Blood after membrane sweep
Symptoms & Signs of Labor
Overview
What is a bloody show?
A bloody show is a common symptom during late pregnancy when a small amount of blood and mucus is released from the vagina. A bloody show occurs because the cervix starts to soften and thin (efface) and widen (dilate) in preparation for labor.
When your cervix dilates, it's making room for your baby to pass through. Because it's filled with blood vessels, it can bleed easily when dilation occurs. What you see in a bloody show is blood from your cervix, mixed with mucus from the mucus plug.
It sounds scary, but a bloody show is a very normal sign that your cervix is changing in preparation for labor. The length of time between having a bloody show and entering labor can vary between women.
What does a bloody show look like?
A bloody show will look different for everyone. The blood can be red, brown or pink and can contain all or parts of the mucus plug. It will be a jelly-like, stringy texture. Some bloody shows are more mucus-like with streaks of blood. Some women lose the mucus plug all at once. In some cases, a bloody show will happen gradually.
How much blood is in a bloody show?
The bloody show should not produce more than a tablespoon or two of discharge. Severe bleeding at any time can be a sign of a complication. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience heavy bleeding during pregnancy.
What is the difference between a bloody show and a mucus plug?
A bloody show and a mucus plug are closely related. The mucus plug blocks the opening of the cervix during pregnancy to protect the baby from bacteria. As your body prepares for labor, the cervix dilates (expands). This causes the mucus plug to dislodge. When blood from your cervix is mixed in with the mucus plug, it is called a bloody show.
What does a bloody show mean?
A bloody show usually means labor is coming soon. Some women experience a bloody show weeks before labor and others don't have a bloody show until they are in labor. It’s a good indication that your body is getting ready and your baby is in the final stages of development.
It’s a good indication that your body is getting ready and your baby is in the final stages of development.
How long does a bloody show last?
The amount of time the bloody show lasts will vary. It's usually seen in your underwear or on toilet paper. Some women will see the bloody show in one blob while others may notice it gradually.
Possible Causes
What are the causes of a bloody show?
A bloody show occurs as a natural progression of labor. Your cervix goes through big changes to prepare for delivery. As your cervix begins to open, the blood vessels of the cervix rupture — this is the bloody show.
A bloody show can also be triggered by:
- Sexual intercourse: Your cervix thins and dilates in the last weeks of pregnancy. Having sex can loosen the mucus plug or cause light bleeding.
- Membrane sweeping: Your healthcare provider may sweep your membranes while checking your cervix for dilation. They will use gloved fingers to loosen the baby’s bag of water (amniotic sac) from your uterus.
 This is done to encourage labor but can also cause some bleeding.
This is done to encourage labor but can also cause some bleeding. - Trauma: Falling or being in a car accident could cause your body to go into labor or bleed. If you have experienced any trauma, call your healthcare provider or go to a hospital to get checked.
Women who notice vaginal bleeding should contact their healthcare provider to be safe. Bleeding during pregnancy can be normal, but it can also be a sign of a more serious complication.
What are the signs of a bloody show?
The biggest sign that the bloody show has occurred is you may notice a bloody mucus discharge from your vagina. In some cases, there are no signs.
Some women experience other symptoms of labor with a bloody show:
- Cramping: You may feel period-like cramps that come and go over the course of hours or even days.
- Pelvic pressure: As the baby drops down from your abdomen, you may experience pressure in your pelvis (referred to as lightening), vagina or back.
- Contractions: You may feel tightening in your uterus that increases in duration and intensity.
These signs are good indications that your cervix is dilating to prepare for labor.
Is a bloody show a sign of labor?
A bloody show is a sign that labor is coming. There is not an exact timing as to how long after a bloody show labor will occur. This varies from woman to woman and from pregnancy to pregnancy.
Can you get a bloody show after a cervical exam?
If your healthcare provider does a cervical exam (cervix check), it’s normal for spotting (or light bleeding) to occur. After 37 weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare provider may ask if you would like your cervix checked. They are checking the dilation and effacement (thinning) of your cervix. This could irritate your cervix and cause it to bleed, but it's not necessarily the bloody show.
Will doing a membrane sweep cause a bloody show?
A sweeping of your membranes can cause a bloody show. If successful, the membrane sweep will trigger your cervix to dilate. This could cause a bloody show. It could also be blood caused by the cervix becoming irritated. Membrane sweeping is a practice that varies amongst healthcare providers and is not always performed.
If successful, the membrane sweep will trigger your cervix to dilate. This could cause a bloody show. It could also be blood caused by the cervix becoming irritated. Membrane sweeping is a practice that varies amongst healthcare providers and is not always performed.
Is cramping a side effect of a bloody show?
Yes, some cramping can occur when you have a bloody show. Your cervix is opening, softening and expanding in preparation for birth. This can cause period-like cramping or aches. You may also feel a cramping pressure in your pelvis as the baby descends. These are common side effects of the bloody show because they are all signs labor is coming.
Will I know when I have a bloody show?
It varies. You may not be aware that your bloody show has occurred. In some cases, the discharge is so light and gradual it's virtually undetected. You might also have a blood-tinged glob all at once and know it's a bloody show. It’s best to contact your healthcare provider if you believe your bloody show has occurred.
Care and Treatment
How is a bloody show diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider may ask you the color, consistency and amount of discharge. These details can help determine if you’ve had a bloody show. Since it's a normal progression in pregnancy, there is not a treatment.
What do I do when I have a bloody show?
You should write down or take a picture of the discharge. Note the color, consistency and amount. Your healthcare provider will be able to determine if this was a bloody show. They may also want to check your cervix for dilation. It's also a good time to monitor yourself for other signs of labor.
How long after a bloody show will labor start?
Every pregnancy is different, so it's difficult to say when labor will start after the bloody show happens. The bloody show means your cervix is dilating in preparation for labor. Labor can come within the next few hours, or it could still be days away.
When to Call the Doctor
When should I call the doctor after a bloody show?
It's best to contact your healthcare provider if you think you have experienced a bloody show.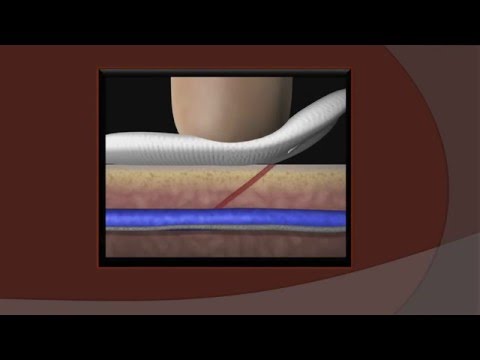 Spotting or light bleeding in pregnancy can be common. Severe bleeding or bleeding earlier than the last few weeks of pregnancy can be signs of premature labor or other complications.
Spotting or light bleeding in pregnancy can be common. Severe bleeding or bleeding earlier than the last few weeks of pregnancy can be signs of premature labor or other complications.
Does a bloody show mean it’s time to go to the hospital?
A bloody show means your cervix is preparing for labor. For some women, labor begins shortly after the bloody show, but for others it could still be several days away. If you are unsure if you are experiencing a bloody show or think you are in the early stages of labor, contact your healthcare provider.
When is it bad to have a bloody show?
A bloody show is usually not a concern if it happens after 37 weeks of pregnancy. Some light bleeding can be a normal part of pregnancy. Bleeding heavily or uncontrollably could indicate a more serious complication. If you have bloody discharge, you should contact your healthcare provider to be sure.
A note from Cleveland Clinic:
It's normal to feel excited and nervous about labor and delivery.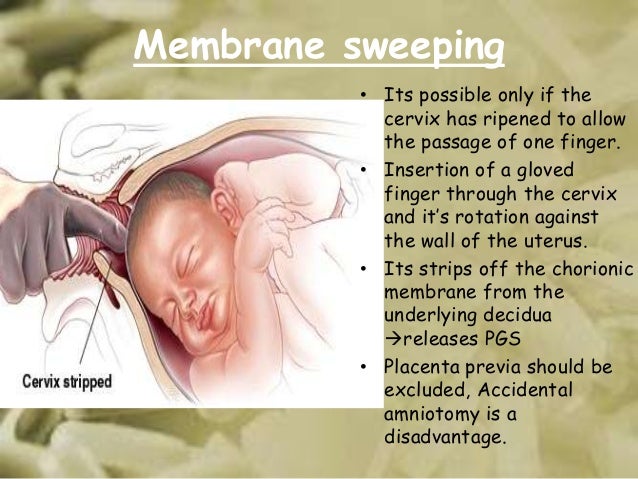 Discussing the signs and symptoms with your healthcare provider can help you know what to expect. Don't hesitate to voice your concerns about any vaginal bleeding during your pregnancy.
Discussing the signs and symptoms with your healthcare provider can help you know what to expect. Don't hesitate to voice your concerns about any vaginal bleeding during your pregnancy.
How much blood is taken after a membrane sweep?
You might feel mild cramps or contractions for up to 24 hours afterward. You may also have slight spotting (a small amount of bleeding on your underwear) for up to 3 days. This bleeding can be reddish, pink, or brown and may be mixed with mucus. Spotting and cramping after membrane sweeping are normal.
Takedown request | View complete answer on onlinelibrary.wiley.com
How long does it take to give birth after membrane sweep?
