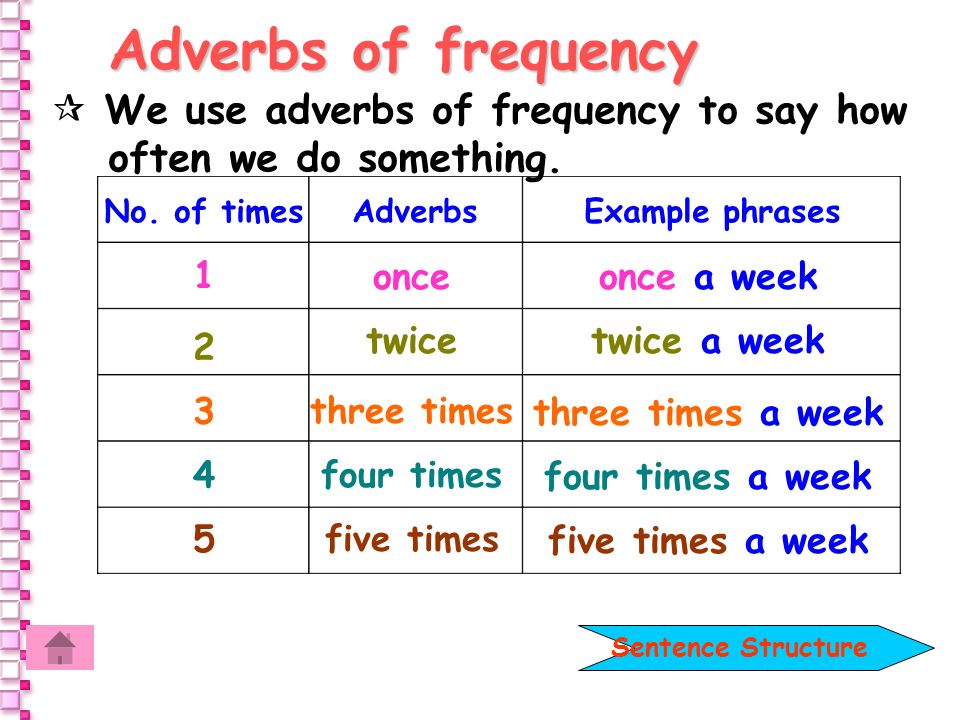
How often is it normal to pee
Urinary Frequency | Bladder & Bowel Community
Frequency refers to the number of times you go to the toilet to pass urine in a day. If you need to go to the toilet very often, more than seven times a day on drinking approximately 2 litres of fluid, you may have a frequency problem.
This can be caused by an overactive bladder. The bladder might contract even when it doesn’t need to; for example, if your bladder only has a small amount of urine in it, or may be oversensitive. This means that you feel the need to go to the toilet more often.
Frequency is often associated with urgency and urge incontinence. You can find information about treatment options available if you find yourself going to the toilet too often.
What Is Normal Urination Frequency?
As with many things in life, everyone is different. This also applies to normal urinary frequency. For most people, the normal number of times to urinate per day is between 6 – 7 in a 24 hour period. Between 4 and 10 times a day can also be normal if that person is healthy and happy with the number of times they visit the toilet.
Normal urinary frequency also depends on how much fluid you drink in a day and the types of fluid that you drink. If you are taking medication for high blood pressure for instance, it may increase because of the way some medication works; for example medicines called “Diuretics”. How healthy and active you are can have an influence, and to some extend your age e.g the normal frequency of urination in children can be different to that of an adult.
Identifying A Frequency Problem
If you are concerned about how often you urinate and it is starting to affect your day to day life make an appointment to see your doctor, continence nurse or specialist physiotherapist. A continence nurse and specialist physiotherapist are healthcare professionals who specialise in bladder and bowel problems.
You can use our find a healthcare professional service to locate the nearest specialist to you.
Once you have made an appointment, your doctor or healthcare professional will assess you. They may ask you some of the following questions:
They may ask you some of the following questions:
- How often do you go to the toilet to pass urine?
- How much urine do you pass?
- How often do you leak urine?
- When do you leak urine?
- What medication do you take?
- What do you normally eat or drink?
- Is it painful / uncomfortable when you pass urine?
- How many times do you get up at night to pass urine?
- Do you ever wet the bed?
