Herpes outbreaks during pregnancy
Genital herpes and pregnancy: Understanding the risks | Your Pregnancy Matters
Be honest with your doctor about your history with herpes – or if you suspect you may have herpes. This allows them to take additional precautions beyond what they might normally provide during pregnancy, labor, and delivery to safeguard your baby from contracting the virus.Genital herpes is one of the most common health conditions in the U.S. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that 1 in 6 people between the ages of 14 and 49 have it. Approximately 22% of pregnant women in the U.S. have genital herpes. Two percent contract it during pregnancy – that's 1 in 50 pregnant women.
Two viral strains can cause genital herpes. HSV-2 (herpes simplex virus) is the most common and typically spreads through sexual contact. HSV-1, which is best known for causing cold sores, can also produce genital lesions (blisters or open sores). More than half of adults in America get HSV-1 at some point in their lives.
Herpes is generally manageable in adults. However, it can cause serious health problems in newborns. During delivery, your baby may be exposed to the virus, even if you are not having an outbreak.
Herpes infection occurs in less than 1% of births, but it can cause severe illness in newborns, such as:
- Blindness
- Deafness
- Seizures
- Serious infections, such as viral meningitis
- Recurrent sores on the skin, eyes, genitals, or mouth
- organ damage, including to the liver, lungs, and heart
Tell your doctor if you or your partner have herpes or if you may have been exposed. By knowing, we can take extra precautions to reduce your baby's risk of infection during delivery and in their first few weeks at home. If you’re not certain but think you may have had herpes in the past, we can do a blood test to determine whether you have had the infection.
If you are concerned about privacy, we will note in your chart not to discuss the condition in front of anyone at your appointments – we are happy to accommodate this common request.
"Tell your doctor if you or your partner have herpes or if you may have been exposed. By knowing, we can take extra precautions to reduce your baby's risk of infection during delivery and in their first few weeks at home."
Robyn Horsager-Boeher, M.D.
How can I manage herpes during pregnancy?
There is no evidence to suggest pregnancy causes flare-ups. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says 75% of pregnant women who have herpes, however, can expect to have an outbreak during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, you should watch for symptoms of the virus becoming active, such as tingling, itching, or burning around where the sore will eventually appear.
If you have a history of herpes (or your blood test is positive), your provider may prescribe an antiviral medication such as acyclovir (Valtrex) to reduce the risk of spreading the virus or having an outbreak around the time of your delivery.
We typically recommend starting an antiviral at 36 weeks or sooner if you are at risk for preterm birth. The antiviral medications are safe during pregnancy. In fact, we can give the same medications to your baby if needed.
Will I need a C-section if I have herpes?
A cesarean (C-section) can’t completely prevent herpes transmission. But it does substantially decrease the risk to your baby if you have a lesion or report typical symptoms by bypassing contact with the vagina and labia.
Once you go into labor, we’ll carefully examine you for genital lesions. If we see something suspicious, we will recommend a C-section.
If you have no symptoms and no sores in the genital region, a vaginal delivery may be safe. Lesions can sometimes appear in other areas, such as the legs or back. If this is the case, we’ll cover them to make sure the baby doesn’t come into contact with them.
If this is the case, we’ll cover them to make sure the baby doesn’t come into contact with them.
How can I protect my newborn from getting herpes?
If your partner has herpes and you don’t, do not have sex and oral sex the last few weeks of pregnancy. Condoms can reduce the risk of transmission but aren’t 100% effective. There’s no reason to risk a new infection close to delivery.
In the unlikely event your baby has been exposed, we’ll treat the baby with antiviral medications. HSV can’t be passed through breast milk, so unless you have sores or lesion on your breasts, breastfeeding is safe.
With visitors, do not allow anyone who has a cold sore or has had one recently to hold your baby. Same goes for people who have a cold or virus. Insist that anyone who wants to hold or touch your newborn wash their hands first – this should be the norm anyway due to COVID-19.
Genital herpes is a common condition, and we are well-equipped to help reduce your baby's risks. If you or your partner has a history of herpes, talk with your Ob/Gyn. We are eager to help you have a safe pregnancy and delivery.
If you or your partner has a history of herpes, talk with your Ob/Gyn. We are eager to help you have a safe pregnancy and delivery.
To visit with an Ob/Gyn, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
Pregnancy and herpes Information | Mount Sinai
HSV; Congenital herpes; Herpes - congenital; Birth-acquired herpes; Herpes during pregnancy
Newborn infants can become infected with herpes virus during pregnancy, during labor or delivery, or after birth.
Infants may acquire congenital herpes from a mother with an active, possibly inapparent herpes infection at the time of birth. Aggressive treatment with antiviral medicine is required, but may not be effective in the case of systemic herpes.
Aggressive treatment with antiviral medicine is required, but may not be effective in the case of systemic herpes.
Causes
Newborn infants can become infected with herpes virus:
- In the uterus (this is unusual)
- Passing through the birth canal (birth-acquired herpes, the most common method of infection)
- Right after birth (postpartum) from being kissed or having other contact with someone who has herpes mouth sores
If the mother has an active outbreak of genital herpes at the time of delivery, the baby is more likely to become infected during birth. Some mothers may not know they have herpes sores inside the vagina.
