White discharge during first trimester pregnancy
Weird Early Pregnancy Symptoms: 10 Unexpected Ones
Weird Early Pregnancy Symptoms: 10 Unexpected OnesMedically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Annamarya Scaccia on January 3, 2018
Everyone knows the classic signs of pregnancy. You’ve missed your period. Your breasts are tender. And you’re tired all the time.
But pregnant women also experience a whole host of symptoms beyond these first signs. From mucus discharge to tasting metal to headaches, expect the unexpected.
Here’s a list of 10 weird early pregnancy symptoms no one tells you about.
While many women experience vaginal discharge, it’s not often associated with pregnancy. But most pregnant women will secrete sticky, white, or pale-yellow mucus early on in the first trimester and throughout their pregnancy.
Increased hormones and vaginal blood flow cause the discharge. It increases during pregnancy to prevent infections as your cervix and vaginal walls soften. Visit your doctor if the discharge starts to:
- smell
- burn
- itch
- turn greenish-yellow
- becomes very thick or watery
These may be signs of an infection.
Share on Pinterest
When you first wake up in the morning after ovulation, your body temperature is slightly elevated. It stays that way until you get your next period.
But if this temperature, known as basal body temperature, stays elevated for more than two weeks, you may be pregnant.
Share on Pinterest
It’s not uncommon for pregnant women to feel lightheaded or dizzy in the first trimester. Pregnancy causes blood pressure to drop and blood vessels to dilate.
But pay close attention to your symptoms. Severe dizziness coupled with vaginal bleeding and severe abdominal pain could be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy. In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. Make sure to see a doctor right away to avoid life-threatening complications.
Share on Pinterest
You may feel bloated, like you want to pass gas or go number two. But it’s just not happening. That’s because pregnancy’s hormonal changes can lead to constipation, as can prenatal vitamins.
Your digestive system slows down during pregnancy. This gives nutrients just enough extra time to absorb into your bloodstream and reach your little one.
If you can’t go, add more fiber into your diet, drink plenty of fluids, and exercise regularly. If needed, you can also check with your doctor about adding a pregnancy-safe stool softener.
Share on Pinterest
About 25 to 40 percent of pregnant women will lightly bleed or notice spotting early on in their pregnancy. The slight bleeding can happen when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining. This is known as implantation bleeding. It’s common about two weeks after conception.
Bleeding can also be caused by cervical irritation, an ectopic pregnancy, or a threatened miscarriage. Make sure to get medical help right away if your light bleeding gets heavier or is accompanied by severe cramps, back pain, or stabbing pains.
Share on Pinterest
Pregnancy lowers your immunity. This means you’re more prone to a cough, colds, and the flu. It’s not uncommon for pregnant women to experience cold- or flu-like symptoms early in pregnancy.
Talk to your doctor about pregnancy-safe treatment options. Pregnant women are more vulnerable to severe illnesses from the flu. This can lead to serious health problems for your baby.
Share on Pinterest
Hormones change everything during pregnancy. This includes the valve between your stomach and esophagus. This area becomes relaxed during pregnancy, which can cause stomach acid to leak into your esophagus, causing heartburn.
Fight back by eating smaller, more frequent meals. Also cut out fried grub. Try to avoid fizzy drinks, citrus fruits, juices, and spicy foods.
Share on Pinterest
Your hormones suddenly change when you become pregnant. This can throw your emotions out of whack. You’ll feel unusually weepy and emotional. Your libido goes from hot to cold then back to hot again. You might also experience mood swings. This is very common during early pregnancy.
You might also experience mood swings. This is very common during early pregnancy.
Share on Pinterest
Increases in estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy can lead to changes in taste for many pregnant women.
A condition called dysegusia has some pregnant women tasting metal. You’ll feel like you were chomping on some old pennies with your lunch. Get rid of the metallic flavor by munching on saltines and chewing sugarless gum. Also try drinking colder liquids or eating spicier foods.
Some of the symptoms listed above may make you think you’re just stressed and run down. But experienced together, they can point to pregnancy.
Pay attention to what your body is telling you. It might be time to see your doctor for a pregnancy test.
Last medically reviewed on January 4, 2018
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
How we vetted this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations.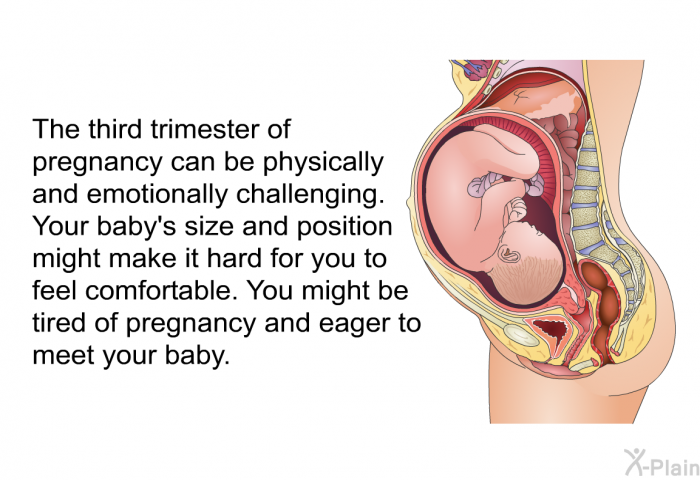 We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Boyle J. (2016). Is spotting during pregnancy normal?
focus.sanfordhealth.org/pregnancy-parenting/pregnancy/is-spotting-during-pregnancy-normal - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2017). Getting Pregnant.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/symptoms-of-pregnancy/art-20043853 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2017). Pregnancy week by week.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/pregnancy/art-20047208 - Pregnancy: Am I pregnant? (2014).