After having a membrane sweep
Most women will go into labour within 48 hours. If you do not go into labour within 48 hours your community midwife will give you an appointment to come for an induction.
| View complete answer on swbh.nhs.uk
Does everyone bleed after a sweep?
It is common to experience some mild bleeding just after a membrane sweep. Some people experience contractions, cramping, or mild discomfort after the procedure. Contact your healthcare provider when the bleeding becomes heavy, or you experience severe pain.
Takedown request | View complete answer on nurturey.com
What are good signs after a membrane sweep?
What happens after a membrane sweep? It's normal to experience some light bleeding after a membrane sweep. Some people experience contractions, cramping or mild discomfort afterward. If the bleeding becomes heavy or you have severe pain, contact your healthcare provider right away.
Takedown request | View complete answer on my. clevelandclinic.org
clevelandclinic.org
How will I know if a sweep has worked?
Some of the most common signs of labour after a sweep include: Your waters breaking. Cramping or pelvic pain. Contractions.
Takedown request | View complete answer on emmasdiary.co.uk
MEMBRANE SWEEP/MEMBRANE STRIP | Inducing Labor With A Stretch and Sweep | The Induction Series Pt 4
Can you go into labor same day as membrane sweep?
You may go into active labour within a few hours, a few days, or not at all—it depends on how ready your body is. “One sweep might not do anything, but if you have a sweep at weeks 38, 39 and 40, it's the cumulative effect of those sweeps,” says Bacon.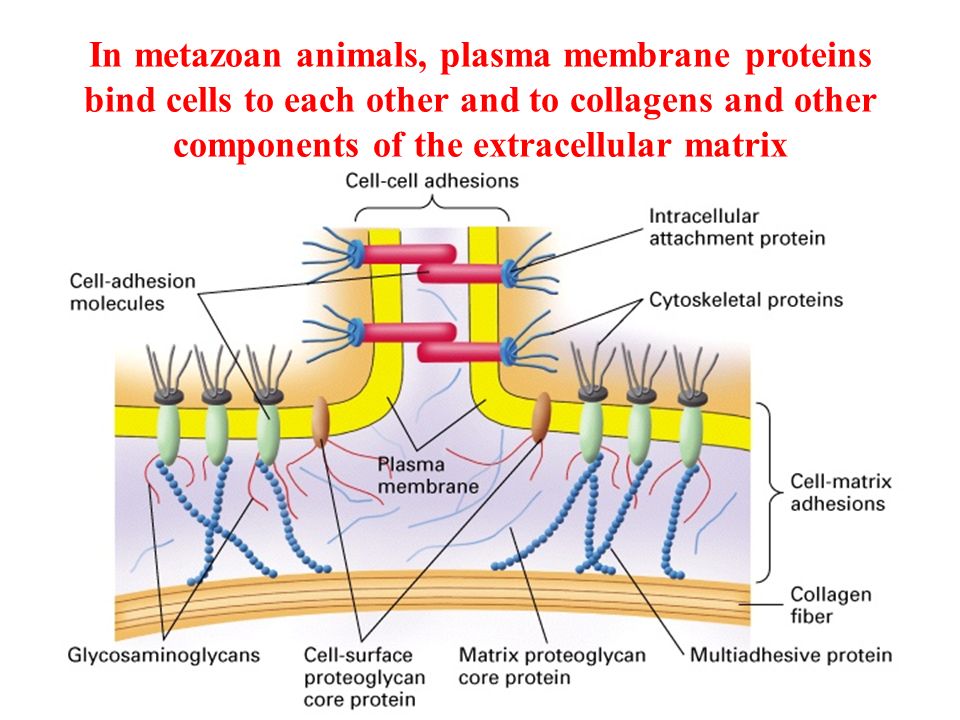
| View complete answer on todaysparent.com
How quickly can a sweep work?
Why is it recommended? Stretch and sweep is used to help start labour and reduce the need for an induction. If it works, you can expect to go into labour within 48 hours. If it does not work, it can be repeated two or three times over the next few days.
Takedown request | View complete answer on thewomens.r.worldssl.net
How long does it take for a successful sweep to work?
A membrane sweep increases the likelihood that labour will start within 48 hours. It has a higher chance of working if the neck of your womb is already softening and preparing for labour.
Takedown request | View complete answer on hse.ie
What happens 24 hours after a sweep?
You might feel mild cramps or contractions for up to 24 hours afterward. You may also have slight spotting (a small amount of bleeding on your underwear) for up to 3 days. This bleeding can be reddish, pink, or brown and may be mixed with mucus. Spotting and cramping after membrane sweeping are normal.
You may also have slight spotting (a small amount of bleeding on your underwear) for up to 3 days. This bleeding can be reddish, pink, or brown and may be mixed with mucus. Spotting and cramping after membrane sweeping are normal.
| View complete answer on onlinelibrary.wiley.com
What to do after membrane sweep to start labor?
After the membrane sweep, you typically go home and wait for labor to start, usually within the next couple days. You may have some spotting and cramping during this time. However, if you're having a lot of bleeding or pain, call your practitioner or go to the hospital.
Takedown request | View complete answer on babycenter.com
What percentage of sweeps bring on labour?
The review found that overall the intervention is associated with a 24% increase in chance of delivering within 48 hours, a 46% increase in chance of delivering within a week and a 74% reduction in likelihood of going 2 weeks over dates.
| View complete answer on midwifery.org.uk
Does bloody show after membrane sweep mean labor is coming?
A bloody show means your cervix is preparing for labor. For some women, labor begins shortly after the bloody show, but for others it could still be several days away. If you are unsure if you are experiencing a bloody show or think you are in the early stages of labor, contact your healthcare provider.
Takedown request | View complete answer on my.clevelandclinic.org
How many hours after bloody show does labor start?
First-time mamas are more likely to see a bloody show before labor begins, but this can happen a few days beforehand. Women who have given birth before often don't see any bloody show until their cervix is dilating; they would expect birth in the next 24 hours.
Takedown request | View complete answer on bellybelly. com.au
com.au
How much bleeding is normal after cervical check?
The author of this answer has requested the removal of this content.
Takedown request | View complete answer on healthline.com
Why is sweep picking so hard?
For some reason, sweep picking infatuates a large segment of the guitar community. Perhaps it's due to the flashy visual nature of the technique. Maybe it's because the robotic sound hypnotizes us into a trance, manipulating us with its cyclical sound.
Takedown request | View complete answer on guitarworld.com
What should you focus on during a sweep?
Focus on accuracy and the speed will follow. If you try to push the speed too soon, you'll end up with a sloppy sweep picking technique. Remember: accuracy is the main goal.
Takedown request | View complete answer on guitargearfinder. com
com
What is the success rate of membrane sweep?
They concluded that membrane stripping can increase the likelihood of spontaneous labor by more than 20%. Doctors usually only need to carry out the procedure once to induce labor successfully.
Takedown request | View complete answer on medicalnewstoday.com
Can contractions start right after membrane sweep?
Stripping membranes does not make the labor more painful. The procedure can cause you discomfort or mild pain and slight bleeding. The pain is due to the release of prostaglandins, which is normal. If the procedure works on you, contractions begin within a few hours.
Takedown request | View complete answer on medicinenet.com
How many centimeters do you have to be for a membrane sweep?
A sweep can't always be performed. Unless you are at least 1 cm dilated, it can't be done. After a sweep you will most likely lose some or all of your mucous plug. It can also cause bleeding and irregular contractions that do not progress into labour.
Unless you are at least 1 cm dilated, it can't be done. After a sweep you will most likely lose some or all of your mucous plug. It can also cause bleeding and irregular contractions that do not progress into labour.
| View complete answer on southeastdoulacare.com
How do you maximize the success of a membrane sweep?
Remember, the more favorable your cervix, the more likely membrane sweeps are to work. Using a firm circular or sweeping motion, your midwife or doctor will sweep and separate the membrane of the amniotic sac from the cervix. Some providers also stretch the cervix to increase the chances of the membrane sweep working.
Takedown request | View complete answer on bellybelly.com.au
How do you properly sweep?
Sweep toward you, instead of away, to help control the pile of debris and limit the amount of dust that rises up into the air. Start in the corners and sweep toward you in short, smooth motions. Then, use a dust pan often to avoid dragging your dirt piles across the clean floor.
Start in the corners and sweep toward you in short, smooth motions. Then, use a dust pan often to avoid dragging your dirt piles across the clean floor.
| View complete answer on oprah.com
← Previous question
Which hormone is dominant in PCOS?
Next question →
How do you get rid of chronic inflammation?
The use of membranes from the patient's blood plasma when increasing the jaw bone tissue
The use of platelet membranes is not a full-fledged alternative to bone grafting - they are not enough to increase the volume of the jawbone. However, they are actively used as an adjunct to sinus lift, when transplanting bone blocks and with the simultaneous installation of implants as a replacement for artificial bone. This is an effective method of postoperative protection, since platelets contain large amounts of tissue growth factors 1 .
