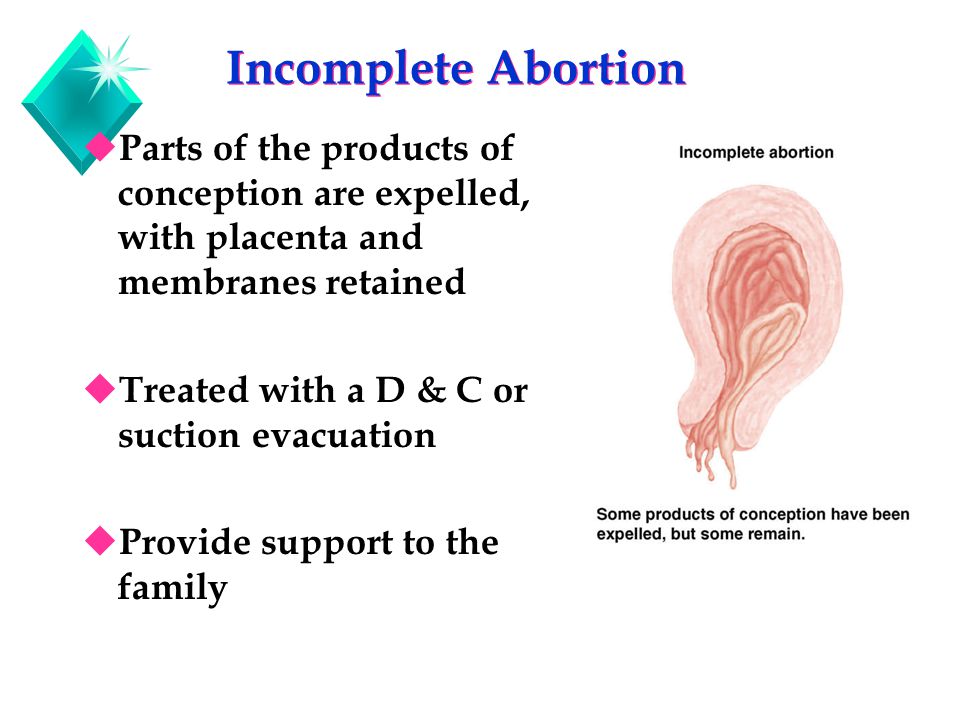
Rare complications of pregnancy
Uncommon Pregnancy Complications - North Shore Associates in Gynecology and Obstetrics
Your pregnancy is going to be completely unique to you and your body. For some women, that might mean encountering some uncommon pregnancy complications. While the word “complication” might sound a little scary–and there are certainly serious complications that exist–not all of them are necessarily alarming. Your body will go through an amazing transformation during your pregnancy, so it’s not surprising that some of those changes might surprise you.
With the help of your OBGYN and Midwife, most uncommon pregnancy complications will ultimately serve as memories and mementoes of your unique pregnancy.
Some Uncommon Pregnancy Complications You May Encounter
Some of the uncommon pregnancy complications women may encounter during their term may include some of the following.
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Most people are fairly familiar with morning sickness, which usually presents during the first trimester. However, in a small percentage of women, morning sickness will start earlier (in weeks 4 or 5) and persist longer–often throughout the entire pregnancy. This persistent morning sickness is known medically as hyperemesis gravidarum.
Generally, hyperemesis gravidarum is managed successfully by pregnant women with no need for intervention. However, your OBGYN or midwife may become involved when your morning sickness begins causing secondary issues. For example, if you begin losing weight or start feeling dizzy, you should immediately contact your doctor. Your OBGYN may also be able to help detect and manage other hyperemesis gravidarum related issues. You should always keep your OBGYN or Midwife apprised of your symptoms.
Excessive Salivation
On a typical day, your body will produce something like one and a half quarts of saliva, most of which you end up swallowing. Some women, when they become pregnant, start producing significantly more saliva. This is known as excessive salivation (or ptyalism or sialorrhea, medically). Some women may start salivating so much that they need to start spitting on a regular basis. Other women may be able to make due with swallowing the excess saliva. Excess salivation can cause some minor discomfort, including heartburn and nausea. Your OBGYN will likely be able to help you manage any discomfort associated with excessive salivation.
