Is diarrhea a sign of ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy - Symptoms - NHS
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy usually develop between the 4th and 12th weeks of pregnancy.
Some women don't have any symptoms at first. They may not find out they have an ectopic pregnancy until an early scan shows the problem or they develop more serious symptoms later on.
Main symptoms
You may have an ectopic pregnancy if you miss a period, have a positive pregnancy test, and have other signs of pregnancy.
Contact your GP or call NHS 111 if you have a combination of any of these symptoms and you think you might be pregnant – even if you haven't had a positive pregnancy test.
Vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding tends to be a bit different to your regular period. It often starts and stops, and may be watery and dark brown in colour.
Some women mistake this bleeding for a regular period and don't realise they're pregnant.
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is relatively common and isn't necessarily a sign of a serious problem, but you should seek medical advice if you experience it.
Tummy pain
You may experience tummy pain, typically low down on one side. It can develop suddenly or gradually, and may be persistent or come and go.
Tummy pain can have lots of causes, including stomach bugs and trapped wind, so it doesn't necessarily mean you have an ectopic pregnancy.
But you should get medical advice if you have it and think you might be pregnant.
Shoulder tip pain
Shoulder tip pain is an unusual pain felt where your shoulder ends and your arm begins.
It's not known exactly why it occurs, but it can be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy causing some internal bleeding, so you should get medical advice right away if you experience it.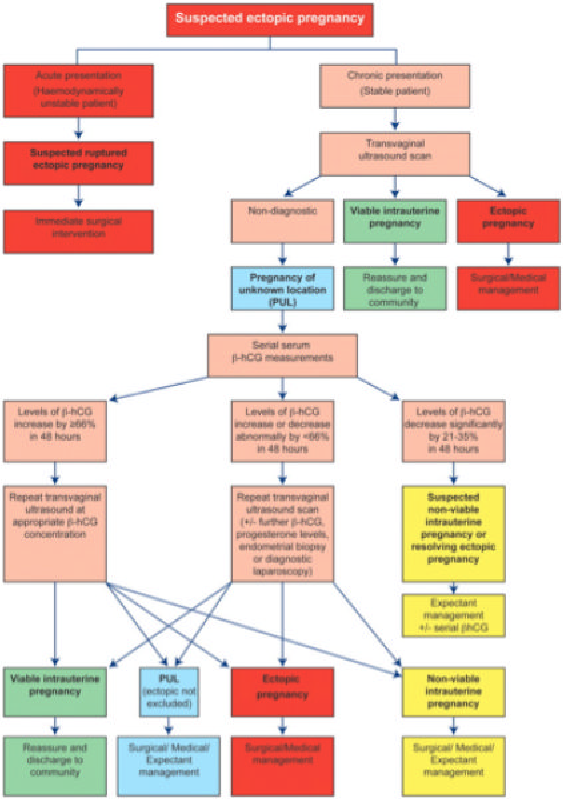
Discomfort when going to the toilet
You may experience pain when going for a pee or poo. You may also have diarrhoea.
Some changes to your normal bladder and bowel patterns are normal during pregnancy, and these symptoms can be caused by urinary tract infections and stomach bugs.
But it's still a good idea to seek medical advice if you experience these symptoms and think you might be pregnant.
Symptoms of a rupture
In a few cases, an ectopic pregnancy can grow large enough to split open the fallopian tube. This is known as a rupture.
Ruptures are very serious, and surgery to repair the fallopian tube needs to be carried out as soon as possible.
Signs of a rupture include a combination of:
- a sharp, sudden and intense pain in your tummy
- feeling very dizzy or fainting
- feeling sick
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E) department immediately if you experience these symptoms.
Page last reviewed: 23 August 2022
Next review due: 23 August 2025
5 Signs Of An Ectopic Pregnancy
Though you have probably heard about ectopic pregnancies, you probably don't know very much about them — like that they are deeply serious and not as rare as you might think. The phenomenon — which occurs when a fertilized egg decides to implant itself outside of the womb (usually in the fallopian tubes, though in exceptional cases it can implant elsewhere in the abdomen) and grow there — affects one in 80 pregnancies, according to the Ectopic Pregnancy Trust; it's not exactly common, but it's also not totally out of the blue. So how do you know if you're having an ectopic pregnancy? It turns out that, unfortunately, there isn't exactly a blueprint we can go by for every single case. But there are certain signs that may seriously help you out if you recognize them.
