Born premature meaning
Premature birth - Symptoms and causes
Overview
A premature birth is a birth that takes place more than three weeks before the baby's estimated due date. In other words, a premature birth is one that occurs before the start of the 37th week of pregnancy.
Premature babies, especially those born very early, often have complicated medical problems. Typically, complications of prematurity vary. But the earlier your baby is born, the higher the risk of complications.
Depending on how early a baby is born, he or she may be:
- Late preterm, born between 34 and 36 completed weeks of pregnancy
- Moderately preterm, born between 32 and 34 weeks of pregnancy
- Very preterm, born at less than 32 weeks of pregnancy
- Extremely preterm, born at or before 25 weeks of pregnancy
Most premature births occur in the late preterm stage.
Products & Services
- Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to Your Baby's First Years
Symptoms
Your baby may have very mild symptoms of premature birth, or may have more-obvious complications.
Some signs of prematurity include the following:
- Small size, with a disproportionately large head
- Sharper looking, less rounded features than a full-term baby's features, due to a lack of fat stores
- Fine hair (lanugo) covering much of the body
- Low body temperature, especially immediately after birth in the delivery room, due to a lack of stored body fat
- Labored breathing or respiratory distress
- Lack of reflexes for sucking and swallowing, leading to feeding difficulties
The following tables show the median birth weight, length and head circumference of premature babies at different gestational ages for each sex.
| Weight, length and head circumference by gestational age for boys | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age | Weight | Length | Head circumference |
| 40 weeks | 7 lbs. , 15 oz. , 15 oz.(3.6 kg) | 20 in. (51 cm) | 13.8 in. (35 cm) |
| 35 weeks | 5 lbs., 8 oz. (2.5 kg) | 18.1 in. (46 cm) | 12.6 in. (32 cm) |
| 32 weeks | 3 lbs., 15.5 oz. (1.8 kg) | 16.5 in. (42 cm) | 11.6 in. (29.5 cm) |
| 28 weeks | 2 lbs., 6.8 oz. (1.1 kg) | 14.4 in. (36.5 cm) | 10.2 in. (26 cm) |
| 24 weeks | 1 lb., 6.9 oz. (0.65 kg) | 12.2 in. (31 cm) | 8.7 in. (22 cm) |
| Weight, length and head circumference by gestational age for girls | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age | Weight | Length | Head circumference |
| 40 weeks | 7 lbs. , 7.9 oz. , 7.9 oz.(3.4 kg) | 20 in. (51 cm) | 13.8 in. (35 cm) |
| 35 weeks | 5 lbs., 4.7 oz. (2.4 kg) | 17.7 in. (45 cm) | 12.4 in. (31.5 cm) |
| 32 weeks | 3 lbs., 12 oz. (1.7 kg) | 16.5 in. (42 cm) | 11.4 in. (29 cm) |
| 28 weeks | 2 lbs., 3.3 oz. (1.0 kg) | 14.1 in. (36 cm) | 9.8 in. (25 cm) |
| 24 weeks | 1 lb., 5.2 oz. (0.60 kg) | 12.6 in. (32 cm) | 8.3 in. (21 cm) |
Special care
If you deliver a preterm baby, your baby will likely need a longer hospital stay in a special nursery unit at the hospital. Depending on how much care your baby requires, he or she may be admitted to an intermediate care nursery or the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).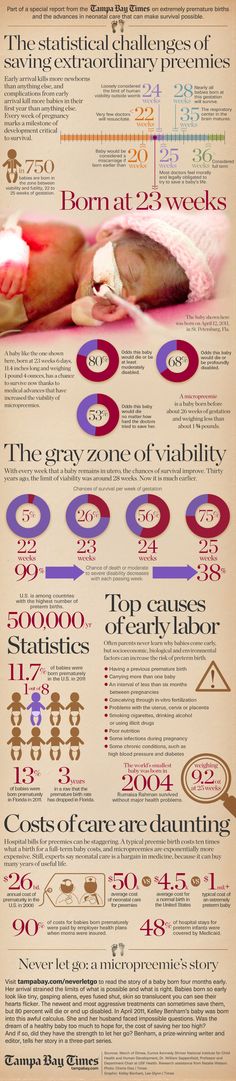 Doctors and a specialized team with training in taking care of preterm babies will be available to help care for your baby. Don't hesitate to ask questions.
Doctors and a specialized team with training in taking care of preterm babies will be available to help care for your baby. Don't hesitate to ask questions.
Your baby may need extra help feeding, and adapting immediately after delivery. Your health care team can help you understand what is needed and what your baby's care plan will be.
Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic
Risk factors
Often, the specific cause of premature birth isn't clear. However, there are known risk factors of premature delivery, including:
- Having a previous premature birth
- Pregnancy with twins, triplets or other multiples
- An interval of less than six months between pregnancies
- Conceiving through in vitro fertilization
- Problems with the uterus, cervix or placenta
- Smoking cigarettes or using illicit drugs
- Some infections, particularly of the amniotic fluid and lower genital tract
- Some chronic conditions, such as high blood pressure and diabetes
- Being underweight or overweight before pregnancy
- Stressful life events, such as the death of a loved one or domestic violence
- Multiple miscarriages or abortions
- Physical injury or trauma
For unknown reasons, black women are more likely to experience premature birth than are women of other races. But premature birth can happen to anyone. In fact, many women who have a premature birth have no known risk factors.
But premature birth can happen to anyone. In fact, many women who have a premature birth have no known risk factors.
Complications
While not all premature babies experience complications, being born too early can cause short-term and long-term health problems. Generally, the earlier a baby is born, the higher the risk of complications. Birth weight plays an important role, too.
