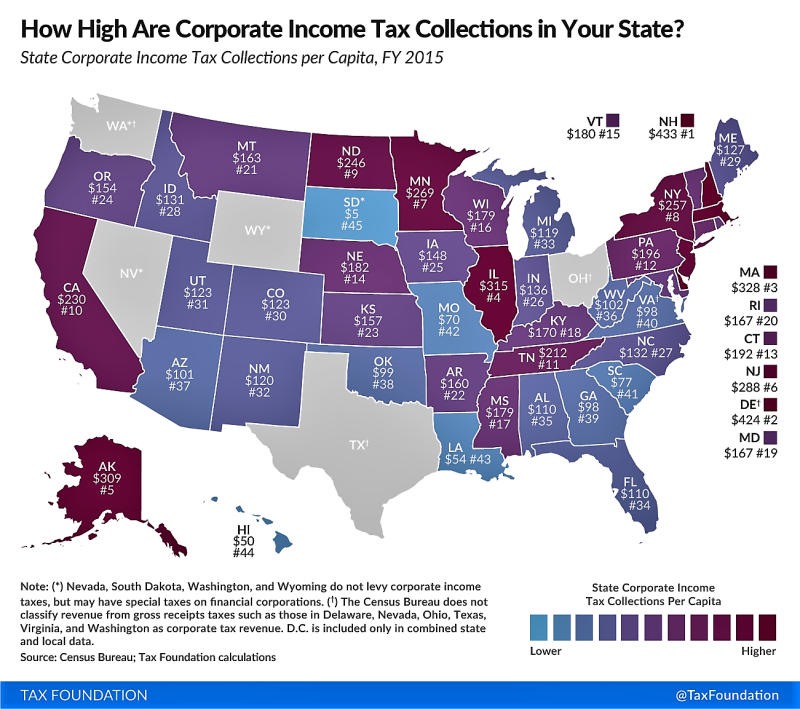
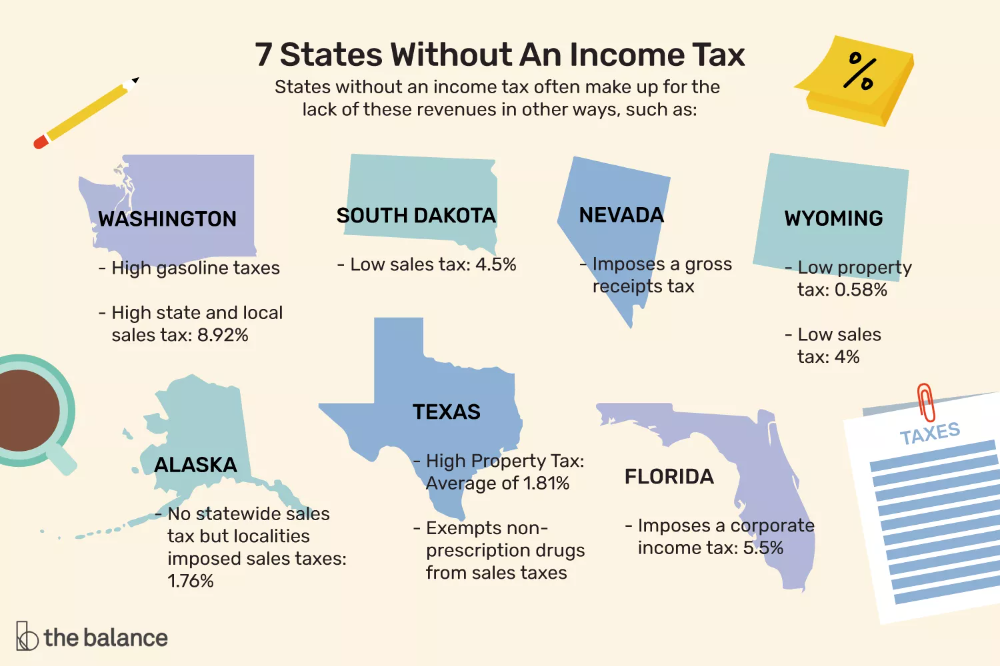
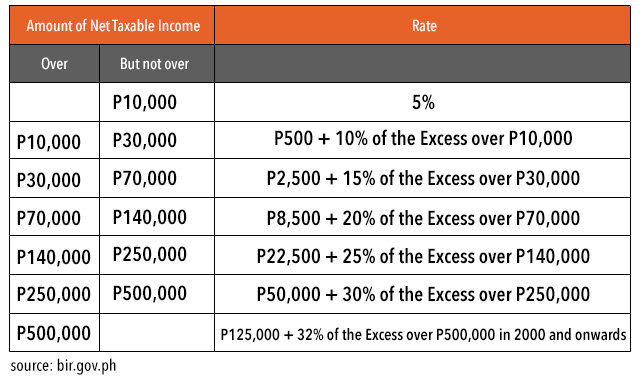
How much per child on income tax
The Child Tax Credit - The White House
To search this site, enter a search termThe Child Tax Credit in the American Rescue Plan provides the largest Child Tax Credit ever and historic relief to the most working families ever – and as of July 15th, most families are automatically receiving monthly payments of $250 or $300 per child without having to take any action. The Child Tax Credit will help all families succeed.
The American Rescue Plan increased the Child Tax Credit from $2,000 per child to $3,000 per child for children over the age of six and from $2,000 to $3,600 for children under the age of six, and raised the age limit from 16 to 17. All working families will get the full credit if they make up to $150,000 for a couple or $112,500 for a family with a single parent (also called Head of Household).
Major tax relief for nearly
all working families:
$3,000 to $3,600 per child for nearly all working families
The Child Tax Credit in the American Rescue Plan provides the largest child tax credit ever and historic relief to the most working families ever.
Automatic monthly payments for nearly all working families
If you’ve filed tax returns for 2019 or 2020, or if you signed up to receive a stimulus check from the Internal Revenue Service, you will get this tax relief automatically. You do not need to sign up or take any action.
President Biden’s Build Back Better agenda calls for extending this tax relief for years and years
The new Child Tax Credit enacted in the American Rescue Plan is only for 2021. That is why President Biden strongly believes that we should extend the new Child Tax Credit for years and years to come. That’s what he proposes in his Build Back Better Agenda.
