What hormone produces breast milk
Causes & How It Works
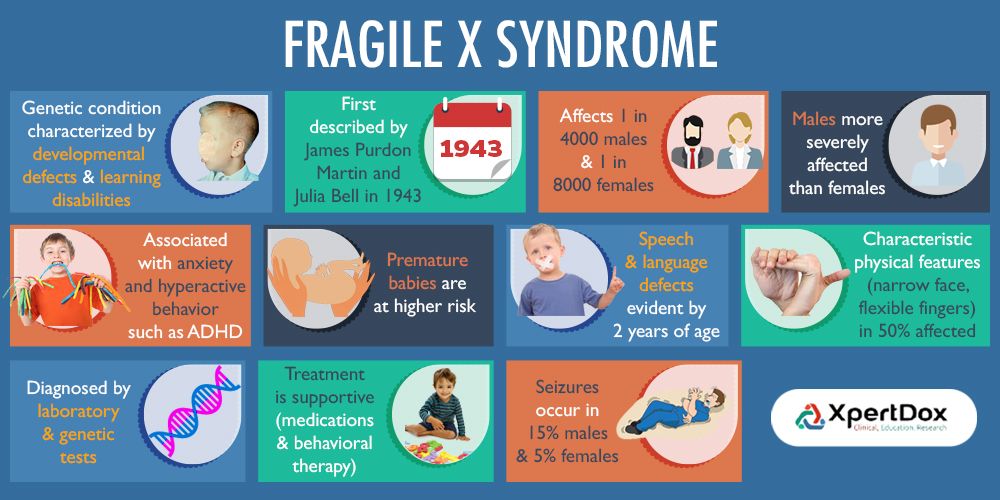
Overview
Lactation is the process of making human milk. It's driven by hormones and results in milk coming from your nipple.What is lactation?
Lactation is the process of producing and releasing milk from the mammary glands in your breasts. Lactation begins in pregnancy when hormonal changes signal the mammary glands to make milk in preparation for the birth of your baby. It’s also possible to induce lactation without a pregnancy using the same hormones that your body makes during pregnancy. Lactation ends once your body stops producing milk.
Feeding your baby directly from your breasts is called breastfeeding (or sometimes chestfeeding) or nursing. You can also feed your baby milk that you have expressed or pumped from your breast and saved in a bottle.
Where does human milk come from?
Human milk comes from your mammary glands inside your breasts. These glands have several parts that work together to produce and secrete milk:
- Alveoli: These tiny, grape-like sacs produce and store milk.
A cluster of alveoli is called lobules, and each lobule connects to a lobe.
- Milk ducts: Each lobe connects to a milk duct. You can have up to 20 lobes, with one milk duct for every lobe. Milk ducts carry milk from the lobules of alveoli to your nipples.
- Areola: The dark area surrounding your nipple, which has sensitive nerve endings that lets your body know when to release milk. To release milk, the entire areola needs stimulation.
- Nipple: Your nipple contains several tiny pores (up to about 20) that secrete milk. Nerves on your nipple respond to suckling (either by a baby, your hands or a breast pump). This stimulation tells your brain to release milk from the alveoli through the milk ducts and out of your nipple.
It helps to think of the lactation system as a large tree. Your nipple is the trunk of the tree. The milk ducts are the branches. The leaves are the alveoli.
Why do people lactate?
The primary reason people lactate is to feed a baby. Lactation is a biological, hormonal response that occurs during and after pregnancy to feed a newborn baby. Your body triggers specific hormones to initiate milk production and ejection (releasing of milk). All mammals lactate for this purpose and it’s possible to induce lactation in men and in non-pregnant women using the right hormone medications.
Lactation is a biological, hormonal response that occurs during and after pregnancy to feed a newborn baby. Your body triggers specific hormones to initiate milk production and ejection (releasing of milk). All mammals lactate for this purpose and it’s possible to induce lactation in men and in non-pregnant women using the right hormone medications.
Function
What triggers lactation?
A series of hormonal events, which begin when you’re pregnant, trigger the lactation process. That process is called lactogenesis.
Stage one lactogenesis: This begins around the 16th week of pregnancy and lasts until a few days after you give birth.
- Estrogen and progesterone rise and cause your milk ducts to grow in number and size. This causes your breasts to become fuller. Your mammary glands begin to prepare for milk production.
- Your nipples darken and your areolas become larger.
- Your Montgomery glands (small bumps on the areola) secrete oil to lubricate your nipple.
- Your body begins making colostrum. It’s highly nutritious and filling and serves as your baby’s first milk.
Stage two lactogenesis: This stage starts about two or three days postpartum (after giving birth). It’s when milk production intensifies.
- Once your baby and placenta are delivered, a sudden drop in your estrogen and progesterone causes the hormone prolactin to take over.
- Prolactin is the hormone that produces milk.
- You’ll notice your milk production increases dramatically at this stage. It’s often referred to as milk “coming in.”
- Your breasts are often engorged (or overly full of milk) to the point where they feel sore, painful or tender.
Stage three lactogenesis: This describes the rest of the time you lactate.
- Lactation generally continues as long as milk is removed from your breast.
- The more milk that’s removed, the more milk your body makes to replace it. Frequent feeding or pumping will cause your body to make more milk.

Hormones for lactation
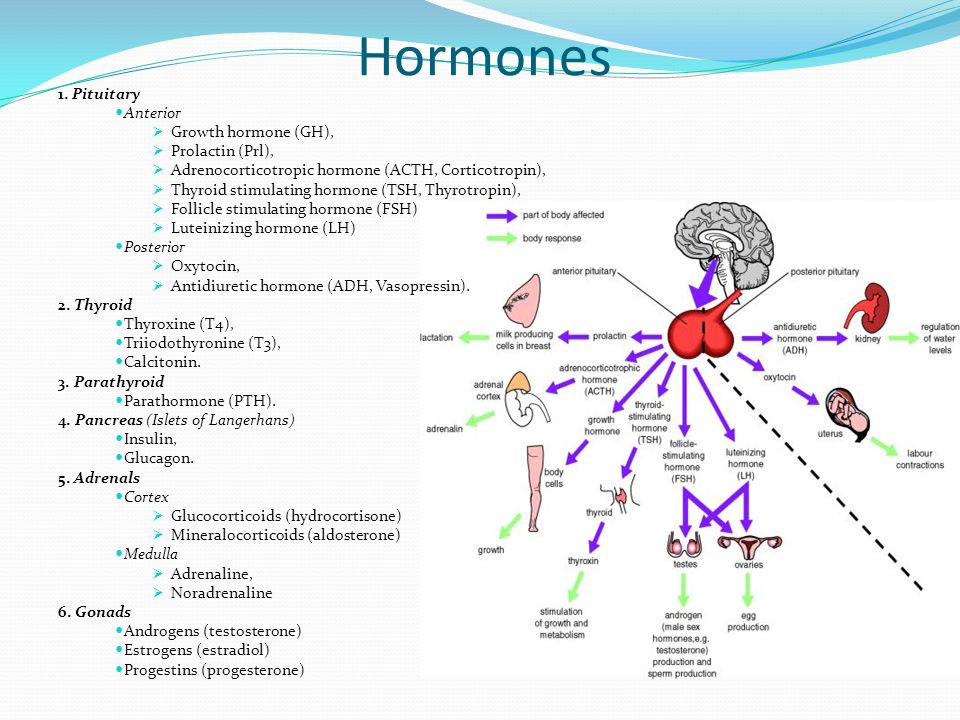
The hormone prolactin controls the amount of milk you produce, and your body begins producing prolactin early in pregnancy. At first, the high levels of estrogen, progesterone and other pregnancy hormones suppress prolactin. Once you deliver the placenta, those pregnancy hormones drop and prolactin takes charge.
