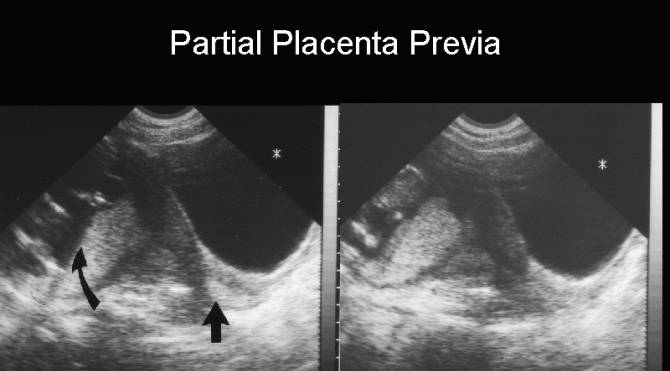
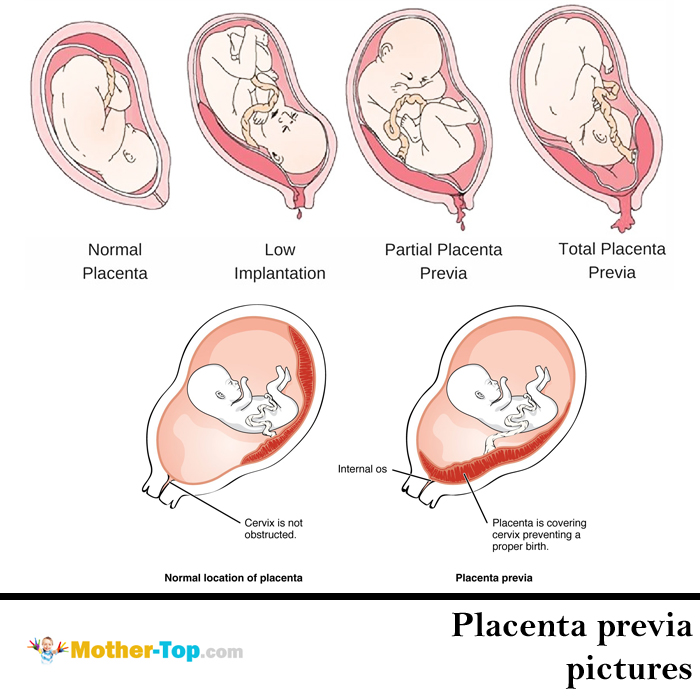
Signs of low lying placenta
Low-lying placenta (placenta praevia) | Tommy's
Is a low-lying placenta common?
The position of your placenta will be checked at your mid-trimester ultrasound scan, at around 18-21 weeks of pregnancy. If your placenta is low-lying, you have another scan later in your pregnancy (usually about 32 weeks).
Because the lower part of the womb stretches more as the baby grows, the placenta usually moves into the upper part of the womb by this point. 90% of women who have a low-lying placenta at 20 weeks will not go on to have a low-lying placenta later in the pregnancy.
If you have had a baby by caesarean section before, the placenta is less likely to move upwards.
Only 1 in every 200 women have placenta praevia at the end of their pregnancy.
Am I likely to have placenta praevia?
Placenta praevia is more likely if you:
- smoke cigarettes
- have had fertility treatment to get pregnant, such as in vitro fertilisation (IVF)
- have had 1 or more caesarean sections
- are aged 40 or older
- are having more than 1 baby
- have had surgery on the womb
- are a cocaine user
- are expecting a boy
- have endometriosis.
Is there anything I can do to help the placenta move up?
Unfortunately not. The best thing you can do is concentrate on staying as healthy as you can. You may need extra scans, so make sure you go to all your antenatal appointments and follow your healthcare professional’s advice.
How can placenta praevia affect me and my baby?
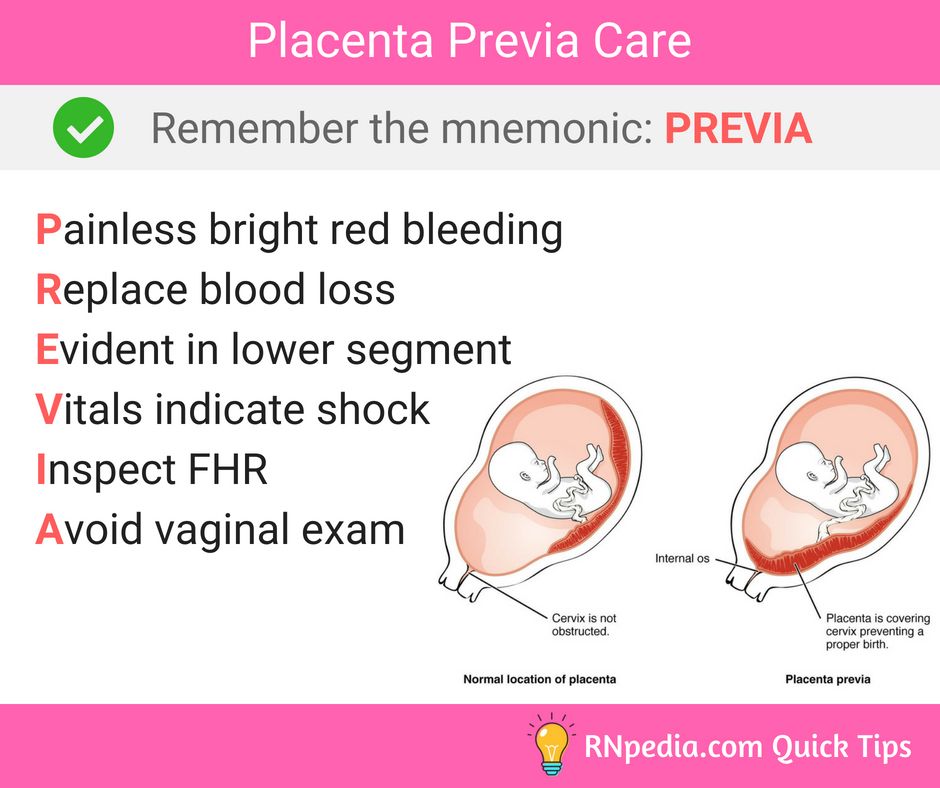
There is a risk that you may have vaginal bleeding, particularly towards the end of your pregnancy. Bleeding from placenta praevia may be very heavy and can sometimes put mum and baby at risk.
How is a low-lying placenta diagnosed?
Your midwife or doctor will look at your placenta’s position at your 18 to 21 week ultrasound scan.
If your placenta is low, you'll be offered an extra ultrasound scan later in your pregnancy (usually at about 32 weeks) to check its position again.
In 90% of cases, the placenta is no longer low-lying by this point.
Your midwife or doctor may think you have placenta praevia if:
- you have bleeding during the second or third trimester – this is usually painless and may happen after sex
- if the baby is lying in an unusual position, for example bottom first (breech) or lying across the womb (transverse)
If you have any bleeding during pregnancy, with or without pain, you should always get checked out straight away.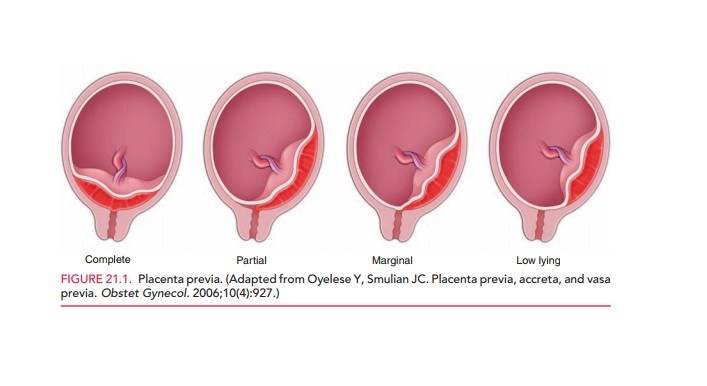 If you’re in your first trimester, contact your doctor, midwife or Early Pregnancy Unit. If you are more than 12 weeks pregnant, go to your local A&E or contact your hospital maternity unit immediately.
If you’re in your first trimester, contact your doctor, midwife or Early Pregnancy Unit. If you are more than 12 weeks pregnant, go to your local A&E or contact your hospital maternity unit immediately.
You may be advised to avoid having sex (including the use of penetrative sex toys) for the rest of your pregnancy.
What treatment will I have?
Extra scans
If your placenta is low-lying at your 20-week scan, you’ll be offered another ultrasound scan at around 32 weeks. This may include a transvaginal ultrasound scan, which is when a probe is gently placed inside the vagina to check exactly where your placenta is lying. Don’t worry, this is safe for you and your baby.
The length of your cervix may also be measured at your 32-week scan to predict whether you may go into labour early and whether you are at increased risk of bleeding.
If the placenta hasn’t moved up, you should be offered another ultrasound scan at 36 weeks. The results of this scan will help you and your doctor plan the safest way for you to give birth.
Medication
If you have placental praevia, there is a risk you may give birth prematurely. So you may be offered a course of steroid injections between 34 and 36 weeks of pregnancy to help your baby’s lungs to become more mature.
If you do go into labour early, you may be offered medication to try to stop your contractions. This will give you time to have a course of steroid injections. If you have severe bleeding or progressing labour your baby may need to be delivered.
If you have vaginal bleeding, you may need to be admitted to hospital. This is because there is a small risk that you could bleed suddenly and heavily. If this happens, you may need an emergency caesarean section.
What do I need to do if I have a low-lying placenta?
If you know you have a low-lying placenta, you should contact the hospital immediately if you have:
- vaginal bleeding, including spotting
- contractions
- pain, including any vague, period-like aches.
If you have any bleeding, your doctor may need to do an internal examination to check where it’s coming from. This is safe and they will ask for your permission before they start.
Anaemia
Anaemia is a blood condition that develops when you don’t have enough red blood cells. Red blood cells contain haemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen around your body and to your baby.