Easy sign up for low-income families to reduce child poverty
If you don’t make enough to be required to file taxes, you can still get benefits.
The Administration collaborated with a non-profit, Code for America, who created a non-filer sign-up tool that is easy to use on a mobile phone and also available in Spanish.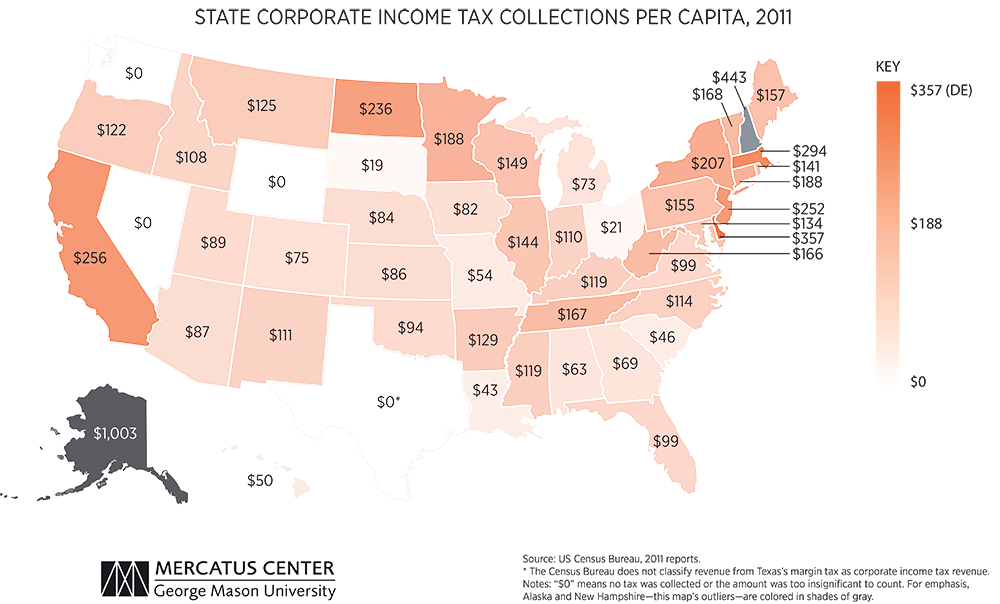 The deadline to sign up for monthly Child Tax Credit payments this year was November 15. If you are eligible for the Child Tax Credit but did not sign up for monthly payments by the November 15 deadline, you can still claim the full credit of up to $3,600 per child by filing your taxes next year.
The deadline to sign up for monthly Child Tax Credit payments this year was November 15. If you are eligible for the Child Tax Credit but did not sign up for monthly payments by the November 15 deadline, you can still claim the full credit of up to $3,600 per child by filing your taxes next year.
See how the Child Tax Credit works for families like yours:
-
Jamie
- Occupation: Teacher
- Income: $55,000
- Filing Status: Head of Household (Single Parent)
- Dependents: 3 children over age 6
Jamie
Jamie filed a tax return this year claiming 3 children and will receive part of her payment now to help her pay for the expenses of raising her kids. She’ll receive the rest next spring.
- Total Child Tax Credit: increased to $9,000 from $6,000 thanks to the American Rescue Plan ($3,000 for each child over age 6).
- Receives $4,500 in 6 monthly installments of $750 between July and December.

- Receives $4,500 after filing tax return next year.
-
Sam & Lee
- Occupation: Bus Driver and Electrician
- Income: $100,000
- Filing Status: Married
- Dependents: 2 children under age 6
Sam & Lee
Sam & Lee filed a tax return this year claiming 2 children and will receive part of their payment now to help her pay for the expenses of raising their kids. They’ll receive the rest next spring.
- Total Child Tax Credit: increased to $7,200 from $4,000 thanks to the American Rescue Plan ($3,600 for each child under age 6).
- Receives $3,600 in 6 monthly installments of $600 between July and December.
- Receives $3,600 after filing tax return next year.
-
Alex & Casey
- Occupation: Lawyer and Hospital Administrator
- Income: $350,000
- Filing Status: Married
- Dependents: 2 children over age 6
Alex & Casey
Alex & Casey filed a tax return this year claiming 2 children and will receive part of their payment now to help them pay for the expenses of raising their kids.
 They’ll receive the rest next spring.
They’ll receive the rest next spring.- Total Child Tax Credit: $4,000. Their credit did not increase because their income is too high ($2,000 for each child over age 6).
- Receives $2,000 in 6 monthly installments of $333 between July and December.
- Receives $2,000 after filing tax return next year.
-
Tim & Theresa
- Occupation: Home Health Aide and part-time Grocery Clerk
- Income: $24,000
- Filing Status: Do not file taxes; their income means they are not required to file
- Dependents: 1 child under age 6
Tim & Theresa
Tim and Theresa chose not to file a tax return as their income did not require them to do so. As a result, they did not receive payments automatically, but if they signed up by the November 15 deadline, they will receive part of their payment this year to help them pay for the expenses of raising their child. They’ll receive the rest next spring when they file taxes.
 If Tim and Theresa did not sign up by the November 15 deadline, they can still claim the full Child Tax Credit by filing their taxes next year.
If Tim and Theresa did not sign up by the November 15 deadline, they can still claim the full Child Tax Credit by filing their taxes next year.- Total Child Tax Credit: increased to $3,600 from $1,400 thanks to the American Rescue Plan ($3,600 for their child under age 6). If they signed up by July:
- Received $1,800 in 6 monthly installments of $300 between July and December.
- Receives $1,800 next spring when they file taxes.
- Automatically enrolled for a third-round stimulus check of $4,200, and up to $4,700 by claiming the 2020 Recovery Rebate Credit.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Child Tax Credit:
Overview
Who is eligible for the Child Tax Credit?
Getting your payments
What if I didn’t file taxes last year or the year before?
Will this affect other benefits I receive?
Spread the word about these important benefits:
For more information, visit the IRS page on Child Tax Credit.
Download the Child Tax Credit explainer (PDF).
