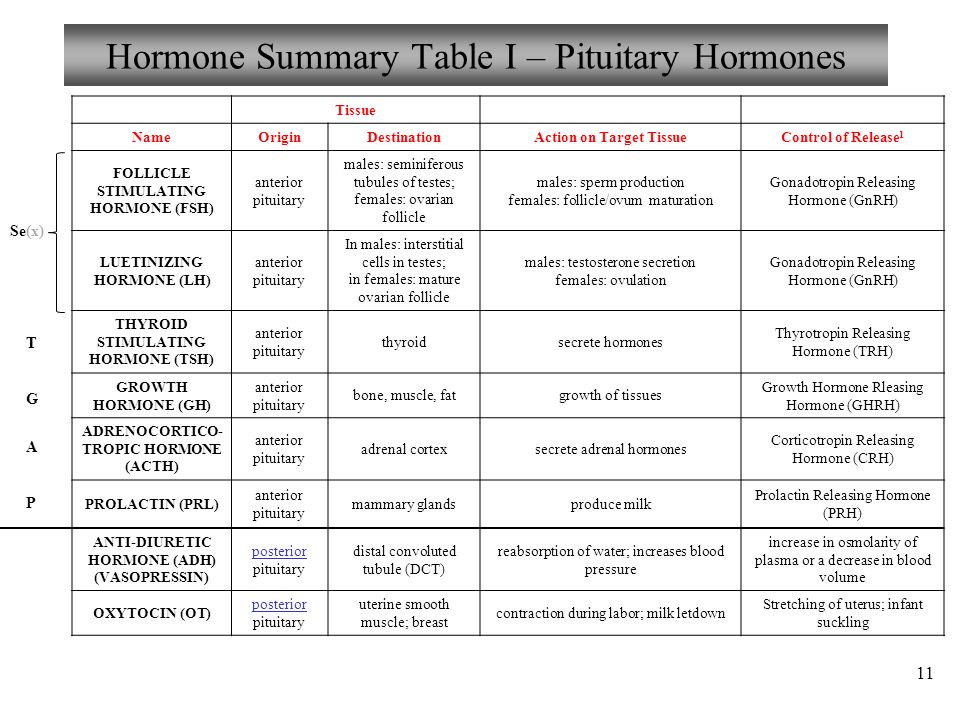
Open sores on the breast
Is Your Rash a Breast Infection or Inflammatory Breast Cancer?
Written by Stephanie Booth
Medically Reviewed by Kumar Shital, DO on March 19, 2021
- Infection
- Skin Conditions
- More Serious Conditions
- What to Do for a Breast Rash
- When to See a Doctor
If your breast looks red or swollen, there’s no need to panic. A tender area or rash on your breast often signals a common problem like an infection. In other cases, it's a symptom of a common, treatable skin condition.
Rarely, a rash and soreness can be signs of inflammatory breast cancer, a form of the disease that can grow quickly, often in weeks or months.
Here’s how you can tell what's going on.
Infection
Infected breast tissue, also called mastitis, is most common in women who are nursing. It can happen when milk gets trapped in your breast. You might also get it if something clogs one of your milk ducts or bacteria get into your breast through a cracked nipple.
Mastitis often happens within the first 6 to 12 weeks after you give birth, but sometimes women who aren’t breastfeeding get it, too.
If you have mastitis, your symptoms may come on without warning. Common signs include:
- Tender, warm, or swollen breasts
- A red patch of skin, often in a wedge shape
- Pain or burning when you breastfeed
- A fever of 101 F or higher
- Chills
Skin Conditions
There are several common skin conditions that can put a rash on your breast, like:
Hives. Red, itchy welts on your skin that often result from an allergy
Psoriasis. Scaly, itchy patches of skin that show up when your immune system goes haywire and attacks your body
Scabies. Bites from the human itch mite. They form a line of little bumps on your skin and get really itchy at night
Shingles. Painful, itchy blisters that result from the same virus that causes chickenpox
Yeast. This fungus lives on your skin. When too much grows, it can lead to an itchy rash in places where skin touches skin.
This fungus lives on your skin. When too much grows, it can lead to an itchy rash in places where skin touches skin.
Intertrigo. It happens when the skin under your breast rubs together too much. It can trap moisture and create friction. Besides a red or brown rash, your skin may swell and itch. It may have a funny smell.
Nipple eczema. It can lead to a rash around one or both of your nipples. The skin around them may get dry and scaly, or you could have a rash that feels moist to the touch. You may notice a burning feeling if you’re nursing. Nipple eczema often affects women about 5 to 6 months after giving birth.
More Serious Conditions
Inflammatory breast cancer symptoms result from a buildup of fluid in your breast. Many women don’t feel a lump. Instead, you may notice a rash that looks like an insect bite.
You could also have:
- Itching that doesn’t go away
- A nipple that goes inward or gets flat
- Swelling and redness that affect at least a third of your breast
- Pink, purple-red, or bruised skin
- Skin that looks ridged or pitted like an orange peel
- A sudden increase in breast size
- Breast tenderness or a “heavy” feeling
- Swollen lymph nodes under your arm or near your collarbone
Paget’s disease is a rare skin disorder that’s often linked to breast cancer in the tissues behind your nipple. It can cause a red, scaly rash. You could also have discharge or bleeding from your nipple.
It can cause a red, scaly rash. You could also have discharge or bleeding from your nipple.
What to Do for a Breast Rash
If you notice a change in your breasts, try not to worry. Because the hormones in your body are constantly changing, so are your breasts. Many of these differences aren’t cause for concern.
It can help to:
Avoid scratching. This will only make your rash worse.
Take a warm bath, or place a warm washcloth over your breast. This may help soothe your skin.
Look for a cause. Did you try a new perfume or laundry detergent? Stop using any recently added products and see if your rash improves.