If you have a low-lying placenta, it’s important to try to avoid developing anaemia, which can be common in pregnancy. Eating a healthy, balanced diet will help you either prevent or manage anaemia. Iron supplements may also help, if your healthcare team recommends them.
How will my baby be born?
Your healthcare team will talk to you about what your options are for giving birth.
You may be advised to give birth early if you have any heavy bleeding before your due date.
If the edge of your placenta is very close (less than 20mm) to your cervix (entrance to the womb), the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists state that the safest way to give birth is by caesarean section. This will usually be between 36 and 37 weeks. Your doctor will discuss your options with you, but how you give birth is ultimately your decision. But if you have had vaginal bleeding during your pregnancy, you may be advised to have your caesarean earlier than this.
This will usually be between 36 and 37 weeks. Your doctor will discuss your options with you, but how you give birth is ultimately your decision. But if you have had vaginal bleeding during your pregnancy, you may be advised to have your caesarean earlier than this.
If the placenta is further than 20mm from your cervix, you may be able to have a vaginal birth if you want one.
If you are having a caesarean section, a senior obstetrician (a doctor who specialises in pregnancy) will be there. This is because you may have heavy bleeding during the surgery. If this happens, you may need a blood transfusion. This is more likely if you have placenta praevia.
Talk to your doctor before your surgery if, for any reason, you do not want a blood transfusion.
Unfortunately, complications are more common in caesarean sections if you have a low-lying placenta. Your doctor should talk to you about the risks of major bleeding and hysterectomy (removal of the womb) before your caesarean.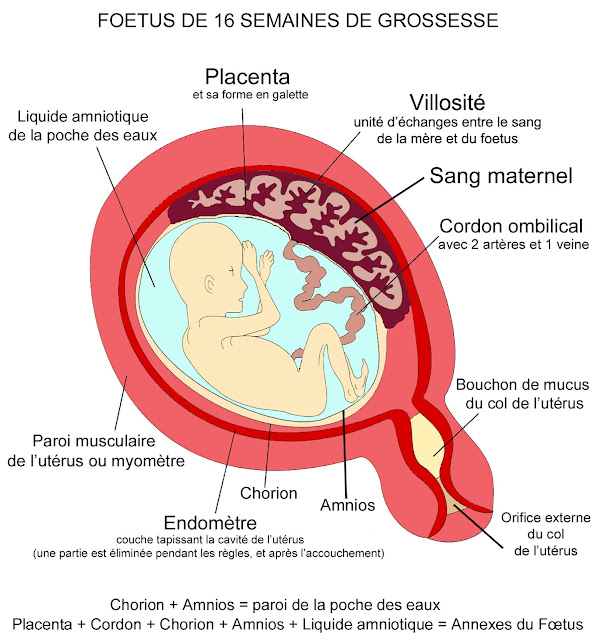 For most women, the risk of hysterectomy is low and will only occur as a last resort if other measures to control bleeding are not effective.
For most women, the risk of hysterectomy is low and will only occur as a last resort if other measures to control bleeding are not effective.
If you have placenta praevia:
- you are at higher risk of having your baby early (less than 37 weeks).
- your baby will need to be born by caesarean section because the placenta is blocking the birth canal.
Your mental health
Being diagnosed with complications in pregnancy can be hard. And being asked to look out for certain symptoms, such as bleeding, and needing extra appointments and check-ups can cause anxiety and stress. It may also be a lonely experience when those around you don’t understand what it’s like.
Remember that you can tell your midwife or doctor how you feel. They will do their best to reassure you and answer any questions you may have.
You can also call our pregnancy line on 0800 014 7800 (Monday to Friday, 9am to 5pm), or email us at [email protected]
If you are struggling to cope, there is professional support available.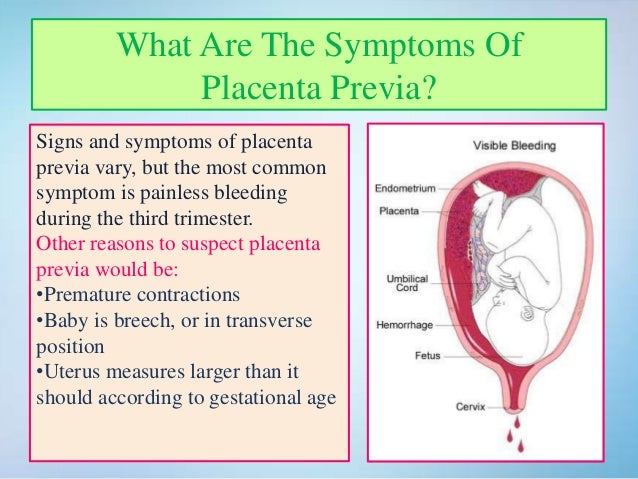 Don’t suffer in silence. Tell your midwife or GP how you feel. They will help you access the support you need.
Don’t suffer in silence. Tell your midwife or GP how you feel. They will help you access the support you need.
Find out more about looking after our mental health in pregnancy.
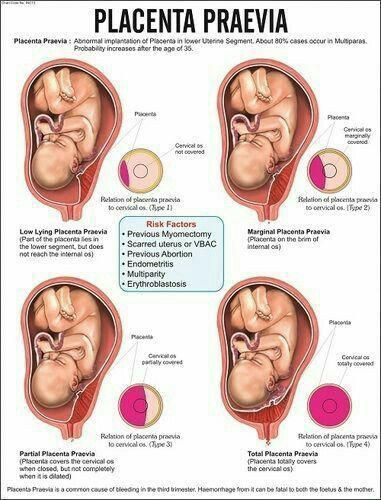
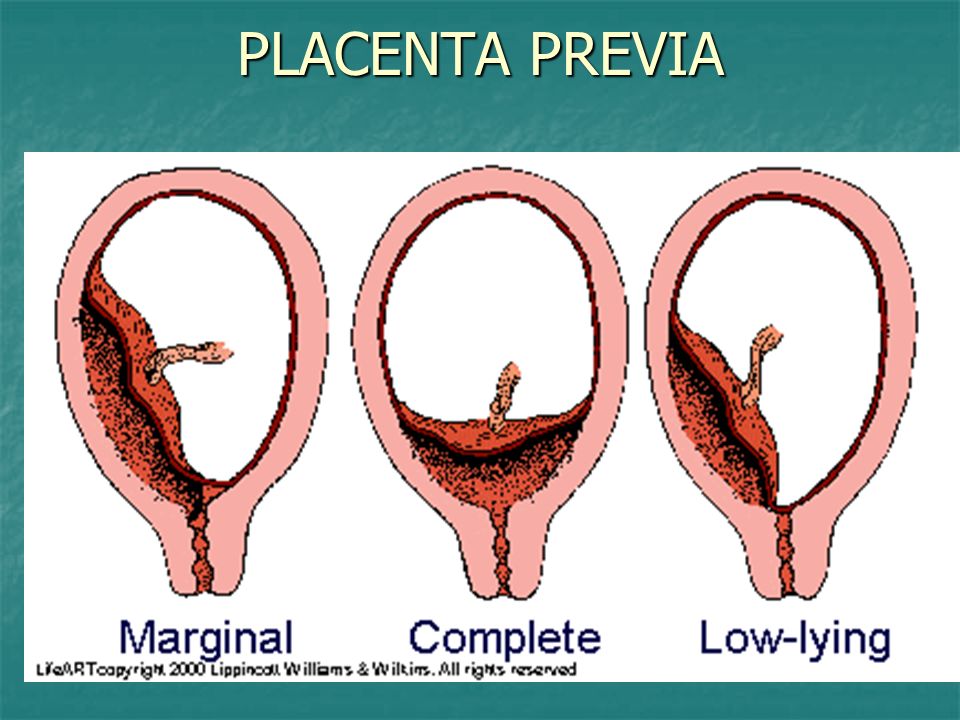
Placenta Previa
Placenta previa occurs when the placenta covers the opening of the cervix during the last months of pregnancy. This condition can cause severe bleeding before or during labor.
The placenta develops in a pregnant person’s uterus during pregnancy. This sac-like organ provides the developing baby with food and oxygen. It also removes waste products from the baby’s blood. The placenta is also referred to as “afterbirth” because it exits the body after the baby is born.
During pregnancy, the uterus stretches and grows. It’s normal for the placenta to be low in the uterus in early pregnancy. As the pregnancy continues and the uterus stretches, the part of the uterine the placenta was stuck to moves, usually away from the cervical opening.
By the third trimester, the placenta should be near the top of the womb.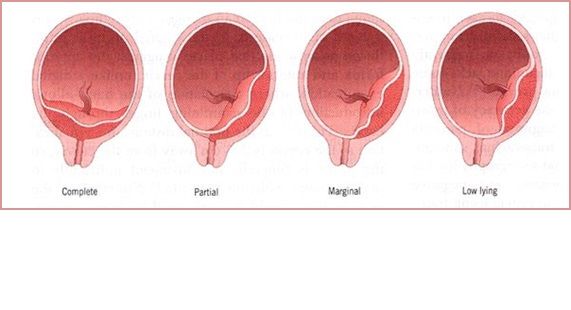 This position allows the cervix, or the entrance to the womb at the bottom of the uterus, a clear path for delivery.
This position allows the cervix, or the entrance to the womb at the bottom of the uterus, a clear path for delivery.
If the placenta attaches instead to the lower part of the uterus, it can cover part or all of the internal opening or “os” of the cervix. When the placenta covers the cervical os during the last months of pregnancy, the condition is known as placenta previa.
Most pregnant people with placenta previa will require pelvic rest. This typically includes abstaining from having sexual intercourse, limiting any procedures like an obstetrical check for dilation, and possibly restricting any exercises that may strain the pelvic floor.
