Weight gain with twins
Moderate weight gain may be healthiest in twin pregnancies
By Carolyn Crist
4 Min Read
(Reuters Health) - Pregnant women may be “eating for two” - or more - but when it comes to twin pregnancies, gaining too much weight may be as bad as gaining too little, a U.S. study suggests.
There isn’t a lot of evidence for an ideal amount of weight gain in a twin pregnancy, the study team writes in Obstetrics & Gynecology. But in a large analysis of twin pregnancies, they found that both very high and very low weight gain was associated with more preterm births and infant death.
Gaining too little weight was also linked with having babies that were small for their gestational age, and gaining too much was tied to overly-large babies and cesarean deliveries.
“Twin pregnancies have high rates of complications, so it is important to identify factors that we can modify during pregnancy to lessen these risks,” said Lisa Bodnar of the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania, who led the study.
During the past 40 years, the number of twins born in the U.S. has doubled, Bodnar noted, and twins account for about 3% of births but more than 20% of preterm births. Women carrying twins are also more likely to experience diabetes, preeclampsia and cesarean deliveries.
The National Academy of Medicine recommends that women who are normal-weight or underweight gain 17-25 kilograms (37-55 pounds) during a twin pregnancy, and that overweight women gain no more than 11-19 kg (24-42 lbs).
“We’ve known for a long time that twin pregnancies carry a much higher risk of poor outcomes, and weight gain is a very common conversation for a pregnant woman and her doctor to have,” Bodnar told Reuters Health by email. “However, the lack of evidence on what that optimal range is left women and their doctors to make educated guesses or not to discuss weight gain at all.”
Bodnar and colleagues analyzed data from nearly 55,000 twin births in Pennsylvania from 2003 to 2013. Small-for-gestational-age and preterm birth before 32 weeks were most common among women who were underweight before pregnancy, they found. And large-for-gestational-age birth and cesarean delivery were more common with higher pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI, a measure of weight relative to height).
And large-for-gestational-age birth and cesarean delivery were more common with higher pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI, a measure of weight relative to height).
For normal-weight women, pregnancy weight-gain also appeared to influence risk. For example, compared with a weight gain of 20 kg, or about 44 lbs, a gain of 27 kg, or 60 lbs, was associated with 2.2 fewer cases of small-for-gestational-age but 2.9 more cases of large-for-gestational-age and 3.7 more cases of cesarean delivery.
Over the study period, weight gains in nearly one in three women fell outside the National Academy of Medicine guidelines, the authors note.
“We are not saying that gaining within the weight ranges identified by our study is necessarily best for the health of the mother and her babies, but simply that gaining above or below them carries greater risk of poor health,” Bodnar said. “Ongoing conversation between a patient and her obstetrician about weight gain while pregnant is an important part of prenatal care. ”
”
Researchers are still trying to find the optimal range, especially as obesity increases nationwide, which underscores the importance of nutrition and gestational weight gain, said Dr. Roger Newman of the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“There is nothing that a mother can do to help ensure a happy outcome of her twin or triplet pregnancy that is more important than achieving an optimal nutritional balance and gestational weight gain,” said Newman, who co-authored the book “When You’re Expecting Twins, Triplets or Quads.”
“Many women are afraid to gain the amount of weight advised and are resistant,” he said by email. “Evidence shows that if a woman does not over-gain recommended weight, then she will lose that weight as well as (after) a singleton pregnancy.”
SOURCE: bit.ly/2Pc9OIs Obstetrics & Gynecology, online October 8, 2019.
Twin Pregnancy Weight Gain
Created by Łucja Zaborowska, MD, PhD candidate
Reviewed by Rijk de Wet
Based on research by
Institute of Medicine Recommendations “Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines“ (2009)
Last updated: Oct 22, 2022
Table of contents:- Why do you gain weight during pregnancy?
- Guidelines for twin pregnancy weight gain
- More about pregnancy with twins or multiples
The maternal weight gain in twin pregnancies has its own rules that are a bit different from singleton pregnancies. Let's find out how much weight you should gain every week, how to keep yourself healthy carrying two or multiple babies, and discover the most significant differences in pregnancy weight gain in different types of gestations.