When to See a Doctor
Signs that you should call your doctor right away include:
- Fever
- Intense pain
- Red streaks coming from your breast
- Yellow or green pus
- Open sores
You should also see your doctor if any symptoms get worse. They’ll do an exam to figure out what’s causing your rash so they can prescribe the best treatment.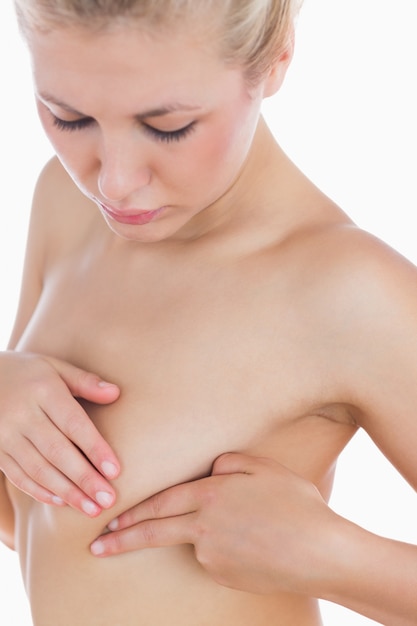 Some simple rashes go away quickly with a special cream.
Some simple rashes go away quickly with a special cream.
If you do have a breast infection, you’ll need antibiotics. Make sure you finish all your medicine, even if you start feeling better right away.
Unless your doctor suggests otherwise, you won’t need to stop nursing. Try to fully empty your breasts so you’re less likely to get an abscess -- a pocket of pus that may need draining.
Drink plenty of fluids and get lots of rest to help your body fight off a breast infection.
Your doctor may want you to get a mammogram. This can give them a better idea of what’s going on inside your breast.
If your symptoms don’t clear up soon, your doctor may also want to do a biopsy. They’ll remove a small piece of your breast tissue and look closely at it under a microscope.
Pyoderma Gangrenosum: A Rare Cause of Breast Ulceration
1. Hasselmann DO, Bens G, Tilgen W, Reichrath J. Pyoderma gangrenosum: clinical presentation and outcome in 18 cases and review of the literature. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2007 Jul;5(7):560–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2007 Jul;5(7):560–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
2. Tromm A, May D, Almus E, et al. Cutaneous manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease. Z Gastroenterol. 2001 Feb;39(2):137–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
3. Powell FC, Schroeter AL, Su WP, Perry HO. Pyoderma gangrenosum and sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1984 Jul;120(7):959–960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
4. Jorizzo JL, Solomon AR, Zanolli MD, Leshin B. Neutrophilic vascular reactions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988 Dec;19(6):983–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
5. Newell LM, Malkinson FD. Commentary: pyoderma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 1982 Oct;118(10):769–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
6. Powell FC, Schroeter AL, Su WP, Perry HO. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a review of 86 patients. Q J Med. 1985 May;55(217):173–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
7. Ackerman AB. Questions to the Editorial Board. Am J Dermatopath. 1983;;5(4):409–410. [Google Scholar]
8. Levitt MD, Ritchie JK, Lennard-Jones JE, Phillips RK. Pyoderma gangrenosum in inflammatory bowel disease. Br J Surg. 1991 Jun;78(6):676–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Levitt MD, Ritchie JK, Lennard-Jones JE, Phillips RK. Pyoderma gangrenosum in inflammatory bowel disease. Br J Surg. 1991 Jun;78(6):676–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
9. von den Driesch P. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a report of 44 cases with follow-up. Br J Dermatol. 1997 Dec;137(6):1000–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
10. Bennett ML, Jackson JM, Jorizzo JL, Fleischer AB, Jr, White WL, Callen JP. Pyoderma gangrenosum. A comparison of typical and atypical forms with an emphasis on time to remission. Case review of 86 patients from 2 institutions. Medicine (Baltimore) 2000 Jan;79(1):37–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
11. Greenstein AJ, Janowitz HD, Sachar DB. The extra-intestinal complications of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: a study of 700 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1976 Sep;55(5):401–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
12. Kirsch B, Gerhardt H, Gladisch R, Heine M, Rohr G, Weiss J. Dermatosen bei chronisch entzündlichen Darmerkrankungen. Ergebnisse einer Untersuchung Von 119 Morbus-Crohn-/colitis Patienten. Akt Dermatol. 1992;;18((1-2)):17–22. [Google Scholar]
Ergebnisse einer Untersuchung Von 119 Morbus-Crohn-/colitis Patienten. Akt Dermatol. 1992;;18((1-2)):17–22. [Google Scholar]
13. Lamers CB. Treatment of extraintestinal complications of ulcerative colitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1997 Sep;9(9):850–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
14. McCord ML, Hall RP. Cutaneous manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. In: Shanahan F, editor. Targan Sr. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: From Bench to Bedside. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins;; 1994. pp. 682–694. [Google Scholar]
15. Bargen JA. Complications and sequelae of chronic ulcerative colitis. Ann Intern Med. 1929 Oct;3(4):335–352. [Google Scholar]
16. Crowson AN, Mihm MC, Jr, Magro C. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a review. J Cutan Pathol. 2003 Feb;30(2):97–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
17. Tay CH. Letter: pyoderma gangrenosum and leukemia. Arch Dermatol. 1973 Oct;108(4):580–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
18. Jacobs P, Palmer S, Gordon-Smith EC. Pyoderma gangrenosum in myelodysplasia and acute leukaemia. Postgrad Med J. 1985 Aug;61(718):689–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jacobs P, Palmer S, Gordon-Smith EC. Pyoderma gangrenosum in myelodysplasia and acute leukaemia. Postgrad Med J. 1985 Aug;61(718):689–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
19. Struthers GR. Pyoderma gangrenosum, seronegative polyarthropathy and inflammatory bowel disease. J R Soc Med. 1979 Apr;72(4):284–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
20. Labat JP, Simon H, Metges JP, Lucas B, Malhaire JP. [Pyoderma gangrenosum and breast cancer: a new case] Ann Med Interne (Paris) 2000 Jun;151(4):314–315. French. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
21. Perry HO, Brunsting LA. Pyoderma gangrenosum; a clinical study of nineteen cases. AMA Arch Derm. 1957 Mar;75(3):380–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
