Gaining weight too fast pregnancy
Second trimester weight gain? That's probably normal!
Home / Preg-U / Science / Research / Gaining Weight “Too Fast” in your 2nd trimester? That’s Probably Normal.
At my 24-week appointment when I was pregnant with my first, I finally felt pretty good, happily ensconced in the “best” trimester. My nausea had faded, my energy was back, and I was working out again after a two-month hiatus.
Then came the weigh-in.
According to my doctor, I had gained “too much weight” in the last month. I was shocked. Up until then, my trajectory predicted a healthy 30 pound gain. But now, she explained, I was projected to gain 40 lbs. Five pounds over the recommended 25-35 lbs.
The lecture began – “Eat only half the sandwich. Don’t eat for two.”
Okay, I’ll confess, at that point, I stopped listening, and started wondering: Does this even make sense?
Is gaining weight in pregnancy really supposed to be constant? The same amount week after week, month after month – as she and her nifty weight gain chart seem to assume?
Should weight gain be consistent throughout pregnancy?
The answer? Of course not.
The good folks at the Institutes of Medicine (IOM) who came up the current weight gain guidelines for pregnant women agree:
“The pattern of Gestational Weight Gain is most commonly described as sigmoidal, with mean weight gains higher in the second than the third trimester across BMI categories, except for obese women”
– IOM 2009 report on pregnancy weight gain, pg. 101.
Unfortunately, the IOM explained this in such obscure researcher-speak that the message may have gotten lost.
In plain English: pregnant women usually gain more weight in their second trimesters than in their third.
Yup, that’s right. A higher second trimester weight gain is normal. You are not doing something wrong. You are not destined to put on too much weight by the end of pregnancy.
A higher second trimester weight gain is normal. You are not doing something wrong.
Go ahead and eat your whole darn sandwich.
Why do women gain the most weight in their second trimester?
For one, you add a ton of water weight in the second trimester. Did you notice that around month 5 you are suddenly constantly, unquenchable thirst, despite downing what feels like a gallon of water every day? It’s not all in your head, it’s biology.
In your second trimester, your belly swells up with a couple extra pounds of amniotic fluid and a rapidly growing uterus. Welcome to the world, bump! At the same time, your blood volume soars by nearly 50%.
Once you’re past your second trimester, weight gain usually slows down. (Unless you are lucky enough to have full body swelling, which can add an additional seven pounds of water weight in your arms and legs. Isn’t pregnancy fun!)
In your second trimester, your belly swells up with a couple extra pounds of amniotic fluid and a rapidly growing uterus. Welcome to the world, bump!
I do not mean to dismiss the real risks of gaining too much in pregnancy, especially for women who start out pregnancy with a high BMI. Women who go over the IOM guidelines (see below) are at higher risk for C-sections, for large babies with a risk of getting stuck on their way out (ouch!), and for difficulty losing weight postpartum.
Women who go over the IOM guidelines (see below) are at higher risk for C-sections, for large babies with a risk of getting stuck on their way out (ouch!), and for difficulty losing weight postpartum.
Very rapid weight gain (more than 2 lbs in a week) can signal preeclampsia, a serious and dangerous condition involving high blood pressure and protein in your urine. If you notice you a sudden jump in weight in a short period of time, definitely talk to your doctor.
When it comes to second trimester weight gain, keep this in mind:
Weight gain in one week of pregnancy does not predict weight gain in the next week.
So, for the majority of us without specific risk factors, let’s put this “trajectory” idea to rest?
Weight gain in pregnancy is not a steady climb. It’s not meant to be. And gaining a lot during your second trimester weight gain—that’s perfectly normal.
Enjoy your sandwich.
Looking for a perfect week-by-week nutrition guide? Check out our Baby Building Blocks Newsletter! It’s the what, when, why and how of prenatal nutrition.
This article was originally posted on expectingscience.com
YOUR PREGNANCY SMARTS. Delivered.
Sign up for the Preg U Newsletter!
How Can I Slow My Weight Gain?
How Can I Slow My Weight Gain
I want to be healthy for me & my baby
How Much Weight Should I Gain?