Ectopic means "in an abnormal position," and in an ectopic pregnancy, the causes of the egg's misplaced implantation aren't always clear to medical professionals. Sometimes it's due to scarring in the fallopian tubes, something abnormal in the shape of the reproductive system, or previous infections; and certain things, like smoking and pelvic inflammatory disease, are known to cause higher rates of ectopic pregnancies, likely due to related pelvic damage. But we're still not completely clear about why it happens in all cases.
Sometimes it's due to scarring in the fallopian tubes, something abnormal in the shape of the reproductive system, or previous infections; and certain things, like smoking and pelvic inflammatory disease, are known to cause higher rates of ectopic pregnancies, likely due to related pelvic damage. But we're still not completely clear about why it happens in all cases.
The key thing to know about ectopic pregnancies, beyond their symptoms, is how early in pregnancy they turn up: generally between the 4th and 12th week of pregnancy, which means you may not even know you're pregnant at the time. Ectopic pregnancies will likely, but not always, cause positive pregnancy tests.
Here are five signs that, individually or together, may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. If you're having any of them, get to a GP or a hospital immediately.
1. Shoulder Tip Pain
The reason that ectopic pregnancies create a medical emergency isn't necessarily the placement of the egg outside the uterus; it's what happens as it grows — most often, particularly with eggs that have implanted in the fallopian tubes, the fertilized egg can cause ruptures where they grow and possibly serious internal bleeding.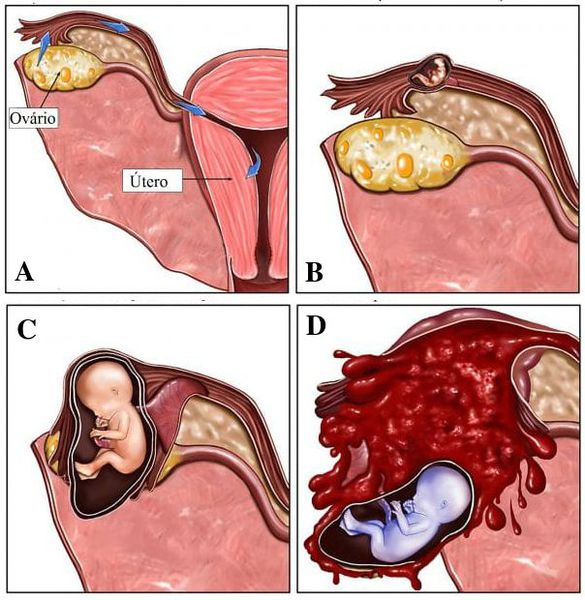 That's what makes this so dangerous, and what leads to the shoulder-tip sign.
That's what makes this so dangerous, and what leads to the shoulder-tip sign.
Pain at the very tip of the shoulder, where the shoulder ends and the arm begins, is a signal of specific internal bleeding. As the rupture bleeds into the abdomen, it creates pressure on the diaphragm, which in turn stresses nerves that run into the shoulder. This pain may intensify if you lie down, and is, in its weirdness, a pretty reliable sign that something is badly wrong.
2. Light Brown Discharge
Discharge can differ radically between ectopic pregnancies; it depends on where the egg has implanted and what it's done to the area around it. You could get anything from no discharge to heavy flow, but the most common reported symptom is brownish discharge, clearly containing old blood but not in itself a period. This is a signal of internal bleeding or rupture and needs to be noted.
The wide variety of ectopic implantation locations can cause a lot of variation in symptoms. Eggs can turn up in the fallopian tubes, the cervix, the ovaries, within an old Caesarian scar, or elsewhere in the abdomen. Depending on their location and other factors, the ectopic pregnancy can "dissolve" back into the body, be miscarried and require surgical intervention to remove, or keep growing for longer periods before causing issues. There's a lot of different possibilities in play here, so if you experience any symptoms, it is incredibly important to talk to a doctor.
