What to expect in first month of pregnancy
Pregnancy Week By Week | First Month Symptoms and Signs
In This Section
- Month by Month
- What happens in the second month?
- What happens in the third month?
- What happens in the fourth month?
- What happens in the fifth month?
- What happens in the sixth month?
- What happens in the seventh month?
- What happens in the eighth month?
- What happens in the ninth month?
- What happens in the tenth month?
What happens in the first month of pregnancy?
Pregnancy is divided into 3 trimesters. Each trimester is a little longer than 13 weeks. The first month marks the beginning of the first trimester.
What’s gestational age?
Pregnancy timing is measured using “gestational age.” Gestational age starts on the first day of your last menstrual period (LMP).
Gestational age can be confusing. Most people think of pregnancy as lasting 9 months. And it’s true that you’re pregnant for about 9 months. But because pregnancy is measured from the first day of your last menstrual period — about 3-4 weeks before you’re actually pregnant — a full-term pregnancy usually totals about 40 weeks from LMP — roughly 10 months.
Many people don’t remember exactly when they started their last menstrual period — that’s OK. The surest way to find out gestational age early in pregnancy is with an ultrasound.
What happens during week 1 - 2?
These are the first 2 weeks of your menstrual cycle. You have your period. About 2 weeks later, the egg that’s most mature is released from your ovary — this is called ovulation. Ovulation may happen earlier or later, depending on the length of your menstrual cycle. The average menstrual cycle is 28 days.
Ovulation may happen earlier or later, depending on the length of your menstrual cycle. The average menstrual cycle is 28 days.
After it’s released, your egg travels down your fallopian tube toward your uterus. If the egg meets up with a sperm, they combine. This is called fertilization. Fertilization is most likely to occur when you have unprotected vaginal sex during the 6 days leading up to — and including the day of — ovulation.
What happens during week 3 - 4?
The fertilized egg moves down your fallopian tube and divides into more and more cells. It reaches your uterus about 3–4 days after fertilization. The dividing cells then form a ball that floats around in the uterus for about 2–3 days.
Pregnancy begins when the ball of cells attaches to the lining of your uterus. This is called implantation. It usually starts about 6 days after fertilization and takes about 3–4 days to be complete.
Pregnancy doesn’t always happen, even if an egg is fertilized by a sperm. Up to half of all fertilized eggs pass out of your body when you get your period, before implantation is complete.
Up to half of all fertilized eggs pass out of your body when you get your period, before implantation is complete.
What are the signs of pregnancy?
For a lot of people, the first sign of pregnancy is a missed period. Most pregnancy tests will be positive by the time you’ve missed your period. Other early pregnancy symptoms include feeling tired, feeling bloated, peeing more than usual, mood swings, nausea, and tender or swollen breasts. Not everyone has all of these symptoms, but it’s common to have at least 1 of them.
Was this page helpful?- Yes
- No
Help us improve - how could this information be more helpful?
How did this information help you?
Please answer below.
Are you human? (Sorry, we have to ask!)
Please don't check this box if you are a human.
You’re the best! Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.
We couldn't access your location, please search for a location.
Zip, City, or State
Please enter a valid 5-digit zip code or city or state.
Please fill out this field.
Service All Services Abortion Abortion Referrals Birth Control COVID-19 Vaccine HIV Services Men's Health Care Mental Health Morning-After Pill (Emergency Contraception) Pregnancy Testing & Services Primary Care STD Testing, Treatment & Vaccines Transgender Hormone Therapy Women's Health Care
Filter By All Telehealth In-person
Please enter your age and the first day of your last period for more accurate abortion options. Your information is private and anonymous.
Your information is private and anonymous.
I'm not sure This field is required.
AGE This field is required.
Or call 1-800-230-7526
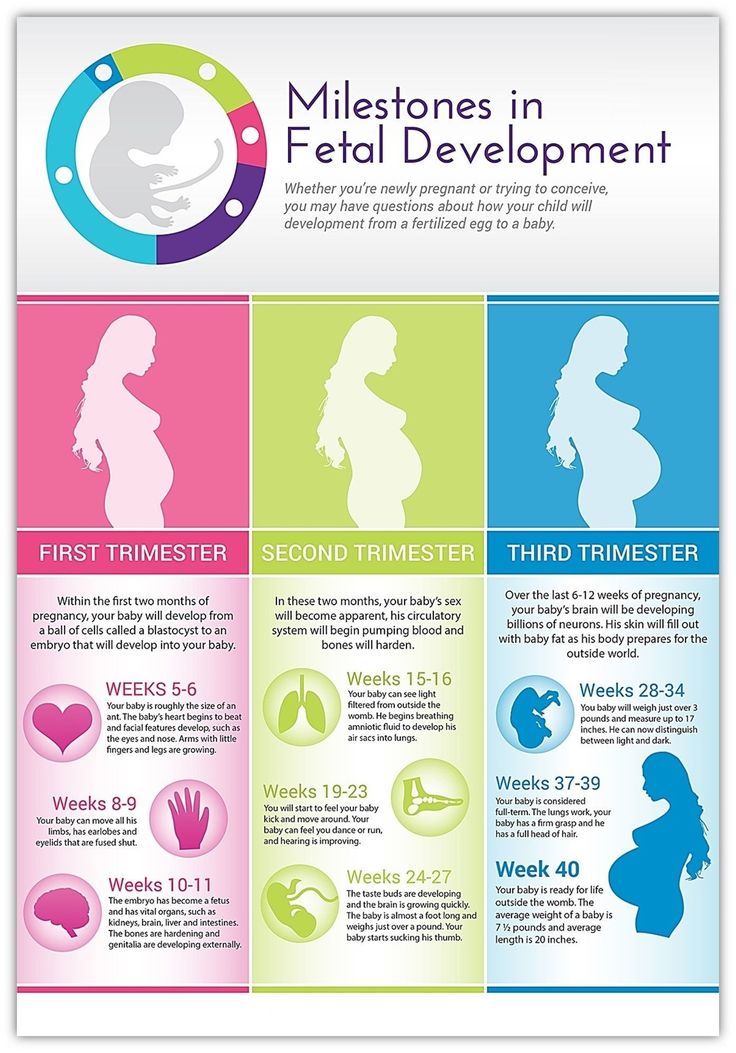
First Trimester Of Pregnancy: What To Expect
What is the first trimester of pregnancy?
