Normal temperature for pregnancy
Adults, babies, pregnancy, and more
Normal body temperatures vary depending on many factors, including a person’s age and activity levels.
The average adult body temperature is around 98.6°F (37°C). However, people’s baseline body temperature can be slightly different.
In this article, we discuss typical temperature ranges for adults, children, and those who are pregnant. We also consider factors affecting body temperature and when to call a doctor.
Body temperature readings vary depending on where a person takes the measurements on the body. For example, rectal temperature readings are higher than oral readings, while armpit readings tend to be lower.
Body temperature readings can also vary depending on the following factors:
- a person’s age
- the time of day, typically lowest in the early morning and highest in the late afternoon
- a person’s recent activity
- food and fluid intake
According to reviews, the average adult body temperature across all different reading sites is 97. 86°F (36.59°C).
Researchers also found that the average orally-taken adult body temperature falls between 97.2–98.6°F (36.24–37°C).
Average body temperature can vary across demographics. A study of almost 35,500 people found that older adults had the lowest temperatures, and African American women had higher temperatures than white men.
The researchers also found that certain medical conditions can affect body temperature. For example, people with an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) tended to have lower temperatures, while people with cancer had higher temperatures.
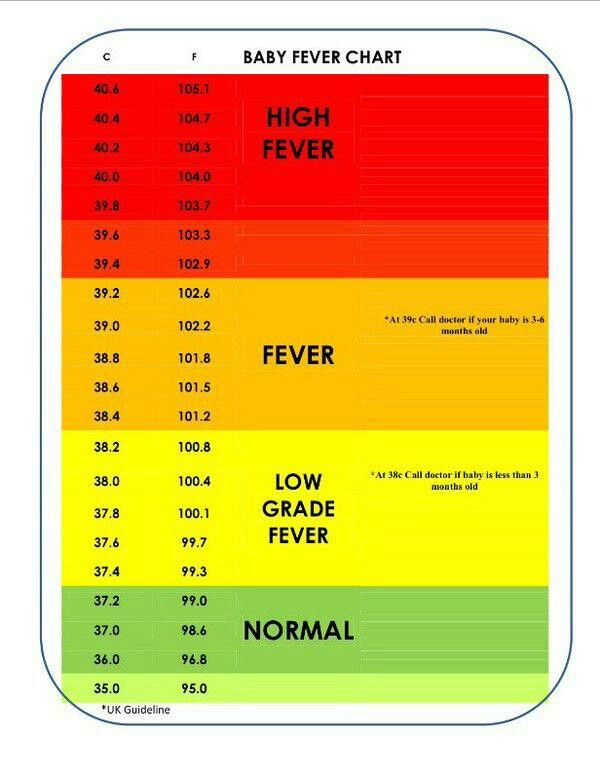
Typically, the following temperatures suggest that someone has a fever:
- at least 100.4°F (38°C) is a fever
- above 103.1°F (39.5°C) is a high fever
- above 105.8°F (41°C) is a very high fever
A fever may be a symptom of COVID-19.
For more advice on COVID-19 prevention and treatment, visit our coronavirus hub.
The average body temperature for children is around 97.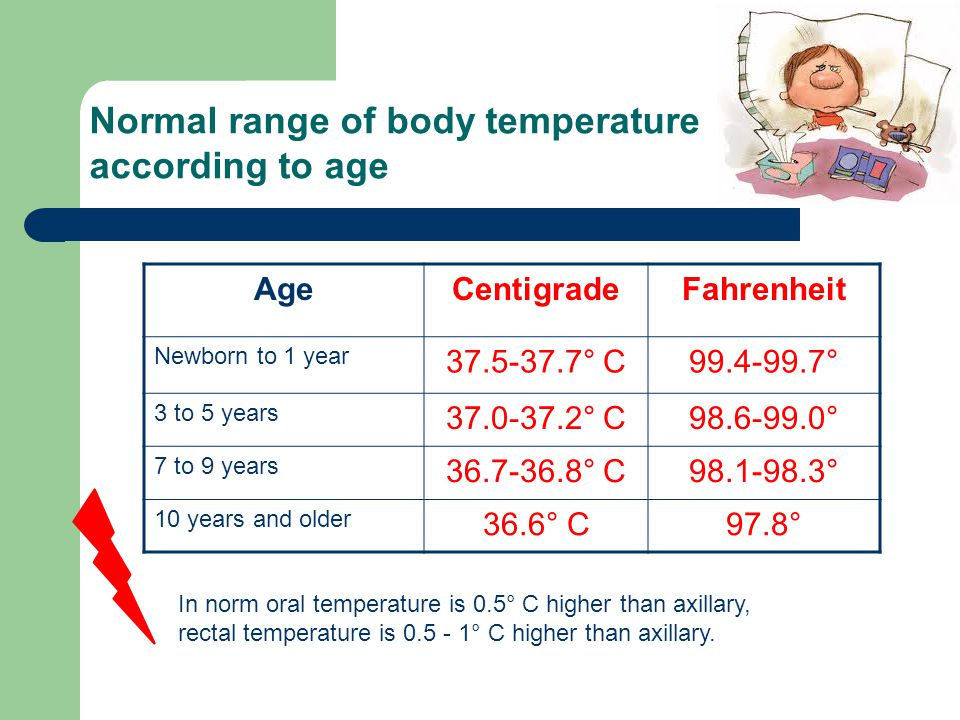 52°F (36.4°C), but this can vary. As with adults, a temperature above 100.4°F (38°C) may indicate a fever in children.