Navigation
- Indications and contraindications
- Benefits
- Technology and training
- Defects
- Prices
The patient's blood plasma is widely used in medicine.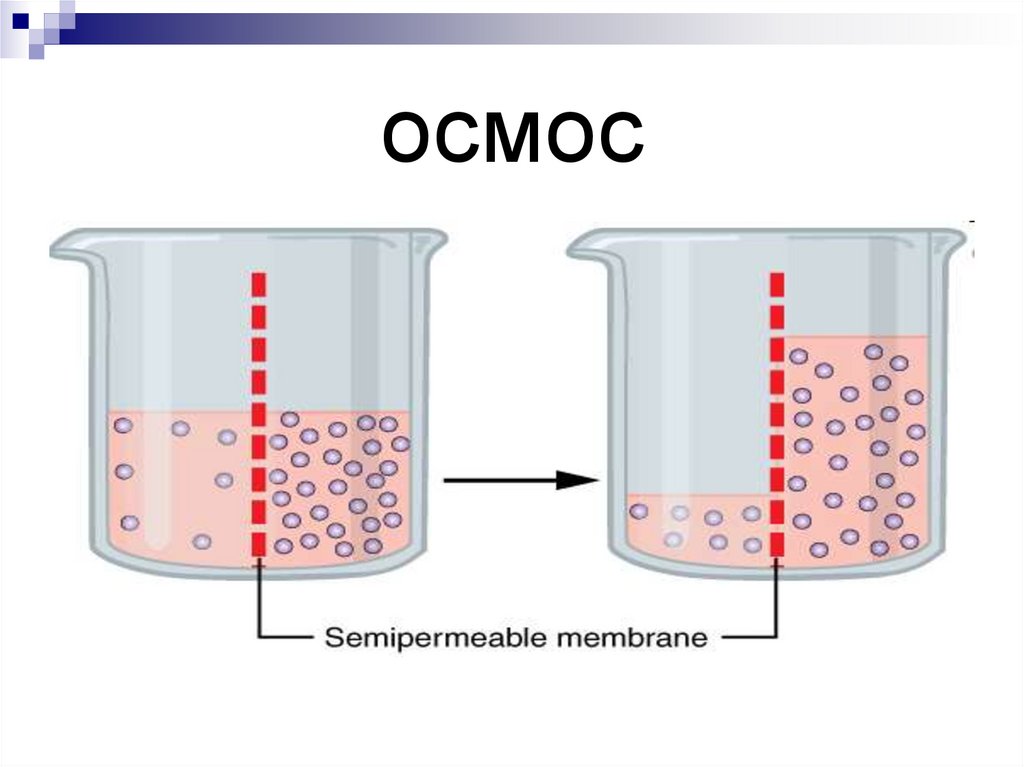 With the help of special equipment (centrifuge), the blood is divided into fractions or components: directly plasma - a liquid that has a yellowish color and contains a large amount of fibrin; fibrin clot enriched with platelets. And another part, the thickest, is a mixture of leukocytes and erythrocytes. It is plasma, as well as fibrin clot, that are actively used in dentistry.
With the help of special equipment (centrifuge), the blood is divided into fractions or components: directly plasma - a liquid that has a yellowish color and contains a large amount of fibrin; fibrin clot enriched with platelets. And another part, the thickest, is a mixture of leukocytes and erythrocytes. It is plasma, as well as fibrin clot, that are actively used in dentistry.
This technology is called PRF (Platelet Rich Fibrin). Fibrin is a protein that is responsible for clogging blood vessels when damaged. Platelets are cells responsible for wound healing and accelerating cell growth. Thus, membranes created from the patient's blood plasma containing fibrin and platelets can significantly accelerate the regeneration of cells and tissues during various surgical interventions.
This technology has been used in Europe and the USA for over 30 years. But in Russia it is considered innovative. The use of blood plasma is an effective addition to implantation, extraction of teeth, surgical gum plastic surgery, as well as in conjunction with the implantation of artificial bone tissue substitutes.
Indications
- acceleration of tissue healing during sinus lift or bone block grafting,
- plastic surgery of the oral mucosa, treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease,
- activation of bone tissue growth after tooth extraction,
- implant placement and simultaneous bone augmentation,
- performing various surgical operations.
Contraindications
- malignant tumors,
- systemic blood diseases that do not allow the isolation of platelet plasma, or its use will not be effective,
- acute disorders of the immune system, infectious diseases in the acute stage,
- antibiotic therapy,
- mental disorders.
The benefits of using blood plasma
The use of PRF membranes allows natural stimulation of the growth of jawbone cells or periodontal tissues, which significantly accelerates their growth.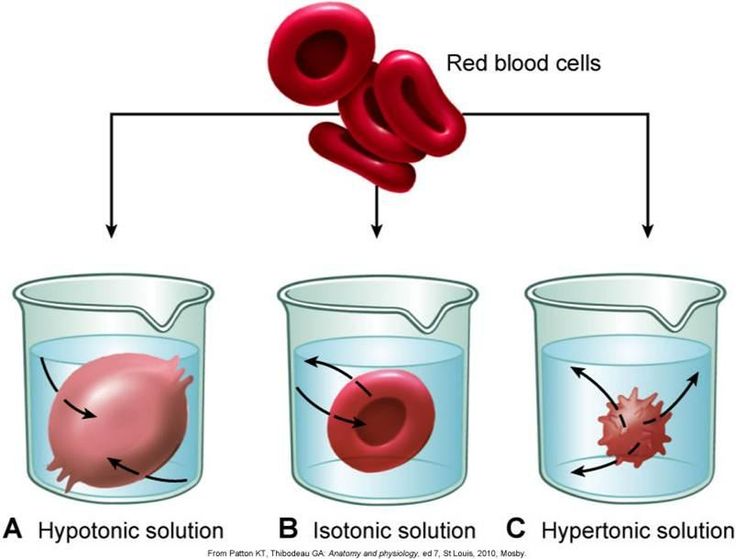 Rehabilitation and engraftment of implants or bone material is faster, and the risks of inflammatory processes are significantly reduced.
Rehabilitation and engraftment of implants or bone material is faster, and the risks of inflammatory processes are significantly reduced.
The use of blood plasma has a positive effect on the following processes:
- acceleration of bone tissue growth after implantation,
- no allergic reactions that may occur when using artificial materials,
- rapid healing of soft mucous membranes after dental implants or plastic surgery,
- Prevention of the risk of peri-implantitis after implant placement,
- reduction of tissue swelling, reduction of pain after any surgical intervention,
- rapid tissue repair after tooth extraction,
- reduction of inflammation during gingival curettage and cleaning of gingival pockets.
Expert opinion
Namdakov Nikolai Vladimirovich Maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist, orthopedist
Work experience 19+
“The specialists of our clinic have been actively using this technology in their work for many years - they have received the necessary training and know hematology, they understand the mechanisms of blood coagulation.Therefore, we have no difficulties in working with this equipment. Each person has his own characteristics of both the body and the circulatory system, so we use a strictly individual approach even in such a matter as obtaining PRF membranes.”
Technology and preparation features
Preparation for the procedure does not have any specific features. The most important thing is to exclude fatty and spicy foods, alcohol the day before. It is also advisable to get a good night's sleep. Blood sampling is not carried out against the background of taking antibacterial drugs - it is necessary to wait for the end of therapy.
The procedure takes a little time and is carried out as follows:
- blood is taken from a vein directly in the clinic,
- tubes are placed in a centrifuge. Isolation of fractions takes from 10-15 minutes to half an hour or even 40 minutes (depending on the patient, since the platelet sedimentation rate is different for each person),
- thick plasma is taken from the test tube - such a membrane can be cut, sutured, used in various techniques.
 It is placed in the required amount during surgical operations.
It is placed in the required amount during surgical operations.
Ready membranes are stored for a maximum of 4 hours, so blood sampling and processing is carried out immediately on the day of implant placement or other surgical interventions.
Disadvantages of the method
The method has no disadvantages. The only thing that can be highlighted is the increase in cost. Nevertheless, the membranes are very effective, make the process of surgical interventions more comfortable for the patient and reduce the risk of postoperative complications. And in some situations, the use of this technology is even cheaper than classical bone grafting.
When performing bone grafting using plasma-derived membranes, Smile-at-Once Clinic also uses special growth activators (PrefGel and Emdogein from Straumann), which provide cavity cleansing and additional stimulation of bone and gingival tissue growth, which necessary to accelerate the healing process of implants, especially when using methods of one-stage implantation with immediate loading.
1 Tolstov D.A., Bogdan V.G. Platelet concentrates: classification, production technologies, biological effects, 2012.
Yaroslavl Dialysis Center - To prevent blood clotting during hemodialysis.
To prevent blood clotting during hemodialysis. About heparin and other anticoagulants
From Living with Chronic Kidney Disease. Zemchenkov A.Yu., Gerasimchuk R.L., Kostyleva T.G., Vinogradova L.Yu., Zemchenkova I.G. St. Petersburg, 2011
The standard procedure for cleaning the blood of patients with kidney damage (hemodialysis) lasts an average of four hours. And all four hours the human body struggles with such a cruel external "invasion", trying to stop the "bleeding" by the formation of blood clots.
In turn, experts have come up with many ways to prevent thrombosis and reduce unwanted blood clotting in this case. Among the most commonly used in practice methods of anticoagulation during continuous renal replacement therapy is the use of heparins (unfractionated high and low molecular weight - clexane, frasiparin, fragmin, anfibra), citrate-containing solutions (reduce blood clotting and non-anticoagulant drugs - such as sodium citrate, used as a flavoring additive in the composition of carbonated drinks), as well as a combination of these agents with each other.