Pregnancy has three trimesters or stages. Each trimester is about 13 weeks or three months long. A full-term pregnancy lasts 40 weeks or between nine and 10 months. Your healthcare provider will talk to you about fetal development in terms of weeks. Your first trimester of pregnancy lasts until the 13th week of pregnancy.
It may seem strange, but your pregnancy actually begins on the first day of your last menstrual period. This is called the gestational age of the pregnancy. A pregnancy care provider calculates your due date by adding 40 weeks to the first day of your last menstrual period. So this means, by the time you know you’re pregnant, you’re already about four weeks along. This can be very confusing!
Understanding weeks of pregnancy
The first two weeks of pregnancy are part of your normal menstrual cycle — the first week is your period and the second week is ovulation. Once you ovulate, your egg travels through your fallopian tube to your uterus. If it meets up with sperm, they combine and conception occurs (fertilization).
Once you ovulate, your egg travels through your fallopian tube to your uterus. If it meets up with sperm, they combine and conception occurs (fertilization).
During the third week of pregnancy, the fertilized egg travels to your uterus. On its way down to your uterus, it divides into more cells. Once it reaches your uterus, it implants into your uterine lining. This triggers your body to recognize that you’re pregnant and a series of changes begin to happen. Most people miss their period and then get a positive pregnancy test.
How long is the first trimester?
The first trimester begins before you’re pregnant. It starts on the first day of your last menstrual period and goes until the 13th week of pregnancy.
What can I expect in my first trimester?
Your first trimester of pregnancy is full of many physical and emotional changes. It can be a very overwhelming time, and your mind may be racing with questions. Plus, your hormones are in overdrive. In fact, your body produces more estrogen during one pregnancy than it does during your entire life when you’re not pregnant. This surge in hormones can cause some unpleasant pregnancy symptoms. You may find yourself feeling moody, bloated and tired. While you may not see a prominent baby bump yet, your uterus is expanding and your blood volume is increasing.
This surge in hormones can cause some unpleasant pregnancy symptoms. You may find yourself feeling moody, bloated and tired. While you may not see a prominent baby bump yet, your uterus is expanding and your blood volume is increasing.
It’s OK to feel both excited and nervous. Talking to your friends, partner or a healthcare provider may help you feel better as you navigate your pregnancy journey.
What should I do in my first trimester?
Your first trimester is very important. You might not look or feel pregnant, but lots of changes are happening.
If you don’t have a healthcare provider or a pregnancy care provider, you should find one as soon as possible. Getting early pregnancy care can help you avoid any potential complications. Make a list of questions or concerns you have so you’re ready for your first appointment. Check with your health insurance about pregnancy coverage so you know what to expect and where you can get care. If you don’t have health insurance, there are programs and agencies to help you get prenatal care.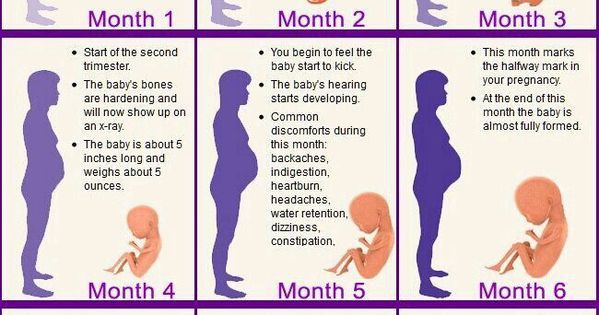
There are different types of pregnancy care providers that take care of you during pregnancy, labor, delivery and postpartum. These include obstetricians, midwives, and sometimes, primary care physicians. In addition to selecting a pregnancy care provider, you may also consider places to deliver your baby. While most people choose to give birth in a hospital, some people prefer birthing centers or home births.
Now is a great time to think about your overall health and what lifestyle changes you may need to make now that you’re pregnant. For example, think about how pregnancy affects your work, finances, habits and daily activities.
How does my baby develop in the first trimester of pregnancy?
Several developments occur in the first trimester. Although you can’t see it happening, there’s a lot going on inside your body after sperm fertilizes an egg.
Weeks one to four of pregnancy
During the first month of pregnancy, several important structures form. These structures are a tiny clump of cells, but will grow to become the amniotic sac, placenta and umbilical cord. A tube that becomes your baby’s brain and spinal cord form, as well as their circulatory system. A face, circles for eyes and the beginning of a mouth take shape.