You should gain weight gradually during your pregnancy, with more of the weight gained in the last 3 months. Many health care providers suggest women gain weight at the following rate:
- 1 to 4 pounds total during the first 3 months (first trimester)
- 2 to 4 pounds per month during the 4th to 9th months (second and third trimesters)
The total amount of weight to gain during pregnancy depends on how much you weighed when you became pregnant. Talk with your health care provider and WIC nutritionist to find out what amount is right for you.
Talk with your health care provider and WIC nutritionist to find out what amount is right for you.
General Guidelines:
| Pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI) | BMI (kg/m2) | Total Weight Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Underweight | <18.5 | 28-40 pounds |
| Normal Weight | 18.5-24.9 | 25-35 pounds |
| Overweight | 25-29.9 | 15-25 pounds |
| Obese | ≥30 | 11-20 pounds |
Did you know? Women pregnant with multiples need to gain more weight to help support the growth of multiple babies. Normal weight women should gain 37-54 pounds, overweight, 31-50 pounds and obese, 25-42 pounds during pregnancy.
Risks of Gaining Too Much Weight
Women who gain extra weight during pregnancy are more likely to have…
- Gestational diabetes and high blood pressure
- Backaches, leg pain and varicose veins
- A cesarean section or other problems with delivery due to a larger than normal baby
- Trouble returning to pre-pregnancy weight
- Long term health problems from obesity
Did You Know? Gaining too much weight during pregnancy increases your baby’s risk of being overweight during childhood?
What Can I Do To Slow Weight Gain?
If you’re gaining more weight than recommended, talk to your health care provider or WIC nutritionist. You should never try to lose weight during pregnancy. But slowing weight gain can help you have a healthier pregnancy and delivery, and an easier time getting back to your pre-pregnancy weight.
You should never try to lose weight during pregnancy. But slowing weight gain can help you have a healthier pregnancy and delivery, and an easier time getting back to your pre-pregnancy weight.
To slow weight gain
- Enjoy your food, but eat less
- Avoid oversized portions
- Make half your plate fruits and vegetables
- Switch to fat-free or low-fat (1%) milk. Calcium- fortified soy milk is a good choice for those that choose not to drink milk.
- Make at least half your grains whole grains
- Drink water instead of sugary drinks
- Find your balance between food and physical activity
Did You Know? Pregnancy only requires around 300 extra calories a day.
Why Should I Exercise During Pregnancy?
Staying active during pregnancy will help you to slow weight gain and have a healthier pregnancy and delivery. Exercise is safe for most pregnant women. Talk to your health care provider to find out what type of physical activity is safe for you.
- Benefits of exercise during pregnancy
- Slows weight gain
- Helps with constipation, backaches
- Improves sleep
- Gives you more energy
- Improves mood
Did You Know? Women who exercise during pregnancy may have shorter labors and easier deliveries.
Guidelines for Exercise in Pregnancy
Avoid contact sports, activities that increase your risk of falling and jerky, bouncing movements.
- Don’t exercise on your back after the 1st trimester
- Avoid working out in very hot weather
- Exercise at least 30 minutes on all or most days of the week (150 minutes total per week)
- Warm up and cool down
- Take frequent breaks and drink plenty of fluids
- Never exercise to the point of exhaustion
Stop exercising and call your health care provider if you experience faintness, headache, pain, bleeding or have trouble walking.
References:
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Healthy Eating During Pregnancy
- Staying Healthy
- Pregnancy Weight Gain – ChooseMyPlate.
 org
org - Physical Activity Guidelines
- Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines
Pregnancy weight gain - What is BMI?
- Contents
Every woman gains a certain amount of weight during pregnancy. But in this case, it cannot be called superfluous, since each kilogram appears for a reason. You should not be afraid of such weight gain, because often after childbirth, most women manage to quickly return to their usual form. However, one should not “launch” oneself either - too rapid weight gain at each stage of pregnancy can have negative consequences. Everything should be in moderation, and in order to control it, you need to know in advance what should be the rate of weight gain during pregnancy.
What is the normal weight gain during pregnancy?