This is known as excessive salivation (or ptyalism or sialorrhea, medically). Some women may start salivating so much that they need to start spitting on a regular basis. Other women may be able to make due with swallowing the excess saliva. Excess salivation can cause some minor discomfort, including heartburn and nausea. Your OBGYN will likely be able to help you manage any discomfort associated with excessive salivation.
Pica Disorder
Pregnancy is also commonly associated with cravings. Popular culture tends to emphasize the more unusual and outlandish cravings. Sometimes, those unusual cravings can manifest in a condition called Pica disorder. Women who have pregnancy-induced Pica will begin to crave non-food substances of little or no nutritional value. Common examples include burnt matchsticks, coffee grounds, toothpaste, or charcoal.
Eating toxic non-food items can, of course, be detrimental to your health. Managing Pica disorder, therefore, usually means talking to your OBGYN about your symptoms and ensuring that you don’t eat any non-food substances.
Nosebleeds
You’ve probably had a nosebleed before. They can happen for a wide variety of reasons, from dry air to skin irritation. When you’re pregnant, the blood vessels in your nose expand. This creates a bit more pressure on those capillaries and arteries, which can lead to more frequent nosebleeds. This can make nosebleeds when you’re pregnant a much more common occurrence. There isn’t usually anything to worry about when it comes to nosebleeds, but if you find them happening regularly, you should certainly consult with your OBGYN and keep an eye on the issue.
Gestational Diabetes
- Diabetes is a condition in which your body can no longer correctly process glucose. Typically, diabetes develops due to chronically high blood sugar or because of genetic factors (specifically those associated with the pancreatic production of insulin). But many women can also develop what’s called gestational diabetes. If you develop gestational diabetes, you might have problems with high blood sugar while you’re pregnant.
In most cases, your body chemistry returns to normal after your baby is delivered, but gestational diabetes can lead to longer term issues, so it’s important to monitor and discuss this possible uncommon pregnancy complication with your OBGYN. You may have to closely monitor your diet if you develop gestational diabetes. Your OBGYN will be able to help ensure that you keep your gestational diabetes under control for the duration of your pregnancy.
Yeast Infections
To a certain degree, yeast is common in the vagina, so there’s almost always at least a little yeast present. However, because the vagina is an especially well balanced organ, any yeast present is usually kept under control by various other microorganisms present. Pregnancy can throw the yeast-to-microorganism relationship out of balance. This means that during your pregnancy, you may experience more frequent yeast infections, in part because the increased estrogen in your body makes it easier for the yeast to grow. If you’ve noticed more frequent than usual yeast infections, you can talk to your OBGYN about possible treatments.
If you’ve noticed more frequent than usual yeast infections, you can talk to your OBGYN about possible treatments.
Melasma
Sometimes called “the mask of pregnancy,” melasma presents as discoloration of the skin. Often, this discoloration can be focused on the face (but not exclusively). If you are noticing darker than normal splotches on your face–especially if they are somewhat symmetrical–melasma may be the source.
Typically, melasma presents no danger to your health, though you may feel self-conscious about your change in skin tone. Typically, melasma will recede several months after the birth of your baby.
Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums are certainly an uncommon pregnancy complication, but they’re usually nothing to worry about. In most cases, bleeding gums are caused by gingivitis, which is a swelling of the gums and precursor to gum disease. Women who are pregnant can develop gingivitis because of changes in their body chemistry. In most cases, regular dental cleanings will be able to prevent the gingivitis from doing any long term damage to your teeth. And if your teeth are in good health, your gingivitis should resolve itself after your pregnancy.
In most cases, regular dental cleanings will be able to prevent the gingivitis from doing any long term damage to your teeth. And if your teeth are in good health, your gingivitis should resolve itself after your pregnancy.