Some women have had herpes infections in the past, but are not aware of it, and may pass the virus to their baby.
Herpes type 2 (genital herpes) is the most common cause of herpes infection in newborn babies. But herpes type 1 (oral herpes) can also occur.
Symptoms
Herpes may only appear as a skin infection. Small, fluid-filled blisters (vesicles) may appear. These blisters break, crust over, and finally heal. A mild scar may remain.
Small, fluid-filled blisters (vesicles) may appear. These blisters break, crust over, and finally heal. A mild scar may remain.
Herpes infection may also spread throughout the body. This is called disseminated herpes. In this type, the herpes virus can affect many parts of the body.
- Herpes infection in the brain is called herpes encephalitis
- The liver, lungs, and kidneys may also be involved
- There may or may not be blisters on the skin
Newborn infants with herpes that has spread to the brain or other parts of the body are often very sick. Symptoms include:
- Skin sores, fluid-filled blisters
- Bleeding easily
- Breathing difficulties such as rapid breathing and short periods without breathing, which can lead to nostril flaring, grunting, or blue appearance
- Yellow skin and whites of the eyes
- Weakness
- Low body temperature (hypothermia)
- Poor feeding
- Seizures, shock, or coma
Herpes that is caught shortly after birth has symptoms similar to those of birth-acquired herpes.
Herpes the baby gets in the uterus can cause:
- Eye disease, such as inflammation of the retina (chorioretinitis)
- Severe brain damage
- Skin sores (lesions)
Exams and Tests
Tests for birth-acquired herpes include:
- Checking for the virus by scraping from vesicle or vesicle culture
- EEG
- MRI of the head
- Spinal fluid culture
Additional tests that may be done if the baby is very sick include:
- Blood gas analysis
- Coagulation studies (PT, PTT)
- Complete blood count
- Electrolyte measurements
- Tests of liver function
Treatment
It is important to tell your health care provider at your first prenatal visit if you have a history of genital herpes.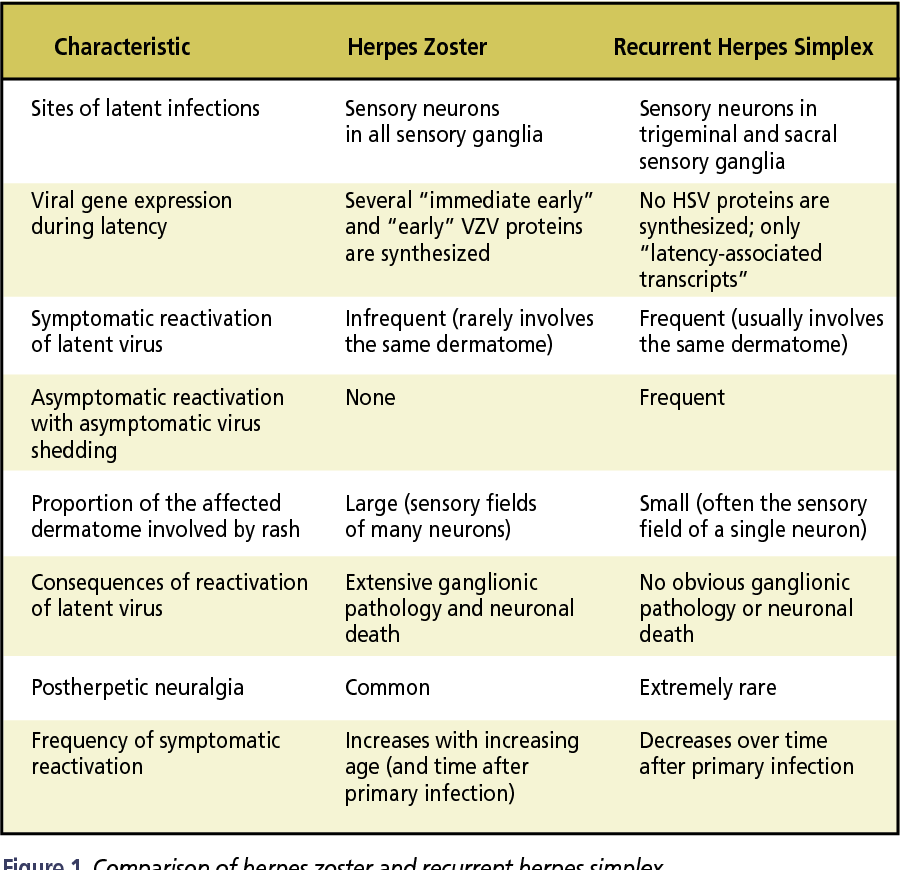
- If you have frequent herpes outbreaks, you'll be given a medicine to take during the last month of pregnancy to treat the virus. This helps prevent an outbreak at the time of delivery.
- C-section is recommended for pregnant women who have a new herpes sore and are in labor.
Herpes virus infection in infants is generally treated with antiviral medicine given through a vein (intravenous). The baby may need to be on the medicine for several weeks.
Treatment may also be needed for the effects of herpes infection, such as shock or seizures. Because these babies are very ill, treatment is often done in the hospital intensive care unit.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Infants with systemic herpes or encephalitis often do poorly. This is despite antiviral medicines and early treatment.