When your baby suckles, it stimulates nerves that tell your body to release prolactin and oxytocin. Prolactin causes the alveoli to make milk and oxytocin causes muscle contractions that push out of the alveoli and through the milk ducts.
When milk is released, it’s called a “letdown,” and it takes about 30 seconds of suckling before the letdown occurs. Because you can’t control which breast receives the hormones, the letdown can cause milk to drip from both nipples.
Inducing lactation in people who aren’t pregnant requires medication that mimics hormones your body makes during pregnancy. Suckling from the nipple can initiate lactation, either with a breast pump or by a baby.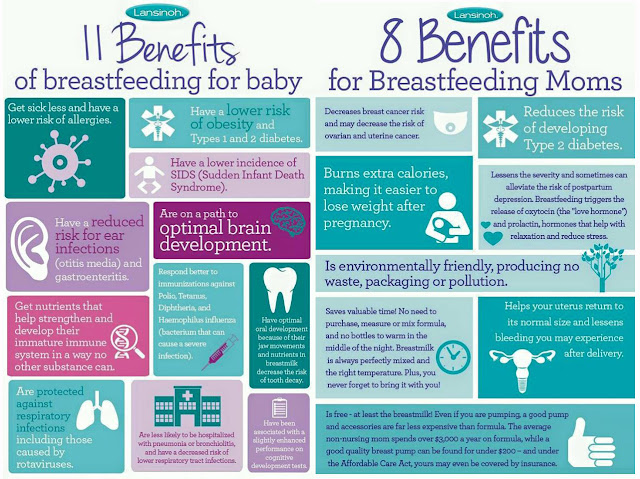 This is a complex process that involves working closely with a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
This is a complex process that involves working closely with a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
When do you lactate during pregnancy?
Lactation begins as early as a few weeks into the second trimester of your pregnancy. As estrogen and progesterone levels rise, your body prepares for lactation by increasing the number of milk ducts in your breasts, and those milk ducts will transport milk from the alveoli to your nipples. About midway through pregnancy, your body creates colostrum, which is your baby’s first milk.
Can you lactate when you’re not pregnant?
Yes, it’s possible to lactate if you’re not pregnant. Inducing lactation is a complex process that usually involves using hormone-mimicking drugs for several months to produce milk. The second part of lactation is expressing the milk through your nipple. Stimulation from infant suckling, pumping with a breast pump or hand-expressing signals the brain to release the milk. It’s common for people in this situation to receive assistance from a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
It’s common for people in this situation to receive assistance from a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
How do you stop lactation?
There are many reasons why you might need to stop producing milk, and you can stop lactating either naturally or with the help of hormonal drugs.
Natural milk suppression
Lactation is a supply-and-demand process. Your milk supply gradually goes down as your baby relies less on breast milk, or as you reduce the number of times you nurse or pump. Generally, if you decrease the volume of milk removed from your breasts, your body will slow milk production.
Suppressing your milk can feel uncomfortable and most people will become engorged (the term for overfilled breasts). You may also leak milk or develop a clogged milk duct. However, you can treat that pain by taking an over-the-counter pain reliever, wearing a firm bra or using an ice pack on your breasts.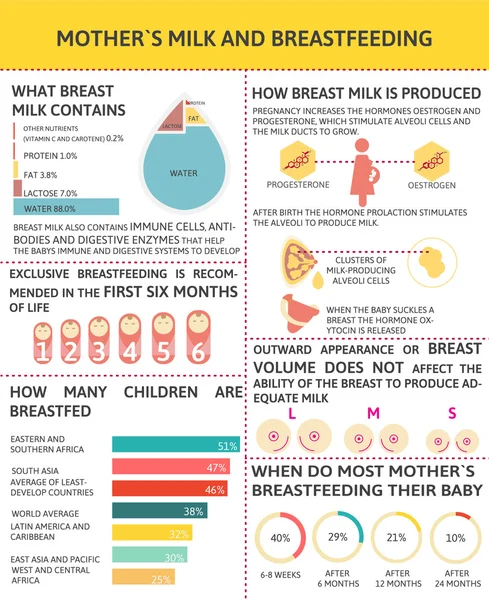
Medication suppression
Medications can also be an option if you need to stop producing milk. Your healthcare provider can explain more about lactation-suppressing drugs, as well as the benefits and possible side effects.
Anatomy
Where are the mammary glands located?
Mammary glands are commonly called breasts and both genders have them. They are located on your chest and are composed of connective tissue, fat and special glandular tissue that makes milk. A woman’s glandular tissue is slightly different because it contains the alveoli and lobules necessary for producing milk. Women also have much more glandular tissue.
Conditions and Disorders
What are common conditions that affect your ability to lactate?
The ability to lactate and the length of time you’re able to produce milk varies. Some can produce milk for years, while others have trouble producing enough milk for their baby.
Some common factors that can impact lactation or breastfeeding are:
- Hormonal levels and conditions.

- Medications.
- Undergoing radiation therapy in the past.
- Trauma to your breast or nipples.
- Breast augmentation, reconstruction or other breast surgeries.
- Other medical conditions like HIV infection.
- Use of drugs and alcohol.
If you’re nursing or pumping your milk to bottle-feed your baby, you should always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new medications or treatments. Many medications can pass to your baby through breast milk, which may have dangerous effects on your baby.
What is lactational amenorrhea?
Lactation amenorrhea (ah-men-oh-re-uh) means you aren’t menstruating (getting a period) due to lactation. When you’re lactating, your body produces prolactin, the hormone that produces milk. Prolactin reduces the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your body, which helps trigger the release of an egg during ovulation. If you aren’t producing enough LH, you can’t ovulate or get your period.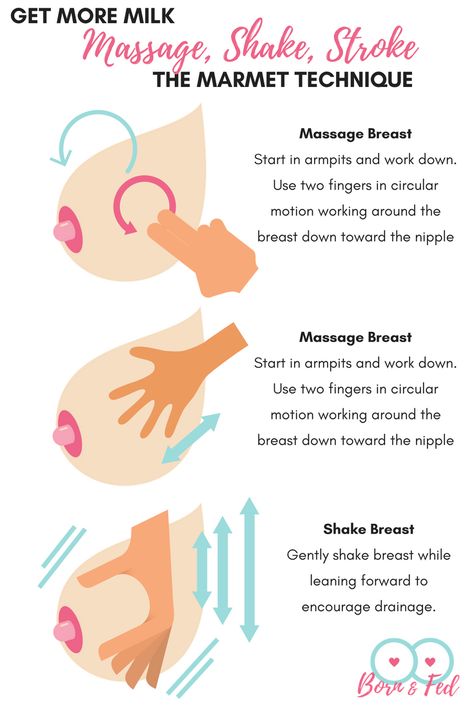 The length of time you can be amenorrheic due to lactation varies from a few months or until you’re completely done lactating.
The length of time you can be amenorrheic due to lactation varies from a few months or until you’re completely done lactating.
Does lactation reduce my risk of any diseases?
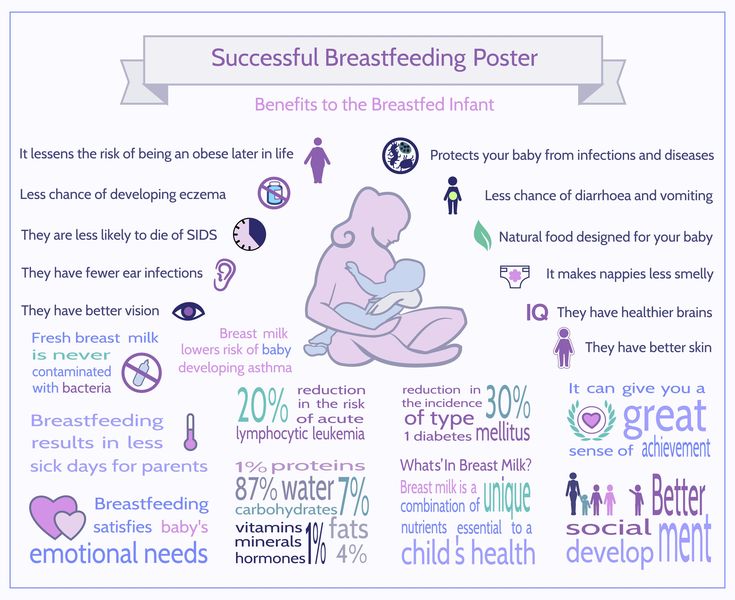
Studies have shown that breastfeeding reduces a woman’s risk of ovarian and breast cancers. It can also lower your risk for Type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure.