52°F (36.4°C), but this can vary. As with adults, a temperature above 100.4°F (38°C) may indicate a fever in children.
Infants tend to have higher body temperatures than older children and adults. The average body temperature for newborn babies is around 99.5°F (37.5°C).
A baby’s temperature is higher because they have a larger body surface area relative to their body weight. Their bodies are also more metabolically active, which generates heat.
Babies’ bodies do not regulate temperature as well as adults’ bodies. They sweat less when it is warm, meaning their bodies hold more heat. It may also be more difficult for them to cool down during a fever.
Learn more about fever in babies here.
During pregnancy, a person’s basal metabolic rate (BMR) is higher. This means the body produces more heat.
One study found that body temperature peaks at 96–99.5°F (35.6–37.5°C) around the 12th week of pregnancy. The average body temperature reaches its lowest point of around 95. 5–99.1°F (35.3–37.3°C) just after the 33rd week.
5–99.1°F (35.3–37.3°C) just after the 33rd week.
There are many types of thermometers available.
Digital thermometers
Digital thermometers are readily available and can produce accurate temperature results. A person may use these at different parts of the body.
- Rectal measurement: Specialized digital rectal thermometers are a common option for taking the temperature of young children. A person should clean and lubricate the end of these devices before inserting them into the anus. The device will alert the user when it has made a reading and is safe to remove.
- Oral measurement: Standard digital thermometers are simple to use orally (by mouth). First, a person must make sure the tip of the device is clean. They will then place this under their tongue toward the back of their mouth and close their lips. The device will produce a reading on an integrated display.
- Axillary (armpit) measurement: A person can place a digital thermometer at their, or someone else’s, armpit.
 The arm must then remain tight to the body to ensure a good reading. This is a noninvasive option for taking a child’s temperature.
The arm must then remain tight to the body to ensure a good reading. This is a noninvasive option for taking a child’s temperature.
Infrared thermometers
Infrared thermometers can take temperature readings at a distance. However, these are not as accurate as other methods.
People may use tympanic thermometers to take readings from the ear canal. To use, a person will:
- insert the device’s tip into their ear
- align it with their ear canal
- activate the device until it produces a result
Temporal thermometers use an infrared signal to measure a person’s temperature. The user will typically hold the thermometer a few centimeters from a person’s forehead and wait for the device to produce a reading.
One study concluded that while forehead and ear measurements are viable, nontraumatic screening options for infants, they are still not as accurate as rectal measurements.
It is important for people to always follow the instructions on the thermometer package.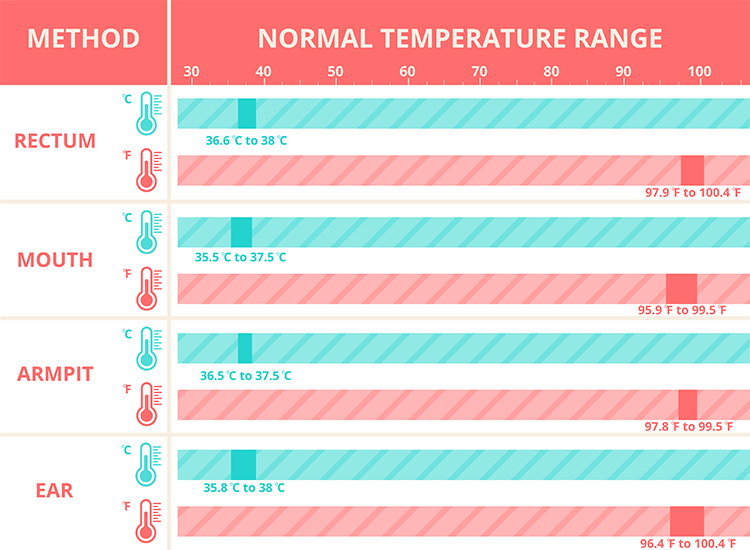
If a thermometer indicates a person’s body temperature is too high or too low, they may wish to take another reading to confirm the result.
In all age ranges, a high temperature may result from short-term illnesses and usually does not cause significant harm in adults with otherwise good overall health.
If a person has a high temperature, it is important they rest and drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration. These at-home treatments also apply to children and babies.
In hot climates, exercise or other physical activity may cause hyperthermia — an abnormally high body temperature. Unlike infection or fever, this is typically the result of outside factors. Moving to a cooler space and taking fluids will usually remedy hyperthermia.
However, if a high temperature persists or increases, people should seek medical help.
If a person’s temperature is below 95°F (35°C) they have hypothermia and should seek medical assistance.
