Full term stillbirth
What is Stillbirth? | CDC
The loss of a baby due to stillbirth remains a sad reality for many families and takes a serious toll on families’ health and well-being. Learn more about stillbirth below.
A stillbirth is the death or loss of a baby before or during delivery. Both miscarriage and stillbirth describe pregnancy loss, but they differ according to when the loss occurs. In the United States, a miscarriage is usually defined as loss of a baby before the 20th week of pregnancy, and a stillbirth is loss of a baby at or after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Stillbirth is further classified as either early, late, or term.
- An early stillbirth is a fetal death occurring between 20 and 27 completed weeks of pregnancy.
- A late stillbirth occurs between 28 and 36 completed pregnancy weeks.
- A term stillbirth occurs between 37 or more completed pregnancy weeks.
View and print fact sheet » [482 KB / 2 pages]
How Many Babies Are Stillborn?
Stillbirth affects about 1 in 175 births, and each year about 21,000 babies are stillborn in the United States. 1 That is about the same as the number of babies that die during the first year of life. Because of advances in medical technology over the last 30 years, prenatal care (medical care during pregnancy) has improved, which has dramatically reduced the number of late and term stillbirths. However, the rate of early stillbirth has remained about the same over time.
What Increases the Risk of Stillbirth?
Stillbirth with an unknown cause is called “unexplained stillbirth.” The further along a woman is in her pregnancy the more likely it is that the stillbirth will be unexplained. Having an autopsy on the baby and other laboratory tests is important in trying to understand why the baby died before birth. Your health care provider can share more information about this.
Stillbirth occurs in families of all races, ethnicities, and income levels, and to women of all ages. However, stillbirth occurs more commonly among certain groups of people including women who:
- are of black race
- are 35 years of age or older
- are of low socioeconomic status
- smoke cigarettes during pregnancy
- have certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes and obesity
- have multiple pregnancies such as triplets or quadruplets
- have had a previous pregnancy loss
This does not mean that every individual of black race or older age is at higher risk for having a stillbirth. It simply means that overall as a group, more stillbirths occur among all mothers of black race or older age when compared to white mothers and mothers under 35 years of age. Some factors that might contribute to these stillbirth disparities include differences in maternal preconception health, socioeconomic status, access to quality health care, and stress.2 More research is needed to determine what is underlying reason why some of these factors are associated with stillbirths.
It simply means that overall as a group, more stillbirths occur among all mothers of black race or older age when compared to white mothers and mothers under 35 years of age. Some factors that might contribute to these stillbirth disparities include differences in maternal preconception health, socioeconomic status, access to quality health care, and stress.2 More research is needed to determine what is underlying reason why some of these factors are associated with stillbirths.
Many of these factors are also associated with other poor pregnancy outcomes, such as preterm birth.
What Can Be Done?
CDC works to learn more about who might have a stillbirth and why. CDC does this by tracking how often stillbirth occurs and researching what causes stillbirth and how to prevent it. Knowledge about the potential causes of stillbirth can be used to develop recommendations, policies, and services to help prevent stillbirth. While we continue to learn more about stillbirth, much work remains. To learn more about CDC’s activities, visit the Stillbirth CDC Activities page.
To learn more about CDC’s activities, visit the Stillbirth CDC Activities page.
References
- Gregory ECW, Valenzuela CP, Hoyert DL. Fetal mortality: United States, 2020. National Vital Statistics Reports; vol 71 no 4. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2022. [Read report]
- Pruitt SM, Hoyert DL, Anderson KN, et al. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Fetal Deaths — United States, 2015–2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:1277–1282.
- MacDorman MF, Kirmeyer SE, Wilson EC. Fetal and perinatal mortality, United States, 2006. National vital statistics reports; vol 60 no 8. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2012. [Read data brief pdf icon[432 KB / 23 pages]
Stillbirth: Definition, Causes & Prevention
Overview
What is a stillbirth?