ZIP Code-level data on eligible non-filers is available from the Department of Treasury: PDF | XLSX
The Child Tax Credit Toolkit
Spread the Word
What is the Child Tax Credit (CTC)? – Get It Back
What is the Child Tax Credit (CTC)?
This tax credit helps offset the costs of raising kids and is worth up to $3,600 for each child under 6 years old and $3,000 for each child between 6 and 17 years old. You can get half of your credit through monthly payments in 2021 and the other half in 2022 when you file a tax return. You can get the tax credit even if you don’t have recent earnings and don’t normally file taxes by visiting GetCTC.org through November 15, 2022 at 11:59 pm PT. Learn more about monthly payments and new changes to the Child Tax Credit.
Raising children is expensive—recent reports show that the cost of raising a child is over $200,000 throughout the child’s lifetime. The Child Tax Credit (CTC) can give you back money at tax time to help with those costs. If you owe taxes, the CTC can reduce the amount of income taxes you owe. If you make less than about $75,000 ($150,000 for married couples and $112,500 for heads of households) and your credit is more than the taxes you owe, you get the extra money back in your tax refund. If you don’t owe taxes, you will get the full amount of the CTC as a tax refund.
The Child Tax Credit (CTC) can give you back money at tax time to help with those costs. If you owe taxes, the CTC can reduce the amount of income taxes you owe. If you make less than about $75,000 ($150,000 for married couples and $112,500 for heads of households) and your credit is more than the taxes you owe, you get the extra money back in your tax refund. If you don’t owe taxes, you will get the full amount of the CTC as a tax refund.
Click on any of the following links to jump to a section:
- How much can I get with the CTC?
- Am I eligible for the CTC?
- Credit for Other Dependents
- How to claim the CTC
Depending on your income and family size, the CTC is worth up to $3,600 per child under 6 years old and $3,000 for each child between ages 6 and 17. CTC amounts start to phase-out when you make $75,000 ($150,000 for married couples and $112,500 for heads of households). Each $1,000 of income above the phase-out level reduces your CTC amount by $50.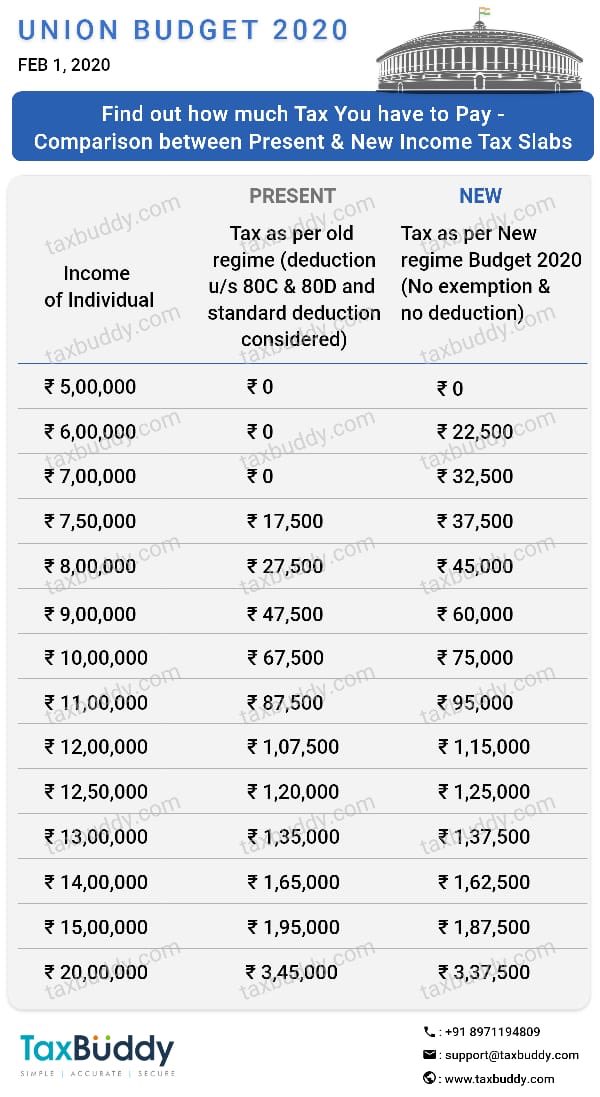
If you don’t owe taxes or your credit is more than the taxes you owe, you get the extra money back in your tax refund.
There are three main criteria to claim the CTC:
- Income: You do not need to have earnings.
- Qualifying Child: Children claimed for the CTC must be a “qualifying child”. See below for details.
- Taxpayer Identification Number: You and your spouse need to have a social security number (SSN) or an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN).
To claim children for the CTC, they must pass the following tests to be a “qualifying child”:
- Relationship: The child must be your son, daughter, grandchild, stepchild or adopted child; younger sibling, step-sibling, half-sibling, or their descendent; or a foster child placed with you by a government agency.
- Age: The child must be 17 or under on December 31, 2021.
- Residency: The child must live with you in the U.
 S. for more than half the year. Time living together doesn’t have to be consecutive. There is an exception for non-custodial parents who are permitted by the custodial parent to claim the child as a dependent (a waiver form signed by the custodial parent is required).
S. for more than half the year. Time living together doesn’t have to be consecutive. There is an exception for non-custodial parents who are permitted by the custodial parent to claim the child as a dependent (a waiver form signed by the custodial parent is required). - Taxpayer Identification Number: Children claimed for the CTC must have a valid SSN. This is a change from previous years when children could have an SSN or an ITIN.
- Dependency: The child must be considered a dependent for tax filing purposes.
A $500 non-refundable credit is available for families with qualifying dependents who can’t be claimed for the CTC. This includes children with an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number who otherwise qualify for the CTC. Additionally, qualifying relatives (like dependent parents) and even dependents who aren’t related to you, but live with you, can be claimed for this credit.