The main symptom of placenta previa is sudden light to heavy bleeding from the vagina. Any bleeding can be representative of problems with the placenta and needs investigation by a physician. Specific symptoms may include:
- cramps or sharp pains
- bleeding that starts, stops, and begins again days or weeks later
- bleeding after intercourse
- bleeding during the second half of pregnancy
Risk factors for the development of placenta previa include:
- unusual position of the baby, including breech (buttocks first) or transverse (lying horizontally across the womb)
- previous surgeries that involve the uterus: cesarean delivery, surgery to remove uterine fibroids, dilation and curettage (D&C)
- pregnant with twins or other multiples
- prior miscarriage
- large placenta
- abnormally shaped uterus
- having already given birth to one child
- prior diagnosis of placenta previa
Pregnant people who are smokers, who are older than 35, or who are of Asian descent are also at higher risk of developing placenta previa.
Usually, the first signs of placenta previa will show up during the routine 20-week ultrasound. These initial signs are not necessarily a cause for worry, since the placenta is often lower in the uterus during the early part of a pregnancy.
The placenta usually corrects itself. According to the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, only 10 percent of people with low-lying placenta at 20 weeks will have a low-lying placenta at their next ultrasound. Only .5 percent will have placenta previa at the end of their pregnancy.
If you experience any bleeding in the second half of your pregnancy, doctors will monitor the position of the placenta using one of these preferred methods:
- Transvaginal ultrasound. Your doctor places a probe inside the vagina to provide an inside view of your vaginal canal and cervix. This is the preferred and most accurate method for determining placenta previa.
- Transabdominal ultrasound. A healthcare technician places gel on your abdomen and moves a handheld unit called a transducer around your abdomen to view the pelvic organs.
 The sound waves make a picture on a TV-like screen.
The sound waves make a picture on a TV-like screen. - MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). This imaging scan will help clearly determine the placenta’s location.
Doctors will decide how to treat your placenta previa based on:
- the amount of bleeding
- the month of your pregnancy
- the baby’s health
- the position of the placenta and the baby
The amount of bleeding is a doctor’s main consideration when deciding how to treat the condition.
Minimal to no bleedingFor cases of placenta previa with minimal or no bleeding, your doctor will likely suggest pelvic rest. This means refraining from putting anything into your vagina during pregnancy in order to prevent medical complications.
You’ll also be asked to avoid sex and likely exercise as well. If bleeding occurs during this time, you should seek medical care as soon as possible.
Heavy bleedingIn the case of heavy bleeding, your doctor will advise scheduling a cesarean delivery as soon as it’s safe to deliver — preferably after 36 weeks. If the C-section needs to be scheduled sooner, your baby may be given corticosteroid injections to speed up their lung growth.
If the C-section needs to be scheduled sooner, your baby may be given corticosteroid injections to speed up their lung growth.
In the case of uncontrolled bleeding, an emergency cesarean delivery will have to be performed.
During labor, the cervix will open to allow the baby to move into the vaginal canal for birth. If the placenta is in front of the cervix, it will begin to separate as the cervix opens, causing internal bleeding.
This can necessitate an emergency C-section, even if the baby is premature, as the pregnant person could bleed to death if no action is taken. Vaginal birth also poses too many risks for the pregnant person, who could experience severe hemorrhaging during labor, delivery, or after the first few hours of delivery.
A placenta previa diagnosis can be alarming for people who are expecting a baby. Here are some ideas for how to cope with your condition and how to prepare yourself for delivery.
Get educated. The more you know, the more you’ll know what to expect. Get in contact with other people who have been through placenta previa births.
Be prepared for your cesarean delivery. Depending on the type of your placenta previa, you might not be able to have a vaginal birth. It’s good to remember the ultimate goal — the health of you and your baby.
Rest. Pelvic rest is important while you are experiencing this condition. Additionally you should not engage in any strenuous activity or heavy lifting. You can use the time wisely by catching up on small projects, such as:
- putting together a photo album
- writing letters
- reading about your upcoming lifestyle change
Pamper yourself. Indulge in small pleasures, such as:
- buying a new pair of comfortable pajamas
- reading a good book
- watching your favorite TV program
- keeping a gratitude journal
Be sure to rely on your circle of friends and family for conversation and support.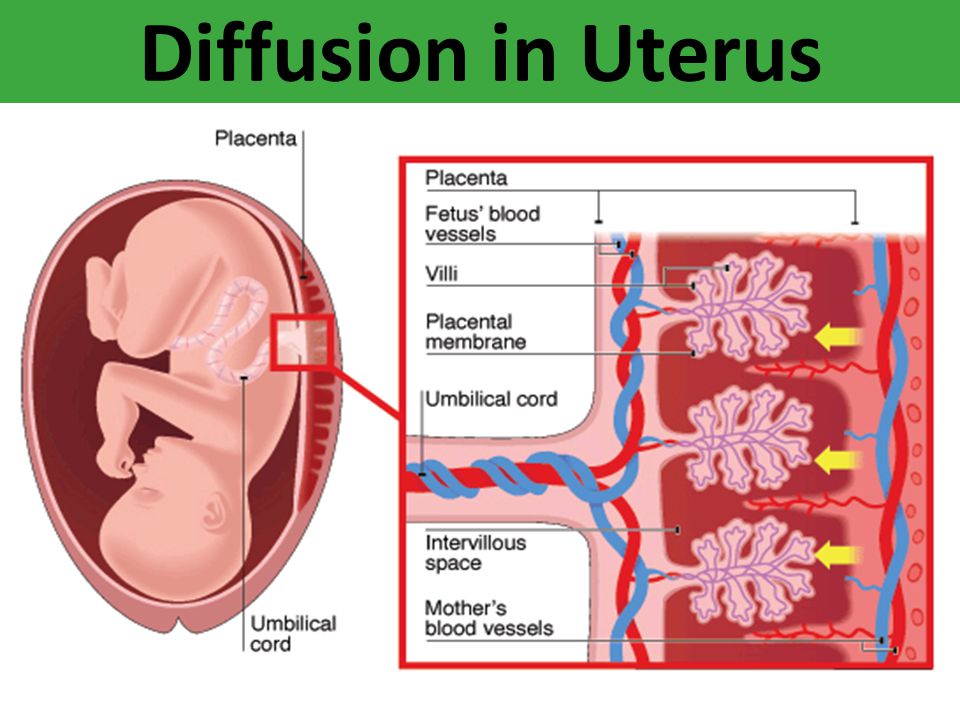
Low placenta
Home / Gynecologist / Low placenta
Placenta is a temporary organ that is formed in the body of a pregnant woman in order to maintain a connection between her body and the fetus. She filters the blood , which the unborn baby feeds on, cleansing it of toxins and other harmful substances.
This pathology can be very dangerous in some cases, while in others it goes away without any treatment and does not bring problems.
Types of location of the placenta
Usually the placenta is attached to the posterior wall of the uterus closer to its bottom . It is worth noting that the uterus is an inverted vessel, and its bottom is located on top. This is the best option for the location of the placenta. However, this does not always work out. In some cases, the placenta is attached to the anterior wall. Which is also not a pathology.
The low position of the placenta during pregnancy is much more dangerous.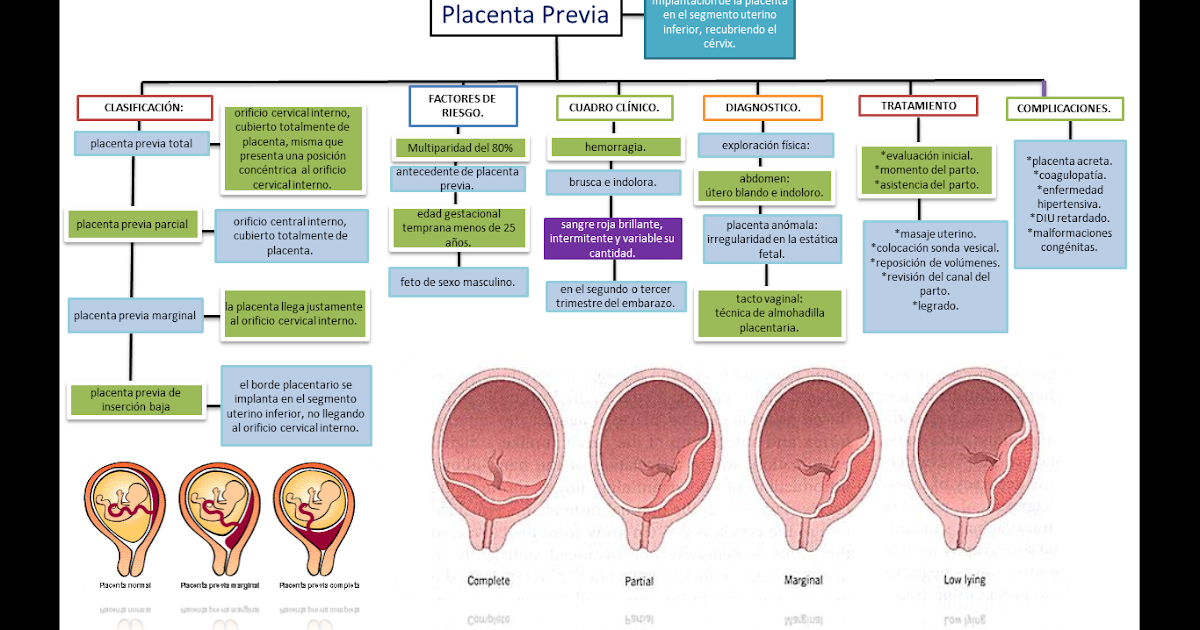 If the placenta is located low, it is subjected to stronger pressure from the fetus, and even with any external influence, the risk is damage to the placenta or its detachment increases. In addition, in the later stages, an actively moving baby can also damage the placenta, or squeeze the umbilical cord.
If the placenta is located low, it is subjected to stronger pressure from the fetus, and even with any external influence, the risk is damage to the placenta or its detachment increases. In addition, in the later stages, an actively moving baby can also damage the placenta, or squeeze the umbilical cord.
A placenta is said to be low when there is less than 6 cm between its lower edge and the os of the uterus. The anterior wall has a greater tendency to stretch, and migration is also characteristic of it, however, the direction of migration is opposite: usually the placenta moves in the opposite direction, down to the cervix.
