Bump on infants head
Skin Lump
Is this your child's symptom?
- A skin lump or bump covered by normal skin
- Skin swelling just in one spot (localized) is also included
Causes of Skin Lumps
- Insect Bites. The most common cause of an itchy bump is a mosquito bite. Other insects can also cause little bumps.
- Stings. A bee sting can cause a painful bump. The swelling can become quite large.
- Lymph Nodes. Most common cause of a lump or mass felt under the skin. Commonly found in the neck or groin. Nodes have a boundary or edge and are movable. This is not the case for the swelling seen with insect bites. Lymph nodes become larger with infections.
- Scalp Hematoma. The most common cause of a lump on the head is a scalp hematoma (goose egg). In a child under 2 years of age the injury may not have been seen.
- Injuries. New lumps anywhere can be caused by an injury that wasn't observed.
A bruise is often present with the swelling.
- Callus. Broken bones heal with new bone formation. The medical term is callus. The callus feels like a bony knot that is larger than the bone itself. A callus is most commonly felt after a collarbone fracture.
- Boils. A boil is a skin abscess. It causes a very painful red lump.
Lumps that are a Normal Part of the Body
- Breast Bud. A small disc-shaped lump felt under the nipple. It indicates the onset of puberty in 7-12 year old girls.
- External Occipital Protuberance. The bony lump felt at the base of the skull in back.
- Mastoid Process. The bony lump felt behind each lower ear.
- Xiphoid Process. A small hard lump felt at the lower end of the sternum (breastbone).
Common Objects Used to Guess the Size
- Pea or pencil eraser: ¼ inch or 6 mm
- Dime: ¾ inch or 1.
 8 cm
8 cm - Quarter: 1 inch or 2.5 cm
- Golf ball: 1 ½ inches or 3.8 cm
- Tennis Ball: 2 ½ inches or 6.4 cm
When to Call for Skin Lump
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Redness spreading from the lump with fever
- Groin swelling and painful
- Age less than 12 months and on scalp. Exception: normal bump in back at base of skull.
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Redness spreading from the lump without fever
- Boil suspected (painful, non-itchy, red lump)
- Age 12 months or older and on scalp. Exception: normal bump in back at base of skull.
- Can't move nearest joint normally (bend and straighten completely)
- Swelling is painful and cause not known
- You think your child needs to be seen, but the problem is not urgent
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- Large lump more than 1 inch (2.
 5 cm) and cause not known
5 cm) and cause not known - Small lump lasts more than 7 days and cause not known
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Small lump present 7 days or less and cause not known. Reason: probably due to insect bite not observed.
- Breast bud - normal lump under the nipple
- External occipital protuberance - normal lump on back of head
- Mastoid process - normal lump behind each lower ear
- Xiphoid process - normal lump at bottom of breastbone
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice
Treatment for a Small Lump or Swelling
- What You Should Know:
- Most new swellings are due to insect bites.
 Mosquito bites account for 90% of them. Your child may not even know that he got bit.
Mosquito bites account for 90% of them. Your child may not even know that he got bit. - Suspect an insect bite if there are bites on other parts of the body.
- While most insect bites cause a small red bump, some are larger (like a hive).
- This does not mean your child has an allergy or the bite is infected.
- Here is some care advice that should help.
- Most new swellings are due to insect bites.
- Cold Pack for Swelling:
- Apply a cold pack or cold wet washcloth for 20 minutes.
- Steroid Cream for Itching:
- If the swelling is itchy, use 1% hydrocortisone cream (such as Cortaid). No prescription is needed.
- Do this 3 times per day.
- Allergy Medicine for Itching:
- If itching becomes severe, give a dose of Benadryl.
- No prescription is needed. Age limit: 1 and older.
- What to Expect:
- Most insect bites itch or hurt for 1 or 2 days.
- The swelling usually peaks in 2 days, but may last a week.

- If the swelling becomes larger or doesn't go away, it needs to be examined.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Swelling becomes very painful
- Fever occurs
- Swelling becomes large (over 1 inch or 2.5 cm)
- Swelling lasts over 7 days
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
Lumps that are a Normal Part of the Body
- Breast Buds - Normal Lump Under the Nipple:
- Breast buds are normal, small disc-shaped rubbery lumps felt under the nipple.
- Age. They normally occur in 8-12 year old girls and are the first sign of puberty. Sometimes, they are even normal in 7 year olds.