Itchy Skin
During pregnancy, your skin is going to shift and stretch and grow anew. As a result, it’s not unusual for some women to experience occasional itching throughout their pregnancy. Usually, this itching is temporary, and it will go away when your skin reaches a kind of equilibrium. In some cases, though, the itching can extend throughout the entirety of your pregnancy.
Thankfully, your OBGYN can help you treat the symptoms of itching, so you don’t feel compelled to scratch for your entire pregnancy. If you experience severe or uncontrollable itching, you should contact your OBGYN or Midwife immediately, as this may be a sign of a serious condition.
Uncommon Complications and Unique Bodies
These uncommon pregnancy complications are–by definition–not something that every mother-to-be should anticipate coming across. When they do occur, however, pregnancy complications are something you should discuss with your OBGYN. The vast majority of complications are relatively minor, but serious complications can have significant outcomes. Your OBGYN can help walk you through which complications need more attention and which may actually be signs of a healthy pregnancy.
When they do occur, however, pregnancy complications are something you should discuss with your OBGYN. The vast majority of complications are relatively minor, but serious complications can have significant outcomes. Your OBGYN can help walk you through which complications need more attention and which may actually be signs of a healthy pregnancy.
But it’s helpful to know that, as your body changes, it will likely transform in ways that are unique to you. That means your pregnancy will be a journey of self discovery, and your OBGYN will be by your side to help ensure that the end result is a healthy, happy baby. Your OBGYN may also be able to offer screenings and tests for many possible pregnancy complications, allowing you to anticipate and prepare for some changes before they occur.
If you have questions for our OBGYNs, contact our Wilmette or Glenview offices to schedule an appointment today.
Pregnancy complications | Tommy's
Sometimes things go wrong during pregnancy and you need extra care. In this section you will find information and support for pregnancy complications.
In this section you will find information and support for pregnancy complications.
A-Z of pregnancy complications
-
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Beth Braine is sharing her story to raise awareness of a rare pregnancy complication: Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy.
Read more about ' Acute fatty liver of pregnancy ' -
Anaemia and pregnancy
Anaemia can be common in pregnancy. Find out what causes anaemia and how you can try to avoid it by eating a healthy, balanced diet.
Read more about 'Anaemia and pregnancy' -
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)
Antiphospholipid syndrome is an immune system disorder. It can cause pregnancy complications, but treatment can help to reduce the risks for you and your baby.
Read more about 'Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)'
-
Weak cervix (cervical incompetence or cervical insufficiency)
A weak cervix is when the cervix shortens and opens in the second or early in the third trimester, without any other symptoms of labour.
Read more about 'Weak cervix (cervical incompetence or cervical insufficiency) '
-
Cytomegalovirus and pregnancy
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) can cause long-term problems for babies who become infected before they are born. This is known as congenital CMV infection.
Read more about 'Cytomegalovirus and pregnancy' -
Type 1 or 2 diabetes in pregnancy
If you have type 1 or 2 diabetes, the risks are higher for both mother and the baby. However, there are lots of things you can do to reduce the risks.
Read more about 'Type 1 or 2 diabetes in pregnancy'
-
Fetal growth restriction (Intrauterine growth restriction)
Fetal growth restriction (FGR) or IUGR is a condition where a baby is smaller than expected or when a baby's growth slows or stops during pregnancy.
Read more about 'Fetal growth restriction (Intrauterine growth restriction)' -
Foetal alcohol syndrome
Foetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is a condition that a baby may develop if a woman drinks alcohol during her pregnancy.
Read more about 'Foetal alcohol syndrome' Find out more.
Find out more. -
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that can develop during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes is fairly common: it affects around 18% of pregnant women.
Read more about 'Gestational diabetes'
-
Group B strep (strep B) and pregnancy
Group B strep (also known as GBS or strep B) is a common bacteria carried in the body. It is usually harmless but sometimes it can infect a baby during labour.
