How long do you know if your pregnant
16 early signs of pregnancy
You’ve got one question on your mind: Could I be pregnant?
A pregnancy test is the only way to know for sure. But if it’s too early to take a test, you may be on the lookout for early signs – or maybe you think you’re already experiencing some early pregnancy symptoms.
Is it too early to tell if you’re pregnant? What symptoms may be the earliest signs of pregnancy? Below, we answer those questions and more.
How early can you tell if you’re pregnant?
Again, you’ll need to take a pregnancy test at the right time to confirm your hopes or suspicions. But when it comes to the first symptoms of pregnancy, everyone is different. Some people start to notice changes within a week after conception. Others might not notice anything until they miss their period.
When should you take a pregnancy test?
It’s usually recommended that you take a pregnancy test after you’ve missed your period. This is because pregnancy tests measure the level of human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) in your body, which is a hormone that starts to build up when you conceive. It can take around three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for there to be enough hCG in your body to show up on a test.
What are the first symptoms of pregnancy?
The most common sign of early pregnancy? A missed period.
Your menstrual cycle is your body’s way of preparing for a possible pregnancy each month. Part of that is the thickening of your uterine lining, which is where a fertilized egg would implant to begin a pregnancy.
If you’re not pregnant, your period is how your uterus sheds that extra lining. If you are pregnant, that lining stays put and you don’t get your normal flow. This is why a missed period is often the earliest sign of pregnancy.
Of course, a delayed or missed period doesn’t always mean you’re pregnant. If your body is under a lot of stress or you have a hormonal imbalance, you could be experiencing an irregular menstrual cycle.
What other symptoms can be early signs of pregnancy?
Every person – and every pregnancy – is different. So, if you are pregnant, you’ll likely experience a unique combination of common, not-so-common and sometimes overlapping symptoms. And, they may show up earlier or later than expected. Here are more than a dozen possible symptoms of early pregnancy.
So, if you are pregnant, you’ll likely experience a unique combination of common, not-so-common and sometimes overlapping symptoms. And, they may show up earlier or later than expected. Here are more than a dozen possible symptoms of early pregnancy.
1. Spotting or light bleeding
Many women are surprised to learn that spotting or light bleeding can be an early sign of pregnancy, but about one-third of women experience it. This is often called implantation bleeding because doctors believe it occurs as the fertilized egg attaches (or implants) itself into the uterine lining. This is different from bleeding that could occur from something like a miscarriage – which is usually heavier.
When does implantation bleeding occur?
Implantation bleeding typically occurs 10 to 14 days after conception, which is just before or right around the time your period is due. So, you may think you’ve gotten your period.
But implantation bleeding is a light flow, which may start and stop over a couple days. And while it can take on a range of colors, it’s more likely to be pink, brown or light red.
And while it can take on a range of colors, it’s more likely to be pink, brown or light red.
Your period, on the other hand, may start off light in flow and in color but after a couple days becomes heavier, changes to a crimson red color and lasts up to a week or so.
2. Lower abdominal pain or cramping
While cramps and lower-abdominal pain can signal a coming period, they can also be a sign of egg implantation.
What do implantation cramps feel like?
Implantation cramps can occur with or without spotting or bleeding, and may feel different from period cramps. For example, you might feel mild to moderate prickling, pulling or tingling that comes and goes over a few days.
But menstrual cramps can often feel like a throbbing or dull ache, and typically start a day or two before your period.
3. Higher basal body temperature
If you’ve been tracking your basal body temperature (BBT) to increase your chances of getting pregnant, you probably know that your BBT goes up slightly right after ovulation. If you’re pregnant, your temperature may remain elevated rather than dipping back down.
If you’re pregnant, your temperature may remain elevated rather than dipping back down.
Of course, you could be running hot for other reasons, but if it lasts more than a few weeks, pregnancy may be the explanation.
4. Changes in cervical mucus
If you’ve already been checking your cervical mucus to figure out when you’re most fertile, here’s a reason to continue: In the first few weeks of pregnancy, the amount of cervical discharge may increase and become stickier and whiter.