A stillbirth is when a fetus dies after the mother’s 20th week of pregnancy. The fetus may have died in the uterus weeks or hours before labor. Rarely, the fetus may die during labor. Although prenatal care has drastically improved over the years, the reality is stillbirths still happen and often go unexplained.
Although prenatal care has drastically improved over the years, the reality is stillbirths still happen and often go unexplained.
A stillbirth is classified as either an early stillbirth, a late stillbirth, or a term stillbirth. Those types are determined by the number of weeks of pregnancy:
- Early stillbirth: The fetus dies between 20 and 27 weeks.
- Late stillbirth: The fetus dies between 28 and 36 weeks.
- Term stillbirth: The fetus dies the 37th week or after.
How common are stillbirths?
A stillbirth occurs in about one of 160 births (about 24,000 babies per year in the United States).
Who is at risk of having a stillbirth?
A stillbirth can happen to pregnant people of any age, background, or ethnicity. They can be unpredictable — 1 in 3 cases go unexplained. There are some ways you can reduce your risk, though. You’re more likely to have a stillbirth if you:
- Smoke, drink alcohol, or use recreational drugs.

- Are over the age of 35.
- Have poor prenatal care.
- Are malnourished.
- Are Black.
- Are having multiple births (twins or more).
- Have a preexisting health condition.
- Have obesity (body mass index above 30).
What’s the difference between a stillbirth and a miscarriage?
Like a stillbirth, a miscarriage is also a pregnancy loss. However, while a stillbirth is the loss of a fetus after 20 weeks of pregnancy, a miscarriage happens before the 20th week.
Symptoms and Causes
What causes a stillbirth?
The cause of the stillbirth is vital not only for the healthcare providers to know, but for the parents to help with the grieving process. The cause is not always known (1 in 3 stillbirths cannot be explained), but the most likely causes include:
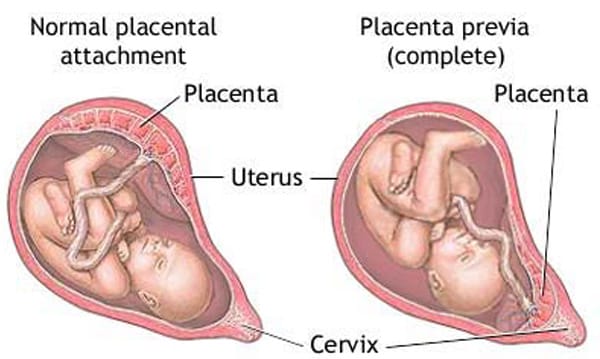
- Problems with the placenta and/or the umbilical cord. Your placenta is an organ that lines your uterus when you’re pregnant. Through it and the umbilical cord, the fetus gets blood, oxygen and nutrients.
 Any problems with your placenta or umbilical cord and the fetus will not develop properly.
Any problems with your placenta or umbilical cord and the fetus will not develop properly. - Preeclampsia. Preeclampsia is high blood pressure and swelling that often happens late in pregnancy. If you have preeclampsia, you have twice the risk of placental abruption or stillbirth.
- Lupus. A person who has lupus is at risk of having a stillbirth.
- Clotting disorders. A person with a blood clotting disorder like hemophilia is at a high risk.
- The pregnant person's medical conditions. Other illnesses can sometimes cause stillbirths. The list includes diabetes, heart disease, thyroid disease, or a viral or bacterial infection.
- Lifestyle choices. If your lifestyle includes drinking, using recreational drugs and/or smoking, you’re more likely to have a stillbirth.
- Birth defects. One or more birth defects cause about 25% of stillbirths.
 Birth defects are rarely discovered without a thorough examination of the fetus, including an autopsy.
Birth defects are rarely discovered without a thorough examination of the fetus, including an autopsy. - Infection. An infection between week 24 and week 27 can cause fetal death. Usually, it’s a bacterial infection that travels from your vagina to your uterus. Common bacteria include Group B Streptococcus, E. coli, klebsiella, enterococcus, Haemophilus influenza, chlamydia and mycoplasma or ureaplasma. Additional problems include rubella, the flu, herpes, Lyme disease and malaria, among others. Some infections go unnoticed until there are serious complications.