Read more about 'Group B strep (strep B) and pregnancy' -
Intrauterine infection (chorioamnionitis)
Intrauterine infection, also known as chorioamnionitis, is when the membranes that surround the baby in the womb are infected.
Read more about 'Intrauterine infection (chorioamnionitis)' -
Low-lying placenta (placenta praevia)
The placenta is your baby’s support system in the womb.
Read more about 'Low-lying placenta (placenta praevia)' If the placenta doesn’t work properly, your baby is at risk of health problems.
If the placenta doesn’t work properly, your baby is at risk of health problems.
-
Pelvic pain in pregnancy (SPD)
Pelvic pain is common in pregnancy and is known as Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction (SPD) or Pelvic Girdle Pain (PGP). Find out the causes here.
Read more about 'Pelvic pain in pregnancy (SPD)' -
Pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a serious condition that affects some pregnant women, usually after 20 weeks or soon after their baby is delivered.
Read more about 'Pre-eclampsia' -
Retained placenta
This is when part of the placenta remains in the womb after giving birth. A retained placenta needs to be treated early to prevent complications.
Read more about 'Retained placenta'
Rare and acute complications of endometriosis in pregnant women | Vaulina
1. Leone Roberti Maggiore U, Ferrero S, Mangili G, Bergamini A, Inversetti A, Giorgione V, Viganò P, Candiani M. A systematic review on endometriosis during pregnancy: diagnosis, misdiagnosis, complications and outcomes. Hum Reprod Update. 2016;22(1):70-103. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmv045
Leone Roberti Maggiore U, Ferrero S, Mangili G, Bergamini A, Inversetti A, Giorgione V, Viganò P, Candiani M. A systematic review on endometriosis during pregnancy: diagnosis, misdiagnosis, complications and outcomes. Hum Reprod Update. 2016;22(1):70-103. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmv045
2. Vassilopoulou L, Matalliotakis M, Zervou MI, Matalliotaki C, Spandidos DA, Matalliotakis I, Goulielmos GN. Endometriosis and in vitro fertilization. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(2):1043-1051. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.6307
3. Dubrovina S.O., Bezhenar V.F., red. Endometriosis. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment. Moscow: GEOTAR-Media; 2020
4. Li H, Zhu HL, Chang XH, Li Y, Wang Y, Guan J, Cui H. Effects of Previous Laparoscopic Surgical Diagnosis of Endometriosis on Pregnancy Outcomes. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017;130(4):428-433. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.199840
5. Zullo F, Spagnolo E, Saccone G, Acunzo M, Xodo S, Ceccaroni M, Berghella V. Endometriosis and obstetrics complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(4):667-672.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.07.019
Fertil Steril. 2017;108(4):667-672.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.07.019
6. Kohl Schwartz AS, Wölfer MM, Mitter V, Rauchfuss M, Haeberlin F, Eberhard M, von Orelli S, Imthurn B, Imesch P, Fink D, Leeners B. Endometriosis, especially mild disease: a risk factor for miscarriages . Fertil Steril. 2017;108(5):806-814.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.08.025
7. Tanbo T, Fedorcsak P. Endometriosis-associated infertility: aspects of pathophysiological mechanisms and treatment options. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2017;96(6):659-667. https://doi.org/10.1111/aogs.13082
8. Miura M, Ushida T, Imai K, Wang J, Moriyama Y, NakanoKobayashi T, Osuka S, Kikkawa F, Kotani T. Adverse effects of endometriosis on pregnancy: a case-control study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19(1):373. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-019-2514-1
9. Exacoustos C, Lauriola I, Lazzeri L, De Felice G, Zupi E. Complications during pregnancy and delivery in women with untreated rectovaginal deep infltrating endometriosis . Fertil Steril. 2016;106(5):1129-1135.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.06.024.
Fertil Steril. 2016;106(5):1129-1135.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.06.024.