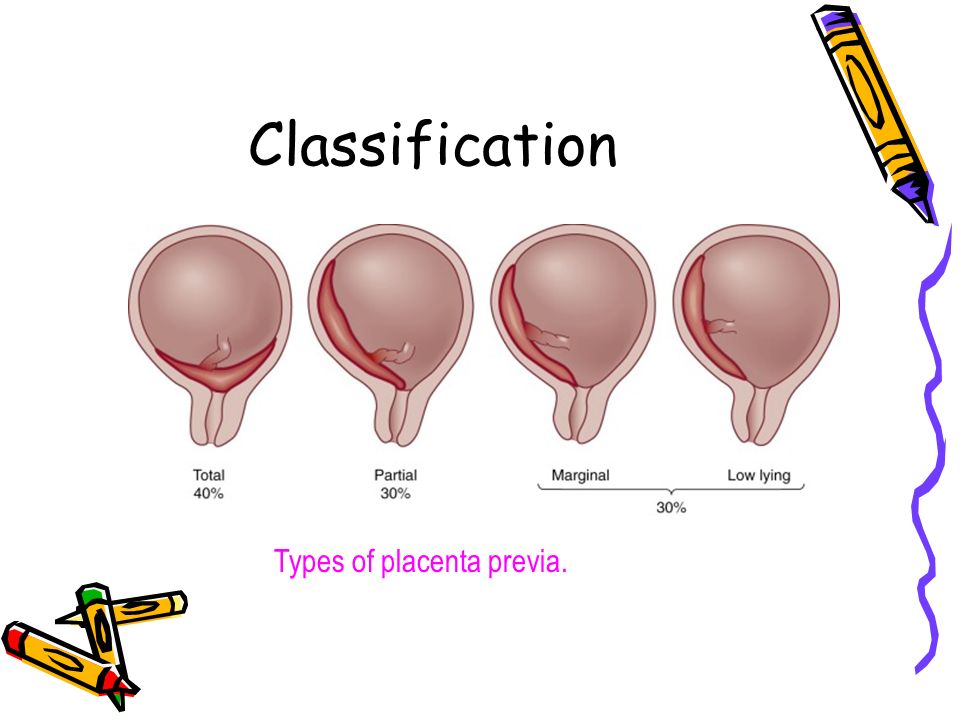
An even more complex and dangerous pathology of the location of the placenta is its partial or complete presentation . Previa is a condition when the placenta partially or completely obscures the cervix of the uterus.
Causes of low placenta
Many causes of low placenta are due to internal factors - diseases during pregnancy and the condition of the female genital organs .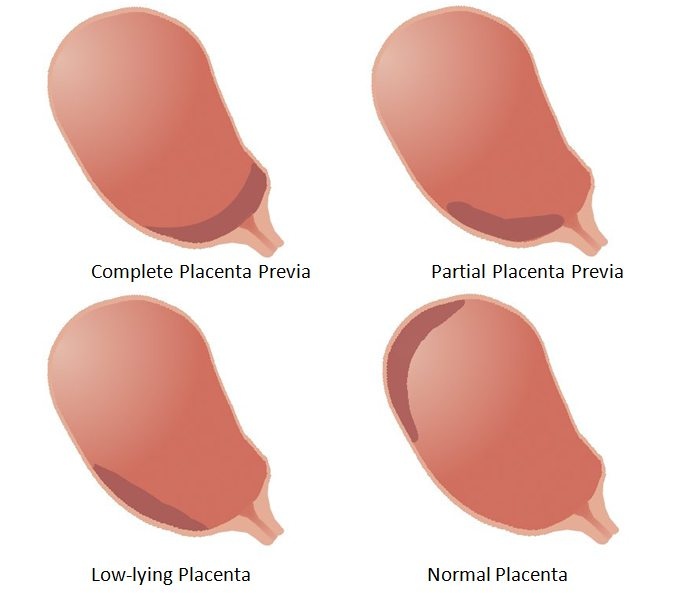 They can be:
They can be:
- damage to the mucous membrane of the uterus;
- inflammatory processes;
- infections;
- previous abortions;
- miscarriages in the past;
- cesarean section;
- various gynecological operations;
- pathology of the structure, development, functioning of the uterus;
- multiple pregnancy;
- unhealthy lifestyle: active smoking, excessive alcohol consumption;
- previous diseases of the uterus: endometritis, fibroids;
- parity - many births in the past;
- the woman's age is over 35 years.
Curettage of the uterus in the past is the main cause of this pathology. Damage to the mucosa prevents the fetal egg from gaining a foothold in the upper segment of this organ, and it remains below, at the neck.
Symptoms of low placenta
The danger of this pathology is that it practically does not manifest itself. Usually, signs that not everything is in order with the placenta are the result of already running and irreversible processes - for example, its detachment. It can be:
It can be:
- drawing pains, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- bloody discharge with a low location of the placenta is an alarm signal that it is necessary to call an ambulance;
- freezing of the fetus in the womb for a long time, or, conversely, its too violent activity - this is caused by hypoxia;
- on ultrasound with such a pathology in 50% of cases is the wrong presentation of the fetus;
- in 30% of cases, women suffer from severe toxicosis.
A pregnant woman herself cannot suspect that she has a low placenta. This can only be seen on planned ultrasounds, which must be passed by everyone. After an ultrasound examination, they can not only clarify or refute the diagnosis, but also determine the type of pathology.
Treatment and prevention of low placentation
Management of pregnancy with low placentation is always very careful. A woman will have to undergo ultrasound many times, limit physical activity and stop sexual activity. For a long time, increased uterine tone can provoke detachment of an improperly located placenta, from there bleeding, and possible death of the fetus as a result of acute hypoxia, if placental abruption is large. Bleeding can even provoke a gynecological examination of the cervix, therefore, for no particular reason, doctors try not to conduct examinations on the chair.
For a long time, increased uterine tone can provoke detachment of an improperly located placenta, from there bleeding, and possible death of the fetus as a result of acute hypoxia, if placental abruption is large. Bleeding can even provoke a gynecological examination of the cervix, therefore, for no particular reason, doctors try not to conduct examinations on the chair.
Listen to the doctors and hope for the best. Many women give birth on their own or by caesarean section of healthy babies with low placenta previa.
If you need help from an experienced gynecologist, sign up for a consultation by calling 8 (49244) 9-32-49, 8 (910) 174-77-72.
News All
Happy birthday, dear doctor!
Read more...
Murina Natalya Mikhailovna is the receptionist of small patients in our center.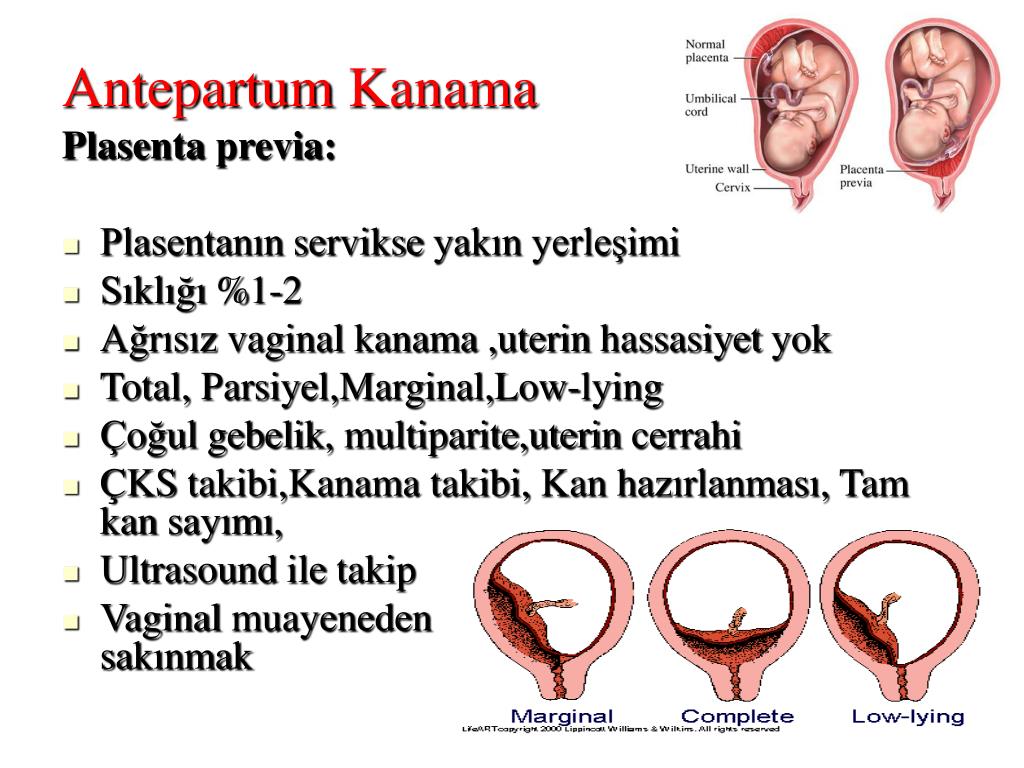 A good pediatrician becomes a reliable support for many years.
A good pediatrician becomes a reliable support for many years.
Read more...
Poll
What other doctors would you like to see in our center
| Traumatologist | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surgeon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ophthalmologist | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dentist | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allergist | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oncologist | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| no. | Name | Active ingredient | Release form | Mode of action |
| 1 | Ginipral | Hexoprenaline | Tablets, solution for intravenous administration | Reduces the tone of the uterus and reduces the contractile activity of the myometrium, inhibits spontaneous contractions. |
| 2 | Ferlatum | Protein iron succinylate | Oral solution | Antianemic drug. Increases the level of hemoglobin during bleeding. |
| 3 | Curantyl | Dipyridamole | Tablets | Improves blood circulation, dilates blood vessels, improves nutrition of placental tissue. |
| 4 | Utrozhestan | Progesterone | Capsules | Replenishes the lack of the hormone progesterone produced by the placenta. |
How is labor with a low placenta?
