Baby trauma birth
Birth Trauma | Physical and Emotional Harm at Birth
What Is Birth Trauma?
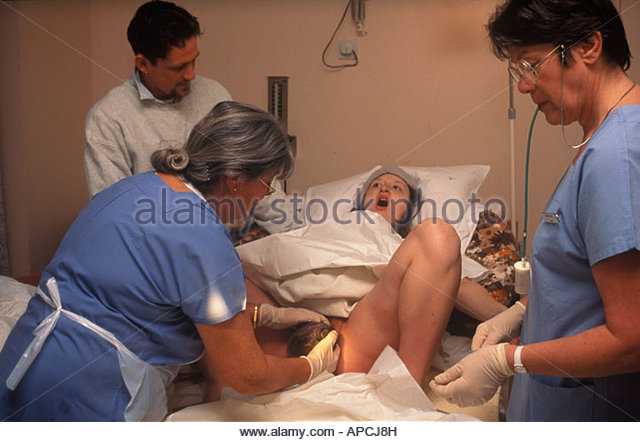
Birth trauma occurs when a baby’s organs or tissues are damaged during a difficult delivery. A traumatic birth can lead to lasting medical problems in the infant, such as brachial plexus injuries, brain damage, and more.
When birth trauma is caused by negligence or medical malpractice, parents have the right to pursue legal compensation for their children’s injuries. Whether the obstetrician failed to medically intervene, used excessive force, or was otherwise responsible for the infant’s injuries, parents can file a medical malpractice claim.
Compensation from a birth injury lawsuit can help parents pay for their child’s health care expenses, as well as any mental health treatment they may need for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), postpartum or postnatal depression, or anxiety disorders caused by psychological trauma from the birth experience.
Free Legal Case ReviewDo you suspect your child’s birth injury was caused by medical malpractice?
Get a Free Case Review
Causes of Birth Trauma
Each year, approximately 3. 8 million babies are born in the United States. Sadly, more than 21,000 of the babies born will not survive. Others will be victims of birth trauma.
While some trauma may occur naturally, many traumatic childbirth experiences are preventable or caused by an obstetrician’s failure to recognize warning signs or use medical interventions when necessary.
Causes of traumatic childbirth include:
- Abnormal birth position
- Acceleration and stimulation of the birth
- Breech and obstetric turn
- Cephalopelvic disproportion (child’s head is too big to fit through the mother’s pelvis during a natural delivery)
- Fast deliveries or delayed/prolonged deliveries
- Improper delivery procedures, such as forceful use of vacuum extractors or forceps
Regardless of whether the cause of the birth trauma was preventable, medical professionals in obstetrics or pediatrics have a duty to intervene to keep the mother and baby as safe as possible.
If an obstetrician or other health care provider fails to take immediate, necessary action during and after birth — for example, waiting too long to perform an emergency cesarean section (C-section) — a traumatic birth injury can occur and lead to severe consequences.
Do you believe medical malpractice led to your child’s birth injury? Get a free case review today!
Birth Trauma Risk Factors
Some fetal or women’s health issues put babies at a higher risk for a traumatic birth. Medical professionals should be especially alert before and during the birth process to identify and treat these risk factors.
Risk factors for a traumatic or difficult birth include:
- Abnormal amniotic fluid volume
- Abnormal biophysical profile (BPP)
- Abnormal fetal heart rate
- Cramping or vaginal bleeding
- Decreased fetal movement
- Gestational diabetes
- Insufficient or excessive weight gain
Birth Trauma Effects on Baby
Birth injuries involving the head, neck, and shoulders are the most common since most babies exit the womb head first. Birth traumas can have lasting effects on the baby. Some of the most common types of birth trauma are detailed below.
Birth traumas can have lasting effects on the baby. Some of the most common types of birth trauma are detailed below.
Bell’s Palsy
When a baby’s facial nerves are damaged during labor or delivery, sometimes caused by improper use of forceps, Bell’s palsy can occur.
The condition may be noticeable when the baby cries, as the injured nerve prevents movement of their face or the closing of the eye on the side where the trauma occurred. Bell’s palsy often clears on its own, but surgery may be required to restore nerve function, and some babies may never fully recover.
Bruising and Broken Bones
As the baby is pushed out through the birth canal, the pressure and physical stress of exiting the womb can cause bruising and, in some cases, broken bones.
Fractures generally affect the collarbone during breech deliveries or when the baby’s shoulder gets stuck above the mother’s pubic bone during vaginal delivery (shoulder dystocia).
A doctor’s use of forceps or vacuum extractors can also cause lacerations, bruising, or broken bones, primarily if an improper amount of force is used. Proactive monitoring of the baby’s size, position, and mother’s health before labor can often prevent this type of birth trauma.
Proactive monitoring of the baby’s size, position, and mother’s health before labor can often prevent this type of birth trauma.
Do you suspect your child’s birth injury was caused by medical malpractice?
Get a Free Case Review
Caput Succedaneum
Caput succedaneum, or swelling of the scalp, is typically caused by pressure during delivery. This pressure can occur after a difficult birth experience or when the amniotic sac breaks, leaving the head unprotected during the birthing process. Vacuum extraction after long delivery periods has also been shown to lead to caput succedaneum.
Fortunately, this condition is not life-threatening and usually clears up without treatment.
Cephalohematoma
A cephalohematoma is an accumulation of blood below the protective membrane that covers a baby’s skull. It can display as soft lumps that appear on the head hours after birth. These lumps often grow in size until the body reabsorbs the blood.
Cephalohematomas occur if there is too much pressure on a baby’s head during delivery due to long labor, the use of forceps or vacuum extractors, and other factors. This condition may lead to other complications, such as jaundice or the breakdown of red blood cells.