Some problems may be apparent at birth, while others may not develop until later.
Short-term complications
In the first weeks, the complications of premature birth may include:
-
Breathing problems. A premature baby may have trouble breathing due to an immature respiratory system. If the baby's lungs lack surfactant — a substance that allows the lungs to expand — he or she may develop respiratory distress syndrome because the lungs can't expand and contract normally.
Premature babies may also develop a lung disorder known as bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
 In addition, some preterm babies may experience prolonged pauses in their breathing, known as apnea.
In addition, some preterm babies may experience prolonged pauses in their breathing, known as apnea. - Heart problems. The most common heart problems premature babies experience are patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) and low blood pressure (hypotension). PDA is a persistent opening between the aorta and pulmonary artery. While this heart defect often closes on its own, left untreated it can lead to a heart murmur, heart failure as well as other complications. Low blood pressure may require adjustments in intravenous fluids, medicines and sometimes blood transfusions.
- Brain problems. The earlier a baby is born, the greater the risk of bleeding in the brain, known as an intraventricular hemorrhage. Most hemorrhages are mild and resolve with little short-term impact. But some babies may have larger brain bleeding that causes permanent brain injury.
-
Temperature control problems.
 Premature babies can lose body heat rapidly. They don't have the stored body fat of a full-term infant, and they can't generate enough heat to counteract what's lost through the surface of their bodies. If body temperature dips too low, an abnormally low core body temperature (hypothermia) can result.
Premature babies can lose body heat rapidly. They don't have the stored body fat of a full-term infant, and they can't generate enough heat to counteract what's lost through the surface of their bodies. If body temperature dips too low, an abnormally low core body temperature (hypothermia) can result.Hypothermia in a premature baby can lead to breathing problems and low blood sugar levels. In addition, a premature infant may use up all of the energy gained from feedings just to stay warm. That's why smaller premature infants require additional heat from a warmer or an incubator until they're larger and able to maintain body temperature without assistance.
- Gastrointestinal problems. Premature infants are more likely to have immature gastrointestinal systems, resulting in complications such as necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). This potentially serious condition, in which the cells lining the bowel wall are injured, can occur in premature babies after they start feeding.
 Premature babies who receive only breast milk have a much lower risk of developing NEC.
Premature babies who receive only breast milk have a much lower risk of developing NEC. -
Blood problems. Premature babies are at risk of blood problems such as anemia and newborn jaundice. Anemia is a common condition in which the body doesn't have enough red blood cells. While all newborns experience a slow drop in red blood cell count during the first months of life, the decrease may be greater in premature babies.
Newborn jaundice is a yellow discoloration in a baby's skin and eyes that occurs because the baby's blood contains excess bilirubin, a yellow-colored substance, from the liver or red blood cells. While there are many causes of jaundice, it is more common in preterm babies.
- Metabolism problems. Premature babies often have problems with their metabolism. Some premature babies may develop an abnormally low level of blood sugar (hypoglycemia). This can happen because premature infants typically have smaller stores of stored glucose than do full-term babies.
 Premature babies also have more difficulty converting their stored glucose into more-usable, active forms of glucose.
Premature babies also have more difficulty converting their stored glucose into more-usable, active forms of glucose. - Immune system problems. An underdeveloped immune system, common in premature babies, can lead to a higher risk of infection. Infection in a premature baby can quickly spread to the bloodstream, causing sepsis, an infection that spreads to the bloodstream.
Long-term complications
In the long term, premature birth may lead to the following complications:
- Cerebral palsy. Cerebral palsy is a disorder of movement, muscle tone or posture that can be caused by infection, inadequate blood flow or injury to a newborn's developing brain either early during pregnancy or while the baby is still young and immature.
- Impaired learning. Premature babies are more likely to lag behind their full-term counterparts on various developmental milestones. Upon school age, a child who was born prematurely might be more likely to have learning disabilities.

- Vision problems. Premature infants may develop retinopathy of prematurity, a disease that occurs when blood vessels swell and overgrow in the light-sensitive layer of nerves at the back of the eye (retina). Sometimes the abnormal retinal vessels gradually scar the retina, pulling it out of position. When the retina is pulled away from the back of the eye, it's called retinal detachment, a condition that, if undetected, can impair vision and cause blindness.
- Hearing problems. Premature babies are at increased risk of some degree of hearing loss. All babies will have their hearing checked before going home.
- Dental problems. Premature infants who have been critically ill are at increased risk of developing dental problems, such as delayed tooth eruption, tooth discoloration and improperly aligned teeth.
- Behavioral and psychological problems. Children who experienced premature birth may be more likely than full-term infants to have certain behavioral or psychological problems, as well as developmental delays.

- Chronic health issues. Premature babies are more likely to have chronic health issues — some of which may require hospital care — than are full-term infants. Infections, asthma and feeding problems are more likely to develop or persist. Premature infants are also at increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
Prevention
Although the exact cause of preterm birth is often unknown, there are some things that can be done to help women — especially those who have an increased risk — to reduce their risk of preterm birth, including:
- Progesterone supplements. Women who have a history of preterm birth, a short cervix or both factors may be able to reduce the risk of preterm birth with progesterone supplementation.
-
Cervical cerclage. This is a surgical procedure performed during pregnancy in women with a short cervix, or a history of cervical shortening that resulted in a preterm birth.

During this procedure, the cervix is stitched closed with strong sutures that may provide extra support to the uterus. The sutures are removed when it's time to deliver the baby. Ask your doctor if you need to avoid vigorous activity during the remainder of your pregnancy.
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Associated Procedures
Products & Services
Premature babies | March of Dimes
Premature babies may have more health problems than babies born later. These include problems with their brain, lungs, heart, eyes and other organs.
