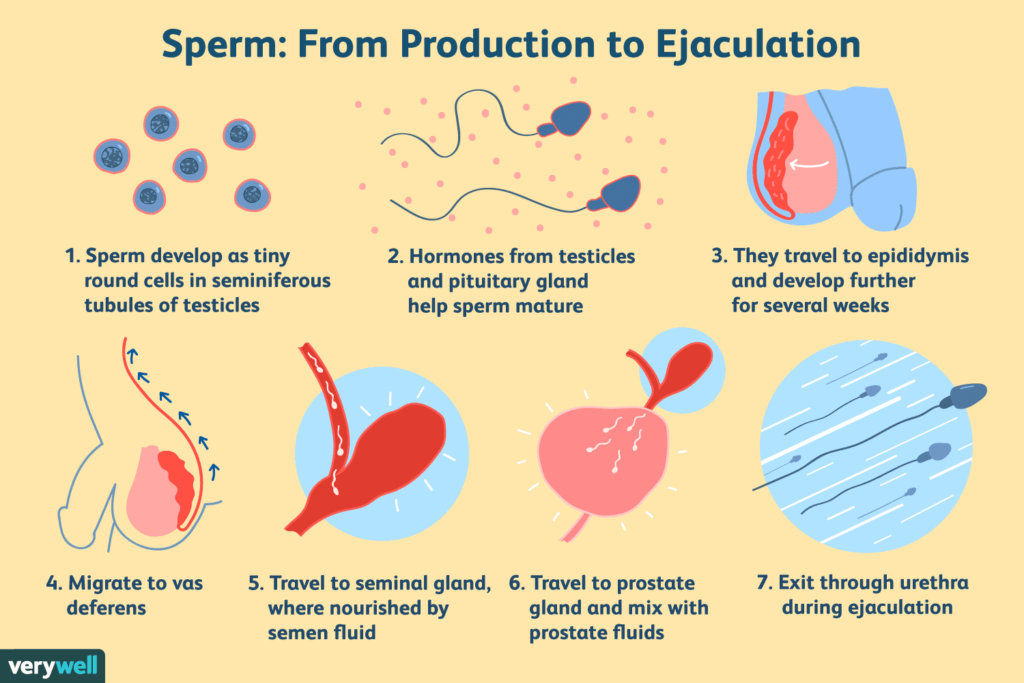
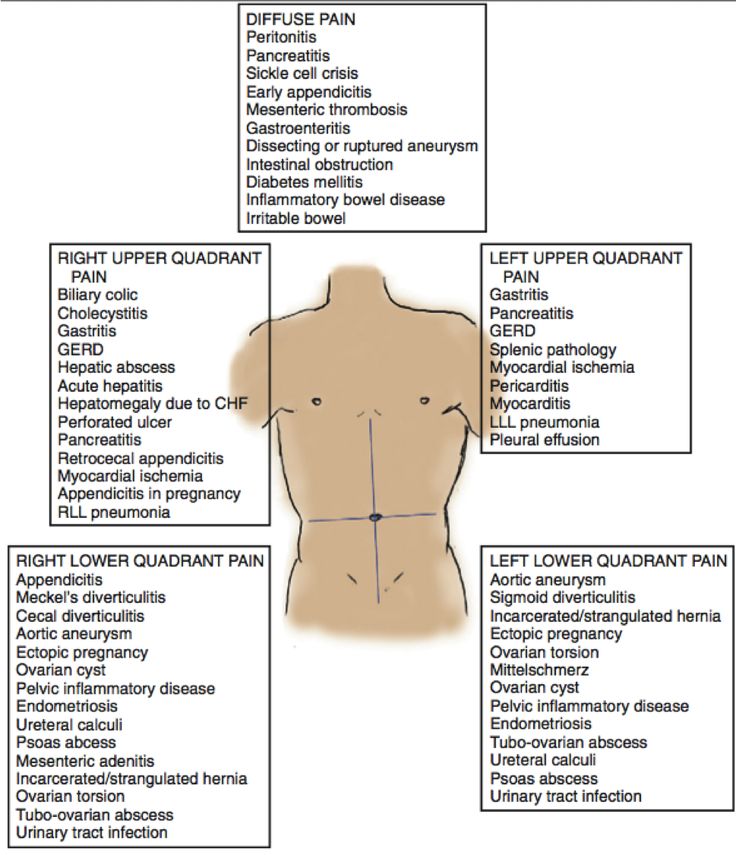
When do you feel pain from ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy - NHS
An ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilised egg implants itself outside of the womb, usually in one of the fallopian tubes.