5. Breast tenderness, swelling or tingling
When you’re pregnant, your body experiences big changes in hormones – specifically, increases in estrogen and progesterone – to support your growing baby. This change in hormones can contribute to many symptoms, including breast tenderness.
Oftentimes, increased breast tenderness, swelling or tingling start to become noticeable a few days before a missed period.
If you usually experience breast tenderness leading up to your period or shortly after it begins, pregnancy-related breast tenderness and swelling will likely be more intense than you’re used to and stick around. You may also experience nipple soreness.
You may also experience nipple soreness.
6. Fatigue
Fatigue in early pregnancy is common, and some women might notice it before they know they’re pregnant. In fact, fatigue may set in as soon as one week after conception. This is thanks to those sudden changes in hormone levels, particularly increasing progesterone.
7. Frequent urination
If you’re making more trips to the bathroom than usual around the time your next period is due, it may be a sign of pregnancy.
Certainly, your drinking habits play a big role in how many times you pee in a day. However, pregnancy increases the amount of blood in your body, which gives your kidneys more fluid to filter and more waste to get rid of.
So if you’re pregnant, you may notice you’re peeing a lot more – a symptom that can start early on and (unfortunately) last throughout your pregnancy.
8. Nausea or vomiting
Morning sickness might be the most well-known of all pregnancy symptoms, taking the form of food aversion or nausea, and even vomiting for some. This symptom can set in as early as two weeks after conception, which is around the fourth week of pregnancy and right around the time you’d miss your period if you were pregnant.
This symptom can set in as early as two weeks after conception, which is around the fourth week of pregnancy and right around the time you’d miss your period if you were pregnant.
But some may not experience nausea or vomiting at all. And despite its name, morning sickness can actually happen at any time of the day or night.
9. Darkening areolas
When you’re pregnant, your areolas (the areas round your nipples) will likely grow and darken. Usually, these changes are gradual and continue throughout pregnancy. However, some women notice these changes really early on in combination with other symptoms.
10. Bloating or constipation
We all experience bloating or constipation from time to time, but both are quite common during pregnancy. Once again, those changing hormones are the culprit. They slow down digestion, which can cause a buildup of air in the gut and lead to constipation.
Early on, bloating or constipation may be mild and accompanied with other pregnancy symptoms. But – as a heads up – if you really are pregnant, these symptoms may stick around throughout your whole pregnancy.
But – as a heads up – if you really are pregnant, these symptoms may stick around throughout your whole pregnancy.
11. Metallic taste in your mouth
Many women report a metallic taste in their mouth during pregnancy. Once again, hormones are to blame – specifically, estrogen.
Typically, this symptom (as well as changes in taste overall) is common in the first trimester but may occur at other times too – including before a missed period.
12. Sensitivity to smell
Many women report that sensitivity to smell was one of their first signs of pregnancy. In fact, as many as two-thirds of women become more sensitive or reactive to the smells around them during pregnancy.
And oftentimes, this heightened sense of smell can stick around through the first trimester or beyond, and contribute to other symptoms such as nausea, and food cravings or aversions.
13. Mood changes
From a stressful day at work to the natural wonders of your menstrual cycle, there are a lot of things that can affect your mood. But changes in mood are very common during pregnancy – and they may be especially noticeable early on as your body gets a sudden burst of estrogen and progesterone.
But changes in mood are very common during pregnancy – and they may be especially noticeable early on as your body gets a sudden burst of estrogen and progesterone.
If you are pregnant, any mood changes you’re experiencing are likely coupled with other symptoms such as fatigue or nausea. You may feel more sensitive or weepy. Or perhaps your fuse is a little shorter and you’re more easily annoyed.
14. Headaches
Headaches are a part of life. They come with colds and allergies. They come with stress or fatigue, or when you cut down on caffeine to help prepare your body for pregnancy. But they can also come with pregnancy.
Headaches can happen thanks to the increasing blood volume and hormonal changes that occur in early pregnancy. You can also get headaches if you’re dehydrated as a result of nausea.