This is despite antiviral medicines and early treatment.
In infants with skin disease, the vesicles may keep coming back, even after treatment is finished.
Affected children may have developmental delay and learning disabilities.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If your baby has any symptoms of birth-acquired herpes, including skin blisters with no other symptoms, have the baby seen by the provider right away.
Prevention
Practicing safe sex can help prevent the mother from getting genital herpes.
People with cold sores (oral herpes) should not come in contact with newborn infants. To prevent transmitting the virus, caregivers who have a cold sore should wear a mask and wash their hands carefully before coming in contact with an infant.
Mothers should speak to their providers about the best way to minimize the risk of transmitting herpes to their infant.
Dinulos JGH. Sexually transmitted viral infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 11.
Kimberlin DW, Baley J; Committee on infectious diseases; Committee on fetus and newborn. Guidance on management of asymptomatic neonates born to women with active genital herpes lesions. Pediatrics. 2013;131(2):e635-e646. PMID: 23359576 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/23359576/.
gov/23359576/.
Kimberlin DW, Gutierrez KM. Herpes simplex virus infections. In: Wilson CB, Nizet V, Maldonado YA, Remington JS, Klein JO, eds. Remington and Klein's Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 27.
Schiffer JT, Corey L. Herpes simplex virus. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 135.
Last reviewed on: 7/1/2020
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Herpes during pregnancy - consequences of lichen for pregnant women
Herpes viruses are many-sided and very dangerous for humans.
 Of particular concern is the infection in a woman expecting a baby.
Of particular concern is the infection in a woman expecting a baby. Doctor's consultation
You can get the consultation of the necessary specialist online in the Doctis application
Laboratory
You can undergo a comprehensive examination of all major body systems
- Genital herpes in early pregnancy
- Genital herpes in late pregnancy
- Pregnancy herpes test
- Chicken pox and herpes zoster during pregnancy
- Prevention of infection of the newborn with chickenpox
- Treatment and prevention of exacerbations of herpes
There is an opinion that if a pregnant woman is infected with the herpes simplex virus, then the unborn danger! But everything is not so scary if the disease does not manifest itself (is in stable remission) or a pregnant woman with an active form of the disease is observed by an infectious disease specialist. Today approaches to maintaining patients with genital herpes changed
Today approaches to maintaining patients with genital herpes changed
Why is herpes dangerous during pregnancy
I am pregnant, short term, and I have genital herpes. Does this mean that I need to terminate the pregnancy?
No way! Genital herpes is not an indication for abortion. Virus crosses the placenta extremely rarely. But for a child, herpes is dangerous if it first appeared a month before birth. or repeated a few days before the birth, since there is a risk of infection of the baby at the time of his passage through the infected birth canal. If infected, the infant will develop severe the disease is neonatal herpes, often occurring with damage to the central nervous system.
Although during pregnancy the risk of transmission of herpes virus from mother to fetus minimal, tolerate the manifestations of genital herpes and not take antiviral drugs, being afraid the consequences of treatment for the unborn child are not worth it.
After 14 weeks of pregnancy, if genital herpes occurs, treatment with an antiviral drug is possible acyclovir. After 22 weeks, therapy with valaciclovir is possible.
In the vast majority of cases, the herpes simplex virus is transmitted from the mother child during childbirth, so the closer to the end of pregnancy there is a recurrence of genital herpes, the higher the risk of infection of the child and the more relevant the treatment of the disease.
If primary genital herpes or recurrence occurs at or after 36 weeks of gestation, clinicians do not limit treatment to 5-10 days, but continue the entire period until the moment of delivery. As in the case very frequent recurrences of genital herpes during pregnancy (one outbreak in 1-2 months) - at week 36, proactive treatment with acyclovir or its analogues begins and continues until the moment childbirth. The goal of proactive treatment is to prevent recurrence shortly before delivery and to reduce the likelihood of asymptomatic carriage.
It must be remembered that it is the asymptomatic shedding of the virus from the urogenital tract that can often be cause of infection of the child during childbirth.
Even when there seems to be no cause for concern, since the manifestations genital herpes are absent in the last months of pregnancy, still at 32-34 weeks pregnancy, it is necessary to conduct a smear (scraping) examination from the cervical canal for the presence of DNA herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 by PCR.
This analysis is necessary for primary genital herpes or its recurrence in the 1st and / or 2nd trimester, relapses genital herpes before pregnancy, relapses of genital herpes in a sexual partner, lesions urogenital tract of unknown cause, antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 IgM class, detected during a routine examination during pregnancy.
For rashes or virus shedding on Wednesday within 7 days before delivery, especially in the presence of genital herpes by the beginning of childbirth, a caesarean section is performed to reduce the risk of transmission virus from mother to child.
I'm just planning a pregnancy. And I want to get rid of herpes recurrences that have been haunting me for a long time me. How do you feel about the treatment of genital herpes with interferon inducers and immunomodulators?
Widespread use of immunomodulators and interferon preparations in Russian medical centers (viferon, polyoxidonium, isoprinosine, etc.) for the treatment of herpesvirus infections is completely unreasonable. The so-called "ozone therapy" will not help the patient either. You will not find these methods in international protocols, recommendations for the treatment of viral infections in children and adults, including pregnant women women. Neither in Russia nor abroad have studies been conducted proving the effectiveness of these drugs in accordance with all international regulations.
