Ultrasound two months
What To Expect, Purpose & Results
Overview
What is an ultrasound in pregnancy?
A prenatal ultrasound (or sonogram) is a test during pregnancy that checks on the health and development of your baby. An obstetrician, nurse midwife or ultrasound technician (sonographer) performs ultrasounds during pregnancy for many reasons. Sometimes ultrasounds occur to check on your baby and make sure they’re growing properly. Other times your pregnancy care provider orders an ultrasound after they detect a problem.
During an ultrasound, sound waves are sent through your abdomen or vagina by a device called a transducer. The sound waves bounce off structures inside your body, including your baby and your reproductive organs. Then, the sound waves transform into images that your provider can see on a screen. It doesn’t use radiation, like X-rays, to see your baby.
Even though prenatal ultrasounds are safe, you should only have them when it’s medically necessary. If there’s no reason for an ultrasound (for example, if you just want to see your baby), your insurance company might not pay for it.
Prenatal ultrasounds may be called fetal ultrasounds or pregnancy ultrasounds. Your provider will talk to you about when you can expect ultrasounds during pregnancy based on your health history.
Why is a fetal ultrasound important during pregnancy?
An ultrasound is one of the few ways your pregnancy care provider can see and hear your baby. It can help them determine how far along you are in pregnancy, if your baby is growing properly or if there are any potential problems with the pregnancy. Ultrasounds may occur at any time in pregnancy depending on what your provider is looking for.
What can be detected in a pregnancy ultrasound?
A prenatal ultrasound does two things:
- Evaluates the overall health, growth and development of the fetus.
- Detects certain complications and medical conditions related to pregnancy.
In most pregnancies, ultrasounds are positive experiences and pregnancy care providers don’t find any problems.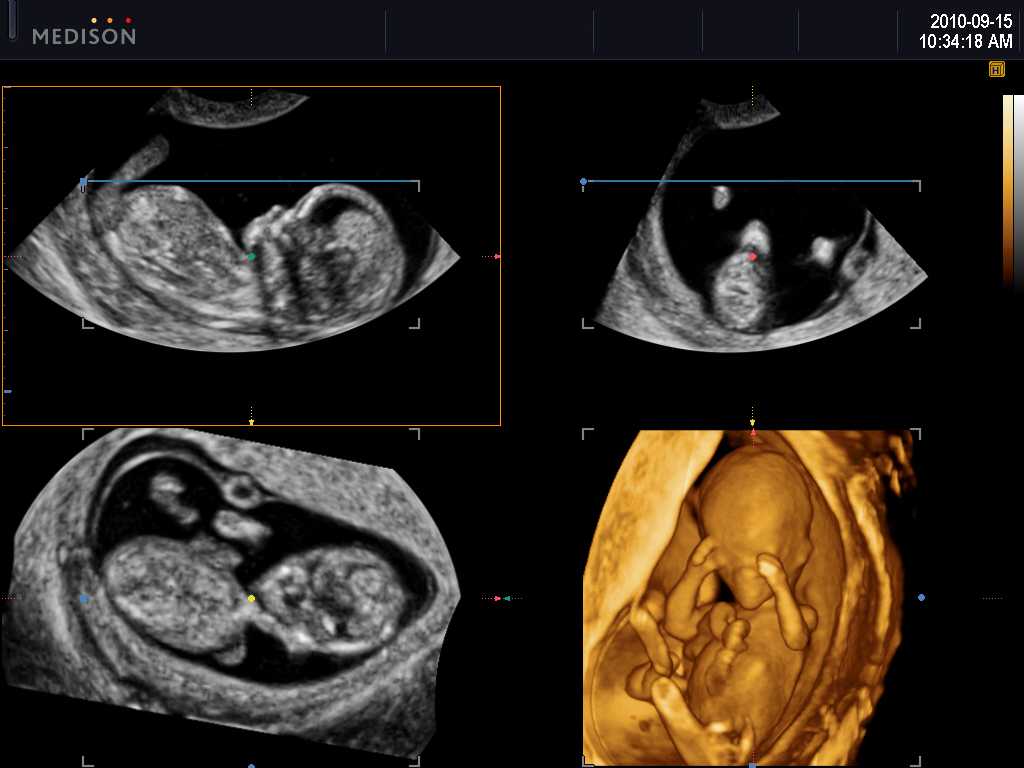 However, there are times this isn’t the case and your provider detects birth disorders or other problems with the pregnancy.