It would be a good idea to keep a record of your bladder activity for a few days before your appointment with your doctor or healthcare professional. Keep a record for at least 3 days.
Use our Frequency Volume Chart to record how often and the amount that you urinate each day.
Frequency Volume Chart
[BBC:019] Frequency Volume Chart
A Frequency Volume Chart records the volumes voided as well as the time of each visit to the toilet, both during the day and night.
Frequent urination or the urge to urinate often can interfere with day to day life enormously, and can also be the cause of embarrassment and worry, especially if you tend to lose urine if you fail to reach the toilet in time.
Don’t forget to get your Just Can’t Wait Toilet Card which can help you gain access to a toilet when you are out and about.
The RADAR key also provides you with access to over 9,000 accessible public facilities around the UK. They can be found in many shopping centres, pubs, cafes, cinemas, bus and rail stations.
You can find yourself living your whole life around your problem! It is not just the number of times you go to the toilet that is a problem, but also experiencing an uncomfortable feeling of needing to urinate, which prevents you from relaxing and enjoying life.
Please explore our frequency treatment section to find information that could assist. We also have a selection of downloadable resources which you may find useful.
For further information speak to your GP or doctor in detail to discuss the appropriate treatment for your particular situation.
Bladderbladder conditionsfrequency
Why Am I Peeing So Much and How Often Should I Pee?
If you’ve ever wondered how often you should pee on a daily basis, you’re not alone.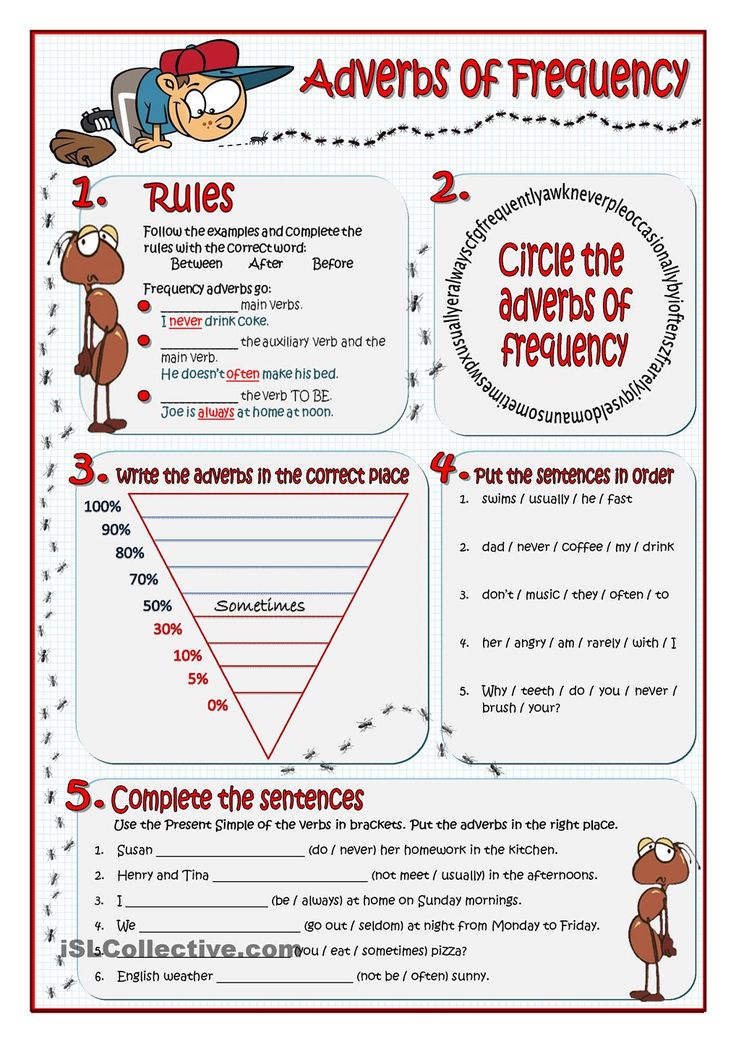 How often you urinate is actually an important sign of your overall health, beginning in infancy and continuing throughout your life. Keep reading to learn more about urination and when peeing frequently may signal that you need to visit your doctor.
How often you urinate is actually an important sign of your overall health, beginning in infancy and continuing throughout your life. Keep reading to learn more about urination and when peeing frequently may signal that you need to visit your doctor.