These structures are a tiny clump of cells, but will grow to become the amniotic sac, placenta and umbilical cord. A tube that becomes your baby’s brain and spinal cord form, as well as their circulatory system. A face, circles for eyes and the beginning of a mouth take shape.
The embryo is about one-fourth inch long — smaller than a grain of rice.
Weeks five to eight of pregnancy
Several major organs begin to develop during the sixth week of pregnancy including the fetal lungs, heart, ears, arms and legs. Bones begin to replace tissue. Its head is large in proportion to the rest of its body, but it look more human now. The fetus has a distinct mouth, nose and face. Some providers do an early ultrasound to confirm a heartbeat during this time.
By the end of the eighth week of pregnancy, the embryo becomes a fetus. It’s about 1 inch long or the size of a raspberry.
Weeks nine to 12 of pregnancy
Towards the end of your first trimester, the fetus will have toes, fingers and nails.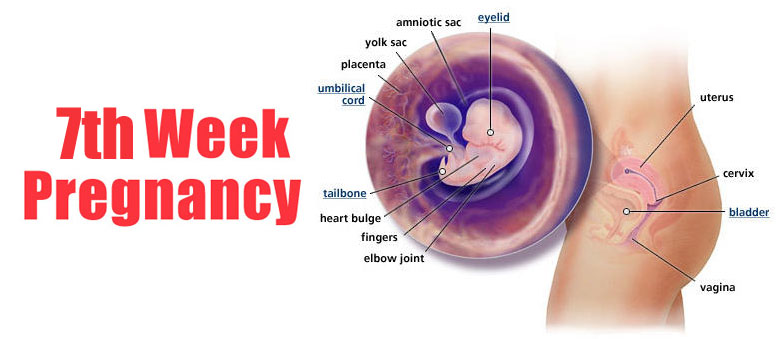 It will start to move by opening and closings its hands and mouth. The fetus's urinary and digestive systems are also fully functioning. At around 12 weeks of pregnancy, your provider can listen to the fetal heart using a Doppler ultrasound. It also has either a vagina or a penis at this point (though your provider can’t see it on an ultrasound).
It will start to move by opening and closings its hands and mouth. The fetus's urinary and digestive systems are also fully functioning. At around 12 weeks of pregnancy, your provider can listen to the fetal heart using a Doppler ultrasound. It also has either a vagina or a penis at this point (though your provider can’t see it on an ultrasound).
By the end of the 12th week of pregnancy, the fetus is between 3 and 4 inches long — about the size of a plum. It weighs about 1 ounce.
Why is the first trimester of pregnancy so critical?
The first trimester is so important because most of the fetus's major organs and body systems are developing. Toxins, harmful substances and infection can severely damage a fetus’s growth and development during this time. It could increase your baby’s risk of being born with a congenital disorder.
What are the most common symptoms during the first trimester?
Every person and every pregnancy is unique. An increase in hormones cause most pregnancy symptoms. Some of the most common are:
Some of the most common are:
- Sore breasts: Hormones may make your breasts feel tender and large. It’s common to need bigger bras before the end of your first trimester. The veins in your breasts may become noticeable because they’re carrying more blood. Other changes to your breasts may include darkened areolas or changes to your nipples.
- Nausea: Morning sickness is one of the telltale signs of early pregnancy. Despite its name, it can last all day and all night. Try eating smaller meals or bland, low-fat foods. Some people find relief by eating foods containing ginger.
- Mood swings: The sudden rush of hormones may put you on a rollercoaster of emotions. You may alternate between feeling anxious or scared to excited or weepy within a span of 30 minutes. It may be helpful to talk through your feelings with a friend or your partner.
- Feeling tired: Your body is hard at work during the first trimester of pregnancy.
 This may leave you feeling exceptionally tired. Be sure to get plenty of rest. Most people get some energy back in the second trimester.
This may leave you feeling exceptionally tired. Be sure to get plenty of rest. Most people get some energy back in the second trimester. - Needing to pee: Your uterus begins to grow to support the pregnancy. It may begin pressing on your bladder, causing you to need to pee more often.
- Acne or other skin changes: Hormones cause your skin to create more oil during pregnancy. This can lead to clogged pores and acne in some people. There are other skin conditions that appear during pregnancy, but most appear in the second or third trimesters.
- Mild shortness of breath: You may feel short of breath with light physical activity.
Your heart is pumping more blood during pregnancy. This means your pulse may be quicker and you may find yourself losing energy more easily. Be mindful of how much demand pregnancy puts on your body and take rests when you feel tired or out of breath.
What tests will I have in the first trimester of pregnancy?
Checkups, screenings and other tests during pregnancy help keep you and the fetus healthy. Care during pregnancy is commonly referred to as prenatal care. Prenatal care appointments are important because your pregnancy care provider discusses what you can expect during pregnancy and delivery, performs checkups and screenings and answers any questions you have.
Care during pregnancy is commonly referred to as prenatal care. Prenatal care appointments are important because your pregnancy care provider discusses what you can expect during pregnancy and delivery, performs checkups and screenings and answers any questions you have.