However, there are times this isn’t the case and your provider detects birth disorders or other problems with the pregnancy.
Reasons why your provider performs a prenatal ultrasound are to:
- Confirm you’re pregnant.
- Check for ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy, miscarriage or other early pregnancy complications.
- Determine your baby’s gestational age and due date.
- Check your baby’s growth, movement and heart rate.
- Look for multiple babies (twins, triplets or more).
- Examine your pelvic organs like your uterus, ovaries and cervix.
- Examine how much amniotic fluid you have.
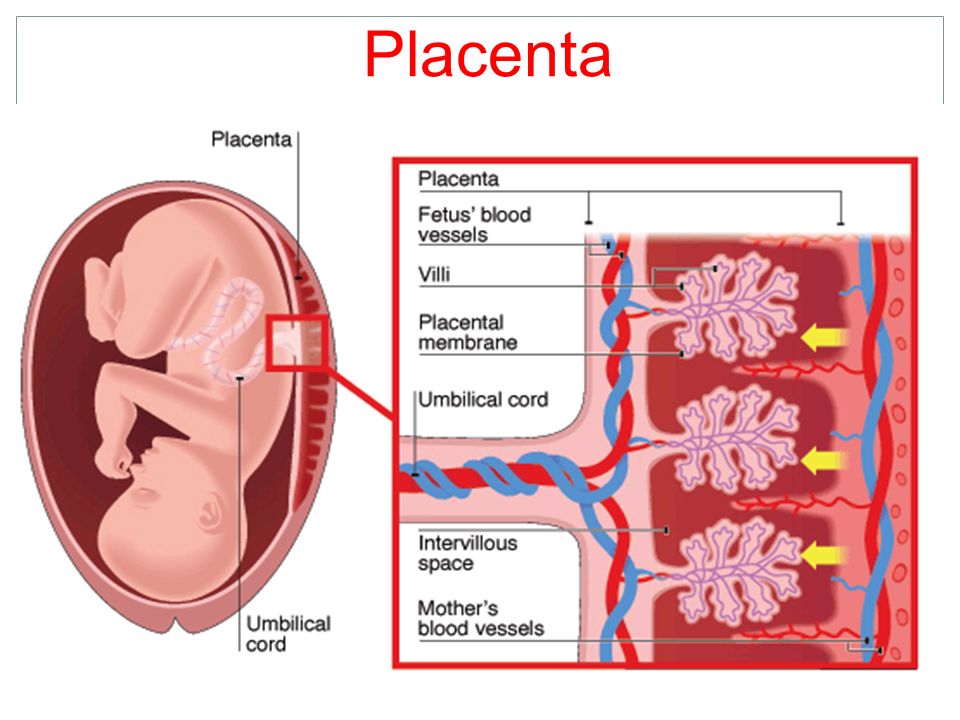
- Check the location of the placenta.
- Check your baby’s position in your uterus.
- Detect problems with your baby’s organs, muscles or bones.