The need for medical assistance can vary between age groups.
In many cases, a person with a fever will not require medical attention. However, if a person has a temperature of or higher, they should contact their doctor.
A person should also seek medical assistance if they experience any of the following alongside a fever:
- dehydration
- lightheadedness
- severe cramps
- a persistent, or worsening fever
The following people should also seek medical assistance if they experience fever:
- recent transplant participants
- people with compromised immune systems
- those on immunosuppressants
- those who have recently undergone cancer treatments
If a person’s temperature is over 106.7°F (41.5°C), they have hyperpyrexia, a very high fever. This can lead to permanent organ damage and death. Hyperpyrexia requires urgent medical assistance.
If a person’s body temperature is too low, they may have hypothermia. This is a medical emergency, and they should seek assistance immediately.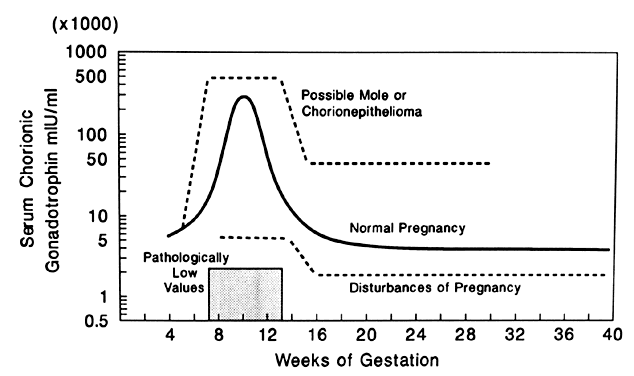 Doctors define hypothermia as a temperature dropping below 95°F (35°C).
Doctors define hypothermia as a temperature dropping below 95°F (35°C).
A person should contact emergency services if a child has a temperature over 104°F (40°C). They should also seek medical help if a child has a high temperature that lasts for 5 days or more or is experiencing dehydration, vomiting, or diarrhea.
If a child’s temperature drops below 95°F (35°C), medical assistance is essential.
BabiesIf an infant 3 months or younger has a temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) or above, seek emergency medical attention. In young babies, a slight fever can signal a serious infection.
In babies up to 6 months of age, a temperature of 102.2°F (39°C) or more is also reason to contact emergency services.
As with adults and older children, if a baby’s temperature drops below 95°F (35°C), they will require immediate emergency assistance.
An area of the brain called the hypothalamus regulates body temperature. If body temperature rises above or dips below the 98.6°F (37°C) mark, the hypothalamus works to regulate the temperature.
If body temperature rises above or dips below the 98.6°F (37°C) mark, the hypothalamus works to regulate the temperature.
If the body is too cold, the hypothalamus sends signals to make the body shiver, which warms the body. If the body is too hot, it sends messages to begin sweating, letting heat leave the body.
Infections cause most fevers. A fever develops as the body’s natural way of reacting to and fighting infection.
Doctors consider a fever to be a body temperature that reaches or exceeds 100.4°F (38°C). Other symptoms include:
- appetite loss
- chills
- headache
- irritability
- muscle aches
- shivering
- sweating
- weakness
The ideal body temperature in adults is around 98.6°F (37°C), but this varies based on age, physical activity, and health. Body temperature also changes throughout the day. A temperature of above 100.4°F (38°C) signals a fever.
Babies may have higher body temperatures than adults, but even a slight fever in babies can indicate a severe infection.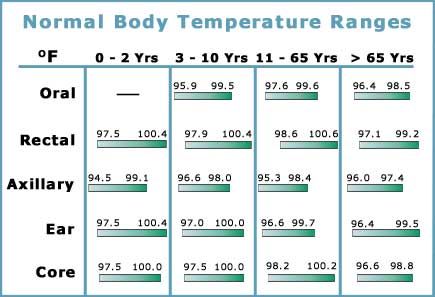
Temperature readings from different body parts give a range of body temperatures that doctors consider normal. Rectal readings are higher than oral readings, and armpit readings tend to be lower.
If a person has an unusually high or low temperature, they should seek medical attention immediately.
Read this article in Spanish.
What Is a Normal Pregnancy Temperature?
By now, most experts agree that not everyone has a normal body temperature of 98.6. Some people tend to run a little warmer when they’re healthy; others tend to be a little cooler. If you have a good idea of your normal baseline temperature, it’s important to know this: It’s usually a little higher in pregnancy. There are a few factors that go into this temperature increase, but it can and does happen. Here’s what you need to know about a normal pregnancy temperature, plus what it means for you.
In this article:
What’s considered a normal pregnancy temperature?
Dangers of a high body temperature when pregnant
What constitutes a fever during pregnancy?
What’s Considered a Normal Pregnancy Temperature?