Since this credit is non-refundable, it can only help reduce taxes owed.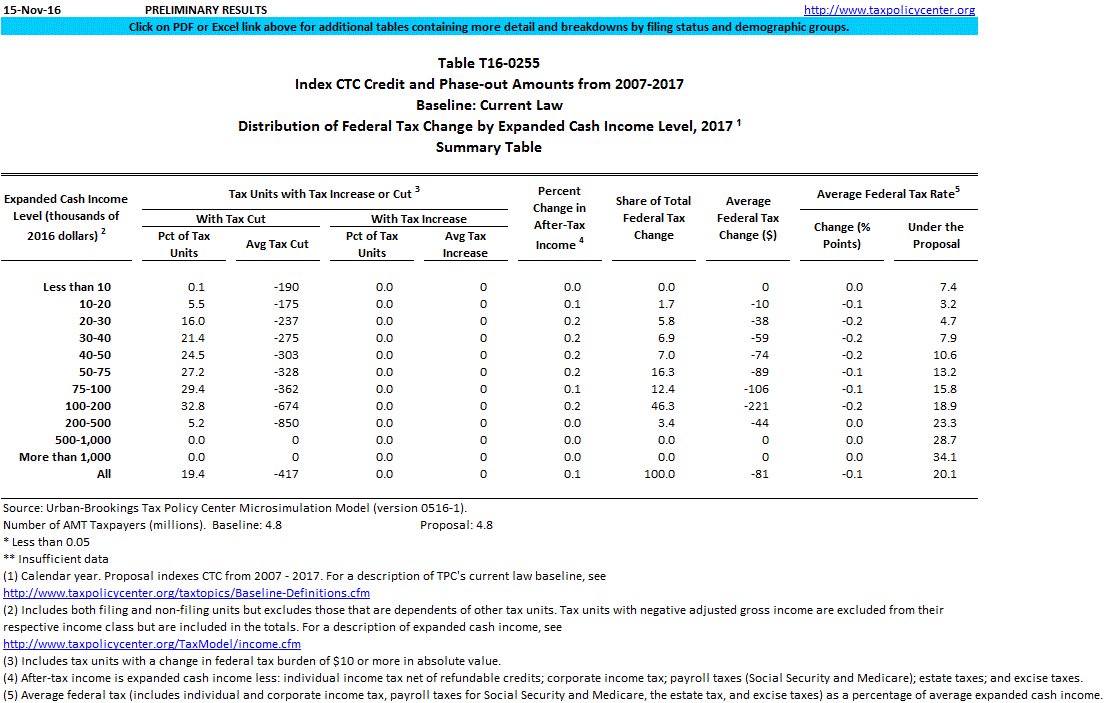 If you can claim both this credit and the CTC, this will be applied first to lower your taxable income.
If you can claim both this credit and the CTC, this will be applied first to lower your taxable income.
There are two steps to signing up for the CTC. To get the advance payments, you had to file 2020 taxes (which you file in 2021) or submitted your info to the IRS through the 2021 Non-filer portal (this tool is now closed) or GetCTC.org. If you did not sign up for advance payments, you can still get the full credit by filing a 2021 tax return (which you file in 2022).
Even if you received monthly payments, you must file a tax return to get the other half of your credit. In January 2022, the IRS sent Letter 6419 that tells you the total amount of advance payments sent to you in 2021. You can either use this letter or your IRS account to find your CTC amount. On your 2021 tax return (which you file in 2022), you may need to refer to this notice to claim your remaining CTC. Learn more in this blog on Letter 6419.
Going to a paid tax preparer is expensive and reduces your tax refund.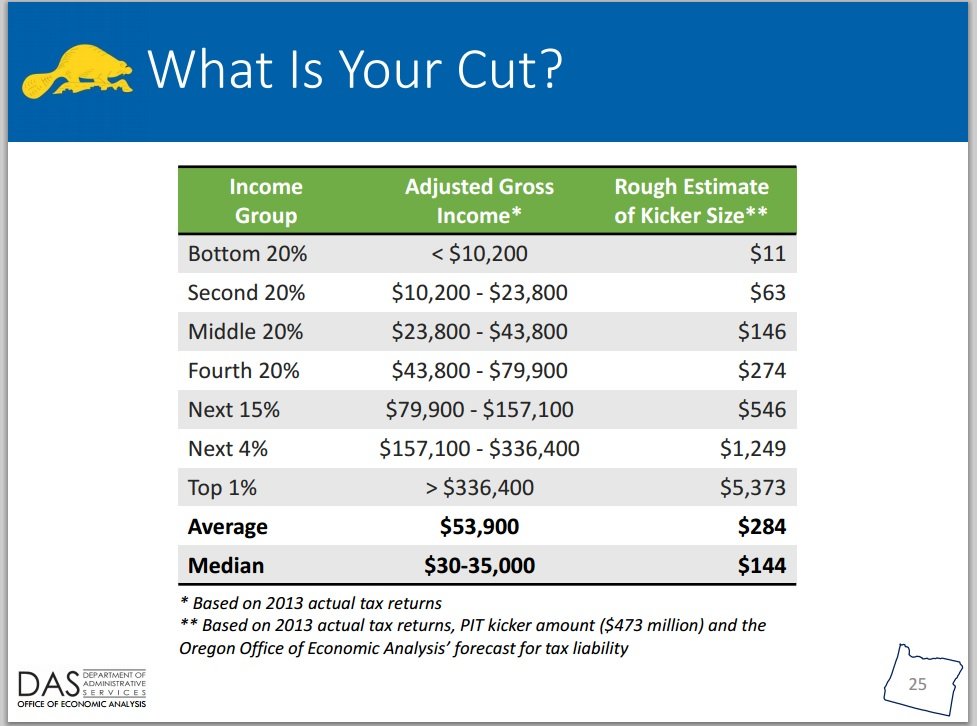 Luckily, there are free options available. You can visit GetCTC.org through November 15, 2022 to get the CTC and any missing amount of your third stimulus check. Use GetYourRefund.org by October 1, 2022 if you are also eligible for other tax credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or the first and second stimulus checks.
Luckily, there are free options available. You can visit GetCTC.org through November 15, 2022 to get the CTC and any missing amount of your third stimulus check. Use GetYourRefund.org by October 1, 2022 if you are also eligible for other tax credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or the first and second stimulus checks.
The latest
By Christine Tran, 2021 Get It Back Campaign Intern & Reagan Van Coutren,…
Internet access is essential for work, school, healthcare, and more. The Affordable Connectivity…
If you receive unemployment compensation, your benefits are taxable. You will need to…
Latvian State Portal
- Home
- Life events
- Finances and taxes
- Work, taxes and tax book
Life events
02. 11.2020.