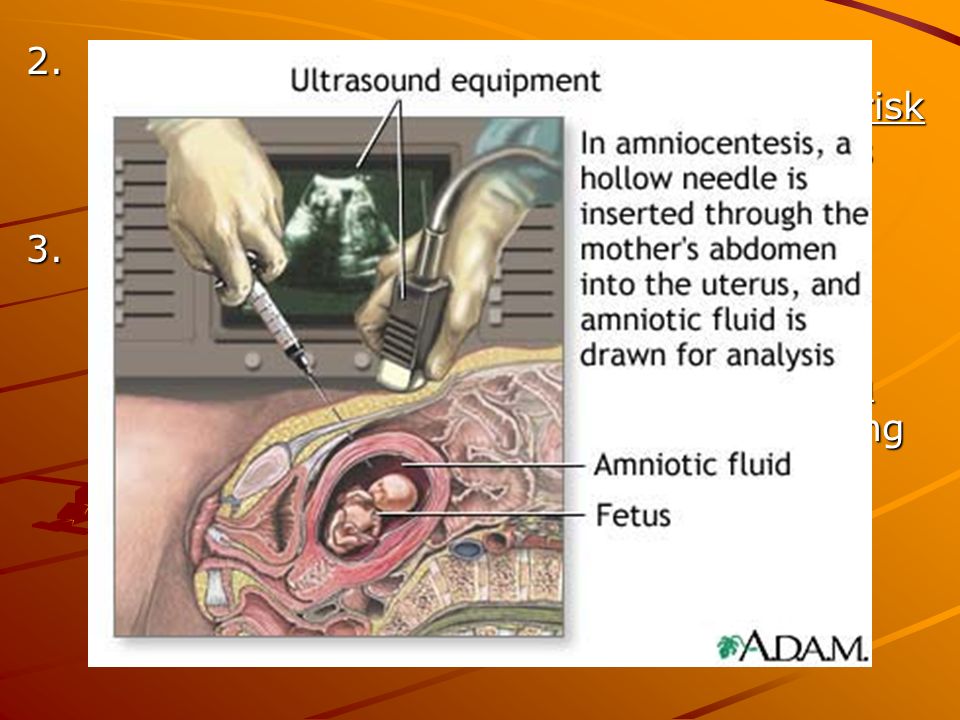
Ultrasound is also an important tool to help providers screen for congenital conditions (conditions your baby is born with). A screening is a type of test that determines if your baby is more likely to have a specific health condition. Your provider also uses ultrasound to guide the needle during certain diagnostic procedures in pregnancy like amniocentesis or CVS (chorionic villus sampling).
Your provider also uses ultrasound to guide the needle during certain diagnostic procedures in pregnancy like amniocentesis or CVS (chorionic villus sampling).
An ultrasound is also part of a biophysical profile (BPP), a test that combines ultrasound with a nonstress test to evaluate if your baby is getting enough oxygen.
How many ultrasounds do you have during your pregnancy?
Most pregnant people have one or two ultrasounds during pregnancy. However, the number and timing vary depending on your pregnancy care provider and if you have any health conditions. If your pregnancy is high risk or if your provider suspects you or your baby has a health condition, they may suggest more frequent ultrasounds.
When do you have your first prenatal ultrasound?
The timing of your first ultrasound varies depending on your provider. Some people have an early ultrasound (also called a first-trimester ultrasound or dating ultrasound). This can happen as early as seven to eight weeks of pregnancy. Providers do an early ultrasound through your vagina (transvaginal ultrasound). Early ultrasounds do the following:
Providers do an early ultrasound through your vagina (transvaginal ultrasound). Early ultrasounds do the following:
- Confirm pregnancy (by detecting a heartbeat).
- Check for multiple fetuses.
- Measure the size of the fetus.
- Help confirm gestational age and due date.
Some providers perform your first ultrasound closer to 12 weeks of pregnancy.
20-week ultrasound (anatomy scan)
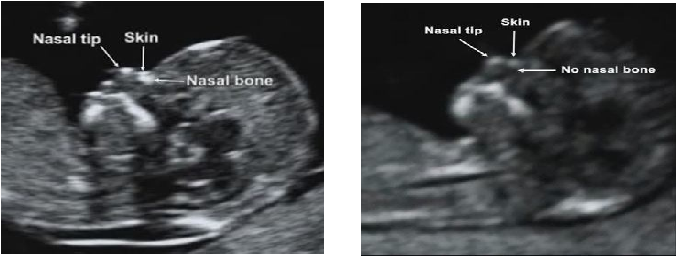
You can expect an ultrasound around 18 to 20 weeks in pregnancy. This is known as the anatomy ultrasound or 20-week ultrasound. During this ultrasound, your pregnancy care provider can see your baby’s sex (if your baby is in a good position for viewing their genitals), detect birth disorders like cleft palate or find serious conditions related to your baby’s brain, heart, bones or kidneys. If your pregnancy is progressing well and with no complications, your 20-week ultrasound may be your last ultrasound during pregnancy. However, if your provider detects a problem during your 20-week ultrasound, they may order additional ultrasounds.
How soon can you see a baby on an ultrasound?
Pregnancy care providers can detect an embryo on an ultrasound as early as six weeks into the pregnancy. An embryo develops into a fetus around the eighth week of pregnancy.
If your last menstrual period isn’t accurate, it’s possible that it may be too early to detect a fetal heart rate.