Your normal body temperature may rise during pregnancy, but it’s unlikely to be a huge increase, says Christine Greves, MD, an ob-gyn at the Winnie Palmer Hospital for Women & Babies in Orlando, Florida. So what is a normal body temperature for a pregnant woman? “It could rise about 0.2 degrees Fahrenheit,” she says. For example, if your baseline body temperature pre-pregnancy was 98.2, your body temperature when pregnant could be 98.4. “It’s super, super subtle,” says G. Thomas Ruiz, MD, lead ob-gyn at MemorialCare Orange Coast Medical Center in Fountain Valley, California.
So what is a normal body temperature for a pregnant woman? “It could rise about 0.2 degrees Fahrenheit,” she says. For example, if your baseline body temperature pre-pregnancy was 98.2, your body temperature when pregnant could be 98.4. “It’s super, super subtle,” says G. Thomas Ruiz, MD, lead ob-gyn at MemorialCare Orange Coast Medical Center in Fountain Valley, California.
So why is your pregnancy temperature different than your pre-pregnancy body temp? It rises slightly when you’re expecting due to the increase in your body’s blood volume to meet the demands of your growing baby, explains women’s health expert Jennifer Wider, MD. “Due to this increase and the increases in body metabolism, the core temperature rises,” she says.
Your early pregnancy temperature range starts out higher, particularly in the first trimester, Greves says, and then falls as your pregnancy progresses. In fact, if you were using your basal body temperature to track your ovulation, you may have noticed that it rose slightly (and stayed elevated) after you conceived, Wider says. While your body temperature when pregnant is highest in the first trimester, keep in mind that your core temperature will increase more easily later in your pregnancy when you exercise or are out and about in hot weather, Wider says.
While your body temperature when pregnant is highest in the first trimester, keep in mind that your core temperature will increase more easily later in your pregnancy when you exercise or are out and about in hot weather, Wider says.
If your normal body temperature hasn’t risen during pregnancy, don’t panic. Your core body temperature has a range, Wider says, making it hard to get an exact read on what your new body temp is. Given that it goes up only slightly during pregnancy, it’s also difficult to determine an exact number for your new pregnancy temperature. Either way, it’s not a cause for concern if that number on the thermometer doesn’t rise. “The change in temperature really isn’t significant,” Ruiz says.
Dangers of a High Body Temperature When Pregnant
Illness and fevers happen, but do your best to avoid developing a fever or letting one persist during pregnancy. That’s because if your internal temperature gets too high, especially in your first trimester, it can potentially increase the risk of miscarriage, neural tube defects (aka birth defects of the brain, spine or spinal cord) and developmental problems, including cleft lip and palate and congenital heart defects, according to the doctors we spoke with.
In general, you want to do what you can to avoid raising your body temperature when pregnant, Greves says. That includes avoiding the use of a hot tub or sauna, taking a piping hot bath (where the water is hotter than 100 degrees) or being outside for too long on very hot days. However, you can use a heating pad on localized areas, like your back, legs or feet. “It shouldn’t increase your core body temperature,” Greves says. Just don’t use it for more than 15 minutes, and make sure the pad is below 100 degrees Fahrenheit.
What Constitutes a Fever During Pregnancy?
Because the increase in pregnancy temperature is so low, doctors still consider the standard marker of a fever—100.4 degrees or above—as a fever during pregnancy, Ruiz says.
If you have a mild fever, you can take acetaminophen (Tylenol) to try to bring it down, Ruiz says. Drinking a lot of fluids can help too, he says. It’s important to let your doctor know what’s going on, even if your fever is low. “We want to know other symptoms,” Greves says. “If you have a stiff neck and rash, I would address that immediately, as opposed to someone having a few sniffles and a mild fever.” Call your doctor immediately if you have a fever of 102 or higher, which would require additional attention.
“We want to know other symptoms,” Greves says. “If you have a stiff neck and rash, I would address that immediately, as opposed to someone having a few sniffles and a mild fever.” Call your doctor immediately if you have a fever of 102 or higher, which would require additional attention.
About the experts:
Christine Greves, MD, FACOG, is an ob-gyn at the Orlando Health Winnie Palmer Hospital for Women & Babies in Orlando, Florida. She received her medical degree from the University of South Florida College of Medicine.
G. Thomas Ruiz, MD, is the lead ob-gyn at MemorialCare Orange Coast Medical Center in Fountain Valley, California. He earned his medical degree from UC Irvine School of Medicine and has been practicing medicine in Orange County since 1993.
Jennifer Wider, MD, is a New York City-based women’s health expert and author. She received her medical degree from the Mount Sinai School of Medicine.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
Why Am I Always Hot During Pregnancy
What to Do for a Fever During Pregnancy
How Moms-to-Be Can Enjoy a Bath Safely
Early pregnancy | Shchelkovsky perinatal center
Pregnancy is a wonderful period! However, the changes taking place in the body at this time can greatly frighten you. The phenomena characteristic of pregnancy are different for all women, and will not necessarily be repeated during each subsequent gestation. Let's analyze the most common symptoms, their causes and possible methods of correction.
1. Frequent urination.
Frequent, painless (!) urge to urinate is one of the signs of pregnancy. This is due to increased secretion of progesterone (pregnancy hormone), changes in metabolism and pressure from the growing uterus on the bladder.