This indicator is individual. Some gain only 5-6 kg, feeling fine, having no problems with bearing a child. There are those who gain more than 20 kg, also without complaints and complications.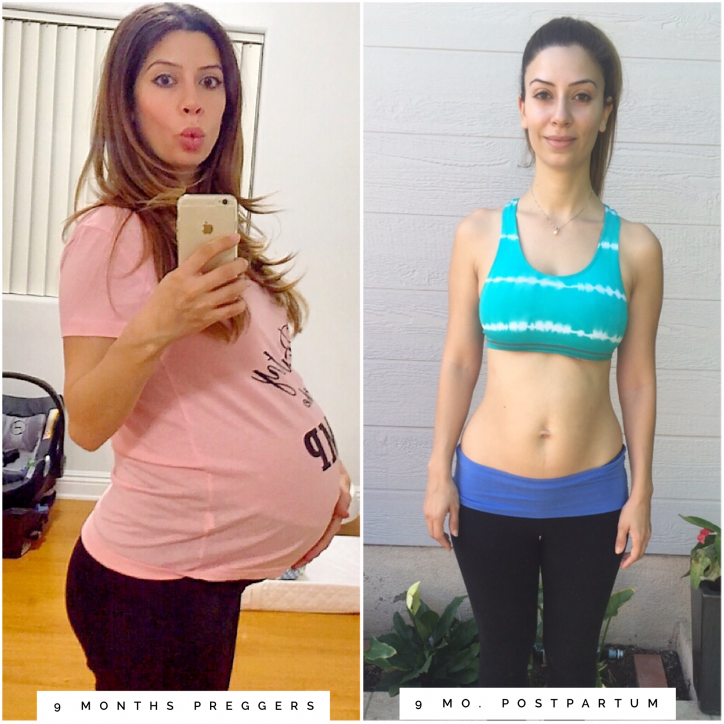 However, in most cases, the rate of weight gain during pregnancy is average between these values - 9-14 kg when carrying one child and 16-21 kg if the pregnancy is multiple.
However, in most cases, the rate of weight gain during pregnancy is average between these values - 9-14 kg when carrying one child and 16-21 kg if the pregnancy is multiple.
It is also important to remember that in the first trimester a pregnant woman may not notice weight gain. Firstly, the fetus is just being formed, and it is too early to talk about its growth. Secondly, many during this period have severe toxicosis, accompanied by a deterioration in appetite and vomiting. As a result of such conditions, a woman can, on the contrary, lose a couple of kilograms. Starting from the second trimester, weight gain becomes more noticeable. Usually it is about 1 kg per month. The sharpest jump can be seen in recent months - then a woman can recover more than 400 g per week.
Keep in mind that these are only generalized data, and should not be taken as a hard rate of weight gain during pregnancy. Only a doctor can determine whether this or that weight gain is acceptable for a woman and her fetus. This is especially true in cases where a pregnant woman has concomitant health problems, or she bears more than three children.
This is especially true in cases where a pregnant woman has concomitant health problems, or she bears more than three children.
What increases the weight of a pregnant woman?
So that a pregnant woman is not afraid of the fact that she is gaining kilograms, she needs to understand where they come from.
The main sources of weight gain are:
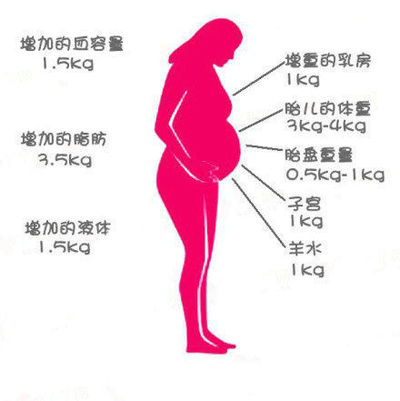
- Fetal weight. The child in the womb is getting bigger every day, respectively, this affects the weight indicator, adding up to 3-4 kg.
- Increased uterus and amniotic fluid volume. Usually, at their expense, a pregnant woman gains up to 2 kg before giving birth.
- Increased blood volume in the body. This indicator can vary greatly, but usually about 1.5 kg is assigned to it.
- The appearance of additional fluid in the body. Its weight can be from 1.5 to 3 kg.
Do not forget that in the last weeks before childbirth, a woman's mammary glands begin to increase - milk accumulates in them. This process increases the total weight by about 0.5 kg.
This process increases the total weight by about 0.5 kg.