- Trauma. Trauma such as a car crash can result in a stillbirth.
- Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP). Also known as obstetric cholestasis, this is a liver disorder that includes severe itching.
What physical symptoms does the mother have after stillbirth?
If you have a fever, bleeding, chills, or pain, be sure to contact your healthcare provider right away because these may be signs of an infection.
Will I lactate after a stillbirth?
After the delivery of the placenta, the milk-producing hormones may be activated (lactation). You might start to produce breast milk. Unless you have preeclampsia, you can take medicines called dopamine agonists that may stop your breasts from producing milk. You can also choose to let the lactation stop naturally.
Does stillbirth cause infertility?
No. A stillbirth does not cause infertility and it doesn’t indicate that there is a problem with it.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is the diagnosis made?
Usually, you’ll notice that the fetus isn’t as active as it used to be. An ultrasound will confirm if the fetus has passed.
How can I find out what caused my stillbirth?
To discover the cause, your healthcare provider will perform one or more of the following tests:
- Blood Tests. Blood tests will show if you have preeclampsia, obstetric cholestasis or diabetes.
- Examination of the umbilical cord, membranes and placenta.
 These tissues attach to your fetus. An abnormality could prevent the fetus from receiving oxygen, blood and nutrients.
These tissues attach to your fetus. An abnormality could prevent the fetus from receiving oxygen, blood and nutrients. - Tests for infection. Healthcare providers will take a sample of your urine, blood, or cells from your vagina or cervix to test for infection.
- Thyroid function test. This test will determine if there’s something wrong with your thyroid gland.
- Genetic tests. Your healthcare provider will take a sample of the umbilical cord to determine if the fetus had genetic problems such as Down’s syndrome.
Your healthcare provider will also review medical records and the circumstances surrounding the stillbirth. With your consent, an autopsy can be performed to determine the cause of fetal death. An autopsy is a surgical procedure performed by a skilled pathologist. Incisions are made carefully to avoid disfigurement, and the incisions are surgically repaired afterward. You have the right to limit the autopsy to eliminate any incisions on your baby that are uncomfortable for you. Be sure to write these requests on the autopsy permission form.
Be sure to write these requests on the autopsy permission form.
Some hospitals don't perform autopsies, so your baby may have to be transported to another hospital. Be sure you feel comfortable with where your child is being taken. You also have the right to deny an autopsy, if that is your wish.
An autopsy may be legally required in some cases, including when:
- A baby died within 24 hours of a surgical operation.
- A healthcare provider can't certify the cause of death.
- A baby was alive and then died suddenly.
Management and Treatment
What happens after a stillborn baby passes away?
If the fetus passes away before you’re in labor, you have three options:
- Induced labor.
- Natural birth.
- Cesarean section.
Induced labor. Healthcare providers recommend induced labor as the best option after a stillbirth. It should be done immediately if you:
- Have severe preeclampsia (high blood pressure).

- Have a serious infection.
- Have a broken amniotic sac (the bag of water around the fetus).
- Have any clotting disorder.
The labor is induced using medicine dispensed in one of five ways:
- A tablet inserted into your vagina.
- A gel inserted into your vagina.
- A swallowed tablet.
- A drip into a vein.
- A Foley bulb. A mechanical balloon that widens the cervix.
Natural birth. Waiting for birth to happen naturally is an option but, as time goes by, the fetal body may deteriorate in your uterus. The fetus may look different than you expect. The deterioration also makes it more difficult to determine the cause of death.
Cesarean section. A cesarean section is not recommended because it’s not as safe as a natural birth or induced labor.
What happens after a stillborn baby is delivered?
You'll be able to hold your baby, and your healthcare providers will allow you as much time as you need to spend with your child. You may feel uncomfortable with this idea at first.
You may feel uncomfortable with this idea at first.