Erb’s Palsy and Other Brachial Plexus Injuries
The brachial plexus is a group of nerves that connect the spinal cord and control muscles in the arm, wrist, hands, and fingers. If the brachial plexus becomes damaged, Erb’s Palsy may occur, disrupting mobility and potentially leading to muscle weakness or paralysis.
When pressure is placed on the neck or shoulders during delivery, the brachial plexus nerves can be stretched, ruptured, or severed. Erb’s palsy and other brachial plexus injuries are typically caused by shoulder dystocia or the misuse of vacuum extractors or forceps.
You may be able to file an Erb’s palsy lawsuit to help your family secure financial compensation to help pay for treatment costs.
Get your free legal case review and see if you are entitled to financial compensation
Get a Free Case Review
Infant Hematoma
Infant hematoma occurs when there is bleeding in the brain following a head injury. This bleeding may form blood clots, putting additional pressure on the brain. In extreme cases, doctors may need to perform surgery or remove a portion of the skull to relieve pressure.
Oxygen Deprivation
When the umbilical cord wraps around a baby’s neck, or if the placenta separates prematurely, it can cut off an adequate supply of oxygen that the baby’s brain needs. Oxygen deprivation can damage the part of the brain controlling body motor functions (cerebellum) and has been linked to cerebral palsy.
If babies cannot breathe independently or return to normal oxygen levels within minutes, the brain cells may become damaged. Even with intensive care, oxygen deprivation can lead to seizures, coma, and death.
Spinal Cord Injuries
Most spinal cord injuries are caused by trauma to the neck area, and they require immediate medical attention. That said, many spinal cord injuries do not heal and cause life-long disabilities, including loss of sensation and function in the lower half of the body (paraplegic) or a loss of feeling in movement from the chest down (quadriplegic).
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
A subconjunctival hemorrhage is bleeding that occurs when blood vessels in the eyes burst. It presents as a bright red band around the iris. It typically does not cause permanent damage to the eyes and disappears over time.
Prognosis for Children With Birth Traumas
The outlook for babies suffering from common birth traumas can vary greatly.
| Examples | Treatments | Recovery Time | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Birth Trauma | Caput succedaneum, mild bruises | Little to no treatment required | May resolve within days or weeks |
| Moderate Birth Trauma | Erb's palsy and other brachial plexus injuries | Treatments may include medications, therapy, and/or surgery | May take several months or years for full recovery |
| Severe Birth Trauma | Cerebral palsy, spinal cord injuries | Lifelong treatments (medications, therapy) will be required — periodic surgery may also be needed | A child cannot completely recover, but the condition can be managed |
One of the most critical factors in dealing with birth trauma is recognizing and treating the injury early on.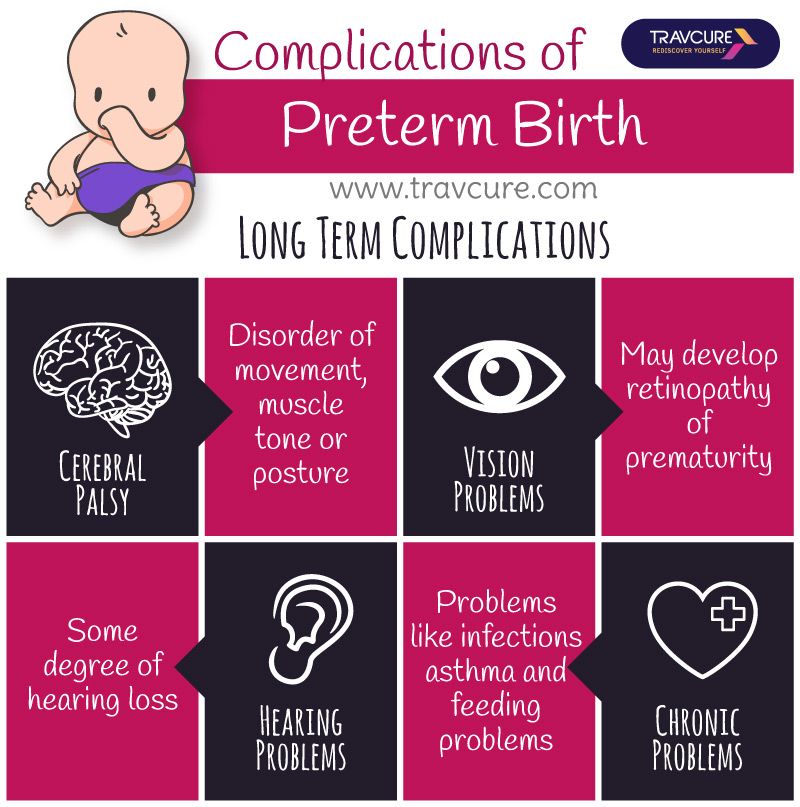 Birth traumas may need immediate treatment by pediatric doctors to prevent any potential long-term damage.
Birth traumas may need immediate treatment by pediatric doctors to prevent any potential long-term damage.
If medical professionals do not take the right action at the right time, the consequences of the traumatic experience can be severe.
Compensation for Birth Trauma
Life after birth trauma can be uncertain — but help is available. With legal assistance, you may be able to receive financial compensation to cover any medical expenses that stem from your child’s injury. You can also use this money to pay for anything else your child needs, such as a wheelchair, medications, and different types of therapy.
If your child suffered from preventable birth trauma, don’t wait to see if you can access financial aid. Speak with a birth injury attorney who can tell you more about pursuing compensation after a birth injury. To start this process now, get a free case review.
Birth injury (in the baby)
Birth injury (in the baby) | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
What is birth injury?
Having a baby in Australia is very safe, although it’s estimated that more than 1,000 babies are injured during childbirth each year. It can be very upsetting if your baby has been injured, but most birth injuries are only temporary.
It can be very upsetting if your baby has been injured, but most birth injuries are only temporary.