Your first prenatal visit
You’ll have between two and three prenatal visits during your first trimester. This can vary depending on your provider or if you’re a high-risk pregnancy. You can expect to discuss your personal medical history, gynecological and obstetrical history (prior pregnancies and births), as well any family medical history that may affect your pregnancy. This visit is very thorough to make sure you and your growing baby are healthy.
At your first prenatal visit your provider will calculate your due date. You can also expect them to perform the following:
- A physical exam, including checking your weight and blood pressure.
- A pelvic exam.
- A Pap test (if you’re due for one).
- Tests to check for certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Check your pee for bacteria, protein and glucose (sugar).
- Order blood tests to check hormone levels, Rh factor, iron levels and certain diseases.
- Check the fetal heart rate.
Some providers use transvaginal ultrasound at your first appointment to confirm pregnancy and measure the fetal heart rate and size. This ultrasound also shows if you’re expecting multiples. A transvaginal ultrasound involves your provider placing a wand inside your vagina. Most pregnant people are offered at least one ultrasound in their first trimester, but the exact timing varies depending on your provider. If you’re expecting multiples, you may be offered additional ultrasounds in your first trimester.
Your provider may suggest other screening tests during pregnancy. Screening tests identify if you or the fetus are at risk for certain health conditions. Based on the results of your screening, you may need diagnostic tests. Diagnostic tests confirm or rule out health problems. In the first trimester, your provider may suggest a screening to detect a higher risk of chromosomal disorders like Down syndrome. Talk to your provider about the screenings they recommend.
Diagnostic tests confirm or rule out health problems. In the first trimester, your provider may suggest a screening to detect a higher risk of chromosomal disorders like Down syndrome. Talk to your provider about the screenings they recommend.
What should I not do in the first trimester of pregnancy?
Once you find out you’re pregnant, it’s normal to have to make some lifestyle changes. These changes help ensure that everyone is healthy. You should avoid the following things during your first trimester of pregnancy:
- Alcohol.
- Cigarettes and tobacco.
- Recreational drugs like opioids.
- Contact sports like football or activities that put pressure on your abdomen.
- Foods like raw fish (sushi), fish high in mercury, uncooked or undercooked meats, lunchmeat and unpasteurized milk, cheese or juice.
- Hot tubs and saunas.
How do I take care of myself in the first trimester of pregnancy?
Staying healthy is important throughout all three trimesters of pregnancy. Here are some helpful tips on staying healthy during the first 13 weeks of pregnancy:
Here are some helpful tips on staying healthy during the first 13 weeks of pregnancy:
- Stay active as much as you can. Listen to your body and stop for rest if you feel any discomfort while exercising. You may need to modify your exercise routine during pregnancy.
- Take a prenatal vitamin containing folic acid.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods including fruits, vegetables, meat, eggs and whole grains.
- Get plenty of rest.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Attend all of your prenatal appointments.
Is it normal to bleed during the first trimester of pregnancy?
Light bleeding or spotting during pregnancy is usually OK in the first few weeks of pregnancy. Some people experience implantation bleeding (when a fertilized egg burrows unto your uterine lining). Call your pregnancy care provider if you’re bleeding heavily or the bleeding lasts more than one day.
What prenatal vitamin should I take?
The vitamins and minerals in your food (or in prenatal vitamins) help support your baby as it grows and develops. Most providers recommend taking a prenatal vitamin as soon as you begin trying to get pregnant. Vitamins containing folic acid, iron and calcium help support a healthy pregnancy. Talk to your provider if you’re unsure about which prenatal vitamin to take.
Most providers recommend taking a prenatal vitamin as soon as you begin trying to get pregnant. Vitamins containing folic acid, iron and calcium help support a healthy pregnancy. Talk to your provider if you’re unsure about which prenatal vitamin to take.
Can I drink caffeine during pregnancy?
Most healthcare providers recommend limiting caffeine consumption to under 200 milligrams per day during pregnancy. That’s about 12 ounces of coffee or three cans of Mtn Dew®. This is because a fetus can’t metabolize caffeine so it can build up in their body and cause complications.
When should I call my pregnancy care provider during the first trimester?
Call your provider right away if you have:
- A fever higher than 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Heavy bleeding or unusual vaginal discharge.
- Severe cramping in your belly, arms or legs or abdominal pain.
- Persistent vomiting and/or diarrhea.
- Fainting spells or dizziness.
- Swelling in your hands, fingers or face.

- Blurred vision or spots before your eyes.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Pregnancy is an exciting, and sometimes scary, time in your life. You may feel overwhelmed with information and have lots of questions. During the first trimester of pregnancy, your body is growing and changing rapidly. Your baby is growing and developing, too. In fact, by the end of the first trimester the fetus is the size of a lemon. You may begin having symptoms of pregnancy like nausea, sore breasts or needing to pee more often. Schedule an appointment with a pregnancy care provider as soon as you know you’re pregnant. Regular prenatal care is important so you and the fetus stay healthy and strong during pregnancy.
First pregnancy, what you need to know?