Let's find out how much weight you should gain every week, how to keep yourself healthy carrying two or multiple babies, and discover the most significant differences in pregnancy weight gain in different types of gestations.
💡 This article is a part of a bigger series, based on our pregnancy weight gain calculator.
We try our best to make our Omni Calculators as precise and reliable as possible. However, this tool can never replace a professional doctor's assessment. If any health condition bothers you, consult a physician.
Why do you gain weight during pregnancy?
Gestational weight gain is a must when it comes to pregnancy — your entire body is changing to support a baby growing inside of you. The amount of weight you gain depends not only on your baby's birth weight or the number of children you're carrying; all parts of your body need to adjust to this new situation:
- Your breasts and uterus both grow 2 lb.

- Your blood increases its volume by 50%.
- Your body accumulates water and starts producing amniotic fluid.
- A new organ is created — a 1.5 lb placenta!
If you're pregnant with twins, the situation's a little bit different. If all the babies have separate placenta, each one of them is on average 17% smaller. The difference grows to 24% in tripleton pregnancies. - A lot of extra fat tissue. It serves as a source of ingredients for pregnancy hormones production.
These values are usually different for singleton and twin pregnancies — women carrying twins and multiple pregnancies are expected to hold even more considerable weight.
Guidelines for twin pregnancy weight gain
As we've already mentioned in multiple articles, the expected weight gain during pregnancy depends on your pre-pregnancy weight and height, computed into BMI (body mass index):
BMI=weight [kg](height [m])2\text{BMI} = \frac{ \text{weight [kg]} }{ (\text{height [m]})^2 }BMI=(height [m])2weight [kg]
As you may expect, these values are slightly higher for women with twin pregnancies. After all, you're carrying two souls under your heart! 👶👶
After all, you're carrying two souls under your heart! 👶👶
Here's the chart of weight gain recommendations for twin pregnancies:
- Underweight (BMI <18.5)
- Expected weight gain: 28–40 pounds (12.7–18.1 kg)
- Normal weight (BMI 18.5–24.9)
- Twin pregnancy expected weight gain: 37–54 pounds (16.8–24.5 kg)
- Overweight (BMI between 25 and 29.9)
- Twin pregnancy expected weight gain: 31–50 pounds (14–22.7 kg)
- Obese (BMI over 30)
- Twin pregnancy expected weight gain: 25–42 pounds (11.3–19 kg)
Some studies estimate that the weekly weight gain while pregnant with twins should be close to approximately 0.75 kg (1.5 lb) during pregnancy's second and third trimesters. However, every pregnancy and every woman is different — talk to your health care provider about your individual, healthy weight range.
Remember that excessive gestational weight gain may harm pregnancy outcomes! Weight gain during twin pregnancies is twice as significant. These gestations are already considered high risk or very high risk, depending on the chronicity, which is the number of placentas in the womb.
💡 Dichorionic (two placentas) twin pregnancies are the safest and most common type.
Possible threats for obese and overweight women include preterm birth (already increased in twins) and an even greater risk of preeclampsia.
What about low gestational weight?
Lower weight gain in twin pregnancies is associated with a higher incidence of low birth weight and an even greater risk of anemia.
→Check the birth weight percentile calculator to find out more.
More about pregnancy with twins or multiples
As we already know, an average woman gains around 30–50 pounds when pregnant with twins. What about multiple pregnancies? It is estimated that every additional fetus adds another 10 pounds (4.5 kg).
What about multiple pregnancies? It is estimated that every additional fetus adds another 10 pounds (4.5 kg).
-
Normal-BMI women with twins should eat around 30–45 kcal/kg extra each day.
-
Some sources recommend increasing the daily intake by:
- 300 kcal per baby in the 1st semester;
- 340 kcal per baby in the 2nd semester; and
- 452 kcal per baby in the 3rd semester.