- One Side. They sometimes start just on one side. Don't worry about that. Within 2 or 3 months, a breast bud will also appear on the other side.
- Importance. The entire breast develops entirely from the breast bud, taking 2 or 3 years to completion.

- Symptoms. Breast buds normally can be somewhat tender.
- Caution: Never squeeze or massage breast buds. Reason: Can cause a serious infection.
- Risks. None. Breast buds have no risk of turning into cancer.
- Follow-up. You can have your child's doctor check the breast bud during the next regular office visit.
- External Occipital Protuberance - Normal Lump on Back of Head:
- The lump you feel at the base of the skull in back is normal. It is a bony part of the skull that sticks out and feels hard.
- If you feel carefully, you will find one on yourself or other children.
- This is not caused by any injury.
- Mastoid Process - Normal Lump Behind the Ear:
- The mastoid process is a bony lump you can feel behind the lower ear.
- Muscles that turn the neck attach to the mastoid process.
- The process is larger in men because of larger neck muscles.

- The mastoid is filled with air cells that connect to the inner ear.
- Xiphoid Process - Normal Lump at Bottom of Breastbone:
- The small hard lump at the lower end of the sternum (breastbone) is normal. It is called the xiphoid process. You can feel it.
- It is more prominent in babies and slender children. Sometimes, it's more visible when breathing in.
- If you feel carefully, you will find one on yourself or other children.
- It's made of cartilage, but turns to bone in adults.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- You have other questions or concerns
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 11/13/2022
Last Revised: 01/13/2022
Copyright 2000-2022. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
What to Look For and When to Seek Help
You see baby teeter, then totter, and then — in a “Matrix”-like moment that somehow occurs both in slow motion and in the blink of an eye — they tumble. Oh, the screams. The tears. And a big goose egg that’s growing by the second.
We know how scary it can be when your precious baby bumps their head. And if you’re living this right now — icing your little one’s knot while searching for what to do next — you’re in the right place.
First, take a deep breath and try to remain calm. Most of the time, fall-related bumps to the head are minor and don’t require medical attention.
In fact, this 2015 study concluded that fall-related head injuries in young children don’t usually cause serious harm.
At the same time, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that falls are the leading cause of traumatic brain injury-related emergency department visits up in children up to age 4. Keep in mind that this is rare.
Keep in mind that this is rare.
So in the rarer case, there are a few cues that should alert you to seek emergency medical help.
First, some reassuring stats: According to one study on short falls in young children, only about 2 to 3 percent of falls lead to a simple linear skull fracture, and most of these don’t cause neurological problems. Only about 1 percent of skull fractures related to accidental falls cause moderate to severe brain injury.
That said, it’s still important to be aware of the symptoms of a traumatic brain injury, including concussions, which usually present within 24 to 48 hours of the accident.
If your baby is showing any of these symptoms after experiencing an injury to their head, call 911 or take them to the nearest emergency room immediately:
- uncontrolled bleeding from a cut
- a dent or bulging soft spot on the skull
- excessive bruising and/or swelling
- vomiting more than once
- unusual sleepiness and/or difficulty staying alert
- loss of consciousness or not responding to voice/touch
- blood or fluid draining from the nose or ears
- a seizure
- a suspected neck/spinal cord injury
- trouble breathing
Accidental bumps to the head are one of the most common injuries among infants and toddlers. But this fact alone might not stop you from continuously replaying the scene in your head while thinking about how you would rewrite the ending.
But this fact alone might not stop you from continuously replaying the scene in your head while thinking about how you would rewrite the ending.
But a fall-related knock to the noggin is often largely due to a baby’s physical stature and development — not your parenting. Babies’ heads are often proportionally larger than their bodies, making it easier for them to lose their balance.
In addition, babies’ physical strength and abilities are constantly changing, which affects their stability and coordination. The same adorable wobbly walk could put them in harm’s way when encountering a new, uneven surface or a fun object to run toward.
This, coupled with a baby’s tendency to engage in more daredevil acts that have them climbing, jumping, or trying to fly just for the thrill, can be the perfect equation for a nasty plunge. In fact, babies are notorious for these common head injury culprits:
- slipping in the tub
- falling backwards
- falling off a bed or changing table
- falling after climbing on furniture or up on countertops
- falling in or out of the crib
- tripping over rugs or objects on the floor
- falling down steps or stairs
- falling while using an infant walker (one of the reasons why such walkers are considered unsafe)
- falling from playground swing sets
The height from which a baby falls is correlated to the severity of injury, so if your child fell from a higher distance (such as from a crib or countertop) they’re at a greater risk of serious injury.