An infectious disease specialist, a professional in his field, will never turn to immunomodulators and inducers interferon, but will look for the cause of the disease and prescribe therapy that acts on the pathogen itself - drugs acyclovir, valaciclovir or famaciclovir.With primary genital herpes for 10 days, with relapses diseases - in appropriate doses for 5 days.
Therapy should be started as early as possible at the very first signs of an exacerbation. Application possible antiherpetic drugs as a preventive treatment - 2-3 days before the expected relapse, if the patient is aware of the factors that provoke it, and for the entire period of the risk factor. If genital herpes disturbs a person more than 6 times a year and / or relapses reduce the quality of life of the patient and bring him not only physical, but also serious psychological discomfort, should be discussed with the patient long-term (at least 12 months) daily suppressive antiviral therapy (for example, valaciclovir). The effectiveness of such treatment tactics for the prevention of recurrence of herpes infection has been proven. all international rules.
Sequelae of chickenpox during pregnancy
How dangerous are chicken pox and shingles for a pregnant woman?
These diseases are caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which also belongs to the herpesvirus family. infect women are most often children who easily tolerate the disease. At the same time, chickenpox in an adult can be severe and dangerous to his health.
infect women are most often children who easily tolerate the disease. At the same time, chickenpox in an adult can be severe and dangerous to his health.
Infection is transmitted by airborne droplets from person to person already 48 hours before the onset of the rash, during the entire period of the rash and for a week after appearance of the last bubbles.
Expectant mothers who catch chickenpox may develop severe herpes pneumonia. Therefore, when sick chickenpox during pregnancy should be observed by an infectious disease specialist and in most cases of antiviral therapy.
In maternal varicella at 8 to 20 weeks of gestation infection fetus with the varicella-zoster virus can lead to fetal chickenpox with the development of a "syndrome congenital chicken pox" with severe malformations - damage to the brain, eyes, skeletal defects. Therefore, if a woman falls ill with chicken pox in the 1-3rd month of pregnancy, the doctor the woman should be informed about all possible risks of the disease for the fetus and discussed with her the question of a possible termination of pregnancy.
Second and third trimesters infectious disease doctor monitors the state of the future mothers. If the infection is severe or the infection occurred in the last month of pregnancy, prescribe antiviral treatment with acyclovir or its analogues. If ultrasound does not detect fetal pathology, pregnancy is not interrupted.
Within 96 hours (preferably within the first 48 hours) after contact a pregnant woman with chickenpox in the absence of IgG class antibodies to VVZ it is possible to introduce a specific VVZ-immunoglobulin as a measure to prevent the development of the disease. Immunity persists for 3-4 weeks, may be re-introduced after 21 days.
If the mother-to-be becomes ill with chicken pox in the last month of pregnancy , then the child may be born with skin rashes. If a woman falls ill in the last few days of pregnancy or in the first days after childbirth in a newborn infected during childbirth, the symptoms of chickenpox appear in the first 11 days of life. Chickenpox is most severe in infants whose mothers fell ill 5 days before or 2-3 days after delivery. In case of chickenpox in mothers, newborn children are given a specific immunoglobulin to prevent the development of the disease. In case of its severe course - appoint acyclovir for intravenous administration.
Chickenpox is most severe in infants whose mothers fell ill 5 days before or 2-3 days after delivery. In case of chickenpox in mothers, newborn children are given a specific immunoglobulin to prevent the development of the disease. In case of its severe course - appoint acyclovir for intravenous administration.
Infection of a child with VVV a few days after birth may manifest as postnatal varicella in the period of 12-28 day of his life. This form of the disease is less severe, it is possible to introduce a specific immunoglobulin with the risk of the disease and the appointment of intravenous acyclovir for destructive skin lesions.
Vaccination against the varicella-zoster virus is not given to pregnant women because this is a live vaccine. Therefore, if a young woman does not have IgG antibodies to VVZ before planning pregnancy, it is advisable to vaccinate against chicken pox.
Herpes zoster ("secondary" VVZ infection) in a pregnant woman is not dangerous for a child. Contact seronegative pregnant woman with herpes zoster is not desirable, although the threat of her infection There is practically no VVZ.
Contact seronegative pregnant woman with herpes zoster is not desirable, although the threat of her infection There is practically no VVZ.
I'm just planning a pregnancy. And I want to get rid of herpes recurrences that have been haunting me for a long time me. How do you feel about the treatment of genital herpes with interferon inducers and immunomodulators?
Widespread use of immunomodulators and interferon preparations in Russian medical centers (viferon, polyoxidonium, isoprinosine, etc.) for the treatment of herpesvirus infections is completely unreasonable. The so-called "ozone therapy" will not help the patient either. You will not find these methods in international protocols, recommendations for the treatment of viral infections in children and adults, including pregnant women women. Neither in Russia nor abroad have studies been conducted proving the effectiveness of these drugs in accordance with all international regulations.
Infectionist, a professional in his field will never turn to immunomodulators and interferon inducers, but will look for the cause of the disease and prescribe an effective pathogen therapy - drugs acyclovir, valaciclovir or famaciclovir. With primary genital herpes for 10 days, with relapses of the disease - in appropriate doses for 5 days.