Some premature babies have to spend time in a hospital’s newborn intensive care unit (also called NICU) to get special medical care.
Premature birth can lead to long-term challenges for some babies, including intellectual and developmental disabilities.
After they leave the hospital, premature babies get regular checkups to monitor their health and development.

If you’re worried about your baby’s health or development at any time, tell your baby’s provider right away.
What is a premature baby?
A premature baby is one who is born too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Each year, about 1 in 10 babies in the United States is born prematurely. Premature babies may not be fully developed at birth. They may have more health problems and may need to stay in the hospital longer than babies born later. Thanks to advances in medical care, even babies born very prematurely are more likely to survive today than ever before.
Your baby’s health care provider may use these terms to describe your baby’s birth:
- Late preterm: Your baby is born between 34 and 36 completed weeks of pregnancy.
- Moderately preterm: Your baby is born between 32 and 34 weeks of pregnancy.
- Very preterm: Your baby is born at less than 32 weeks of pregnancy.

- Extremely preterm: Your baby is born at or before 25 weeks of pregnancy.
Some health problems related to premature birth can last a lifetime. Other problems, like intellectual or developmental disabilities, can show up as your baby grows and later in childhood. These are problems with how the brain works that can cause a person to have trouble or delays in physical development, learning, communicating, taking care of himself or getting along with others.
The earlier in pregnancy a baby is born, the more likely he is to have health problems. Babies born before 34 weeks of pregnancy are mostly likely to have health problems, but babies born between 34 and 37 weeks of pregnancy are also at increased risk of having health problems related to premature birth. Some premature babies need to spend time in a hospital’s newborn intensive care unit (also called NICU). This is the nursery in a hospital where sick newborns get medical care. Premature babies stay in the NICU until their organs develop enough to stay alive without medical support. Some babies need NICU care for weeks or months until they can breathe on their own, eat by mouth and maintain their body temperature and body weight.
Some babies need NICU care for weeks or months until they can breathe on their own, eat by mouth and maintain their body temperature and body weight.
Do premature babies need special medical care?
Talk to your baby’s health care providers about any health conditions your baby has. He may be healthy enough to go home soon after birth, or he may need to stay in the NICU for special care. Your baby can probably go home from the hospital when he:
- Weighs at least 4 pounds
- Can keep warm on his own, without the help of an incubator. An incubator is a clear plastic bed that helps keep your baby warm.
- Can breastfeed or bottle-feed
- Gains weight steadily
- Can breathe on his own
Your baby may need special medical equipment, medicine or other treatment after he leaves the hospital. Your baby’s provider and the staff at the hospital can help you with these things and teach you how to take care of your baby at home. They may recommend that you bring your baby to a neonatologist for checkups after your baby leaves the hospital. A neonatologist is a doctor who specializes in caring for premature babies and children. Talk to your baby’s provider if you have any questions about your baby’s health or long-term effects of premature birth. Hospital staff also can help you find parent support groups and other resources in your area that may be able to help you care for your baby.
They may recommend that you bring your baby to a neonatologist for checkups after your baby leaves the hospital. A neonatologist is a doctor who specializes in caring for premature babies and children. Talk to your baby’s provider if you have any questions about your baby’s health or long-term effects of premature birth. Hospital staff also can help you find parent support groups and other resources in your area that may be able to help you care for your baby.
What kinds of health problems can premature babies have?
Health problems that may affect premature babies include:
Anemia. This is when a baby doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to the rest of the body. Anemia can cause low levels of oxygen and glucose (sugar) in a baby’s blood and make it hard for a baby’s organs to work properly. Premature babies in the NICU may have anemia because they get regular blood tests to check their health. They often can’t make new blood cells quickly enough to replace the blood cells they lose during blood tests.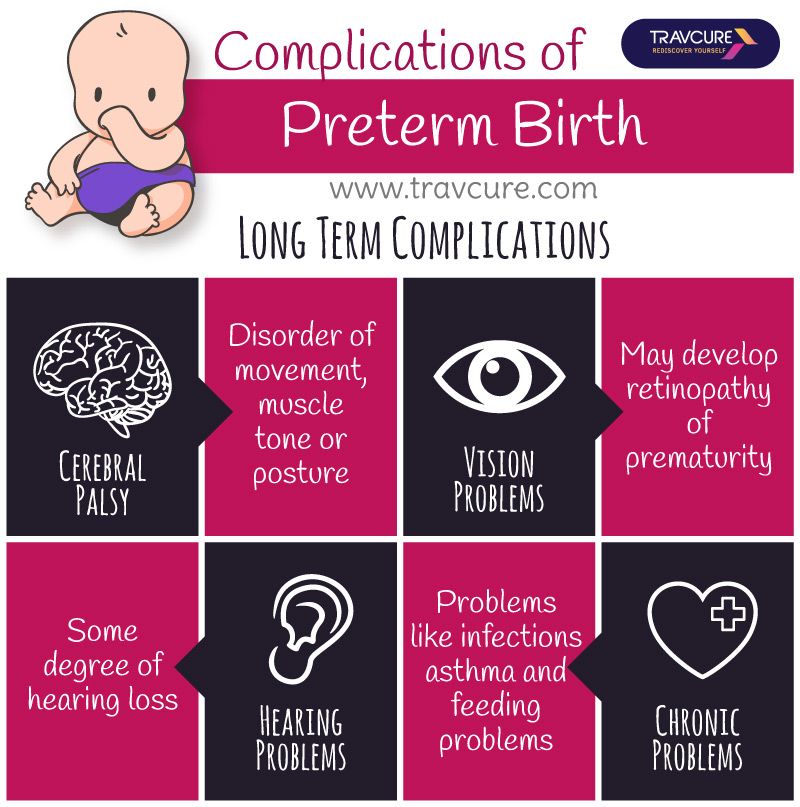 This can lead to anemia.