The term “head injury” encompasses the entire range of injuries, from a small forehead lump to a traumatic brain injury. Most short fall-related injuries among babies fall under the “mild” category.
Mild head injuries
Mild head injuries are considered closed, meaning they don’t involve any skull fractures or underlying brain injury. In these cases, swelling and a large “bump” or bruise on the skin may appear without any further symptoms.
If your baby’s fall resulted in a cut or laceration, there may be significant bleeding that requires medical attention to clean and suture the wound, even if there’s no brain or skull injury.
After a bump to the head, babies can experience a headache and discomfort. However, at this age, it’s difficult for them to communicate this feeling. It might surface as increased fussiness or difficulty sleeping.
Moderate to severe head injuries
Moderate to severe brain injuries represent the minority of those related to infant falls.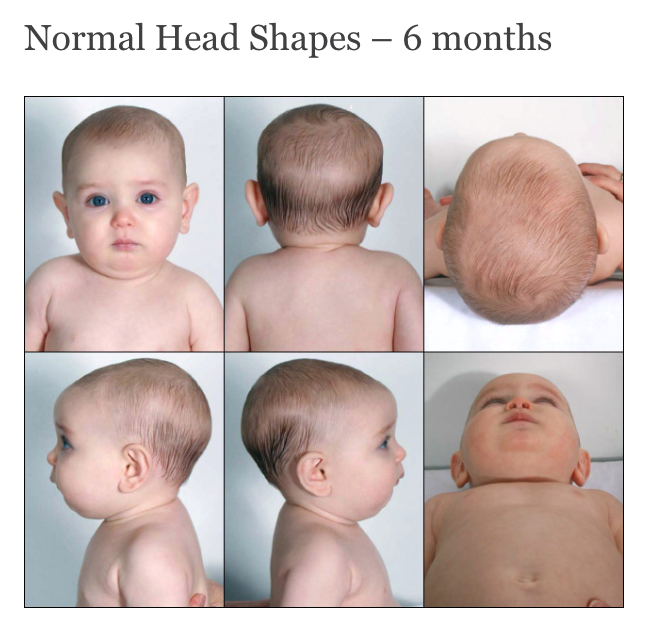 They can involve:
They can involve:
- skull fractures
- contusions (when the brain is bruised)
- concussions (when the brain is shaken)
- bleeding in the brain or around the layers surrounding the brain
Concussions are the most common and least severe type of traumatic brain injury. A concussion can affect multiple brain regions, causing problems in brain function. Signs of a concussion in children can include:
- headaches
- loss of consciousness
- changes in alertness
- nausea and vomiting
While super rare, more severe injuries can involve a fracture of the skull, which can put pressure on the brain and also cause swelling, bruising, or bleeding around or inside of the brain. These are the most serious circumstances that require emergency medical attention.
It’s critical that medical treatment is administered as soon as possible to reduce the potential for long-term brain damage and loss of physical and cognitive function.
In most cases, “watch and wait” (with lots of extra TLC) is the most appropriate course of action after a baby’s minor head bump.
Keep the symptoms of a more serious head injury in mind, watching for any changes in behavior or neurological deficits within 48 hours of the accident.
Other ways to care for your injured little one during the watch and wait period:
- apply ice as tolerated by your baby
- clean and bandage any minor cuts or abrasions to the skin
- check for changes/consistency in the size of your baby’s pupils
- monitor your baby while they’re sleeping during naps and at night
- call your baby’s pediatrician for guidance if you’re concerned
When to call your child’s pediatrician
You know your baby best, so if you’re even remotely worried, don’t hesitate to call your child’s pediatrician for expert advice on what to do next. They might want to evaluate your baby out of precaution and to document the injury for their medical record.
To evaluate for a head injury, the pediatrician or emergency room doctor will likely ask you about how the injury occurred, what your baby was doing before the injury, and what symptoms your baby experienced after the injury.
They might also do a series of neurological exams — looking at your baby’s eyes and responses to voice and touch — and a general physical exam, too.
If something in this exam triggers concern of a serious brain injury, the doctor may order an imaging test such as a CT scan. CT scans are usually only performed when there’s evidence of a severe brain injury.