Therapy should be started as early as possible at the very first signs of an exacerbation. Application possible antiherpetic drugs as a preventive treatment - 2-3 days before the expected relapse, if the patient is aware of the factors that provoke it, and for the entire period of the risk factor. If genital herpes disturbs a person more than 6 times a year and / or relapses reduce the quality of life of the patient and bring him not only physical, but also serious psychological discomfort, should be discussed with the patient long-term (at least 12 months) daily suppressive antiviral therapy (for example, valaciclovir). The effectiveness of such treatment tactics for the prevention of recurrence of herpes infection has been proven. all international rules.
The effectiveness of such treatment tactics for the prevention of recurrence of herpes infection has been proven. all international rules.
If you have any questions, you can ask your doctor obstetrician-gynecologist or infectious disease specialist online at Doctis app.
The author of the article: Vasily Iosifovich Shakhgildyan
Reproductive Health Education CenterReproductive Health Education Center
Having genital herpes does not mean that you cannot have children. According to the American Public Health Association (ASHA), only 0.1% of cases of herpes are transmitted during pregnancy from mother to unborn child. Most women with genital herpes have a successful pregnancy and give birth to healthy children .
Breastfeeding during herpes recurrence is possible. Except when herpetic eruptions are located on the nipples or mammary gland. If your doctor prescribes oral antiviral drugs during breastfeeding, the question of the advisability of continuing breastfeeding during the course of suppressive therapy should be discussed with your doctor.
Primary episode of genital herpes is usually a tragedy during pregnancy. It is characterized by pronounced manifestations, tk. there are no antibodies in the mother's body that protect against herpes. For the fetus, the risk is especially high when infected with genital herpes in the first and third trimesters. As a rule, fetal death and miscarriage occur in the first trimester. Damage to the developing organs of the fetus, the occurrence of congenital deformities are possible. Infection in the III trimester, especially after 36 weeks of pregnancy, is fraught with damage to the nervous system of the fetus, skin, liver, spleen. Despite postpartum treatment, up to 80% of newborns with a primary episode of genital herpes in the mother die or become severely disabled. Even intravenous administration of acyclovir to a newborn does not help. Fortunately, such situations are extremely rare and it takes several decades to work in obstetrics to see fetal lesions caused by a primary episode of herpes during pregnancy.
HOW TO DETECT THAT I HAVE A PRIMARY EPISODE OF GENITAL HERPES?
What does primary episode mean? It means that in your life there has never been a recurrence of genital herpes and the body has not yet developed protective antibodies to HSV.
In some cases it is difficult to determine: what is it? Whether the first episode of genital herpes in life or the first recurrence with visible symptoms of genital herpes that was previously asymptomatic or with atypical symptoms. The fact is that in most people infected with HSV, the disease is almost asymptomatic. It is especially difficult to identify the disease in women if relapses occur inside her genitals, for example, on the cervix or in response to a relapse, a slight redness with cracks appears on the labia, which the woman takes for irritation. She lives and does not suspect that she has RGH. But here, during pregnancy, so that a miscarriage does not occur, hormonal changes occur in the woman's body, aimed at a physiological decrease in immunity - immunosuppression. Against this background, recurrences of herpes can become visible and rashes can come out, for example, on the labia, clitoris, perineum with manifestation in the form of itching, burning, vesicles and crusts, etc. In order to distinguish the primary episode of genital herpes from the first recurrence with visible symptoms, the patient needs to donate blood from a vein for antibodies to HSV-1,2. If there is Ig G (G class immunoglobulin) in the blood, then herpes is recurrent and there is practically no threat to the fetus or embryo. If there is no Ig in the blood, but there is Ig M or Ig M is also absent, then this is the very first episode of genital herpes in life. In this case, you need to consult a doctor and be examined.
Against this background, recurrences of herpes can become visible and rashes can come out, for example, on the labia, clitoris, perineum with manifestation in the form of itching, burning, vesicles and crusts, etc. In order to distinguish the primary episode of genital herpes from the first recurrence with visible symptoms, the patient needs to donate blood from a vein for antibodies to HSV-1,2. If there is Ig G (G class immunoglobulin) in the blood, then herpes is recurrent and there is practically no threat to the fetus or embryo. If there is no Ig in the blood, but there is Ig M or Ig M is also absent, then this is the very first episode of genital herpes in life. In this case, you need to consult a doctor and be examined.
There are no specific methods for preventing the transmission of genital herpes during pregnancy. From non-specific, monogamous relationships, constant use of a condom can be recommended. If it is known that the father of the child is infected with genital herpes, and the mother is not, then you should either completely refrain from sexual activity during pregnancy (until the moment of delivery). Or a man should constantly use a condom + valaciclovir 1 tablet daily throughout the pregnancy. This measure will help to reduce the risk of transmission of genital herpes by 75%.
Or a man should constantly use a condom + valaciclovir 1 tablet daily throughout the pregnancy. This measure will help to reduce the risk of transmission of genital herpes by 75%.