22. Callen JP. Pyoderma gangrenosum. Lancet. 1998 Feb 21;351(9102):581–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
23. Perry HO, Winkelmann RK. Bullous pyoderma gangrenosum and leukemia. Arch Dermatol. 1972 Dec;106(6):901–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[PubMed] [Google Scholar]
24. Prystowsky JH, Kahn SN, Lazarus GS. Present status of pyoderma gangrenosum. Review of 21 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1989 Jan;125(1):57–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
25. Thornton JR, Teague RH, Low-Beer TS, Read AE. Pyoderma gangrenosum and ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1980 Mar;21(3):247–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
26. Angiò LG, Pirrone G, Rivoli G, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum of the “sinus mammarum” in ulcerative colitis. G Chir. 2003 Jun-Jul;24((6-7)):247–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
27. Johnson WT, Norva WM. Cutaneous manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. In: Lukash WM, Johnson RB, editors. The Systemic Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas Publisher, Ltd; 1975. p. 212. [Google Scholar]
28. Chow RK, Ho VC. Treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996 Jun;34(6):1047–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
29. Schwaegerle SM, Bergfeld WF, Senitzer D, Tidrick RT. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988 Mar;18(3):559–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schwaegerle SM, Bergfeld WF, Senitzer D, Tidrick RT. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988 Mar;18(3):559–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
30. Reichrath J, Bens G, Bonowitz A, Tilgen W. Treatment recommendations for pyoderma gangrenosum: an evidence-based review of the literature based on more than 350 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005 Aug;53(2):273–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
31. Wines N, Wines M, Ryman W. Understanding pyoderma gangrenosum: a review. MedGenMed. 2001 Jun 27;3(3):6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
32. Powell FC, Su WP, Perry HO. Pyoderma gangrenosum: classification and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996 Mar;34(3):395–409. 410–412. quiz. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
33. Davies MG, Piper S. Pyoderma gangrenosum: successful treatment with minocycline. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1981 Mar;6(2):219–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
34. Holmlund DE, Wählby L. Pyoderma gangrenosum after colectomy for inflammatory bowel disease. Case report. Acta Chir Scand. 1987 Jan;153(1):73–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Case report. Acta Chir Scand. 1987 Jan;153(1):73–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
35. Mayer L, Janowitz HD. Extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. In: Kirsner JB, Shorter RG, editors. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Philadelphia, PA: 1988. p. 299. [Google Scholar]
36. Talansky AL, Meyers S, Greenstein AJ, Janowitz HD. Does intestinal resection heal the pyoderma gangrenosum of inflammatory bowel disease? J Clin Gastroenterol. 1983 Jun;5(3):207–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
37. Sheldon DG, Sawchuk LL, Kozarek RA, Thirlby RC. Twenty cases of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: diagnostic implications and management. Arch Surg. 2000 May;135(5):564–568. discussion 568-569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
38. Goldstein F, Krain R, Thornton JJ. Intralesional steroid therapy of pyoderma gangrenosum. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1985 Dec;7(6):499–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
39. The Stop Gap Trial. UK Dermatology Clinical Trials Network. 2011. July. http://www.stopgaptrial.co.uk/. Accessed 01 October 2011.
2011. July. http://www.stopgaptrial.co.uk/. Accessed 01 October 2011.
40. Mitchell E. RCT of treatments for Pyoderma gangrenosum: time to get involved. Wounds UK. 2010;;6(4):27–32. [Google Scholar]
41. Kaddoura IL, Amm C. A rationale for adjuvant surgical intervention in pyoderma gangrenosum. Ann Plast Surg. 2001 Jan;46(1):23–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
42. Long CC, Jessop J, Young M, Holt PJ. Minimizing the risk of post-operative pyoderma gangrenosum. Br J Dermatol. 1992 Jul;127(1):45–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
43. Mansur AT, Balaban D, Göktay F, Takmaz S. Pyoderma gangrenosum on the breast: a case presentation and review of the published work. J Dermatol. 2010 Jan;37(1):107–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
44. Duval A, Boissel N, Servant JM, Santini C, Petit A, Vignon-Pennamen MD. Pyoderma gangrenosum of the breast: a diagnosis not to be missed. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011 Jan;64(1):e17–e20. Epub 2010 Sep 18.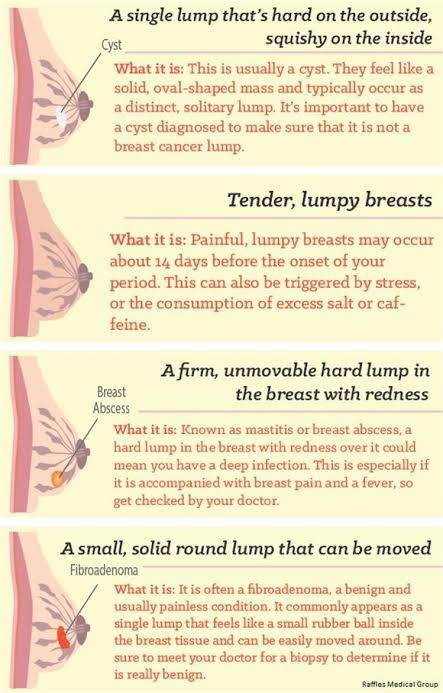 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[PubMed] [Google Scholar]
45. Goshtasby PH, Chami RG, Johnson RM. A novel approach to the management of pyoderma gangrenosum complicating reduction mammaplasty. Aesthet Surg J. 2010 Mar;30(2):186–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
46. Maigre M, Bouachour G, Varache N, Alquier P, Verret JL. [Pseudo-septicemic pyoderma gangrenosum and breast cancer. Apropos of a case caused by an intramuscular injection] Rev Med Interne. 1991 Nov-Dec;12(6):452–454. French. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
47. Beurey J, Weber M, Delrous JL, Chaulieu Y. [Pyoderma gangrenosum: Clofazimine therapy] Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1977 Oct;104(10):631–634. French. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
48. Caterson SA, Nyame T, Phung T, Lee B, Tobias AM. Pyoderma gangrenosum following bilateral deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstruction. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2010 Sep;26(7):475–479. Epub 2010 Jun 9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Symptoms and signs of breast cancer.