You may want to ask for any mementos and keepsakes of your child, such as a blanket, a lock of your child’s hair, the hospital ID bracelet, etc. You can take pictures. This may also be uncomfortable, but it may be a cherished possession at a later time and may help you during your grieving process. Most hospitals will issue the family a birth certificate, but make sure you ask and request that it include the baby's handprints and footprints.
Prevention
Can a stillbirth be prevented?
Usually, a stillbirth can't be prevented. It often occurs because the fetus wasn't developing normally. Generally, improving your health, including managing preexisting conditions and lifestyle choices, increases your chances of a successful pregnancy. You’re also less likely to have a stillbirth if, when you know you’re high-risk, you’re carefully monitored through routine ultrasounds and/or fetal heart rate monitoring. If your healthcare provider finds a problem, they can have your baby delivered early if necessary.
How can I reduce my risk of having a stillbirth?
Because the reason why a stillbirth happens isn't always understood, it is difficult to prevent. However, there are some steps you can take to increase your chances of having a healthy baby:
- Avoid recreational drugs, smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Contact your healthcare provider if there’s any bleeding during the second half of your pregnancy.
- Do what’s called a daily “kick count.” Around 26-28 weeks, familiarize yourself with fetal movements. Figure out what’s normal for the fetus. Then, if they stop acting normally, contact your healthcare provider.
- Before you get pregnant, work toward a weight that's healthy for you. If you’re already pregnant, talk with your healthcare provider about diet and exercise options.
- Protect yourself against infections.
- Avoid certain foods including some types of fish and some types of cheese. Also, double-check to make sure that any meat or poultry you eat is thoroughly cooked.

- Report any stomach pain, itching, or vaginal bleeding immediately.
- Sleep on your side, not your back. If you’ve been pregnant for 28 weeks or more, sleeping on your back can double the risk of stillbirth. It’s not completely clear why that makes a difference, but experts suspect that it has something to do with the flow of blood and oxygen to the fetus.
- Get routine tests, including your blood pressure and urine. These will help your healthcare provider see if there are any illnesses or conditions that may affect the health of your baby.
Can the food I eat prevent stillbirth?
Unfortunately, eating or avoiding a specific food can’t guarantee you won’t have a stillbirth. However, there are some foods you should stay away from to improve the chances of a healthy pregnancy in general. Avoid the following:
- Mold-ripened soft cheeses and soft blue cheeses.
- Unpasteurized milk and unpasteurized milk products.
- Raw or undercooked meat.

- Liver products.
- Pâté.
- Game meats.
- Raw or partially cooked eggs.
- Duck, goose or quail eggs.
- Swordfish, marlin, shark and raw shellfish.
- Limit caffeinated drinks and herbal teas.
Outlook / Prognosis
When should I see my healthcare provider after the natural birth or induced labor?
You’ll likely have a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider a few weeks later. At that time the post-mortem and test results will be discussed and you can voice concerns about future pregnancies.
Can I get pregnant after I've delivered a stillborn baby?
Yes. Most people who deliver stillborn babies go on to have normal pregnancies and births. If the stillbirth was caused by a birth defect or umbilical cord problem, the chances of another stillbirth is slight. If the cause was an illness the pregnant person has or a genetic disorder, the risk is somewhat higher. The chance that your next pregnancy will result in stillbirth is about 3%, which means that most post-stillbirth pregnancies result in healthy babies.
How long after a stillbirth should I get pregnant again?
Discuss the timing of your next pregnancy with your healthcare provider to make sure you are physically ready to begin a new pregnancy. Some healthcare providers recommend waiting a certain amount of time (from six months to one year) before trying to conceive again. Some studies have shown that people who wait at least one year to conceive may have less depression and anxiety during a later pregnancy.
Statistics show that about 60% of couples take up to six months to conceive after delivery of a stillborn baby, and another 30% take up to 12 months. Don't be surprised if things don't happen quickly.
Living With
Is a funeral necessary after a stillbirth?
After the death of your baby, one of the first decisions you will be faced with is whether or not to need to arrange a funeral.