Should refrain from oral sex. Because if you have never had herpes of the lips in your life, and the husband or father of the child had it, then during cunniling he can bring the herpes simplex virus type I to your genitals. And since If you have never had HSV-1, then there are no protective antibodies in your body, the fetus may suffer (this situation is called a non-primary episode of genital herpes during pregnancy). We also recommend to refrain from blowjob.
Treatment with acyclovir and valtrex. However, these drugs do not always allow to achieve good success in treatment.
According to the Centers for Disease Control (USA), the use of antiviral drugs Zovirax and Valtrex by women during pregnancy was highly effective in preventing infection in newborns and did not adversely affect the development of the fetus. (Source: Centers for Disease Control, USA, Valaciclovir (VALTREX) and Acyclovir (ZOVIRAX) Pregnancy Registry, December, 1997).
(Source: Centers for Disease Control, USA, Valaciclovir (VALTREX) and Acyclovir (ZOVIRAX) Pregnancy Registry, December, 1997).
Against the background of a primary episode of genital herpes, the loss of a desired pregnancy is a severe psychological trauma for both potential parents. But in any case, there is hope. The next pregnancy will proceed already against the background of recurrent genital herpes. After the first outbreak, antibodies will circulate in the mother's blood until her death (in very advanced years), which will preserve the unborn child.
Recurrent genital herpes during pregnancy
As blasphemous as it may sound, but recurrent genital herpes is the most favorable option during pregnancy. If a woman before the onset of this pregnancy already had relapses of genital herpes, then the fetus is protected from infection by maternal antibodies that block the action of the herpes simplex virus. There is a 99% chance that your child will not get herpes.
STATISTICS:
During pregnancy, infection of a newborn with the herpes simplex virus from a mother with recurrent genital herpes occurs quite rarely: in approximately 0.02% of cases.
The risk of infection of a child in childbirth from a mother suffering from recurrent genital herpes is less than 1% (According to the study: Brown ZA, Wald A, Morrow RA, Selke S, Zeh J, Corey L. Effect of serological status and cesarean delivery on transmission rates of herpes simplex virus from mother to infant JAMA 2003;289: 203-9).
BEFORE PREGNANCY: Plan the onset of pregnancy , eliminate bad habits from your life, cure chronic diseases, take a course of restorative treatment, cure foci of chronic infection before pregnancy (sore teeth, sinusitis, gastritis).
In some cases, a woman cannot know whether she had recurrences of genital herpes before or not. This happens with herpes that occurs without symptoms or with an atypical course. In addition, it should be borne in mind that, unlike the stronger sex, the female genital organs are “not visible”. In order to find out if you have ever had a relapse, you should do a serological analysis. Donate blood for antibodies (immunoglobulins Ig G & Ig M) to HSV-1,2. If Ig G is present in the blood, then herpes is recurrent - herpes practically does not threaten pregnancy. The Ig G index is qualitative (higher than diagnostic titers). Regardless of the titer (the amount of Ig G & M), you can become pregnant.
In order to find out if you have ever had a relapse, you should do a serological analysis. Donate blood for antibodies (immunoglobulins Ig G & Ig M) to HSV-1,2. If Ig G is present in the blood, then herpes is recurrent - herpes practically does not threaten pregnancy. The Ig G index is qualitative (higher than diagnostic titers). Regardless of the titer (the amount of Ig G & M), you can become pregnant.
DURING PREGNANCY:
- When having sex always use a condom ;
- Avoid oral sex
If you get cold sores during pregnancy, you can transfer it to the penis of the father of your unborn child during oral sex. And he will transfer the infection to your genital tract with this member. This can lead to bad consequences for the child. On the other hand, if you allow your husband to cunniling and he has cold sores on his lips, he may bring a different type of herpes to your genitals. That's why it's better not to joke with oral sex during pregnancy - 9You can grind months in the name of a new life.
PROPHYLAXIS DURING PREGNANCY:
To prevent recurrence during pregnancy after 36 weeks, your doctor may prescribe a course of preventive treatment with acyclovir or valaciclovir. During pregnancy, it is better to use acyclovir, manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline under the name Zovirax or Valtrex. Unlike Russian and Indian analogues, the safety of Zovirax has been proven by clinical trials and experience in using this drug for more than 25 years. Take a multivitamin for pregnant and lactating women.
According to the Centers for Disease Control (USA), the use of antiviral drugs Zovirax and Valtrex by women during pregnancy was highly effective in preventing infection in newborns and did not adversely affect the development of the fetus. (Source: Centers for Disease Control, USA, Valaciclovir (VALTREX) and Acyclovir (ZOVIRAX) Pregnancy Registry, December, 1997).
Dynamic monitoring : Examination of pregnant women includes a mandatory three-time ultrasound examination: at 10-14 weeks of gestation, when the thickness of the nuchal space of the fetus is mainly assessed; at 20-24 weeks, ultrasound is performed to detect malformations and echographic markers of chromosomal diseases; an ultrasound examination at 32-34 weeks is performed in order to detect malformations with their late manifestation, as well as for the purpose of a functional assessment of the fetal condition. In the period of 16-20 weeks, blood samples are taken from all pregnant women to study their levels of at least two serum markers: alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
In the period of 16-20 weeks, blood samples are taken from all pregnant women to study their levels of at least two serum markers: alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Treatment: Only under medical supervision and prescription! Outwardly, you can use an ointment based on acyclovir. Ointments and creams are over-the-counter products. The ointment does not affect the fetus, because. it is not absorbed into the blood. To prevent rashes 2 weeks before delivery, the doctor may prescribe valacyclovir or acyclovir orally.