 Booking Health
Booking Health Currently, due to the difficulties associated with organizing treatment in Turkey, Switzerland, South Korea and India, we have suspended the processing of applications in these areas.
If you are interested in organizing treatment in Germany, please leave a request and our specialists will contact you as soon as possible.
If you need information about innovative treatments for stage 4 breast cancer in Germany, you can find it
Here
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world. Pathology ranks first among female malignant tumors. The tumor often occurs in reproductive age. Therefore, every woman should know the main symptoms of breast cancer in order to detect it in time, consult a doctor and receive timely treatment. Indeed, in this case, oncologists manage not only to completely cure the disease, but also to avoid complete removal of the mammary gland. nine0005
nine0005
Contents
- The first symptoms of breast cancer
- Subjective signs of breast cancer in women
- Does the breast hurt with cancer
- What symptoms are objectively detected in breast cancer?
- Self-examination
- Late symptoms
- Clinics and cost of treatment
- Breast cancer treatment in Germany
Early symptoms of breast cancer
Often, the disease is usually not detected in the early stages, since breast cancer usually begins without symptoms. In addition, a woman may not attach much importance to them and not see a doctor for a long time, although the tumor continues to grow. nine0005
With breast cancer, the first signs in most cases can only be detected by palpation (when probing the breast). Visible changes in the skin or shape of the breast usually do not occur if the tumor is inside the duct and is less than 5 cm in diameter. It can be:
- Enlargement of one gland in size
- Its displacement upwards or to the side
- Increased mobility of one breast or its fixation, limiting mobility
- Indrawing of the nipple, change in its shape, rash or ulceration - possible early signs of breast cancer
- Discharge from the nipple (this can be blood, pus, colostrum)
- Changes in the skin over the breast - its bulge, tension or swelling
- Local expansion of blood vessels over one of the areas of the breast
- The presence of weeping surfaces
- Redness of the skin
Sometimes the first signs of breast cancer are symptoms of intoxication and an increase in axillary lymph nodes. Especially in cases where the mammary glands are large. Then changes in them visually begin to be determined much later. nine0005
Especially in cases where the mammary glands are large. Then changes in them visually begin to be determined much later. nine0005
With breast cancer, early symptoms should be a reason to see a doctor and get diagnosed. It is likely that the detected signs do not indicate a malignant tumor, but speak of mastopathy, inflammation of the mammary gland, or a benign neoplasm. But still, it is better to make sure of this, so that in the case of cancer, it will not be allowed to go to the stage when the treatment becomes ineffective.
Subjective signs of breast cancer in women
Signs that are based on a woman's feelings are considered subjective in breast cancer. In fact, these are complaints with which the patient turns to a mammologist or oncologist.
The main subjective signs of breast cancer:
- Pulling sensations in the mammary gland
- Itching in breast cancer is observed with swelling of the skin, the appearance of rashes on the nipple
- Possible signs of intoxication syndrome in breast cancer: fever, nausea
- Rarely noted pain
- Women may also complain of swelling of the breast, discharge from the nipples
In most cases, breast cancer appears only in the later stages. Therefore, an objective examination is required for timely diagnosis.
Therefore, an objective examination is required for timely diagnosis.
Can breast cancer hurt
Patients often ask their doctor if breast cancer hurts. Some of them believe that the presence of pain in the mammary gland is a sign of a malignant tumor. But it's not. nine0005
If you have chest pain, it is more likely that dishormonal processes are causing this symptom than cancer. Because the chest hurts with cancer, usually already in the later stages, when the fact of the presence of a tumor is also determined by other clinical signs.
But there are forms of the disease when the breast hurts with breast cancer. This is primarily an edematous-infiltrative form. It is accompanied by an inflammatory process. This is associated with breast cancer pain. In other cases, the pain syndrome appears only in the later stages, when the neoplasm reaches a large size. In this case, the disintegration of the tumor begins, hemorrhages into it are possible. The neoplasm compresses the nerves and surrounding tissues, causing pain. nine0005
nine0005
Choose a specialized clinic and treatment
What symptoms are objectively detected in breast cancer?
Objective signs and symptoms are most important in breast cancer. That is, those that the doctor detects during the examination and probing of the mammary glands.
In most cases, breast cancer has little to no symptoms in its early stages. The main of them is the presence of a palpable tumor in the mammary gland. Nevertheless, in some cases, some symptoms of breast cancer in women can not only help determine the very fact of the presence of a malignant neoplasm, but also suggest its histological form and location. nine0005
When examining a woman, the doctor pays the most attention to:
- The shape of the mammary glands
- Their symmetry
- The condition of the nipples
- Their location
- Changes in the skin of the breast
- )
- Condition of the inguinal lymph nodes
- The function of the hand on the side of the alleged lesion and the condition of the pectoral muscles
On examination, the doctor often reveals reddening of the skin of the breast. It can be local or total. The palpable tumor is fixed to the chest wall and is not always displaced. The skin above it is not only hyperemic, but often swollen. nine0005
It can be local or total. The palpable tumor is fixed to the chest wall and is not always displaced. The skin above it is not only hyperemic, but often swollen. nine0005
Lemon peel symptom of breast cancer develops. Swelling and redness may spread to the skin of the hand. Sometimes ulcers appear on the mammary gland. On palpation, seals in the form of nodules or diffuse (uniform) hardening of the breast tissue are determined.