Care
How do you maintain milk production?
Maintaining lactation is mostly based on supply and demand. The more your baby breastfeeds or the more milk you express with a breast pump, the more your body will make. There are ways to suppress lactation with hormones or oral contraceptives. If you wish to maintain lactation, some things you should do are:
- Continue nursing on-demand or pump milk frequently (approximately every four hours).
- Eat a healthy diet with enough calories. Low-calorie diets can decrease milk supply.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. Human milk is primarily water.
- Avoid smoking, drugs or alcohol.
 These can reduce your supply and transfer to your milk.
These can reduce your supply and transfer to your milk.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between lactation and colostrum?
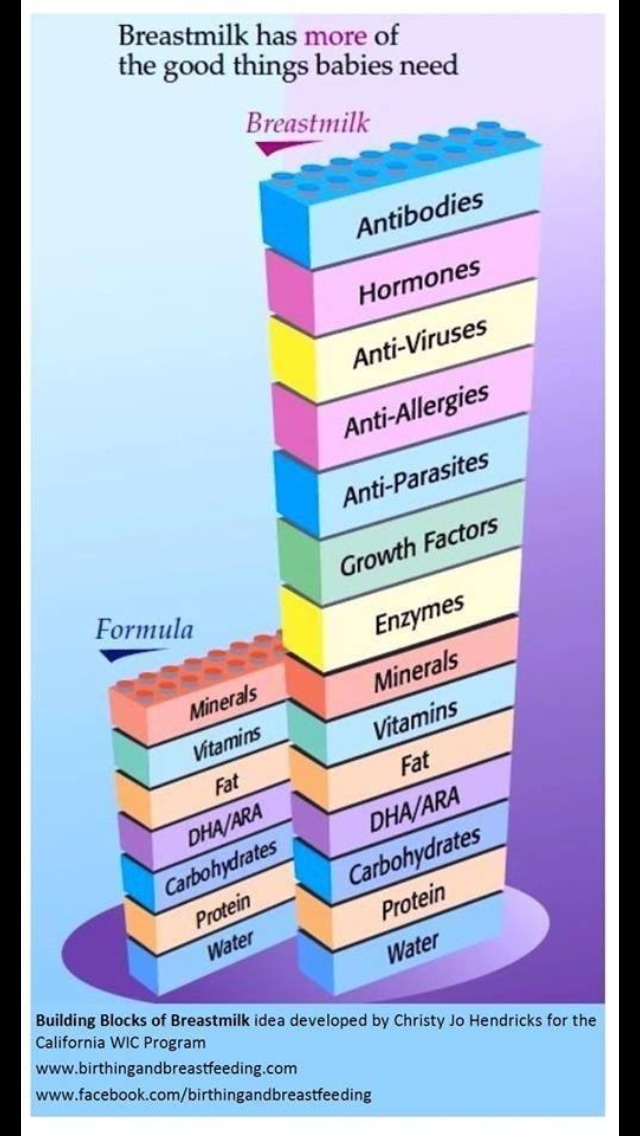
Lactation describes the process of making and secreting milk from your breast. Colostrum is the first milk your breasts create during lactation and the first milk your baby drinks. It’s thick, yellow and commonly called “liquid gold.” Colostrum is high in protein, minerals, vitamins and antibodies.
What is hormone therapy for inducing lactation?
Couples or families who wish to induce lactation, maybe because of adoption, surrogacy or other reasons, can try hormone therapy. Induced lactation means you’re creating a milk supply without being pregnant. It’s a process that involves taking estrogen and progesterone for several months to make your body believe it’s pregnant. This helps prepare your breasts for lactation. Some medications and herbs are believed to help establish a milk supply, too.
Several weeks before your baby arrives, begin pumping your breasts with a breast pump. This encourages your body to release prolactin, which produces milk. Ideally, you express your milk several times a day, just like you would if you had a baby. This helps establish a supply. You can also freeze any milk you produce for use once your baby arrives.
This encourages your body to release prolactin, which produces milk. Ideally, you express your milk several times a day, just like you would if you had a baby. This helps establish a supply. You can also freeze any milk you produce for use once your baby arrives.
If you’re considering this as an option, you should talk to your healthcare provider about your desire to feed your baby with human milk. Induced lactation works for many people, but not all.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you want to feed your baby human milk, it’s helpful to understand the process of lactation so you know what to expect. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to best prepare for nursing or expressing milk. Remember, lactation can look different for everyone depending on your circumstances and health history. If you struggle with lactation at any point, you may feel embarrassed or even ashamed. But struggling with lactation is very common, and lactation specialists and other healthcare providers can help you as you try to overcome these difficulties.
Causes & How It Works
Overview
Lactation is the process of making human milk. It's driven by hormones and results in milk coming from your nipple.What is lactation?
Lactation is the process of producing and releasing milk from the mammary glands in your breasts. Lactation begins in pregnancy when hormonal changes signal the mammary glands to make milk in preparation for the birth of your baby. It’s also possible to induce lactation without a pregnancy using the same hormones that your body makes during pregnancy. Lactation ends once your body stops producing milk.
Feeding your baby directly from your breasts is called breastfeeding (or sometimes chestfeeding) or nursing. You can also feed your baby milk that you have expressed or pumped from your breast and saved in a bottle.
Where does human milk come from?
Human milk comes from your mammary glands inside your breasts. These glands have several parts that work together to produce and secrete milk:
- Alveoli: These tiny, grape-like sacs produce and store milk.
 A cluster of alveoli is called lobules, and each lobule connects to a lobe.
A cluster of alveoli is called lobules, and each lobule connects to a lobe. - Milk ducts: Each lobe connects to a milk duct. You can have up to 20 lobes, with one milk duct for every lobe. Milk ducts carry milk from the lobules of alveoli to your nipples.
- Areola: The dark area surrounding your nipple, which has sensitive nerve endings that lets your body know when to release milk. To release milk, the entire areola needs stimulation.
- Nipple: Your nipple contains several tiny pores (up to about 20) that secrete milk. Nerves on your nipple respond to suckling (either by a baby, your hands or a breast pump). This stimulation tells your brain to release milk from the alveoli through the milk ducts and out of your nipple.
It helps to think of the lactation system as a large tree. Your nipple is the trunk of the tree. The milk ducts are the branches. The leaves are the alveoli.
Why do people lactate?
The primary reason people lactate is to feed a baby. Lactation is a biological, hormonal response that occurs during and after pregnancy to feed a newborn baby. Your body triggers specific hormones to initiate milk production and ejection (releasing of milk). All mammals lactate for this purpose and it’s possible to induce lactation in men and in non-pregnant women using the right hormone medications.
Lactation is a biological, hormonal response that occurs during and after pregnancy to feed a newborn baby. Your body triggers specific hormones to initiate milk production and ejection (releasing of milk). All mammals lactate for this purpose and it’s possible to induce lactation in men and in non-pregnant women using the right hormone medications.
Function
What triggers lactation?
A series of hormonal events, which begin when you’re pregnant, trigger the lactation process. That process is called lactogenesis.
Stage one lactogenesis: This begins around the 16th week of pregnancy and lasts until a few days after you give birth.