Regardless of how a woman eats during pregnancy, avoiding the accumulation of body fat is extremely rare. The norm can be considered a situation when their weight does not exceed 3-4 kg. This indicator can be considered the most unstable. If a woman was actively involved in sports before pregnancy, she may gain less. If a pregnant woman allows herself to eat too much, or takes hormonal drugs to preserve the fetus, this can lead to a significant increase in this indicator.
What factors influence weight gain during pregnancy?
Although the sources of weight gain are clearly identified, there are internal and external factors that can affect the amount of weight gained.
The main ones are:
- Initial weight of a woman. Of course, this factor cannot be considered decisive, but it shows that usually thin women gain more extra pounds during pregnancy than obese women.
- Growth of a pregnant woman.
 Tall women tend to gain more kg.
Tall women tend to gain more kg. - Tendency to be overweight. If a woman has such a predisposition, she needs to be especially careful, because during pregnancy she can gain a lot of extra pounds.
- Strong increase in appetite. This factor is not common to everyone, but to the majority. Feeling a sharp increase in appetite, women can succumb to it, or vice versa - try to restrain themselves, controlling weight gain in themselves and in the fetus.
- The presence of toxicosis. If such conditions are frequent and severe, it can lead to weight loss, which is highly undesirable during pregnancy.
- Presence of comorbidities, such as diabetes. In this case, a violation of metabolic processes is possible, which will cause weight gain.
It is worth remembering that age can also affect the rate of weight gain. The older a woman is, the more difficult it is for her to control her weight gain during pregnancy. Therefore, for those who give birth in adulthood, it is important to pay special attention to this issue.
BMI when calculating weight gain
BMI is one of the basic concepts that can be used to control the process of weight gain during pregnancy. This indicator is calculated quite simply - according to the formula: the usual weight of a person must be divided by his height (m) squared.
The resulting figure can be attributed to 3 types of figure:
- up to 19.8 (Group 1) - the thinnest women
- 19.8-26 (Group 2) - women with an average build
- from 26 (3 group) - obese women
For example
With a height of 1.75 m, a woman weighs 65 kg.
- 1.75*1.75≈3
- 65:3=21.6
It is the body mass index that is used when calculating the rate of weight gain during pregnancy by trimesters or weeks. The easiest way to do this is to use a weight gain calculator.
Risk of being underweight during pregnancy
Severe weight loss during pregnancy or simply underweight can adversely affect the health of both the woman and the baby.
Possible risks are:
- premature birth, which can be very dangerous for both the mother and the baby
- too low birth weight, which can cause health problems
- baby's weight in the first months after birth
To exclude the possibility of such unpleasant situations, it is important to notice the underweight in time and determine its cause. It may consist in malnutrition, severe toxicosis, etc. Usually, such conditions can be successfully corrected by taking special medications or diets.
What is the danger of too rapid weight gain during pregnancy?
Rapid weight gain during pregnancy, as well as its reduction, is fraught with the following pathologies:
- development of gestational diabetes mellitus
- increased blood pressure
- risk of preeclampsia - severe deterioration of the pregnant woman in the last weeks before childbirth pain
- premature aging of the placenta
- metabolic disorder
It is important to remember that if the mother-to-be recovers rapidly, the same happens to the fetus. Its large weight can complicate the process of natural childbirth, because of which you will have to do a caesarean. It also increases the risk of preterm birth with complications.
Its large weight can complicate the process of natural childbirth, because of which you will have to do a caesarean. It also increases the risk of preterm birth with complications.
How to maintain a correct BMI during pregnancy: nutrition tips
No matter how much a woman gains weight during pregnancy, it is important for her to follow a healthy diet. In addition to the ability to maintain normal weight, it will also help maintain the health of the pregnant woman and the child.
The following recommendations can be considered universal:
- Exclusion from the diet of a large number of sweet dishes, primarily flour.
- The use of fermented milk products in sufficient quantities (they will help improve metabolic processes).
- Selection of foods that contain folic acid. If this is not possible, you can take the appropriate drugs.
- Refusal of fatty, fried and smoked foods - such food can not only cause weight gain, but also negatively affect the health of the fetus, as it worsens blood quality.

- Emphasis on fresh fruits and vegetables - they will improve digestion, provide the bodies of a pregnant woman and a child with the necessary vitamins.