Also called 'neonatal birth trauma', birth injury to a newborn baby can include many things, from bruising to nerve damage to a broken bone. Sometimes an injury occurs as a result of life-saving procedures.
About 49 in every 10,000 babies born in Australian hospitals suffer a birth injury. Here are some of the types of birth injury affecting babies.
Bruises and swelling of the scalp
Sometimes a baby can be born with minor, temporary injuries to their head or face. These include bruises, swelling (sometimes called a chignon), lumps caused by fluid under the skin (caput succedaneum) or bleeding under the skin (cephalohematomas), and blood inside the eye (subconjunctival haemorrhage).
Fractures
Fractures (breaks) can occur when there is difficulty getting a baby through the birth canal. The bone that most often breaks is the collarbone (clavicle), and this can happen when the baby's shoulder gets stuck (shoulder dystocia), or if the baby is born breech (bottom first).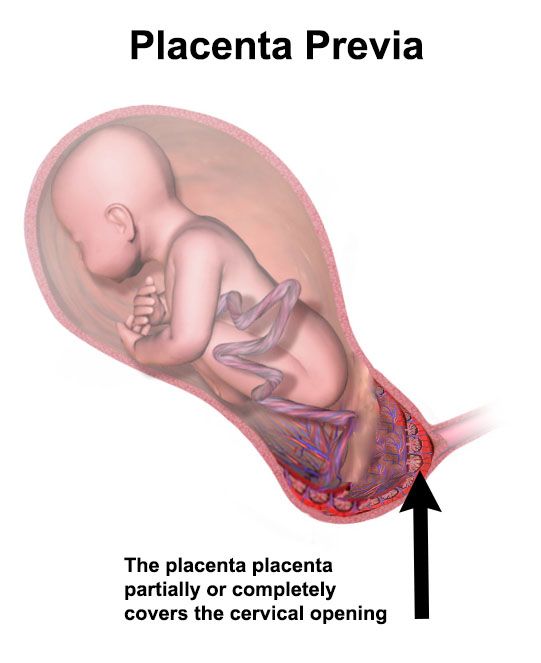
Nerve damage
Nerves can be damaged during childbirth, particularly in the baby's face (which can lead to facial paralysis) and the shoulder (which can lead to brachial palsy — loss of arm movement). Usually, nerve damage in a newborn is only temporary.
Brain injury
In very rare cases, a baby can suffer a brain injury during childbirth. If the baby doesn’t get enough oxygen for a long time during labour (perinatal asphyxia), they can experience brain damage. Cerebral palsy is a type of brain damage, but only a very small percentage of cerebral palsy cases is due to complications at birth.
Bleeding on the brain
In rare cases, a baby can suffer bleeding in or around the brain during childbirth. This is more common among very premature babies, and most infants with bleeding don't have symptoms. Others may be lethargic, have difficulty feeding and/or have seizures.
What causes birth injury?
Birth injuries can occur simply because of the pressure and resistance involved in giving birth vaginally.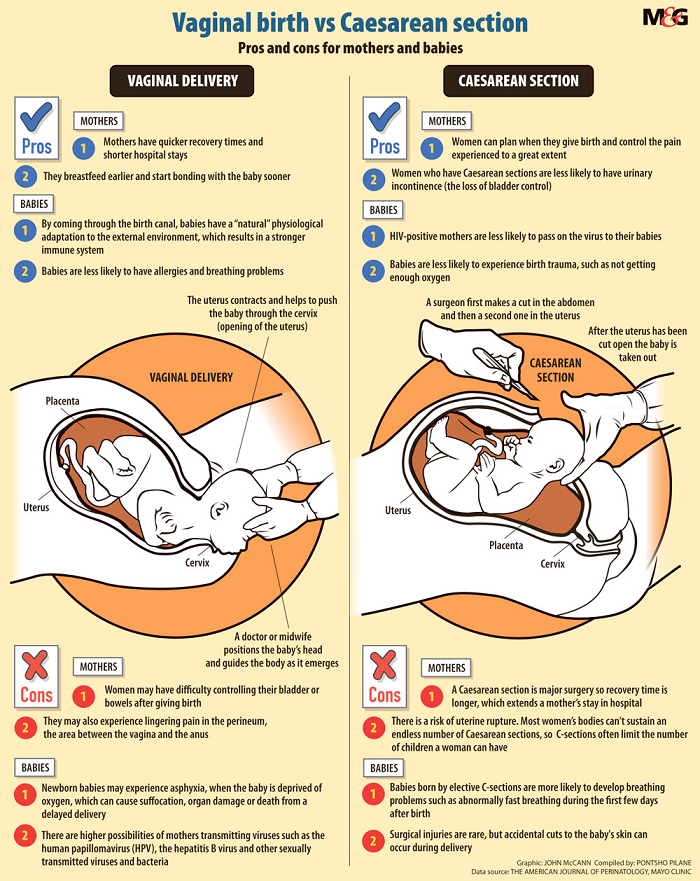 When the baby moves through the birth canal, there's pressure on its skull and body from the mother's pelvic bones.
When the baby moves through the birth canal, there's pressure on its skull and body from the mother's pelvic bones.
Large birth weight (more than 4kg) can increase the risk of injury during childbirth. There is also a greater risk if the baby is in a difficult position for labour and birth (such as the breech position). Premature babies born before 37 weeks are typically more fragile and may be injured more easily.
Other causes of birth injury to a baby include a difficult or prolonged labour, the shoulder becoming stuck in the birth canal and cephalopelvic disproportion (if the mother's pelvis isn't large enough or shaped in a way that allows for a vaginal birth).
Babies born with the assistance of forceps or ventouse (vacuum) are at higher risk of bruising, marks or swelling on the baby's head or face.
Lack of oxygen to the baby during birth could be caused by a number of things, such as problems with the umbilical cord, serious events in the mother such as haemorrhage or fever during labour, uterine rupture or abruption of the placenta (when it comes away from the uterus prematurely).