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9709-pregnancy-am-i-pregnant - Pregnancy: Having a healthy pregnancy. (2016).
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/5186-pregnancy-having-a-healthy-pregnancy - Pregnant women and influenza (flu). (2017).
cdc.gov/flu/protect/vaccine/pregnant.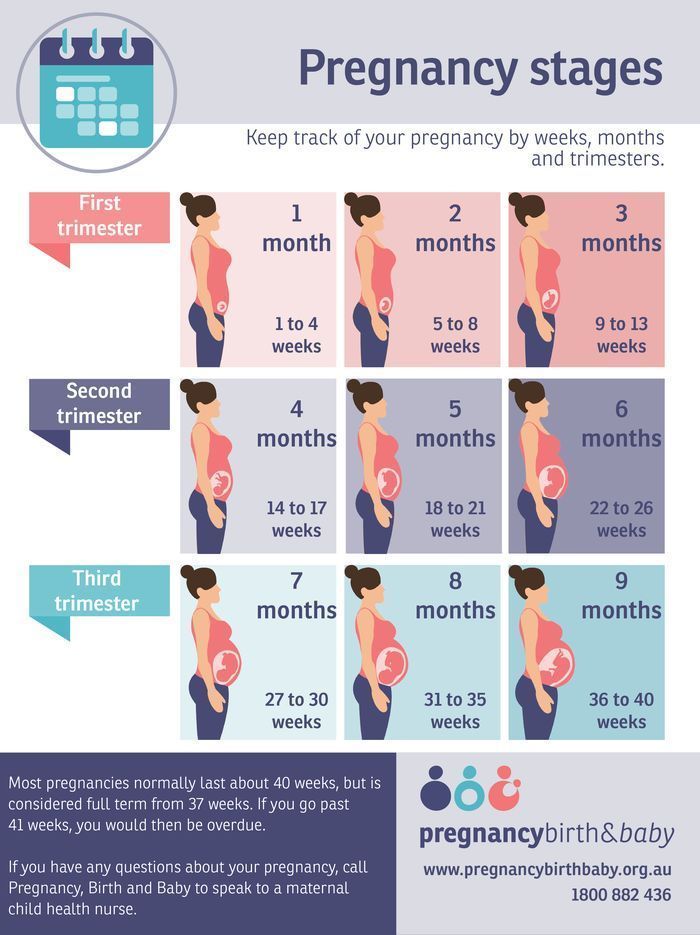 htm
htm - Vaginal discharge in pregnancy. (2015).
nhs.uk/conditions/pregnancy-and-baby/vaginal-discharge-pregnant
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Jan 4, 2018
By
Annamarya Scaccia
Edited By
Frank Crooks
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Annamarya Scaccia on January 3, 2018
related stories
4 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Tips, and More
Early Pregnancy Symptoms
7 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Tips, and More
Cramps but No Period: 7 Early Pregnancy Symptoms
6 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Tips, and More
Read this next
4 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Tips, and More
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.
 D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHTAt week 4 of pregnancy, you may not have many symptoms yet and the ones do have may be confused with premenstrual syndrome. Learn more.
READ MORE
Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
What are the telltale early symptoms of pregnancy? Every person is different, but here are a few top signs.
READ MORE
7 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Tips, and More
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
When you’re 7 weeks pregnant, you may wonder what to expect next. Now that your baby is the size of a blueberry, find out what else you should know.
READ MORE
Cramps but No Period: 7 Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Medically reviewed by Kimberly Dishman, MSN, WHNP-BC, RNC-OB
If you're experiencing cramping but don't get your period, you might be pregnant.
 Here are seven common early pregnancy symptoms.
Here are seven common early pregnancy symptoms.READ MORE
6 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Tips, and More
Medically reviewed by Tracy Stickler
Although you won’t look pregnant yet, your body is going through many changes by week 6. Symptoms include nausea, constipation, and more.
READ MORE
PMS Symptoms vs. Pregnancy Symptoms
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
It's definitely that time of the month, but for some reason, your period has yet to make its appearance. Are you pregnant, or is it merely late?
READ MORE
What Bodily Changes Can You Expect During Pregnancy?
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
The hormonal and physiologic changes during pregnancy are unique in the life of women.
 Discover what they are here.
Discover what they are here.READ MORE
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Pregnancy: What You Need to Know
Medically reviewed by Nancy Carteron, M.D., FACR
Learn about potential problems associated with rheumatoid arthritis and pregnancy, including triggers, preeclampsia, premature birth, and low birth…
READ MORE
Can You Get Your Period and Still Be Pregnant?
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Many women claim to still get their period during early pregnancy, but is this possible? Here’s the truth.
READ MORE
5 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Tips, and More
At 5 weeks pregnant, your baby is the size of a sesame seed. Here's what to know about being 5 weeks pregnant and what to expect.