10. Farland LV, Prescott J, Sasamoto N, Tobias DK, Gaskins AJ, Stuart JJ, Carusi DA, Chavarro JE, Horne AW, RichEdwards JW, Missmer SA. Endometriosis and Risk of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134(3):527-536. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000003410
11. Chen I, Lalani S, Xie RH, Shen M, Singh SS, Wen SW. Association between surgically diagnosed endometriosis and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Fertil Steril. 2018;109(1):142-147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.09.028
12. Jeon H, Min J, Kim DK, Seo H, Kim S, Kim YS. Women with Endometriosis, Especially Those Who Conceived with Assisted Reproductive Technology, Have Increased Risk of Placenta Previa: Meta-analyses. J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(34):e234. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e234
13. Yi KW, Cho GJ, Park K, Han SW, Shin JH, Kim T, Hur JY. Endometriosis Is Associated with Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: a National Population-Based Study. Reprod Sci. 2020;27(5):1175-1180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-019-00109-1
Reprod Sci. 2020;27(5):1175-1180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-019-00109-1
14. Benaglia L, Candotti G, Papaleo E, Pagliardini L, Leonardi M, Reschini M, Quaranta L, Munaretto M, Viganò P, Candiani M, Vercellini P, Somigliana E. Pregnancy outcome in women with endometriosis achieving pregnancy with IVF. Hum reproduction. 2016;31(12):2730-2736. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dew210
15. Nirgianakis K, Gasparri ML, Radan AP, Villiger A, McKinnon B, Mosimann B, Papadia A, Mueller MD. Obstetric complications after laparoscopic excision of posterior deep infltrating endometriosis: a case-control study. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(3):459-466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.04.036
16. Saraswat L, Ayansina DT, Cooper KG, Bhattacharya S, Miligkos D, Horne AW, Bhattacharya S. Pregnancy outcomes in women with endometriosis: a national record linkage study. BJOG. 2017;124(3):444-452. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.13920
17. Minebois H, De Souza A, Mezan de Malartic C, Agopiantz M, Guillet May F, Morel O, Callec R. Endométriose et fausse couche spontanée. Meta-analyse et revue systématique de la littérature [Endometriosis and miscarriage: Systematic review]. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2017;45(7-8):393-399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gofs.2017.06.003
Endométriose et fausse couche spontanée. Meta-analyse et revue systématique de la littérature [Endometriosis and miscarriage: Systematic review]. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2017;45(7-8):393-399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gofs.2017.06.003
18. Porpora MG, Tomao F, Ticino A, Piacenti I, Scaramuzzino S, Simonetti S, Imperiale L, Sangiuliano C, Masciullo L, Manganaro L , Benedetti Panici P. Endometriosis and Pregnancy: A Single Institution Experience. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(2):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph27020401
19. Kobayashi H, Kawahara N, Ogawa K, Yoshimoto C. A Relationship Between Endometriosis and Obstetric Complications. Reprod Sci. 2020;27(3):771-778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-019-00118-0