Paget's cancer, which affects the nipple, shows a rash or weeping patches on the areola. There are such clinical forms of this disease:
- Psoriasis-like - the appearance of plaques and scales
- Eczematous - weeping eczema on the areola or rash
- Ulcerative - characterized by the appearance of ulceration
- Tumor - a tumor-like formation is visualized in the nipple area
Well-marked external signs of breast cancer appear in acute forms of the malignant process. They are considered the most unfavorable in terms of prognosis.
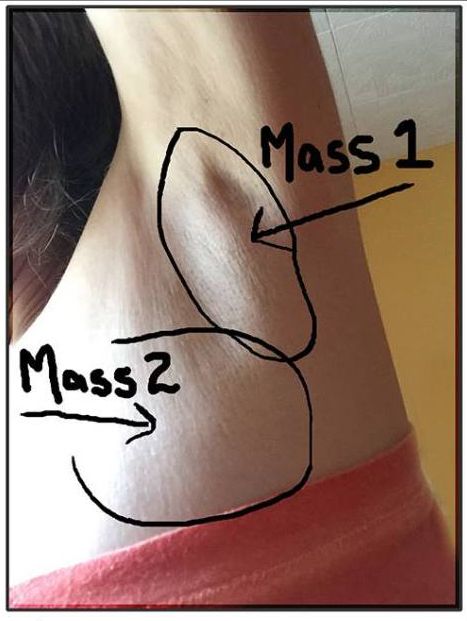
In this case, with breast cancer, a bump in the mammary gland is not even always detected, since other symptoms are more pronounced:
- Improvement of body temperature and general signs of intoxication
- Elevated inflammation of the mammary gland - redness and infiltration of the skin of the breast, its loading
- Increase lymph nodes
- Cloud discharge from the nipple
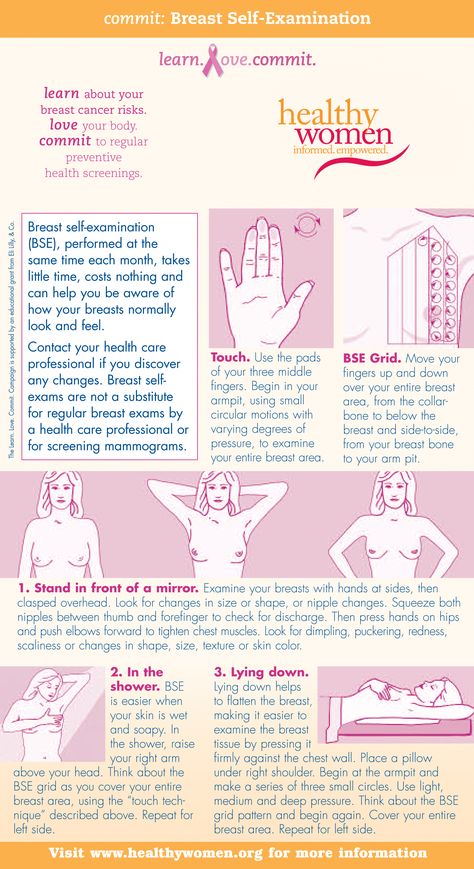
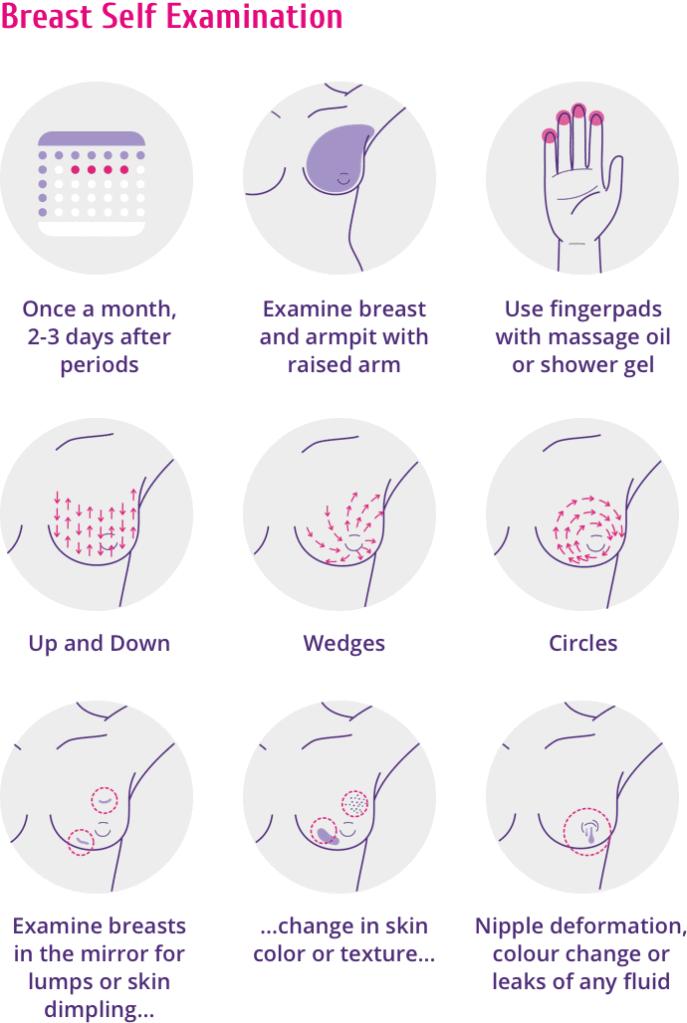
Self -surveillance of 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 stages, if you regularly engage in self-diagnosis. Breast examinations are recommended for women from the age of 20, since breast cancer can be detected at almost any age. It is carried out once a month. nine0005
Self-examination is especially important in developing countries where cancer screening is poorly organized. So, in the CIS countries, on average, in 80% of cases, women manage to determine breast cancer on their own, which becomes the reason for visiting a doctor. And only in 20% of cases, the tumor is first detected by doctors.