READ MORE
Bleeding during pregnancy: When to worry about spotting in pregnancy
A little light bleeding or spotting during pregnancy is common, especially during the first trimester. Heavier or more consistent bleeding could signal a problem with the pregnancy. Early pregnancy bleeding can happen when the fertilized egg implants, or it could be from something more serious like a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Common causes of bleeding later in pregnancy include placental problems or preterm labor. Any bleeding is worth letting your doctor know about as soon as possible, especially if it's heavy or it doesn't stop.
Heavier or more consistent bleeding could signal a problem with the pregnancy. Early pregnancy bleeding can happen when the fertilized egg implants, or it could be from something more serious like a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Common causes of bleeding later in pregnancy include placental problems or preterm labor. Any bleeding is worth letting your doctor know about as soon as possible, especially if it's heavy or it doesn't stop.
Is it normal to have spotting during pregnancy?
A little light bleeding or spotting during pregnancy is common, especially in early pregnancy. Up to one in four pregnant women have some light bleeding in their first trimester. But even if the bleeding seems to have stopped, call your doctor, just to make sure everything is okay.
Spotting or light bleeding in pregnancy is probably from something minor. But it could also be a sign of a serious problem, such as an ectopic pregnancy, a miscarriage, or an infection.
Your doctor may want to do some tests, which can include a physical exam, an ultrasound, and blood tests, to check how well you and your baby are doing and to rule out any complications.
If you're actively bleeding or you have severe pain and can't reach your doctor, head to the emergency room right away.
What's the difference between spotting and bleeding during pregnancy?
Spotting is very light bleeding, similar to what you may have at the very beginning or end of your period. It will look like small drops of blood on your underwear, varying in color from pink to red to brown (the color of dried blood). Pregnancy spotting is common, especially during the first three months.
Bleeding means that you need to wear a panty liner or pad to avoid soaking your underwear. And heavy bleeding will soak through one or more pads. Continued or heavy bleeding could signal a problem with your pregnancy, which is why it's important to share with your doctor right away.
Early pregnancy bleeding: What causes it?
The most common causes of light spotting or bleeding during early pregnancy include:
Implantation. Some women have spotting even before they know they're pregnant, about a week or so after they ovulate. It's called "implantation bleeding" because it happens when the fertilized egg burrows (or implants) into the blood-rich lining of the uterus, a process that starts just six days after fertilization.
It's called "implantation bleeding" because it happens when the fertilized egg burrows (or implants) into the blood-rich lining of the uterus, a process that starts just six days after fertilization.
If you have a day or two of spotting in the week before your period is due, take a home pregnancy test. If the result is negative, wait a few days or a week. If your period doesn't start when you expect it, try testing again.
Subchorionic hematoma. Also called a subchorionic hemorrhage, this kind of bleeding can happen when the outer layer of the amniotic sac (chorion) separates from the wall of the uterus. It’s usually harmless and stops on its own. Small collections of blood like this early on are typically harmless. But if the collection of blood is larger, it will take longer to reabsorb, or go away. This can raise the risk of miscarriage or preterm labor, so your doctor may want to check on it regularly with ultrasound.
Miscarriage. Spotting or bleeding in the first trimester, especially if you also have abdominal pain or cramping, can be an early sign of miscarriage. But it isn't necessarily a sign, and actually, about half of women who miscarry don't have any bleeding prior to diagnosis. Other signs of a possible miscarriage are discharge of liquid or tissue from your vagina, and no longer feeling any pregnancy symptoms (like morning sickness). If feeling better is your only symptom, however, try not to worry! Many pregnant women don't experience nausea in the first trimester and have very healthy pregnancies.
Spotting or bleeding in the first trimester, especially if you also have abdominal pain or cramping, can be an early sign of miscarriage. But it isn't necessarily a sign, and actually, about half of women who miscarry don't have any bleeding prior to diagnosis. Other signs of a possible miscarriage are discharge of liquid or tissue from your vagina, and no longer feeling any pregnancy symptoms (like morning sickness). If feeling better is your only symptom, however, try not to worry! Many pregnant women don't experience nausea in the first trimester and have very healthy pregnancies.
Ectopic pregnancy. Early pregnancy bleeding also can warn of an ectopic pregnancy – when the embryo implants outside the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes. Sometimes bleeding is the only sign, but other common symptoms include pain in the belly, pelvis, or shoulder. An ectopic pregnancy can be life-threatening, so let your doctor know right away if you have bleeding or moderate to severe pain in your first trimester.
Molar pregnancy. This rare complication happens when the placenta doesn't develop properly, and it can't sustain the embryo. A molar pregnancy can be serious, and it needs prompt treatment.
Infection. An infection can irritate or inflame your cervix and make it more likely to bleed, especially after you have sex. These are some of the infections that can cause bleeding:
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Herpes
- Yeast infection
- Trichomoniasis
Because certain infections can cause pregnancy complications, your doctor might prescribe antibiotics or another treatment.
You might also notice some spotting or light bleeding after sexual intercourse or a pelvic exam. More blood flows to your cervix during pregnancy, so it's not unusual. A cervical polyp (a noncancerous growth on the cervix) can also cause spotting or bleeding after sex or an exam.
What causes second or third trimester bleeding?
Bleeding later in pregnancy might also be nothing to worry about. Light bleeding could be a sign of harmless inflammation, a cervical polyp, or other changes in your cervix. And a few days before your delivery date, bloody discharge called "show" is a sign that your cervix is getting ready for labor.
Light bleeding could be a sign of harmless inflammation, a cervical polyp, or other changes in your cervix. And a few days before your delivery date, bloody discharge called "show" is a sign that your cervix is getting ready for labor.