How are birth injury in babies treated?
Most birth injuries in babies are temporary. If the injury was to the soft tissue, then no treatment is normally needed — the medical team will just monitor the baby and may run tests to check for other injuries.
If there has been a fracture, your baby may need an x-ray or other imaging. The limb may need to be immobilised and some babies may need surgery.
If your baby has damaged nerves, the medical team will monitor them closely and recovery can take a few weeks. For more serious nerve damage, your baby may need special care.
Resources and support
- Talk to your doctor, midwife or obstetrician/gynaecologist.
- You can call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to speak with a maternal child health nurse (7 days a week, 7am to midnight AEST).
- Call the healthdirect helpline on 1800 022 222.
- Contact the Australian Birth Trauma Association for support and resources.
Sources:
Stanford Children’s Health (Birth injury), Medical Hypotheses (The significance of incomplete skull fracture in the birth injury), Mater Mothers’ Hospital (Labour and birth — an assisted vaginal birth), Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care (Neonatal birth trauma), Cerebral Palsy Alliance (What causes cerebral palsy), Medscape (Birth trauma), Birth Asphyxia (Birth asphyxia), Merck Manual (Birth injuries in newborns), Mater Mothers' Hospital (Shoulder dystocia)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: May 2021
Back To Top
Related pages
- Neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)
- Special care nursery (SCN)
- When birth doesn't go to plan
- Birth trauma (emotional)
- Birth injury (to the mother)
Need more information?
What is Birth Trauma? - Birth Trauma
The delivery of a baby is a positive event for many women, but for some it can be a mixed experience or even very negative, resulting in physical and/or
Read more on Australasian Birth Trauma Association website
Birth After Birth Trauma - Birth Trauma
This is a question that we hear often. How can I have another baby?
Read more on Australasian Birth Trauma Association website
Considerations for birthing after birth trauma - Birth Trauma
In this post we consider some important points when making decisions about birthing after a birth trauma experience.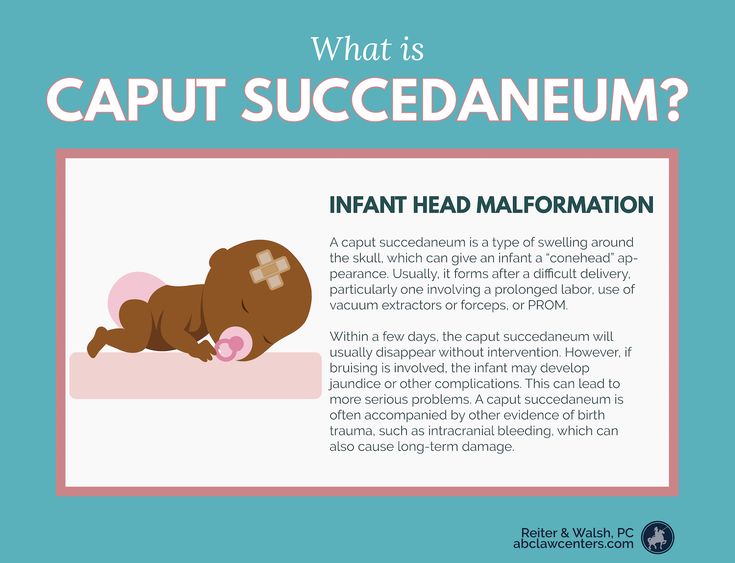
Read more on Australasian Birth Trauma Association website
Family & Friends - Birth Trauma
If you are reading this then you may have someone close to you that has been impacted by a difficult birth experience, be it a partner, loved one or someone
Read more on Australasian Birth Trauma Association website
Birth and beyond - Ngala
Exciting times are ahead!Birth comes after lots of anticipation and preparation
Read more on Ngala website
Physical Trauma - Birth Trauma
For many women who have suffered from physical trauma as a result of childbirth, and who are struggling to cope, is it vital that healthcare providers
Read more on Australasian Birth Trauma Association website
Early Postnatal - Birth Trauma
The early postnatal period is a time of emotional change for most women. Some women may experience distress or symptoms of depression at this time if they
Some women may experience distress or symptoms of depression at this time if they
Read more on Australasian Birth Trauma Association website
Childbirth trauma and recovery | PANDA
While many pregnant women and their partners know birthing their baby will be hard work, very few expect labour and childbirth could be complicated.
Read more on Perinatal Anxiety and Depression Australia (PANDA) website
Postpartum Trauma Disorders (e.g. PTSD) - Birth Trauma
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is one of a group of trauma and stressor-related disorders. People often associate these with war veterans, police
Read more on Australasian Birth Trauma Association website
Recovering from a traumatic birth - COPE
COPE's purpose is to prevent and improve the quality of life of those living with emotional and mental health problems that occur prior to and within the perinatal period.
Read more on COPE - Centre of Perinatal Excellence website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Birth injuries: types, symptoms, complications
Birth injuries: types, symptoms, complications
Sometimes babies get injured during childbirth - according to statistics, about 10% of newborns need medical care. Birth injuries are not always easy to spot at a glance. They are easy to identify by characteristic signs that indicate the need for medical intervention.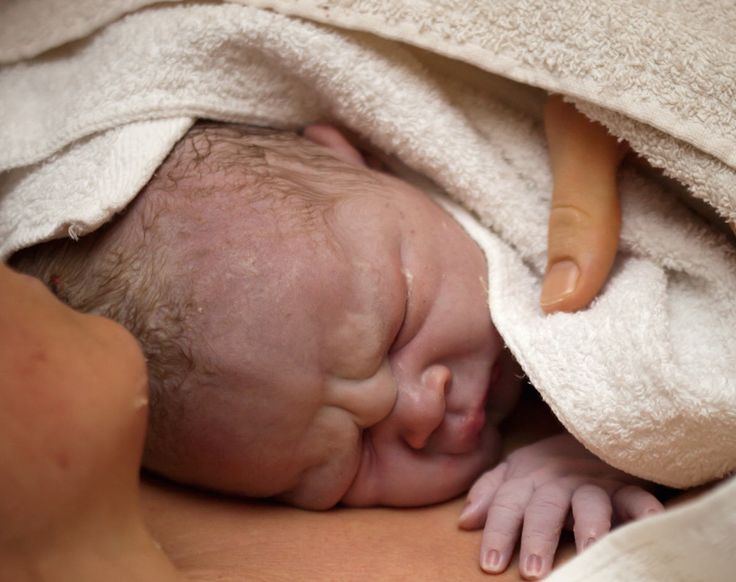 The sooner the child gets help, the less likely complications are.