Depending on their location and other factors, the ectopic pregnancy can "dissolve" back into the body, be miscarried and require surgical intervention to remove, or keep growing for longer periods before causing issues. There's a lot of different possibilities in play here, so if you experience any symptoms, it is incredibly important to talk to a doctor.
3. Pain On One Side Of The Abdomen
As is probably unsurprising in the case of an egg growing somewhere it shouldn't, pain is a fairly common symptom in ectopic pregnancies — particularly in situations where the egg has caused damage and bleeding. In tubal ectopic pregnancies, in which the egg lodges one of the fallopian tubes, the pain will be centered on one side of the abdomen, depending on which tube has an egg implanted within it. Interestingly, women who manage to get pregnant while they're using an IUD or are on the mini-pill (which is progesterone-only) are more likely to have ectopic pregnancies, as both methods make it actively difficult for fertilized eggs to implant in the uterus.
4. Bowel Problems
In one of the more confusing aspects of ectopic pregnancies, they can present symptoms similar to gastroenteritis: a tender abdomen, vomiting, and either constipation or diarrhea. (Hence why things like the shoulder tip test are essential.)
Any bowel issues that come from an ectopic pregnancy aren't because the egg has itself lodged in the bowel; rest assured that that's essentially impossible. Rather, it's most often a response to internal bleeding, pressure or rupturing in the abdomen. If you do suspect an ectopic pregnancy, note your bladder and bowel responses since pain or symptoms began, and mention them to your doctor.
5. Serious Pain And Collapse
Fallopian tube ruptures are deeply unpleasant. The fallopian tubes don't have a lot of internal stretch and an implanted egg that doesn't dissolve is likely to split them, which counts as a medical emergency and will require immediate surgery to resolve. The accompanying pain and internal blood loss will likely be severe, which means you may well faint. Charming, right? However, this isn't inevitable, and if you do need surgery, they won't remove everything in your reproductive system, and will likely only focus on removing the part of the tube with the egg in it.
Charming, right? However, this isn't inevitable, and if you do need surgery, they won't remove everything in your reproductive system, and will likely only focus on removing the part of the tube with the egg in it.
But it may not get to that point. If you are diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, which usually happens with an ultrasound and blood tests, you may be able to be able to stop the egg's growth with a dose of methotrexate, a cancer and psoriasis drug that interferes with cell growth. People who are able to take this generally don't have to get surgery in addition — but methotrexate (which would stop the egg growing in the fallopian tube by preventing cells from dividing, prompting the egg's slow reabsorption) can only be used if it is very early in the pregnancy, the tubes aren't ruptured, and you go through very intensive monitoring while taking it. It's considered better than surgery with regard to being able to get pregnant again in the future, but once you get diagnosed, your doctors should walk you through all your options, from keyhole procedures to doing a "wait and see" approach, in case the ectopic pregnancy resolves on its own.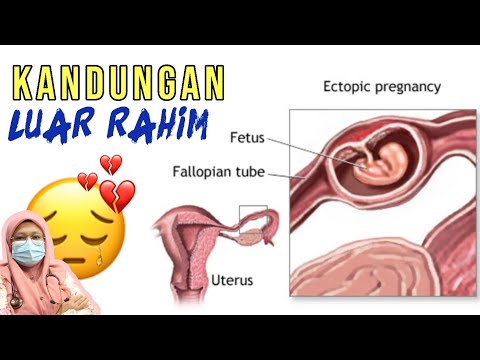 Just remember: it may be scary, but you have options.
Just remember: it may be scary, but you have options.