Heavy bleeding late in your pregnancy is a more worrisome sign. It's worth making a call to your doctor right away.
Here are some common causes of bleeding in your second and third trimesters:
Placental problems. Bleeding or spotting after the first trimester can be a sign of a problem with the placenta, such as:
- Placenta previa, when the placenta partially or fully covers the cervix; usually this is diagnosed at your mid-pregnancy ultrasound or anatomy scan. Your placental location will continue to be monitored as pregnancy progresses, and your obstetrician will recommend that you abstain from intercourse as long as the placenta is over or near the cervix.
- Placenta accreta, when the placenta becomes abnormally embedded in the uterine wall.
 Although this is a rare complication, the risk slowly increases with each cesarean delivery.
Although this is a rare complication, the risk slowly increases with each cesarean delivery. - Placental abruption, when the placenta entirely or partially separates from the wall of the uterus. This is more likely to occur as a result of trauma (car accident, domestic violence), uncontrolled hypertension, or labor.
Late miscarriage. Most miscarriages happen in the first trimester, but bleeding between 13 weeks and the middle of your pregnancy can be a sign of late miscarriage.
Preterm labor. Bleeding is one sign of preterm labor (labor that starts before 37 weeks). Other symptoms are:
- Abdominal pain, cramps, or contractions
- Low backache
- Changes in vaginal discharge
- Pressure in your pelvis or lower abdomen
How much bleeding during pregnancy is normal?
Some light bleeding is normal, especially early in your pregnancy when the fertilized egg implants. But really, bleeding can happen at any point in your pregnancy, and for many different reasons. And because some causes are more serious than others, it's always a good idea to let your doctor know about it.
And because some causes are more serious than others, it's always a good idea to let your doctor know about it.
Heavier bleeding that soaks through a pad, or bleeding that doesn't go away is more concerning. It could signal a serious problem with your pregnancy that needs immediate medical attention. Calling your doctor right away or going to an emergency room could help you head off a problem and protect both your health and your baby's.
When should I call my doctor about spotting or bleeding during pregnancy?
Any type or amount of bleeding in pregnancy is worth calling your doctor about, to make sure that nothing is wrong. This is important, even if your last ultrasound showed that your baby is healthy and growing according to schedule.
Heavy or consistent bleeding is a reason to call immediately. Your doctor can check for any problems, and either reassure you that you're ok, or treat the problem.
When you call your doctor, let them know how long you've been bleeding and how much you've bled. Also tell them about other symptoms, like cramps, that you've had along with the bleeding. Also, be sure to be honest with them about recent sexual activity and medical history when you call.
Also tell them about other symptoms, like cramps, that you've had along with the bleeding. Also, be sure to be honest with them about recent sexual activity and medical history when you call.
Lastly, whenever the bleeding occurs, if your blood type is RH-negative, your doctor will want to make sure you get a Rhogam shot to protect future pregnancies. Call your doctor if you are RH-negative and have bleeding anytime in pregnancy. If you are RH-positive, this isn't something you have to worry about.
Learn more:
- Pregnancy symptoms you should never ignore
- Vaginal discharge during pregnancy
- Rectal bleeding during pregnancy
advertisement | page continues below
why they appear in the early and late periods, in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester, what to do at home
Expectant mothers are worried about any changes in the body. Noticing an unusual white discharge, some pregnant women begin to worry. "Komsomolskaya Pravda" together with obstetrician-gynecologist Susanna Grigoryan and obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound diagnostics doctor, candidate of medical sciences Daiva Pikauskaite understands in which cases white discharge is the norm, and in which they are dangerous for the woman and the fetus.
Characteristics of white discharge during pregnancy
White discharge is distinguished by the following characteristics.
| Color | Available in clear, whitish or light colors. |
| Odor | Should normally be absent, but slight sourness is acceptable. |
| Structure | There must be no bloody inclusions, lumps, cheesy flakes. |
| Consistency | May be slimy, thin, thick or viscous. |
| Sensations | Discharge should not be accompanied by pain, burning, itching, swelling of the vaginal mucosa. |
Liquid consistency
Sometimes a thin white discharge seems so normal that it is difficult for a doctor to recognize signs of pathology in them. However, they can be one of the symptoms of an infectious-inflammatory disease. For example, a fishy smell may indicate a violation of the vaginal microflora, and blood streaks - about inflammation of the cervix or its erosion. Also, such discharge may occur due to an allergic reaction to intimate hygiene products or pads.
However, they can be one of the symptoms of an infectious-inflammatory disease. For example, a fishy smell may indicate a violation of the vaginal microflora, and blood streaks - about inflammation of the cervix or its erosion. Also, such discharge may occur due to an allergic reaction to intimate hygiene products or pads.
Cheesy consistency
Cheesey discharge usually indicates candidiasis. May be accompanied by a sour smell, burning and itching. Unpleasant symptoms are aggravated after sexual contact, water procedures and at night. During pregnancy, the disease worsens due to changes in hormonal levels. The danger of pathology for the expectant mother 一 the risk of losing a child. The appearance of symptoms of candidiasis before childbirth increases the risk of infection of the child at the time of his passage through the birth canal.