- Estrogen and progesterone rise and cause your milk ducts to grow in number and size. This causes your breasts to become fuller. Your mammary glands begin to prepare for milk production.
- Your nipples darken and your areolas become larger.
- Your Montgomery glands (small bumps on the areola) secrete oil to lubricate your nipple.

- Your body begins making colostrum. It’s highly nutritious and filling and serves as your baby’s first milk.
Stage two lactogenesis: This stage starts about two or three days postpartum (after giving birth). It’s when milk production intensifies.
- Once your baby and placenta are delivered, a sudden drop in your estrogen and progesterone causes the hormone prolactin to take over.
- Prolactin is the hormone that produces milk.
- You’ll notice your milk production increases dramatically at this stage. It’s often referred to as milk “coming in.”
- Your breasts are often engorged (or overly full of milk) to the point where they feel sore, painful or tender.
Stage three lactogenesis: This describes the rest of the time you lactate.
- Lactation generally continues as long as milk is removed from your breast.
- The more milk that’s removed, the more milk your body makes to replace it. Frequent feeding or pumping will cause your body to make more milk.

Hormones for lactation
The hormone prolactin controls the amount of milk you produce, and your body begins producing prolactin early in pregnancy. At first, the high levels of estrogen, progesterone and other pregnancy hormones suppress prolactin. Once you deliver the placenta, those pregnancy hormones drop and prolactin takes charge.
When your baby suckles, it stimulates nerves that tell your body to release prolactin and oxytocin. Prolactin causes the alveoli to make milk and oxytocin causes muscle contractions that push out of the alveoli and through the milk ducts.
When milk is released, it’s called a “letdown,” and it takes about 30 seconds of suckling before the letdown occurs. Because you can’t control which breast receives the hormones, the letdown can cause milk to drip from both nipples.
Inducing lactation in people who aren’t pregnant requires medication that mimics hormones your body makes during pregnancy. Suckling from the nipple can initiate lactation, either with a breast pump or by a baby.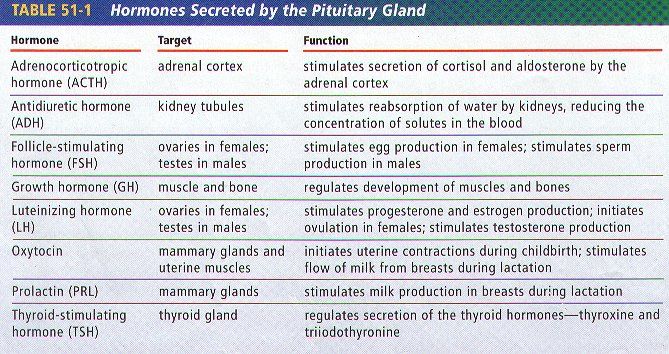 This is a complex process that involves working closely with a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
This is a complex process that involves working closely with a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
When do you lactate during pregnancy?
Lactation begins as early as a few weeks into the second trimester of your pregnancy. As estrogen and progesterone levels rise, your body prepares for lactation by increasing the number of milk ducts in your breasts, and those milk ducts will transport milk from the alveoli to your nipples. About midway through pregnancy, your body creates colostrum, which is your baby’s first milk.
Can you lactate when you’re not pregnant?
Yes, it’s possible to lactate if you’re not pregnant. Inducing lactation is a complex process that usually involves using hormone-mimicking drugs for several months to produce milk. The second part of lactation is expressing the milk through your nipple. Stimulation from infant suckling, pumping with a breast pump or hand-expressing signals the brain to release the milk.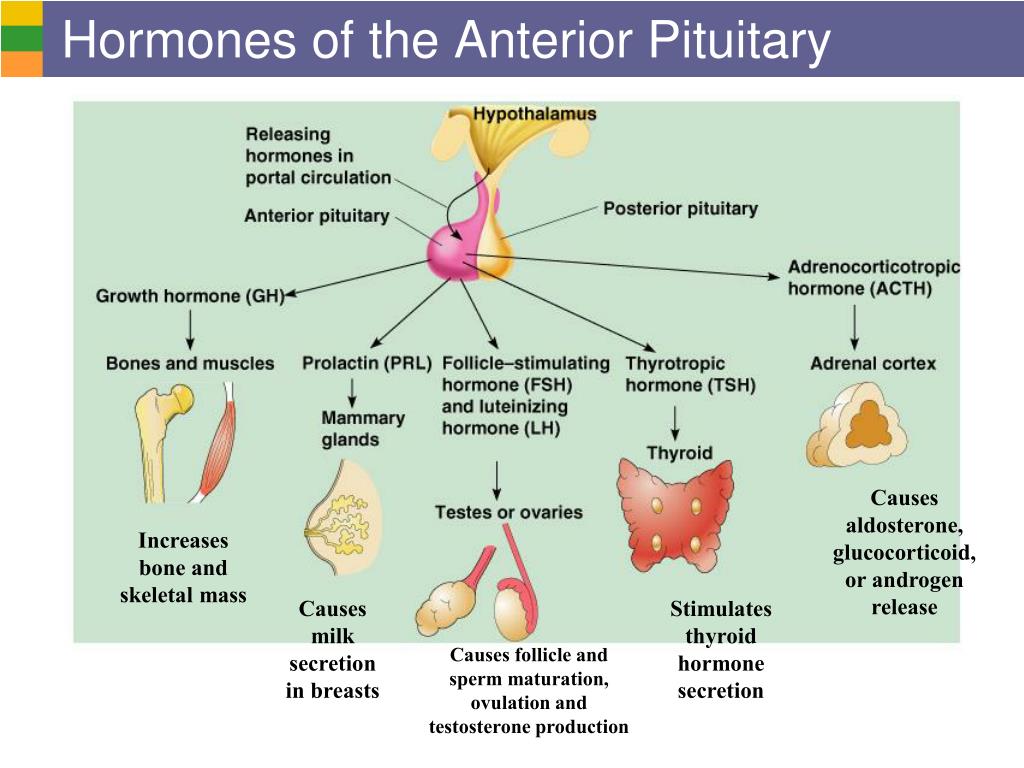 It’s common for people in this situation to receive assistance from a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
It’s common for people in this situation to receive assistance from a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
How do you stop lactation?
There are many reasons why you might need to stop producing milk, and you can stop lactating either naturally or with the help of hormonal drugs.
Natural milk suppression
Lactation is a supply-and-demand process. Your milk supply gradually goes down as your baby relies less on breast milk, or as you reduce the number of times you nurse or pump. Generally, if you decrease the volume of milk removed from your breasts, your body will slow milk production.
Suppressing your milk can feel uncomfortable and most people will become engorged (the term for overfilled breasts). You may also leak milk or develop a clogged milk duct. However, you can treat that pain by taking an over-the-counter pain reliever, wearing a firm bra or using an ice pack on your breasts.
Medication suppression
Medications can also be an option if you need to stop producing milk. Your healthcare provider can explain more about lactation-suppressing drugs, as well as the benefits and possible side effects.
Anatomy
Where are the mammary glands located?
Mammary glands are commonly called breasts and both genders have them. They are located on your chest and are composed of connective tissue, fat and special glandular tissue that makes milk. A woman’s glandular tissue is slightly different because it contains the alveoli and lobules necessary for producing milk. Women also have much more glandular tissue.
Conditions and Disorders
What are common conditions that affect your ability to lactate?
The ability to lactate and the length of time you’re able to produce milk varies. Some can produce milk for years, while others have trouble producing enough milk for their baby.
Some common factors that can impact lactation or breastfeeding are:
- Hormonal levels and conditions.
- Medications.
- Undergoing radiation therapy in the past.
- Trauma to your breast or nipples.
- Breast augmentation, reconstruction or other breast surgeries.
- Other medical conditions like HIV infection.
- Use of drugs and alcohol.