If the placenta has not risen by 37-38 weeks, the expectant mother is advised to go to the hospital in advance, and not wait for contractions. How the birth goes with low placentation - the doctor chooses, based on the condition of the woman in labor and the baby. The main condition for natural childbirth is the proximity of the operating room, so that at any time the woman can be provided with the necessary assistance.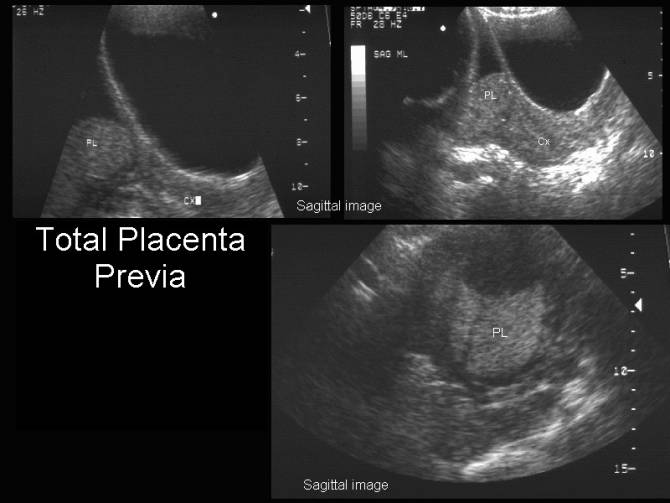
Often the placenta rises before childbirth. If the gap between her and the cervix is more than 2 cm, the risk of bleeding during childbirth is not higher than in the absence of pathology, and the woman can give birth herself.
If placenta previa is present, the placentation is even lower than it was, the child experiences hypoxia, there is
entanglement of the umbilical cord - then a caesarean section is performed. This condition threatens to damage the vessels that unite the walls of the uterus and the placenta, and profuse bleeding.
What should expectant mothers do if doctors see that the placenta has dropped low? A few recommendations:
- Reduce physical activity. Physical exercise, sports, active work increase the risk of detachment and increase spotting. Until childbirth, it is better for a woman to avoid excessive tension - this means that she needs to stand and walk less, and choose a semi-lying position for rest. The optimal position during rest is lying with your legs elevated, you can put a pillow under them.

- Monitor own state. Since the low location of the embryonic organ is accompanied by pain in the lower back and abdomen and discharge from the vagina, the pregnant woman must carefully monitor the intensity of the symptoms. Increased discharge or pain intensity is a reason to contact a gynecologist.
- Follow the recommendations of the gynecologist. You can not neglect your well-being and the health of the baby. A woman should attend all scheduled ultrasounds, take tests, drink medicines prescribed by doctors, wear a bandage and wait for the placenta to rise.
- Reduce the number of trips on public transport. Vibration, shocks, crush - all this worsens the condition of a woman. If possible, you should abandon buses, trains in favor of a private car or taxi. Are air travel acceptable with low placentation? Of course, flights are best avoided, but if the case is urgent, you should definitely consult a doctor. Until 18-19, sometimes up to 20 weeks, flights are not dangerous, then it is better to refuse them.

The low location of the placenta during pregnancy is not considered a serious pathology by physicians. Subject to all the recommendations given by doctors, it does not lead to a miscarriage, but you still should not forget about the caution of the expectant mother.
screening, a pregnant woman may hear the diagnosis of "low placenta" or "low placenta." As a rule, this diagnosis causes a lot of fears and concerns. What is the danger of such a diagnosis, what lifestyle is shown before childbirth, what options for delivery, what it depends on.
What is low placentation in pregnant women
Sometimes the placenta develops somewhat lower than it should be, the location of the placenta closer than 5.5-6 cm from the internal os of the uterus to the lower edge of the placenta is considered low. This condition can pose a certain danger during pregnancy.
The low location of the placenta can also be called low placentation.
With a low location, as the fetus grows, it puts more and more pressure on the placenta, increasing the risk of external influence on it or premature detachment of the placenta.
In the later stages, with a low placenta, there is a risk of the fetus clamping the umbilical cord and damaging the placenta due to active movements. In addition, the lower segments of the uterus are less well supplied with blood compared to the day of the uterus, which is fraught with the formation of fetal hypoxia.
It must be understood that the diagnosis of "low placenta" or "low placentation", made before 30-34 (and sometimes up to 36) weeks of pregnancy, is not yet a final diagnosis. The placenta can move (below about placental migration), the walls of the uterus stretch unevenly, and there is a high probability that by 34 weeks the placenta will be higher than 5-6 cm from the internal os of the uterus. At the same time, if the diagnosis was made, even in the early stages, a pregnant woman must follow certain lifestyle recommendations and be examined regularly (as prescribed by the doctor).
If the location of the placenta after 34 weeks remains low, then there is a risk that the birth will be through.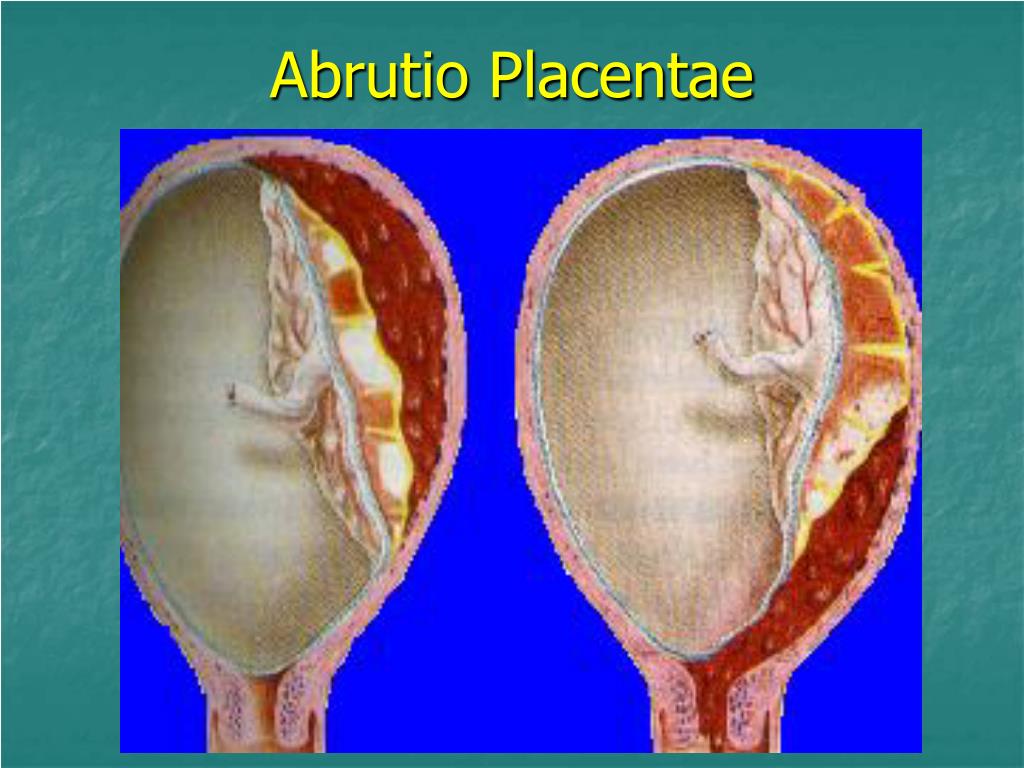 But, in fairness, it should be noted that most women simply need more attention from the obstetrician. There will also be ongoing monitoring of the condition of the fetus and the contractile activity of the uterus.
But, in fairness, it should be noted that most women simply need more attention from the obstetrician. There will also be ongoing monitoring of the condition of the fetus and the contractile activity of the uterus.
Placental migration with low placentation
During pregnancy, the placenta slightly changes its thickness and total volume, this is due to the fact that some parts of the placenta grow, while others atrophy (reduce), thereby changing both the type of placenta and its localization.
A low placenta is often detected early, but as the fetus grows and the uterus grows, it grows closer to the fundus of the uterus. As a rule, closer to the time of childbirth, the child's place occupies the correct position. This happens when the placenta attaches to the back wall.
The anterior wall is more extensible, but the low attachment of the placenta to the anterior wall is more dangerous.
With the location of the placenta along the anterior wall, and only in this case, conditional downward migration of the placenta can occur. This happens due to the fact that the anterior wall is more extensible, and if the posterior wall stretches in the direction from the cervix and up to the bottom, then the anterior wall - both from the center, and to the sides, and to the bottom and to the cervix. Therefore, it can happen, as it were, "placental descent", that is, the uterus itself will come out upwards, while the placenta will remain close to the cervix.
This happens due to the fact that the anterior wall is more extensible, and if the posterior wall stretches in the direction from the cervix and up to the bottom, then the anterior wall - both from the center, and to the sides, and to the bottom and to the cervix. Therefore, it can happen, as it were, "placental descent", that is, the uterus itself will come out upwards, while the placenta will remain close to the cervix.
These will be the preconditions for the formation of a low placentation, or even.
Causes of low placentation
Under normal conditions, in young and healthy women, the placenta is attached in a normal position. The causes of low placentation are usually problems inside the uterus:
- inflammation of the walls of the uterus;
- infectious lesions of the walls of the uterus;
- consequences and abortions;
- curettage of the uterus;
- scars after caesarean section;
- stitches after operations;
- uterine fibroids;
- underdevelopment of the uterus, bicornuate, saddle uterus, infantile uterus;
- multiple pregnancy;
- mother's age is over 30-35 years old.
Sensation of low placentation
Most often, low placentation does not manifest itself externally and in sensations. Sometimes it can also occur in the lower back or "blood smearing". The latter is a sign of placental abruption in a small area. That is why it is so important to inform your doctor about the appearance of even the smallest bleeding.
Low placentation is more often detected during routine or additional ultrasound.