The fallopian tubes are the tubes connecting the ovaries to the womb. If an egg gets stuck in them, it won't develop into a baby and your health may be at risk if the pregnancy continues.
Unfortunately, it's not possible to save the pregnancy. It usually has to be removed using medicine or an operation.
In the UK, around 1 in every 90 pregnancies is ectopic. This is around 11,000 pregnancies a year.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy doesn't always cause symptoms and may only be detected during a routine pregnancy scan.
If you do have symptoms, they tend to develop between the 4th and 12th week of pregnancy.
Symptoms can include a combination of:
- a missed period and other signs of pregnancy
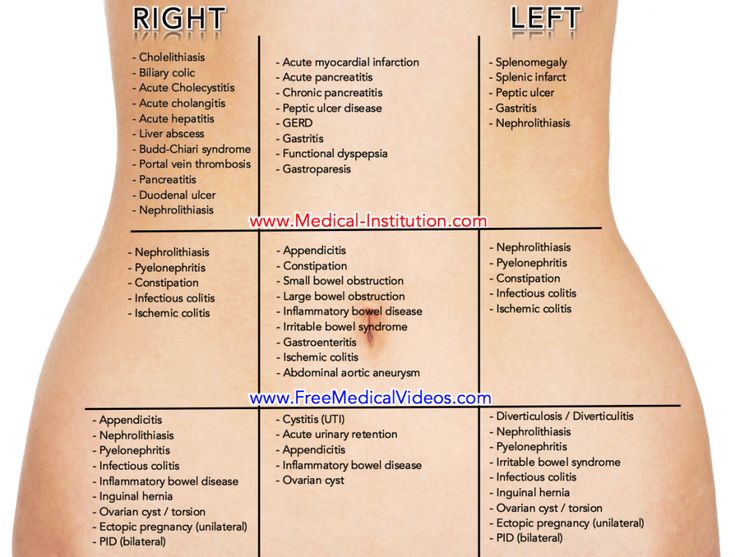
- tummy pain low down on one side
- vaginal bleeding or a brown watery discharge
- pain in the tip of your shoulder
- discomfort when peeing or pooing
But these symptoms aren't necessarily a sign of a serious problem. They can sometimes be caused by other problems, such as a stomach bug.
Read more about the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.
When to get medical advice
Contact your GP or call NHS 111 if you have a combination of any of the above symptoms and you might be pregnant – even if you haven't had a positive pregnancy test.
An ectopic pregnancy can be serious, so it's important to get advice right away.
Your GP will ask about your symptoms and you'll usually need to do a pregnancy test to determine if you could have an ectopic pregnancy.
You may be referred to a specialist early pregnancy clinic for further assessment, where an ultrasound scan and blood tests may be carried out to confirm the diagnosis.
Read more about ectopic pregnancy tests.
When to get emergency help
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E) department immediately if you experience a combination of:
- a sharp, sudden and intense pain in your tummy
- feeling very dizzy or fainting
- feeling sick
- looking very pale
These symptoms could mean that your fallopian tube has split open (ruptured). This is very serious and surgery to repair the fallopian tube needs to be carried out as soon as possible.
This is very serious and surgery to repair the fallopian tube needs to be carried out as soon as possible.
A rupture can be life threatening, but fortunately they're uncommon and treatable, if dealt with quickly. Deaths from ruptures are extremely rare in the UK.
How an ectopic pregnancy is treated
There are 3 main treatments for an ectopic pregnancy:
- expectant management – you're carefully monitored and 1 of the treatments below is used if the fertilised egg doesn't dissolve by itself
- medicine – an injection of a powerful medicine called methotrexate is used to stop the pregnancy growing
- surgery – keyhole surgery (laparoscopy) is performed under general anaesthetic to remove the fertilised egg, usually along with the affected fallopian tube
You'll be told about the benefits and risks of each option. In many cases, a particular treatment will be recommended based on your symptoms and the results of the tests you have.
In many cases, a particular treatment will be recommended based on your symptoms and the results of the tests you have.
Some treatments may reduce your chances of being able to conceive naturally in the future, although most women will still be able to get pregnant. Talk to your doctor about this.