If you’re nursing or pumping your milk to bottle-feed your baby, you should always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new medications or treatments. Many medications can pass to your baby through breast milk, which may have dangerous effects on your baby.
What is lactational amenorrhea?
Lactation amenorrhea (ah-men-oh-re-uh) means you aren’t menstruating (getting a period) due to lactation. When you’re lactating, your body produces prolactin, the hormone that produces milk. Prolactin reduces the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your body, which helps trigger the release of an egg during ovulation. If you aren’t producing enough LH, you can’t ovulate or get your period.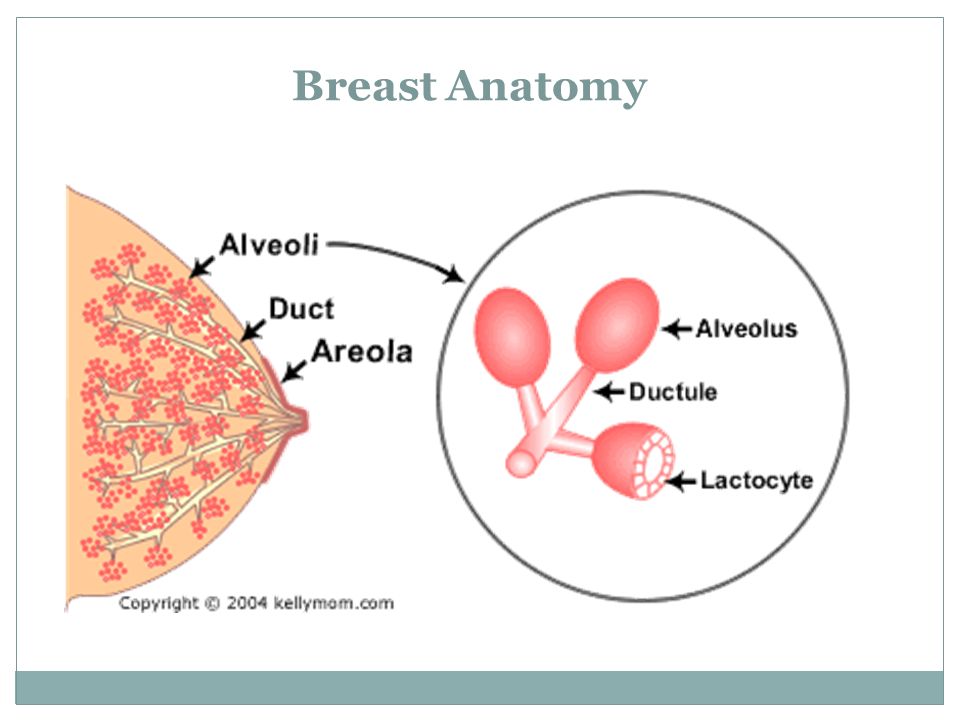 The length of time you can be amenorrheic due to lactation varies from a few months or until you’re completely done lactating.
The length of time you can be amenorrheic due to lactation varies from a few months or until you’re completely done lactating.
Does lactation reduce my risk of any diseases?
Studies have shown that breastfeeding reduces a woman’s risk of ovarian and breast cancers. It can also lower your risk for Type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure.
Care
How do you maintain milk production?
Maintaining lactation is mostly based on supply and demand. The more your baby breastfeeds or the more milk you express with a breast pump, the more your body will make. There are ways to suppress lactation with hormones or oral contraceptives. If you wish to maintain lactation, some things you should do are:
- Continue nursing on-demand or pump milk frequently (approximately every four hours).
- Eat a healthy diet with enough calories. Low-calorie diets can decrease milk supply.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. Human milk is primarily water.
- Avoid smoking, drugs or alcohol.
 These can reduce your supply and transfer to your milk.
These can reduce your supply and transfer to your milk.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between lactation and colostrum?
Lactation describes the process of making and secreting milk from your breast. Colostrum is the first milk your breasts create during lactation and the first milk your baby drinks. It’s thick, yellow and commonly called “liquid gold.” Colostrum is high in protein, minerals, vitamins and antibodies.
What is hormone therapy for inducing lactation?
Couples or families who wish to induce lactation, maybe because of adoption, surrogacy or other reasons, can try hormone therapy. Induced lactation means you’re creating a milk supply without being pregnant. It’s a process that involves taking estrogen and progesterone for several months to make your body believe it’s pregnant. This helps prepare your breasts for lactation. Some medications and herbs are believed to help establish a milk supply, too.
Several weeks before your baby arrives, begin pumping your breasts with a breast pump.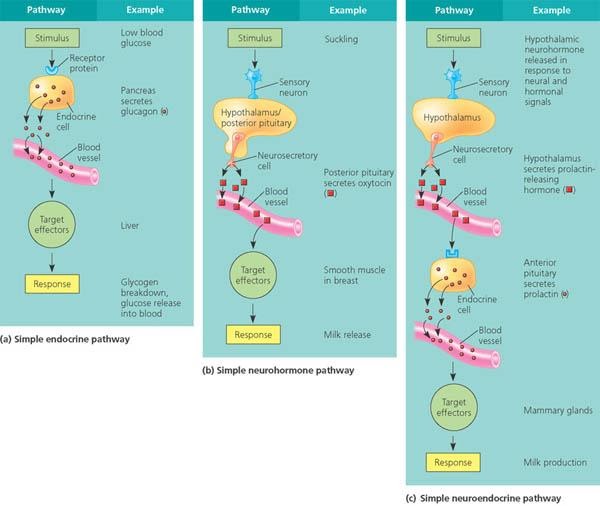 This encourages your body to release prolactin, which produces milk. Ideally, you express your milk several times a day, just like you would if you had a baby. This helps establish a supply. You can also freeze any milk you produce for use once your baby arrives.
This encourages your body to release prolactin, which produces milk. Ideally, you express your milk several times a day, just like you would if you had a baby. This helps establish a supply. You can also freeze any milk you produce for use once your baby arrives.
If you’re considering this as an option, you should talk to your healthcare provider about your desire to feed your baby with human milk. Induced lactation works for many people, but not all.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you want to feed your baby human milk, it’s helpful to understand the process of lactation so you know what to expect. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to best prepare for nursing or expressing milk. Remember, lactation can look different for everyone depending on your circumstances and health history. If you struggle with lactation at any point, you may feel embarrassed or even ashamed. But struggling with lactation is very common, and lactation specialists and other healthcare providers can help you as you try to overcome these difficulties.
How to increase your breast milk supply
WHO recommends that breastfeeding be continued for as long as possible and not stopped if difficulties arise (eg lactation crisis). To maintain lactation throughout the feeding period, it is necessary to properly and often attach the baby to the breast, follow a complete diet and avoid harmful foods. How to achieve sufficient milk production throughout the entire period of feeding - read in our material.
1. Your mental attitude
This is the first condition for stable milk production. The hormone prolactin is responsible for milk production, and the hormone oxytocin is responsible for its release from the breast. Prolactin is released in response to nipple stimulation (whether it's sucking or pumping). And the production of oxytocin is affected not only by the frequency and duration of breastfeeding, but also by the feelings and mood of the mother. A positive attitude and confidence in success is the key to successful breastfeeding. Remember that every woman has the opportunity to lay the foundation for the healthy development of her baby by breastfeeding him from birth.
Remember that every woman has the opportunity to lay the foundation for the healthy development of her baby by breastfeeding him from birth.
2. Attachment to the breast after birth
Placement of a healthy newborn baby on the mother's stomach immediately after birth and early attachment to the breast contributes to successful start breastfeeding.
3. Correct grip
It is important that feeding takes place in a comfortable environment. The baby should properly grasp the breast (his lips are twisted and capture the areola), and the mother should not experience pain during feeding.
4. Feeding on demand
Frequent breastfeeding from the first day promotes the production of breast milk in the required amount, prevents breast engorgement and promotes uterine contraction in the postpartum period.