This can lead to anemia.
Breathing problems. These include:
- Apnea of prematurity (also called AOP). This is a pause in breathing for 15 to 20 seconds or more. It may happen together with a slow heart rate called bradycardia.
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (also called BPD). This is a lung disease that can develop in premature babies as well as babies who have treatment with a breathing machine. Babies with BPD have a higher risk of lung infections than other babies and BPD sometimes leads to lung damage.
- Respiratory distress syndrome (also called RDS). If a baby has RDS, her lungs can’t make enough of a substance called surfactant. Surfactant is a slippery substance that keeps small air sacs in a baby's lungs from collapsing.
Infections or neonatal sepsis. Premature babies can get infections more easily than other babies because their immune systems aren’t fully developed. The immune system protects your body from infection. Infection in premature babies can lead to sepsis, when the body has an extreme response to infection. Sepsis can be life-threatening.
The immune system protects your body from infection. Infection in premature babies can lead to sepsis, when the body has an extreme response to infection. Sepsis can be life-threatening.
Intraventricular hemorrhage (also called IVH). This is bleeding in the fluid-filled spaces (also called ventricles) in the brain. The more premature a baby is, the more likely he is to have IVH.
Newborn jaundice. This is when your baby’s skin and the white parts of his eye look yellow. It’s caused by the build-up of a substance called bilirubin in your baby’s blood. Jaundice happens when a baby’s liver isn't fully developed or isn't working well.
Necrotizing enterocolitis (also called NEC). This is a common, but very serious problem that can affect a newborn baby’s intestines. Intestines are long tubes that are part of your digestive system. Your baby’s digestive system helps his body break down food, take in nutrients and remove waste. NEC happens when the tissue of the intestine is injured (damaged) or begins to die.
NEC happens when the tissue of the intestine is injured (damaged) or begins to die.
Patent ductus arteriosus (also called PDA). This is a heart condition that happens when a blood vessel called the ductus arteriosus doesn’t close properly. The ductus arteriosus helps blood go around a baby’s lungs before birth. Once a baby’s born and her lungs fill with air, the ductus arteriosis isn’t needed anymore and usually closes on its own a few days after birth. If it doesn’t close properly, too much blood may flow into the lungs. This can cause heart and breathing problems.
Retinopathy of prematurity (also called ROP). This is an eye disease that happens when a baby’s retina’s don’t fully develop in the weeks after birth. The retina is the nerve tissue that lines the back of the eye. ROP usually affects both eyes. Most babies with ROP have a mild case and don’t need treatment. But babies with severe ROP can have vision problems or blindness.
Last reviewed: October, 2019
Meaning, Definition, Suggestions . What is born prematurely
- Online translator
- Grammar
- Video lessons
- Textbooks
- Vocabulary
- Professionals
- English for tourists
- Abstracts
- Tests
- Dialogues
- English dictionaries
- Articles
- Biographies
- Feedback
- About project
Examples
Meaning of the word "BORN"
To be (-be) born as a result of childbirth.
Watch all meanings of the word Born
The meaning of the word “prematurely”
See all meanings of the word premature
sentences with “Born premature”
| The younger brother F-16 was born prematurely, without a name, and he has no name, and he I had to catch up with the others. | |
| Prince Karim was born in Geneva, Switzerland on 13 December 1936 and was declared healthy despite being born prematurely. | |
| One of the frozen embryos was implanted one year after transplantation and the boy was born prematurely at 31 weeks after the mother developed preeclampsia. | |
| He was born prematurely at his mother's family estate, Broad Oak, a farmhouse on the border of Flintshire and Shropshire. | |
| The couple have two sons, one born prematurely in 2015 and the other in 2018. | |
| He was born prematurely in Rapallo, near Genoa, to Giuseppe Liseti and Maria Fini when the family moved from Recco. | |
| Other results | |
| But the end of anti-Americanism, which Russian nationalists prematurely rejoice in, promises to be the beginning of a destabilizing crisis within Russia. | |
| It's a little premature to say this, if not presumptuous, but I'd think twice about having kids with someone who doesn't like Christmas. | |
| She gave birth prematurely to a stillborn baby from shock and died. | |
| Their daughter was born prematurely and suffered pulmonary complications, living only two hours. | |
| The working title of the novel was Strike, but Rand believed that this title would reveal the mystery of the novel prematurely. | |
| She was said to have been born prematurely and was the only legitimate child of James to outlive him. | |
| In scaphocephaly, the sagittal suture fuses prematurely, preventing the skull from growing perpendicular to the suture. | |
| Witch's milk is more likely to be excreted by full-term babies than by premature babies. | |
| The hatched larvae dig tunnels inside apples and cause them to fall prematurely, creating unsightly brown spots. | |
| She was abducted and taken to her home in Iowa, where she gave birth prematurely and was told her daughter was missing. | |
| She was visiting her sister in Guildford when Wodehouse was born prematurely there. | |
| The wife recovered, but she gave birth to a child prematurely. | |
| Babies can be born prematurely with low birth weight and have meconium-stained amniotic fluid or a large placenta. | |
| premature aging of the bones, which can eventually lead to growth retardation and short stature in adulthood. | |
| I thought the deposit your parents gave us for the house was like a premature inheritance. | |
| Dithyramb used at his festivities, referring to his premature birth. | |
| The video shows Green raging at his family on Christmas morning for opening presents prematurely without waiting for him. | |
| And economists are not sure that the idea of premature rotation of personnel will justify itself. | |
| Information designed to shed light on efforts to end extreme poverty and reduce premature mortality should also act as a stimulus. | |
| Since 1979, pediatric endocrinologists in Puerto Rico have noted an increase in the number of patients with premature thelarche. | |
| Forced to work at a young age due to the premature death of his parents, Fritz studied medicine on his own. | |
This page provides the definition (meaning) of the phrase / expression "born prematurely", as well as synonyms, antonyms and sentences, if available in our database. We strive to make the English-Grammar.Biz explanatory dictionary, including the interpretation of the phrase / expression "born prematurely", as correct and informative as possible. If you have suggestions or comments about the correctness of the definition of "born prematurely", please write to us in the "Feedback" section.