Creamy consistency
A whitish-transparent creamy discharge due to increased blood flow to the vagina. (1) Congested blood vessels cause temporary disturbances in the functioning of the bladder, ureters, and kidneys.:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/2785562/original/028627600_1556001360-shutterstock_1019963743.jpg) The reproductive system reacts to changes with abundant secretions, similar to cream.
The reproductive system reacts to changes with abundant secretions, similar to cream.
Mucus discharge
Mucous discharge that is not accompanied by an unpleasant odor, burning or itching is considered normal. This is the result of the formation of a mucous plug that prevents infections from entering the vagina. The mucous secretion may acquire a milky hue, contain dense clots. The formation of a cork is completed by about the 12th week of pregnancy, then the nature of the discharge changes.
Foamy discharge
A common cause of frothy discharge during pregnancy is trichomoniasis. Illness in the early stages can lead to miscarriage. Self-treatment is strictly contraindicated. Having found foamy discharge, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible and follow all the instructions.
Why white discharge occurs during early pregnancy
– Vaginal discharge without unpleasant symptoms is an absolute norm and is observed in most pregnant women, says obstetrician-gynecologist Daiva Pikauskaite. - From the first to the third trimester, their number increases.
- From the first to the third trimester, their number increases.
However, there are also warning signs:
- discoloration to reddish or greenish;
- significant and abrupt increase in excretions;
- odor change;
- burning, itching or pain.
Any of these factors is a reason to see a doctor as soon as possible. (2)
1st trimester
Conceiving a child always affects a woman's body. Hormonal changes begin, often accompanied by light or white discharge. Also, the cause of secretion is the fixation of the embryo in the uterine cavity or the formation of a mucous plug that protects the embryo from infection.
Over time, the amount of discharge decreases. They become more viscous and transparent.
Why white discharge occurs during late pregnancy
White discharge is most often safe in late pregnancy.
- Slight, odorless discharge is considered normal. Usually they are transparent or slightly milky in color. The consistency is reminiscent of raw egg white, - says obstetrician-gynecologist Daiva Pikauskaite, - the secretions are mainly protective, preventing ascending infection of the fetus.
2nd trimester
In the 2nd trimester, a thin, white discharge is considered normal. (3) They help keep the vagina healthy. The main thing is that there should be no foreign inclusions and smell. Any deviation from the norm is a reason to contact a gynecologist.
Photo: @amina-filkins, pexels.com3rd trimester
Toward the end of pregnancy, white discharge may indicate the following processes:
- the mucous plug begins to move;
- the head of the fetus is pressed closer to the exit from the birth canal, that is, to the cervix;
- amniotic fluid leakage (usually occurs later in pregnancy).
– In the event of unusual discharge and an increase in its amount, you should immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will assess the nature of the secretions and their volume in order to exclude leakage of amniotic fluid and the presence of infectious and inflammatory diseases, explains obstetrician-gynecologist Suzanna Grigoryan.
How to deal with white discharge during pregnancy at home
– If the discharge does not bother you, then nothing needs to be done about it, especially at home, says Daiva Pikauskaite. - It is only important to observe intimate hygiene, undergo examinations at the doctor on time and take the necessary tests. For any warning signs, it is recommended to consult a gynecologist.
Frequently asked questions and answers
White discharge is most often the norm during pregnancy. However, expectant mothers may be concerned. The most popular questions are answered by gynecologists Daiva Pikauskaite and Susanna Grigoryan.
What should you not do when you notice a white discharge?
If discharge bothers you, do not do the following:
● use medications on your own;
● Douching or sitz baths with medicinal herbs;
● use soap for intimate hygiene, it dries out the mucous membranes, their protective functions are impaired;
● Wear panty liners or synthetic underwear.
How to distinguish amniotic fluid from abundant discharge?
At the end of pregnancy, the amount of discharge increases. Often they become so plentiful that it seems to the expectant mother that her water is leaking. It is possible to distinguish amniotic fluid from secretions.
The discharge is thicker, leaving a dried stain or a characteristic white color on the laundry.
Amniotic fluid is water. It doesn't stretch and doesn't leave marks when it dries.
In case of doubt, it is best to consult a doctor, who will accurately determine the cause. Also, the pharmacy sells special tests that show whether there is water leakage.
Can I use the pool if I have white discharge?
If the discharge does not bother, the pregnant woman can swim in the pool, river, sea and any other body of water. In case of doubt, it is recommended to obtain a doctor's approval.
Sources
- Cervicitis in pregnant women / Sverdlova E.
 S. // 2010. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/tservitsity-u-beremennyh
S. // 2010. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/tservitsity-u-beremennyh - Bacterial infections during pregnancy / Zheksembayeva G.K., Zhumadullaeva G.S., Kadirsizova G.K., Musaeva R.G. // 2011. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/bakterialnye-infektsii-vo-vremya-beremennosti
- Pregnancy, childbirth, motherhood / Burmistrova E.A. // 2012.
Vaginal discharge - useful information for womenTraining Center for Reproductive Health
Pregnancy is an extremely important period in the life of any woman. Discharge from the genitals almost always causes anxiety, so it is extremely important to know the mechanisms of their occurrence, types and possible consequences for the body.
Outside of pregnancy, the cervix constantly produces mucus, with several types of mucus being produced during the menstrual cycle:
- the first half of the menstrual period. The work of the whole organism, primarily the organs of the reproductive system, is aimed at the release of the egg from the ovary and possible fusion with the sperm.