The type of arrangements you make may play an important role in the grieving process. It is a decision that only you and the other parent can make together. You may find that you need time to make your decisions and arrangements. It is quite common for families to take up to a week (and sometimes longer) to make arrangements. This is okay.
You may find that you need time to make your decisions and arrangements. It is quite common for families to take up to a week (and sometimes longer) to make arrangements. This is okay.
No matter what your choice is, you have the right to change your mind. Be sure you ask whoever is carrying out your arrangements about how long you have to make any changes.
How should I communicate with my other children after a stillbirth?
You may find your children are a comfort, a worry, or just too hard to deal with. These are normal reactions. Take time to grieve and say goodbye to the child you lost. You will eventually feel normal feelings for your living children again, and the bond you have with them may possibly become stronger.
No matter how much you may want to shelter your children from pain, they can sense the emotion around them. Honesty is the best way to help your children cope with this painful experience. Children have a different understanding of death at different developmental stages.
What can I do to cope with a stillbirth?
Take as much time as you need to heal physically and emotionally after a stillbirth. Regardless of the stage of pregnancy during which your loss occurred, you are still a parent and the life you nurtured was real. It is completely normal for you to experience depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Above all, don't blame yourself. Give yourself time to cope, grieve and accept your devastating loss.
Counseling is available. Pregnancy loss support groups may also be a good resource for both parents. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about counseling and support groups.
What questions should I ask my healthcare provider after a stillbirth?- What was the cause of the stillbirth?
- Is there anything else I can do to prevent a stillbirth in the future?
- Do you recommend a psychiatrist?
- Do you recommend a counselor?
- Do you recommend a support group?
- How soon do you recommend I get pregnant again?
- Does this hospital keep records of stillbirths?
- Can I get a copy of the records/birth certificate?
- When should I return for another appointment?
- How will I be cared for in the next pregnancy?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
A stillbirth can be devastating. It can be overwhelming and depressing for the parents, their children, the grandparents, and other family members and friends. The grieving can be even worse when a stillbirth happens for no known reason. Remember that it’s normal to have difficulty coping. Access mental health professionals if you need help.
It can be overwhelming and depressing for the parents, their children, the grandparents, and other family members and friends. The grieving can be even worse when a stillbirth happens for no known reason. Remember that it’s normal to have difficulty coping. Access mental health professionals if you need help.
Stay in contact with your healthcare providers before, during and after your pregnancy. Share your worries and ask questions. Do your best to avoid risk factors such as smoking and drinking. Also, remember that if you’ve had a stillbirth, you can get pregnant again. There is a 3% chance of another stillbirth.
Decree and the death of a child - an algorithm for the actions of an accountant in 1C programs - Accounting without worries
- Posted on 06/29/2020 08:59
- Author: Administrator
- Views: 25080
The accrual of maternity benefits for standard pregnancy usually does not cause many questions for accountants. But in practice, there are also non-standard cases, such as complicated births or multiple pregnancies. To help our readers, we decided to release a number of publications that will help you understand the nuances and correctly reflect complex cases in 1C software products. Recently, we already wrote an article From decree to decree in 1C: Salary and personnel management, ed. 3.1. Now let's talk about a difficult life situation. We all hope that this will never affect us, but, unfortunately, not all pregnancies end in the birth of a healthy baby. It happens that a child dies in the first minutes of life or is born already dead. What to do in such cases with maternity leave, in which the employee is already on, we will talk further.
To help our readers, we decided to release a number of publications that will help you understand the nuances and correctly reflect complex cases in 1C software products. Recently, we already wrote an article From decree to decree in 1C: Salary and personnel management, ed. 3.1. Now let's talk about a difficult life situation. We all hope that this will never affect us, but, unfortunately, not all pregnancies end in the birth of a healthy baby. It happens that a child dies in the first minutes of life or is born already dead. What to do in such cases with maternity leave, in which the employee is already on, we will talk further.