Although rare, the doctor may advise you to go to the nearest emergency room for more immediate evaluation, diagnosis, or critical care. Or, they may want to observe your baby for a few hours during a medically supervised “watch and wait” period.
Treatment for head injuries depend on the severity. In mild cases, ice, rest, and extra cuddles are the best medicine. (Not a bad treatment for adult head bumps, either. )
)
After a concussion, frequent monitoring might be advised by your baby’s pediatrician, as well as activity restrictions.
For more serious injuries, it’s important to follow a doctor’s direction. Usually, only severe traumatic head injuries require critical hospital-based intervention that can include medical and surgical treatments as well as physical therapy.
Most minor bumps to the head in young children don’t pose any risk of long-term complications, thank goodness.
But there is a body of research that does bring to light long-term concerns with even minor traumatic brain injuries. A 2016 study that followed a Swedish cohort concluded a possible correlation between a traumatic brain injury (including mild concussions) in childhood with an increased risk for mental health problems, disability, and even mortality into adulthood. As you may expect, children with multiple head injuries had even greater long-term risks.
The American Academy of Pediatrics echoes this with research presented at its 2018 national conference. In the study of children diagnosed with a traumatic brain injury from mild to severe, 39 percent developed neuropsychiatric symptoms up to 5 years after the injury, such as headache, mental disorder, intellectual disability, depression/anxiety, seizure, or brain damage.
In the study of children diagnosed with a traumatic brain injury from mild to severe, 39 percent developed neuropsychiatric symptoms up to 5 years after the injury, such as headache, mental disorder, intellectual disability, depression/anxiety, seizure, or brain damage.
This message is empowering to help prevent more serious accidental falls that could affect your little one’s health, growth, and development.
While a minor head bump is bound to happen from time to time, here are a few tips to help keep your baby out of harm’s way.
- Install and secure baby gates on the top and bottom of stairs.
- Watch for wet areas on hard floors (especially around pool and bath surfaces).
- Install non-skid mats in the bathtub and rugs on the bathroom floor.
- Firmly secure furniture to walls.
- Keep young children away from dangerous things to climb.
- Don’t sit or leave your baby up on countertops.
- Avoid using infant walkers with wheels.
- Remove tripping hazards.

- Be cautious at playgrounds that don’t have softer surfaces.
There’s no doubt about it — when your baby takes a tumble, their tears can equal fears and tears of your own. It’s normal to worry, but rest assured that most minor bumps to the head don’t cause a serious brain injury or require emergency medical attention.
However, there are rare instances where a more serious traumatic brain injury can result. In this case, know the symptoms to watch for and always call your child’s pediatrician or seek emergency medical care if you feel it’s necessary.
Read this article in Spanish.
A bump on the head of a newborn baby
Advice for mothers
Types of bumps on a newborn baby
Basically, formations on the head of a child occur during childbirth or due to the fact that the body has not yet adapted to new living conditions. Only in 0.5% they may indicate any serious illness.
A newborn may have a lump during childbirth
- Photo
- Getty
0003
- birth swelling;
- cephalohematoma;
- atheroma;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.

Small swellings that move easily under the skin when touched, these are not bumps, but lymph nodes. If their size does not exceed a pea, then they are in a normal state.
A birth tumor is a hematoma that an infant receives during childbirth. If he has a large head, and the woman in labor has a narrow pelvis, the appearance of a bump is inevitable. The same thing happens when the baby is not properly located in the womb at the time of birth. Such a tumor disappears in 2-3 days or develops into a cephalohematoma. This formation is located in the region of the sutures of the bones of the skull and has a clear outline.
Atheroma is a round-shaped subcutaneous wen that occurs under the skin where there is hair. It appears due to a metabolic failure, in the absence or poor-quality hygiene of the child or poor ecology.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in newborns occurs behind the ears and on the back of the head. They appear due to the work of the immune system, which is trying to adapt to the conditions of the outside world.
What to do if a newborn has a bump
In most cases, bumps in children go away on their own. A birth tumor and kaphalohematona are noticed even in the maternity hospital. Other species appear already at home. In any case, you should show the baby to the doctor. Even harmless formations should be observed by a pediatrician.
Signs that the bump needs urgent treatment:
- it is steadily increasing;
- redness and peeling appear around the swelling;
- the tumor thickens, hardens;
- an open bleeding wound occurs;
- pus appears.