The sooner the child gets help, the less likely complications are.
Sometimes during childbirth, children are injured - according to statistics, about 10% of newborns require medical care. Birth injuries are not always easy to spot at a glance. They are easy to identify by characteristic signs that indicate the need for medical intervention. The sooner the child gets help, the less likely complications are. nine0003
Most common birth injuries
Medicine knows many of their types. The following deviations occur most frequently:
- injuries of cranial bones;
- damage to duplications of the dura mater;
- epidural hemorrhages;
- cephalohematomas;
- birth tumors.
They are also fraught with serious consequences that can greatly affect the child's quality of life. It is impossible to avoid complications without qualified medical care. Injuries received by the child during childbirth lead to the following complications: nine0003
- general developmental delay;
- delayed speech development;
- sleep disorders;
- epileptic syndrome;
- autism;
- clubfoot;
- cerebral palsy;
- hyperactivity;
- as well as a number of other diseases.
Damage affects the development of internal organs, the brain, the central nervous system, the spine, and the skeletal system. In the future, they can cause serious complications. nine0003
How to recognize a birth injury?
The consequences, as a rule, are not immediately noticeable - the problem worsens gradually, in some cases the process is delayed for 2-3 years. There are characteristic signs that indicate the need to show the baby to a specialist:
- Restless behavior of the child;
- frequent regurgitation;
- hand or foot movement disorders;
- skull asymmetry;
- reflex disorders; nine0014
- sleep disorders.
These signs are expressed to a greater or lesser extent - sometimes violations are visible immediately, but in most cases only a specialist can determine them
Risk group
Children at risk must be examined by a specialist. How do you know if your baby is in this group? It includes children who have had a hard time coming into the world.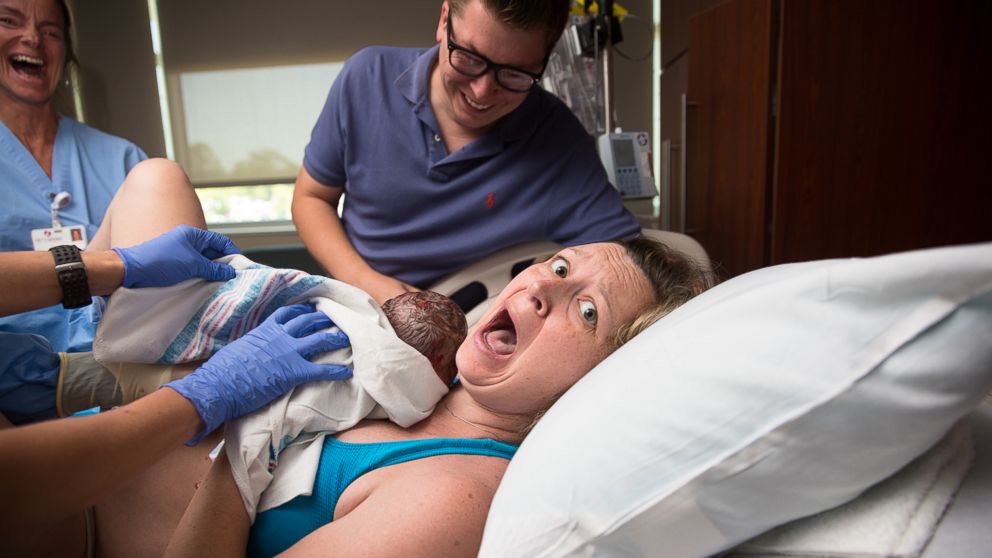 This can be judged by the following features: nine0003
This can be judged by the following features: nine0003
- cesarean section;
- large fruit weight - over 4 kg;
- state of hypoxia;
- cephalohematoma - swelling on the skull of a newborn;
- induction of labor and obstetric manipulations.
Children born as a result of difficult childbirth must be shown to a specialist. Qualified medical care will help to avoid the development of complications, even if the child was injured during childbirth. The Baby Plus Medical Center has all the necessary equipment for examination and laboratory tests. Our center is located in the village of VNIISSOK (Odintsovsky district, residential complex "Gusarskaya Ballada"). You can make an appointment right now! Our experts are ready to come to the residents of the Odintsovo district at home - they do not have to make an appointment for an examination. nine0003
Date of publication: 13.12.2018 17:05:16
Birth injury - causes of disease, methods, prevention Clinic "OSTEOMED" provides treatment of birth injuries, rehabilitation after birth injuries in newborns, infants (infants), babies.