15. Dizziness
As blood flow increases during pregnancy, blood pressure can also decrease and lead to dizzy spells. Usually, dizziness is more of a second trimester symptom, but some women may notice it very early on, too.
16. Nasal congestion
A lot of people are shocked to learn that nasal congestion can be a pregnancy symptom. You may wonder if you’re coming down with something or your allergies are acting up. But if you’re noticing a stuffy or runny nose along with other pregnancy signs, you might be taking a pregnancy test in the near future.
The mucous membranes in the nose are also affected by hormones and increased blood flow throughout your body. This can cause blood vessels to swell, resulting in congestion and even sneezing.
Could you have early pregnancy symptoms and not be pregnant?
Yes. As we’ve mentioned, many early pregnancy symptoms can overlap with symptoms of other conditions, especially premenstrual symptoms. So, the best way to know if the symptoms you’re experiencing are pregnancy related is to try to relax and patiently wait until it’s time to take a pregnancy test.
When should you see a doctor about a new pregnancy?
If you’ve taken a pregnancy test and it’s positive, go ahead and make your first prenatal visit right away. This is also a great time to start looking into educational resources like the myHealthyPregnancy app.
This is also a great time to start looking into educational resources like the myHealthyPregnancy app.
At the first prenatal visit, you’ll get a physical exam and other tests to make sure everything is looking healthy, and you’ll learn about the rest of your prenatal appointment schedule. You’ll also get to talk through any expectations and questions you have, such as which foods to eat and avoid while pregnant.
Questions or concerns about your symptoms? Our 24/7 nurse line is free for our members and patients.
Positive pregnancy test? Schedule a visit.
How They Work, Types & Accuracy
How Does a Pregnancy Test Work.What is a pregnancy test?
A pregnancy test is a way to determine if you’re pregnant by looking at the amount of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in your body. From the very beginning of pregnancy, your body starts to go through changes to support growth in the grouping of cells that will develop into your baby. One thing that happens very quickly is production of hCG. This chemical is only found in pregnant women and it starts to build up once the fertilized egg implants in the uterus — about 10 days after conception.
This chemical is only found in pregnant women and it starts to build up once the fertilized egg implants in the uterus — about 10 days after conception.
There are two main types of pregnancy tests — urine tests and blood tests. Often, you’ll take a urine test at home with a home pregnancy test kit. This type of test can be purchased over-the-counter (you don’t need a prescription from your healthcare provider) and is available in a variety of price ranges. Blood tests to check for pregnancy are done in your healthcare provider’s office.
There are several reasons why you might take a pregnancy test. You could be trying to get pregnant and hoping for a positive result. You might have experienced an issue with your birth control. You might even be about to have a medical procedure or start a new medication that could be complicated by pregnancy. No matter what the reason, if you ever have any questions about your test results, the best thing to do is reach out to your healthcare provider. A pregnancy can also be confirmed through an ultrasound. Later in a pregnancy, an ultrasound is actually used to not only look at your baby, but make sure the timeline of development matches the dates of your conception and missed period.
A pregnancy can also be confirmed through an ultrasound. Later in a pregnancy, an ultrasound is actually used to not only look at your baby, but make sure the timeline of development matches the dates of your conception and missed period.
How do pregnancy tests work?
When you take a pregnancy test, it’s looking for the amount of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in your body. You can find hCG in your urine or blood. However, this chemical needs time to build up in your body, which can cause very early pregnancy tests to come back negative. Each day of early pregnancy, your body will create more hCG. As the weeks go on, you’ll have more and more hCG in your body, which will make it more likely that a pregnancy test will show as positive.
Pregnancy tests work by reacting to the amount of hCG in either your urine or blood. In a urine test, a piece of reactive paper detects the hCG. This might then show a plus sign, double vertical lines or even the word “pregnant.” Different tests will show a positive result in unique ways. Read the directions that come with the test to know what a positive result will look like. On the test, there will also be a control window that will show up first. Seeing a symbol in this window will tell you that the test is working. Keep in mind that different brands of tests will take different amounts of time to process.