This is due to increased secretion of progesterone (pregnancy hormone), changes in metabolism and pressure from the growing uterus on the bladder.
Be sure to see a doctor if:
- painful urination (this may be a sign of an infection)
- urine of strange color (stained with blood, brown)
- the amount of urine excreted per day is much less than the liquid drunk per day
Life hack! Under no circumstances should fluid intake be restricted! To alleviate the condition and reduce the frequent urge to urinate, it is necessary to exclude products that have a diuretic effect: tea, coffee, zucchini, watermelon; as well as salty, spicy and fried foods. It is better to drink water or juice. Wear comfortable cotton underwear that does not squeeze the lower abdomen.
2. Nausea, vomiting, heartburn, increased susceptibility to smells.
Nausea is one of the common symptoms of early pregnancy. The range of issues related to nausea and vomiting during pregnancy is quite wide. From "it's good, I don't even feel sick" (with relief), "I don't feel sick, what's wrong with me?" (with anxiety) to "when will this nausea pass" (with hope). Indeed, these symptoms are not at all a mandatory accompaniment of gestation, they can manifest at 7-8 weeks and last up to 12-14 weeks. The duration of this condition can sometimes be delayed, but rarely persists throughout pregnancy.
The range of issues related to nausea and vomiting during pregnancy is quite wide. From "it's good, I don't even feel sick" (with relief), "I don't feel sick, what's wrong with me?" (with anxiety) to "when will this nausea pass" (with hope). Indeed, these symptoms are not at all a mandatory accompaniment of gestation, they can manifest at 7-8 weeks and last up to 12-14 weeks. The duration of this condition can sometimes be delayed, but rarely persists throughout pregnancy.
Life hack! For nausea, eat before feeling hungry. Solid, non-hot food and drinks at a cool temperature are best. With heartburn, you should eat small portions of food and often, and most importantly, sit, stand or walk for at least 30 minutes after eating, but do not lie down.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- vomiting occurs even after drinking water
- vomiting is exhausting, accompanied by dizziness, weakness
- dryness, jaundice and flaking of the skin appear
- Nausea and vomiting interfere with proper nutrition, accompanied by weight loss
To reduce nausea and vomiting in the morning, try eating something before you get out of bed. It can be a cracker, a cookie, a piece of hard cheese. And salty food is preferable to sweet. You can have a snack in the same way at night when you get up to go to the toilet. Do not lie down immediately after eating, this will only increase nausea. Vitamins for pregnant women with nausea should be taken in the evening after meals. Cool water with lemon, ginger, mint tea, or ginger or mint candies can alleviate the condition. It is necessary to exclude those foods, drinks and smells that are unpleasant to you. Brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth often can also reduce nausea.
It can be a cracker, a cookie, a piece of hard cheese. And salty food is preferable to sweet. You can have a snack in the same way at night when you get up to go to the toilet. Do not lie down immediately after eating, this will only increase nausea. Vitamins for pregnant women with nausea should be taken in the evening after meals. Cool water with lemon, ginger, mint tea, or ginger or mint candies can alleviate the condition. It is necessary to exclude those foods, drinks and smells that are unpleasant to you. Brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth often can also reduce nausea.
3. Pain or cramps in the lower abdomen, constipation, pain in the lumbar region.
The simplest and most easily controlled cause of pain is delayed and incomplete bowel movements. An increase in the concentration of progesterone relaxes the smooth muscles, which are located not only in the uterus, but also in other hollow organs. In this case, the correction of the diet and the restoration of the passage of feces will help. If the measures are ineffective, the doctor may prescribe safe drugs for you. A special type of pain that occurs during exclusivity in pregnant women is pain in the round ligament of the uterus. This acute, rather intense pain occurs, as a rule, on the one hand with a sharp change in body position (for example, when getting up from a chair or leaving a car). This pain occurs due to stretching, and then a sharp contraction, like a spring, of the round uterine ligaments. The pain quickly passes if you immediately take a comfortable position and does not require special treatment.
If the measures are ineffective, the doctor may prescribe safe drugs for you. A special type of pain that occurs during exclusivity in pregnant women is pain in the round ligament of the uterus. This acute, rather intense pain occurs, as a rule, on the one hand with a sharp change in body position (for example, when getting up from a chair or leaving a car). This pain occurs due to stretching, and then a sharp contraction, like a spring, of the round uterine ligaments. The pain quickly passes if you immediately take a comfortable position and does not require special treatment.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- pain is accompanied by spotting bloody discharge from the external genitalia
- increasing duration and intensity of pain
- abdominal pain accompanied by dizziness, fever, loss of consciousness
Life hack! To normalize bowel movements, eat more vegetables and fruits, drink water and move more during the day. Try to eat often and in small portions.
Try to eat often and in small portions.
4. Enlargement and soreness of the mammary glands.
Hormonal restructuring of the body during gestation is accompanied, among other things, by an increase in the size of the mammary glands and an increase in their sensitivity. By the end of the first trimester, the soreness usually disappears, no additional methods of treatment are needed.
