigrate to Canada as a doctor or medical specialist
Are you wondering how to immigrate to Canada as a doctor? There are several ways to immigrate that you can use. To the delight of all would-be Canadian residents, there are dozens of friendly immigration programs in Canada that will help you get into the country if you meet certain requirements.
Some of the most popular immigration programs where doctors apply to immigrate to Canada:
- Express Entry
- Provincial Candidate Program
- Federal Skilled Worker Program
- Work visa
- Study Permit for Postgraduate Visa
Steps to immigrate to Canada as a doctor
The steps to immigrate to Canada are technically the same for all health professions in the respective NOC codes. Please note that the immigration path you are applying for may require special steps from you. However, the following processes are mandatory if you want to immigrate to Canada as a doctor.
Step 1: Pass the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada certification exams.
Step 2: Apply to immigrate to Canada as a doctor by choosing your preferred immigration path. (You may or may not need to create an Express Entry profile.)
Step 3: If you submit your profile to the Express Application Pool, you will receive an Invitation to Apply (ITA) upon completion of the requirements.
Step 4: Use your ITA to apply for permanent residence with Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC).
Finally, step 5: You can legally travel to Canada and resume your practice as a doctor after receiving a residence permit.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it easy to immigrate to Canada as a doctor?
Migrating to Canada as a doctor is easy if you take the right steps. A successful migration experience is knowing which immigration path is best for you. People immigrate to Canada in different ways. The most common ways are Express Entry and Provincial Nominee Program.
Can Indian doctors emigrate to Canada?
Trained doctors from India can immigrate to Canada. To do this, they must pass the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada certification exams and then apply to immigrate through any immigration program of their choice.
Do I need a job offer to immigrate to Canada as a doctor?
A job offer is not a requirement to immigrate to Canada as a doctor unless required by the immigration program you are applying for. If you have received a job offer, you can apply for a work permit directly or indicate it on your Express Entry profile. A job offer can increase your CRS scores.
Conclusion
There are several job opportunities for foreign doctors who wish to immigrate to Canada. The first step towards realizing this dream is to pass professional exams and obtain other special certificates. Thus, you may be considered a qualified doctor to work in Canada.
Are you from Costa Rica? Find out how to immigrate to Canada here.
How doctors live in Canada. How many years do professionals study their profession? | Healthy life | Health
Alena Zhukova
Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
16129
AiF Health No. 49. Russians donate over $1 billion to charity 04/12/2014
49. Russians donate over $1 billion to charity 04/12/2014 shutterstock.com
Our Expert – MD, PhD, Public Health Specialist in Epidemiology Armen Parsyan .
Various systems
In Canada, future doctors study at the university for four years (in Russia - six). After four years of study, they enter the residency, where they receive a specialization. In the specialty, doctors are engaged in another five years. An exception is made for the training of family doctors, as their shortage is a sore point for Canada. They are trained for two years. So, to become a general surgeon, you need to study in residency for five years. Then, if there is an intention to specialize, for example, in thoracic, gastric, vascular, cardiac or other areas of surgery, study for at least another two years.
Overcoming difficulties
Russian doctors who are trying to build a career abroad leave the country with the brightest hopes. But getting a job in the West is very difficult. To work as a doctor in North America, one must pass the American or Canadian qualifying exams and enroll in a residency, even if the doctor has already completed it in Russia. That is, to repeat all postgraduate education. In Canada, there are very few places in residency, there are not enough of them even for those who graduated from medical schools in this country.
But getting a job in the West is very difficult. To work as a doctor in North America, one must pass the American or Canadian qualifying exams and enroll in a residency, even if the doctor has already completed it in Russia. That is, to repeat all postgraduate education. In Canada, there are very few places in residency, there are not enough of them even for those who graduated from medical schools in this country.
Canadian surgical residencies, for example, have an average of 4-5 positions. Approximately 300 Canadian graduates and the same number of foreign graduates apply. The first stage of selection usually goes through about 50 people, the bulk of which are Canadian graduates.
At the same time, we have to carry out research work, which is highly appreciated here. And spend large sums of money to participate in scientific symposiums.
But if an emigrant is ready to go through all these difficulties and trials, he has at least a small but chance to get settled in Canada. After all, after residency it is not difficult to find a job - the country really needs doctors.
After all, after residency it is not difficult to find a job - the country really needs doctors.
Life in a hospital
– Life as a doctor in Canada is life in a hospital. I don’t talk to my family for weeks,” says our expert. I get up at 5 am, come home at 7 pm. Plus night shifts. It's interesting, but very exhausting. But, despite all the difficulties, I do not look back and do not reproach myself for the choice.
In Canada, people are taught healthy lifestyles from an early age. Unfortunately, I'm not used to it. That's all I'm trying to go to the gym near the house. Only you have to get home first after 12 hours of work ...
Well, if you didn't succeed in becoming a doctor in Canada, you can always retrain as a nurse, whose work here is also well paid. I personally know two sisters who were good doctors in the USSR, and after moving to Canada, they began to engage in ultrasound diagnostics. Here, this work is not the competence of the doctor, it is the level of highly qualified middle staff. Once every few years, the sisters are visited by their father from Russia, who has been working in healthcare for more than 50 years. He is the most famous therapist in a small Siberian town, an honored doctor of the Russian Federation, a labor veteran. But, if not for the financial assistance of his daughters, could he travel the world?
Once every few years, the sisters are visited by their father from Russia, who has been working in healthcare for more than 50 years. He is the most famous therapist in a small Siberian town, an honored doctor of the Russian Federation, a labor veteran. But, if not for the financial assistance of his daughters, could he travel the world?
The main difference between Russian and Canadian doctors is that Canadian doctors, unlike Russians, don't worry about how to support their families after many years of study.
See also:
- Mikhail Paltsev: “Our task is to improve the practical training of doctors” →
- Doctors from the CIS countries got acquainted with Israeli medicine →
- How is treatment in Turkey? Pros and Cons of Turkish Medicine →
Canadahealth
Next article
You may also be interested in
- Chief Physician of City Clinical Hospital No.