 For this, the woman's body produces a rich and liquid secret, the purpose of which is to facilitate the movement of spermatozoa;
For this, the woman's body produces a rich and liquid secret, the purpose of which is to facilitate the movement of spermatozoa; - the second half of the menstrual period. When the egg is fertilized, the woman's body prepares for its direct introduction into the uterus. In this case, an opaque and viscous mucus is produced, the purpose of which is to protect the entrance to the uterus from foreign microorganisms.
The first half of the cycle is regulated by the female sex hormone estrogen, the second half by the hormone progesterone. In the first trimester of pregnancy, the work of the uterus and its appendages is regulated by progesterone. She produces a small amount of thick discharge. However, starting from the thirteenth week, the female body begins to produce significant amounts of estrogen, so the vaginal discharge becomes plentiful and liquid.
Normal pregnancy discharge
The course of the first trimester of pregnancy (the first twelve weeks) is determined by the influence of the female sex hormone progesterone. At first, it is secreted by the corpus luteum of the ovarian menstruation (it is formed after the rupture of the follicle, from which the egg is released during ovulation). After fertilization of the egg occurs, the corpus luteum of ovulation expands under the action of the pituitary luteinizing hormone and then turns into the corpus luteum of pregnancy, producing large amounts of progesterone. This hormone helps to retain the embryo (fertilized egg) in the uterine cavity by blocking the exit from the cavity of this organ (a thick mucous plug forms in the cervical canal), as well as suppressing the contractility of its muscles.
At first, it is secreted by the corpus luteum of the ovarian menstruation (it is formed after the rupture of the follicle, from which the egg is released during ovulation). After fertilization of the egg occurs, the corpus luteum of ovulation expands under the action of the pituitary luteinizing hormone and then turns into the corpus luteum of pregnancy, producing large amounts of progesterone. This hormone helps to retain the embryo (fertilized egg) in the uterine cavity by blocking the exit from the cavity of this organ (a thick mucous plug forms in the cervical canal), as well as suppressing the contractility of its muscles.
Under the influence of progesterone, very thick, glassy, transparent, in some cases whitish discharges appear directly in the first trimester of pregnancy, which can be found on linen in the form of mucus clots. This is the norm only in cases where the discharge does not have any odor and does not bother the pregnant woman, that is, it does not cause itching, burning and other unpleasant sensations.
In the event of such symptoms, it is necessary to look for another reason, that is, immediately seek help from a gynecologist.
After the first trimester of pregnancy, when the fetus is firmly strengthened in the uterine cavity and the placenta almost matures (the organ that connects the mother and fetus and provides the latter with all the necessary nutrients, hormones, biologically active compounds), they again begin to be excreted in large quantities estrogen. The task of this period is the development of the uterus (it is the organ in which the fetus develops, therefore it must constantly increase in size) and the mammary glands (new glandular tissue begins to form in them and new milk ducts begin to form).
Under the influence of these hormones in the second half of pregnancy, women develop copious discharge, colorless or slightly whitish in color, from the genitals. They should not be classified as any pathological conditions, however, such discharge should not have an unpleasant odor, cause symptoms such as itching, burning and other manifestations of discomfort.
White discharge during pregnancy
White discharge occurs most often during pregnancy. They can be a cause for concern in women, but only in extremely rare cases are they associated with any pathological condition.
The composition of the secretions includes the following components:
- mucus. Its source is the numerous glands of the woman's reproductive system: the uterus, her cervix, vestibule, and also the vagina itself;
- microorganisms. The microflora is always present in the vagina, which can have a diverse composition, which is different for each woman. If it is healthy, then it is mainly the so-called lactic acid bacteria. The presence of other microorganisms does not yet allow us to judge the development of any disease;
- epithelial cells. They cover all the structures of the female reproductive system, are constantly exfoliated and replaced by new ones.
Vaginal discharge can be both pathological and normal. Usually, white discharge is directly related to the menstrual cycle. In its first half, there are not abundant discharges of a watery consistency, with the course of ovulation they become thick and viscous, and may acquire a beige tint. By the end of the menstrual period, the amount of discharge increases again. White discharge can also appear due to other factors: after intercourse, accompanied by the use of hormonal contraceptives. Pathological white discharge may be associated with infectious diseases, such as candidiasis.
Usually, white discharge is directly related to the menstrual cycle. In its first half, there are not abundant discharges of a watery consistency, with the course of ovulation they become thick and viscous, and may acquire a beige tint. By the end of the menstrual period, the amount of discharge increases again. White discharge can also appear due to other factors: after intercourse, accompanied by the use of hormonal contraceptives. Pathological white discharge may be associated with infectious diseases, such as candidiasis.
White discharge can be called the first sign of pregnancy. At this stage, they are associated with the influence of the hormone progesterone. From the thirteenth week, its influence decreases, increases, respectively, the action of estrogen. During this period, the discharge becomes more abundant, they are transparent and do not have a certain smell. They do not cause unpleasant symptoms, such as burning, itching, which is extremely important for the diagnosis of pathological conditions.
Despite the fact that such discharge during pregnancy is quite normal, it is necessary to pay attention to their consistency, color and amount. A change in these indicators may indicate the addition of an infection, hormonal status disorders, and diseases of the genital organs. The most common cause of such changes is candidiasis or thrush of the female genital organs. In this case, the discharge will look like cottage cheese, exude a beer smell and become plentiful. Other conditionally pathogenic microflora can also join, since during pregnancy there is a decrease in immunity.