Sometimes it is necessary to completely abandon the use of an anticoagulant due to a decrease in blood clotting.
Heparin (Heparinum), a substance known as a direct anticoagulant that prevents blood clotting, is most commonly used in hemodialysis in Russia. Synonyms: Heparin sodium salt, Heparin sodium, Heparin-Richter, Thrombophobe, Likvembin, Pularin, Thrombolikvin, Vetren, Heparinbene sodium, Thrombofot.
Heparin is also used for the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic diseases, during operations on the heart and blood vessels, to maintain the liquid state of blood in heart-lung machines, and to prevent blood clotting in laboratory studies.
For medicinal purposes, heparin is obtained from the liver, lungs and intestinal mucosa of cattle and pigs.
The discovery of heparin dates back to 1916, when it was discovered by accident, then a medical student at Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, USA), Jay McLean. McLean's supervisor gave his student the task of finding out how to increase blood clotting, and the student "accidentally" found out how to reduce this clotting . ..
..
In medicine, the amount of heparin is often measured in action units (U) or international units (IU) according to its biological activity - ability to prevent blood clotting.
The effect after heparin administration develops quite quickly, with intravenous administration (during hemodialysis, for example) - almost immediately, but lasts for a short time. So, with a single intravenous injection, clotting inhibition occurs immediately and lasts about 4-5 hours, with intramuscular injection, the effect of heparin appears after 15-30 minutes and lasts up to 6 hours, when injected into the subcutaneous tissue, the effect occurs after 40-60 minutes and lasts 8 ocloc'k.
The anticoagulant effect of heparin is enhanced by the simultaneous use of other anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Ergot alkaloids, thyroxine, tetracycline, antihistamines, nicotine can reduce the anticoagulant potential of heparin.
Heparin must not be mixed in the same syringe with other medicinal products.
Like any other drug, heparin can cause side effects from various body systems:
- bleeding: at the site of gastrointestinal ulcers, in areas subjected to pressure, from surgical wounds, as well as hemorrhages in other organs;
- reaction of the digestive system: nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, impaired activity of liver enzymes;
- allergic reactions: skin flushing, pruritus, fever, urticaria, rhinitis, bronchospasm, collapse, anaphylactic shock, lacrimation;
- loss of bone mineral substance, increased parathyroid hormone activity. Heparin therapy lasting more than 5 months can cause osteoporosis, spontaneous fractures are possible.
Hemodialysis Vascular Access
Effective hemodialysis treatment requires that at least 250 ml of blood per minute be pumped through the dialyzer. No peripheral vein (from which blood is usually taken for tests or donated blood) is capable of providing even half of the required flow: it simply does not flow so much through the vein, it makes up 20th of all blood pumped by the heart (the minute volume of the heart is 4-5 liters ). Modern high-flow dialysis and hemodiafiltration require a blood flow of 300–400 ml/min. To obtain such a blood flow, several possibilities are used:
Modern high-flow dialysis and hemodiafiltration require a blood flow of 300–400 ml/min. To obtain such a blood flow, several possibilities are used:
creation of an arteriovenous fistula (“native” - from own vessels)
installation of a vascular prosthesis
installation of a catheter in the central veins
Arteriovenous fistula is an optimal vascular access. It is created surgically (typically under local anesthesia) by suturing a large peripheral vein to the artery. Blood begins to flow into the vein under arterial pressure, which ensures sufficient blood flow through the vein. In addition, due to the same blood pressure, the vein gradually expands, sometimes several times, its wall thickens, and it is fixed in the surrounding tissues. These changes take time - several weeks, and the process itself is referred to as "maturation of the fistula." The vein is now designated as "fistula", or - with some simplification - "fistula" (actually "fistula", from Latin fistula - a tube is the very connection of an artery and a vein). An enlarged vein is easier to puncture, and the thickened walls of the vein exclude bleeding after multiple punctures. The maturation time of the fistula can be somewhat accelerated by training it. Training consists in creating increased pressure in the fistula: a venous tourniquet is applied to the arm, and the work of the muscles (exercises with the carpal expander or simply clenching the fist) increases blood flow through the arm. Workouts are performed for 2-3 minutes many times a day. Before starting such training, you should get detailed instructions from your doctor.
An enlarged vein is easier to puncture, and the thickened walls of the vein exclude bleeding after multiple punctures. The maturation time of the fistula can be somewhat accelerated by training it. Training consists in creating increased pressure in the fistula: a venous tourniquet is applied to the arm, and the work of the muscles (exercises with the carpal expander or simply clenching the fist) increases blood flow through the arm. Workouts are performed for 2-3 minutes many times a day. Before starting such training, you should get detailed instructions from your doctor.
The typical location of the fistula is the lower third of the forearm: here the veins are located close to the surface, relatively inactive, and of a suitable caliber. Unfortunately, sometimes, due to congenital features or vascular or other diseases, it is not possible to create a fistula on the forearm. Then the vein and artery are connected above - in the cubital fossa. Unfortunately, the vein on the shoulder runs deeper, and often surgeons have to lift it to the surface; the volume of surgical intervention increases, general anesthesia is often required. The larger caliber of the veins in this zone creates the prerequisites for excessive discharge of blood from the arterial system into the venous system. If usually about 10% of the minute volume of the heart passes through the fistula on the forearm, then this proportion can increase significantly through the shoulder fistula, which increases unnecessary stress for the heart: more blood needs to be pumped. An arteriovenous fistula can also be created using other vessels: femoral and even large cervical ones, but due to the risks of infection and bleeding, they are used very rarely. The second choice after the failure to create a fistula on the arm is to use a vein transferred from the thigh or an artificial vessel prosthesis (Ecoflon and Gortex available in Russia). The prosthesis itself functions, as a rule, well and is available for punctures after two weeks (when a connective tissue membrane forms around it). However, the place of its connection with the vein often narrows after a few months, and there is a risk of thrombosis of the prosthesis.
The larger caliber of the veins in this zone creates the prerequisites for excessive discharge of blood from the arterial system into the venous system. If usually about 10% of the minute volume of the heart passes through the fistula on the forearm, then this proportion can increase significantly through the shoulder fistula, which increases unnecessary stress for the heart: more blood needs to be pumped. An arteriovenous fistula can also be created using other vessels: femoral and even large cervical ones, but due to the risks of infection and bleeding, they are used very rarely. The second choice after the failure to create a fistula on the arm is to use a vein transferred from the thigh or an artificial vessel prosthesis (Ecoflon and Gortex available in Russia). The prosthesis itself functions, as a rule, well and is available for punctures after two weeks (when a connective tissue membrane forms around it). However, the place of its connection with the vein often narrows after a few months, and there is a risk of thrombosis of the prosthesis. As a result, after 1 and 2 years, 3/4 and half of the prostheses are preserved, respectively.
As a result, after 1 and 2 years, 3/4 and half of the prostheses are preserved, respectively.
To increase the duration of the functioning of fistulas and vascular prostheses, it is advisable to regularly measure the blood flow through them using Doppler ultrasound. A fistula flow of less than 400 ml/min and a prosthesis of less than 600 ml/min indicate a high chance of thrombosis in the near future and require intervention. A fistula with a blood flow of less than 400 ml/min from the outset will probably never be ready for dialysis. Your careful attitude to the fistula and, moreover, to the prosthesis will give them additional chances for long-term functioning.
First of all, remember that a lot of blood flows through this vessel, and damage to it will lead to massive bleeding: protect your hand from accidental injuries. It is difficult to stop the resulting bleeding by applying a bandage to the injury site; it is necessary to clamp either the fistula vein below the bleeding site, or the site of the anastomosis of the artery and vein. You can find it yourself in advance (this is the place where the pulsation of the fistula vein begins) and check your sensations together with your doctor.
You can find it yourself in advance (this is the place where the pulsation of the fistula vein begins) and check your sensations together with your doctor.
When a fistula is punctured for a dialysis session, the integrity of both the skin and the vein wall is violated. Therefore, a zone of relative asepsis (absence of microorganisms) is created in the puncture zone, which is achieved by treating the skin with a disinfectant solution and covering the hand with a sterile napkin. Of course, within 4-5 hours this area will not remain completely sterile (as it was immediately before the puncture), but it makes sense to try to keep it clean. Cleaning with a disinfectant solution will be effective if you enter the dialysis room after thoroughly washing your forearm with a fistula and wiping it dry. Do not use rag towels hanging by sinks; If you don't have disposables, bring your own.
For long-term safe functioning of the fistula, the puncture sites should be distributed over the entire available length. If you prick the same place many times in a row, puncture becomes less painful, it also becomes easier to get into the fistula vein; patients and staff are tempted not to deviate from a point once chosen. However, you must understand that this leads to thinning of both the vessel wall and the skin tissues lying above it. Over time, such a place will become dangerous in terms of possible bleeding. In addition, an aneurysm can form in this place - a local expansion of the vessel, which can become the starting point for the development of fistula thrombosis or bleeding. The patient and the staff of the department should strive to distribute the fistula puncture sites over the entire available length.