-
Keep a maternal weight gain record — step on a scale once a week at the same time of the day and write it all down.
-
It is essential to recognize multiple and singleton pregnancies early on. If you're pregnant with twins, but don't know it yet, you may needlessly worry about your "excessive" weight gain and try to impose some interventions that are not needed at all.

-
Try to exercise as long as you can — walk at least 150 minutes per week.
-
Fill your diet with proteins, vitamins, dairy products, and wholemeal products.
-
Maximize your calcium intake. Pregnancy may have a significant impact on your bones and teeth.
-
Increase your folic acid intake.
Łucja Zaborowska, MD, PhD candidate
Before pregnancy
Height
Weight
You are...
Weight during pregnancy
Min. weight
Max. weight
Min. weight gain
Max. weight gain
Check out 32 similar fertility & pregnancy calculators 🤰
BBTBirth controlBishop score… 29 more
Pregnant twins need to carefully monitor nutrition
- Login
- Registration
Login via:
Login
Password
Remember me
Forgot your password?
Registration with:
Login
Password
Confirm password
By registering on the site or logging in through social networks, you accept the terms of the User Agreement, including the terms of the Privacy Policy.
Receive the most interesting from our site by mail (we promise not to spam)
Pregnant women can "eat for two", but when it comes to the fact that a woman will soon become a mother of twins, gaining too much body weight is just as bad as too little. A large-scale study of expectant mothers was published in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology, including scientists sorted out what should be the weight gain in expectant mothers of twins.
The authors analyzed data on 55,000 twin births in Pennsylvania, USA, from 2003 to 2013. They found that very large and small weight gains are associated with premature birth and infant death. nine0046 Too little weight gain has also been associated with babies who were underweight for their fetal age. And too big - with a mass of fruits above the norm and their birth by caesarean section.
“Twin pregnancy is often accompanied by complications, so it is important to identify factors that we can change during pregnancy to reduce these risks. Over the past 40 years, the number of twins born in the United States has doubled, and such births account for about 3% of births and more than 20% of premature outcomes. Women who are pregnant with two fetuses are more likely to suffer from gestational diabetes and preeclampsia, and delivery by cesarean section, ”said study leader Lisa Bodnar from the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania. nine0046 The US National Academy of Medicine recommends that normal or underweight women who are pregnant with twins should gain up to 17–25 kg, and those who are overweight, no more than 11–19 kg during pregnancy.
The authors note that during the study period, weight gain in almost one in three women was outside the guidelines of the National Academy of Medicine. The results of the study show that weight gain above or below these limits carries a greater risk of complications. Advice on weight gain during pregnancy should be an important part of antenatal care. nine0046 “The best thing a mother can do to give birth to healthy twins or triplets is to achieve the optimal balance of nutrition and normal weight gain during pregnancy,” said Dr. Roger Newman of the Medical University of South Carolina at Charleston, co-author of the book When You Expect Twins, triplets or quadruplets.
Advice on weight gain during pregnancy should be an important part of antenatal care. nine0046 “The best thing a mother can do to give birth to healthy twins or triplets is to achieve the optimal balance of nutrition and normal weight gain during pregnancy,” said Dr. Roger Newman of the Medical University of South Carolina at Charleston, co-author of the book When You Expect Twins, triplets or quadruplets.
Source: Medscape.