Urinating as much as seven times in 24 hours is considered typical, with most people urinating about six to seven times. But it’s not out of the ordinary to urinate more or less on any given day. How much you pee depends on many factors, such as:
- age
- how much you drink in a day
- what you drink
- medical conditions, such as diabetes or a urinary tract infection (UTI)
- medication usage
- bladder size
Regularly urinating more than seven times per day may be normal for some people and may not be a sign of a health problem. But the National Institute of Aging suggests talking to your doctor if you regularly urinate eight or more times.
Reasons you may urinate more frequently include:
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
A UTI is a common condition that can affect how often you urinate. Anyone can develop UTIs, although they’re more common in women. A UTI can make you feel an urgent need to urinate, even if you recently emptied your bladder.
Anyone can develop UTIs, although they’re more common in women. A UTI can make you feel an urgent need to urinate, even if you recently emptied your bladder.
During an infection, you may find yourself urinating more often, but in smaller amounts. You’ll also likely feel a burning sensation when you urinate.
There are many possible causes for a UTI, so it’s best to see a doctor if you suspect an infection of your urinary tract.
Pregnancy
Special circumstances, such as pregnancy and the weeks after giving birth, can affect how often you urinate. During pregnancy, a person urinates more frequently due to hormonal changes along with bladder pressure from the growing fetus. After birth, they continue to have increased urinary output for weeks. This is because of the extra fluids they may have received during labor from an IV, or medicine, as well as the body’s natural response to mobilize and eliminate fluids after birth.
Urinary retention
Urinary retention is when you can’t fully empty your bladder. It can cause a persistent feeling like you need to urinate, pain in your lower abdomen, and frequent urination. It can be caused by:
It can cause a persistent feeling like you need to urinate, pain in your lower abdomen, and frequent urination. It can be caused by:
- neurological factors
- infections
- bladder muscle dysfunction
- obstruction
- medications
Diabetes
If you have diabetes or undiagnosed diabetes, you may urinate more often than usual. More frequent urination is your body’s way of getting rid of the extra sugar in your bloodstream.
Hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia
If the calcium levels in your body are too high or too low — conditions that are known as hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia — your urine frequency may change.
Low potassium (hypokalemia)
Low potassium can impair your kidneys’ ability to concentrate urine and may lead to excessive thirst or excessive urination.
Medications
People with heart problems, high blood pressure, or poor kidney function often take medications that are called diuretics. Diuretics work to help the kidney filter out more fluid into the urine. Taking diuretics may cause you to urinate more frequently. Some common diuretics include:
Taking diuretics may cause you to urinate more frequently. Some common diuretics include:
- chlorothiazide (Diuril)
- chlorthalidone (Thalitone)
- hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
- indapamide
- metolazone
- bumetanide (Bumex)
- furosemide (Lasix)
- torsemide (Demadex)
- amiloride (Midamor)
- eplerenone (Inspra)
- spironolactone (Aldactone)
- triamterene (Dyrenium)
Certain foods and supplements
Some foods or supplements are natural diuretics and can increase the amount of fluid your body eliminates. These include:
- caffeine
- dandelion
- hawthorn
- horsetail
- juniper
- green tea and black tea
- parsley
- hibiscus
- watermelon
- grapes
- berries
- celery
Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia can affect kidney function. Damaging the kidneys means that they can’t do their job as well, and more urine is made. This creates the need to urinate more frequently
This creates the need to urinate more frequently
Congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure can make it difficult for your body to get rid of excess fluid, especially in your lower body. When you lie down at night, your body may produce more urine to try to get rid of this fluid.
Up to half of people with congestive heart failure experience an overactive bladder and urinary incontinence.
Tachycardia
Tachycardia is an abnormally fast heartbeat. Tachycardia-polyuria is increased urine output due to tachycardia, defined as a heartbeat over 120 beats per minute for more than 30 minutes. A decrease of antidiuretic hormone and production of atrial natriuretic peptide are thought to be involved in increasing urine output.
Medical procedures
If you’ve recently had a test that involved injecting dye into your body, such as a CT scan, you may pee more as your body eliminates the extra fluid.
Alcohol and caffeine
Alcohol and caffeine can have diuretic effects, causing you to urinate more than usual. When consuming these substances, frequent urination probably isn’t a sign of a medical issue.