11.2020.
One of the most significant situations in life is the beginning of a new employment relationship.
The first employment relationship can be started from the age of 13. There are special regulations for the employment of minors. However, it is important for an employee of any age to know how to use government-provided e-solutions and services for a successful employment relationship.
For information about the conditions and services that are essential before starting work and were in an employment relationship, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the sections below.
Rhododendron from estilo do site daApple, que usa um truque com checkBox para, solução 100% in CSS Para mostrar ou recolher um Men. Aqui troque o checkBox Por Divs e Links.
At the beginning of a career, we often face doubts whether a certain field of activity is suitable for us and the work will bring joy, or whether we are strong enough and competitive in this area. Various tests are available at the State Employment Agency (SEA) career opportunities for learning to determine interests, abilities and motivation. Self-help will help you decide which area of professional activity is most suitable for you. Tests will also be a good helper for those who have been working in any area of professional activity for a long time, but want to develop their career in another direction.
Various tests are available at the State Employment Agency (SEA) career opportunities for learning to determine interests, abilities and motivation. Self-help will help you decide which area of professional activity is most suitable for you. Tests will also be a good helper for those who have been working in any area of professional activity for a long time, but want to develop their career in another direction.
If you need help interpreting your career test results , eligibility, education, or job search, use GAS career counseling and other career services. With the help of the GAS in the e-learning module “Preparing a letter of motivation and preparing for a job interview”, you can prepare for a job interview, master the course of life and work (CV) and prepare a letter of motivation. At the end of the training, a knowledge test may be completed.
Job descriptions are also available in electronic form Description of professions in catalog .
Use the Labor Market Forecasting Tool and check out changes in labor demand across occupations and industry groups, regions and the country as a whole. Additionally (by clicking on a profession), information is available on the number of employees and the average remuneration by profession.
After finding out the areas of interest and relevant areas of activity, you can familiarize yourself with job offers, as well as create or update your CV on the corporate portal GAZ . The portal is suitable for both employees and employers. This covers all vacancies registered with GAZ and its use is free of charge.
When planning to enter into a new employment relationship it is important to be sure that the future employer, whether it is a business or another institution, is in good faith and acts in accordance with the laws of the state. With the help of the Business Register (UR) website search engine, it is possible to check basic information about registered registries and find out the business reputation of a potential employer, for example, information on business insolvency proceedings, commercial liens or liquidation.
Detailed information about a legal entity or natural person , including insolvency proceedings of an individual, an insolvency administrator, can be obtained using the e-service “Issue of information from the information website of the register of enterprises”.
In the register insolvency, it is possible to find out the insolvency status by searching for information by the debtor's registration number, first name or last name
With the help of the State Revenue Service (SRS) Tax Debtors List, you can find out if the company has suspended economic activity, if the potential employer is between those those who pay less than the national minimum monthly wage, as a whole, paid taxes in the previous year.
Payroll tax book (ANG) is a section of the electronic declaration system of the State Revenue Service (SRS). From June 1, 2014, it is available only in the form of an electronic document and is contained in the SRS.
In the SRS EDS section “Payroll Tax Book” it is possible to: The payroll tax book ensures the application of the non-taxable minimum and allows you to make entries on the basis of which the employer applies the established tax benefits. Entries about dependents in the payroll tax book must be made by each resident himself. For persons who have not been assigned the payroll tax book , you must connect the SRS EDS, and it must be activated by clicking the “open” button in the “payroll tax book” section, and then “get the payroll tax book ". The payroll tax book must be submitted to the person's main place of income . For example, if a person has two jobs, then the payroll tax book can only be filed in one of them. If the SRS does not have information confirming your right to tax benefits or additional tax benefits , you must submit to the SRS information justifying their application. These documents must be submitted electronically. Open the SRS EDS section “prepare a document” and select “from the form”. Then, in the "other" group of documents, open "information in the state revenue service", where you can add the scanned document and fill in the comment box. Electronically with a secure electronic signature, a confirmed document can be sent to the SRS using an e-address or to the official e-mail address of the institution [email protected]. Also, the said documents can also be submitted in paper form at any SRS customer service center, as well as by presenting an identity document to the SRS employee. For individuals who cannot use the EDS SRS, the SRS customer service centers provide assistance in opening an electronic fee tax book, as well as in printing out the information contained in it. In order to receive personal income tax benefits , dependent persons must be registered with the State Revenue Service (SRS) when making an entry in their electronic payroll tax book. To add a dependent, connect SRS Electronic Declaration System and open the payroll tax book in your individual profile. In the payroll tax book, in the “dependants” section, click the “add dependent” button. Typically, the system can automatically identify individuals who may be dependents. In this case, you must select the proposed dependent, fill in the necessary details (start date, justification, degree of relationship) and click the “Approve” button. If the dependent is not automatically proposed, it must be identified with the first name, last name and personal code. If you can no longer apply the tax relief for a dependent person , you must inform the SRS about this within 10 days, indicating the end date of the dependent in your payroll tax book. If a dependent starts an employment relationship , then the dependent status is lost. However, for example, if the monthly income received by the student, for example, income from hired labor, does not exceed the established amount of tax relief (in 2021 - 250 euros per month), the benefit for the parent of dependents remains. The exception that parental tax relief is maintained regardless of income from employment is if a student under the age of 19 works in paid work during the summer months from 1 June to 31 August. To remove a person from the dependency record, you can use one of the following methods: As school ends, more and more young people are starting to look for summer job opportunities. Parents are also starting to think about how to take care of their underage children. The State Employment Agency (SEA), in cooperation with entrepreneurs, local governments and state institutions, offers the opportunity to work in the summer for ages 15 to 20 who are studying and continuing their education in educational institutions of general, special or vocational education in the next academic year. More information about the event is available here. You can also ask your local government about summer job opportunities. Employment of children in permanent jobs is prohibited. For the purposes of the Act, a child is a person under 15 years of age or who, until the age of 18, continues to receive basic