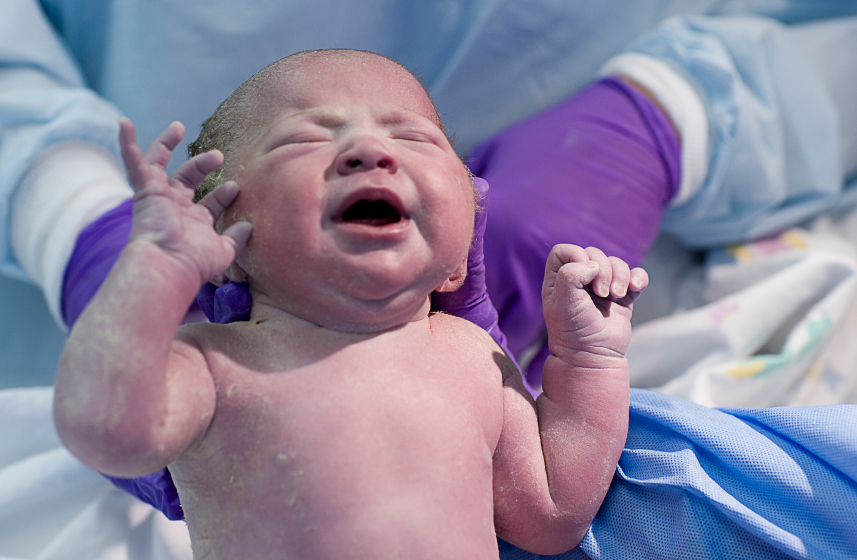 Birth trauma is treated with effective osteopathic methods. Traditional and modern methods of reflexology (reflexotherapy) are actively used in the treatment. We carry out the restoration of the child's nervous system (NS), recovery after birth injuries. In pediatric practice, an osteopathic approach is mainly used, which is absolutely gentle and safe for babies. The osteopath applies gentle hand pressure on the baby's head and body to ease the effects of birth stress, and correct tension in the skull bones and restore their proper movement. Children and babies feel great after treatment and sleep better. nine0003
Birth trauma is treated with effective osteopathic methods. Traditional and modern methods of reflexology (reflexotherapy) are actively used in the treatment. We carry out the restoration of the child's nervous system (NS), recovery after birth injuries. In pediatric practice, an osteopathic approach is mainly used, which is absolutely gentle and safe for babies. The osteopath applies gentle hand pressure on the baby's head and body to ease the effects of birth stress, and correct tension in the skull bones and restore their proper movement. Children and babies feel great after treatment and sleep better. nine0003 Birth trauma is damage to tissues or organs of the fetus during childbirth (birth act) due to local action of mechanical forces on the fetus. Unfortunately, birth injuries in newborns are quite common.
90% of children have a birth injury, most often it is the cervical spine. If the diagnosis of "birth trauma" is not made, it is advisable for you to contact an osteopath if the following situations occurred during childbirth:
- long dry period
- Opening the fetal bladder by a doctor in the maternity hospital
- Stimulation of labor
- Obstetric manipulations: imposition of forceps, fruit squeezing
- The birth of a child in the pelvic presentation
- Caesarean section
- epidural (spinal) anesthesia in women in women in women and after 35 years
- the birth of a large fetus, more than 4 kg
- if your child was born in a state of hypoxia: blue, did not cry right away, there was an entanglement of the umbilical cord, low Apgar scores
- if your child had a cephalohematoma (swelling on the baby's head) - this indicates a serious injury to the bones of the skull
- your child has been diagnosed with PEP (perinatal encephalopathy), IUGR (intrauterine growth retardation)
Predisposing factors for birth trauma
The main predisposing factors leading to birth trauma are as follows:
1. Pathology of the prenatal period.
Pathology of the prenatal period.
2. Pathology of the antenatal period. nine0003
3. Wrong course of pregnancy.
4. Toxicosis, preeclampsia.
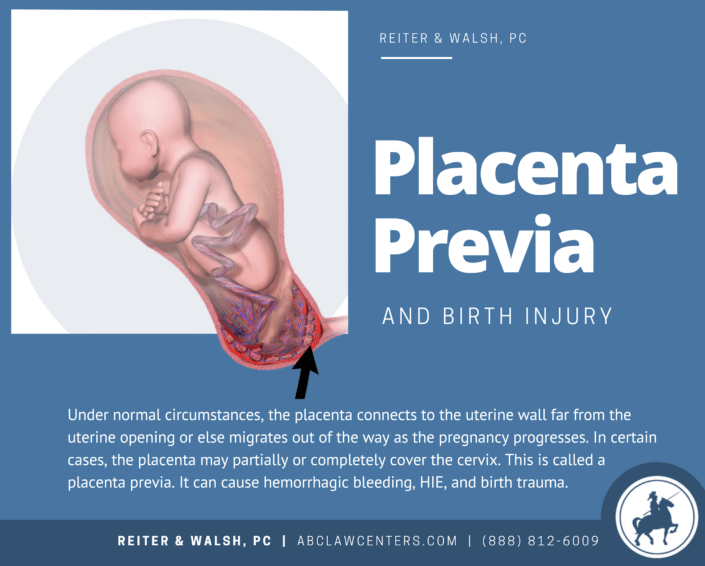
5. Placenta previa.
6. Infection of the birth canal (vagina, uterus, etc.).
7. Genital diseases of the mother (woman), diseases of the genital organs: salpingitis, inflammation of the appendages, salpingoophoritis, endometritis, vaginitis, vulvovaginitis, sexually transmitted diseases (venous diseases, venous diseases), infections, inflammatory diseases of the genital organs. nine0003
8. Extragenital diseases (diseases) of the mother. Diseases of the cardiovascular system, Rh incompatibility (Rh conflict) have a particularly strong influence.