If you prick the same place many times in a row, puncture becomes less painful, it also becomes easier to get into the fistula vein; patients and staff are tempted not to deviate from a point once chosen. However, you must understand that this leads to thinning of both the vessel wall and the skin tissues lying above it. Over time, such a place will become dangerous in terms of possible bleeding. In addition, an aneurysm can form in this place - a local expansion of the vessel, which can become the starting point for the development of fistula thrombosis or bleeding. The patient and the staff of the department should strive to distribute the fistula puncture sites over the entire available length.
Pressure bandages are applied to the puncture site after each dialysis. Initial pressure should be significant, but after 20–30 minutes the tight bandage should be removed, leaving only a protective bandage, since the tight bandage interferes with blood flow through the fistula and can lead to thrombosis. The ideal option is to use devices for local pressure on the puncture site. After removing the pressure bandage, it is convenient to use a patch with a hemostatic sponge.
The ideal option is to use devices for local pressure on the puncture site. After removing the pressure bandage, it is convenient to use a patch with a hemostatic sponge.
You spend no more than 10% of your time in a dialysis center. The rest of the time, the monitoring of essential medical parameters lies with you. One such parameter, the evaluation of which cannot be limited to the length of stay in the dialysis center, is the functioning of the fistula. On the one hand, making sure it works is simple and takes almost no time. Attach your fingers to the site of the anastomosis of the artery and vein, and you will feel the “murmur” of the fistula in time with the pulse. The source of these fluctuations is the turbulent flow of blood through the fistula from the artery to the vein. The same phenomenon can be heard by pressing the area of the anastomosis on the forearm to the ear (more conveniently - to the opposite). This way you can make sure that the fistula is working in a matter of seconds. Only pulsation in the fistula area cannot reliably confirm the efficiency of the fistula, since thrombosis could happen further along the vein (closer to the armpit), and in this case the pulsation is limited to a segment of the vein that does not flow anywhere. It is important to be well versed in this because the earlier thrombosis of the fistula is detected, the greater the chances of its recovery (perhaps even without surgical intervention). If you have any doubts about the operation of the fistula, you should immediately come to the dialysis center.
Only pulsation in the fistula area cannot reliably confirm the efficiency of the fistula, since thrombosis could happen further along the vein (closer to the armpit), and in this case the pulsation is limited to a segment of the vein that does not flow anywhere. It is important to be well versed in this because the earlier thrombosis of the fistula is detected, the greater the chances of its recovery (perhaps even without surgical intervention). If you have any doubts about the operation of the fistula, you should immediately come to the dialysis center.
The fistula is justified to be used after 4 weeks (ideally 2-3 months after its formation), the vascular prosthesis can be used after 2 weeks. If hemodialysis is needed immediately, you have to install a catheter in one of the central veins. As a rule, catheters are placed during the formation of a permanent access, since it is difficult to expect that they will function for a long time. Catheters are an unfavorable factor due to the risk of infection.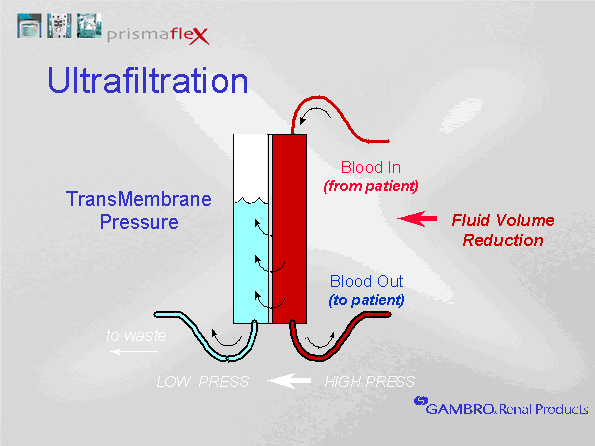 From the surface of the skin, it is easy for bacteria to get along the catheter into the blood and tissues surrounding the vessel. And then close to sepsis - blood poisoning. To reduce the risk of infection, the catheter exit site must be carefully cared for by dressing daily. Some catheters are antibacterial coated (eg silver impregnated) which drastically reduces the risk of infection.
From the surface of the skin, it is easy for bacteria to get along the catheter into the blood and tissues surrounding the vessel. And then close to sepsis - blood poisoning. To reduce the risk of infection, the catheter exit site must be carefully cared for by dressing daily. Some catheters are antibacterial coated (eg silver impregnated) which drastically reduces the risk of infection.
If the catheter is to be used for a relatively long time, catheters with a sleeve attached to them, called permanent ones, are used. Connective tissue grows into the loose material of the sleeve located in the subcutaneous tunnel, forming a strong barrier to infection along the catheter. It is more difficult to install such a catheter, in fact, it is a small operation. To prevent the catheter from thrombosing, it must be flushed daily with a solution of heparin (or other anticoagulant).
HEMODIALYSIS
Hemodialysis (HD) is a blood purification procedure outside the body using an artificial filter (dialyzer) through which the patient's blood passes and is freed from toxins and excess fluid.
A dialyzer is a device in which a semi-permeable membrane separates the patient's blood to be purified from the cleansing (= "dialysis") solution. In order for standard dialysis (= “cleansing”) to be effective enough, several conditions must be met:
Dialyzer membrane area must be 1–2 m2;
blood flow must be at least 250 ml/min;
dialysate must flow at a rate of at least 500 ml/min.
In modern dialyzers, the membrane consists of capillary fibers approximately 200 micrometers (0.2 mm) in diameter, within which blood flows, and outside the capillaries is washed by the dialysis solution. As a result, 1–2 m2 of membranes are “packed” into a compact cylinder 30 cm high and 5 cm in diameter. Note that this was not always the case: the first flat dialyzers were a multi-kilogram device on a special table. The first ever dialysis membranes were cellophane "sleeves" borrowed from sausage manufacturers. More recently, the production of cellulose dialysis membranes has been replaced by the use of fully synthetic membranes or modified cellulose (semi-synthetic) membranes. Modern semi-synthetic and synthetic membranes differ slightly in their characteristics, and each has a wide range of options. Modern membranes are divided into low-flux (low flux), medium-flux (middle flux), high-flux (high flux) depending on their ability to pass medium and high molecular weight compounds through them.
Modern semi-synthetic and synthetic membranes differ slightly in their characteristics, and each has a wide range of options. Modern membranes are divided into low-flux (low flux), medium-flux (middle flux), high-flux (high flux) depending on their ability to pass medium and high molecular weight compounds through them.
All membranes have almost the same ability to remove low molecular weight compounds such as urea, creatinine, uric acid, excess potassium, sodium, water. But in recent decades it has become clear that many components of the uremic syndrome are due to a delay in the body not so much of low molecular weight compounds as of medium and high molecular weight substances. If at first they were designated by the general term "mid-molecular toxins", then over the past decade, the number of established compounds responsible for specific manifestations of uremia has exceeded one hundred. Many of them have a sufficiently high molecular weight and are not removed even by high-flux membranes. Unfortunately, it is impossible to increase the permeability of the dialysis membrane indefinitely: after all, the dialyzer models only the first phase of kidney function - filtration. The kidneys, after filtering almost all the liquid part of the blood into the primary urine, then reabsorb (suck) everything that is needed back, finally removing only unnecessary and harmful products. In the most daring modern projects, there are not even the beginnings of a similar function for artificial kidneys. Therefore, the permeability of the dialysis membrane is limited to some reasonable value, far removed from the permeability of the natural kidney filter.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to increase the permeability of the dialysis membrane indefinitely: after all, the dialyzer models only the first phase of kidney function - filtration. The kidneys, after filtering almost all the liquid part of the blood into the primary urine, then reabsorb (suck) everything that is needed back, finally removing only unnecessary and harmful products. In the most daring modern projects, there are not even the beginnings of a similar function for artificial kidneys. Therefore, the permeability of the dialysis membrane is limited to some reasonable value, far removed from the permeability of the natural kidney filter.
There is another limitation for the selection of high permeability membranes. The fact is that the permeability of the membrane is bilateral. If there is something in the dialysate that is not in the blood, it will enter the blood if it can pass the membrane. And this is what we expect in dialysis, for example, with regard to bicarbonate: there is little of it in the blood of a dialysis patient, and this deficiency is compensated by the flow of bicarbonate from the dialysis solution into the blood. But harmful substances can also enter the blood in the same way. It is clear that no one will specifically mix harmful substances into the dialysis solution, but, unfortunately, the water from which the dialysis solution is prepared may not be free from chemical impurities and bacteria, as well as their metabolic products.
But harmful substances can also enter the blood in the same way. It is clear that no one will specifically mix harmful substances into the dialysis solution, but, unfortunately, the water from which the dialysis solution is prepared may not be free from chemical impurities and bacteria, as well as their metabolic products.
Tap water undergoes multi-stage purification and is freed from most chemical contaminants to a safe level, as well as from bacteria; but at the same time, chlorine is removed from the water, which prevents the growth of bacteria in the water, due to which, if the water and dialysate supply system is not properly treated, bacteria can grow in some stagnant parts of the system. The bacterial wall contains, among other things, large molecules of lipopolysaccharides, which are endotoxins - that is, substances that provoke inflammatory and other adverse reactions in the human body. Of course, if the bacteria themselves enter the dialyzer with the current of the dialysis solution, they will not penetrate the membrane into the blood. But after the breakdown of the bacterial cell, endotoxins from the dialysate may well enter the patient's bloodstream. And the higher the permeability of the dialysis membrane, the greater the likelihood.