Life hack! Choose comfortable supportive underwear (it should not leave marks on the skin at the end of the day). You may need a larger size or a sports bra. Pain in the mammary glands is relieved by a warm shower at the end of the day.
You should definitely see a doctor if:
- the pain is intense
- mammary glands are very dense with redness and body temperature is increased
- discharge from the nipples appears (purulent, bloody)
5. Increased body temperature.
In early pregnancy, an increase in body temperature to 37.5 ° C is not necessary, but is possible due to the peculiarities of the action of progesterone. Because of this, it is difficult for pregnant women to endure stuffy, hot rooms. Self-medication is dangerous: an attempt to bring down the temperature even with a seemingly harmless folk method - tea with raspberries - can mask the true cause of hyperthermia and delay the diagnosis. Due to the increased body temperature, pregnant women should dress in layers and avoid stuffy and hot rooms and spaces so that they can always “adjust” their temperature on their own.
- temperature above 37.5 °C
- along with fever, any pain occurs
- runny nose, cough, body aches appear
6. Nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, nosebleeds.
These symptoms can be explained by the individual reaction of the vascular system to the increase in blood volume that occurs during pregnancy. Another possible reason is dry air in the room, the operation of central heating batteries.
Another possible reason is dry air in the room, the operation of central heating batteries.
Life hack! The easiest way to deal with nasal congestion is to use a humidifier. If you don't have one, you can put a damp towel on the battery - less effective, but better than nothing. It is possible to use sprays with sea salt, but you need to carefully read the instructions and especially the "Indications" section, it should contain information about the safety of the product during pregnancy.
You should definitely see a doctor if:
- symptoms of a cold occur
- nasal congestion accompanied by ear congestion
- These symptoms appeared after exposure to the allergen known to you
7. Blood pressure fluctuations.
An ideal option for the course of any pregnancy is the stability of the blood pressure throughout the gestation. However, this is extremely rare. A small (up to 10 units) increase in pressure from the usual reference may be due to an increase in the load on the cardiovascular system as a result of changes in body weight, hormonal changes, and uterine pressure on the vessels.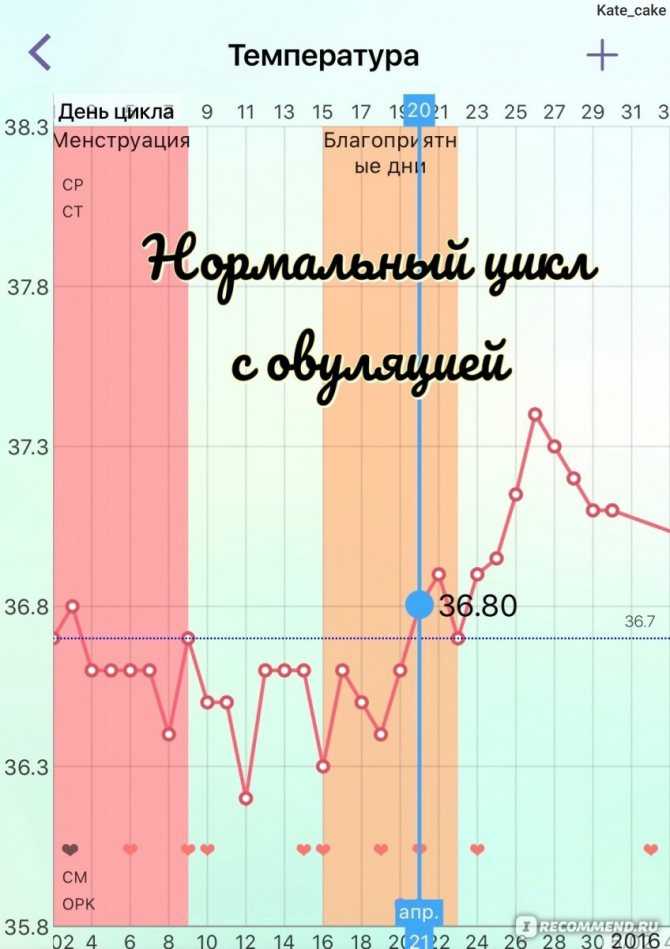 Normal pressure: systolic below 130 mm Hg, diastolic no more than 85 mm Hg. Blood pressure in the range of 130-139/ 85–89 mm Hg considered high to be normal. High numbers are often observed in patients of older reproductive age, suffering from diabetes mellitus and kidney disease, obesity, etc. However, it is imperative to tell the doctor about all these concomitant pathological conditions at the first appointment and, if necessary, consult a neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist and other related specialists . Reasonable physical activity, adherence to sleep and wakefulness, a balanced diet, and the rejection of coffee and strong tea allow you to keep pressure within limits. Of the completely exotic for our days, but no less significant - the prevention of stress.