Read the directions that come with the test to know what a positive result will look like. On the test, there will also be a control window that will show up first. Seeing a symbol in this window will tell you that the test is working. Keep in mind that different brands of tests will take different amounts of time to process.
If you take a blood test, your provider will take a sample of your blood and send it to a lab. The lab will determine the amount of hCG is in your blood.
What are the different types of pregnancy tests?
There are two main types of pregnancy tests: urine and blood tests. Urine tests are typically done at home — though you can have a urine test done at your healthcare provider’s office — while blood tests are done by your provider.
At-home pregnancy test
An at-home test usually uses your urine to look for hCG in your body. According to most manufacturers, at-home pregnancy tests are about 99% effective when used as instructed. That’s about the same accuracy rate as urine pregnancy tests done in your healthcare provider’s office. These tests are available in most pharmacies or grocery stores and they don’t need a prescription. They can take different amounts of time depending on the brand. It’s important to read the instructions on these tests before taking them.
That’s about the same accuracy rate as urine pregnancy tests done in your healthcare provider’s office. These tests are available in most pharmacies or grocery stores and they don’t need a prescription. They can take different amounts of time depending on the brand. It’s important to read the instructions on these tests before taking them.
When you go to take an at-home pregnancy test, you’ll typically place one to several drops of urine on a prepared chemical strip or place the strip in the urine stream. The strip is specially-designed to detect hCG. For many of these tests, hCG can be detected in your urine about 10 days after conception. However, taking it after your missed period reduces the chance of getting a false-negative.
There are a few things to keep in mind when you take a home pregnancy tests, including:
- Using your first morning urine when possible. This is the time of day when your hCG levels will be the most concentrated and easily detected. If you do it at another time of day, try and make sure your urine has been in your bladder for at least four hours.

- Not drinking excessive amounts of fluids before you take a pregnancy test. Many people think this will increase the volume of urine, but it can also dilute (thin out) your hCG levels.
- Reading the directions that come with the test thoroughly before starting the test, and following every step precisely.
Blood test
Another type of pregnancy test that can be used is a blood test. Blood tests are rarely done because they’re expensive and tend to have the same result as a urine test. This type of pregnancy test is done using a small sample of blood that’s analyzed at a hospital or healthcare provider’s office. This blood test not only detects whether the pregnancy hormone is in your body, but can also determine how much of hormone is present.
A blood test for pregnancy might be done in special circumstances, such as for women who are having infertility treatments or when the healthcare provider thinks there might be a problem.
These blood tests are slightly more sensitive than urine tests because they can detect very small levels of hCG. That means they can provide a more accurate answer very early on in pregnancy — within nine to 12 days after conception. For this test, your blood sample is taken and sent to a lab for analysis. Results might take anywhere from a few hours to more than a day.
That means they can provide a more accurate answer very early on in pregnancy — within nine to 12 days after conception. For this test, your blood sample is taken and sent to a lab for analysis. Results might take anywhere from a few hours to more than a day.
Your provider might also choose to use a blood test to compare hCG levels during the pregnancy. Your hCG levels usually double about every two days during the first few weeks of pregnancy. If the levels don’t rise, it might suggest a problem with the pregnancy. Extremely high hCG levels might mean that your carrying twins or that there’s an issue with the pregnancy.
When should I take a pregnancy test?
If you think you could be pregnant, it’s a good idea to take a test and make sure. If you are pregnant, you will need to begin prenatal care. Home pregnancy tests can differ in how early they’ll detect a pregnancy. In many cases, you might get a positive from an at-home test as early as 10 days after conception. For a more accurate result, wait until after you’ve missed your period to take a test. Remember, if you take a test too soon it could be negative even if you are pregnant. If you get a negative test and then miss your period, take another test or contact your healthcare provider.
Remember, if you take a test too soon it could be negative even if you are pregnant. If you get a negative test and then miss your period, take another test or contact your healthcare provider.