9. Preterm pregnancy (fetal miscarriage).
10. Prolongation of pregnancy (post-term fetus).
11. Intrauterine fetal hypoxia (VGP, VUG, VUGP), chronic intrauterine hypoxia (lack of oxygen).
12. Cesarean section (birth trauma during caesarean section).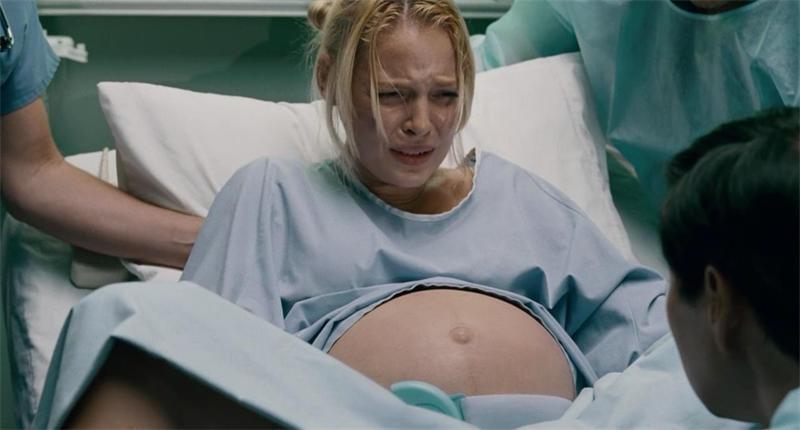
13. The use of a vacuum extractor in childbirth (vacuum extraction, vacuum extractors, a comprehensive vacuum system for obstetrics, a vacuum extractor). Vacuum fruit extraction.
14. Rapid delivery, stimulation in childbirth.
15. Stress, neurosis, neurasthenia.
16. Increased risk if previous pregnancies ended badly (miscarriage, stillbirth, stillbirth, congenital malformations - congenital malformations). nine0003
Mechanism of development, pathogenesis of birth trauma
What is the mechanism of development of birth trauma, its pathogenesis? All of the above factors cause fetal hypoxia and reduce the resistance of its organs and tissues, especially the brain. All this leads to traumatic effects during childbirth.
Classification of lesions of the nervous system in children
Neonatologist, neurologist, neuropathologist, microneuropathologist distinguish 2 main types of birth injuries (classification by localization): nine0003
1. Birth trauma of the central nervous system (CNS).
Birth trauma of the central nervous system (CNS).
2. Birth trauma of the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
There are also the following pathologies: obstetric paralysis (obstetric paralysis), intracranial birth injury (for example, traumatic brain birth injury of the head, brain, cerebellum), birth injury of the spinal cord (for example, birth injury of the cervical spine, neck), birth injuries of peripheral nerves , birth injury of soft tissues (for example, birth tumor), birth injury of bones, skeletal system (for example, fracture of the collarbone), birth injury of internal organs. Separately, obstetric trauma due to obstetric manipulations is singled out, especially in case of an abnormal course of childbirth. nine0003
Consequences of birth injuries
The consequences of birth trauma are varied. Hemorrhages in the brain, paralysis (paralysis), paresis (paresis), retarded growth and development of arms or legs, impaired muscle tone, convulsions, hypertension syndrome, intracranial hypertension, hydrocephalus, convulsive and non-convulsive seizures, damage to cranial nerves, liquorodynamic disorders, decerebrate rigidity, cerebral palsy (ICP), perinatal encephalopathy (PEP), psychomotor retardation, speech retardation, minimal brain dysfunction, pneumonia, urosepsis and the worst consequences.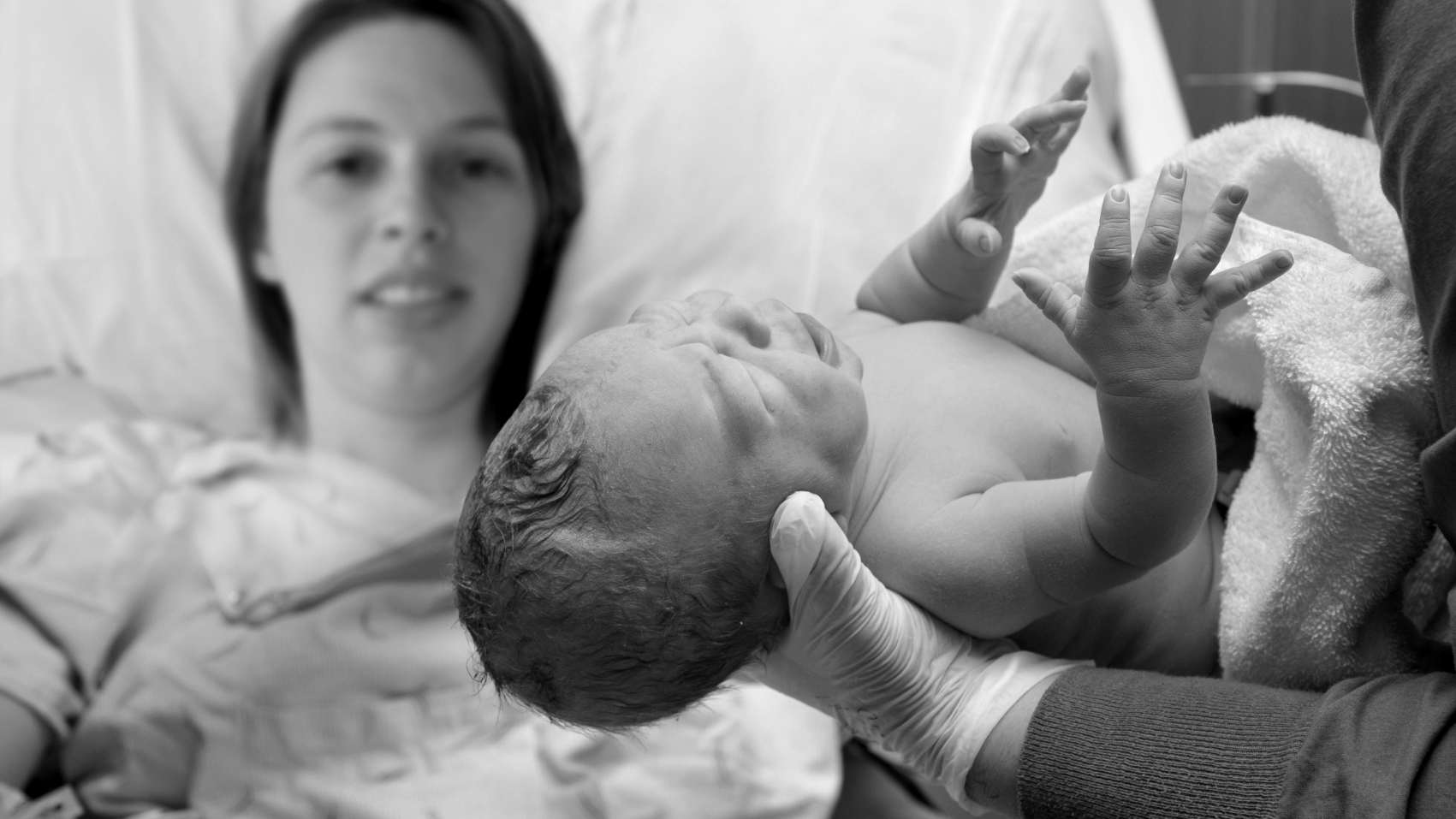 nine0003
nine0003
Birth trauma prevention
How to avoid birth trauma in newborns? To avoid birth injuries, you must follow a number of recommendations:
- Plan conception and pregnancy in advance.