Images: ilkersener/E+/Getty Images, Giphy
Diarrhea during pregnancy: symptoms, causes and consequences, diagnosis and treatment
Diarrhea during pregnancy: causes, diagnosis and treatment Average reading time: 9 minutes
Contents:
Causes and symptoms of diarrhea during pregnancy
Diagnostic features
The consequences of diarrhea in pregnant women
Directions of treatment
When treatment is required in the hospital
Diets
Can I use the Imodium ® Express during pregnancy
of pregnancy in the early periods can be earned during pregnancy, not only a deterioration in well-being, but also unwanted unrest for a woman who is expecting a baby. Frequent defecation causes significant discomfort and is often accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms. In addition, this condition can pose a serious danger to the woman and the fetus due to the threat of dehydration and other risks. One of the difficulties is that with diarrhea in pregnant women in the first trimester, not all antidiarrheal drugs can be drunk. The active components of some drugs can have a negative effect on the fetus. That is why with frequent bowel movements it is necessary to consult a specialist. The doctor will diagnose and tell you what to do with diarrhea.
In addition, this condition can pose a serious danger to the woman and the fetus due to the threat of dehydration and other risks. One of the difficulties is that with diarrhea in pregnant women in the first trimester, not all antidiarrheal drugs can be drunk. The active components of some drugs can have a negative effect on the fetus. That is why with frequent bowel movements it is necessary to consult a specialist. The doctor will diagnose and tell you what to do with diarrhea.
Back to top
Causes and symptoms of diarrhea during pregnancy
Infectious. Bacterial and viral infections (eg, noro- or rotavirus) can cause bowel dysfunction. They are usually transmitted by airborne droplets or the fecal-oral route. Pathogenic microorganisms also often enter the gastrointestinal tract through the use of low-quality foods or contaminated water. Infectious diarrhea during pregnancy in the second and third trimester may be accompanied by fever, chills, nausea and vomiting, painful abdominal cramps, and general weakness. An admixture of mucus often appears in the feces.
An admixture of mucus often appears in the feces.
Non-infectious. This form of diarrhea can be caused by a variety of factors: changes in diet, frequent stress, disorders of digestion and absorption, some chronic diseases, taking certain medications. In this case, the pregnant woman may be disturbed by frequent defecation (sometimes with imperative, i.e., strongly pronounced, irresistible urges), abdominal pain in the upper or lower section. With organic lesions of the colon, an admixture of blood sometimes appears in the feces. In the later stages, violations of the frequency of bowel movements may be associated with fetal pressure on the digestive tract.
Up to content
Diagnostic features
When diagnosing a disease that caused diarrhea, it is important to exclude surgical, urological and obstetric pathologies. For this, an examination is mandatory, if necessary, the doctor prescribes an additional examination. Early diarrhea may be a manifestation of ectopic pregnancy, appendicitis, urinary tract infections, pyelonephritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and acute pancreatitis. That is why it is important to quickly establish the cause of the disruption of the intestines and select adequate therapy. It is also mandatory to monitor (monitor observation) the condition of the fetus at 37, 38 and 39weeks of pregnancy.
That is why it is important to quickly establish the cause of the disruption of the intestines and select adequate therapy. It is also mandatory to monitor (monitor observation) the condition of the fetus at 37, 38 and 39weeks of pregnancy.
Back to Contents
Effects of Diarrhea in Early Pregnancy
Prolonged diarrhea can lead to dehydration, a condition that is dangerous for both the expectant mother and the fetus. It is manifested by severe weakness, dry mucous membranes, thirst. With a strong degree of dehydration, cardiac and respiratory activity can be disturbed. Diarrhea can also in some cases increase the risk of miscarriage due to an increase in the contractile activity of the uterus, and can lead to impaired uteroplacental blood flow.
Up to content
Directions for treatment
How to treat diarrhea should be decided by the doctor, taking into account the woman's condition, the cause of indigestion, gestational age and other factors. Typically, therapy includes the following areas.