What are the advantages of using a home pregnancy test?
There are quite a few advantages to using a home pregnancy test, including:
- Pregnancy tests are inexpensive.
- They’re easy to use.
- Home tests provide results quickly.
According to pregnancy kit manufacturers, most at-home pregnancy tests are 97% to 99% accurate when you use them as instructed. Positive results can be trusted, but you can get a falsely negative result very early in pregnancy.
Blood tests tend to be more expensive and, for many women, the wait for an appointment can be difficult. Home tests allow you to quickly know if you’re pregnant shortly after conception.
Are all home pregnancy testing methods the same?
Most brands of at-home pregnancy tests are reliable. Although the exact testing method of different pregnancy tests can differ from one type to the other, they all look for hCG in your body. Some tests might do this through urine while others look for the pregnancy hormone in your blood. If you’re using an at-home test, most will give you the same result. The difference with your at-home tests will be the sensitivity of the test. Some might be more sensitive than others and produce a positive result — detect hCG in your urine — sooner than others. For the most accurate reading, it’s still recommended that you wait till you’ve missed your period. At that point, all tests should be accurate.
Although the exact testing method of different pregnancy tests can differ from one type to the other, they all look for hCG in your body. Some tests might do this through urine while others look for the pregnancy hormone in your blood. If you’re using an at-home test, most will give you the same result. The difference with your at-home tests will be the sensitivity of the test. Some might be more sensitive than others and produce a positive result — detect hCG in your urine — sooner than others. For the most accurate reading, it’s still recommended that you wait till you’ve missed your period. At that point, all tests should be accurate.
Are there any medications that can change the result of my pregnancy test?
For the most part, medications do not change your pregnancy test results. Antibiotics, birth control, alcohol and many other drugs do not impact your test results. The main reason for a false-negative is testing too early. You might also get a false-negative if you use a home test incorrectly. It’s important to follow the directions on your test kit to make sure you get an accurate result.
It’s important to follow the directions on your test kit to make sure you get an accurate result.
However, fertility drugs are one exception. These medications can sometimes cause a false-positive on your pregnancy test. If you’re taking fertility medications, reach out to your healthcare provider about your results to make sure they are accurate.
What should I do after getting a positive pregnancy test?
If you take a pregnancy test at home and it’s positive, there are a few things you should do, including:
- Take your prenatal vitamins — pick a vitamin with folic acid included in the ingredient list. It’s recommended that you actually start taking these vitamins before becoming pregnant. This is because the folic acid can help prevent birth defects.
- Call your healthcare provider for an appointment. This appointment might not happen for a while — sometimes several weeks — but it’s a good idea to call your provider and make the appointment.
- Make sure to pursue healthy habits.
 It’s recommended that you don’t drink alcohol or smoke during pregnancy. You may also want to limit the amount of caffeine you consume each day during pregnancy.
It’s recommended that you don’t drink alcohol or smoke during pregnancy. You may also want to limit the amount of caffeine you consume each day during pregnancy.
Signs of pregnancy - Clinic Zdorovye 365 Yekaterinburg
Symptoms of pregnancy - what is it?
Symptoms of pregnancy or signs of pregnancy are, as a rule, a combination of certain physiological changes in the body that a woman notices in herself already in the early stages of pregnancy.
Sometimes one hears that it is wrong to say “pregnancy symptoms”, because if there are symptoms, then there is an illness, and pregnancy is not an illness. But if we dig into dictionaries, we find that the word “symptom” comes from the Greek sýmptoma, i.e. "sign", "case", "coincidence". Thus, "pregnancy symptoms" is just a synonym for the phrase "signs of pregnancy", which is absolutely correct. The symptoms of early pregnancy or the first symptoms of pregnancy are different from the symptoms that occur in the later stages.
Knowing the signs of pregnancy allows a woman in the early stages to show increased attention to her health, and, consequently, to the health of the unborn baby, a pregnant woman will be able to determine pregnancy in the earliest possible time and, accordingly, resolve the issue for herself in time about its prolongation (preservation, continuation).