It is also important to ensure that the diet is balanced in terms of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. If it is not possible to independently develop the correct nutrition schedule, then it is better to consult a doctor who will suggest the optimal diet. To do this, you can visit the Ivimed reproductive health clinic. Thanks to this, the norm of weight during pregnancy will be observed.
Weight during pregnancy. What increase is considered optimal?
Why is excessive weight gain during pregnancy particularly harmful? What should be the calorie content of the diet? How to build your diet so that you can eat varied (and tasty), but at the same time not gain too much? Let's figure it out.
What makes up weight gain during pregnancy?
An increase in the subcutaneous fat layer during pregnancy is a normal and natural process.
While the baby is growing inside you, he needs energy and external protection. But during pregnancy, weight increases not only and not so much due to the adipose tissue of the mother: there is more fluid in the body, the uterus grows, the fetus and placenta develop, and the breasts increase in preparation for the feeding process.
Interestingly, weight loss during the period of toxicosis can later provoke its increase: the body will try to regain what was lost.
Expectant mothers especially actively gain weight in the second trimester and the beginning of the third, but closer to childbirth, a pregnant woman can even lose 1-2 kilograms.
As long as the weight increases more or less evenly and does not go beyond the upper limit of the norm, there is nothing to worry about. But if your weight is rapidly going up, you should be wary.
How to correctly calculate the weight, and what increase is considered optimal?
In Russian obstetric practice, it is generally accepted that the total increase should not exceed 12 kg.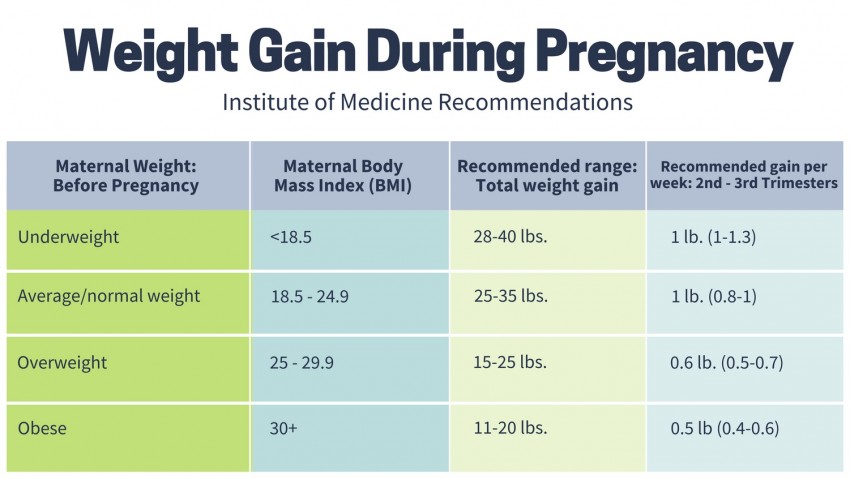 for the entire pregnancy. Of these 12 kg. 5-6 accounts for the fetus, placenta, amniotic fluid, another 1.5-2 - for an increase in the uterus and mammary glands, and only 3-3.5 - for the fat mass of a woman.
for the entire pregnancy. Of these 12 kg. 5-6 accounts for the fetus, placenta, amniotic fluid, another 1.5-2 - for an increase in the uterus and mammary glands, and only 3-3.5 - for the fat mass of a woman.
But this is a general indicator, a kind of "average temperature in the hospital." The optimal increase is calculated individually and depends on the initial weight of the pregnant woman, her age, the number of fetuses and the size of the child (children), physical activity.
WHO recommends that optimal weight gain be calculated based on Body Mass Index (BMI).
It is determined by the formula: body weight (kg) / height squared (m).
| BMI | Recommended weight gain |
|---|---|
| 19.8-26 (normal body weight) | 12.5-15 kg |
| 26.1-29 (overweight) | 11.5 - 14 kg |
| over 29 (obese) | 7-9 kg |
How to calculate the optimal weight gain?
To do this, use the following chart:
- Calculate your BMI: divide your initial weight in kg.
 for height in meters squared.
for height in meters squared.
For example, your "pre-pregnancy" weight was 60 kg with a height of 170 cm.
BMI = 60: (170 x 170) = 20.76.