But after the breakdown of the bacterial cell, endotoxins from the dialysate may well enter the patient's bloodstream. And the higher the permeability of the dialysis membrane, the greater the likelihood.
The cleaning capacity (clearances) of a dialyzer is determined not only by the membrane material (and, accordingly, permeability), but also by the area of the membrane, which in the line of similar dialyzers ranges from 1 to 2.3 m2. As already mentioned, for effective dialysis, the blood flow rate should be at least 250-300 ml / min, and for hemodiafiltration and high-flow hemodialysis - 350-400 ml / min. The blood flow through the line is provided by the so-called peristaltic pump, which, pressing a special segment of the line to the track with two rollers, pushes the next portions of blood between the rollers forward along the line.
A dialysis session usually lasts 4-5 hours. In short, a dialysis session can be only if the patient has significant residual kidney function (at the initial stage of hemodialysis treatment), when he does not yet need more powerful dialysis, or the patient receives more than 3 dialysis sessions per week. By increasing the size of the dialyzer, the session time cannot be reduced. The fact is that the task of dialysis is to purify not only the blood, but also all the tissues of the body, or rather, all the water sectors (or spaces) of the body, since it is in the body fluids that the substances that are to be removed are dissolved. Such water spaces are: blood - 5 liters, intercellular fluid - 10 liters, intracellular - 15 liters. Only the blood is purified directly in the dialyzer. The blood, in turn, takes the substances to be removed from the interstitial fluid. And only the intercellular fluid takes toxic substances from the intracellular space, namely, it has the largest volume, and it takes time to “pull out” uremic toxins from this space, which is the most remote from the dialysis solution. In addition, substances are removed from different tissues at different rates. In parallel, water is removed - and also unevenly. As a result, during hemodialysis, the balance of concentrations of various substances between tissue cells, intercellular fluid and blood is disturbed; the state is denoted by the Latin word disequilibrium - “disturbed balance”.
By increasing the size of the dialyzer, the session time cannot be reduced. The fact is that the task of dialysis is to purify not only the blood, but also all the tissues of the body, or rather, all the water sectors (or spaces) of the body, since it is in the body fluids that the substances that are to be removed are dissolved. Such water spaces are: blood - 5 liters, intercellular fluid - 10 liters, intracellular - 15 liters. Only the blood is purified directly in the dialyzer. The blood, in turn, takes the substances to be removed from the interstitial fluid. And only the intercellular fluid takes toxic substances from the intracellular space, namely, it has the largest volume, and it takes time to “pull out” uremic toxins from this space, which is the most remote from the dialysis solution. In addition, substances are removed from different tissues at different rates. In parallel, water is removed - and also unevenly. As a result, during hemodialysis, the balance of concentrations of various substances between tissue cells, intercellular fluid and blood is disturbed; the state is denoted by the Latin word disequilibrium - “disturbed balance”. Unfortunately, this is an inevitable consequence of intermittent dialysis: if the kidneys (and peritoneal dialysis) work 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, then standard hemodialysis is performed for 4-5 hours every other day. The sensitivity of disequilibrium in different patients is different: someone does not notice it, someone can hardly endure it. Disequilibrium can be reduced by lengthening dialysis (with a less powerful dialyzer) or by increasing the frequency of sessions (with a less powerful dialyzer or shorter sessions). On the other hand, it is possible to reduce the sensitivity to disequilibrium by coping with some of the complications of uremia; first of all, these are anemia (hemoglobin level in a dialysis patient should be in the range of 110-120 g/l, and this requires iron and erythropoietin), protein deficiency (albumin level in a dialysis patient should be at least 40 g/l, and This requires proper nutrition and the absence of inflammation).
Unfortunately, this is an inevitable consequence of intermittent dialysis: if the kidneys (and peritoneal dialysis) work 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, then standard hemodialysis is performed for 4-5 hours every other day. The sensitivity of disequilibrium in different patients is different: someone does not notice it, someone can hardly endure it. Disequilibrium can be reduced by lengthening dialysis (with a less powerful dialyzer) or by increasing the frequency of sessions (with a less powerful dialyzer or shorter sessions). On the other hand, it is possible to reduce the sensitivity to disequilibrium by coping with some of the complications of uremia; first of all, these are anemia (hemoglobin level in a dialysis patient should be in the range of 110-120 g/l, and this requires iron and erythropoietin), protein deficiency (albumin level in a dialysis patient should be at least 40 g/l, and This requires proper nutrition and the absence of inflammation).
During dialysis, along with blood purification, excess water is removed. The removal of water from the blood occurs due to the fact that the dialysate fluid flows in the dialyzer under negative pressure, which creates a hemodialysis machine. Modern devices control this negative pressure in such a way that a given amount of fluid is removed during the session - the volume that has accumulated since the last dialysis session. This volume is estimated by weight gain since the end of the last session: in two days, muscle mass or body fat could not change significantly, which means that all weight gain after the last session is the result of water entering the body. Often we hear from patients that they do not drink water, and they don’t know where such an increase came from. The explanation (if only the patient is sincere about drinking) is simple: most foods contain a significant amount of water: more than 9Many fruits consist of 0% water, a significant amount of it is in vegetables (depending on the method of preparation), and we don’t eat dry cereals: in cereals, water is at least 70%.
The removal of water from the blood occurs due to the fact that the dialysate fluid flows in the dialyzer under negative pressure, which creates a hemodialysis machine. Modern devices control this negative pressure in such a way that a given amount of fluid is removed during the session - the volume that has accumulated since the last dialysis session. This volume is estimated by weight gain since the end of the last session: in two days, muscle mass or body fat could not change significantly, which means that all weight gain after the last session is the result of water entering the body. Often we hear from patients that they do not drink water, and they don’t know where such an increase came from. The explanation (if only the patient is sincere about drinking) is simple: most foods contain a significant amount of water: more than 9Many fruits consist of 0% water, a significant amount of it is in vegetables (depending on the method of preparation), and we don’t eat dry cereals: in cereals, water is at least 70%.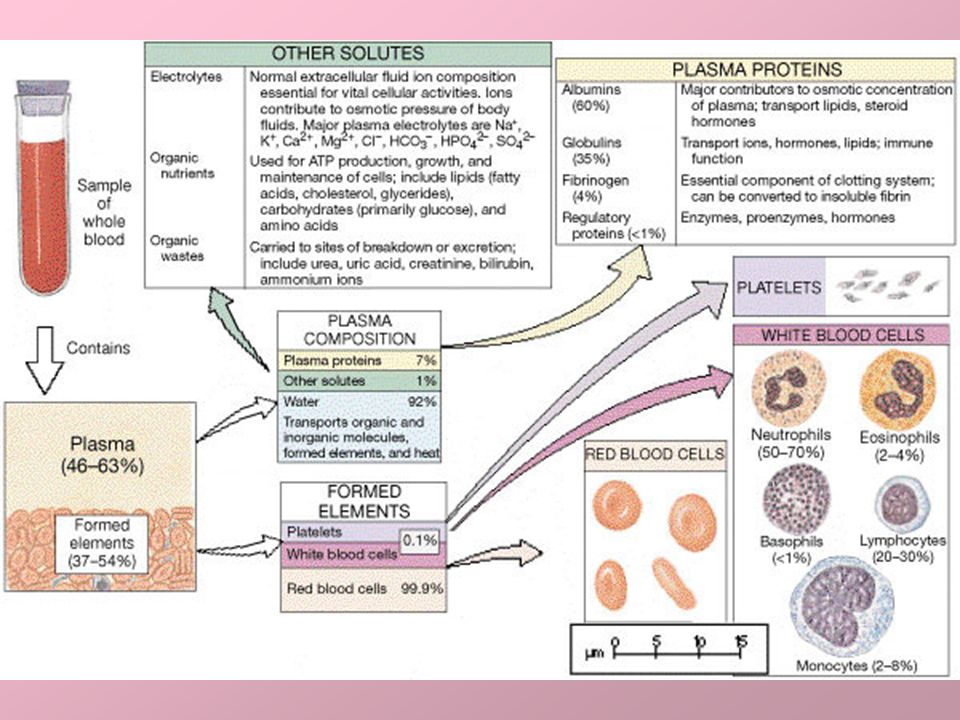 Calculating the amount of water in all products every day is a difficult task. Moreover, there is another source of water. In the process of metabolism and oxidation of hydrogen, which is part of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, endogenous “oxidation water” is formed, and its amount depends on the type of decaying substrates and the level of metabolism. So, at rest, during the oxidation of 100 g of fat, more than 100 ml of water is formed, 100 g of protein - about 40 ml of water, 100 g of carbohydrates - 55 ml of water. Increased physical activity leads to a sharp increase in endogenous water production, as increased energy demand leads to more complete oxidation of the substrates.
Calculating the amount of water in all products every day is a difficult task. Moreover, there is another source of water. In the process of metabolism and oxidation of hydrogen, which is part of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, endogenous “oxidation water” is formed, and its amount depends on the type of decaying substrates and the level of metabolism. So, at rest, during the oxidation of 100 g of fat, more than 100 ml of water is formed, 100 g of protein - about 40 ml of water, 100 g of carbohydrates - 55 ml of water. Increased physical activity leads to a sharp increase in endogenous water production, as increased energy demand leads to more complete oxidation of the substrates.