What threatens low placentation during pregnancy
In most cases, in the third trimester, the placenta rises and expectant mothers do not have a trace of past experiences.
- If the placenta is low at the first ultrasound at 12-16 weeks, there is no hearth to stir. Most likely, as the uterus grows, the placenta will change its position and rise up. In this case, the process of bearing the fetus is not disturbed, and childbirth takes place independently. Without any complications.
- If low placentation is detected within 20 weeks, you should also not worry, it is from this period that the active growth of the fetus and the rise of the placenta will begin.
- If low placentation is detected after 30 weeks, additional monitoring will be required. But also do not worry too much, because the placenta can migrate up to 34-36 weeks inclusive.
It is important to remember that if during the second follow-up ultrasound screening up to 20 weeks, the sonologist ascertains the location of the placenta, then this does not mean anything. Remember that the placenta grows up to 36 weeks.
The very fact of low placentation is not a cause for concern, especially during the first half of pregnancy. This is just a hint for the observing doctor so that he understands that this pregnancy has its own individual characteristics.
Reasons for excitement will be a very low location of the placenta with the formation of partial or complete presentation. Again, the doctor, based on the results of the ultrasound and your condition, tells you exactly how low the placenta is and what the prognosis is.
If after 36 weeks of pregnancy the position of the placenta has not returned to normal, then at 38 weeks the woman is hospitalized in a hospital and is under the supervision of doctors.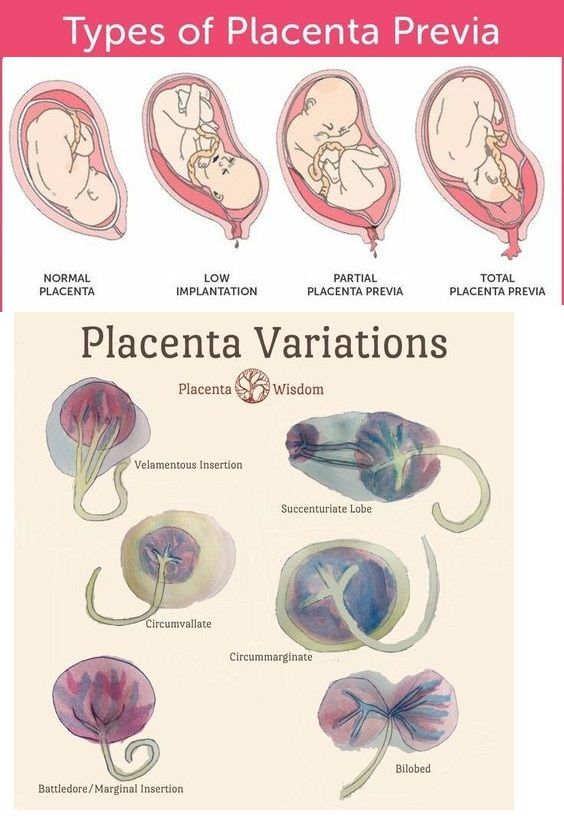
Again, in most cases, there is no cause for concern.
Prohibited for low placentation
When a low-lying placenta is detected, it is necessary to monitor the situation in dynamics, for this it makes sense to do a control ultrasound at 24-26 and 34-36 weeks.
- Avoid strenuous exercise, abdominal tension, running and jumping. This leads to contractions of the walls of the uterus and their tension, which increases the risk of placental abruption.
- Maximum rest, frequent, long rest, sleep is a must.
- Heavy lifting, sudden movements and jerks are prohibited.
- Harmonious mental state, the expectant mother should be relaxed and calm. Stress is absolutely contraindicated!
- For night and daytime sleep, for rest it is worth putting a pillow under your feet so that they are slightly above the level of the pelvis.
Sex with low placentation
With low placentation, if the placenta lies closer than 5 cm from the edge of the internal os of the uterus, and this is indicated by the second ultrasound screening, it is temporarily worth giving up intimate life and keeping it.
This is explained by the fact that in this position the placenta is close to the cervix and rhythmic tremors, contraction and tension of the muscles of the uterus during orgasm can lead to the threat of placental abruption.
It is not worth the risk if the placenta is still low after 20-22 weeks. Until this time, if there is no threat to pregnancy, sex is acceptable, but only without sudden movements and deep penetration.
Let us remind you once again that in 95% of cases the placenta assumes its normal position without any problems.
You need to sleep well and stay calm and wear comfortable maternity clothes. Buy from Mom's Shop:
- comfortable
Low placenta - hundreds of women hear this diagnosis in the second trimester. This pathology can be very dangerous in some cases, while in others it goes away without any treatment and does not bring problems. Let's figure out what the placenta is, what is its normal and pathological location, what pathology threatens and how to avoid problems.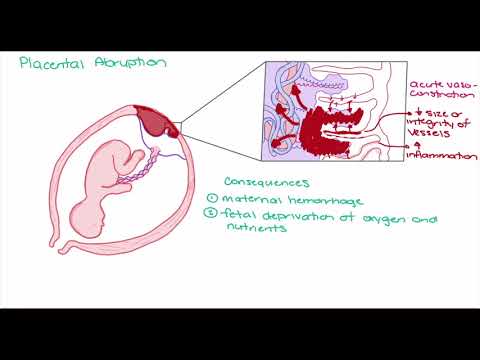
The placenta is a temporary organ through which the mother's body transfers the substances necessary for life to the child's body, removes all unnecessary and provides oxygen. In addition, the placenta produces hormones necessary for the progression of pregnancy and protects against infections. Normally, the placenta begins to develop at a distance of at least 6 cm from the internal os of the uterus (inner part of the cervix), otherwise doctors diagnose " low placentation", and this threatens with a number of problems during gestation, such as bleeding and malpresentation of the fetus, which often lead to operative delivery, and in severe cases, even to the death of the mother and child.
Why does low placenta previa occur in a pregnant woman? This pathology is more typical for women over the age of 30 who have repeatedly given birth and had abortions. Repeated inflammatory processes, neoplasms of the uterus lead to tissue degradation, and the fertilized egg has no choice but to look for the most favorable place for development, and it may just be the internal pharynx.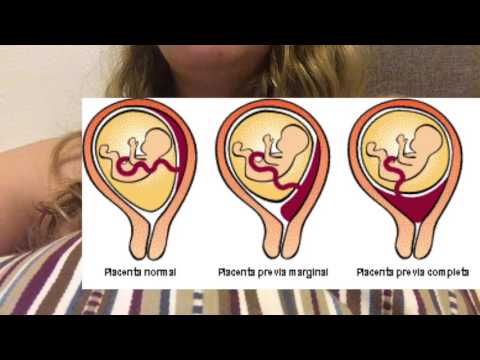 The low location of the placenta has numerous reasons, and every woman who cares about her health and wants to have children in the future should understand that any gynecological disease, any intervention in the uterus, can lead to such dangerous consequences in the future.
The low location of the placenta has numerous reasons, and every woman who cares about her health and wants to have children in the future should understand that any gynecological disease, any intervention in the uterus, can lead to such dangerous consequences in the future.
But not everything is so bad, the low placenta often happens before the third trimester, but by 32 weeks it rises by itself, this is due to the growth of the uterus. According to statistics, only 5 percent of women have this pathology until the very birth. In addition, not every low position of the placenta during pregnancy, even preserved by the last trimester, is very dangerous for a woman and a child and serves as an absolute indication for a caesarean section. The child's place may not completely cover the internal pharynx, but only touch it with the edge, in such cases, an experienced doctor will be able to take a natural birth from a woman.
Management of low placentation pregnancy is always very careful.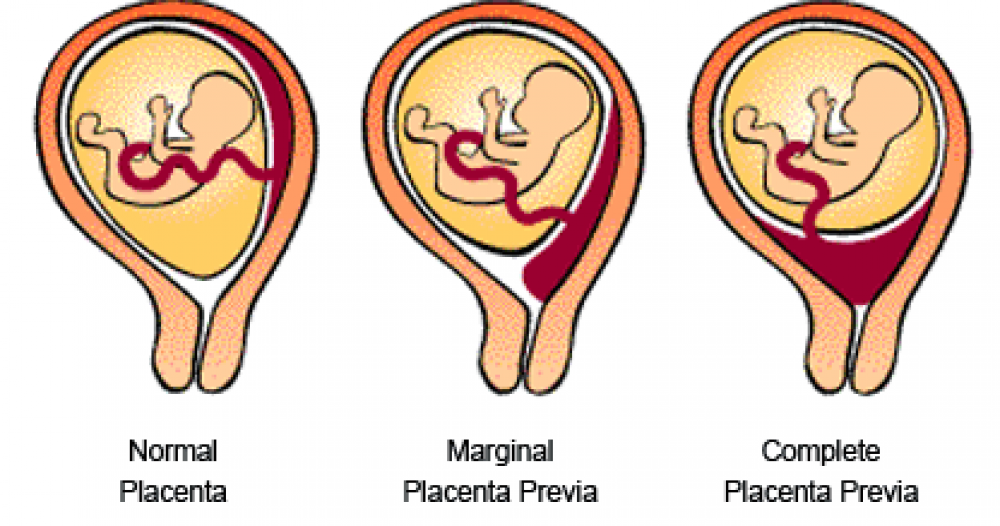 A woman will have to undergo ultrasound many times, limit physical activity and stop sexual activity. For a long time, an increased tone of the uterus can provoke detachment of an improperly located placenta, from there bleeding, and possible death of the fetus as a result of acute hypoxia, if placental abruption is large. Bleeding can even provoke a gynecological examination of the cervix, therefore, for no particular reason, doctors try not to conduct examinations on the chair.
A woman will have to undergo ultrasound many times, limit physical activity and stop sexual activity. For a long time, an increased tone of the uterus can provoke detachment of an improperly located placenta, from there bleeding, and possible death of the fetus as a result of acute hypoxia, if placental abruption is large. Bleeding can even provoke a gynecological examination of the cervix, therefore, for no particular reason, doctors try not to conduct examinations on the chair.