Typically, therapy includes the following areas.
| Restoration of water and electrolyte balance | Replenishment of fluid deficiency in pathologies accompanied by diarrhea is an important measure to prevent severe and life-threatening conditions. To restore the water and electrolyte balance, pregnant women, on the recommendation of a doctor, can drink non-carbonated mineral water or rehydration solutions. The latter contain the salts necessary for the body, which are excreted from it along with the liquid. It should be borne in mind that with severe dehydration, drinking a solution of salts may no longer be enough. In this case, rehydration drugs are infused intravenously (in a hospital setting, if recommended by a doctor). |
| Elimination of toxins | To reduce the load on the body, it is necessary to help it get rid of toxic substances. In some cases, gastric lavage is performed for this purpose. |
| Restoration of normal intestinal microflora | To normalize the processes of digestion and absorption, it is necessary that beneficial bacteria be present in the intestine. They can be obtained from food (for example, fermented milk products with live cultures). In addition, according to indications, the doctor may prescribe probiotic preparations that help restore intestinal microflora. |
| Relieve the cause of diarrhea | If frequent bowel movements are a symptom of a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be used to treat them. Such remedies can help eliminate the cause of diarrhea by destroying pathogenic microorganisms. |
Back to Table of Contents
When Hospital Treatment is Necessary
Diarrhea is not always treated at home. With severe dehydration, the risk of miscarriage, severe concomitant diseases, the doctor may suggest that the pregnant woman go to the hospital. Such a measure allows for constant medical supervision, which in such cases is often simply necessary. Urgently seek medical attention and urgent hospitalization may be required if:
- severe abdominal pain of any location;
- blood in feces;
- general lethargy.
Standard clinical indications for inpatient treatment are moderate to severe diarrhea accompanied by dehydration. It is also necessary to go to the hospital if home therapy does not work for 3-4 days (the pregnant woman does not get better, the symptoms persist).
Important! Even on an outpatient basis, the treatment of conditions accompanied by diarrhea should be carried out under the supervision of a physician.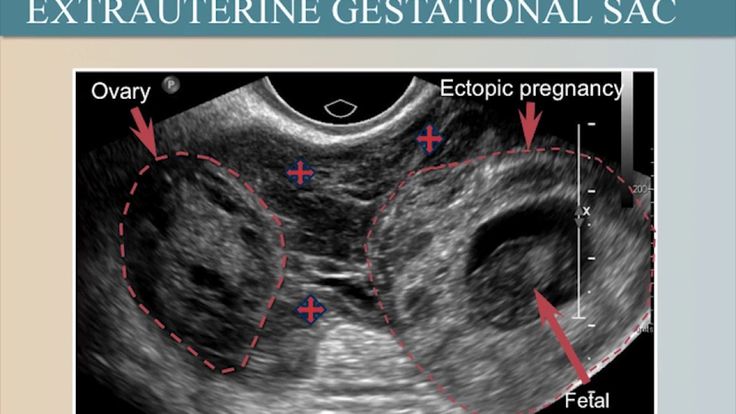
Back to Contents
Diet
During the treatment of diarrhea, it is very important to adjust your diet in order to reduce the load on the digestive tract and help the body cope with the problem faster. In case of violations of the intestines, accompanied by frequent defecation, spicy, sour, fatty foods are excluded from the diet. With an intestinal disorder, you can not use whole milk, fresh fruits and vegetables, legumes, sweets, spices, smoked snacks. Liquid, semi-liquid, pureed, steamed products are allowed. They should be served warm, but not hot or cold. In the early days of infectious diarrhea, experts may recommend a starvation diet. Then, rice water, liquid cereals from oatmeal or buckwheat are introduced into the diet.
Up to content
Can I use IMODIUM
® Express in early pregnancy? The active substance of the drug is loperamide, data on the teratogenic or embryotoxic effect of which are absent. However, the drug can not be used at any stage of pregnancy. According to the instructions, in the first trimester and while breastfeeding, the use is not allowed 1 . In the II and III trimesters IMODIUM ® Express can be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor 1 . A remedy for diarrhea is prescribed only if the expected benefit to the woman outweighs the risk to the fetus. Before use, you should consult with a specialist and read the instructions.
According to the instructions, in the first trimester and while breastfeeding, the use is not allowed 1 . In the II and III trimesters IMODIUM ® Express can be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor 1 . A remedy for diarrhea is prescribed only if the expected benefit to the woman outweighs the risk to the fetus. Before use, you should consult with a specialist and read the instructions. The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional medical advice. For diagnosis and treatment, contact a qualified specialist.