Read more about treating an ectopic pregnancy.
Help and support after an ectopic pregnancy
Losing a pregnancy can be devastating, and many women feel the same sense of grief as if they had lost a family member or partner.
It's not uncommon for these feelings to last several months, although they usually improve with time. Make sure you give yourself and your partner time to grieve.
If you or your partner are struggling to come to terms with your loss, you may benefit from professional support or counselling. Speak to your GP about this.
Speak to your GP about this.
Support groups for people who have been affected by loss of a pregnancy can also help.
These include:
- The Ectopic Pregnancy Trust
- Ectopic Pregnancy Foundation
- Miscarriage Association
- Cruse Bereavement Care
Read more about dealing with loss and find bereavement support services in your area.
Trying for another baby
You may want to try for another baby when you and your partner feel physically and emotionally ready.
You'll probably be advised to wait until you've had at least 2 periods after treatment before trying again to allow yourself to recover.
If you were treated with methotrexate, it's usually recommended that you wait at least 3 months because the medicine could harm your baby if you become pregnant during this time.
Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy will be able to get pregnant again, even if they've had a fallopian tube removed. Occasionally, it may be necessary to use fertility treatment such as IVF.
The chances of having another ectopic pregnancy are higher if you've had one before, but the risk is still small.
If you do become pregnant again, it's a good idea to let your GP know as soon as possible so early scans can be carried out to check everything is OK.
What can cause an ectopic pregnancy?
In many cases, it's not clear why a woman has an ectopic pregnancy. Sometimes it happens when there's a problem with the fallopian tubes, such as them being narrow or blocked.
The following are all associated with an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy:
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) – inflammation of the female reproductive system, usually caused by a sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- previous ectopic pregnancy – the risk of having another ectopic pregnancy is around 10%
- previous surgery on your fallopian tubes – such as an unsuccessful female sterilisation procedure
- fertility treatment, such as IVF – taking medicine to stimulate ovulation (the release of an egg) can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy
- becoming pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) or intrauterine system (IUS) for contraception – it's rare to get pregnant while using these, but if you do you're more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy
- smoking
- increasing age – the risk is highest for pregnant women aged over 35
You can't always prevent an ectopic pregnancy, but you can reduce your risk by using a condom when not trying for a baby to protect yourself against STIs, and by stopping smoking if you smoke.
Page last reviewed: 23 August 2022
Next review due: 23 August 2025
Ectopic Pregnancy | Cedars-Sinai
ABOUT CAUSES DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT NEXT STEPS
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
A pregnancy that develops outside the uterus is called an ectopic pregnancy. It almost always happens in a fallopian tube. Because of this, it’s often called a tubal pregnancy. In rare cases, an ectopic pregnancy will happen in an ovary, in the cervix, or the belly (abdomen).
What causes an ectopic pregnancy?
A fertilized egg normally moves down a fallopian tube and into the uterus. But the egg can get stuck in the tube if the tube is blocked. This might be from an infection or scar tissue. If the fertilized egg can't reach the uterus, it begins to develop in the tube.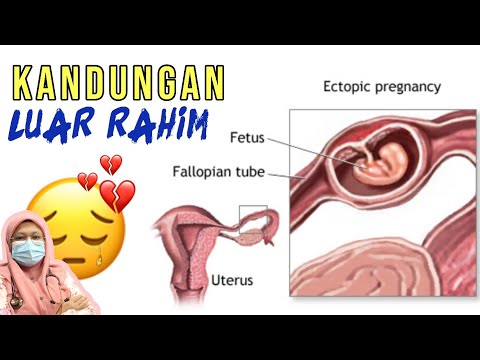
Who is at risk for an ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy is more common in women who:
- Have had trouble getting pregnant (infertility)
- Have endometriosis. This is when uterine tissue grows in other areas of the pelvis.
- Have a sexually transmitted disease. This can cause infection and scarring in the pelvis.
- Had tubal surgery
- Use an IUD
- Had an ectopic pregnancy in the past
- Have multiple sex partners
- Smoke
- Are older
What are the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy?