Every woman is remarkably different, so the symptoms a woman may experience during pregnancy may vary. Some women feel pregnant even before the test is positive. Below are nine symptoms of pregnancy.
The first symptom of pregnancy is implantation bleeding.
This is one of the earliest symptoms. On the sixth - twelfth day after conception, the introduction (attachment, implantation) of the embryo into the wall of the uterus occurs. Some women notice a small amount of red discharge (spots), which may be pink or reddish brown. If you have pain along with spotting or bleeding, see your doctor immediately as this could be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy.
The second symptom of pregnancy, also the main one, is the delay in menstruation
This symptom must be present during a normal pregnancy. You should be aware that sometimes bleeding occurs during pregnancy. The main thing is not to confuse them with menstruation, especially on those days when you should have started your period, that is, at 4, 8, 12 weeks of pregnancy. Bleeding during pregnancy is a sign of a threatened abortion. Therefore, if you notice this symptom in yourself, then immediately contact a specialized medical institution. With timely treatment, there is every chance to save the desired pregnancy. Menstruation does not occur throughout pregnancy and, as a rule, during breastfeeding.
The third symptom of pregnancy is increased basal body temperature.
Basal temperature rises above 37 degrees during pregnancy. If you notice some symptoms of pregnancy in yourself or even confirmed it with a doctor and at the same time observe a decrease in basal temperature, consult a doctor. A decrease in basal temperature may be due to the threat of miscarriage. For the result to be reliable, measure the temperature correctly. It should be measured in the rectum, immediately after waking up, in the morning.
A decrease in basal temperature may be due to the threat of miscarriage. For the result to be reliable, measure the temperature correctly. It should be measured in the rectum, immediately after waking up, in the morning.
The fourth symptom of pregnancy is profuse discharge.
In this case, we mean non-bleeding. Women know that normal vaginal discharge is odorless and almost colorless. Their number increases during ovulation and, as you now know, during pregnancy. On 9/10, you are pregnant if you have a missed period, heavy discharge, and an elevated basal body temperature.
The fifth symptom of pregnancy is swelling and (or) increased sensitivity of the mammary glands.
Many women say that the sensitivity of the mammary glands changes. This symptom may appear 1 to 2 weeks after conception. Swelling and increased sensitivity of the breast may appear not only as a result of pregnancy. Other causes are: premenstrual syndrome (PMS), birth control pills, or hormonal imbalances.
Other causes are: premenstrual syndrome (PMS), birth control pills, or hormonal imbalances.
The sixth symptom of pregnancy is toxicosis.
Nausea or vomiting in the morning usually does not occur early in pregnancy, but some women experience nausea as early as the third week. Many women believe that toxicosis is morning sickness and vomiting. But it is not so. In addition to nausea and vomiting, signs of toxicosis include a heightened sense of smell and aversion to certain foods. Many pregnant women cannot tolerate certain smells during early pregnancy. A heightened sense of smell is a side effect of a rapidly rising level of estrogen in your blood. Aversion to certain foods is even more common than cravings for certain foods during pregnancy. You may suddenly find that certain foods, even your favorites, disgust you.
The feeling of fatigue, which will be discussed below, is also referred to by some obstetricians as manifestations of toxicosis. Toxicosis, most often, goes away on its own by 12-14 weeks of pregnancy.
Toxicosis, most often, goes away on its own by 12-14 weeks of pregnancy.
The seventh symptom of pregnancy is feeling tired.
Fatigue can be as pronounced as if you had run a marathon. Fatigue is caused by increased levels of progesterone and other hormones necessary for the development of the child.
The eighth symptom of pregnancy is frequent urination and constipation.
You may suddenly become aware that you are going to the bathroom with alarming frequency.
The ninth symptom of pregnancy is headache and migraine.
Usually headaches are caused by hormonal changes in the body. If headaches occur, you should not self-medicate, since most known painkillers are contraindicated during pregnancy, especially in the early stages.