The placenta is a special organ that forms during pregnancy. Starting from the 7th week, it provides the fetus with nutrition, oxygen, and waste products are removed with its help. In other words, the placenta is a very important organ that provides intrauterine life to your unborn baby.
Placenta with low attachments - how is it?
It is normal if the placenta is located in the upper part of the uterus (near the bottom). Pathology is considered to be its location in the immediate vicinity of the entrance to the cervix (internal os).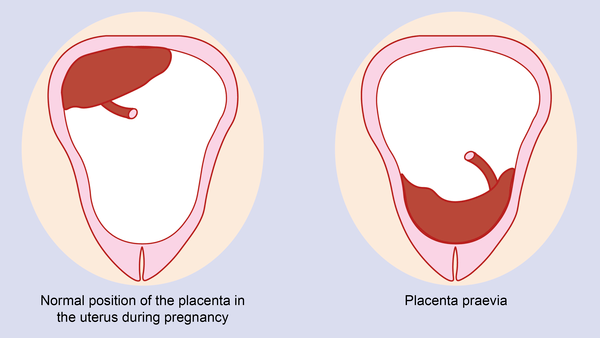 during pregnancy, this is the case when the placenta is attached at a distance of approximately 5 cm from the entrance to the cervix. If the attachment occurred at the entrance to the cervix, up to 5 cm from the internal os, this condition is called It can be lateral, marginal or complete, depending on how much the placenta overlaps the area of the internal os. Low attachment of the placenta and its presentation are different things, the second condition is considered a more serious pathology and requires more attention. While the low location of the placenta during pregnancy, with the approaching term of childbirth, it may cease to be a problem at all. The fact is that, according to statistics, low placental attachment occurs in approximately 30% of women in early pregnancy, and after the 20th week, the uterus begins to grow rapidly, and the placenta usually “migrates” upwards, and only in one of two hundred cases remains in place , near the cervix. And yet, despite such favorable forecasts, you should not neglect your health and let everything take its course, with the hope that “maybe it will resolve itself.
during pregnancy, this is the case when the placenta is attached at a distance of approximately 5 cm from the entrance to the cervix. If the attachment occurred at the entrance to the cervix, up to 5 cm from the internal os, this condition is called It can be lateral, marginal or complete, depending on how much the placenta overlaps the area of the internal os. Low attachment of the placenta and its presentation are different things, the second condition is considered a more serious pathology and requires more attention. While the low location of the placenta during pregnancy, with the approaching term of childbirth, it may cease to be a problem at all. The fact is that, according to statistics, low placental attachment occurs in approximately 30% of women in early pregnancy, and after the 20th week, the uterus begins to grow rapidly, and the placenta usually “migrates” upwards, and only in one of two hundred cases remains in place , near the cervix. And yet, despite such favorable forecasts, you should not neglect your health and let everything take its course, with the hope that “maybe it will resolve itself.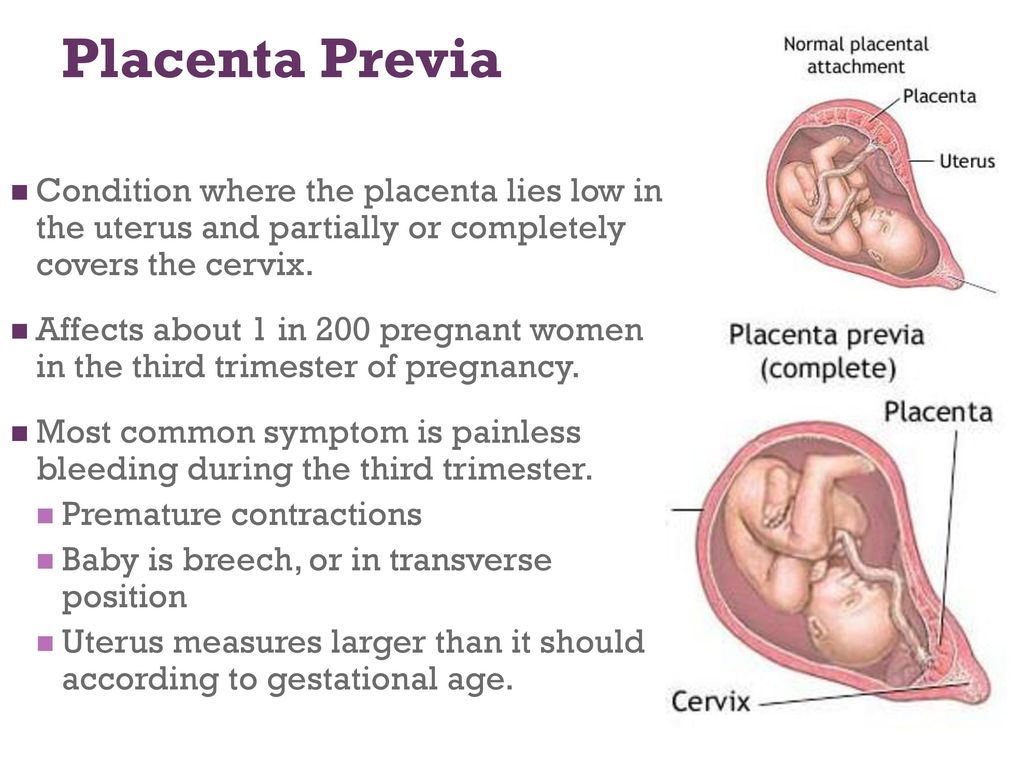 ” If at the first ultrasound you have determined the low location of the placenta during pregnancy, this is a reason for serious observation by a doctor throughout the entire period of gestation.
” If at the first ultrasound you have determined the low location of the placenta during pregnancy, this is a reason for serious observation by a doctor throughout the entire period of gestation.
Why did this happen?
It is not always easy to determine the causes of this pathology. Of course, for those who have been diagnosed with a similar condition, on a large occasion, the reasons are not so important. It is important to carry out, if necessary, adequate treatment, and give birth to a healthy child. But it is important for your attending physician to know if you have done any operations on the uterus before, because the main reason is a violation of the uterine wall. Most often, the placenta, the attachment of which is below the permissible norm, is found in those who smoke, have abortions, who have had miscarriages, frequent inflammation of the genital organs, a sick heart, kidneys, etc. Hence the conclusion, take care of yourself, take care of your health even before pregnancy.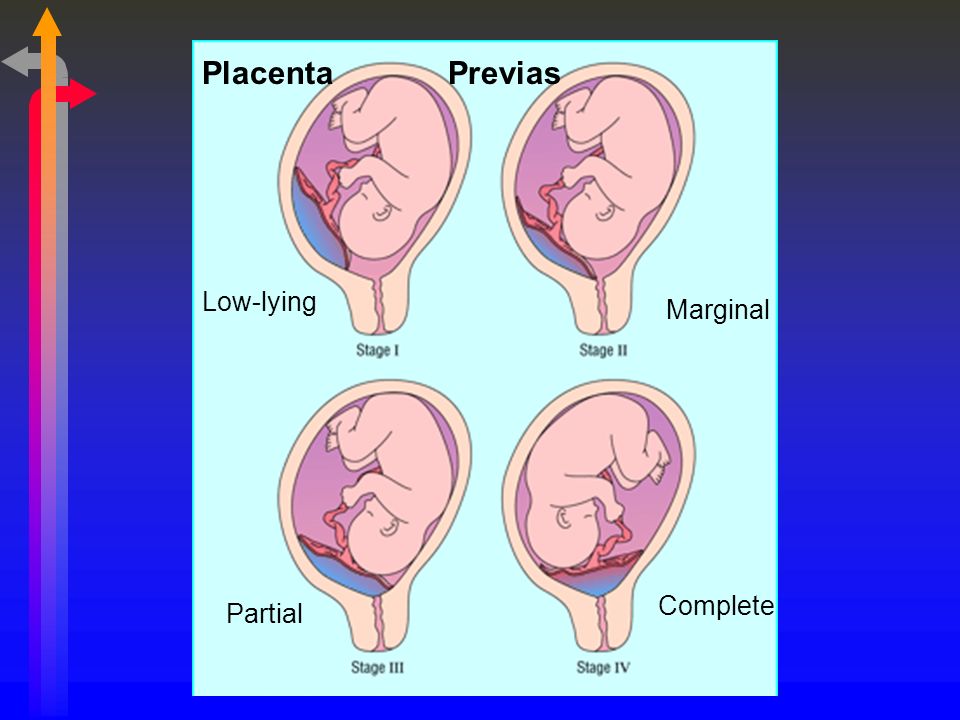
Is it possible to determine this pathology by symptoms without ultrasound?
The main method for diagnosing the low location of the placenta during pregnancy is ultrasound, since the symptoms of this pathology are not always pronounced. A woman may have scanty spotting, accompanied by unpleasant (not painful) sensations in the lower abdomen, hemoglobin in the blood is almost always reduced.
What to do, how to treat low placenta attachment?
Without unnecessary emotions and panic, you should regularly visit a doctor who monitors pregnancy, the main treatment for this condition is constant monitoring. If life-threatening complications for the fetus are detected, it is advisable for a woman to be hospitalized, protected from physical exertion and emotional experiences, and provide good nutrition. If you do not follow all the recommendations of the doctor, you can lose the baby (great since the low position of the placenta is often accompanied by fetal hypoxia.
 Normally, the egg is attached to the bottom of the uterus, but sometimes it falls below and is fixed on the wall or even near the pharynx itself. If the placenta is located near the cervix, we can talk about a low placenta, but if it covers the pharynx - about presentation.