Cephalhematoma usually disappears in 2–3 months, lymph nodes decrease by the age of six months, and atheroma is observed up to 3 years. If by this time the bump has not disappeared or other symptoms have appeared, fluid can be pumped out of the swelling or removed surgically.
Often the bumps are not dangerous for the baby, but in any case they should be shown to the doctor.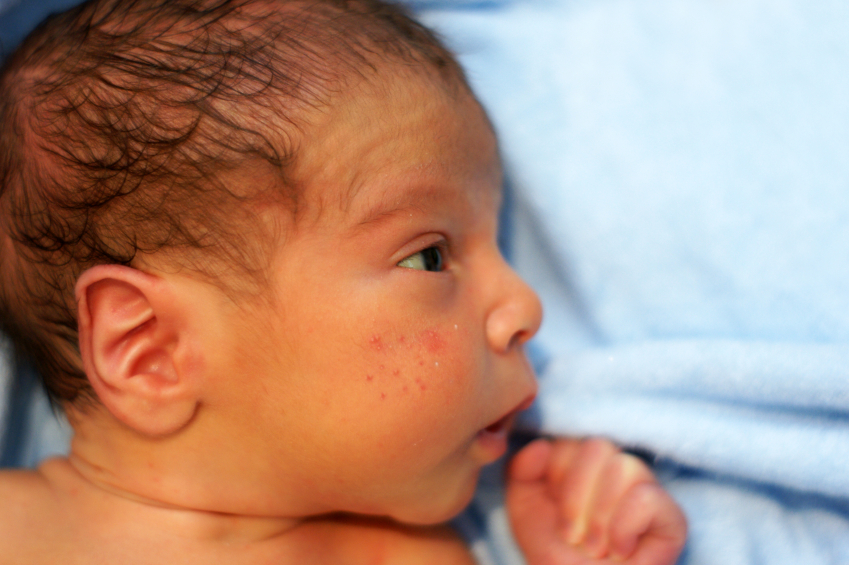 Excessive caution does not hurt, especially since the doctor can advise on how to properly care for a newborn with formations and how to monitor the condition of the bumps.
Excessive caution does not hurt, especially since the doctor can advise on how to properly care for a newborn with formations and how to monitor the condition of the bumps.
See also: bronchial asthma in children
Wday.ru editors
Read today0002 Not angels at all: 30 photos of what newborns really look like
They will bring bad luck: 7 things that you should never bring into the house
Kill on the spot: 20 super sexy lingerie sets from AliExpress at an affordable price
These 3 signs of the zodiac will meet their love in 2023 - check if it's you And in the event of a lump on the head of a newborn child, it is necessary to immediately inform the doctor about it. The origin of the bump may be different. There are several types of neoplasms, so it is not worth treating and diagnosing them on your own. This can lead to serious consequences. What should parents do if, after birth, a newborn has a bump on his head? Soft or hard, it doesn't matter. It is necessary to identify the disease and cure it in time.
It is necessary to identify the disease and cure it in time.
Lymph nodes
The most common bumps that appear in young children are considered to be lymph nodes. Their size does not exceed a pea. The appearance of this formation in a newborn is quite common. Sometimes it is very difficult to determine the size of this bump, as it moves under the skin. Such education does not increase the level of discomfort of the baby. Often, these types of neoplasms on the head of young children appear at the moment when their own immune system is being formed. They both appeared on their own and will disappear. To eliminate them, you do not need to carry out any special therapeutic procedures.
Injuries
Unfortunately, it is not uncommon for a baby to have a lump as a result of a birth injury. A doctor or obstetrician can make a mistake and cause injury with a gynecological instrument. This in the future will lead to the appearance of a hematoma or a small tumor. Such a neoplasm disappears on its own after a few days.
Cephalohematoma
This is the third, fairly common reason why newborns may develop a small tumor. The neoplasm is an accumulation of fluid. During palpation, a discoloration may appear on the skin. In medical practice, this is considered the norm. Such an education passes in 5-14 days, leaving no consequences.
What is a cephalohematoma?