Which ultrasound is most important during pregnancy?
All ultrasounds during pregnancy are important. Your pregnancy care provider uses ultrasound to tell them important information about your pregnancy.
Test Details
What are the two main types of pregnancy ultrasounds?
The two main types of pregnancy ultrasound are transvaginal ultrasound and abdominal ultrasound. Both use the same technology to produce images of your baby. Your pregnancy care provider performs a transvaginal ultrasound by placing a wand-like device inside your vagina. They perform an abdominal ultrasound by placing a device on the skin of your belly.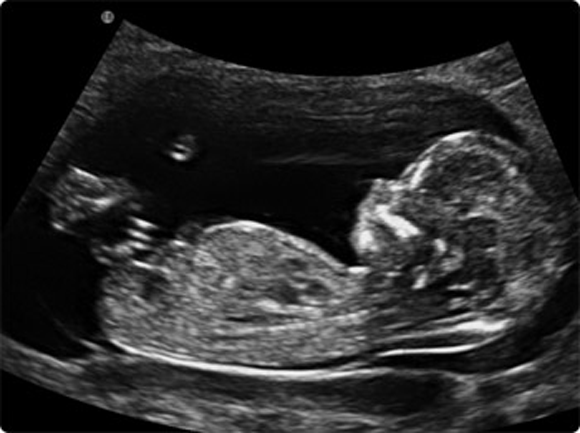
Transvaginal ultrasound
During a transvaginal ultrasound, your pregnancy care provider places a device inside your vaginal canal (similar to how you place a tampon). In early pregnancy, this ultrasound helps to detect a fetal heartbeat or determine how far along you are in your pregnancy (gestational age). Images from a transvaginal ultrasound are clearer in early pregnancy as compared to abdominal ultrasound.
Abdominal ultrasound
Your pregnancy care provider performs an abdominal ultrasound by placing a transducer directly on your skin. Then, they move the transducer around your belly (abdomen) to capture images of your baby. Sometimes slight pressure has to be applied to get the best views. Providers use abdominal ultrasounds after about 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Traditional ultrasounds are 2D. More advanced technologies like 3D or 4D ultrasound can create better images. This is helpful when your provider needs to see your baby’s face or organs in greater detail. Not all providers have 3D or 4D ultrasound equipment or specialized training to conduct this type of ultrasound.
Not all providers have 3D or 4D ultrasound equipment or specialized training to conduct this type of ultrasound.
Your provider may recommend other types of ultrasounds. Examples of additional ultrasounds are:
- Doppler ultrasound: This type of ultrasound checks how your baby’s blood flows through its blood vessels. Most Doppler ultrasounds occur later in pregnancy.
- Fetal echocardiogram: This type of ultrasound looks at your baby’s heart size, shape, function and structure. Your provider may use it if they suspect your baby has a congenital heart condition, if you had another child that had a heart condition or if you have certain health conditions that warrant taking a closer look at the heart.
How do I prepare for the test?
There’s no special preparation for an ultrasound. Some pregnancy care providers ask that you come with a full bladder and don’t use the restroom before the test. This helps them view your baby better on the ultrasound.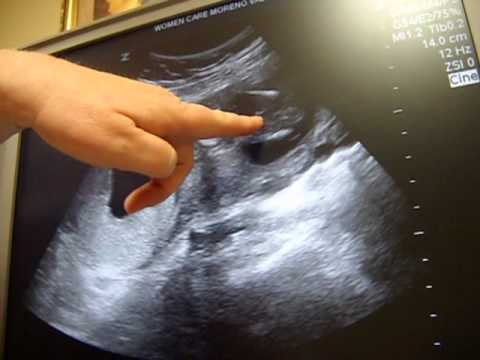 You can bring a support person, but bringing children is discouraged as this is an important test that requires complete focus.
You can bring a support person, but bringing children is discouraged as this is an important test that requires complete focus.
You may be asked to change into a hospital gown, but this isn’t usually required for abdominal ultrasounds. If your provider is performing a transvaginal ultrasound in your first trimester, you’ll put on a hospital gown or undress from the waist down.
What should I expect during a prenatal ultrasound?