- Treat chronic conditions before pregnancy.
- Eliminate alcohol (alcoholic beverages), smoking (quit smoking) 3 months before conception and during pregnancy.
- Carry out activities aimed at the prevention and treatment of intrauterine fetal hypoxia. nine0014
- Give birth in a good health facility.
- Prior to delivery (1 month in advance) to communicate with such specialists as an obstetrician, gynecologist, midwife, neonatologist, neurologist, microneurologist, neuropathologist, resuscitator who will take part in childbirth.
- Eat well and take vitamins during pregnancy.
- During pregnancy, attend childbirth preparation courses.
- During pregnancy, rest more and work less, walk in the fresh air.
- During pregnancy, regularly visit a medical institution such as a antenatal clinic, conduct the necessary tests, examinations, and studies.

- During pregnancy, avoid contact with infectious patients (especially those with diseases such as influenza, adenovirus infection, parainfluenza, MS infection (respiratory syncytial infection), rotavirus infection (rotavirus infection), SARS, herpes (herpetic infection), rubella, measles, mumps (mumps, mumps), chicken pox (chickenpox), chlamydia, Ebola, plague, HIV infection, tuberculosis, diphtheria, tetanus, echinococcosis, toxoplasmosis, teratogenic infections). nine0014
- Carry out activities aimed at preventing Rh conflict (take into account the Rh blood of the father and mother Rh, use a condom during oral sex).
- During pregnancy, try to avoid exposure to such a pathological factor as ionizing radiation, radio waves (microwave ovens, microwave ovens, microwave ovens, x-rays, radiography, MRI - magnetic resonance imaging, NMRI (nuclear magnetic resonance imaging), CT (computed tomography), cellular phone, smartphone, tablet, computer). nine0014
- Exclude the intake of the following: medicines, medicines, medicines, medicines, dietary supplements, dietary supplements not prescribed by a doctor.
 Do not engage in self-medication, uncontrolled intake of drugs.
Do not engage in self-medication, uncontrolled intake of drugs.
Signs of birth trauma
Many parents, fathers and mothers ask us: “What are the first signs that a child has a birth injury?”, “How to determine a birth injury in a child, a newborn?” “Does the baby have a birth injury?” "What are the signs of birth trauma, the consequences of birth trauma?". You should consult a doctor if you notice any of the following symptoms: nine0003
Online entry
Online record
Date of visit
22.12.2022
Doctors
Our specialists
Smirnov Andrey Valerievich
Clinic Osteomeda, neurologist-Osteopat, candidate of medical sciences, member of ENRO, ENRO, ENER doctor of osteopathy in Europe (registration number 248041051021), lecturer at the "School of Osteopathy on the Neva" at the Department of Neurology, St. Petersburg Institute of Higher Education
Kristina Aleksandrovna Zoller
Neurologist-osteopath, candidate of medical sciences, member of ENRO and ROSA, doctor of osteopathy in Europe (registration number 204115070812), director of the "School of Osteopathy on the Neva", head of the course of osteopathy at the Department of Neurology, SPbIUVE
Kaprielov Karen Aleksandrovich
Osteopath, member of ENRO, doctor of osteopathy of Europe (registration number 244046031012), chiropractor
Cherny Roman Anatolyevich
Osteopath, member of ENRO, doctor of osteopathy of Europe (registration number 22212) School of Osteopathy on the Neva" at the Department of Neurology, St. Petersburg Institute of Higher Education
Petersburg Institute of Higher Education
Poznyak Alina Alekseevna
Neurologist-osteopath, member of ENRO, Doctor of Osteopathy of Europe
Bekuzarova Svetlana Anatolyevna
Otopat doctor, manual therapist, kinesiotepection specialist
Komyakhov Andrey Valerievich
Neurologist-Osteopath, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of osteopathy of Europe, member of the ENRO (registration number 635042181721)
Azommedova Sakhila Khaladdinovna Narodinovna Narodinovna Narodinovna. , member of ENRO, M.D., Medicine Doctor (registration number 637042181712)
Tsivinsky Anton Dmitrievich
Neurologist-osteopath, candidate of medical sciences, member of ENRO, doctor of osteopathy of Europe (registration number 654051291721), chiropractor, specialist in the manufacture of individual orthopedic insoles
Tsoy Marina Removna
Neurologist-osteopath, Doctor of Osteopathy of Europe, M.D., Medicine Doctor
Vydra Anatoly Alexandrovich
Neurologist-osteopath, specialist in articulation, kinesiotherapy (registration number 589102271521), M.