5. Night feedings
Prolactin, which is responsible for milk production, peaks between 3-7 am. To ensure sufficient production of breast milk, it is necessary to put the baby to the breast at night and in the early morning. WHO medical experts recommend feeding your baby on demand at any time of the day.
To ensure sufficient production of breast milk, it is necessary to put the baby to the breast at night and in the early morning. WHO medical experts recommend feeding your baby on demand at any time of the day.
6. Healthy nutrition for a nursing mother
- The diet should be balanced and varied - include lean meats and fish, vegetables, fruits, cereals and dairy products in the diet.
- If your baby is at risk of developing allergies, follow a hypoallergenic diet for a breastfeeding mother.
- Eliminate foods that increase gas and the risk of digestive discomfort in the child. Temporarily limit the consumption of milk, caffeine, spicy, spicy, salty, pickled, smoked and canned foods
- Plentiful drink. Drink at least 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day: water, tea, compotes, fresh juices.
If you are having difficulty breastfeeding or are experiencing a lactation crisis, please contact your pediatrician, our specialist hotline, or a breastfeeding support group such as La Leche Liga Russia.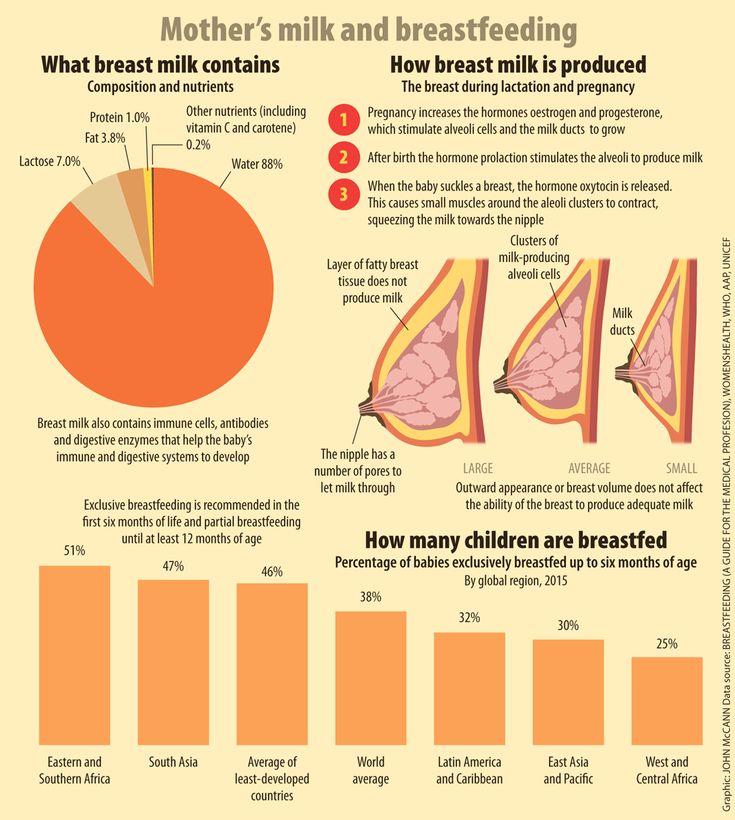
When using any materials from the site nutriclub.ru, a link to the site is required.
© Nutriclub, 2020
You will also be interested
- Nutriclub - healthy nutrition and child development
- 0-12 months
- Breast-feeding
- How to increase the amount of breast milk
Breast milk production | Baby's needs
Did you know that the amount of breast milk adapts to your baby's needs? In this article, you will learn amazing facts about breast milk production in the first days, weeks and months.
Share this information
Your body is able to produce breast milk according to your baby's needs at every stage of development. Understanding how milk production “turns on”, what happens to milk when you feed your baby, and why production adjusts to his needs as he grows, will help you start this amazing process in the right way.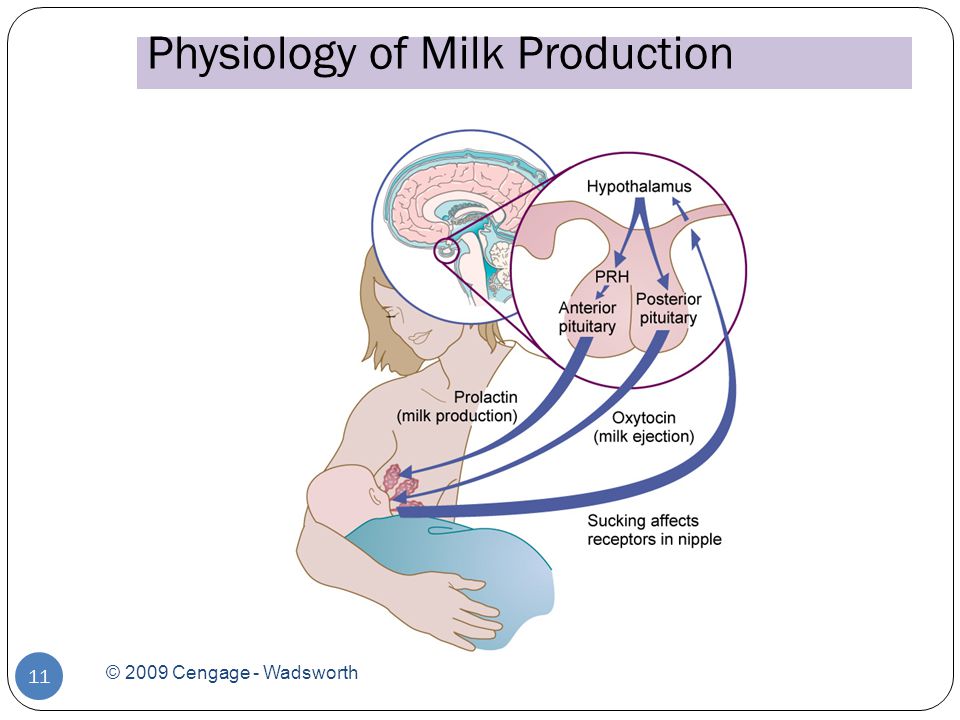
First day: milk production at birth
The baby is usually ready to breastfeed from birth. When he grabs the breast and begins to suck rhythmically, the milk-producing cells “turn on” and the formation of the first breast milk, colostrum, starts. 1 Try to feed your baby as much as possible in the first hour of his life, and then as soon as he shows interest in feeding. This will help lay the foundation for good milk production later on. 2
The first days: the arrival of milk
At this stage, the level of progesterone in your body decreases,
pregnancy hormone, which begins to fall after the placenta is released, and the hormones responsible for milk production, prolactin, insulin and hydrocortisone, are included in the work. These hormones will help start milk production. 3 Approximately on the third day of the baby's life, milk will begin to come in, and you will feel that the breast is full and has become noticeably firmer.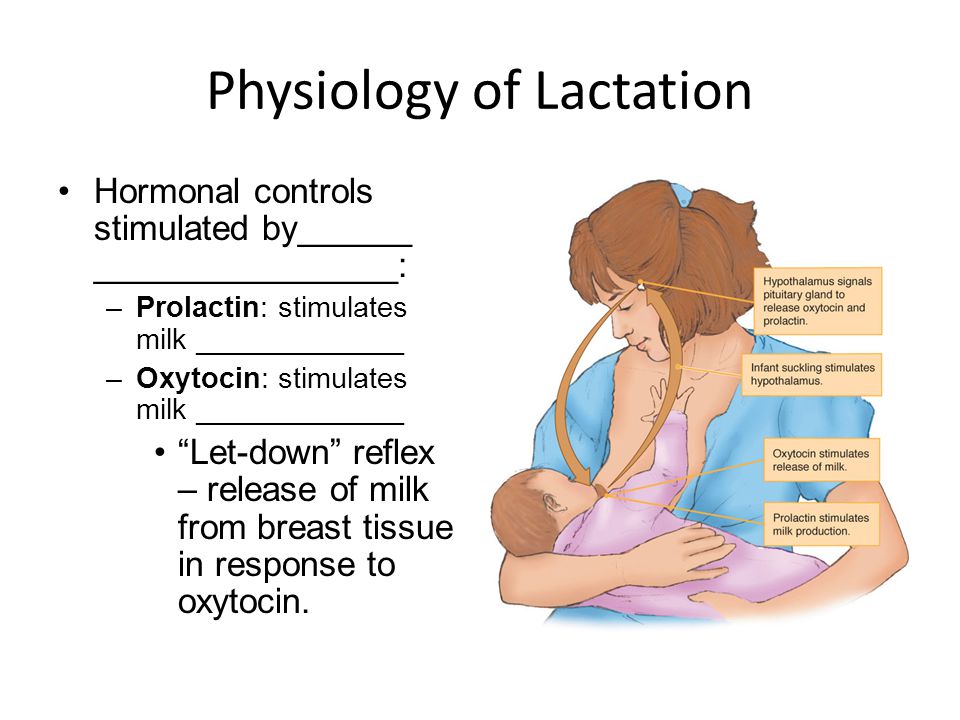 1
1
First month: shaping milk production
During the first weeks, your body will be especially sensitive to the amount of milk produced as it learns to produce the right amount. Prolactin levels increase dramatically each time you empty your breasts, thereby helping shape the lactation process. It also contributes to the maturation of your milk in terms of composition. At this stage, transitional milk is produced and the amount continues to grow. 3.4
For good long-term milk production, it is very important that you are close to your baby during the first few weeks. The more often you breastfeed, the more milk will be produced. This process resembles the law of supply and demand. Each time after emptying the breast, whether it is feeding the baby or pumping, even more milk will be produced.