Feeding premature babies | Breastfeeding premature babies
Premature babies have a special need for breast milk, but it can be difficult to breastfeed them directly. Our expert advice will help you provide your premature baby with healthy breast milk.
Share this information
Professor Katsumi Mizuno, Department of Pediatrics, Showa University Koto Toyosu Hospital:
Katsumi is a Certified Breastfeeding Consultant, Professor of Pediatrics at Showa Medical University, and one of Japan's leading pediatric neonatologists. His research focuses on neonatal suckling skills, breast milk banking, and the use of breast milk for feeding premature babies in neonatal intensive care units.
Babies born before the 37th week of pregnancy are considered premature. 1 The causes of preterm birth are not always obvious, but certain factors increase the likelihood of such an event. These include: twin or multiple pregnancy, certain diseases of the mother or fetus, as well as a history of premature birth.
Because premature babies spend less time in the womb, they are not mature enough and may be more susceptible to infection and disease. They often require hospitalization in the neonatal intensive care unit.
Why is breast milk so important for premature babies?
Breast milk is essential for optimal growth and development of term babies, but it is even more important for premature babies.
During pregnancy, the fetus receives important substances from the mother through the placenta, such as DHA (a fatty acid essential for brain and eye development) and immunoglobulin G (an antibody). 2.3 A premature infant did not receive all of these substances. However, the milk produced by a premature mother contains more fat and secretory immunoglobulin than mothers of full-term babies. 4
In addition, premature babies have an underdeveloped gastrointestinal tract, which can make digestion and absorption of nutrients difficult, so they need food that their sensitive stomach and intestines can easily digest. Breast milk contains enzymes that make it easier for the baby to digest, 5 as well as epidermal growth factor, which accelerates the development of the gastrointestinal tract 6 . Premature infants who are predominantly breastfed have much lower intestinal permeability than formula-fed infants, meaning fewer potentially harmful particles from the stomach and intestines enter their bloodstream. 7
Breast milk contains enzymes that make it easier for the baby to digest, 5 as well as epidermal growth factor, which accelerates the development of the gastrointestinal tract 6 . Premature infants who are predominantly breastfed have much lower intestinal permeability than formula-fed infants, meaning fewer potentially harmful particles from the stomach and intestines enter their bloodstream. 7
Breast milk is so important for premature babies that if the baby's mother does not produce enough breast milk at first for any reason, it is recommended that the deficiency be replenished with donor milk rather than formula.
Does breast milk improve the condition of premature babies?
Breast milk contains protective substances that can prevent serious diseases that preterm infants are susceptible to, such as severe infections, 9 retinopathy of prematurity (which can cause vision loss) 10 and bronchopulmonary dysplasia (chronic lung disease). 11
11
The more milk your baby gets, the lower the risk of disease. 12 Every additional 10 ml of milk per kilogram of body weight per day reduces the risk of sepsis by 19%. 9 The risk of developing necrotizing enterocolitis (a potentially fatal bowel disease) in premature infants who are breastfed is ten times lower than those who are formula fed. 13 That's why every drop counts!
Most importantly, preterm infants who are breastfed are typically discharged an average of two weeks earlier than formula-fed infants. 14 They also have a 6% lower risk of readmission in the first year of life. 15
Breast milk has been proven to have a beneficial effect on mental and physical development in the long term. Studies show that low-birth-weight babies who are breastfed in the neonatal intensive care unit have an average IQ of up to five points higher than those who are not breastfed. 15 In addition, their cardiovascular system works better during their lifetime.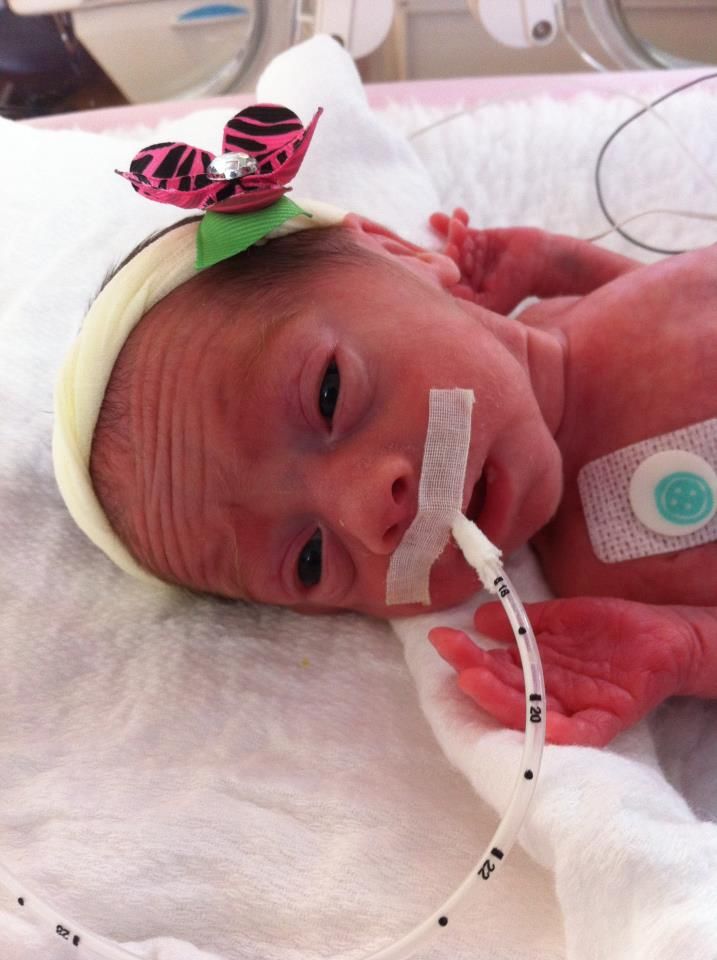 17
17
Will milk be produced if the baby was born prematurely?