Women with an ectopic pregnancy may have irregular bleeding and pelvic or belly (abdominal) pain. The pain is often just on 1 side. Symptoms often happen 6 to 8 weeks after the last normal menstrual period.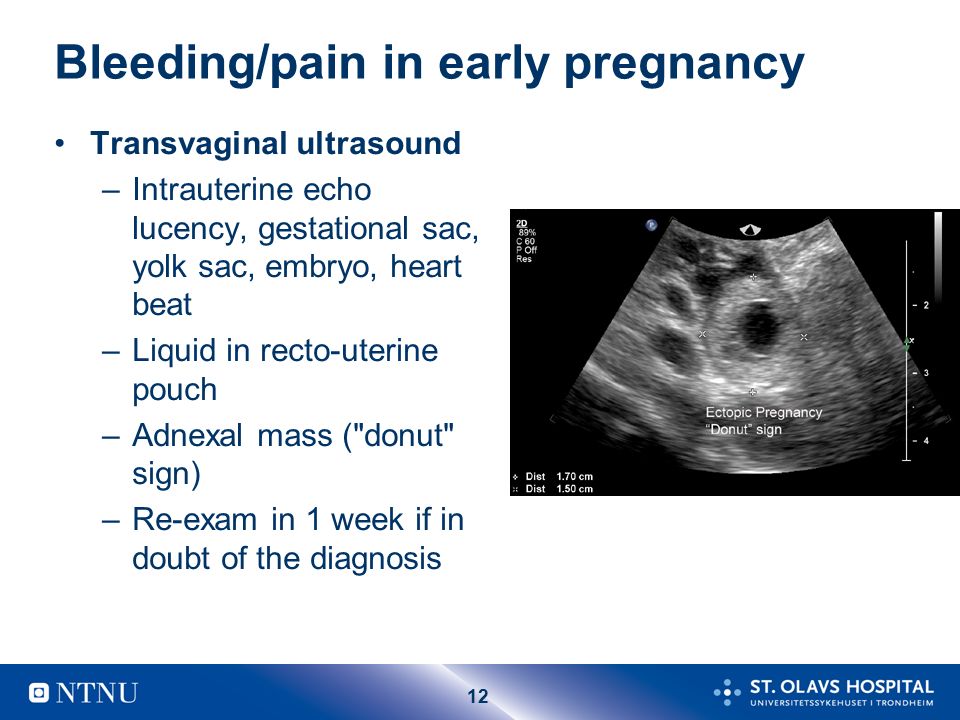 If the ectopic pregnancy is not in the fallopian tube, symptoms may happen later. The classic symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are:
If the ectopic pregnancy is not in the fallopian tube, symptoms may happen later. The classic symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are:
- Belly (abdominal) pain
- No recent period
- Vaginal bleeding not related to a period
How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will measure the level of the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in your blood. They will use ultrasound to check the uterus for a fetus or other pregnancy tissue. In some cases, your healthcare provider will use laparoscopy to diagnose and treat an ectopic pregnancy. This is surgery that uses a lighted tube inserted into your abdomen to check inside the pelvis. It often gives the most accurate diagnosis.
How is an ectopic pregnancy treated?
Ectopic pregnancy may be treated in several ways. This depends on whether the fallopian tube has broken open (ruptured), how far along the pregnancy is, and your hormone levels. Treatments may include:
This depends on whether the fallopian tube has broken open (ruptured), how far along the pregnancy is, and your hormone levels. Treatments may include:
- Letting the ectopic pregnancy heal and the body absorb it on its own. This is only for certain cases.
- Using the medicine methotrexate to stop the pregnancy from growing further
- Using surgery (usually laparoscopy) to make a small opening in the fallopian tube. The surgeon removes the pregnancy and sometimes the tube.
In rare cases, healthcare providers must make a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the ectopic pregnancy or damaged fallopian tube.
What are possible complications of an ectopic pregnancy?
When the embryo implants in the fallopian tube, it does not have enough room to grow or enough blood flow to keep it healthy, so it dies.
The tube may start to let out some of the tissues or bleed. Some embryos do keep growing and may become large enough to burst the fallopian tube. This can cause severe bleeding and shock.
Ectopic pregnancy is the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths during the first 3 months of pregnancy in the U.S.
When should I call the healthcare provider?
Don’t ignore symptoms of ectopic pregnancy. Call your healthcare provider if you have any bleeding or pain in pregnancy.
Key points about ectopic pregnancy
- Pregnancy that develops outside the uterus is called ectopic pregnancy.
- Women with an ectopic pregnancy may have irregular bleeding and pelvic or abdominal pain, often on one side.