In fact, a woman who has given birth is entitled to a full-fledged maternity leave, regardless of the actual outcome of the birth. According to the procedure approved by the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia No. 624n dated June 29, 2011, the withdrawal of a sick leave certificate previously issued by a medical institution is impossible under any circumstances, even in the event of the birth of a dead child or his death subsequently.
The only exception would be if the preterm birth occurred before the 21st week of pregnancy. In such cases, medical institutions issue certificates of incapacity for work as in case of a common illness for a period of at least three calendar days. This procedure is enshrined in paragraph 50 of Order No. 624n.
In this case, if the birth occurred from the 22nd to the 30th week of pregnancy, then the sick leave is issued for a period of 156 days, as in case of complicated birth. If the term has already reached the 31st week or more, then the maternity leave will be the standard 140 calendar days.
What if an employee who has lost a baby wants to interrupt her maternity leave and start working? Unfortunately, there is no single answer in labor legislation.
At the same time, according to the letter of Rostrud No. 1755-TZ dated May 24, 2013. "On early exit from maternity leave" interrupting maternity leave at the request of the employee is not prohibited. Also in part 4 of Art. 15 of Law No. 255-FZ states that the amounts of maternity benefits overpaid to the insured person cannot be recovered from him, except in cases of a counting error.
Also in part 4 of Art. 15 of Law No. 255-FZ states that the amounts of maternity benefits overpaid to the insured person cannot be recovered from him, except in cases of a counting error.
It turns out that the employee for the same period will receive both sick leave payments and wages for the performance of her work.
However, in such a situation, the FSS authorities may consider receiving benefits in an overlapping period unlawful.
Based on this, it turns out that the employer will be able to return the overpaid amount of benefits only if the employee reimburses it voluntarily by writing a corresponding application.
As for the one-time allowance for the birth of a child, it is unfortunately not allowed for an employee who has lost a child. This is stated in Part 3 of Art. 11 of the Federal Law of 19.05.1995 No. 81-FZ "On State Benefits for Citizens with Children".
However, in accordance with par. 4 p. 2 art. 10 of the Federal Law of 12.01.1996. No. 8-ФЗ “On Burial and Funeral Business”, in the event of the birth of a dead child after 154 days of pregnancy, an employee can count on a funeral allowance. It is paid if the appeal was followed no later than six months from the date of death (clause 3, article 10 of Law No. 8-FZ).
10 of the Federal Law of 12.01.1996. No. 8-ФЗ “On Burial and Funeral Business”, in the event of the birth of a dead child after 154 days of pregnancy, an employee can count on a funeral allowance. It is paid if the appeal was followed no later than six months from the date of death (clause 3, article 10 of Law No. 8-FZ).
Algorithm of actions of an accountant in case of death of an employee's child in 1C: ZUP ed. 3.1
So, let's start from the beginning: send an employee on maternity leave. A sick leave is issued in the section "Salary" - "Sick leave".
To enter a new certificate of incapacity for work in the window that opens, click on the "Create" button, specify the accrual period, select an employee and enter the sick leave number.
If this is an electronic sick leave and you have a connection to the personal account of the FSS, then you can fill in the period of the decree and the reason for disability by clicking on the "Get from the FSS" button. If you have previously downloaded the electronic sheet file, then you should click on the "Load from file" button.
If you have previously downloaded the electronic sheet file, then you should click on the "Load from file" button.
When filling out a document from paper, you must manually enter the vacation period and indicate the code “(05) Maternity and maternity leave” as the reason for disability. After that, the program will automatically calculate the charges.
To check the average earnings, on the basis of which the accrual was made, you need to click on the icon next to the "Average earnings" field.
If necessary, at the request of the employee in this window, you can change the years from which the allowance is calculated. We talked about how to do this earlier.
On the Accrued (detailed) tab, you can analyze accruals and their frequency.
After checking the calculation, the document should be saved by clicking on the "Post and close" button.
Payment can be made with the next salary or in advance, as well as in the inter-settlement period.
To generate a statement in the inter-settlement period, in the "Sick leave" window, click on the "Pay" and "Submit and close" buttons.