It is simpler and more reliable, therefore, limiting yourself to a reasonable amount of water in its pure form, take into account the rest of the water, regularly weighing, if necessary - several times a day. Over time, you will understand which foods from your usual diet add water and lead to excess interdialysis weight gain. What increases are considered acceptable? Ideally, to avoid fluctuations in blood pressure between sessions and a mild course of a dialysis session (without ultrafiltration), it would be good if there was no weight gain. Unfortunately, this is not possible for most dialysis patients: diuresis decreases rapidly on hemodialysis. Urine is not the only way to remove water from the body: we exhale about half a liter of water with humidified air from the lungs and about the same amount evaporates from the skin at a comfortable temperature (and several times more in the heat). But these excretion routes, together with residual diuresis, are usually not enough. What is missing has to be removed during dialysis.
What increases are considered acceptable? Ideally, to avoid fluctuations in blood pressure between sessions and a mild course of a dialysis session (without ultrafiltration), it would be good if there was no weight gain. Unfortunately, this is not possible for most dialysis patients: diuresis decreases rapidly on hemodialysis. Urine is not the only way to remove water from the body: we exhale about half a liter of water with humidified air from the lungs and about the same amount evaporates from the skin at a comfortable temperature (and several times more in the heat). But these excretion routes, together with residual diuresis, are usually not enough. What is missing has to be removed during dialysis.
Inter-dialysis weight gain must not exceed 5% of body weight in any case. Better is less! This also applies to the extended inter-dialysis period of time - three days instead of two (including Sunday: from Friday to Monday and from Saturday to Tuesday). Moreover, it is over a longer period of time that more uremic waste accumulates in the blood, and one can expect a more pronounced disequilibrium during dialysis, that is, more complications and worse tolerance of the session if more fluid has to be removed. And in the interdialysis period of time, an excessive increase will quickly raise blood pressure and, accordingly, the risk of serious complications, up to a stroke - cerebrovascular accident. It is known that the end of a long interdialysis interval accounts for up to 40% of all deaths of hemodialysis patients.
And in the interdialysis period of time, an excessive increase will quickly raise blood pressure and, accordingly, the risk of serious complications, up to a stroke - cerebrovascular accident. It is known that the end of a long interdialysis interval accounts for up to 40% of all deaths of hemodialysis patients.
Complications during dialysis
During dialysis, there are complications related to the dialysis procedure itself. The most frequent complications of a dialysis session are associated with the rapid movement of water, electrolytes and osmotically active substances: hypotension (drop in blood pressure), muscle cramps (often in the legs).
Hypotension
A drop in blood pressure (hypotension) occurs when an insufficient amount of blood remains in the vessels: water from the blood is removed into the dialysis solution, and from the interstitial fluid does not flow fast enough. The heart simply has nothing to raise the pressure in the vessels. Hypotension can be difficult to tolerate or almost imperceptible for different patients, begin gradually or suddenly: the fact is that the body has reliable ways to compensate for a decrease in blood volume, first of all, this is vasoconstriction in those organs that the body considers unimportant at the moment . But there are limits to any compensation - and then blood pressure drops. The patient feels sudden weakness, nausea (vomiting may begin), urge to defecate, "blackout", loss of consciousness is possible. In everyday life, we call it “fainting”, only the patient lies in a chair (bed) and cannot fall anywhere. All these are signs of a decrease in blood supply to various organs: muscles, stomach, intestines, retina, brain. In patients suffering from angina pectoris, the heart may be the first to feel a deterioration in blood supply - an attack of retrosternal pain will begin.
But there are limits to any compensation - and then blood pressure drops. The patient feels sudden weakness, nausea (vomiting may begin), urge to defecate, "blackout", loss of consciousness is possible. In everyday life, we call it “fainting”, only the patient lies in a chair (bed) and cannot fall anywhere. All these are signs of a decrease in blood supply to various organs: muscles, stomach, intestines, retina, brain. In patients suffering from angina pectoris, the heart may be the first to feel a deterioration in blood supply - an attack of retrosternal pain will begin.
You can't wait until hypotension is complete! At the first, even dubious signs of hypotension, urgently call the staff. There are simple and quick ways to fix the situation. These methods consist in increasing the volume of circulating blood: either a certain volume of saline is injected intravenously (which immediately eliminates the cause - a lack of blood volume), or osmotically active substances that "pull out" water from the interstitial fluid into the blood (which takes some time). Such osmotically active substances can be: concentrated salt solution ("hypertonic solution - NaCl 10%"), concentrated glucose solution (less effective and unfavorable for patients with diabetes mellitus).
Such osmotically active substances can be: concentrated salt solution ("hypertonic solution - NaCl 10%"), concentrated glucose solution (less effective and unfavorable for patients with diabetes mellitus).
ALL OF THESE WAYS ARE BAD. The fact is that during a dialysis session, water and salt should not be introduced into the patient, but removed. By introducing a saline solution, we destroy the result of ultrafiltration achieved to this point - the removal of fluid. The introduced salt and glucose will spread very quickly throughout all the water spaces of the body, the salt will again have to be removed, and glucose will be included in the metabolism, reduce appetite and be deposited by adipose tissue. In addition, if salt is introduced shortly before the end of the dialysis session, it will not have time to be excreted and will cause increased thirst until the next dialysis session. A vicious circle is formed.
Hypotension must therefore be prevented by all means! The main one is a decrease in the rate of liquid removal. It is hardly possible to significantly lengthen a dialysis session for a number of reasons; it remains to reduce interdialysis weight gain, and hence fluids. And here is the main hope for the reasonable behavior of the patient. We can only help with advice:
It is hardly possible to significantly lengthen a dialysis session for a number of reasons; it remains to reduce interdialysis weight gain, and hence fluids. And here is the main hope for the reasonable behavior of the patient. We can only help with advice:
the main cause of thirst is salt; removing its excess from the diet, you can more easily refuse excess drinking
a lot of salt is contained in ready-made seasonings, canned food
Thirst can be partially quenched without swallowing water, but only by rinsing the mouth and throat, especially with acidified water
some drugs cause dry mouth; discuss with your doctor the possibility of replacing them with others
If interdialysis weight gain is small (less than 3-5% of body weight), and hypotension still occurs, you and your doctor may have set too low a weight to which you aspire - the so-called "dry weight": in fact, your weight should be slightly higher. In this case, hypotension occurs towards the end of the dialysis session. Moving towards an increase in dry weight should be done with great care: if there is a lot of really excess fluid after dialysis, this will become the main cause of an increase in blood pressure in the interdialysis period, which drug therapy will not be able to cope with (see section on arterial hypertension). There are other important ways to prevent hypotension, but their effectiveness is not comparable to the refusal to consume excess salt and water. The propensity for hypotension with acceptable interdialysis weight gain and with properly defined dry weight may increase some adverse factors, their correction may reduce the incidence of hypotension:
Moving towards an increase in dry weight should be done with great care: if there is a lot of really excess fluid after dialysis, this will become the main cause of an increase in blood pressure in the interdialysis period, which drug therapy will not be able to cope with (see section on arterial hypertension). There are other important ways to prevent hypotension, but their effectiveness is not comparable to the refusal to consume excess salt and water. The propensity for hypotension with acceptable interdialysis weight gain and with properly defined dry weight may increase some adverse factors, their correction may reduce the incidence of hypotension:
anemia (low hemoglobin level - likely to require treatment with erythropoietin and iron preparations),
low blood protein (one of the functions of protein is to retain water in the vascular bed; probably requires a revision of the diet, treatment of inflammatory diseases ),
cardiovascular pathology (heart failure, in the first place; moreover, the manifestations of heart failure may be aggravated by taking certain medications, therapy may need to be adjusted),
diabetes (correction of glucose levels is unlikely to reverse the changes that have occurred in the body of a patient with diabetes mellitus, but patients with the initial stages of diabetes mellitus should remember that it is poor correction of glucose levels that leads to heart disease, one of the manifestations of which will be poor dialysis tolerance),
hypothyroidism (low thyroid function, often found in patients with chronic renal failure, contributes to hypotension; hypothyroidism detected by the analysis of thyroid hormone levels is relatively easily compensated by hormone replacement therapy).
Refusal to eat during dialysis can help reduce hypotension: food intake causes a rush of blood to the gastrointestinal tract, and this volume of the cardiovascular system may not be enough to maintain blood pressure.