- Symptoms most often appear 6 to 8 weeks after the last normal menstrual period.
- Ectopic pregnancy may be treated in several ways, depending on whether the fallopian tube has burst.
- Don’t ignore symptoms of ectopic pregnancy. Call your healthcare provider if you have any bleeding or pain in pregnancy.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider:
- Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen.
- Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
- Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you.
- At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you.
- Know why a new medicine or treatment is prescribed, and how it will help you.
 Also know what the side effects are.
Also know what the side effects are. - Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways.
- Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
- Know what to expect if you do not take the medicine or have the test or procedure.
- If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
- Know how you can contact your provider if you have questions.
Medical Reviewer: Irina Burd MD PhD
Medical Reviewer: Donna Freeborn PhD CNM FNP
Medical Reviewer: Heather M Trevino BSN RNC
© 2000-2022 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.
Ectopic pregnancy - Adamant Medical Clinic
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition.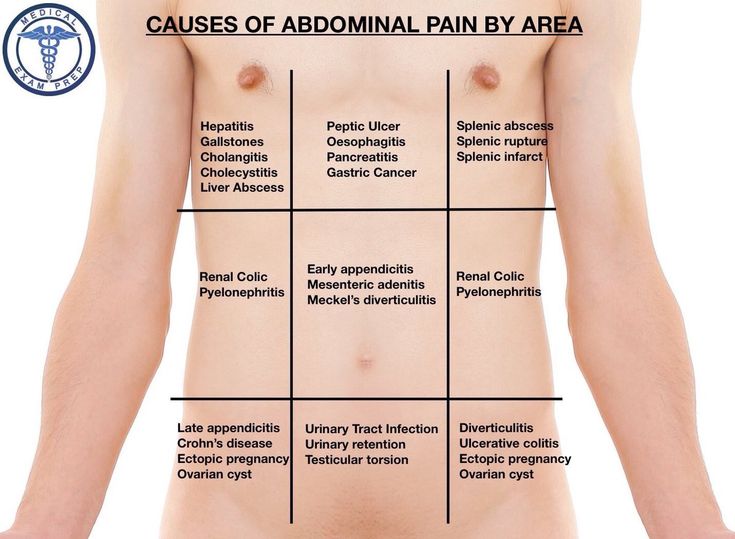 This complication is very dangerous for a woman. If an ectopic pregnancy is not removed on time, there is a risk of intra-abdominal bleeding. And this, in turn, threatens the health and life of the patient. Therefore, noticing the early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, you should immediately see a doctor. This condition requires urgent medical attention.
This complication is very dangerous for a woman. If an ectopic pregnancy is not removed on time, there is a risk of intra-abdominal bleeding. And this, in turn, threatens the health and life of the patient. Therefore, noticing the early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, you should immediately see a doctor. This condition requires urgent medical attention.
The uterus is a muscular organ that exists to bear a child. However, sometimes the egg, having been fertilized, does not enter the uterine cavity, but is fixed in the ovaries, tubes or abdominal cavity. As a result, there are pains during an ectopic pregnancy and a rupture of an organ (for example, a fallopian tube) is possible.
Why does an ectopic pregnancy occur?
Causes of ectopic pregnancy may be as follows:
- pelvic inflammatory disease, especially chronic
- endometriosis
- congenital malformation of the tubes
- IVF complication
The question of why an ectopic pregnancy occurs worries many women. However, it is possible to establish the true causes of an ectopic pregnancy only after a laparoscopic operation to remove it.
However, it is possible to establish the true causes of an ectopic pregnancy only after a laparoscopic operation to remove it.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
Many women wonder how to distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from a normal one. Doctors recommend that you carefully monitor your condition and pay attention to the main symptoms of ectopic pregnancy:
- pain in ectopic pregnancy
- bleeding
Pain during an ectopic pregnancy is aching, cramping in nature. Painful sensations appear from the moment of attachment of the fetal egg. If a rupture occurs, bleeding begins, pain radiates to the anus, and can spread throughout the abdomen, a woman may feel pain during an ectopic pregnancy while urinating or trying to empty the intestines.
Bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy occurs in the abdominal cavity. However, due to a drop in hormone levels, uterine bleeding is often observed. The volume of allocations is usually meager. Bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy lasts a long time.
Bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy lasts a long time.
Both of these symptoms require immediate medical attention. Rarely, bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy is accompanied by fever, which signals the onset of the inflammatory process.