You’ll lie on a padded examining table during the test. Most ultrasounds occur in a dimly lit room, which helps your ultrasound technician (or sonographer) see the screen. Your sonographer applies a small amount of water-soluble gel to the skin of your belly. The gel doesn’t harm your skin or stain your clothes, but it may feel cold. This gel helps transmit sound waves more efficiently.
Next, the sonographer places a transducer on the skin of your abdomen. The transducer sends sound waves into your body, which reflect off internal structures, including your baby.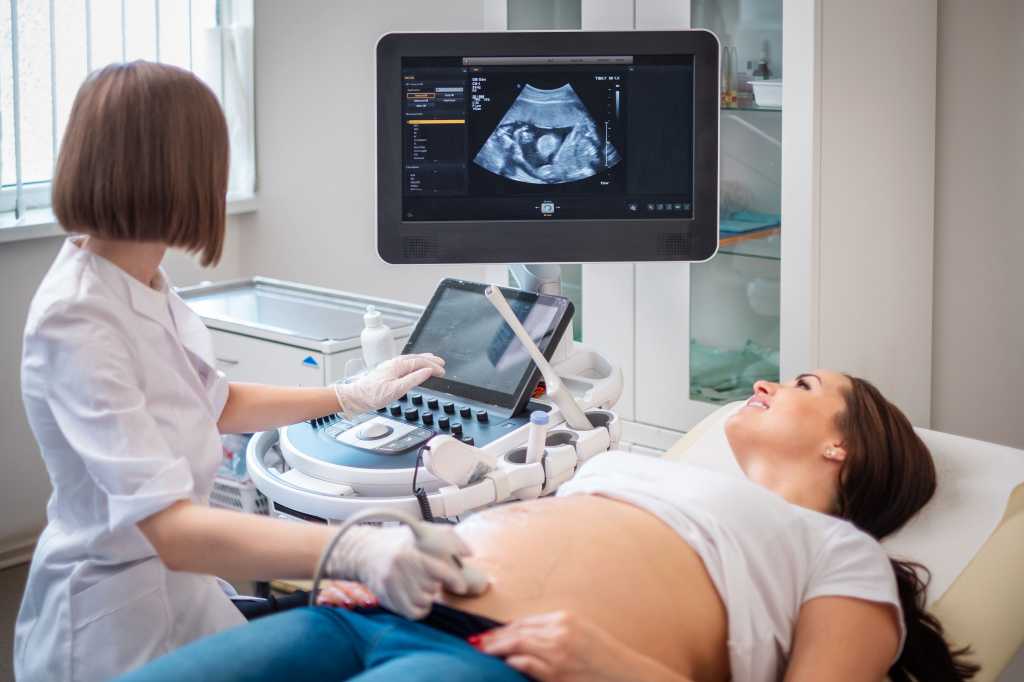 The sound waves that reflect back create pictures on a screen. Your sonographer uses these images to take important measurements such as your baby’s head circumference and length. You may see them making lines on the screen or clicking a button to “freeze” certain angles.
The sound waves that reflect back create pictures on a screen. Your sonographer uses these images to take important measurements such as your baby’s head circumference and length. You may see them making lines on the screen or clicking a button to “freeze” certain angles.
There’s virtually no discomfort during a prenatal ultrasound. You may feel mild discomfort if you have to pee. The ultrasound test takes about 30 minutes to complete.
If you have a transvaginal ultrasound, the process is only different in that the transducer is inside your vagina and not on your belly.
What should I expect after a pregnancy ultrasound?
If you had an abdominal ultrasound, your sonographer wipes the gel off your belly. They may print off some ultrasound pictures for you to take home with you.
In most cases, your sonographer won’t discuss the results of your test with you. If your obstetrician performs your ultrasound, they may discuss what they see as they go along.
If a sonographer performs your ultrasound, an obstetrician will look at the images, then discuss their findings with you at your next appointment.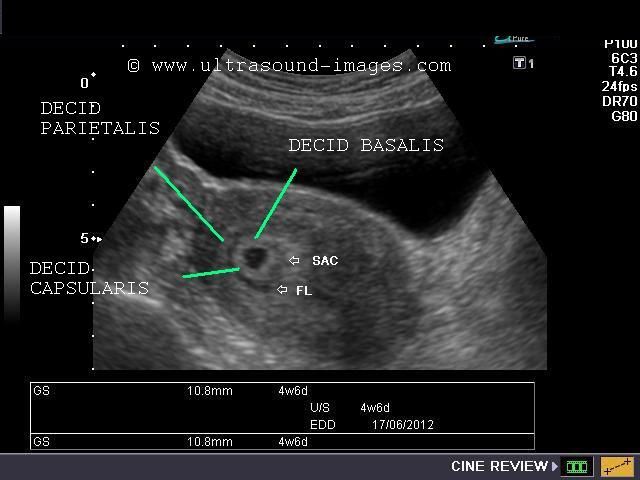 Most practices schedule your appointment right after your ultrasound so you get your results the same day.