Remember that it is normal for newborns to eat frequently, perhaps even every 45 minutes, and this does not mean that they are not getting enough milk.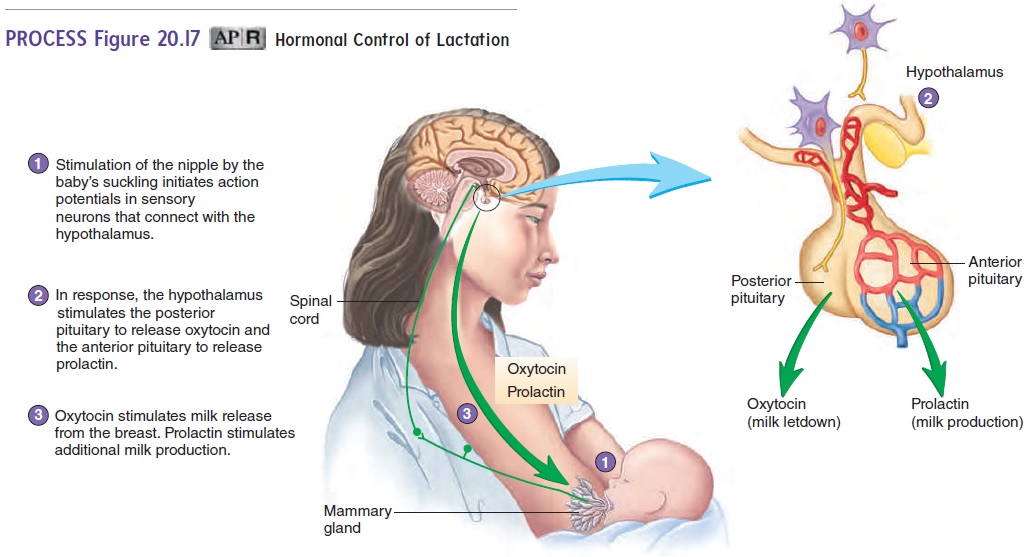 Frequent feedings help shape milk production, so feed your baby on demand, not on a schedule.
Frequent feedings help shape milk production, so feed your baby on demand, not on a schedule.
“In the first few weeks you may feel like you don’t have enough milk because your baby will be feeding all the time, but that’s okay,” says UK mom-of-two Jo, “We tend to think that the baby wants to eat every few hours, but that is not necessarily the case."
Don't forget that babies also breastfeed for comfort. Breastfeeding helps them calm down and adjust to their new life outside the womb. In addition, feeding helps to establish a connection between you.
Stable milk production in the first month
If you follow your baby's needs and feed him as often and for as long as he wants, milk production should adjust. 5
Some mothers try to increase the period between feedings so that the breasts can produce more milk during this time, but this should not be done, as this may have the opposite effect. 2
If you are unable to breastfeed directly for the first two weeks, express your milk to build and maintain your milk supply during this critical period and beyond.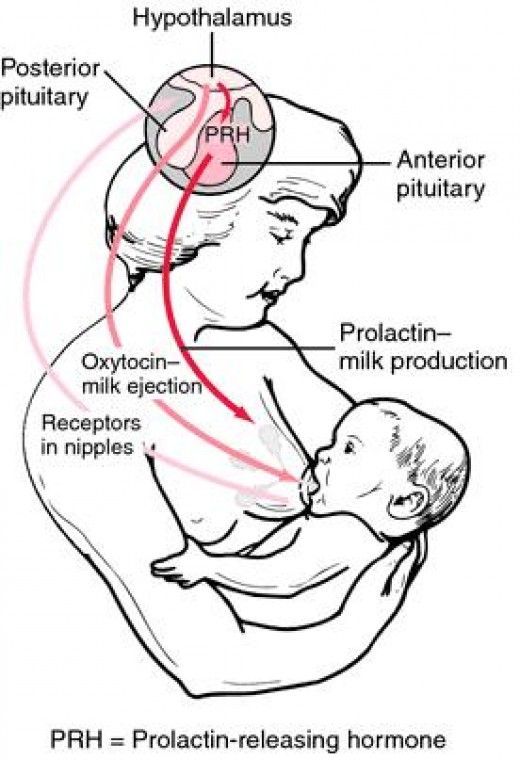
Did you know that feeding your baby extra formula unnecessarily can reduce your milk production? The chest will not receive a signal to increase production, because it will not be emptied. In addition, if the baby sleeps longer after formula, he may miss his usual next feeding time.
This is a kind of “supplementing trap”. After three to four days of formula supplementation, during which the breasts have emptied less, the body will receive a signal that breastfeeding has stopped, and the amount of milk produced will begin to decrease. As a result, the baby will remain hungry and will need additional formula supplementation. And so on in a circle ... As a result, this will lead to really low milk production, and the baby will eat mainly the mixture.