The first pregnancy in a woman's life is always an important event. Information about what to expect during this period is very easy to find. But often the sources of information are not trustworthy and offer conflicting information.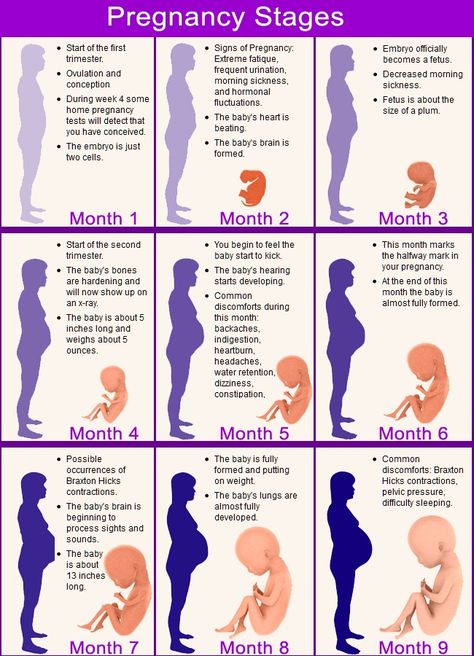
Facts that expectant mothers need to know
Pregnancy normally lasts 40-42 weeks and ends in vaginal delivery or caesarean section. This period will be divided into trimesters, the first - to 13 weeks inclusive, the second - from 14 to 27 weeks, and the third - from 28 weeks to delivery. Each trimester has its own characteristics.
The first trimester is the most unpredictable. It can pass very easily - some women do not even notice their condition. But in the first trimester, side effects of a sharp hormonal change in the body are also possible. Morning sickness, sudden bouts of weakness, low blood pressure, irritability, increased reaction to smells - all this happens due to the fact that the hormonal background changes dramatically in the body. All of these symptoms in the first trimester are normal, but they should be told to the attending physician.
In the first trimester, the laying and formation of the fetal body takes place. Most congenital pathologies are the result of violations during this period. In order not to provoke developmental anomalies, the expectant mother should avoid pathogens. Alcohol, nicotine, a range of drugs, and toxins in the water and air can adversely affect the health of the unborn child. You should also carefully approach the choice of cosmetics and hair products.
Most congenital pathologies are the result of violations during this period. In order not to provoke developmental anomalies, the expectant mother should avoid pathogens. Alcohol, nicotine, a range of drugs, and toxins in the water and air can adversely affect the health of the unborn child. You should also carefully approach the choice of cosmetics and hair products.
Pregnancy: first week
A woman can assume that the first week of pregnancy has begun only if she carefully prepared for the process of conception, calculated the time of ovulation, and chose the time for sexual intercourse. But even in this case, there can be no 100% certainty. For the first two or three weeks, a woman cannot independently determine whether pregnancy has occurred or not. Even if the fertilization of the egg has occurred, and the rapid process of embryo development has begun, it is still so small that it is not felt in the mother's body.
However, from the first days you can switch to a lifestyle suitable for pregnant women. It is recommended to avoid harmful foods, strong drugs, alcohol, smoking, stress; engage in gentle sports, walk in the fresh air.
It is recommended to avoid harmful foods, strong drugs, alcohol, smoking, stress; engage in gentle sports, walk in the fresh air.
In the second trimester, the fetus is almost formed and grows rapidly. At about 4.5 - 5 months, a woman begins to feel the movement of the child. At the same time, the belly appears and begins to grow. The baby acquires the ability to hear sounds, and if the mother or father is talking to him, he can move in response. The second trimester proceeds with a minimum number of complications, this is the best period for official preparation for childbirth: choosing a clinic, paperwork, settling issues with work, and so on. By the end of the second trimester, you should pack a bag for the maternity hospital, and in addition, sign up for a course for new mothers. In such courses, women are taught not only the correct behavior in childbirth, but also the handling of a newborn baby.
In the third trimester, the fetus is already formed, even with the onset of premature birth, the child can be saved. However, normal gestation up to 40-42 weeks is the best option. Due to the large and heavy belly, the expectant mother experiences inconvenience: her back may hurt, her legs may swell, and during sleep, a woman cannot calmly change her position. On the recommendation of a doctor, you can wear a bandage for pregnant women: this is a wide elastic belt that supports the stomach. The third trimester is considered the most difficult.
However, normal gestation up to 40-42 weeks is the best option. Due to the large and heavy belly, the expectant mother experiences inconvenience: her back may hurt, her legs may swell, and during sleep, a woman cannot calmly change her position. On the recommendation of a doctor, you can wear a bandage for pregnant women: this is a wide elastic belt that supports the stomach. The third trimester is considered the most difficult.
Whatever the course of pregnancy, it should be remembered that this is not a disease, but a natural state for a woman. Therefore, the expectant mother should lead a familiar lifestyle, excluding only that which can harm the baby. A pregnant woman can continue to work, travel, engage in her favorite hobby. This will create a good mood for the mother, and the hormones of joy, along with the bloodstream, are transmitted to the baby. The psychological comfort of the expectant mother is no less important than compliance with other recommendations.
is there a period, why does the stomach hurt, the development of the child, the first symptoms and sensations
After conception, changes begin in the woman's body, by which one can guess that pregnancy has come. At first, the expectant mother may feel the usual malaise. But the emergence of more and more new signs suggests: it's time to do a test and visit a gynecologist.
Day after day, the body of a woman carrying a child prepares for the fact that now he will have to work for two. About what symptoms indicate the onset of pregnancy in the first month, how the child develops during this period and what the expectant mother should prepare for, we understand together with obstetrician-gynecologist Tatyana Smirnova .