If the bump is not malignant, its size is very small. When pressure is applied, the fluid moves. If the hematoma contains little blood, the tumor resolves itself in just a few days, a maximum of ten. Unfortunately, it is not uncommon for a cephalohematoma to develop and progress. The disease is on the rise. The innovation is getting bigger. The skin in the place where the bump formed on the head of a newborn child becomes hot, discharge sometimes appears from the cavity. This is very dangerous for the baby, so you need to urgently consult a doctor. Timely treatment will help prevent possible unpleasant consequences. If the tumor begins to grow further, it can lead to paralysis, disruption of life and brain function.
If the tumor begins to grow further, it can lead to paralysis, disruption of life and brain function.
Malignant lumps
Not all buds are safe. There are some that should certainly make parents think and immediately consult a doctor. As soon as observant parents begin to notice the first symptoms of their child and discover the appearance of a tumor, it is necessary to immediately examine the baby. When monitoring a child, it is worth paying attention to the following factors:
- The tumor began to grow soon after the appearance.
- New additional neoplasms appear.
- A rash appears on the bumps and new redness.
- The skin around the lump becomes very hot.
- The formation shows the release of liquid.
Parents should also sound the alarm when the baby shows signs of sleep disturbance. The baby may lose his appetite, he will behave restlessly, be nervous. All this must be paid attention to and go to the pediatrician. He will examine the child and issue a referral to a specific specialist. You can also seek additional advice from a pediatric surgeon.
He will examine the child and issue a referral to a specific specialist. You can also seek additional advice from a pediatric surgeon.
Jaundice
The reason for the development and formation of a tumor in children who have just been born is jaundice or trauma during childbirth. In the event that the child’s immune system develops correctly, the body is able to independently overcome the disease even at such a small age. In other cases, when the immune system is not able to cope with the disease, the bumps grow. This, in turn, poses a great danger to the health of the child or a threat to his life.
Epidermal cyst
Atheroma is a round formation that brings pain to the child. It is formed due to blockage of the sebaceous glands. Such cases are quite common in recently born children. Atheroma is filled with adipose tissue. The skin around this formation does not change color and structure. This disease develops due to increased sweating. This can happen due to poor hygiene, overheating, wearing too tight clothes or underwear made of synthetic fabrics.
Unfortunately, this disease does not go away on its own, the intervention of doctors is necessary. If you let the situation take its course, this will lead to an increase in the size of the tumor. The first sign of the inflammatory process is the appearance of pain in the place where the bump appeared. The neoplasm becomes hot and causes anxiety in the child.
To get rid of a hard bump on the head of a newborn, you will have to resort to surgical intervention. Before sending the baby to the operating table, you need to carefully check everything. First, they do an ultrasound. This will eliminate the brain hernia. If the tumor is small, then it can be removed with a laser. This will take several sessions. Larger formations are excised under general anesthesia.
If the formation of atheroma is small and does not bother the child in any way, the removal procedure should be postponed until the age of three. If you believe the reviews of experts, such a disease does not pose any particular danger to the child.
Doctors advise parents to carefully monitor the neoplasm. If you decide to postpone the operation for some time, do not forget that atheroma can begin to develop at any time. As soon as the child begins to complain of discomfort, pain and discomfort, it is necessary to go to the hospital and re-examine. If this examination shows that the tumor has increased, then it is necessary not to wait for a certain age, but to proceed with the removal immediately.
Methods of treatment
As mentioned above, often the appearance of a small lump on the head of a newborn child does not require special attention. Most often, no special treatment is required. It is enough just to observe the child, to make sure that the tumor does not change, does not become larger. It must be handled very carefully so as not to damage it. If parents began to notice that the tumor is rapidly decreasing in size, this suggests that there is no need to worry. This fact is a reason to calm down. It is likely that the neoplasm will disappear on its own after a while and medical intervention will not be required.
When a child has encountered a cephalohematoma, it is recommended to be constantly under the supervision of a doctor. Most likely, he will fix a stable decrease in the bump and reassure the parents, since the immune system often copes on its own. However, it is worth remembering the fact that a child with a bump must have a stable position. It must not be rocked, and the neoplasm must not be touched in any case. This can lead to tissue damage. Bathing a newborn baby must be done very carefully. Doctors also recommend that you stop using soap and shampoos for the duration of the treatment of this disease.
Surgical treatment
If parents have to deal with the fact that a bump on the newborn's head develops after childbirth, this will lead to surgical intervention. Doctors will observe the development of the tumor, conduct several tests, and only after that they will make a small incision. This is necessary in order for the fluid to flow out of the neoplasm. After the fluid is removed, a tight bandage is applied to the sore spot.