20. Brigitte Leeners, Cynthia M Farquhar. Benefits of pregnancy on endometriosis: can we dispel the myths? Fertil Steril. 2019;112(2):226-227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2019.06.002
21. Lier M, Malik RF, van Waesberghe J, Maas JW, van Rumptvan de Geest DA, Coppus SF, Berger JP, van Rijn BB, Janssen PF, de Boer MA, de Vries J, Jansen FW, Brosens IA, Lambalk CB, Mijatovic V. Spontaneous haemoperitoneum in pregnancy and endometriosis: a case series. BJOG. 2017;124(2):306-312. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.14371
Spontaneous haemoperitoneum in pregnancy and endometriosis: a case series. BJOG. 2017;124(2):306-312. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.14371
22. Fonseca EKUN, Bastos BB, Yamauchi FI, Baroni RH. Ruptured endometrioma: main imaging fndings. Radiol Bras. 2018;51(6):411-412. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-3984.2017.0092
23. Denisova V.M., Yarmolinskaya M.I. External genital endometriosis and pregnancy: different facets of the problem. Journal of Obstetrics and Women's Diseases. 2015;64(1):44-52
24. Brosens I, Brosens JJ, Fusi L, Al-Sabbagh M, Kuroda K, Benagiano G. Risks of adverse pregnancy outcome in endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2012;98(1):30-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.02.024
25. Ueda Y, Enomoto T, Miyatake T, Fujita M, Yamamoto R, Kanagawa T, Shimizu H, Kimura T. A retrospective analysis of ovarian endometriosis during pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2010;94(1):78-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.02.092
26. Habib N, Centini G, Lazzeri L, Amoruso N, El Khoury L, Zupi E, Afors K. Bowel Endometriosis: Current Perspectives on Diagnosis and treatment. Int J Women's Health. 2020;12:35-47. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJWH.S190326
Bowel Endometriosis: Current Perspectives on Diagnosis and treatment. Int J Women's Health. 2020;12:35-47. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJWH.S190326
27. Pisanu A, Deplano D, Angioni S, Ambu R, Uccheddu A. Rectal perforation from endometriosis in pregnancy: case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2010 ;16(5):648-51. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i5.648
28. Costa A, Sartini A, Garibaldi S, Cencini M. Deep endometriosis induced spontaneous colon rectal perforation in pregnancy: laparoscopy is an advanced tool to confrm diagnosis . Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2014;2014:907150. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/907150
29. Setúbal A, Sidiropoulou Z, Torgal M, Casal E, Lourenço C, Koninckx P. Bowel complications of deep endometriosis during pregnancy or in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2014;101(2):442-446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.11.001
30. Revzoeva Yu.A., Shakurova E.Yu. Endometriosis as a cause of intra-abdominal bleeding during pregnancy.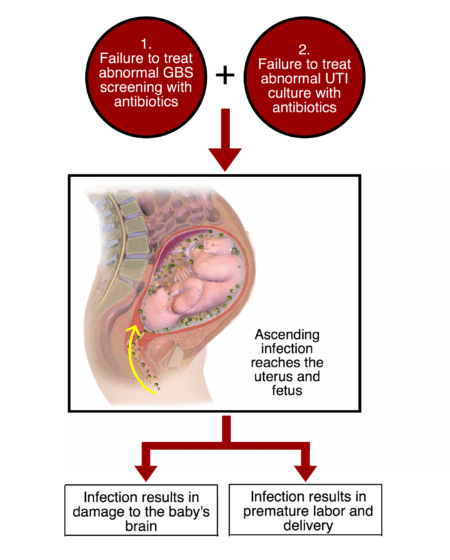 Clinical case. Bulletin of the Peoples' Friendship University of Russia. The medicine. 2019;23(3):283-289 https://doi.org/10.22363/2313-0245-2019-23-3-283-289
Clinical case. Bulletin of the Peoples' Friendship University of Russia. The medicine. 2019;23(3):283-289 https://doi.org/10.22363/2313-0245-2019-23-3-283-289
31. Cozzolino M, Corioni S, Maggio L, Sorbi F, Guaschino S, Fambrini M. Endometriosis-Related Hemoperitoneum in Pregnancy: A Diagnosis to Keep in Mind. Ochsner J. 2015;15(3):262-264.