Determining the gestational age
The formula is simple: the gestational age is counted from the first day of the last menstruation. For example, on May 5, a woman began her period, and on June 20 she comes to the doctor due to a two-week delay. The doctor conducts an examination, after which confirms the pregnancy. This is indicated by an enlarged uterus, changes in the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix. Also, at the first appointment with a gynecologist, you can determine the period. As a rule, it is 4-5 weeks (1).
For example, on May 5, a woman began her period, and on June 20 she comes to the doctor due to a two-week delay. The doctor conducts an examination, after which confirms the pregnancy. This is indicated by an enlarged uterus, changes in the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix. Also, at the first appointment with a gynecologist, you can determine the period. As a rule, it is 4-5 weeks (1).
Key facts about the first month of pregnancy
| Menstruation | Stops. Small spotting is possible, which indicates that the embryo is implanted in the lining of the uterus. |
| Woman's behavior | Irritability or tearfulness may appear. Many women pay attention to changes in taste preferences, a different perception of smells appears. |
| External signs | Not noticeable. In some women, by the end of 1 month of pregnancy, pigmentation and the first stretch marks on the abdomen may appear. |
| Pain | A pregnant woman may feel pain in the lower abdomen when a fertilized egg approaches the uterus. |
| Stage of development of the child | Embryo |
Symptoms, signs and sensations
To determine the duration of pregnancy, doctors take into account presumptive and probable signs.
Suspected include:
- changes in appetite, taste, smell,
- nausea and vomiting, salivation,
- weakness, malaise,
- irritability and tearfulness,
- dizziness and headaches,
- insomnia,
- subcutaneous fat deposition,
- stretch marks on the abdomen,
- skin pigmentation (on the face, along the white line of the abdomen, in the area of the nipples and external genitalia).
It is not only pregnant women who may experience these symptoms. But for the doctor, they have diagnostic value, because some of them occur before the objective signs of pregnancy.
Probable signs objectively confirm pregnancy: in women of childbearing age, menstruation suddenly stops, the mammary glands, uterus, and vaginal mucosa change. Let's dwell on them in a little more detail.
Let's dwell on them in a little more detail.
Breast changes
The mammary glands are enlarged. When pressed, a clear liquid is released from the nipples - colostrum.
Changes in internal organs
The uterus at 1 month of pregnancy increases to the size of a chicken egg. The cervix becomes drier. The mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix becomes bluish and becomes more loose.
Pain
During this period, the abdomen may ache as the uterus prepares to receive a fertilized egg that moves towards it to gain a foothold in the cavity. Round uterine ligaments are located on the front wall of the uterus, they begin to stretch, the uterus increases, and therefore the woman feels pain in the lower abdomen. This is not a threat of termination of pregnancy, but a variant of the norm (2).
Is there a period in the first month of pregnancy
Normally, a pregnant woman should not have menstruation. Some people have spotting for several months or even during their entire pregnancy. This is a menstrual-like reaction, but not menstruation.
Some people have spotting for several months or even during their entire pregnancy. This is a menstrual-like reaction, but not menstruation.
How the belly looks like
In the first month of pregnancy, a woman relies more on sensations: external manifestations are not yet bright enough or are completely absent. For example, in the early stages, the stomach does not increase. It begins to grow by 12-14 weeks, when the uterus rises to the level of the womb.
Photo: pixabay.comChild development in the first month of pregnancy
The embryonic period of development continues from the moment of fertilization to 8-9 weeks of gestation, when the embryo acquires human-specific features (3).
1 week of pregnancy
During this period, follicles mature in the ovaries, one of which will contain the very fateful egg.
There is no embryo yet, but serious preparatory work is underway for its appearance: the uterine cavity is cleared of the endometrium, which was not useful in the last cycle, follicle vesicles with developing eggs inside ripen in the ovaries.
Learn more
2 weeks pregnant
Still no baby. But the process of its origin is rapidly going on. The most active follicle ruptures and releases an egg ready for fertilization. And when the fastest and most tenacious sperm reaches this mature egg, it breaks through its membrane, the nuclei of male and female cells merge and a new life is conceived.
Learn more
3rd week of pregnancy
During this period, the germinal disc with the primary streak is formed - from many cells that are constantly dividing and developing. The size of a fertilized egg at the 3rd week of pregnancy is about 0.13 mm.
Learn more
4th week of pregnancy
By the beginning of the 4th week, the fetal egg enters the uterine cavity, attaches to its wall and continues to develop. The embryonic disk acquires a cylindrical shape, the head and tail of the embryo are formed. By the end of the 28th day, a bend of the body appears, the length in the back reaches 4-5 mm.
Learn more
Examinations in the first month of pregnancy
At the first visit of a pregnant woman, the doctor gets acquainted with her anamnesis, then proceeds to an objective examination: pays attention to the physique and weight of the woman, the condition of her skin, visible mucous membranes, measures temperature, height and body weight, blood pressure, evaluates the condition of the mammary glands and nipples, the presence of colostrum separated from them.
Other methods are used to confirm pregnancy.
Gynecological examination using speculums
This is the simplest and at the same time indispensable method. Even in early pregnancy, it allows you to see the characteristic changes in the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix.
Pregnancy test
Pregnancy confirmation method is suitable if the period is very short and there are doubts about conception. Modern tests are highly informative, and even with a few days of delay, they show that there is a pregnancy.