To leave a comment - you must be an authorized user
nine0000 Height and weight gain for children of the first year of life. Tables Dear parents, your baby is growing and you are worried about whether he is gaining enough weight and height. For control, there are centile tables for assessing the physical development of children, weight and height indicators. At the same time, you must remember that each baby is individual, he cannot grow according to the textbook. These weight and height recommendations are based on an average number of children and 10% deviation is normal. In addition, the centile corridor from 25% to 75% is an average physical indicator. That is why they say: Physical development is mesosomatic, macrosomatic, microsomatic. nine0009
In addition, the centile corridor from 25% to 75% is an average physical indicator. That is why they say: Physical development is mesosomatic, macrosomatic, microsomatic. nine0009
It is important that the weight and height indicators are in the same centile corridor, but no more than two adjacent ones. Then we can talk about harmonious development. If the gap is more than two centile corridors, the development is disharmonious. Then we can think either about an unbalanced diet or about a pathology associated with obesity (paratrophy), or protein-energy deficiency (hypotrophy). In addition, one should not forget about the constitutional characteristics of the child, about genetic predisposition. Therefore, in no case should you compare your child with a neighbor's. To talk about the health of a child, we evaluate his condition according to many criteria. This is neuropsychic development, laboratory examination data, anamnesis, heredity. How many times in my practice have I met children who gained 400-450 g in weight every month, by the year they barely gained 7. 8-8 kg. But at the same time, children already at 10 months began to walk, pronounce syllables, and follow complex instructions. nine0009
8-8 kg. But at the same time, children already at 10 months began to walk, pronounce syllables, and follow complex instructions. nine0009
We'll talk about weight and height gain for term babies. In preterm infants, rates of weight gain and height differ according to the degree of prematurity. In addition, children can be born with intrauterine malnutrition.
The tables for girls and boys are different in terms of numerical indicators, but at 1 year of age, these differences are quite minimal.
Centile tables for assessing the physical development of girls from 0 to 12 months. nine0009
| Body length (height), cm. Centiles in % | Age in months | Body weight, kg. Centiles in % | ||||||||||||
| 3 | nine0008 10 | 25 | fifty | 75 | 90 | 97 | 3 nine0009 | 10 | 25 | fifty | 75 | 90 | 97 | |
nine0008 45.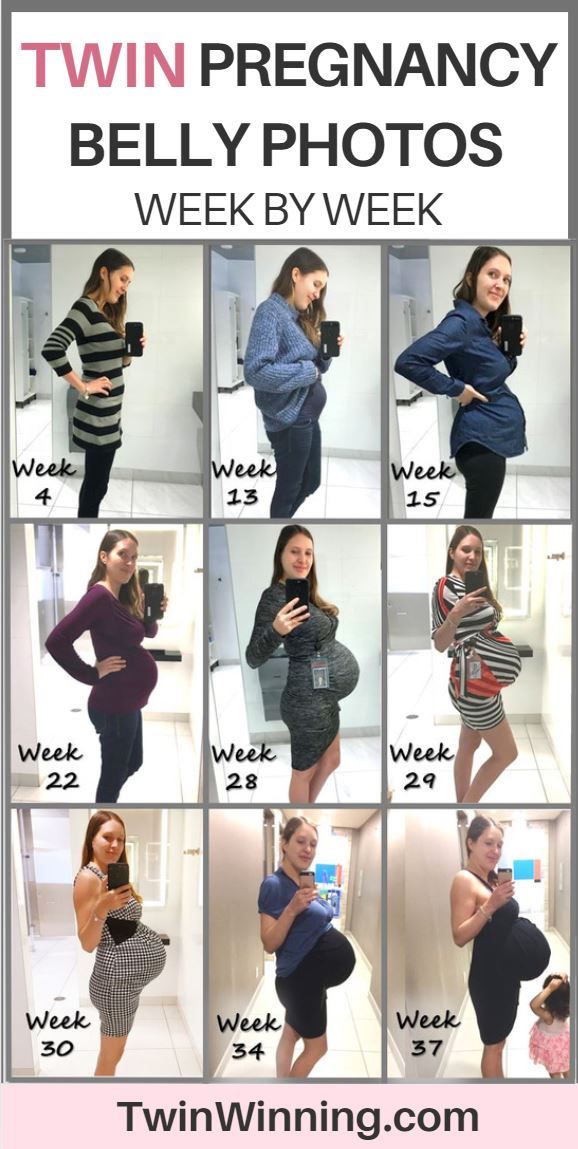 8 8 | 47.5 | 49.8 | 50.7 | 52.0 | 53.1 | 53.9 nine0077 | 0 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 4.1 |
| 48.5 | 50.3 | 52.1 | 53.5 | 55.0 | nine0078 57.3 | one | 3.3 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 4.2 nine0009 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 5.1 | |
| 51.2 | 53.3 | 55.2 | nine0078 58.0 | 59.3 | 60.6 | 2 | 3.8 | 4.2 nine0009 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.9 | |
| 54.0 | nine0008 56.2 | 57.6 | 59.3 | 67.7 | 61.8 | 63.6 | 3 nine0077 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 6.7 nine0009 |
| 56.7 | 58.4 | 60.0 | 61.2 | 62.8 | 64.0 | nine0078 4 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 6.2 | 6.6 nine0009 | 7.0 | 7.5 | |
| 59.1 | 60.8 | 62.0 | 63.8 | nine0078 66.0 | 68.0 | five | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.3 nine0009 | 6.7 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.1 | |