PROPHYLAXIS DURING DELIVERY:
Treatment of the soft birth canal with polyvidone iodine (Betadine, Vocadine) or other antiseptics during childbirth reduces the risk of neonatal herpes infection to the child to Genital herpes - abortion or childbirth?
Many women with recurrent genital herpes wonder how their illness might affect their unborn child.
The editorial office of the server received a letter describing a typical example of the illiterate approach of Soviet doctors to the management of pregnant women with genital herpes:
Professor D ***, from the Chelyabinsk Medical Academy, believes that it is highly undesirable to keep a pregnancy during an exacerbation of genital herpes in the early stages of pregnancy. He believes that it is necessary to achieve remission within 6 months before the onset of pregnancy. What other schools in Russia consider it possible to maintain pregnancy in the event of an exacerbation (manifestation, relapse) of genital herpes in the early stages of pregnancy. They say that this threatens the deformity of the child and other problems. How to proceed. Get another course of treatment. do not want to risk. There are no good specialists in the city, No one can really answer my question. Being pregnant (4-5 weeks) passed tests for herpes. I suspected that I had herpes, because. and before pregnancy there were rashes and tests confirmed my worst assumptions. After that, I had an abortion. How do you think, what threatens the child with the manifestation of herpes in the first months of pregnancy.
He believes that it is necessary to achieve remission within 6 months before the onset of pregnancy. What other schools in Russia consider it possible to maintain pregnancy in the event of an exacerbation (manifestation, relapse) of genital herpes in the early stages of pregnancy. They say that this threatens the deformity of the child and other problems. How to proceed. Get another course of treatment. do not want to risk. There are no good specialists in the city, No one can really answer my question. Being pregnant (4-5 weeks) passed tests for herpes. I suspected that I had herpes, because. and before pregnancy there were rashes and tests confirmed my worst assumptions. After that, I had an abortion. How do you think, what threatens the child with the manifestation of herpes in the first months of pregnancy.
In developed countries, the optimal tactics for managing pregnant women with genital herpes has long been developed, based not on the private opinion of some “Professor D *** from the Chelyabinsk Medical Academy”, but on the data of long-term clinical studies and observations.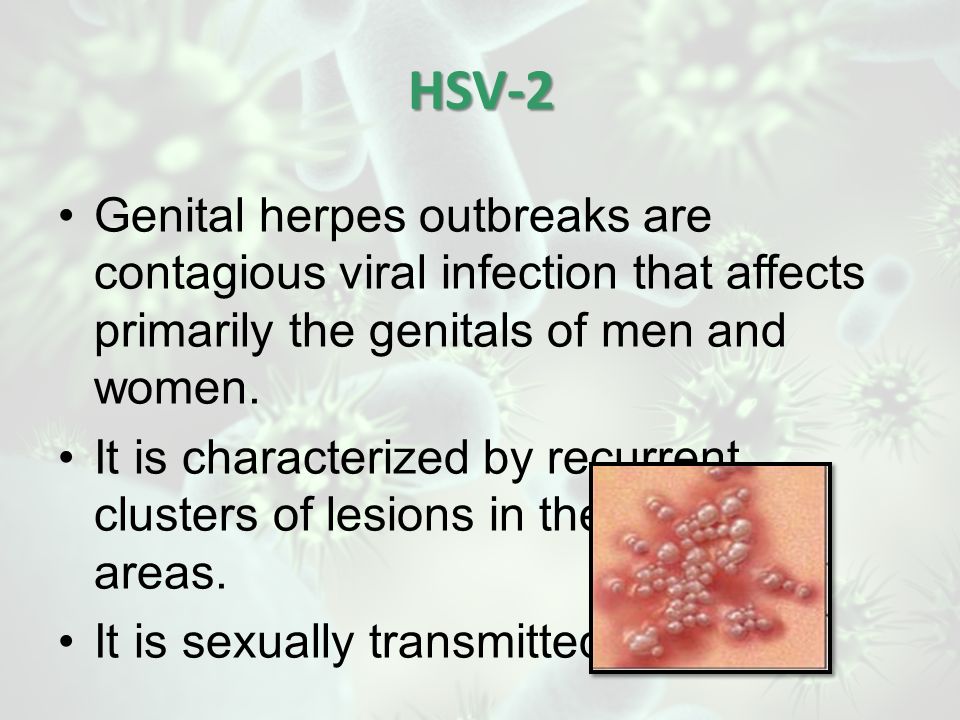
So that someone's subjective opinion does not lead you to an unnecessary abortion, we will tell you once again about what to do if you have herpes and pregnancy.
If a woman has the first time in her life during pregnancy there is a recurrence of genital herpes (primary genital herpes) or if the expectant mother becomes infected with genital herpes during pregnancy, the fetus may be affected. The fact is that in this case, the mother's blood does not contain antibodies to the Herpes Simplex Virus - immunoglobulins G and Em (Ig G and Ig M), which block the pathological effect of the herpes simplex virus on fetal cells.