Normal pressure: systolic below 130 mm Hg, diastolic no more than 85 mm Hg. Blood pressure in the range of 130-139/ 85–89 mm Hg considered high to be normal. High numbers are often observed in patients of older reproductive age, suffering from diabetes mellitus and kidney disease, obesity, etc. However, it is imperative to tell the doctor about all these concomitant pathological conditions at the first appointment and, if necessary, consult a neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist and other related specialists . Reasonable physical activity, adherence to sleep and wakefulness, a balanced diet, and the rejection of coffee and strong tea allow you to keep pressure within limits. Of the completely exotic for our days, but no less significant - the prevention of stress.
Life hack! If you first discovered that you have high normal pressure, repeat the measurement after 15 minutes. If the pressure remains elevated, see a doctor.
Be sure to see a doctor if:
- your blood pressure is above 140/90 mmHg.

- pressure increased by more than 10 mm Hg. relative to your regular
- an increase in the pressure indicator is accompanied by edema, the appearance of "flies" before the eyes
NB! You should also pay attention to lowering blood pressure. Numbers less than 90/60 mmHg - an excuse to see a doctor.
Life hack! Keep a blood pressure diary, especially if you are prone to hypertension. Show your diary to your doctor at every appointment.
8. Heaviness and pain in the legs.
Heaviness and pain in the legs, especially in the evening, are frequent companions of pregnancy. There is an explanation for the occurrence of symptoms: an increase in load due to growing weight and a shift in the center of gravity of the body.
Life hack! Ask your partner/husband to give you a foot massage, relax with your limbs elevated (not too much!) A therapeutic pedicure, dousing the legs with cool water, a contrast shower, a cream or gel for legs with cooling components (menthol, essential oils), as well as compression stockings or stockings of the lightest degree of compression will help.
You should always see a doctor if:
- one or both legs are very swollen or discolored
- previously diagnosed varicose veins, family history of thrombosis
9. Skin changes.
During pregnancy, you may notice dark spots on your skin. Especially often such darkening (hyperpigmentation) is observed in the nipple area, along the white line of the abdomen. Stretch marks (stretch marks) may appear on the skin of the abdomen and thighs. These are normal signs and do not require any treatment. In most cases, skin color will return to normal after breastfeeding ends, and stretch marks will shrink and fade. Itching can be associated with stretching of the skin, especially in the abdomen and mammary glands. This symptom occurs infrequently and is usually successfully stopped by the use of special products to moisturize and soften the skin. By the way, these same remedies usually help in the fight against stretch marks.
Life hack! Oils and moisturizing creams to increase skin elasticity, contrast showers, massage with a hard brush will help reduce the likelihood of skin changes.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- along with itching there are areas of redness, spots, peeling
- itching increases
10. Bleeding gums.
Changes in the characteristics of blood circulation in the body of a pregnant woman can cause bleeding gums. The appearance of minor blood impurities during brushing your teeth, when eating solid foods (for example, an apple) is acceptable. However, the key provision is "insignificant". If you find it difficult to assess your own condition, consult a specialist.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- you have loose teeth, sore gums, bad breath
- bleeding in the gum area increases
11. Fatigue, mood instability.
Fatigue, mood instability.
Tearfulness, lack of strength, forgetfulness, distraction, the whole palette of feelings "here and now"... The list can be continued, and there is only one explanation for this - pregnancy. The most common early symptom is severe fatigue. There is no universal recipe, just as there is no single picture of these states. The main recommendation for all pregnant women is to rest often, relax and even sleep during the day. Most importantly, you need to remember: pregnancy is not a disease, but a great time to prepare for motherhood.
why it rises and why it is dangerous
Published:
Increased body temperature is one of the signals that changes are taking place in the body. During pregnancy, it is especially important to observe their character and monitor their health. What temperature in pregnant women is considered the norm and what can its increase indicate?
During pregnancy, it is especially important to observe their character and monitor their health. What temperature in pregnant women is considered the norm and what can its increase indicate?
Causes of fever during pregnancy
M.D. S. Felson writes that in an adult, normal body temperature ranges from 36.1 ° C to 37.2 ° C. In infants and children, the range is slightly higher, from 36.6°C to 38°C. During pregnancy, normal body temperature can reach 37.4 ° C, but the value of 37 ° C is considered the most comfortable for the development of the fetus in the early stages. In the later stages, this mark decreases, and the temperature indicators correspond to the norms of any adult.
Women's temperature changes during the menstrual cycle. Doctor of Medicine N. Pathak explains that in the 2nd phase of the menstrual cycle, under the influence of progesterone, changes occur in the uterine mucosa and prepare it for the implantation of a fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, the hormone levels return to normal.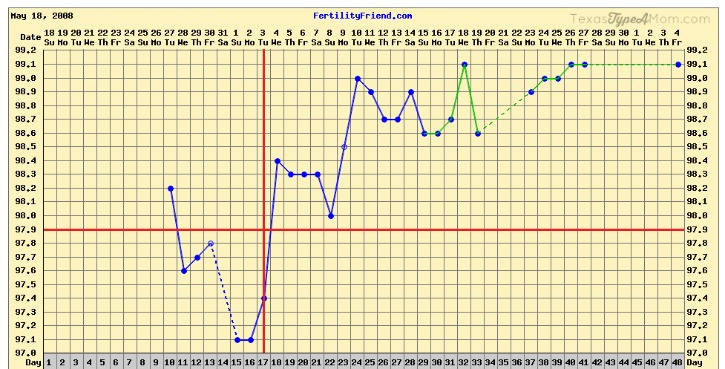
Why is the temperature 37 during pregnancy? When pregnancy occurs, the production of the hormone progesterone increases, which causes an increase in body temperature. This phenomenon most often occurs in the first trimester. In the second trimester, the amount of estrogen (female sex hormone) increases, and the temperature gradually decreases, normalizes.