Most practices schedule your appointment right after your ultrasound so you get your results the same day.
What are the risks of prenatal ultrasounds?
Studies have shown ultrasounds are safe during pregnancy. There are no harmful side effects to you or your baby.
Is it safe to do an ultrasound every month during pregnancy?
While ultrasounds are safe for you and your baby, most major medical associations recommend that pregnancy care providers should only do ultrasounds when the tests are medically necessary. If your ultrasounds are normal and your pregnancy is uncomplicated or low risk, repeat ultrasounds aren’t necessary.
Results and Follow-Up
What results do you get on a pregnancy ultrasound?
Your ultrasound results will be normal or abnormal. A normal result means your pregnancy care provider didn’t find any problems and that your baby is growing and developing normally. An abnormal result means your provider noticed something irregular. If they do, your provider will order additional ultrasounds or diagnostic tests to determine if something is wrong.
If they do, your provider will order additional ultrasounds or diagnostic tests to determine if something is wrong.
Occasionally, the ultrasound is incomplete if there’s difficulty seeing all the structures needed for that particular ultrasound. Your baby’s position or movement sometimes makes it difficult to see everything your provider needs to see. If this is the case, you’ll need a repeat ultrasound and they’ll try again.
There are some limitations to ultrasounds, so your provider may not find certain abnormalities until after birth.
What are reasons you need more ultrasounds during pregnancy?
There are several reasons your pregnancy care provider may order additional ultrasounds during your pregnancy. Some of these reasons include:
- Problems with your ovaries, uterus, cervix or other pelvic organs.
- Your baby is measuring small for their gestational age or your provider suspects IUGR (intrauterine growth restriction).
- Problems with the placenta like placenta previa or placental abruption.
- You’re pregnant with twins, triplets or more.
- Your baby is breech.
- You have too much amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios).
- You have too little amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios).
- You have a condition like gestational diabetes or preeclampsia.
- Your baby has a congenital disorder.
Normal results on pregnancy ultrasounds can vary. Generally, a normal result means your baby appears healthy and your provider didn’t find any issues.