32. Gao FM, Liu GL. Four Case Reports of EndometriosisRelated Hemoperitoneum in Pregnancy. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(4):502-504. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.225048
33. Jang JH, Kyeong KS, Lee S, Hong SH, Ji I, Jeong EH. A case of spontaneous hemoperitoneum by uterine vessel rupture in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2016;59(6):530-534. https://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2016.59.6.530
34. Vigano P, Corti L, Berlanda N. Beyond infertility: obstetrical and postpartum complications associated with endometriosis and adenomyosis. Fertil Steril. 2015;104(4):802-812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.08.030
35. Kim T, Sudhof Leanna S, Liu Fong W, Shainker Scott A. Spontaneous hemoperitoneum in pregnancy due to endometriosis. Journal of Endometriosis and Pelvic Pain Disorders. 2020;12(3):228402652094243. https://doi.org/10.1177/2284026520942432
Kim T, Sudhof Leanna S, Liu Fong W, Shainker Scott A. Spontaneous hemoperitoneum in pregnancy due to endometriosis. Journal of Endometriosis and Pelvic Pain Disorders. 2020;12(3):228402652094243. https://doi.org/10.1177/2284026520942432
36. Kim BH, Park SN, Kim BR. Endometriosis-induced massive hemoperitoneum misdiagnosed as ruptured ectopic pregnancy: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2020;14(1):160. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-020-02486-7
37. Lier MCI, Malik RF, Ket JCF, Lambalk CB, Brosens IA, Mijatovic V. Spontaneous hemoperitoneum in pregnancy (SHiP) and endometriosis - A systematic review of the recent literature. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2017;219:57-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2017.10.012
38. Brosens IA, Fusi L, Brosens JJ. Endometriosis is a risk factor for spontaneous hemoperitoneum during pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2009;92(4):1243-1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.03.091
39. Visouli AN, Zarogoulidis K, Kougioumtzi I, Huang H, Li Q, Dryllis G, Kioumis I, Pitsiou G, Machairiotis N, Katsikogiannis N , Papaiwannou A, Lampaki S, Zaric B, Branislav P, Porpodis K, Zarogoulidis P.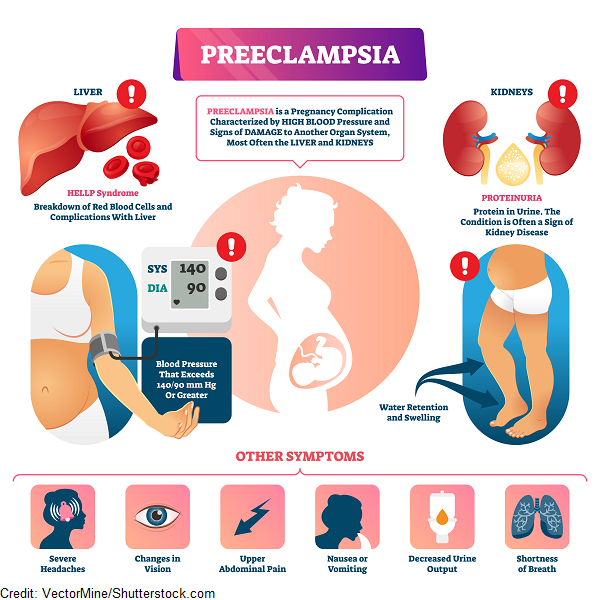 Catamenial pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis. 2014;6(Suppl 4):S448-60. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.08.49
Catamenial pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis. 2014;6(Suppl 4):S448-60. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.08.49
40. Maniglio P, Ricciardi E, Meli F, Vitale SG, Noventa M, Vitagliano A, Valenti G, La Rosa VL, Laganà AS, Caserta D. Catamenial pneumothorax caused by thoracic endometriosis. Radiol Case Rep. 2017;13(1):81-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radcr.2017.09.003
41. El-Jefut M., Artymuk N.V. New about theories of the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Fundamental and clinical medicine. 2019;4(3):77-82 https://doi.org/10.23946/2500-0764-2019-4-3-77-82
Pregnancy complications - articles on pregnancy and childbirth
Preeclampsia
Pregnancy in many women is accompanied by nausea, swelling and headache. In the early stages, this is most often normal and harmless, but in the third trimester the same symptoms can occur as a precursor to preeclampsia. This is a complication of pregnancy that threatens the health and life of both the woman and the baby. To reduce the risks associated with preeclampsia, it is important to recognize it as early as possible. To do this, obstetricians-gynecologists prescribe urine tests to all pregnant women and ask them to control blood pressure. About how to notice in time and how to treat preeclampsia - in our article.