Sodium profiling and ultrafiltration during dialysis may help reduce the incidence of hypotension. The essence of the method is as follows: the first part of dialysis is carried out with an increased sodium content in the dialysis solution. This does not reduce (or even slightly increase) the level of sodium in the blood, which maintains blood pressure. In the same period, an increased rate of ultrafiltration is established - the removal of water. Do not leave a high level of sodium in the dialysis fluid until the end of the dialysis session: this will lead to high sodium in the blood, and as a result, thirst, large weight gain, high blood pressure. Therefore, towards the end of dialysis, the sodium level gradually decreases and the excess sodium is washed away.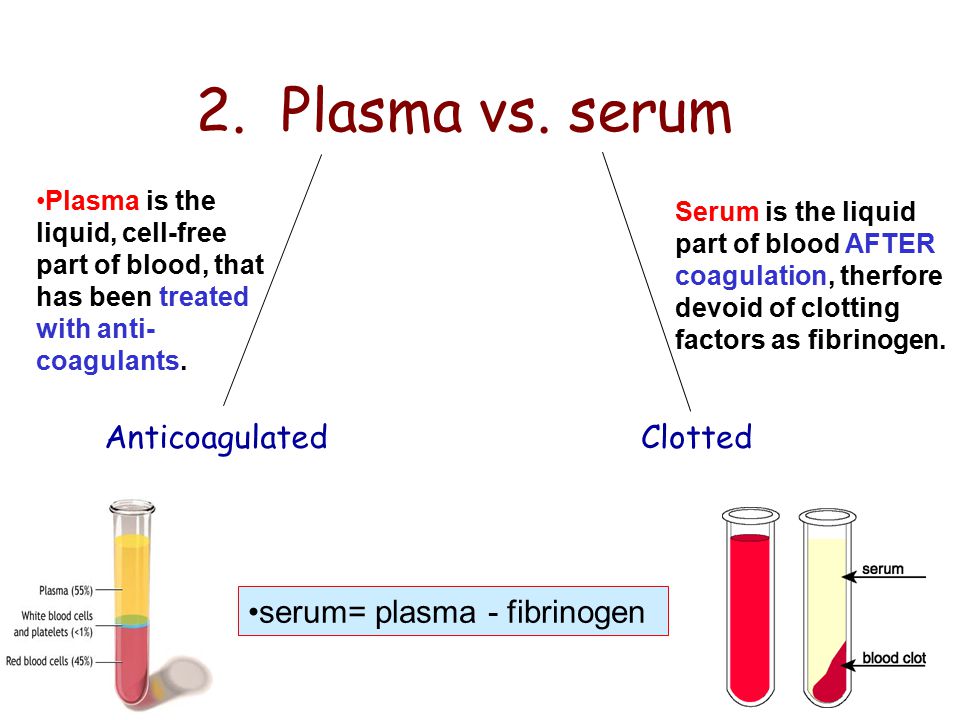 But by this time, another result has already been achieved - the removal of water, and ultrafiltration (which can cause hypotension) is no longer needed. So, by dividing the removal of water and sodium in time, in some patients it is possible to achieve a decrease in the frequency of hypotension.
But by this time, another result has already been achieved - the removal of water, and ultrafiltration (which can cause hypotension) is no longer needed. So, by dividing the removal of water and sodium in time, in some patients it is possible to achieve a decrease in the frequency of hypotension.
A relatively simple way to combat hypotension is to lower the temperature of the dialysis fluid, available in all dialysis machines. In everyday life, everyone knows that coolness always invigorates, and in the heat we “limp”. The explanation is in vascular tone. In an effort to reduce heat loss from the surface of the body in the cold, the vessels narrow, the capacity of the vascular bed decreases, and it is easier for the heart to maintain blood pressure. On the contrary, opening up in the heat, the vessels remove heat from the body, but this increases the capacity of the vascular bed, and at some point there may not be enough blood to maintain pressure. In practice, the temperature of the dialysis solution is reduced gradually, by half a degree for several sessions, evaluating the result and avoiding obvious discomfort.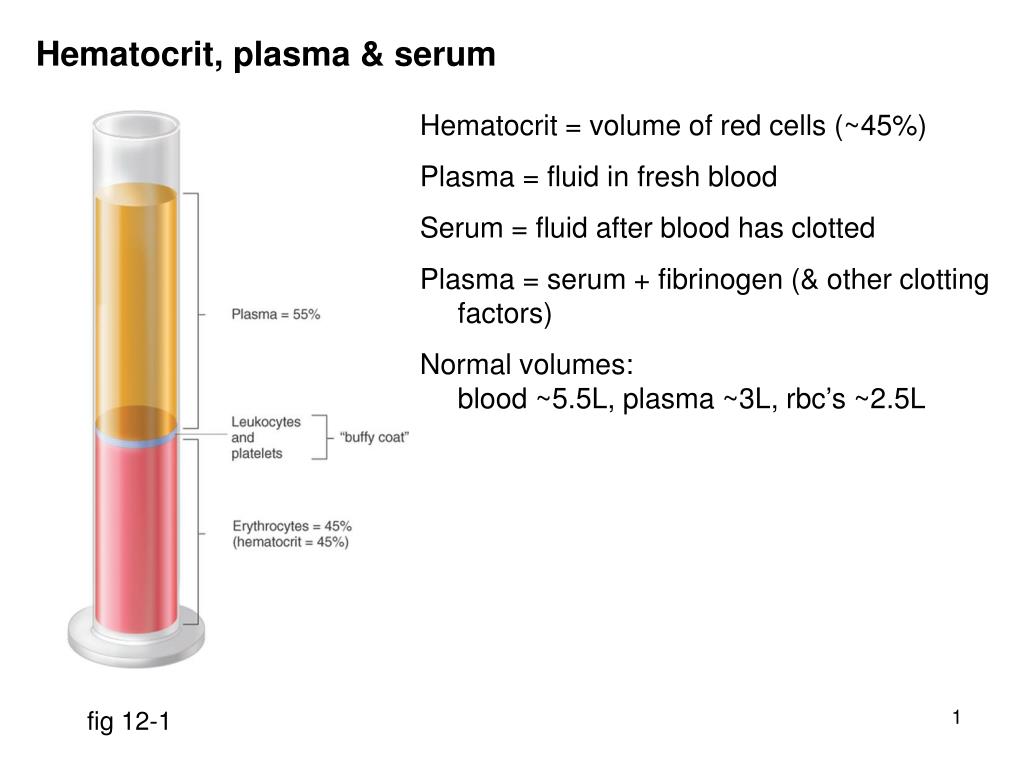 It has been observed that when using chilled dialysate in patients receiving dialysis on the second and third shifts, it is easier to fall asleep and sleep improves. There is no convincing evidence that hypertension therapy can contribute to the development of episodes of hypotension, but it is possible that some patients are justified in taking antihypertensive drugs after dialysis. There is also evidence for the metabolic drug carnitine, which may improve cardiac function.
It has been observed that when using chilled dialysate in patients receiving dialysis on the second and third shifts, it is easier to fall asleep and sleep improves. There is no convincing evidence that hypertension therapy can contribute to the development of episodes of hypotension, but it is possible that some patients are justified in taking antihypertensive drugs after dialysis. There is also evidence for the metabolic drug carnitine, which may improve cardiac function.
Thus, there are a number of possible ways to prevent hypotension, and taking into account the characteristics of your condition, the doctor will choose the necessary and acceptable for you. It is important to emphasize that all efforts can be canceled without a reasonable restriction of salt and water intake. This is a necessary basis for the prevention of episodes of hypotension.
Seizures
Seizures can be local (in a muscle group - more often - on the lower leg or thigh) or general. General convulsions with loss of consciousness are a manifestation of severe brain suffering; they occur on dialysis only during an unfavorable course of the introductory period, and we will not consider them here. For a hemodialysis patient, localized seizures may be typical. As a rule, like hypotension, they become a manifestation of a lack of blood volume and too rapid movements of water and sodium between the water sectors of the body - intracellular, intercellular and blood. The occurrence of convulsions increases significantly when dialysis reaches a weight below the "dry" level, in which case they serve simply as an indication of this fact. An indication, we note - not very good. It is better to avoid it, moving in the direction of the search for "dry weight" - to reduce weight in small steps: after all, excessive removal of fluid can lead to hypotension with all the adverse consequences.
For a hemodialysis patient, localized seizures may be typical. As a rule, like hypotension, they become a manifestation of a lack of blood volume and too rapid movements of water and sodium between the water sectors of the body - intracellular, intercellular and blood. The occurrence of convulsions increases significantly when dialysis reaches a weight below the "dry" level, in which case they serve simply as an indication of this fact. An indication, we note - not very good. It is better to avoid it, moving in the direction of the search for "dry weight" - to reduce weight in small steps: after all, excessive removal of fluid can lead to hypotension with all the adverse consequences.
Seizures can occur during dialysis (as well as after it) and at weight above dry weight. And then this indicates too rapid removal of water or sodium. It may be necessary to lengthen the dialysis session. And, of course, a lot depends on how much weight and what level of sodium you come to the next session. The greater the weight gain and the more salt you have eaten since your last dialysis, the faster you will have to remove them in a fixed session time. And that means - to cause convulsions and hypotension!
The greater the weight gain and the more salt you have eaten since your last dialysis, the faster you will have to remove them in a fixed session time. And that means - to cause convulsions and hypotension!
There are some ancillary drugs that relieve seizures: the metabolic drug carnitine, vitamin E; a number of other drugs carry numerous side effects.
Dry Weight
The patient's "Dry Weight" is the weight you should aim for at the end of a dialysis session. Normally functioning kidneys (along with other organs) are able to accurately maintain the amount of fluid that the body needs for normal functioning. Unfortunately, we do not have a way to replace this kidney function: to determine exactly how much water to leave in the body, that is, what should be the body weight after dialysis. At the same time, it is very important!
Excess weight (= excess water) will lead to an increase in blood pressure that is difficult to control and an excessive load on the heart and blood vessels: some of the excess water will circulate in the circulatory system.