Unfortunately, in most cases, the patient notices changes only when the symptoms become severe: deformity of the mammary gland, skin ulcerations, discharge from the nipple, etc. appear. If you do regular self-examinations, you can understand that you have breast cancer much earlier. And early detection improves the results of treatment, in most cases allowing the disease to be completely cured. nine0005
The following are international recommendations on how to determine breast cancer on your own:
1. It is necessary to conduct an examination one week after menstruation, which is associated with a decrease in the sensitivity of the mammary glands.
2. Be sure to pay attention to the laundry. If it is dirty at the site of the projection of the nipples, this may indicate a discharge. Carefully inspect the areola (pigmented circle around the nipple). See if there are peelings, rashes, ulcers on it. nine0005
3. One way to understand breast cancer is to compare two breasts. Normally, they should be symmetrical. Stand in front of a mirror and put your hands behind your head. Take a close look at your chest.
Normally, they should be symmetrical. Stand in front of a mirror and put your hands behind your head. Take a close look at your chest.
Pay attention to the following changes:
- One breast has become larger than the other (if before they were the same or the other mammary gland had a larger size)0026
- Areas with discoloration of the skin appeared on one breast
The asymmetry of the mammary glands and their different relative positions are not signs of a malignant tumor. After all, it is likely that they have always been different or became so a few years ago. Timely detection of breast cancer helps to monitor the mammary glands in dynamics. If the asymmetry is growing and has appeared recently, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
4. The next step is to palpate the breast. This is the best way to find breast cancer with a small tumor size. Palpation is carried out in a horizontal position. Lie down on your back. The chest in the region of the palpable breast should be slightly elevated. Therefore, a pillow should be placed under the back on the probing side. Feel the chest with three or four fingers of the opposite hand. Remember the "route" of palpation. If it is the same every time, it will help to detect changes in the mammary gland in time. At the end of the self-examination, squeeze the nipple to check for discharge and palpate the axilla for swollen lymph nodes. nine0005
Therefore, a pillow should be placed under the back on the probing side. Feel the chest with three or four fingers of the opposite hand. Remember the "route" of palpation. If it is the same every time, it will help to detect changes in the mammary gland in time. At the end of the self-examination, squeeze the nipple to check for discharge and palpate the axilla for swollen lymph nodes. nine0005
5. Another additional method for recognizing breast cancer is palpation in the shower. Water changes the properties of the skin, and the tumor is sometimes easier to detect. In addition, fingers glide better, which makes examination easier.
If you notice signs of a tumor, see your doctor. There is no need to be afraid, because not every bump in the chest is cancer. Most of the pathological formations that women reveal in themselves are not oncological. After all, there are dozens of other diseases that are found with a much higher frequency than malignant tumors. nine0005
Choose a specialized clinic and treatment
Late symptoms
At stages 3-4, the symptoms and signs of breast cancer are associated with a significant increase in the size of the neoplasm, its germination in the chest wall and other nearby tissues. Distant metastases may be found. They most often affect the bones, spine, spinal cord, lungs, liver.
Distant metastases may be found. They most often affect the bones, spine, spinal cord, lungs, liver.
What breast cancer looks like depends on its clinical form. Often the disease is detected only at stage 3 or later. At this time, the tumor can be seen with the naked eye. It is already growing into the chest wall, which is accompanied by pain. Skin ulcers often appear in breast cancer. Symptoms of intoxication may occur. nine0005
With a large tumor, progressive weight loss is often noted, since the tumor consumes a large amount of nutrients in order to grow, which it "takes" from the blood.
In the advanced stages of breast cancer, open wounds on the skin of the breast may bleed and fester. They don't heal. The neoplasm may be partially located outside the mammary gland, and not inside it. Pus and necrotic masses are discharged from the nipple. Bleeding occurs from time to time. nine0005
In stage 4 breast cancer, the symptoms are also associated with the presence of metastatic foci.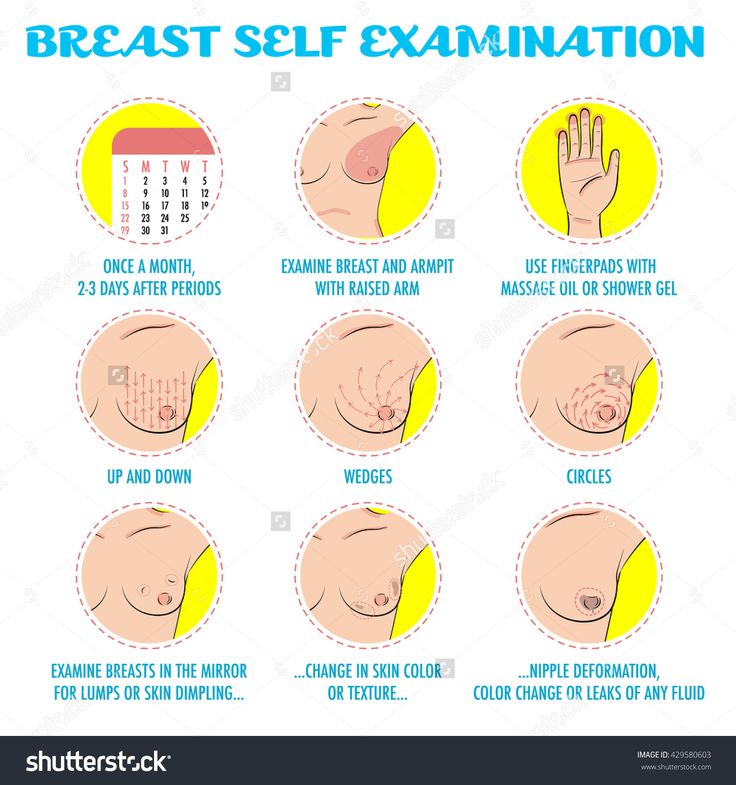 Clinical signs depend on the location of the metastases. If they are present in the bones, painful sensations and pathological fractures are possible.