- A BMI of less than 18.5 indicates underweight. Indicators from 18.5 to 25 are within the norm, from 25 to 30 are above the norm, and a figure greater than 30 indicates obesity.
- Now that you know your BMI, find the optimal weekly increase in the table and compare it with yours.
| Week of pregnancy | Underweight before pregnancy (BMI less than 18.5) | Normal pre-pregnancy weight (BMI 18.5 to 24.9) | Overweight before pregnancy (BMI over 30) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0-0.9 kg | 0-0.7 kg | 0-0.5 kg |
| 6 | 0-1.4 kg | 0-1 kg | 0-0.6 kg |
| 8 | 0-1.6 kg | 0-1.2 kg | 0-0. 7 kg 7 kg |
| 10 | 0-1.8 kg | 0-1.3 kg | 0-0.8 kg |
| 12 | 0-2 kg | 0-1.5 kg | 0-1 kg |
| 14 | 0.5-2.7 kg | 0.5-2 kg | 0.5-1.2 kg |
| 16 | up to 3.6 kg | up to 3 kg | up to 1.4 kg |
| 18 | up to 4.6 kg | up to 4 kg | up to 2.3 kg |
| 20 | up to 6 kg | up to 5.9 kg | up to 2.9 kg |
| 22 | up to 7.2 kg | up to 7 kg | up to 3.4 kg |
| 24 | up to 8.6 kg | up to 8.5 kg | up to 3.9 kg |
| 26 | up to 10 kg | up to 10 kg | up to 5 kg |
| 28 | up to 13 kg | up to 11 kg | up to 5.4 kg |
| 30 | up to 14 kg | up to 12 kg | up to 5. 9 kg 9 kg |
| 32 | up to 15 kg | up to 13 kg | up to 6.4 kg |
| 34 | up to 16 kg | up to 14 kg | up to 7.3 kg |
| 36 | up to 17 kg | up to 15 kg | up to 7.9 kg |
| 38 | up to 18 kg | up to 16 kg | up to 8.6 kg |
| 40 | up to 18 kg | up to 16 kg | up to 9.1 kg |
Recently, doctors are increasingly talking about an individual approach and urge not to panic if the increase is slightly beyond the normal range. When assessing the state of health of a pregnant woman, the doctor focuses not only on weight, but also takes into account the results of tests and examinations and other important indicators.
Why is excessive weight gain dangerous?
Gaining extra pounds can lead to gestational diabetes, hypertension, preeclampsia, or cause a caesarean section.
In addition, excessive weight gain during pregnancy may increase the risk of obesity and associated cardiovascular disease.
What can I do to keep my weight within normal limits during pregnancy?
First of all, consult a nutritionist. If there is no such doctor in the antenatal clinic, it makes sense to contact a specialist on a commercial basis. He will develop an individual diet, which will contain all the useful elements, and will offer to keep a food diary. It will also tell you how to eat right and weigh yourself.
To prevent excessive weight gain during pregnancy, it is enough to follow simple rules of a healthy diet:
- Eat often and in small portions;
- Always have a “healthy snack” on hand: fresh apple wedges, unsweetened crackers, dried fruit, or sugar-free yogurt;
- Refuse soda, chips, sausages and sausages;
- Minimize the consumption of sweets;
- Avoid fast food;
- Limit the use of condiments, especially salt, which retains water in the body;
- Choose steamed dishes;
- Eat more fiber-rich foods such as whole grain bread, bran, vegetables;
The diet of a pregnant woman should be varied. Include grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, meat and fish, legumes, or nuts.
Include grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, meat and fish, legumes, or nuts.
It must be remembered that expectant mothers should never starve and adhere to extreme diets.
How many calories do you need per day during pregnancy?
It is difficult to calculate the energy value per day on your own, and then strictly adhere to a certain number of calories, and it is not necessary, unless it is recommended by a nutritionist or endocrinologist. On average, you can aim for 2000-2500 calories per day, but it is important to understand that the need for calories depends on many factors: age, initial weight, health status and level of physical activity.
When should I be on the alert?
Strictly speaking, it is better for a pregnant woman not to worry and entrust her condition to a doctor who will control the development of pregnancy, analyzes and monitor weight. It is important to take tests to determine the level of fasting blood glucose once a trimester.