To prevent thrush, doctors prescribe probiotics to women during pregnancy, including dairy products. If it is not possible to prevent the development of pathology, then special antifungal drugs are prescribed.
Another source of discharge is bacterial vaginosis. At the same time, they have a watery consistency and a transparent shade, and a rather unpleasant smell.
If pains in the lower abdomen join the secretions, then this condition requires immediate hospitalization, since there is a high risk of ectopic pregnancy and the threat of miscarriage.
Thus, white discharge in women during pregnancy is quite normal, but it is necessary to pay attention to indicators such as smell, appearance.
Yellow discharge during pregnancy
The presence of yellow discharge is not normal, but it may not cause any concern if it is not accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, such as an unpleasant smell, burning, itching and pain. Otherwise, you need to urgently visit a gynecologist, especially if the discharge is dark yellow.
There are several reasons for the appearance of such a pathological sign. The first of these is the presence of inflammatory processes of any nature, which are exacerbated by pregnancy or other factors. Immunity during this period is weakened, which allows pathological microorganisms to easily penetrate the vagina and accumulate there, causing a similar unpleasant symptom. In addition to all this, discharge can be triggered by spontaneous abortion. Therefore, you need to respond to them as quickly as possible.
The appearance of dark yellow discharge may be an allergic reaction to underwear or intimate hygiene products. Certain micro-organisms can also cause a specific yellowish discharge.
If the color of the discharge changes to green, then the problem that has arisen indicates the development of serious abnormalities. For example, this may indicate the presence of sexually transmitted diseases. They are also characterized by the appearance of itching, pain when urinating, burning in this area.
If the discharge is bright yellow, it is most likely caused by inflammation of the fallopian tubes or ovaries, as well as various bacterial infections in the vagina.
Many infections and inflammatory diseases that manifest themselves during pregnancy with specific yellow discharge, at this time only become aggravated, and do not appear in connection with the onset of pregnancy. Therefore, before the moment of conception, the expectant mother must undergo a complete examination. This will help determine the state of the body, identify unwanted pathological conditions and diseases and get rid of them even before the pregnancy period.
This will help determine the state of the body, identify unwanted pathological conditions and diseases and get rid of them even before the pregnancy period.
Brown discharge during pregnancy
Brown discharge can occur suddenly in almost all women during pregnancy. There are several reasons for the development of this condition.
The first of these is an ectopic pregnancy. When it occurs, the egg is inevitably rejected. One of the characteristic signs of its development is brown discharge. Bleeding may also occur. Unfortunately, many women at this time do not even know about the onset of pregnancy.
In many cases, the appearance of brown discharge indicates a threatened miscarriage. In this case, an experienced gynecologist should take all possible measures in order to save the fetus (surgery or conservative treatment). A miscarriage is a serious complication that occurs only in the early stages of pregnancy. At first, bleeding may be minor and not accompanied by pain. However, it is not able to stop within a certain period of time and gradually increases.
However, it is not able to stop within a certain period of time and gradually increases.
Incomplete miscarriage may cause significant bleeding, it is thick red with a brown tint, and clots may be present. All this is accompanied by infrequent, but intense pain in the lower abdomen. In this case, it is necessary to scrape the uterine cavity and remove the remnants of a dead fetal egg.
The appearance of discharge that is brown in late pregnancy may be evidence of placental dysfunction. This organ may disintegrate. As a result, minor bleeding may occur.
The next reason for the appearance of such symptoms may be diseases associated with inflammatory processes or erosion of the cervix.
If the due date is already approaching and brown discharge suddenly appears, then this indicates the onset of childbirth. Another extremely important reason for the appearance of such secretions is uterine rupture. Most often, it develops in those women who have previously had abortions or have scars on the uterus.
Thus, the most common causes of brown discharge are sexual diseases, as well as cervical erosion. To eliminate such pathological conditions, it is necessary to contact a specialist gynecologist.
In case of rupture of the placenta, bed rest is prescribed, any emotional and psychological stress is excluded, as well as the use of hormonal drugs.
Bleeding during pregnancy
Bleeding is quite common, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy. According to statistics, eighty percent of women calmly and without any deviations continue to bear the fetus.
There are many reasons for bleeding. For example, active blood supply to the internal genital organs or their excessive sensitivity. This usually happens after an ultrasound examination, if it is carried out with a special vaginal probe or when used when examining a gynecological speculum.
Similar discharge may also occur after sexual intercourse, as there is irritation of the cervix, as well as the mucous membrane of the vagina. Discharge also begins due to a slight detachment of the placenta: a certain amount of blood accumulates under it. When released to the outside, it has a pinkish tint.
Discharge also begins due to a slight detachment of the placenta: a certain amount of blood accumulates under it. When released to the outside, it has a pinkish tint.
Women often have discharge on days when they had their period before pregnancy. They are also accompanied by pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen. This is due to hormonal disruptions in the body in early pregnancy and it is absolutely safe.
The appearance of blood clots is a signal that indicates dangerous complications. It is urgent to consult a doctor, because, most likely, this is a threat of miscarriage.
If the discharge has a brownish tint, then a hematoma may have formed in the body.
When an ectopic pregnancy develops, the woman may also experience spotting. Another reason is a “frozen” pregnancy. In this case, a week after intrauterine death of the fetus, a spontaneous miscarriage develops.