When consuming these substances, frequent urination probably isn’t a sign of a medical issue.
Caffeine is found in many foods and drinks, including:
- coffee
- tea
- soda
- hot chocolate
- energy drinks
Learn more: The effects of caffeine on the body »
Increasing water intake
Drinking large amounts of water during the day can increase your urine output and frequency.
Overactive thyroid
An overactive thyroid can cause a wide range of symptoms that include frequent urination and persistent thirst. Other common symptoms include:
- difficulty sleeping
- increased appetite
- restlessness
- inability to concentrate
Anxiety
Anxiousness can potentially cause the smooth muscles surrounding your bladder to contract, causing pressure and stimulating the urge to urinate.
Interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis is a condition that causes chronic inflammation of your bladder. Common symptoms include:
Common symptoms include:
- frequent urination
- accidental leakage of urine
- pelvic or abdominal pain and pressure
- urgent need to urinate
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a rare type of blood cancer. One symptom can be high levels of calcium, which can cause increased urination.
Primary aldosteronism
Hyperaldosteronism is an overproduction of the hormone aldosterone by your adrenal glands. Overproduction of this hormone can cause your body to retain sodium and lose more potassium. Low potassium can cause frequent urination.
Polycystic kidney disease
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic condition where cysts grow on your kidneys. People tend not to develop symptoms until they’re between ages 30 to 50. Frequent urination is one potential early symptom.
Kidney stones
About 600,000 people in the United States experience kidney stones each year. They can cause extreme pain along your side and back that may radiate to your belly or groin. Other symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- frequent urination
- pain during urination
- urinary urgency
- blood in urine
- cloudy urine
- fever and chills
Certain conditions may cause you to experience a lower-than-average output of urine. For men, this may be due to an enlarged prostate. An enlarged prostate is often caused by benign prostate enlargement (BPH), which isn’t cancerous or due to prostate cancer. When the prostate becomes enlarged, it can block the flow of urine out of your bladder. This can leave you unable to fully empty your bladder, even after urination.
If you’re peeing so much or so often every day that you feel it’s affecting your quality of life, speak with a doctor. You may have an underlying medical condition, such as an overactive bladder. This can be treated.
You should also speak with a doctor if you’re peeing too infrequently, or feel like your bladder isn’t fully emptying even when you urinate, especially if you’re an older male. Other symptoms that merit a call to a doctor are:
Other symptoms that merit a call to a doctor are:
- fever and back pain
- blood in your urine
- white and cloudy urine
- discolored urine
- strong or abnormal smell to your urine
Your treatment may depend on which condition is causing your symptoms. If you’re pregnant, for example, frequent urination will continue until you give birth.
If your symptoms are caused by a medical condition, treating the condition may help.
- If you have diabetes, managing your blood sugar should reduce your need to urinate.
- If your urination frequency is caused by a UTI, once the UTI has been resolved, your urine output should return to normal.
- If you have an enlarged prostate blocking urine flow, you may need medicine to increase your urine flow or decrease your prostate size.
- If you’re on a diuretic medication for heart failure or high blood pressure, your doctor may try to adjust your dose in order to help your symptoms.

In addition to letting your doctor know difficulties while urinating, here are a few tips to decrease genital and urinary irritation:
- Eat foods rich in probiotics, especially lactobacillus, which is found in yogurt and kefir. Early studies suggest that lactobacillus may be helpful for women with recurrent UTIs.
- If you use soap in the genital area, use an unscented product made for sensitive skin.
- Wear loose, cotton underwear.
- Avoid tight-fitting jeans and leggings.
- Try to urinate every 3 to 4 hours and avoid holding your pee when you need to go.
- Urinate after sex to decrease risk of a UTI.
- Consider not wearing underwear to bed to help your genital area stay cooler.
- Try to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Many experts recommend drinking eight 8-ounce glasses per day, but the exact amount you need varies between people.
- Avoid excessive alcohol, soda, or caffeine consumption.
- Avoid things that may cause bladder irritation, such as artificial sweeteners and cigarettes.

If you’re concerned about the amount you’re urinating, speak with a doctor. They may put your mind at ease and tell you that your urinary output is normal, or they may recognize additional symptoms. A urinalysis, which can be done in a doctor’s office, can provide useful information about your urinary tract health. Identifying underlying problems is the first step in finding a successful treatment plan.