Tests
At an early stage, it is important not to miss an ectopic pregnancy, when implantation does not occur in the uterine cavity, but in the tube or cervix. The signs are similar: at first, it may not differ from a normal pregnancy. Therefore, a blood test for the determination of hCG, the hormone of human chorionic gonadotropin, plays an important role here. With an ectopic pregnancy, its level is lower than expected at this time.
All tests necessary for a woman in each individual case are prescribed by a doctor: a smear for STIs and others.
Photo: MART PRODUCTION, pexels.comUltrasound
Ultrasound diagnostics is an informative and safe examination method even at early stages. On ultrasound, the embryo is clearly visible, which is fixed in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound research methods are used to diagnose pregnancy and its timing. And also in case of complications of pregnancy and fetal development.
Do's and don'ts for expectant mothers
“A pregnant woman can live a normal life,” says obstetrician-gynecologist Tatyana Smirnova. “But we need to reconsider and change what can affect the health of the child and the woman herself and complicate the course of pregnancy. This applies to both nutrition and lifestyle.
“But we need to reconsider and change what can affect the health of the child and the woman herself and complicate the course of pregnancy. This applies to both nutrition and lifestyle.
Healthy food
Pregnant women are advised to lean on vegetables and fruits, mainly grown in their region of residence. Citrus fruits are undesirable - they can cause allergic reactions and set the stage for diathesis in an unborn child.
Useful: herbal teas (if you are not allergic to herbs), vegetable soups and salads, buckwheat porridge. The consumption of sweets should be reduced. Chocolate, coffee, hot spices are not recommended.
Getting rid of bad habits
It will not be superfluous to repeat: the expectant mother should refuse alcohol and cigarettes. The potential harm is great and the risks are beyond doubt.
We treat teeth and chronic diseases
Contrary to common stereotypes, it is possible and necessary to treat teeth during pregnancy.
Dental disease is a potential foci of infection that can be bad for a child. They definitely need to be eliminated.
For the same reason, it is necessary to treat chronic tonsillitis and tonsillitis. If there are diseases not related to gynecology (liver, heart, stomach, etc.), they should ideally be dealt with before conception, and during pregnancy, if necessary, be observed by narrow specialists.
Postponing cosmetic procedures
It is not recommended even to dye your hair during pregnancy, because the chemical components penetrate the woman's body and can have a negative effect. It is advisable to use less cosmetics, limit cosmetic procedures using active chemicals and hardware technologies. Undesirable massage of the lower back, anterior abdominal wall during pregnancy.
You can sunbathe
Sun exposure in reasonable amounts is good. The body receives vitamin D, necessary for the prevention of rickets, the protection of bone tissue. Just do not abuse the sunbathing!
Just do not abuse the sunbathing!
We dose physical exercises
You can go in for sports in the first month of pregnancy if there is no threat of miscarriage and other problems. But exercises should not strain the anterior abdominal wall.
Special gymnastics is highly recommended to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, for a better stretching of the perineum. It is better to swim in the sea than in pools, where reagents that are undesirable for the health of a pregnant woman can be used to purify water. The safest, but at the same time useful activity is walking. This is good for the muscles of the pelvic floor and perineum. You can just walk around the house on tiptoes, sit on a gym ball.
Frequently Asked Questions
During the first month of pregnancy, most women have a variety of questions. Including many are worried that, not knowing about the "interesting" situation, their actions could harm the health of the child. Obstetrician-gynecologist Tatyana Smirnova answers questions, dispelling popular fears and doubts.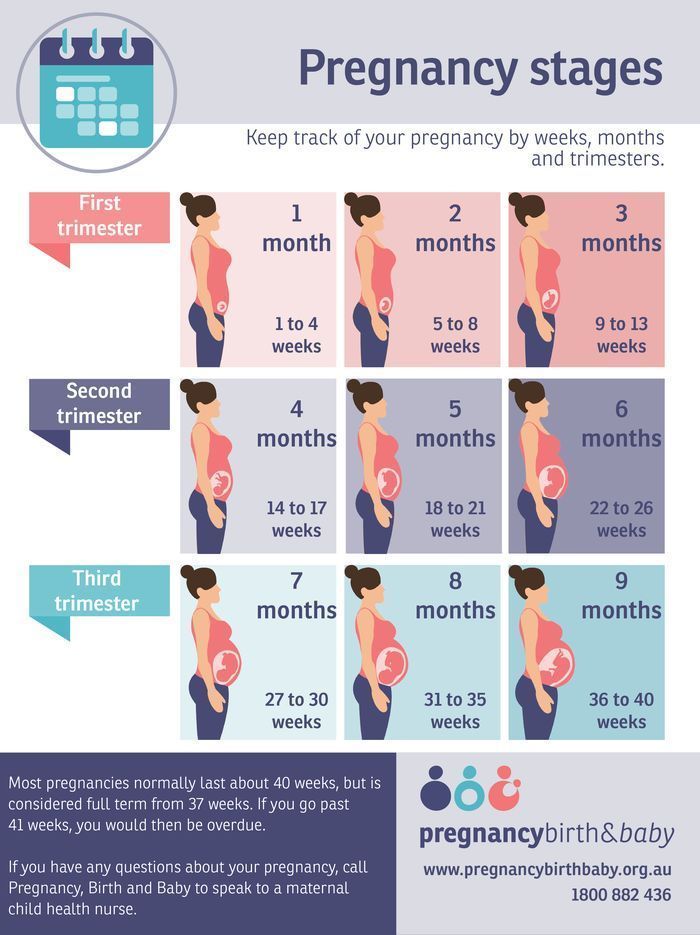
How to cope with toxicosis?