A rare cause of bleeding is hydatidiform mole, in which there is an overgrowth of placental tissue. Allocations in this case are abundant, but they are absolutely painless. The outcome of this condition is the death of the baby.
Allocations in this case are abundant, but they are absolutely painless. The outcome of this condition is the death of the baby.
The most dangerous spotting occurs in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. They can be evidence of pathology, threaten the life of not only the fetus, but also the mother.
Bleeding may also develop in the presence of fibroids, cervical erosion, cervical canal polyps, genital trauma.
Despite the fact that bleeding in most cases does not pose a danger to the fetus and mother, it is necessary to contact a specialist in time in order to exclude the development of dangerous complications and ensure the normal course of pregnancy.
Discharge during early pregnancy
Discharge that occurs early in pregnancy can be either normal or abnormal. A change in discharge in the first weeks after conception is an inevitable process. This is due to the fact that in the female body the secretion of the hormone progesterone increases. It provides attachment to the uterine wall of the egg fertilized by the sperm, is involved in the preservation of the fetus and the formation of the placenta. At the same time, vaginal discharge becomes scarce, opaque and viscous. This nature of the secretions contributes to the formation of a protective plug in the cervical canal, which protects the uterus from the ingress of pathological microorganisms.
It provides attachment to the uterine wall of the egg fertilized by the sperm, is involved in the preservation of the fetus and the formation of the placenta. At the same time, vaginal discharge becomes scarce, opaque and viscous. This nature of the secretions contributes to the formation of a protective plug in the cervical canal, which protects the uterus from the ingress of pathological microorganisms.
On the tenth day immediately after conception, bloody discharge from the vagina may appear, which is also not considered a pathological condition. This is due to the attachment of a fertilized egg to the uterus. This organ has an extensive network of blood vessels and capillaries, which can be slightly damaged when the embryo attaches. This phenomenon is called implantation bleeding and lasts no more than two days. Strong and longer bleeding indicate the development of a pathological condition.
Discharges that are yellowish, brown, greenish in color, curdled in texture and have an unpleasant odor are considered pathological.

Yellowish discharge from the vagina, which has a sharp and unpleasant odor, indicates the presence of inflammation in the uterus and its appendages. Inflammatory processes in the internal organs during pregnancy are very dangerous, as they often lead to its interruption.
If bleeding is observed that does not stop within three days, then this indicates the development of serious complications and requires immediate medical attention, as this is one of the signs of a developing miscarriage. Often, such a sign is accompanied by pulling, severe pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, loss of appetite, and intestinal dysfunction.
Bloody discharge in early pregnancy may be a sign of cervical erosion. They are almost always painless and stop within a few hours.
The appearance of dark red, brown or bloody discharge a few days after conception may indicate the development of an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, the blood is released after the rejection of the fertilized egg. An ectopic pregnancy poses a significant threat to a woman and reduces the chance of a future pregnancy.
An ectopic pregnancy poses a significant threat to a woman and reduces the chance of a future pregnancy.
Thus, white, smooth, stringy, and odorless discharge during early pregnancy is normal and should not cause any concern, while curdled, yellow, malodorous discharge may be a sign of candidiasis or inflammation of the uterus. Abundant brownish, bloody discharge is also an alarming symptom and requires immediate medical attention.
Late discharge
Usually, late pregnancy refers to the period from the thirty-fifth week until the onset of labor. At this time, the body is actively preparing for the birth of a child. The discharge has a mucous consistency, milky color, they have no smell. Normally, they do not cause unpleasant discomfort, burning, itching and any other irritations.
Often before the expected delivery, at about the thirty-seventh week, there may be a discharge of brown color and a mucous consistency. This is due to the fact that the cervical mucosa begins to prepare for childbirth. It softens, then opens slightly and is released from the mucous plug. A similar phenomenon indicates an imminent birth.
This is due to the fact that the cervical mucosa begins to prepare for childbirth. It softens, then opens slightly and is released from the mucous plug. A similar phenomenon indicates an imminent birth.
However, if in the last days of the week foamy discharge with a greenish, bright red or brown tint is observed, then this indicates the development of dangerous complications.
Bright red discharge may indicate placental abruption. In this case, urgent emergency medical care is needed.
Greenish frothy discharge accompanied by itching most likely indicates an infection. In this case, it is extremely important to eliminate their cause before childbirth, since otherwise their course may be complicated and there is a threat of infection of the fetus.
Discharge after pregnancy
After the birth of a child, regardless of the type of delivery, a woman has bloody discharge from the genital tract. Such postpartum discharge is called lochia.
They are caused by the healing process on the inside of the uterus, usually where the placenta was attached to the wall of the uterus. If timely release from all non-viable tissues occurs, then the postpartum period proceeds without any complications.
It is extremely important to pay attention to the length and color of the lochia. Their nature changes - the discharge becomes scarcer over time and changes its color:
- red lochia. They begin in the first two or three days after birth. This is a bright red, bloody, copious discharge with a small amount of blood clots;
- serous lochia. They begin on the fourth day after birth. The discharge turns pale and acquires a serous-sanious (pinkish-brown) color with a high content of leukocytes. During this period, there should be no bright red lochia and hemorrhagic clots.
- white lochia. They begin approximately from the tenth day and continue until the twentieth day. Allocations acquire a yellowish-white or yellow color, become spotting, odorless liquid and blood impurities.