Frequent urination. Frequent urination at night. What is considered frequent urination?
+7 (495) 780-07-71
Call center open 24/7
Ambulancearound the clock
Author
Lukyanchikov Denis Vladimirovich
Leading physician
Urologist
Cashback 1000 rub for all services for a visit in April More All promotions
When should urination be considered frequent?
An adult normally excretes 1.5-2 liters of urine. To do this, he has to visit the toilet 3-7 times a day. Urination in children is more frequent: in children of the first year of life - 12-16 times a day, at the age of one to three years - 10 times a day, from three to nine years old - 6-8 times. The spread of indicators is quite wide. How many times a person needs to go to the toilet depends on many factors. In particular, with a large amount of fluid drunk, it should be expected that the need to urinate will increase. A number of products have a diuretic effect; such are, for example, watermelon, melon, cranberry, lingonberry, cucumber, coffee, alcohol. Eating them is likely to increase the frequency of urination due to increased urine output.
The spread of indicators is quite wide. How many times a person needs to go to the toilet depends on many factors. In particular, with a large amount of fluid drunk, it should be expected that the need to urinate will increase. A number of products have a diuretic effect; such are, for example, watermelon, melon, cranberry, lingonberry, cucumber, coffee, alcohol. Eating them is likely to increase the frequency of urination due to increased urine output.
It is abnormal to increase urination with even fluid intake and a stable diet. As a rule, urination more than 10 times a day in an adult is already regarded as a pathology, however, for such an assessment, the discomfort experienced by a person with such frequent visits to the toilet is also of great importance.
Frequent urination is abnormal if one of the following symptoms is observed:
- constant urge to urinate;
- the amount of urine during urination is negligible. Normally, an adult should excrete about 200-300 ml of urine at a time;
- burning or pain during urination;
- urination interferes with the normal rhythm of life (work, travel, sleep).
Frequent urination at night (nocturia), polyuria and urinary incontinence
Distinguish between frequent urination at night and daytime. Frequent urination during the daytime is called pollakiuria. Particular attention is paid to frequent urination at night. Normally, a person usually gets up to use the toilet no more than once a night. With the increase in nighttime urination, the development of many diseases begins. If most of the urine is excreted at night, then this condition is called nocturia .
Increased urination may be due to the fact that more urine is excreted. If the total amount of urine exceeds 1.8 liters, then this condition is called polyuria . Permanent polyuria is caused by serious diseases, temporary polyuria is also often pathological.
Frequent urination is also associated with such a problem as urinary incontinence . Urinary incontinence occurs when a person can no longer suppress the sudden urge to urinate.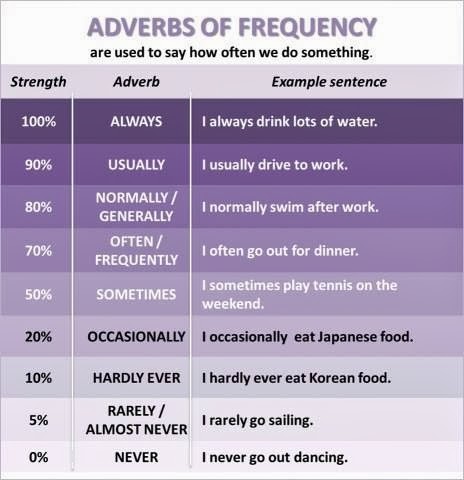 Usually, urinary incontinence develops against the background of frequent urination.
Usually, urinary incontinence develops against the background of frequent urination.
Causes of frequent urination
The physiological causes of frequent urination, in addition to the nutritional factor (heavy drinking, a specific diet), include stress and hypothermia. Frequent urination is also observed in pregnant women, especially in the first and third trimesters. Certain medications can also lead to more frequent urination.
In such cases, frequent urination is observed, as a rule, during the daytime and is temporary. As soon as the factor that caused it ceases to act, the frequency of urination returns to normal.
Pathological nature has frequent urination caused by diseases of the genitourinary system. In most cases, the cause of frequent urination is irritation of the urethra and bladder neck, which have abundant innervation. Irritation can be caused by infection or be mechanical (in the case of urolithiasis or tumors). Normally, the nervous system should receive a signal from receptors in the region of the bladder neck only in one case - if the bladder is full. But as a result of pathological irritation, the signal is given prematurely, and there is a urge to urinate.