| 60.8 | 62.5 | nine0078 65.5 | 67.1 | 68.8 | 70.0 | 6 | 5.9 nine0009 | 6. | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 8.7 | |
| nine0008 62.7 | 64.1 | 65.9 | 67.5 | 69.2 | 70.4 | 71.9 nine0077 | 7 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.3 |
| 64.5 | 66.0 | 67.5 | 69.0 | 70.5 | nine0078 73.7 | eight | 6.7 | 7.2 | 7.6 | 8.2 nine0009 | 8. | 9.3 | 9.7 | |
| 66.0 | 67.5 | 69.1 | nine0078 72.0 | 74.1 | 75.5 | nine | 7.1 | 7.5 nine0009 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 9.2 | 9.7 | 10.1 | |
| 67.5 | nine0078 70.3 | 71.9 | 73.2 | 75.3 | 76.8 | 10 nine0009 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.1 | nine0008 10.5 | |
| 68. | 70.1 | 71.5 | 73.0 | 74.7 | 76.5 nine0009 | 78.1 | eleven | 7.7 | 8.3 | 8.7 | 9.3 | nine0008 9.9 | 10.5 | 10.9 |
| 70.1 | 71.4 | 72.8 | 74.1 nine0009 | 75.8 | 78.0 | 79.6 | 12 | 8.0 | 8.5 | nine0008 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.2 | 10.8 | 11.3 |
At the same time, until the age of three months, the child adds 20-30 grams per day daily, respectively, from 140 to 200 per week. If we talk about the average weight gain by months, then it is only 600 g per month, since the child after birth has physiological weight loss (with urine, feces, transition from intrauterine feeding to breastfeeding during the adaptation period), approximately 10% of the weight, which is 200-300 grams. nine0009
If we talk about the average weight gain by months, then it is only 600 g per month, since the child after birth has physiological weight loss (with urine, feces, transition from intrauterine feeding to breastfeeding during the adaptation period), approximately 10% of the weight, which is 200-300 grams. nine0009
More often, by 3-4 days, the child restores its original weight, and then there is an increase. But I had a case in practice when the child began to gain weight from the 20th day of life, while the girl was active, reflexes were alive, her appetite was good, she could withstand the night interval, stool 4-5 times a day, urination was sufficient, developed according to age. Therefore, do not worry. Our indicator is the well-being of the child. If the baby is active, eats with appetite, sleep is calm, the skin is clean, physiological functions are not disturbed, be calm, your baby is healthy and not hungry. You see from the table the range of weight per year is from 8 to 13 kg. This is the norm. There is no reason to run to the endocrinologist, genetics, to examine the child. nine0009
This is the norm. There is no reason to run to the endocrinologist, genetics, to examine the child. nine0009
Or the opposite situation: in the first months of life, a child gains 1-1.5 kg while breastfeeding. If the baby does not have colic, he does not spit up, there are no gastrointestinal manifestations, he is active, the skin is clean, physiological functions are not disturbed - this is also the norm. Remember, as often happens, premature babies quickly gain weight and catch up with their peers by the year. And large babies gain weight more slowly. In my entire thirty-year practice, only two children weighed 14-15 kg by the year, although their parents were large and tall. By the age of three, they weighed almost the same, added only in height, the rest of their peers caught up with them. nine0009
| Month | Weight gain in grams |
| one | 600.0 |
| 2 | 800. |
| 3 | 800.0 |
| 4 | 750.0 |
| five | 700.0 nine0077 |
| 6 | 650.0 |
| 7 | 600.0 |
| eight | 550.0 | nine0088
| nine | 500.0 |
| 10 | 450.0 |
| eleven | 400.0 |
| 12 | 350.0 |
It is believed that by 4-4.5 months the child should double the weight, and triple by the end of the year.