Early ectopic pregnancy: treatment
There is only one possible way to treat pathology - the removal of an ectopic pregnancy by surgery. However, before proceeding with the operation, doctors conduct a diagnosis. External signs of ectopic pregnancy must be confirmed by laboratory and instrumental methods of examination.
There are three ways that help to make a diagnosis:
1) pregnancy can be diagnosed if menstruation is delayed by 2-3 days. To do this, conduct a test for hCG. There are no signs of an ectopic pregnancy yet.
2) After one and a half to two weeks from the start of the delay, an ultrasound examination can be performed. If a fetal egg is not visualized in the area of \u200b\u200bthe uterus, a second appointment will be scheduled in a few days. If the same picture is observed at the second appointment, the doctor will suspect an ectopic pregnancy. Early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may be absent.
If the same picture is observed at the second appointment, the doctor will suspect an ectopic pregnancy. Early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may be absent.
3) fetal heartbeat appears after 2.5-3 weeks. The first early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may already appear. On an ultrasound, a growing ovum will be seen in the tubes, ovaries, or abdomen.
Ectopic pregnancy is treated only surgically. At Adamant Medical Clinic, surgeries are performed laparoscopically. Often, a woman usually sees a specialist when symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy appear, and the fallopian tube is almost always removed during surgery.
The Department of Operative Gynecology of AMK has everything you need to perform the most complex operations. Our doctors are specialists with extensive experience. They know how to distinguish an ectopic pregnancy and are able to quickly and reliably make a diagnosis. If an operation is necessary, patients are guaranteed an individual approach. We use only modern techniques and materials that allow us to remove an ectopic pregnancy with a minimal risk of complications.
We use only modern techniques and materials that allow us to remove an ectopic pregnancy with a minimal risk of complications.
Ectopic pregnancy - prices for treatment, symptoms and diagnosis of the disease at the clinic "Mother and Child" in Vladivostok
An ectopic pregnancy is said to be when the fetal egg does not enter the uterine cavity and is attached elsewhere, most often it is the fallopian tube. But also a fetal egg can attach to the ovary, pelvic peritoneum, intestines and other internal organs.
This is a serious condition requiring immediate surgical treatment. At any moment, such a pregnancy can be complicated by severe bleeding, rupture of the fallopian tube and other life-threatening conditions.
Ectopic pregnancy in Vladivostok:
Clinic "Mother and Child" Vladivostok
Signs of ectopic pregnancy
They talk about an ectopic pregnancy when the fetal egg does not enter the uterine cavity and is attached in another place, most often it is the fallopian tube.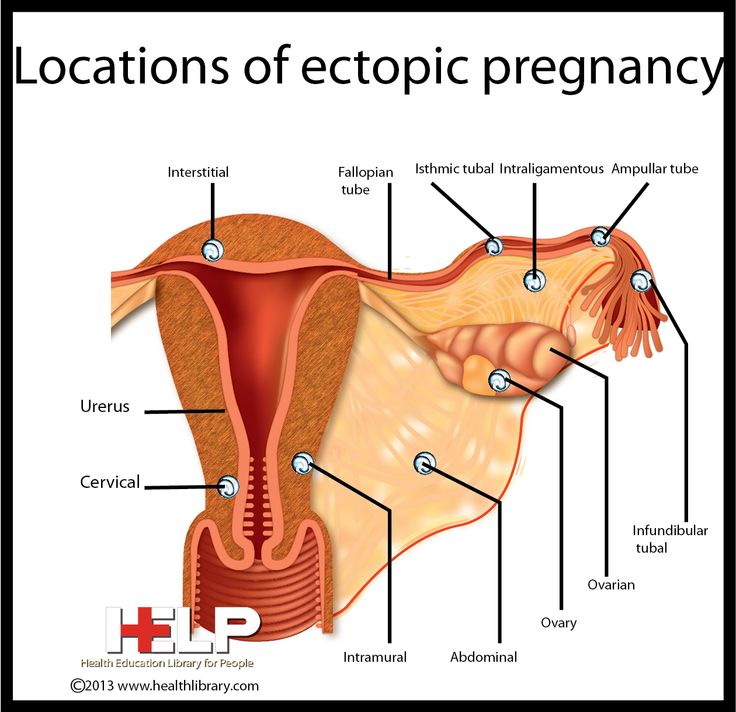 But also a fetal egg can attach to the ovary, pelvic peritoneum, intestines and other internal organs.