But as a result of pathological irritation, the signal is given prematurely, and there is a urge to urinate.
Frequent urination is caused by the following diseases of the genitourinary system :
- prostate adenoma;
- prostatitis;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- urolithiasis;
- weakness of the muscles of the bladder walls.
Also, frequent urination is observed in diseases such as:
- diabetes. In diabetes, the patient is thirsty, drinks more than normal, which leads to increased urination;
- cardiovascular insufficiency.
Any questions?
Leave the phone -
and we will call you back
When is frequent urination a reason to see a doctor?
If the frequency of urination has become an irritant for you or there is reason to suspect that the frequency of urination is pathological (caused by a disease), you should consult a urologist. The first signal is often the urge to urinate at night. If you have become more likely to get up to the toilet at night, do not put off a visit to the doctor. Remember: the earlier the treatment of the disease is started, the easier it is to treat it.
The first signal is often the urge to urinate at night. If you have become more likely to get up to the toilet at night, do not put off a visit to the doctor. Remember: the earlier the treatment of the disease is started, the easier it is to treat it.
Urinary frequency treatment in Moscow
With a complaint of frequent urination, you should consult a urologist.
Urologists of the "Family Doctor" have extensive experience in the treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system. Based on modern diagnostics, Family Doctor urologists will determine the cause of frequent urination and prescribe an effective treatment.
Pediatric urologists of JSC "Family Doctor" will help in case of frequent urination in children.
Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
Thank you for rating
Family offer for three: when buying 3-year programs - 35% discount
Answers to patients' questions
Hello, it hurts to go to the toilet in a small way, the labia seems to prick, pulls in the bottom of the stomach . ..
..
Dubinina Irina Aleksandrovna , Pediatrician
Good afternoon
You should immediately consult a general practitioner or urologist. To exclude information...
Read more
Up to 4 times per night, urination occurs, urine is excreted profusely, painlessly. In the evening, liquid...
Sudakova Natalya Sergeevna , Pediatrician
Good afternoon.
In order to make a correct diagnosis and further prescribe an adequate treatment for you...
Read more
When frequent urination becomes a problem.
2020.10.15
The technical name for your problem is "frequent urination". In most people, the bladder is able to store urine until we find a good time to go to the toilet, usually we need to go to the toilet four to eight times a day. If you have to go to the toilet more than eight times a day or wake up at night, it could mean that you are drinking too much fluid and/or too much before bed.
If you have to go to the toilet more than eight times a day or wake up at night, it could mean that you are drinking too much fluid and/or too much before bed.
Frequent urination can also mean more serious health problems. It can be a symptom of many different problems, from kidney disease to simply drinking too much fluid. Frequent urination, fever, an urgent need to urinate, pain or discomfort in the abdomen are symptoms of a urinary tract infection.
Other possible causes of frequent urination:
Diabetes.
Frequent urination with unusually large amounts of urine is often an early symptom of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Thus, the body tries to get rid of unused glucose in the urine.
Prostate problems.
Men have a walnut-sized prostate that can grow after 25 years. An enlarged prostate can compress the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the bladder) and block the flow of urine. An enlarged prostate can cause weakness and uneven urine flow. As a result, the bladder wall becomes irritated. The bladder begins to contract even when it contains a small amount of urine. You may feel like you need to travel more often, sometimes urgently. Rarely, it can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as cancer. Your doctor can help treat other causes and treat an enlarged prostate.
An enlarged prostate can cause weakness and uneven urine flow. As a result, the bladder wall becomes irritated. The bladder begins to contract even when it contains a small amount of urine. You may feel like you need to travel more often, sometimes urgently. Rarely, it can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as cancer. Your doctor can help treat other causes and treat an enlarged prostate.
Too much alcohol or caffeine
They can act as a diuretic and remove more water from the body.
Interstitial cystitis.