It happens that the increase in height and weight goes in leaps, seasonality, unevenness, and sometimes asymmetry of growth are noted. Pediatricians are concerned about the circumference of the head and chest, by 2-3 months they should be equal. Further, the breast grows faster. This is important so as not to miss the pathology. nine0009
Pediatricians are concerned about the circumference of the head and chest, by 2-3 months they should be equal. Further, the breast grows faster. This is important so as not to miss the pathology. nine0009
The younger the child, the faster his growth. In the first 3 months of life, body length increases by 3 cm monthly, in the second quarter by 2.5-2 cm monthly. In the third - 1.5-2 cm, in the fourth - 1 cm monthly. The total increase in height in the first year of life is about 25 cm.
Centile tables for assessing the physical development of boys from 0 to 12 months.
| Body length (height), cm. nine0009 Centiles in % | Age in months | Body weight, kg Centiles in % | ||||||||||||
| 3 | 10 | 25 nine0009 | fifty | 75 | 90 | 97 | 3 | 10 nine0077 | 25 | fifty | 75 | 90 | 97 | |
| 46. | 48.0 nine0009 | 49.8 | 51.3 | 52.3 | 53.5 | 55.0 | 0 | nine0008 2.7 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 4.4 nine0077 |
| 49.5 | 51.2 | 52.7 | 54.5 | 55.6 | 56.5 | nine0008 57.3 | one | 3.3 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 4.3 | 4.7 | nine0078 5.4 | |
| 53.6 | 53.8 | 55.3 | 57. | 58.2 nine0009 | 59.4 | 60.9 | 2 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 4.6 | nine0008 5.1 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.4 |
| 55.3 | 56.5 | 58.1 nine0009 | 60.0 | 60.9 | 62.0 | 63.8 | 3 | 4.5 | nine0008 4.9 | 5.3 | 5.8 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 7.3 |
| 57.5 | 58.7 | 60.6 | 62.0 | 63.1 | 64.5 | 66. | nine0008 4 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 7.2 | 7.6 | nine0078 |
| 59.9 | 61.1 | 62.3 | 64.3 | 65.6 | 67.0 nine0009 | 68.9 | five | 5.6 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.1 | nine0008 7.8 | 8.3 | 8.8 |
| 61.7 | 63.0 | 64.8 | 66.1 nine0009 | 67.7 | 69.0 | 71.2 | 6 | 6.1 | 6. | nine0008 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.4 | 9.0 | 9.4 |
| 63.8 | 65.1 nine0009 | 66.3 | 68.0 | 69.8 | 71.1 | 73.5 | 7 | nine0008 6.6 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 9.9 nine0077 |
| 65.5 | 66.8 | 68.1 | 70.0 | 71.3 | 73.1 | nine0008 75.3 | eight | 7.1 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 9. | nine0078 10.5 | |
| 67.3 | 68.2 | 69.8 | 71.3 | 73.2 nine0009 | 75.1 | 75.5 | nine | 7.5 | 7.9 | 8.4 | nine0008 9.1 | 9.8 | 10.5 | 11.0 |
| 68.8 | 69.1 | 71.2 nine0009 | 73.0 | 75.1 | 76.9 | 78.8 | 10 | 7.9 | nine0008 8.3 | 8.8 | 9.5 | 10.3 | 10.9 | 11.4 |
| 70. | ||||||||||||||
 8
8  7
7  3
3  8
8  9
9  0 nine0009
0 nine0009  5
5  3
3  3
3  6
6  4
4