Related articles:
Birth certificate
Exchange card. Sick leave. Decree
Decree
Federal Pregnancy Standard
Ultrasound during pregnancy
Below in the lower abdomen
menstrual pain
Signs of pregnancy
hysteroscopy
hysterosalpingography
9000 Uzi of small pelvis 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000005
Prolapse of internal organs
Premature birth
Removal of the uterus
Intimate plastic surgery
Angarsk Perinatal Center: Pregnancy calendar
Regardless of whether this is your first pregnancy or you already have a baby and are expecting another one, for you comes exciting period of life. You began to feel the birth and development of a new life within yourself.
Due date calculation
In most cases, women do not know the exact date of conception, but they can tell exactly when the last menstrual cycle began. This is the point from which pregnancy is usually counted. For most women, the most likely period of fertilization (ovulation) lies in the middle of their monthly cycle, in other words, two weeks before the start of the next menstrual cycle.
Based on this date, the pregnancy lasts about 280 days, or 40 weeks, from the start of the last menstrual period. So you can get your estimated due date by adding 280 days to the date you started bleeding in your last cycle. The same result can be obtained by adding 7 days to the date of the last menstrual period and subtracting 3 months. For example, if your last period started on February 20, then your due date is expected to be November 27.
This calculation of pregnancy determines the so-called gestational, or menstrual, age of the fetus. It is on this “calendar” that doctors and nurses will track the development of the fetus. Gestational age is different from ovulation, or fertilization, age, which is two weeks earlier and is counted from the actual date of conception.
Many people calculate their pregnancy in weeks. This is the easiest and most convenient way to avoid confusion. For example, if your doctor says that you are 10 weeks pregnant (remember that the count is from the start of your last menstrual period), then you conceived about 8 weeks ago and will go into labor in 30 weeks because your total pregnancy is 40 weeks.
There is also a large unit of measurement - trimester. The trimesters divide the pregnancy into three phases. Each such phase, lasting 13 weeks, has its own characteristics.
You may also have heard of another unit of time, the lunar month. It corresponds to the cycle of lunar phases and is 28 days. The full gestation period, equal to 280 days, is 10 lunar months.
The calendar is based on a 42-week pregnancy schedule. The expected time of labor (ETD) is at the end of the 40th week. This way you will know the age of the developing fetus at any point during the pregnancy.
It is important to understand that the RID is an estimate, not a precise date. Only one woman in 20 gives birth on the exact day0 percent of women give birth a week earlier or a week later. Therefore, one cannot rely on the date of the OVR. It may turn out that it will come, and the child will not be born for some time. Consider this date as a guideline - a deadline for which you must prepare.
There is no fundamental difference how to count the time of pregnancy. Still, the process will not go faster. It will continue as long as nature allotted. After all, a miracle happens - a new life grows and develops in your body!
Your menstrual cycle
You estimate that your menstrual cycle probably ends at the beginning of the second week of pregnancy or a few days earlier. The usual interval between periods is 28 days, but they can occur after 21 and even after 35 days , and there is nothing abnormal in this. Actually menstruation in most cases lasts from 4 to 6 days. Discharge from the uterus is a mixture of sloughed uterine mucosa and blood. Clotted blood clots may also appear. On average, during menstruation, a woman loses 25-60 ml of blood. Blood loss can be different for different women, and for one woman it can change from one cycle to another.
Two important biological cycles occur almost simultaneously in a woman's body. As a result of the ovulation cycle (ovulation), a mature egg appears, ready for fertilization, and during the endometrial cycle, the uterine wall is prepared for implantation of the fertilized cell. Both cycles are closely related to each other because endometrial changes are regulated by hormones that are released in the ovary.
Both cycles are closely related to each other because endometrial changes are regulated by hormones that are released in the ovary.
The normal alternation of the ovulation and menstrual cycles (with the production of one egg for fertilization) is the rule, not the exception. Some women experience uneven cycles of egg production. Such cycles can take place without ovulation. This is quite rare compared to regular and predictable menstrual cycles and hormonal changes.