The term "toxicosis" in the medical community is considered obsolete. Now they say "drooling, vomiting." But the essence does not change: in the early stages, progesterone (yellow body of pregnancy) is produced in the ovaries, due to which vomiting occurs. The simplest remedy against it is alkaline drinking. It can be either mineral water or a solution of baking soda (1 teaspoon per glass of boiled water) 2-3 times a day. When the placenta is formed and progesterone starts to be produced in it, this nausea will pass. This usually happens by 16 weeks even without treatment.
Is it dangerous to drink alcohol in the first month of pregnancy if you do not know about your condition?
It's okay if it happened out of ignorance. The main thing is to stop drinking alcohol when you already know about your pregnancy. In Europe, pregnant women are allowed some dry wine. And our doctors of the old school even treated toxicosis with champagne - a teaspoon 5-6 times a day.
Is it possible to have sex in the first month of pregnancy?
Possible. These are positive emotions and relaxation for a woman. But everything is individual. If there is a threat of miscarriage, severe illness in a pregnant woman, it is necessary to limit sexual life for some time. If there are no contraindications, sex should be with a condom and without fanaticism.
How much weight can you gain in the first month of pregnancy?
Weight gain should not exceed 200 g per week. For the entire pregnancy - 10-12 kg and no more. Therefore, nutrition must be controlled.
What drugs can and cannot be taken during the first month of pregnancy?
Of the drugs for the treatment of arterial hypertension, enaloprils are undesirable, and of anti-inflammatory drugs - sulfadimesines. In diabetes mellitus, tablet preparations are not recommended to lower blood sugar levels - they contribute to disruption of uterine placental blood flow.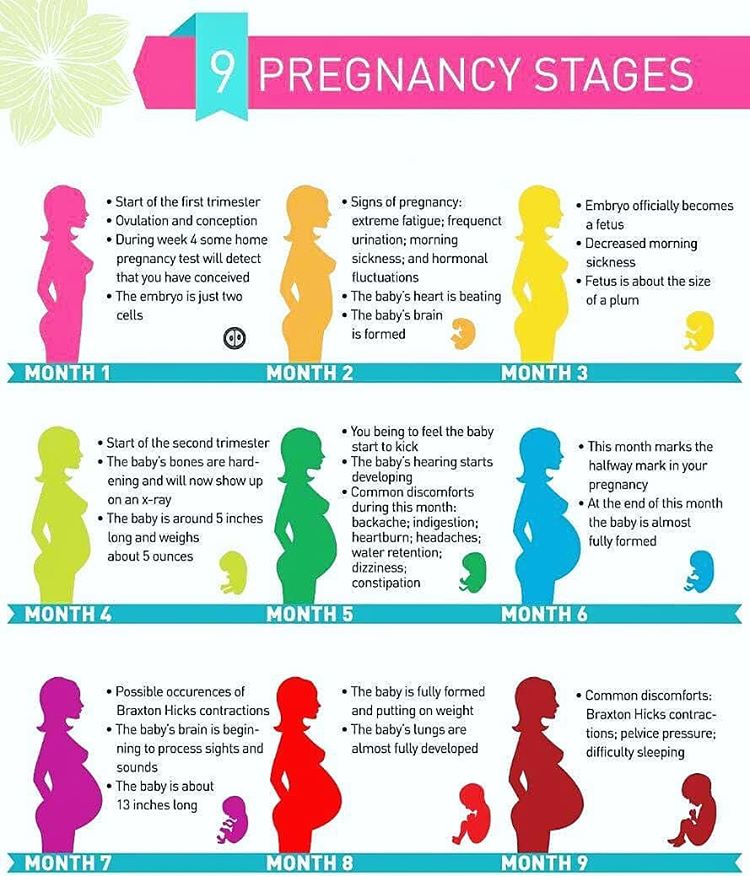 Of the antibiotics, doxycycline, fluoroquinolone drugs are undesirable.
Of the antibiotics, doxycycline, fluoroquinolone drugs are undesirable.
Laxatives are not recommended: they increase intestinal peristalsis and increase uterine tone. Tranquilizers and sedatives are also undesirable.
Vitamin complexes, some antibiotics (penicillin series, macrolides, cephalosporins), aspirin, indomethacin are allowed for use. Herbal sedatives are not prohibited.
Sources
- Normal pregnancy. Clinical guidelines. URL: https://minzdravao.ru/sites/default/files/2020/1/normalnaya_beremennost.pdf
- What are some common signs of pregnancy? National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health. NIH. URL: https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/pregnancy/conditioninfo/signs
- Vinogradov S.Yu., Dindyaev S.V., Vinogradova E.E. Fundamentals of morphogenesis of intrauterine development of a person. URL: https://docplayer.com/29989946-Osnovy-morfogeneza-vnutriutrobnogo-razvitiya-cheloveka-materialy-k-izucheniyu-medicinskoy-embriologii-i-perinatologii.