education. In exceptional cases, the employment of a child under 13 years of age is provided for in Part 3 of Article 37 of the Labor Law. Employment of a child under 13 years of age is allowed only in exceptional cases, if one of the parents (guardian) has given written consent and received a Permit from the State Labor Inspectorate (VDI) for the child to be employed as a performer in cultural, artistic, sports and promotional events, if such an activity is not harmful to the safety, health, morals and development of the child. Such an occupation should not interfere with the education of the child. The VDI website provides instructions on how to complete the authorization form. Useful information about summer job opportunities can be found on the website of the State Labor Inspectorate (VDI) www. Information about a safe working environment for young people can be found on the homepage www.stradavesels.lv in the “Materials” section, and job search tips can be found on the homepage www.atkrapies.lv in the “practical advice” section. If a child who is under the age of 19 is studying in a general, vocational, higher or special educational institution works in a paid job only during the summer months (from June 1 to August 31), the parents retain tax benefits for a dependent person . For more information about paying taxes, see the State Revenue Service on the website www.vid.gov.lv. But if you want to get advice from the State Labor Inspectorate (VDI) or get VDI action on labor rights or labor protection, use the e-service “Application to the Labor Inspectorate and receive a response from the Labor Inspectorate” on the Latvija.lv portal. The application can include a request, complaint, suggestion or question within the scope of the VDI. If an accident occurs at the workplace, it must be reported to VDI. This can be conveniently done using the VDI e-service “Reporting an Accident at Work”. Disability sheets (sickness sheets) are opened, extended and closed electronically. This is done by the patient's family doctor or attending physician. If a person has entered into an employment relationship and at that time falls ill and is unable to perform work duties, she is entitled to sickness benefit, which is granted on the basis of a sickness certificate issued by a doctor. Socially insured person from the age of 15. From this age, the employer pays mandatory social insurance contributions for the person, on which he also depends or will be entitled to sickness benefit and in what amount it will be assigned. The right to sickness benefit only applies if compulsory social contributions to health insurance have been made for at least 3 months during the last 6 months before the first day of incapacity for work or at least 6 months during the last 24 months. When you recover and are ready to return to work , the doctor will electronically complete the disability certificate. As soon as the certificate of incapacity for work is concluded , this information is automatically sent to the State Revenue Service (SRS). Your employer in the SRS will see this information the next day after the conclusion of the disability certificate. If a certificate of incapacity for work B has been issued, information about this is also available to the State Social Insurance Agency (VSAA). If the disability certificate was closed, no further action is required. A sick leave certificate is issued for the first 10 calendar days and sickness money for the working days in which it is necessary to work is paid by the employer. If you have received a certificate of incapacity for work B , you can claim sickness benefit from the SSIA within 6 months from the first day of temporary incapacity for work. Information about certificates of incapacity for work, their statuses and numbers is available on the portal Latvija.lv e-service “received certificates of incapacity for work”. If you work at two workplaces , in the event of illness, the certificate of incapacity for work will be extended to both workplaces. This means that sickness benefit will be calculated and paid in both jobs. For more information about getting sick leave, read the life situations “Actions in case of illness” and “Getting sick leave”. Employer is obliged to pay statutory taxes for his employees - state compulsory social insurance contributions (part of employer and employee contributions) and personal income tax. The mandatory contribution rate is 34.09%, of which 23.59% is paid by the employer and 10.50% by the employee. The employee is provided with a minimum personal income tax exemption. Its size, as well as the possibility of obtaining tax benefits, affects the number of dependents of the employee. Both part of the employee's mandatory contributions and the amount of personal income tax are calculated from the employee's income and paid to the state budget by the employer. Sometimes an employee may have doubts about whether the employer pays for the taxes they set - mandatory contributions to state social insurance and personal income tax. If you want to check whether your employer pays social insurance contributions for you, use the e-service “Information on social insurance contributions and insurance periods” on the Latvija.lv portal. It is important to know whether social contributions are made for you, because this determines whether or not you will be entitled to social insurance benefits, including sickness benefit, and how much it will be. To check the amount of personal income tax withheld from your remuneration , you can use the Electronic Declaration System (EDS) of the State Revenue Service (SRS). In the “reports” section, select “information submitted by taxpayers”. As a result, you will receive information on both social contributions and personal income tax withheld. In the SRS, EDS will find information about your periods of employment, wages paid per year, sickness benefits and economic activities, if you are. Remotely and at any time convenient for themselves and at any time convenient for themselves, anyone in the country can get knowledge about taxes, the state and social budget, the activities of the social insurance system in the e-learning module of the State Employment Agency (SEA) “Financial literacy". The training content includes both theoretical explanation and audio and video materials and dialogue simulations, as well as self-testing opportunities. At the end of the training, a knowledge test may be completed. In order for an intern to officially enter an internship at any enterprise or structure , it is necessary to conclude an internship contract. The law establishes two types of contracts: The law does not establish an obligation for an enterprise to pay a remuneration to an intern for the implementation of an internship. However, if the trainee agrees in writing with the place of practice, such remuneration to the trainee may be paid. Trainee remuneration is subject to personal income tax , as well as mandatory contributions to state social insurance must be paid from it. The enterprise must make deductions from the remuneration established for the trainee, paying it to the budget. In certain cases in internship practice, the remuneration received - a scholarship - is not included in taxable income. Scholarships up to 280 EUR per month, which are paid by the place of practice to a trainee who masters the study program in accordance with the procedure established by the Cabinet, in which he organizes and implements studies based on the working environment, are not subject to tax. Information Center of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (ICMID) State Social Insurance Agency (SSIA) National Health Service (HCZ) State Labor Inspectorate (SLI) Register of Enterprises (RP) 9001D5 State Revenue Service8 9001D5 State Employment Agency (SEA) Did you find the information you are looking for on this page? This website is part of the Your Europe Portal. Give us feedback using the European Commission Feedback Form. Quality review Read more about the country's business ecosystem in Rb.ru: where to go to startups in Israel 
 In the “Dependents” section, click the “Cancel” button. Specify the date from which you want to terminate the dependent, and click the "confirm" button.
In the “Dependents” section, click the “Cancel” button. Specify the date from which you want to terminate the dependent, and click the "confirm" button. 
 vdi.gov.lv.
vdi.gov.lv. 