Yes, the mother's body is ready to produce milk by the middle of pregnancy. After the baby is born and the placenta is born, the level of progesterone, the pregnancy hormone, drops, and the production of colostrum, the first milk, starts in the breast. This usually happens after the newborn is put to the breast and begins to suckle rhythmically, but if the baby was born prematurely, he most likely will not be able to latch on at first.
To replicate the sensations that trigger milk production, you can manually stimulate the breasts and nipples, or use a breast pump to express nutrient-rich colostrum for your baby. 18 Read below for more information on what to do if your premature baby is not yet able to breastfeed.
Breast milk usually comes in two to four days after birth, but if it was premature, the milk supply may be delayed. However, a recent study shows that moms who started pumping within one hour of giving birth had milk coming in as expected. 19 That is why it is important to start expressing breast milk as early as possible.
19 That is why it is important to start expressing breast milk as early as possible.
How to prepare if the baby is expected prematurely?
Visit the neonatal intensive care unit to see how it works and how premature babies are cared for. In addition, it will be useful to learn how breast milk is produced and secreted and why it is not only a healthy food, but also an important medicine for premature babies. Read more about this in our free e-book Surprising Breast Milk Facts .
What if a premature baby cannot breastfeed?
Many babies born before 34 weeks have difficulty coordinating sucking, swallowing and breathing. Until the baby masters these skills, nurses will feed him through a tube that is inserted into the nose or mouth and provides food directly into the stomach. In this way, the baby can be fed continuously until he is ready to breastfeed.
If your baby is too weak to latch on and suckle milk, you can use a breast pump* available at the hospital or maternity hospital to “do the job for the baby”. Breast stimulation with research-based technology, 20 reproduces the rhythm of the suckling of the baby, plays an important role in starting and maintaining milk production in the first hours after childbirth 21 .
Breast stimulation with research-based technology, 20 reproduces the rhythm of the suckling of the baby, plays an important role in starting and maintaining milk production in the first hours after childbirth 21 .
Milk should be expressed at the same frequency as term infants are normally fed every two to three hours, i.e. 8 to 12 times a day.
You can try putting a small amount of expressed breast milk into the baby's mouth with a syringe, or putting milk-soaked cotton swabs in the baby's mouth. 22 This way your baby will recognize the taste of your milk, which will facilitate the transition to breastfeeding in the future. In addition, the protective substances that make up breast milk will help strengthen the local immunity of the baby's oral cavity. You can be involved in the care of your premature baby in a variety of ways - check with your healthcare provider for details.
Very low birth weight babies - less than 1.5 kg - usually need extra protein, calcium and phosphorus, so they are given fortified breast milk. In some countries, such additives are made on human milk, and, for example, in Japan, on cow's milk.
In some countries, such additives are made on human milk, and, for example, in Japan, on cow's milk.
Recommendations for pumping milk
If the baby will be in the neonatal intensive care unit for a long time, neonatologists recommend using a double breast pump for pumping. I always recommend Medela Symphony*. Double pumping not only speeds up the process, but also produces an average of 18% more milk than pumping from each breast in turn. 23
In addition, I advise you to create the most comfortable conditions for pumping. It is generally agreed that it is best to express milk during or after prolonged skin-to-skin contact with the baby (more on this "kangaroo method" below). Another good option is to sit next to the crib and watch your baby while he pumps. Oxytocin (the hormone that stimulates milk flow) is released when you look at your baby, touch him, smell him and think about him, 24 Therefore, comfortable and calm conditions must be created for this in the neonatal intensive care unit.
What is kangaroo care for premature babies?
The so-called kangaroo method involves prolonged skin-to-skin contact between parents and infant. This is extremely beneficial for you and your baby, as well as for milk production. Skin-to-skin contact normalizes the baby's breathing and heartbeat, keeps him warm and allows him to be as close to the parent as possible. Kangaroo care is believed to have a beneficial effect on the health of premature babies, 25 and it helps moms to express more milk 26 and breastfeed longer. 27 Skin-to-skin contact 30-60 minutes before feeding gives baby time to wake up and be hungry so he can eat without being forced.
What if the neonatal intensive care unit offers formula feeding?
Feel free to state that you want to breastfeed your baby instead of formula. If you don't have enough breast milk to feed your baby, ask the ward for help to increase your milk supply.
It is natural for mothers whose babies are in the neonatal intensive care unit to experience anxiety and stress. Sometimes these experiences interfere with milk production, so it's important to ask for any help you may need. Remember that you have the right to seek support. Your healthcare provider may be able to recommend a suitable lactation specialist, such as a lactation consultant, for you.
Sometimes these experiences interfere with milk production, so it's important to ask for any help you may need. Remember that you have the right to seek support. Your healthcare provider may be able to recommend a suitable lactation specialist, such as a lactation consultant, for you.