If an employee decides to use the maternity leave in full in the event of the death of a child, no additional documents need to be entered. At the end of the period of incapacity for work, she will be considered to have left the decree and the calculation of wages will begin on her.
If she decided to interrupt the vacation and wrote an application for the voluntary return of the excess received allowance, this sick leave should be corrected by clicking the "Correct" button in it at the bottom of the window. This will open a new document "Sick leave", in which there will be an inscription: "The document is a correction of another document."
The Month column will be filled with the current period. Next, you need to correct the vacation period by correcting the “to” date. After that, the program will recalculate.
On the "Recalculation of the previous period" tab, we will see the reversed amounts of the previous accrual, and on the "Accrued (detailed)" tab, the new calculated amounts.
Having calculated the salary for the current month, we will form a “Payroll”. To do this, go to the "Salary" section and select the "Salary Reports" item.
If the amount of the employee's wages is less than the amount of the sick leave recalculation, then a debt will be formed for the employee at the end of the period, which will be transferred to subsequent billing periods.
Let's consider how this was reflected in the report "Calculation of insurance premiums". Let's go to the "Reporting, references" section and select the "1C-Reporting" item.
In the window that opens, click on the "Create" button and select the required report in the "Tax reporting" section.
In the Calculation of insurance premiums in Appendix 2 to section 1, we will see the adjusted amount of the benefit accrual.
The algorithm of the accountant's actions in the event of the death of an employee's child in 1C: Enterprise Accounting, ed. 3.0
In this software product, sick leave is calculated in the section "Salary and personnel" - "All accruals".
When you click on the "Create" button in the window that opens, select "Sick leave" from the drop-down list. Filling out the disability certificate is carried out in the same way as described above.
Unfortunately, in this software product, there is no mechanism for correcting a previously entered document with the current period. Therefore, to correct the calculation, you must first reverse the previously entered document, and then enter a new one.
To cancel the previous accruals, go to the "Operations" section and select the "Manually entered operations" item.
In the window that opens, click on the "Operation" button and select the "Document reversal" item. Then, in the column “Reversible document”, indicate the previous sick leave, after which the program will make negative accruals.
Then, in the column “Reversible document”, indicate the previous sick leave, after which the program will make negative accruals.
After saving the document, click the "Save and Close" button to return to the "Salary and Personnel" - "All Accruals" section and enter a new sick leave with new parameters.
Thus, you will receive the correct accruals, and the employee will be able to start working.
Author of the article: Alina Kalendzhan
Like this article? Subscribe to newsletter
Add a comment
Stillbirth 9S
- Popular Topics
- Air pollution
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Hepatitis
- Data and statistics »
- News bulletin
- The facts are clear
- Publications
- Find Country »
- A
- B
- C
- D
- Д
- Е
- Ё
- Ж
- З
- И
- Й
- К
- Л
- М
- Н
- О
- П
- Р
- С
- Т
- У
- Ф
- Х
- Ц
- Ч
- Ш
- Щ
- Ъ
- Ы
- Ь
- Э
- Ю
- Я
- WHO in countries »
- Reporting
- Regions »
- Africa
- America
- Southeast Asia
- Europe
- Eastern Mediterranean
- Western Pacific
- Media Center
- Press releases
- Statements
- Media messages
- Comments
- Reporting
- Online Q&A
- Developments
- Photo reports
- Questions and answers
- Latest information
- Emergencies "
- News "
- Disease Outbreak News
- WHO data »
- Dashboards »
- COVID-19 Monitoring Dashboard
- Basic moments "
- About WHO »
- CEO
- About WHO
- WHO activities
- Where does WHO work?
- Governing Bodies »
- World Health Assembly
- Executive committee
- Main page/
- Health issues/
- Stillbirth
UNICEF/Ramoneda
© A photo
Our activities
Key events
Why is it so important for us to talk about the loss of a child
Read
News
All →Events
Reports
Publications
All → As part of the continuum of reproductive health services, antenatal care (ANC) provides a platform for.