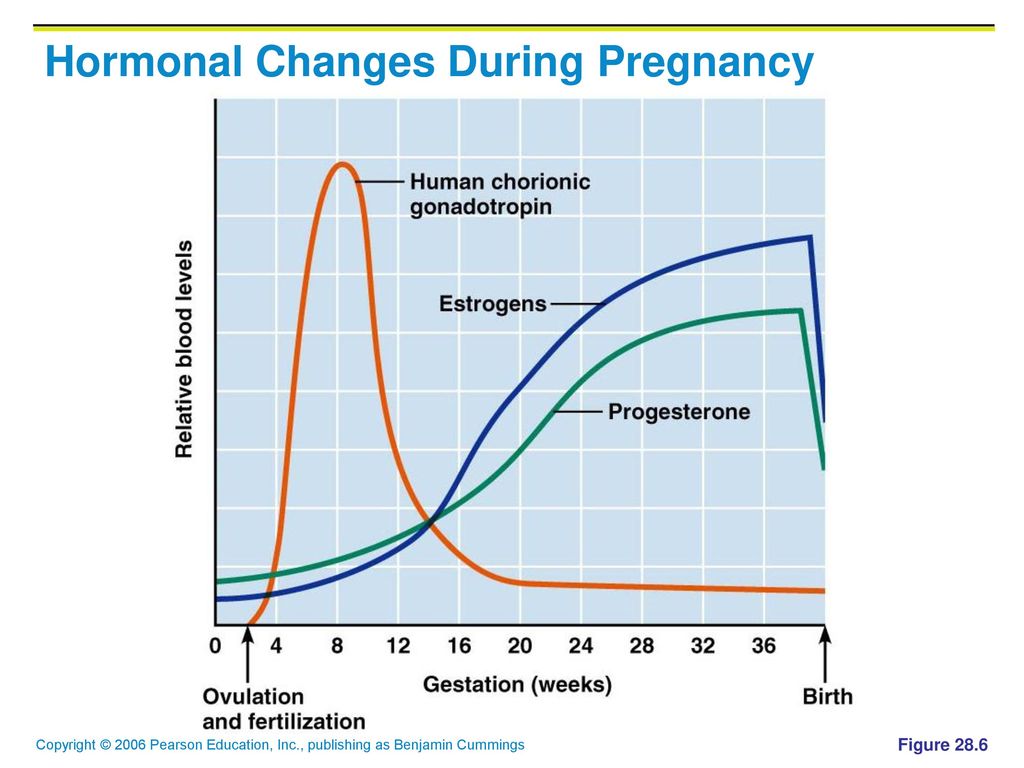
Your body produces many hormones, including follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland, as well as estrogen, progesterone and androgens (testosterone) from the ovary.
The natural purpose of the ovulation cycle is to produce an egg for fertilization. The body of a newly born girl contains about 2 million eggs. Their number is reduced to about 400 thousand by the beginning of puberty. But the maximum number of eggs is formed even before birth. When a fetus is only 5 months old (4 months before birth), it contains approximately 6. 8 million eggs.
8 million eggs.
During the ovulation cycle, 20 or more follicles may begin the process leading to ovulation. And only one of them, bursting, can turn into a mature egg. Before the onset of ovulation, this follicle approaches the wall of the ovary, which becomes progressively thinner. At the time of ovulation, an egg is formed at the site of the burst follicle. The place of rupture of the follicle on the wall of the ovary is called the stigma.
Some women (approximately 25 percent) experience lower abdominal pain or discomfort on the day of ovulation or the next day. It is believed that they are caused by irritation of the ovary with fluid or blood of the follicle when it bursts. Pain is not necessarily felt with every cycle. By the presence or absence of this symptom, one can judge whether ovulation has occurred or not.
Most often, a woman becomes pregnant in the middle of the menstrual cycle, on the 12-14th day from the beginning of the last menstruation. However, the beginning of the last menstruation is considered to be the starting point of ten obstetric months, or forty weeks of pregnancy.