 To receive benefits for the period specified in the disability certificate, you must submit an application to the SSIA. It can be done:
To receive benefits for the period specified in the disability certificate, you must submit an application to the SSIA. It can be done:

 If the trainee is a minor, instead of him the agreement on educational practice is concluded by the parent or legal representative of the trainee;
If the trainee is a minor, instead of him the agreement on educational practice is concluded by the parent or legal representative of the trainee; 
6 Taxes for individuals
Taxes for individuals
Tax resident status
Tax resident status in Israel is assigned if a person spends 183 days a year or more in the country. There is also the principle of the "center of vital interests", which takes into account family, social and economic ties with Israel. If you have confirmed connections, it is enough to be in Israel only 30 days a year.
There is also the principle of the "center of vital interests", which takes into account family, social and economic ties with Israel. If you have confirmed connections, it is enough to be in Israel only 30 days a year.
“If your family lives in Israel, if you spend more time here than in any other country in the world, it makes no sense to count the days and try to spend less than six months a year in Israel, this will not get rid of the status of a tax resident” , explains Eli Gervits, attorney and president of the Israeli Russian-language bar association Eli (Ilya) Gervits.
Income tax (“mas akhnasa”)
Income tax applies to all personal income of individuals: wages, business income (except for agricultural production), pension benefits and others.
Progressive tax rate depending on the amount of income:
| Monthly income (shekel) | Annual income (shekel) | Rate |
| Up to 6 290 | Up to 75 480 | ten% |
| 6 291 - 9 030 | 75 481 - 108 360 | fourteen% |
| 9 031 — 14 490 | 108 361 - 173 880 | twenty% |
| 14 491 - 20 140 | 173 881 - 241 680 | 31% |
| 20 141 - 41 910 | 241 681 - 502 920 | 35% |
| Over 41 911 | Over 502 921 | 47% |
Individuals whose annual income exceeds NIS 647,640 pay an additional 3% on this amount. This is the so-called tax on especially high income with a total rate of 50%.
This is the so-called tax on especially high income with a total rate of 50%.
An example of income tax calculation for a salary of 100,000 shekels per year:
75,480 x 10% + (100,000 - 75,480) x 14% = 7,548 + 3,433 = NIS 10,981
their employer. You need to file a tax return yourself in the following cases:
- if you have several jobs or sources of income;
- if your annual earnings exceed NIS 590,000;
- if you are a non-resident and income tax is not withheld at source.
In general, the principles of taxation of residents and non-residents are the same, but they have different benefits. There are also additional rules for new immigrants, returnees and expats.
Benefits for residents
Israel has a system of "preferential tax units" ("nekudot zikuy"), which allows you to reduce income taxes.
Certain categories of persons are entitled to tax units, each of which in 2021 gives a tax deduction of 218 shekels per month or 2616 per year.
Basic tax units:
- Israeli citizen - 2.25
- Woman - 0.5
- Minor worker (16-18 years old) - 1
- Benefits for children - from 0.5 to 2.5 depending on the age of the child
- Soldiers - 1 to 2 depending on service life
Thus, every Israeli citizen has at least 2.25 points, which gives 5,886 shekels per year. If your income tax does not exceed this amount, then it is actually repaid at the expense of "nekudot zikuy".
Benefits for immigrants and returnees
Immigrants and returnees who return to Israel after 10 years of absence from Israel are subject to special tax rules.
During the first 18 months of their stay in the country, they are entitled to 3 preferential units of "nekudot zikui", the next year - 2 and the third - 1.
An important benefit is a 10-year exemption from tax on most types of passive income earned abroad.
These include dividends, interest, rent, royalties, pensions, and so on.
For example, if you moved to Israel, but at the same time you rent an apartment in Russia, you do not need to pay rental income tax.
Capital gains from the sale of foreign assets will not be taxed for the first 10 years. If you become a tax resident in 2021 and sell an apartment in Russia, say, in 2026, then you will not pay income tax.
Discounts for qualified expats
Experts and lecturers invited from abroad are also eligible for discounts. This applies to highly specialized knowledge and skills that Israeli specialists do not possess.
The confirmed status of a foreign expert allows you to pay no more than 25% tax on a certain amount of income for 3 years, with a possible extension of up to 5 years.
During the first 12 months of employment in Israel, living expenses (up to NIS 330 per day or 50% of wages) and some utilities can also be deducted from tax. To do this, you must keep the lease agreement, hotel bills and utility bills.
To do this, you must keep the lease agreement, hotel bills and utility bills.
Insurance contributions (Bituah Leumi)
In addition to income tax, individuals pay national insurance contributions and health insurance tax.
Taxes for investors
Special rules apply to passive income of individuals: from interest, dividends, royalties and rent.
For tax residents of other countries with which Israel has tax treaties, tax rates may be lower than for Israelis. You can read more about the terms of the Russian-Israeli agreement here.
Interest
Interest income is taxed at the rate of 25%. If you invest in listed securities or financial institutions, the rate can be reduced to 15%.
Dividends
Dividends are taxed at 25%. For some businesses that are subject to the Capital Investment Encouragement Act, a reduced rate of 20% may apply.
Royalties
Income from the sale of the right to use intellectual property is subject to taxation at the rate of 26.5%.
Purchase of real estate
Purchased real estate is subject to tax, the rate of which depends on the type of object, value, status of the buyer (resident, returnee or non-resident) and the presence of other objects in the property. The tax is called "mas rehisha".
For residents and non-residents, there is a progressive tax rate starting from 5% on property worth up to 1.3 million shekels (about $400,000). The maximum tax can reach 10% (for an object more expensive than 17.8 million shekels).
When a resident purchases a first home, up to NIS 1.7 million will not be taxed. “The state supports Israelis who want to solve their housing problem - transactions worth up to half a million dollars are exempt from taxes ,” says Anastasia Faley, an analyst at the Prian. ru portal. - But it is important to understand: if in Russia housing of such a cost belongs to the premium segment, then in Israel it is the middle class.
ru portal. - But it is important to understand: if in Russia housing of such a cost belongs to the premium segment, then in Israel it is the middle class.