Clinical signs depend on the location of the metastases. If they are present in the bones, painful sensations and pathological fractures are possible.
In case of metastatic lesions of the structures of the respiratory system in breast cancer, the fluid in the lungs causes shortness of breath and is often the direct cause of death. Possible damage to the spinal cord with the development of sensory and motor disorders, dysfunction of the pelvic organs. nine0005
Clinics and cost of treatment
The average cost of the main types of treatment is:
- Sectoral resection for breast cancer with further flap plastic - € 12,870
- Radical mastectomy for breast cancer with large or small pectoral fascia - €13 840
- Treatment of breast cancer with lymph node metastases by lumpectomy with lymphadenectomy – €18 680
- Plastic reconstruction of the breast with own tissues using the DIEP flap method – €47 640
- Breast reconstruction after mastectomy with own tissue or implant €18,580
- Breast reconstruction after tumor removal with an expander or alloprosthesis €13,930
- Chemotherapy for breast cancer €6,940
- Treatment of breast cancer (cancer) chest) by embolization or chemoembolization – €42,790
- Radiotherapy for breast cancer – €33,590
- Brachytherapy for breast cancer – €12,570
- Breast cancer treatment with proton therapy €87,620
The total cost of the medical program depends on the treatment plan. It is determined after receiving the results of the initial examination.
It is determined after receiving the results of the initial examination.
The following clinics are leaders in the treatment of breast cancer:
- Helios Clinic Berlin-Buch, Department of Gynecology, Mammology and Obstetrics
- University Hospital Tübingen, Department of Adult and Pediatric Gynecology, Mammology, Obstetrics
- University Hospital Ulm, Department of Obstetrics, Adult and Pediatric Gynecology
- Charité University Hospital Berlin, Department of Adult and Pediatric Gynecology, Mammology
- University Hospital. Goethe Frankfurt am Main, Department of Adult and Pediatric Gynecology, Obstetrics and Mammology
undergo treatment. But it is not equally effective in different countries. nine0005 Germany is one of the world leaders in the treatment of breast cancer and other malignant tumors. You can use the services of German oncologists, and Booking Health will help you with this. Thanks to cooperation with us, you get a number of advantages: Leave a request on the site. Our specialist will contact you and offer several options among the best clinics specializing in the treatment of breast cancer. Having agreed on all the issues, we ourselves will organize treatment for you - you will not have to think about anything but your health. We will contact the administration of the clinic, help prepare the documents and open a visa, translate the documentation into German. nine0005 When you arrive in Germany, we will meet you at the airport, drive you to the clinic and provide you with an interpreter. Contact Booking Health Trustpilot Authors: The article was edited by experts in the field of medicine, medical specialists Doctor Nadezhda Ivanisova, Doctor Sergey Pashchenko. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-treatment! nine0005 Sources: IMTJ - International Medical Travel Journal MedLineplus NHS Read: Why Booking Health - questions and answers as not to be the choice rating of clinics on the website Booking Health Booking Health - Quality Standards Send a request for treatment Booking Health GmbH | Diagnosis and treatment | nine0005 Oncology of breast cancer is extraneous neoplasms that appear in the glandular tissue. The number of subspecies of this disease known to date is about twenty. Cancer cells differ from ordinary ones in their accelerated metabolism and abnormal structure. When breast oncology occurs, these cells constantly grow, and later penetrate into the lymph nodes and other organs. Modern science believes that the main catalyst for breast cancer is a distortion of the hormonal background, as a result of which all other symptoms of cancer occur. Indeed, according to statistics, it is found more often during menopause. After all, this is a period of a sharp change in the production of various hormones by the female body, affecting the state of the mammary gland. Types of breast cancer in women can be according to various criteria, we will give the simplest of the classifications, which even a non-specialist can easily understand. To understand how to determine the stage of breast cancer, you should know how they differ. The diameter of the tumor, the duration of the disease, how affected the body is, what is the prognosis for survival is considered. There are initial and 4 main stages of the development of the disease: nine0005 The question of how quickly the disease develops cannot be answered with absolute certainty. Progress is driven by many factors, including: The last factor in order is one of the most important, since there are more aggressive types of oncological diseases and less aggressive ones. Thus, the transition from stage to stage and the overall progress of the disease in one patient can take a year, and in another 10 years. nine0005 The answer to the question of how long they live with breast cancer lies in the extent to which the oncological disease has spread to the mammary gland. For a more precise definition in medicine, the term “five-year survival rate” is used - the probability of living more than 5 years after diagnosing oncology at a specific stage. At the initial stage, as mentioned above, the average life expectancy for breast cancer is practically no different from the usual one, because it is successfully cured in most patients. But the problem is that at least half of the patients detect cancer at grades 3-4. nine0005 In addition to survival, the issue of recurrence is also relevant. Current medical treatments do not guarantee 100% killing of cancer cells. Therefore, after some time, the disease can return with renewed vigor and affect other important elements of the patient's body. Of all the methods of early diagnosis of breast cancer, self-examination is the most important, because it is extremely important to notice symptoms early. Doctors insist on monthly self-examination for all women over 35 and those who are at risk. It is more likely to identify breast cancer on your own in the second week after the start of the menstrual cycle. The set of tools and techniques for detecting breast cancer in physicians is quite wide. The main ones are: These modern techniques not only make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, differentiating it from, for example, mastopathy, but also give a concrete idea of the position, size of the tumor and its malignancy. Signs of breast cancer in the first stage