In the case of the first recurrence of genital herpes in a woman's life, the virus can penetrate the placenta and multiply in the tissues of the embryo or fetus, which leads to fetal death, miscarriage, congenital deformities, damage to the brain, liver, and other organs of the fetus, non-developing pregnancy. The risk of fetal damage in primary genital herpes is 75%.
If the first recurrence of genital herpes occurs 30 days before delivery, delivery by caesarean section is recommended.
From 36 weeks of pregnancy, a doctor may prescribe Zovirax tablets to prevent the recurrence of herpes.
To prevent infection with genital herpes during pregnancy, it is necessary to use a condom and avoid oral sex, i.e. a man should not caress the sexual organs of a pregnant woman with his mouth. The reverse situation is allowed.
If a woman had recurrences of genital herpes before pregnancy, then antiherpetic antibodies float in the pregnant woman's blood, which limit the infection and neutralize the virus. These antibodies pass through the placenta to the fetus, protecting it. Therefore, recurrent genital herpes is not so dangerous during pregnancy. In this case, due to herpes, there are no deformities and lesions of internal organs.
In recurrent genital herpes , the baby can become infected during childbirth, passing through the birth canal, where the herpes virus is present. The risk of infection is 2 to 5%. Treatment of the birth canal and skin of a child with antiseptics containing polyvidone-iodine reduces the risk of developing neonatal herpes to 1-2%. To prevent the development of neonatal herpes from the 36th week of pregnancy, your doctor may prescribe you Zovirax.
The risk of infection is 2 to 5%. Treatment of the birth canal and skin of a child with antiseptics containing polyvidone-iodine reduces the risk of developing neonatal herpes to 1-2%. To prevent the development of neonatal herpes from the 36th week of pregnancy, your doctor may prescribe you Zovirax.
Recurrent genital herpes is not an indication for abortion.
And despite all our clarifications about the relative safety of recurrent genital herpes during pregnancy, sometimes you have to receive such letters: A woman with recurrent genital herpes writes: “And most importantly, herpes is just natural selection. Nature removes lepers, because their offspring are doomed to death, so I don’t even dream of children ... ”It is ignorant to consider yourself a leper and refuse the happiness of motherhood just because you have recurrent genital herpes (the most favorable form for bearing and childbirth). Although, it cannot be ruled out that this is our medical defect.
There is also such a diagnosis as non-primary genital herpes . What does this mean? Before pregnancy or during pregnancy, the woman was sick with recurrent genital herpes, which was caused by the herpes simplex virus type II. During pregnancy, the husband practiced cunniling (caressing the female genital organs with the mouth). As a result, the Herpes Simplex Virus type I (HSV-I) can enter the female genitalia. Another option is also possible: Before pregnancy, a woman suffered from genital herpes caused by HSV-I, became infected during oral sex. During pregnancy, her sexual partner rewards her with HSV-II. To I or II type of virus, respectively, there are no antibodies. As a result, the clinical picture may be the same as with primary genital herpes. Therefore, it is important to use condoms during pregnancy and not to practice cunnilingus.
What does this mean? Before pregnancy or during pregnancy, the woman was sick with recurrent genital herpes, which was caused by the herpes simplex virus type II. During pregnancy, the husband practiced cunniling (caressing the female genital organs with the mouth). As a result, the Herpes Simplex Virus type I (HSV-I) can enter the female genitalia. Another option is also possible: Before pregnancy, a woman suffered from genital herpes caused by HSV-I, became infected during oral sex. During pregnancy, her sexual partner rewards her with HSV-II. To I or II type of virus, respectively, there are no antibodies. As a result, the clinical picture may be the same as with primary genital herpes. Therefore, it is important to use condoms during pregnancy and not to practice cunnilingus.
Use of immunomodulators during pregnancy
The server editor received a letter describing a typical clinical situation:
« I have a problem that requires urgent consultation. My obstetrician - gynecologist says that everything is fine, but I'm restless. For the second time during pregnancy (now the 31st week) I have a herpes rash on my lip, the gynecologist insisted on a course of Ridostin, and I have already made 1 injection, but the contraindications to the medicine say PREGNANCY. My doctor says that they have been treated with Ridostin for a very long time during pregnancy and nothing has happened. I have a question. How serious are the reasons for such contraindications (maybe this is reinsurance?) and should I do the next injection on Sunday?
My obstetrician - gynecologist says that everything is fine, but I'm restless. For the second time during pregnancy (now the 31st week) I have a herpes rash on my lip, the gynecologist insisted on a course of Ridostin, and I have already made 1 injection, but the contraindications to the medicine say PREGNANCY. My doctor says that they have been treated with Ridostin for a very long time during pregnancy and nothing has happened. I have a question. How serious are the reasons for such contraindications (maybe this is reinsurance?) and should I do the next injection on Sunday?
In my opinion, the use of immunomodulators during pregnancy is IMPOSSIBLE:
* In this case, herpes on the lips of a woman cannot bring any harm to either the woman or the child.
*Long-term effect of immunomodulatory drugs on the fetus is unknown. As you know, some of these drugs, easily penetrating the placenta into the body of the fetus, can cause congenital deformities in the latter, disorders of the immune system, and increase the risk of developing cancer.