Normally, the egg is attached to the bottom of the uterus, but sometimes it falls below and is fixed on the wall or even near the pharynx itself. If the placenta is located near the cervix, we can talk about a low placenta, but if it covers the pharynx - about presentation. 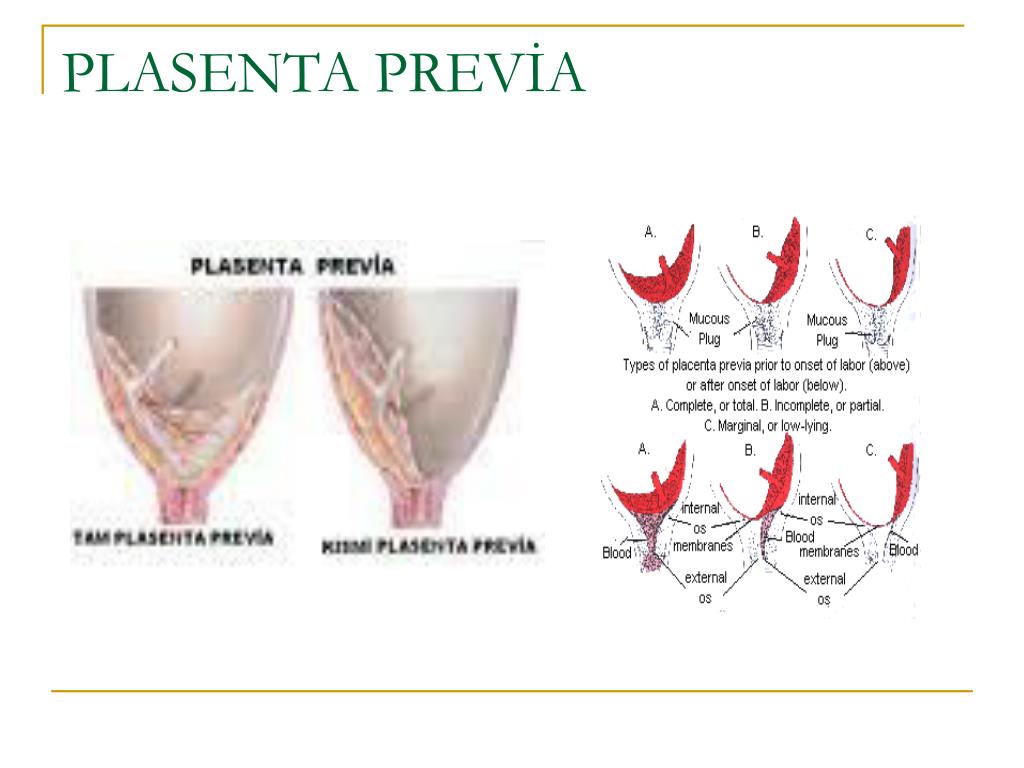 Its diameter is about 15 centimeters, and its weight is about half a kilogram. From the side of the fetus and from the side of the uterus, the placenta is covered with special plates, between which there are many blood vessels.
Its diameter is about 15 centimeters, and its weight is about half a kilogram. From the side of the fetus and from the side of the uterus, the placenta is covered with special plates, between which there are many blood vessels. 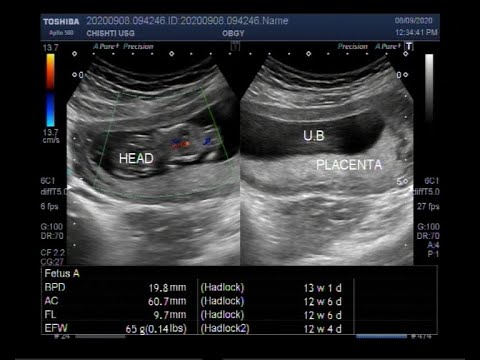
 That is why women with a low location of the placenta in the LCD are watched especially closely. Proper management of pregnancy and childbirth, as well as the correct behavior of the woman herself, minimizes all risks.
That is why women with a low location of the placenta in the LCD are watched especially closely. Proper management of pregnancy and childbirth, as well as the correct behavior of the woman herself, minimizes all risks. 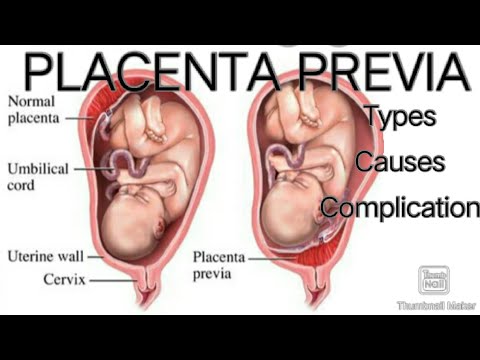 Among the forms of physical activity, leisurely walks in the fresh air can be recommended.
Among the forms of physical activity, leisurely walks in the fresh air can be recommended.  You can give birth naturally and there are usually no differences from other births. Problems arise if the placenta blocks the pharynx. Why is that?
You can give birth naturally and there are usually no differences from other births. Problems arise if the placenta blocks the pharynx. Why is that? 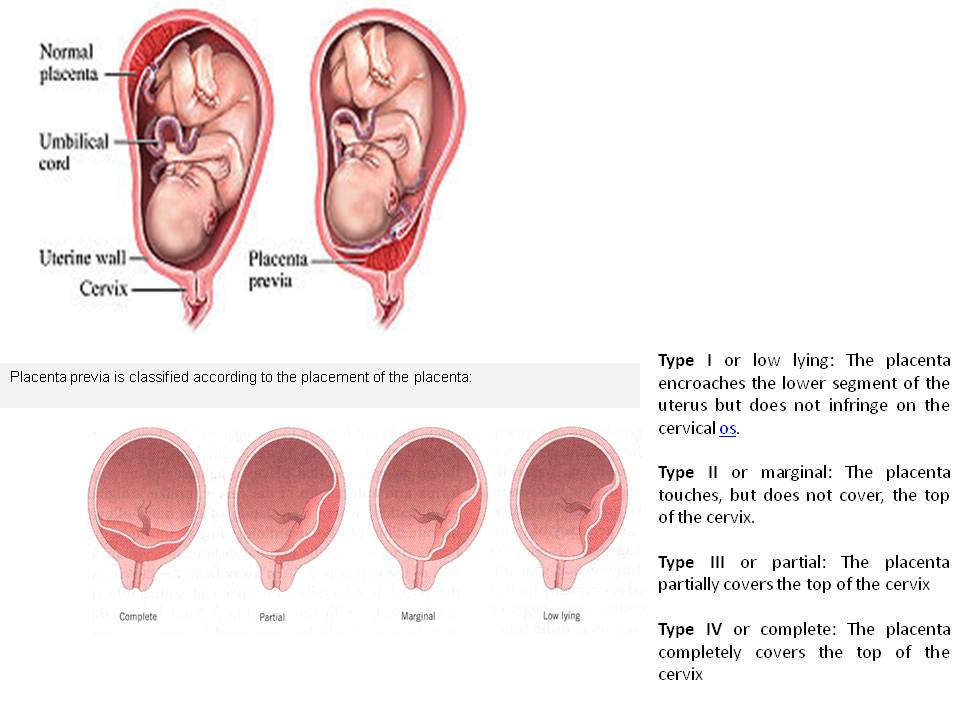 Therefore, with placenta previa, a planned caesarean section is performed. With a properly performed operation, the risks for mother and child are minimal.
Therefore, with placenta previa, a planned caesarean section is performed. With a properly performed operation, the risks for mother and child are minimal. 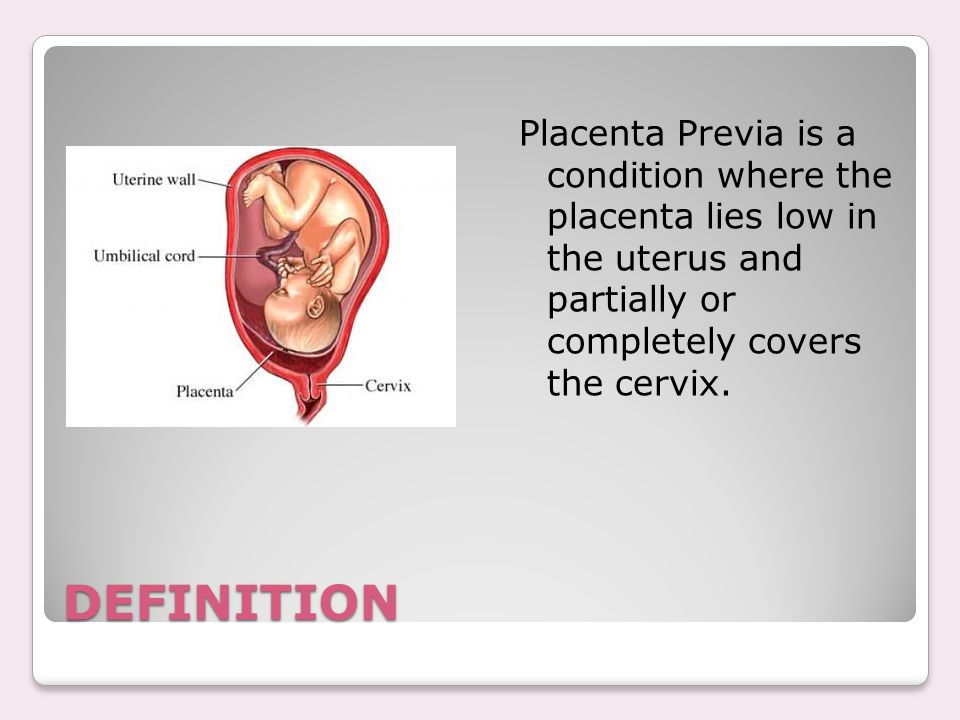
 If you are sure that you can optimize your lifestyle and get to the hospital immediately when you appear, hospitalization is not necessary.
If you are sure that you can optimize your lifestyle and get to the hospital immediately when you appear, hospitalization is not necessary. 
 This increases the likelihood of spontaneous abortion in the first half of gestation and premature birth in the later stages.
This increases the likelihood of spontaneous abortion in the first half of gestation and premature birth in the later stages.  Often this causes entanglement of the umbilical cord of the fetus.
Often this causes entanglement of the umbilical cord of the fetus.