In the early stages, this is most often normal and harmless, but in the third trimester the same symptoms can occur as a precursor to preeclampsia. This is a complication of pregnancy that threatens the health and life of both the woman and the baby. To reduce the risks associated with preeclampsia, it is important to recognize it as early as possible. To do this, obstetricians-gynecologists prescribe urine tests to all pregnant women and ask them to control blood pressure. About how to notice in time and how to treat preeclampsia - in our article.
Mole
Molar pregnancy is a relatively rare complication that occurs in one woman in a thousand. Most often, this pathology is recorded in East Asia.
Complications of pregnancy
Pregnancy without complications - when a woman feels great all nine months - unfortunately, is not common.
What is the placenta
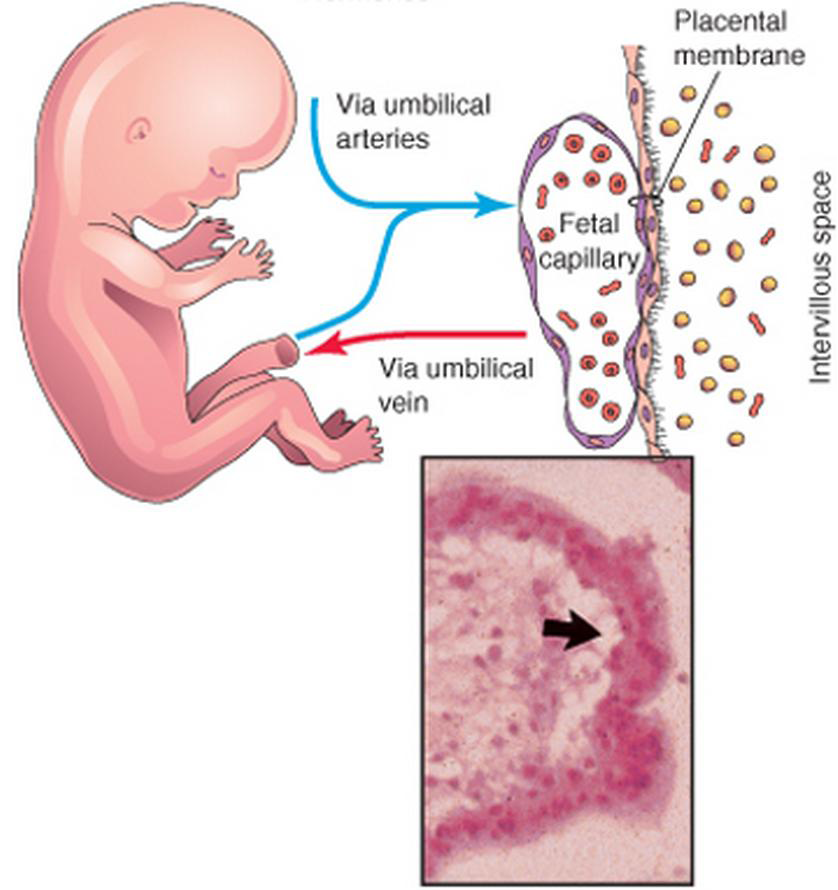
The placenta (“baby place”) is the most important and absolutely unique organ that exists only during pregnancy.
Pregnancy and Rh conflict
Most people have a poor idea of what the Rh factor is, because in ordinary life its presence or absence does not entail any painful consequences.
Early toxicosis of pregnant women
The most important period of pregnancy is the first trimester, when all organs and systems of the child are formed and formed.
Low water. Polyhydramnios
Everything related to the state of amniotic fluid is very important for the health of the child, so doctors carefully monitor what happens to them.
Toxicosis
Toxicosis sometimes acts as an early diagnostic test and tells a woman that she will soon become a mother. This condition occurs in many pregnant women, but it does not always take on dangerous forms. We will tell you what to do, how to eat to cope with nausea and when to seek help from a doctor.
Preeclampsia (late toxicosis of pregnant women)
Too rapid weight gain may indicate preeclampsia (late toxicosis), especially if edema appears, so it is necessary to inform the doctor about this.