But also a fetal egg can attach to the ovary, pelvic peritoneum, intestines and other internal organs.
This is a serious condition that requires immediate surgical treatment. At any moment, such a pregnancy can be complicated by severe bleeding, rupture of the fallopian tube and other life-threatening conditions.
Signs of ectopic pregnancy
Most often, a woman notes signs of pregnancy. There may be a delay in menstruation, engorgement of the mammary glands is often noted. Nausea, aching pain in the lower abdomen and bloody discharge may occur.
In some cases, menstruation delay does not occur and the first manifestation of an ectopic pregnancy is a change in the color of menstrual flow or a decrease in their number. Gradually, the pain in the abdomen begins to intensify, the woman begins to feel weak, dizzy, fainting may occur.
It is far from always possible to recognize this condition before the development of complications and bleeding into the abdominal cavity.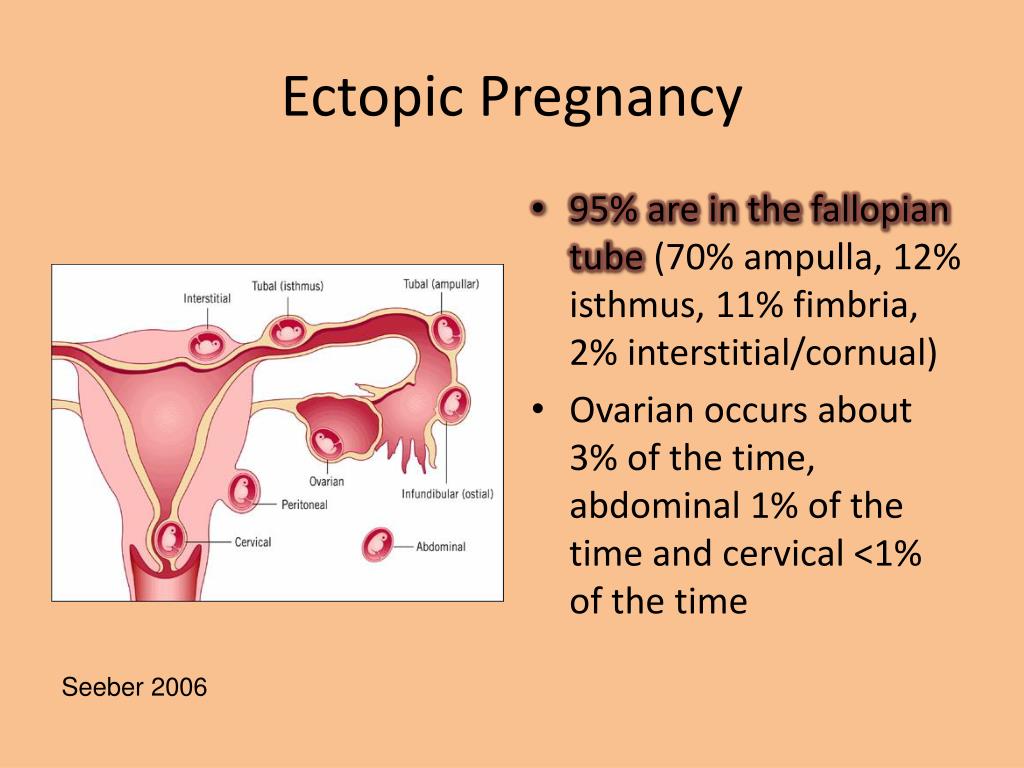
To exclude an ectopic pregnancy, a blood test is performed for hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin, and ultrasound of the pelvic organs. At the clinic "Mother and Child - IDK", at the first appointment, the doctor can perform an ultrasound scan and prescribe an analysis for the content of hCG. Such an analysis, if necessary, can be performed in our laboratory within 1.5–2 hours.
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
If there is a suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy, the patient is indicated for urgent surgery. This operation can be performed endoscopically. During the operation, the patient is under anesthesia. Through several small punctures in the anterior abdominal wall, instruments for the operation and a miniature high-resolution video camera are inserted.
During the operation, the doctor carefully examines the fallopian tubes, uterus, ovaries and abdominal cavity. If an ectopic pregnancy is detected, the fallopian tube with the fetal egg is removed.