How to switch from pumping to breastfeeding?
At whatever stage of pregnancy a baby is born, if the baby is stable enough for skin-to-skin contact, it can seek the breast itself for sedative suckling. This is the perfect way for your baby to learn sucking skills before they learn to coordinate sucking, swallowing and breathing.
Babies love the smell of breast milk, so you can put some milk on the nipple to make him want to suck before putting him on the breast. He might even be able to suck some milk. Don't worry if your baby seems to suck very little - he learns every time. He can start with one or two sips and gradually move on to full breastfeeding. Until then, the baby can be fed through a tube, pressed to the breast, so that the taste of milk and touching the breast is associated with a feeling of satiety.
You can put your baby to the breast for sedative suckling as soon as you are ready for kangaroo care, unless your baby is suffering from bradycardia (slow heartbeat) or low oxygen levels in the blood. You can switch to breastfeeding as soon as the baby is ready for it. Gradually, he will gain enough strength to suckle longer and suck out more milk.
Literature
1 World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland; 2018. Media Centre: Preterm birth fact sheet; November 2017 [03/26/2018]. Available from : http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs363/en/ - Geneva, Switzerland; 2018. "Media Center: Prematurity Fact Sheet"; November 2017 [3/26/2018]. Article at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs363/en/
2 Duttaroy AK. Transport of fatty acids across the human placenta: a review. Prog Lipid Res . 2009;48(1):52-61. - Duttaroy A.K., "Transfer of fatty acids across the human placenta: a review". Prog Lipid Res. 2009;48(1):52-61.
2009;48(1):52-61. - Duttaroy A.K., "Transfer of fatty acids across the human placenta: a review". Prog Lipid Res. 2009;48(1):52-61.
3 Palmeira P et al. IgG placental transfer in healthy and pathological pregnancies. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012: 985646. - Palmeira P. et al., Placental transfer of immunoglobulin
5 Pamblanco M et al. Bile salt - stimulated lipase activity in human colostrum from mothers of infants of different gestational age and birthweight. Acta Paediatr. 1987;76(2):328-331. - Pamblanco M. et al., "Bile salt-activated lipase and its activity in colostrum of mothers of infants of various gestational ages and birth weights." Akta Pediatr. 1987;76(2):328-331.
6 Dvorak B. Milk epidermal growth factor and gut protection. J Pediatr. 2010;156(2): S 31-35. - Dvorak B. , "Epidermal growth factor in milk and gut protection". J Pediatrician (Journal of Pediatrics). 2010;156(2):S31-35.
, "Epidermal growth factor in milk and gut protection". J Pediatrician (Journal of Pediatrics). 2010;156(2):S31-35.
7 Taylor SN et al. Intestinal permeability in preterm infants by feeding type: mother's milk versus formula. Breastfeed Med . 2009;4(1):11-15.- Theilon S.N. et al., "Intestinal permeability in preterm infants and its association with type of feeding: breast milk or formula." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2009;4(1):11-15.
8 Newburg DS. Innate immunity and human milk. J Nutr . 2005;135(5):1308-1312. — Newburgh, D.S., "Natural Immunity and Breast Milk." F Int. 2005;135(5):1308-1312.
9 Patel AL et al. Impact of early human milk on sepsis and health-care costs in very low birth weight infants. J Perinatol . 2013;33(7):514-519. - Patel A.L. et al., "Impact of early breast milk on sepsis and health care costs in extremely low birth weight infants". Zh Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology). 2013;33(7):514-519.
- Patel A.L. et al., "Impact of early breast milk on sepsis and health care costs in extremely low birth weight infants". Zh Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology). 2013;33(7):514-519.
10 Zhou J et al . Human milk feeding as a protective factor for retinopathy of prematurity: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2015;136(6): e 1576-1586. - Zhou Q. et al., "Breastfeeding as a protective factor against retinopathy of prematurity: a meta-analysis." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2015;136(6):e1576-1586.
11 Patel AL et al. Influence of own mother's milk on bronchopulmonary dysplasia and costs. Arch DIS Child FETAL 90UR311 90UP 2017;102(3): F 256- F 261. - Patel A.L. et al., "Effect of breast milk on bronchopulmonary dysplasia and health care costs." Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonate Ed. 2017;102(3): F 256- F 261.
- Patel A.L. et al., "Effect of breast milk on bronchopulmonary dysplasia and health care costs." Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonate Ed. 2017;102(3): F 256- F 261.
12 Meier PP et al . Improving the use of human milk during and after the NICU stay. Clin Perinatol. 2010;37(1):217-245. - Meyer P.P. et al., "Optimizing the use of breast milk during and after a stay in the neonatal intensive care unit." Perinatol wedge. (Clinical perinatology). 2010;37(1):217-245.
13 Lucas A, Cole TJ. Breast milk and neonatal necrotising enterocolitis. Lancet. 1990;336(8730-8731):1519-1523. — Lucas A, Cole TJ, "Breast milk and neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis." Lancet 1990;336(8730-8731):1519-1523.
14 Schanler RJ et al. Randomized trial of donor human milk versus preterm formula as substitutes for mothers' own milk in the feeding of extremely premature infants. Pediatrics. 2005;116(2):400-406. - Chanler R.J. et al., "Randomized Trial of Donor Human Milk Versus Prematurity Formula as a Breast Milk Substitute in Severely Preterm Infants". Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2005;116(2):400-406.
Randomized trial of donor human milk versus preterm formula as substitutes for mothers' own milk in the feeding of extremely premature infants. Pediatrics. 2005;116(2):400-406. - Chanler R.J. et al., "Randomized Trial of Donor Human Milk Versus Prematurity Formula as a Breast Milk Substitute in Severely Preterm Infants". Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2005;116(2):400-406.