This condition of unknown cause is characterized by pain in the bladder and pelvis. Often the symptoms are an urgent and/or frequent urge to urinate. This condition of unknown cause is characterized by pain in the bladder and pelvis. Often the symptoms are an urgent and/or frequent urge to urinate. You may feel like you want to urinate all the time, but when you go to the toilet, little urine comes out.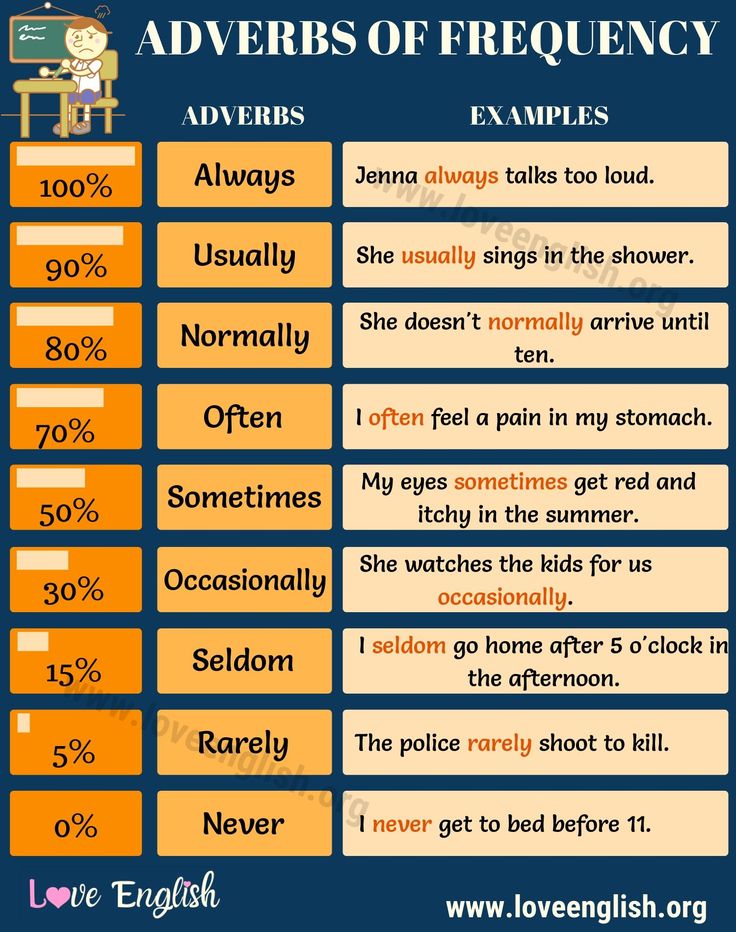 It can damage your lower abdomen, which worsens when you are suffering or after intercourse. This seems to happen when the bladder tissue swells and becomes very sensitive. The reason for this is not always clear. This condition, also called interstitial cystitis, is treated with diet and exercise, medication, surgery, and physical therapy.
It can damage your lower abdomen, which worsens when you are suffering or after intercourse. This seems to happen when the bladder tissue swells and becomes very sensitive. The reason for this is not always clear. This condition, also called interstitial cystitis, is treated with diet and exercise, medication, surgery, and physical therapy.
Use of diuretics.
These medicines, used for high blood pressure or fluid retention, affect the kidneys and excrete excess fluid from the body, resulting in frequent urination.
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
Overactive Bladder Syndrome is very common. The main symptom is a feeling of urging to the toilet, frequent and unpredictable urge to urinate. If you can't urinate quickly, urine may leak undamaged until you get to the toilet. It is treated with bladder training, sometimes with drugs.
Kidney stones
Minerals, salts and proteins can form small kidney stones. You begin to feel like you need to urinate more often. There may be nausea, fever, chills, and severe pain in the side and back that radiates in waves and spreads to the groin. It is more common in people who are overweight, low in fluids, high in protein, and have a poor family history. Stones may be removed during urination or may require surgical removal.
You begin to feel like you need to urinate more often. There may be nausea, fever, chills, and severe pain in the side and back that radiates in waves and spreads to the groin. It is more common in people who are overweight, low in fluids, high in protein, and have a poor family history. Stones may be removed during urination or may require surgical removal.
Tumor
Both malignant and benign tumors can cause frequent urination because they take up more space in or around the bladder. Blood in the urine is the most important sign of cancer. Talk to your doctor if you see blood, notice a lump in your lower abdomen, or notice pain when urinating.
Stroke or other neurological disease.
Damage to the nerves that make up the nerves in the bladder can lead to problems with bladder function, including frequent and sudden urination.
Less common causes include bladder cancer, bladder dysfunction, and radiation therapy.