appear little at all or are barely noticeable. There are, for example, small nodules that appear when feeling. It is curious that painful neoplasms often indicate a benign tumor, but malignant pain does not bring in the initial stages. The knot may be motionless, or it may slightly move under the pressure of the fingers. nine0490 Other signals of breast cancer are a change in the texture of the skin, it may appear folds, wrinkles, swelling, or an orange-like peel. Small sores may also appear, which in the later stages suppurate and bleed. If the disease affects the nipple, then the signal for this is pathological discharge, as well as changes in the skin of the nipple and areola around it. Do not confuse this with secretions during lactation (feeding). If you are extremely concerned about whether breast cancer is being treated, then we are confidently ready to give a positive answer. During treatment, it is necessary to completely remove all tumor cells. Naturally, the easier it is to do this, the earlier the neoplasm was detected. Modern methods of treating breast cancer include many different therapies, but the most effective method has been and remains surgical, in which it is possible to completely remove the breast or remove only the tumor with its small size. nine0005 Mastectomy - the removal of one of the patient's breasts, is indicated in the later stages of cancer. With the current level of development of plastic surgery, such operations are often carried out together with reconstructive ones. That is, immediately after the removal of the breast, an implant is implanted that externally imitates the organ. After a mastectomy, which is usually prescribed from the third degree of cancer, a thorough examination of nearby tissues and lymph nodes is carried out to exclude possible relapses. Other treatments for the disease include the following therapies: nine0005 Treatment should be carried out comprehensively under the constant supervision of a specialist, including after recovery. Note that a number of methods have their own complications and side effects, eliminated by other drugs and other medical means. nine0005 Scientists believe that the key factor in the occurrence of a tumor focus is hormonal. But there are other causes of breast cancer in women. Consider what increases the likelihood of the disease: The number of factors is quite large and all of them play a role in the occurrence of this oncological disease.

Choose treatment abroad and you will definitely get an excellent result!
Breast cancer - types, symptoms and signs, diagnosis and treatment
 P.R.A. Center
P.R.A. Center  nine0490 Both excess and lack of sex hormones are considered negative factors. Thus, the incidence in women who have gone through childbirth and lactation is several times lower than in women who have not given birth or who have had abortions. In the latter, signs of breast cancer are more common.
nine0490 Both excess and lack of sex hormones are considered negative factors. Thus, the incidence in women who have gone through childbirth and lactation is several times lower than in women who have not given birth or who have had abortions. In the latter, signs of breast cancer are more common. Species
 At subsequent stages, it leads to inflammation of the lymph nodes, the progress of the neoplasm, and, accordingly, to an increase in breast volume. Characteristic keratinized skin and open sores may also appear. nine0026
At subsequent stages, it leads to inflammation of the lymph nodes, the progress of the neoplasm, and, accordingly, to an increase in breast volume. Characteristic keratinized skin and open sores may also appear. nine0026
 Instead of the puffiness observed in other species, there is a decrease in the volume of the breast, its pigmentation and the appearance of multiple nodules, which then merge into one large tumor. nine0026
Instead of the puffiness observed in other species, there is a decrease in the volume of the breast, its pigmentation and the appearance of multiple nodules, which then merge into one large tumor. nine0026
Stages
 Such breast cancer in women is of little danger, the chances of being successfully cured are incredibly high and are above 98%. Doctors recommend undergoing a medical examination on their own and in a clinic (antenatal clinic) on a regular basis.
Such breast cancer in women is of little danger, the chances of being successfully cured are incredibly high and are above 98%. Doctors recommend undergoing a medical examination on their own and in a clinic (antenatal clinic) on a regular basis.  The probability of cure is extremely small - up to 10%
The probability of cure is extremely small - up to 10% Development rate
Survival

Stage Five-year survival First Up to 95% Second Up to 80% Third Up to 40% Fourth To 10% nine0557  The more cancer cells have grown before the start of therapy or surgery, the greater the likelihood of recurrence of breast cancer. At the same time, the most dangerous are the first 5 years after a seemingly successful therapy. Therefore, cancer patients should be followed up regularly after the end of treatment. This will make the prognosis for breast cancer more favorable. nine0005
The more cancer cells have grown before the start of therapy or surgery, the greater the likelihood of recurrence of breast cancer. At the same time, the most dangerous are the first 5 years after a seemingly successful therapy. Therefore, cancer patients should be followed up regularly after the end of treatment. This will make the prognosis for breast cancer more favorable. nine0005 Diagnostics
You need to start with a simple examination of the chest with a mirror. If one of them is enlarged relative to the other, deformation is observed, or the skin gradually turns into a lemon peel, you should immediately contact a specialist. This is the simplest initial diagnosis of breast cancer. nine0005  It is easier to recognize it if, when examining, standing or lying down, one hand is thrown behind the head, and the other helps to examine.
It is easier to recognize it if, when examining, standing or lying down, one hand is thrown behind the head, and the other helps to examine.
In addition to visual inspection, it is necessary to check the chest by touch for tumor nodes. If discomfort or pain is felt during palpation, a visit to the mammologist should not be postponed. Abnormal discharge from the nipples is determined by gently squeezing them. Rapid detection of the disease is a guarantee of an absolute cure, so it is vital. nine0005 How to detect breast cancer in a clinical setting
Symptoms and signs
The symptoms of breast cancer also include the growth of lymph nodes, which is typical for grade 2. And at first the nearby nodes under the armpits suffer. nine0005
nine0005 Treatment

Causes