By 2021, the cost of a 4-room apartment (and this is the most common type of housing in Israel) amounted to 1.65 million shekels on average in the country, and, for example, in expensive Tel Aviv - 3.5 million shekels, that is about $1 million."
For new immigrants, the tax on real estate worth up to 1.8 million shekels is 0.5%, more - 5%. According to Anastasia Faley, in some cases, especially when buying expensive real estate, it is more profitable to be a new repatriate than a native citizen of the country.
Interestingly, even those who have not actually moved to Israel yet, but are going to do so in the next two years, can apply for a tax break.
No tax is charged if you purchase real estate on the primary market from a licensed developer.
Property maintenance
There is a municipal fee for property owners in Israel. Its size depends on the location and area of the object and may vary several times. An average apartment costs about 200 shekels per month.
Its size depends on the location and area of the object and may vary several times. An average apartment costs about 200 shekels per month.
Another tax that you will have to pay if you significantly improve your home, thereby increasing its value, is the tax on improvements. It is 50% of the amount by which the value of the object has increased.
Renting
Rental income is taxed on a progressive scale in the same way as the active income of an individual, only in this case the minimum rate will be 31% (for persons over 60 years old - 10%). From the taxable amount, you can deduct the cost of maintaining housing: repairs, depreciation, and so on.
However, if the rental is not a business and the property is rented by one individual to another for living, then you can choose the second option - pay only 10% tax, but without deducting current expenses. In this case, it is important to pay the tax within 30 days after the end of the tax year.
When renting out several apartments, you can choose only one taxation option. For the rental of overseas property, a flat tax rate of 15% applies without the possibility of deducting related costs.
Income up to NIS 5,070 per month (for 2021) is not taxed. If it exceeds this amount by no more than twice, that is, within 10,140 shekels, then you can apply for a partial exemption. In this case, the mechanics of calculating the tax-free amount is not the most obvious, so we will show it right away with an example.
Let's say your income from renting out an apartment is NIS 6,000. The maximum amount exempt from tax in 2021 is NIS 5,070. It is not final yet - your amount will be less. We subtract 5,070 from your income and get the difference - 930 shekels. Next, subtract this amount from the "ceiling" (5,070) and get your tax-free amount - 4,140 shekels. Accordingly, you will pay tax only on the remaining 1,860 shekels.
Tel Aviv
Sale of real estate
When selling a property, a capital gains tax (“mas shevah”) is charged - 25% of net profit, after deducting related expenses.
Israeli residents who sell property every 4 years or their only home are exempt from tax. In the second case, it is important that in the previous 18 months a person did not sell either this or any other apartment.
Corporate taxes
The principal form of business organization for a corporation is Limited Liability Company, Ltd.
Companies pay corporate tax at a rate of 23%. For firms registered in Israel, all worldwide income is subject to taxation, for foreign companies with local branches - only accrued in Israel.
Dividends received from another Israeli company as a result of its income accrued in Israel are exempt from tax. Dividends from abroad, or dividends derived from a company's overseas income, will be taxed at a rate of 25%.
Insurance payments for employees (Bituah Leumi) total from 3.5 to 17.5%. You can use a calculator to calculate them.
Goods and services are subject to VAT at the standard rate of 17%. There is no tax on some tourist services and the sale of vegetables and fruits.
Preferred Enterprise
Preferred Enterprise status can be achieved if the company contributes to the economy's productive potential and employment opportunities. The corporate tax rate is 7.5% (in priority regions) or 16% (in all other regions).
Special Preferred Enterprise
This is a special treatment for very large companies that invest dynamically in productive assets, R&D and job creation.
Such a company must demonstrate high income (from 1 billion shekels per year, as well as participation in a group of companies with a gross income of 10 billion per year) and a serious contribution to the national economy.
For the first 10 years, the tax rate will be 5 or 8% depending on the region. Further, if the company does not provide a new investment program, the Preferred Enterprise mode will be applied to it.
Further, if the company does not provide a new investment program, the Preferred Enterprise mode will be applied to it.
Taxes for small businesses
There are two forms of IP: “osek patur” and “osek murshe”. Only a resident can register them. There is a small exception for foreigners who acquire citizenship. In this case, it is allowed to register a joint business with a local representative, who will temporarily become a tax guarantor. After obtaining citizenship, it will already be possible to re-register the business for yourself.
Entrepreneurs pay income tax from 10 to 50% and insurance premiums. "Esek Patur" is more beneficial in terms of taxes, as it allows you not to pay VAT, and also involves simpler tax reporting. It is suitable for entrepreneurs who sell goods or services to individuals.
An accountant, consultant or dentist can register this way, for example. In this case, the business turnover is limited, the maximum amount changes annually, on average it is 100,000 shekels.
Fruit shop in Tel Aviv
If the business exceeds the maximum allowable turnover, it will go under the rules of taxation "esek murshe" with the need to pay VAT on all goods and services. At the same time, part of the funds spent for business development (purchase of raw materials, maintenance of transport, and so on) can be returned.
“In Israel, the principle of tax neutrality is preached, therefore, apart from low income levels, there is no significant difference between the different ways of “withdrawing” profits: through corporate income tax and dividend tax, through your salary from your company or through an individual entrepreneur. In the last two cases - with the payment of social tax and income tax, - says Eli Gerwitz.
Taxes for innovative companies
The active development of Israel's technology cluster, among other things, is due to government grants and tax incentives for businesses and investors.
Companies investing in R&D are eligible for a deduction for these expenses in the first 2 or 3 years, depending on the industry. The priorities are industry, transport, agriculture and energy.
Individuals investing in R&D companies can deduct the invested funds from the taxation of any other income - up to NIS 5 million for each company. If the investor is a foreign company with an Israeli subsidiary, then it can deduct the investment amount over a three-year period.
In addition, there are special taxation regimes for large enterprises:
Preferred technological enterprise
Preferred technological enterprise status is granted if an IT company spends more than 7% of its income on R&D or is approved by the National Technology Innovation Authority.
The corporate tax rate ranges from 7.5 to 12% depending on the region. Dividend tax - 20%, a reduced rate of 4% may apply to dividends paid to a foreign parent company that owns at least 90% shares.