1 According to the instructions for medical use of the drug IMODIUM ® Express.
* Among products based on Loperamide. According to sales in money for February 2018 - January 2019, according to IQVIA.
terms, signs, symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is the attachment and development of an embryo outside the uterus. The condition is dangerous to health and, in the absence of medical assistance, leads to severe complications or death.
Causes of an ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is formed when the tubes are blocked, due to which the egg cannot enter the uterine cavity. Pathology is caused by such factors:
- adhesive process after an unsuccessful surgical intervention;
- hormonal disorders due to stress, contraceptives, medications, endocrine dysfunction;
- genetic predisposition;
- inflammatory processes;
- genital injuries;
- malignant or benign neoplasms;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the genital organs;
- frequent change of sexual partners, which leads to infectious diseases.
Women who have had a surgical abortion are susceptible to ectopic pregnancy. Curettage destroys the mucous membrane, leads to endometriosis and scarring, which prevents the egg from entering the uterine cavity. The more abortions in history, the higher the risk of pathology.
Curettage destroys the mucous membrane, leads to endometriosis and scarring, which prevents the egg from entering the uterine cavity. The more abortions in history, the higher the risk of pathology.
Women who smoke are 3 times more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy than non-smokers. Nicotine inhibits the epithelial function of the fallopian tubes, which ensures the promotion of the embryo.
The risk of ectopic pregnancy is increased in women aged 35-45 years. This is due to age-related physiological and hormonal changes in the body. The probability of an ectopic pregnancy is 30% higher in women who have already suffered a pathological condition and have not completed a full course of treatment.
How to distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from a normal one
The symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are similar to those of a normal pregnancy approximately until the 3rd week of its development. With a positive result on the test, the second strip may be colored a little lighter. The following symptoms are observed:
The following symptoms are observed:
- dizziness, drowsiness, weakness, nausea;
- absence of menstruation;
- change in taste preferences;
- breast enlargement.
At for a period of 5-6 weeks the growth of the fetal egg becomes more intense, pathological signs appear:
- regular drawing pain that radiates to the perineum or anus;
- diarrhea, vomiting;
- pain during urination or defecation;
- bloody discharge that does not look like menstruation;
- spasmodic pain localized at the site of attachment of the embryo.
If you experience one or more symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, you should consult a gynecologist. Timely medical attention will prevent health complications.
Spontaneous termination of pregnancy begins by 5-8 weeks. The growing embryo causes a rupture of the tube and provokes internal bleeding. The condition is accompanied by weakness, blanching, loss of consciousness. If emergency care is not provided at this stage, the woman may die from hemorrhagic shock.
If emergency care is not provided at this stage, the woman may die from hemorrhagic shock.
Methods for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy
At the beginning of the examination, the doctor conducts an examination and history taking. Based on the results, a diagnosis is made. An ectopic pregnancy is detected in several ways:
- Ultrasound. Detects the presence of an embryo in the uterus. To determine the exact location of the ovum, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed using a transducer.
- Daily monitoring of hCG levels. In contrast to normal, with an ectopic pregnancy, the indicator is different.
- Laparoscopy. Indicated in cases where the position of the ovum cannot be determined by ultrasound. Diagnosis is made with an endoscope through a small incision in the abdomen. If an ectopic pregnancy is detected for a short period, laparoscopic extraction of the embryo is possible if its size does not exceed 2 cm.
 Also, strictly according to the doctor's prescription, you can take enterosorbents. These drugs, passing through the gastrointestinal tract, can bind toxic substances and promote their removal from the body in a natural way. By themselves, such drugs do not interact with the intestinal mucosa or other parts of the digestive tract.
Also, strictly according to the doctor's prescription, you can take enterosorbents. These drugs, passing through the gastrointestinal tract, can bind toxic substances and promote their removal from the body in a natural way. By themselves, such drugs do not interact with the intestinal mucosa or other parts of the digestive tract.  The drugs are used strictly according to the doctor's prescription.
The drugs are used strictly according to the doctor's prescription.