15 Vohr BR et al. Beneficial effects of breast milk in the neonatal intensive care unit on the developmental outcome of extremely low birth weight infants at 18 months of age. Pediatrics. 2006;118(1): e 115-123. - Thief B.R. et al., Developmental Beneficial Effects of Breast Milk in the Intensive Care Unit on Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants by 18 Months of Age. Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;118(1):e115-123.
16 Victora CG et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects. Lancet (Lancet). 2016;387(10017):475-490.
Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects. Lancet (Lancet). 2016;387(10017):475-490.
17 Lewandowski AJ et al. Breast milk consumption in preterm neonates and cardiac shape in adulthood. Pediatrics. 2016;138(1): pii : e 20160050. - Lewandowski, A.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in preterm infants and cardiovascular health in adulthood." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2016;138(1):pii:e20160050.
18 Meier PP et al. Which breast pump for which mother: an evidence-based approach to individualizing breast pump technology. J. Perinatol. 2016;36(7):493-499. - Meyer P.P. et al., Breastpump Selection: A Scientific Approach to Customizing Pumping Technology. Zh Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology). 2016;36(7):493-499.
19 Parker LA et al. Effect of early breast milk expression on milk volume and timing of lactogenesis stage II among mothers of very low birth weight infants: a pilot study. J Perinatol. 2012;32(3):205-209. - Parker L.A. et al., "Effect of early pumping on milk supply and timing of the second stage of lactogenesis in mothers of extremely low birth weight infants: a pilot study." Zh Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology). 2012;32(3):205-209.
Effect of early breast milk expression on milk volume and timing of lactogenesis stage II among mothers of very low birth weight infants: a pilot study. J Perinatol. 2012;32(3):205-209. - Parker L.A. et al., "Effect of early pumping on milk supply and timing of the second stage of lactogenesis in mothers of extremely low birth weight infants: a pilot study." Zh Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology). 2012;32(3):205-209.
20 Meier PP et al. Breast pump suction patterns that mimic the human infant during breastfeeding: greater milk output in less time spent pumping for breast pump-dependent mothers with premature infants. J Perinatol. 2012;32(2):103-110. - Meyer P.P. et al., "Pumping patterns that mimic breastfeeding behavior: more milk and less time for constantly pumping mothers of preterm infants." J Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology). 2012;32(2):103-110.
21 Parker LA et al. Association of timing of initiation of breastmilk expression on milk volume and timing of lactogenesis stage II among mothers of very low-birth-weight infants. Breastfeed Med . 2015;10(2):84-91. - Parker L.A. et al., "Effect of early pumping on milk supply and timing of the second stage of lactogenesis in mothers of extremely low birth weight infants: a pilot study." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(2):84-91.
Association of timing of initiation of breastmilk expression on milk volume and timing of lactogenesis stage II among mothers of very low-birth-weight infants. Breastfeed Med . 2015;10(2):84-91. - Parker L.A. et al., "Effect of early pumping on milk supply and timing of the second stage of lactogenesis in mothers of extremely low birth weight infants: a pilot study." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(2):84-91.
22 Lee J et al. Oropharyngeal colostrum administration in extremely premature infants: an RCT. Pediatrics. 2015;135(2): e 357-366. - Lee J. et al., "Oropharyngeal colostrum ingestion in very preterm infants: a randomized controlled clinical trial." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2015;135(2):e357-366.
23 Prime PK et al. Simultaneous breast expression in breastfeeding women is more efficacious than sequential breast expression. Breastfeed Med 2012; 7(6):442–447. - Prime D.K. and co-authors. "During the period of breastfeeding, simultaneous pumping of both breasts is more productive than sequential pumping." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2012;7(6):442-447.
Breastfeed Med 2012; 7(6):442–447. - Prime D.K. and co-authors. "During the period of breastfeeding, simultaneous pumping of both breasts is more productive than sequential pumping." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2012;7(6):442-447.
24 Uvn ä s Oxytocin effects in mothers and infants during breastfeeding. Infant 2013; 9(6):201–206. - Uvenas-Moberg K, Prime DK, "Oxytocin effects on mother and child during breastfeeding". Infant. 2013;9(6):201-206.
25 Boundy EO et al. Kangaroo mother care and neonatal outcomes: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2015;137(1): e 20152238. - Boundi I.O. and co-authors, "The Kangaroo Method and Its Impact on Newborns: A Meta-Analysis". Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2015;137(1): e20152238.
26 Acuña-Muga J et al. Volume of milk obtained in relation to location and circumstances of expression in mothers of very low birth weight infants. J Hum Lact . 2014;30(1):41-46 - Akunya-Muga, J. et al., "The amount of milk expressed by location and circumstances of pumping in mothers of extremely low birth weight infants." F Hum Lakt. 2014;30(1):41-46
Volume of milk obtained in relation to location and circumstances of expression in mothers of very low birth weight infants. J Hum Lact . 2014;30(1):41-46 - Akunya-Muga, J. et al., "The amount of milk expressed by location and circumstances of pumping in mothers of extremely low birth weight infants." F Hum Lakt. 2014;30(1):41-46
27 Nyqvist KH et al. Towards universal kangaroo mother care: recommendations and report from the first European conference and seventh international workshop on kangaroo mother care. Acta Paediatr . 2010;99(6):820-826.- Nukvist K.H. et al., "On the Universality of the Kangaroo Method: Recommendations and Report from the First European Conference and the Seventh International Kangaroo Method Workshop". Akta Pediatr. 2010;99(6):820-826.
28 American Academy of Pediatrics - Section on Breastfeeding.