When does body temperature rise during pregnancy? In the first trimester, body temperature rises (between 37.2 and 37.4 °C) when the level of the hormone progesterone rises in the blood. In the second and third trimester, fever most often occurs with infectious and viral diseases, poisoning and other inflammatory processes in the body. In such cases, you can not self-medicate. It is important to consult a doctor who will select safe pharmaceutical preparations.
Why a temperature of 37 during pregnancy: Unsplash / Matteo Fusco However, even in the early stages, it is worth remembering that an increase in temperature can be a reaction to diseases, a sign of an ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to listen for additional symptoms. Pregnant women should consult a doctor with a complaint about temperature in such cases:
Therefore, it is important to listen for additional symptoms. Pregnant women should consult a doctor with a complaint about temperature in such cases:
- nausea and vomiting;
- lower abdominal pain;
- spotting;
- runny nose and cough.
What temperature is dangerous during pregnancy? An increase in temperature to 38 ° C is considered dangerous, since there is a threat of premature termination of pregnancy and a risk to the health of the fetus. If the temperature mark exceeds 37.5 ° C and lasts for several days, you should consult a doctor. Such a temperature can be brought down with antipyretics, but whether it is necessary to do this and what means to use, the physician determines.
During pregnancy, the temperature may be below 36°C. Toxicosis, depletion of immunity can lead to a decrease in values. At the same time, the woman feels fatigue, lethargy, loss of strength. If this condition lasts 1-2 days, there is no cause for concern. If the temperature drops below 35 ° C and remains at this level for more than 2 days, you need to seek medical help, as this may be a sign of pathologies of the endocrine system.
If the temperature drops below 35 ° C and remains at this level for more than 2 days, you need to seek medical help, as this may be a sign of pathologies of the endocrine system.
Why fever during pregnancy is dangerous and what to do
In the first months of pregnancy, the formation of fetal organ systems occurs, so it is important to create optimal conditions for the development of the embryo. The brain is also being formed. If these processes take place in adverse conditions, then there is a risk of congenital malformations. Dr. S. Pietersma notes that in recent years it has become clear that fetal abnormalities can be detected already at the end of the first trimester of pregnancy using a two-dimensional ultrasound. Therefore, in developed countries, scanning of abnormalities in the first trimester of pregnancy is increasingly being offered as part of the standard treatment.
Elevated body temperature poses a risk to the health of the fetus and the pregnant woman. Why is fever dangerous during pregnancy? An increase in body temperature leads to a change in the rate of synthesis of a number of proteins and enzymes, which affects cellular processes that cover cell growth and the definition of their functions, the formation of organs and tissues, and the mechanism of cell death. These mechanisms can affect the condition of the fetus, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Why is fever dangerous during pregnancy? An increase in body temperature leads to a change in the rate of synthesis of a number of proteins and enzymes, which affects cellular processes that cover cell growth and the definition of their functions, the formation of organs and tissues, and the mechanism of cell death. These mechanisms can affect the condition of the fetus, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy.
The blood of a pregnant woman becomes thicker, which makes it difficult to deliver nutrients to the fetus and may lead to hypoxia. The risk of thrombosis increases, which can lead to a heart attack, stroke, varicose veins and other pathologies. Increased uterine contractions against the background of elevated temperature can threaten the rejection of the fetus.
Why fever during pregnancy is dangerous: Unsplash / Isaac QuesadaIn the second and third trimesters, fever can have the following consequences:
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- intrauterine infection;
- violation of the structure and function of the placenta;
- premature birth;
- low fetal weight.

What should I do if I have a fever? If in the first trimester a pregnant woman has a temperature of 37-37.2 ° C in the absence of other symptoms, you can not worry. If the value exceeds 38 ° C, you should immediately consult a doctor at any time. Before the consultation, only paracetamol-based preparations can be used. Remember that antipyretics should not be used at temperatures up to 37.5 ° C.
To help the pregnant woman before the doctor arrives, do the following:
- Open the window and ventilate the room.
- Turn on the humidifier or hang a damp towel in the room.
- Apply a cold compress.
- Take off warm clothes, put on clothes made of natural material.
- Do not cover yourself with a blanket.
- Drink warm tea.
An increase in body temperature during pregnancy can be an indication of changes in the body and a symptom of the disease. Therefore, it is important to monitor the state of the body both in the early and late periods.