Breast milk production after six weeks
After a month of breastfeeding, post-feeding spikes in prolactin secretion begin to decrease, milk matures, and the body gets used to producing as much milk as your baby needs.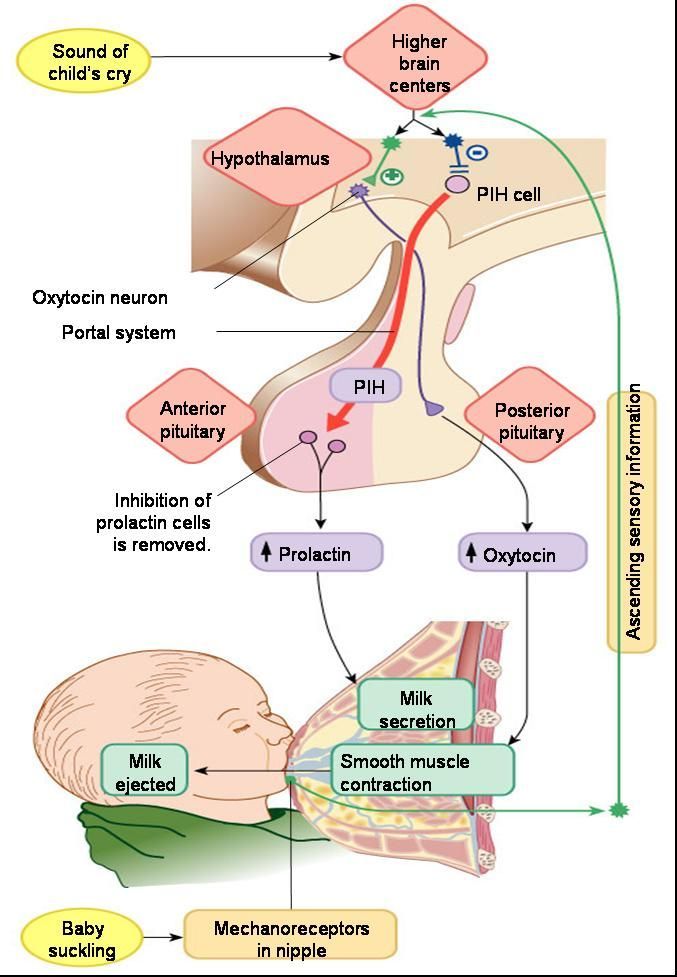 In fact, the chest begins to work "on autopilot." 4 You may also notice at this time that your breasts are softer and your milk flow has stopped.
In fact, the chest begins to work "on autopilot." 4 You may also notice at this time that your breasts are softer and your milk flow has stopped.
At this stage, women often have fears of "losing milk".
However, this only means that milk production has been established and now fully meets the needs of the child. It is noteworthy that although the baby continues to grow, he will consume approximately the same amount of milk both at six weeks and at six months. You may notice that the baby began to suckle the breast longer, but less often. On some days he may eat a little less than usual - his appetite changes in the same way as an adult.
Now your body will produce exactly the amount of milk,
as much as your baby needs. Therefore, the more milk the baby drinks (or you express), the more milk will be produced.
How does this happen? The reason for this is thought to be the so-called "feedback lactation inhibitor" that controls milk production.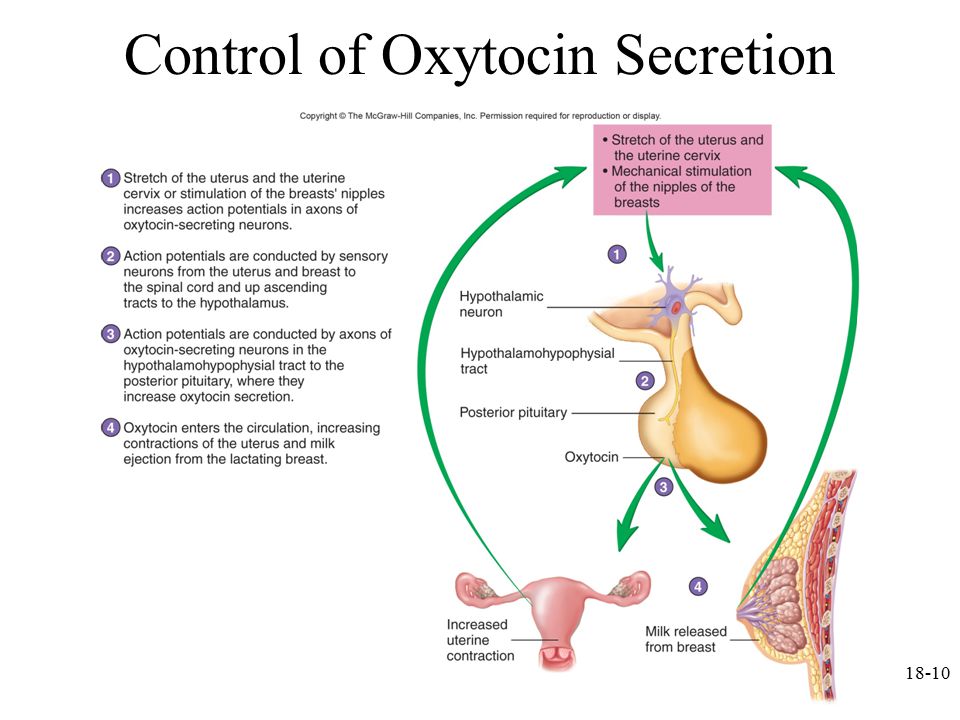 The more milk in the breast, 2 the higher the inhibitor level, so a full breast produces less milk than one that has been emptied.
The more milk in the breast, 2 the higher the inhibitor level, so a full breast produces less milk than one that has been emptied.
What is the rate of milk production?
Mothers often worry about their milk supply and think about how to increase it. However, if the baby is healthy and growing well, problems usually do not arise.
“I was worried that my newborn daughter was not getting enough milk as she was feeding very quickly and always from one breast even though I offered both,” says Marjorie, mother of two in the UK, “But when I pumped from using a breast pump, I was surprised at how much milk I produced, and calmed down. I just had to keep feeding her little and often.”
Keep in mind, however, that not all mothers are able to express a lot of milk right away. You can also try hand expressing milk and see if there is a change in breast fullness.
If you're worried about your milk supply, read our tips for symptoms of too little or too much milk.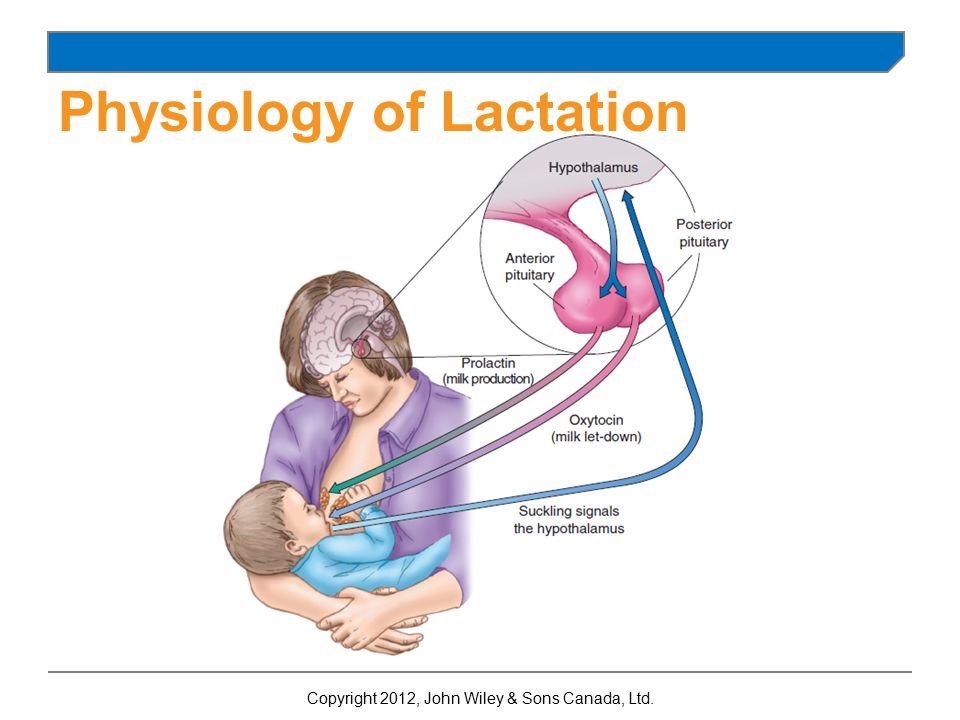
Literature
1 Pang WW, Hartmann PE. Initiation of human lactation: secretory differentiation and secretory activation. J9 Gland Biol Neoplasia . 2007;12(4):211-221. - Pang, W.W., Hartmann, P.I., "Lactation initiation in the lactating mother: secretory differentiation and secretory activation." G Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(4):211-221.
2 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". G Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
3 Ostrom KM. A review of the hormone prolactin during lactation. Prog Food Nutr Sci .