Why do some pregnancy providers schedule ultrasounds differently?
The number of ultrasounds you’ll have and when you have them can vary between providers. Every practice operates differently and some providers do things differently based on your health history or symptoms.
When does a pregnancy ultrasound determine sex?
Your baby’s sex isn’t visible on an ultrasound until about 18 to 20 weeks. Be sure to tell your pregnancy care provider whether or not you want to know the sex of your baby before your ultrasound.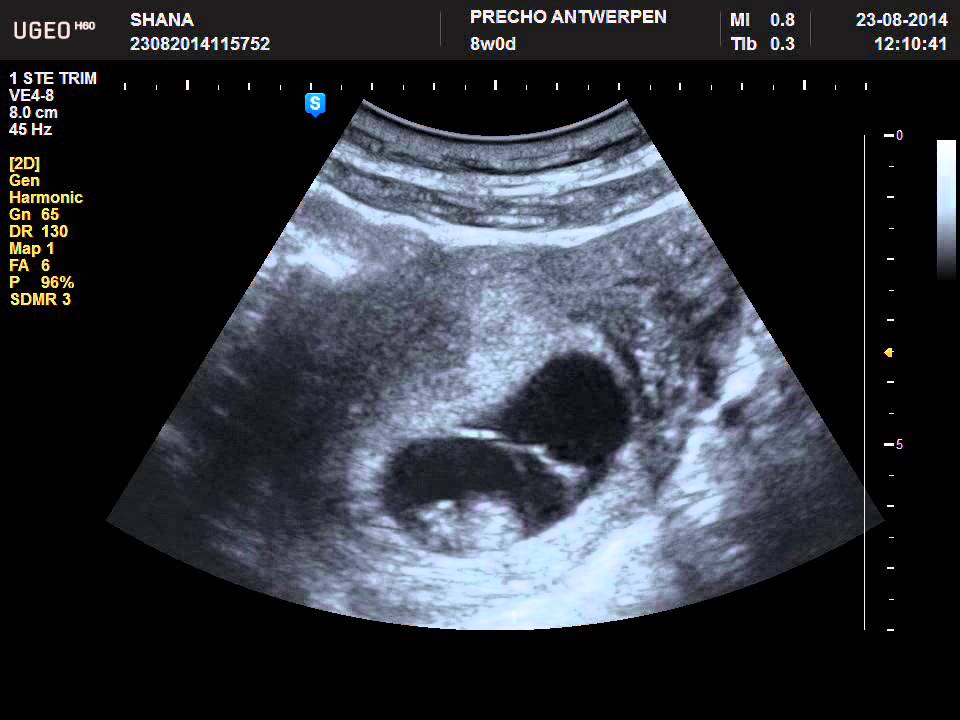
A note from Cleveland Clinic
An ultrasound during pregnancy can be both exciting and terrifying. Your pregnancy care provider uses ultrasound to get a better idea of how your baby is growing and developing. There are different types of ultrasounds, and the exact timing may vary depending on your provider. Most pregnant people have two ultrasounds — one in the first trimester and one in the second trimester. However, if there’s a potential complication or medical reason for more ultrasounds, your provider will order more as a precaution. Talk to your provider about the ultrasound schedule during pregnancy and what you can expect.
What Happens at 2 Months of Pregnancy?
In This Section
- Month by Month
- What happens in the second month?
- What happens in the third month?
- What happens in the fourth month?
- What happens in the fifth month?
- What happens in the sixth month?
- What happens in the seventh month?
- What happens in the eighth month?
- What happens in the ninth month?
- What happens in the tenth month?
The ball of cells turns into an embryo at the start of the 6th week.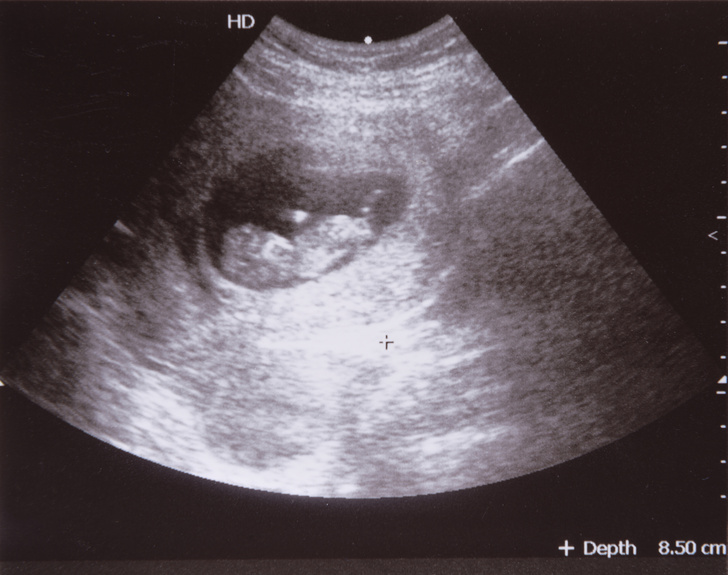 The embryonic stage of pregnancy lasts about 5 weeks. This is when all the major internal organs start developing.
The embryonic stage of pregnancy lasts about 5 weeks. This is when all the major internal organs start developing.
What happens during week 5 - 6?
-
The embryo is less than 1/5 inch (4–5 mm) long.
-
A part of the embryo starts to show cardiac activity. It sounds like a heartbeat on an ultrasound, but it's not a fully-formed heart — it's the earliest stage of the heart developing.
-
Buds for arms and legs develop.
-
The neural tube begins forming. The neural tube will later form the brain, spinal cord, and major nerves.
-
The bud of a tail develops.
- The umbilical cord begins developing.
What happens during week 7 - 8?
-
The embryo is 1/4 to 1/2 inch (7–14 mm) long.
-
The heart has formed.
-
Webbed fingers and toes develop.
-
The arms bend at the elbows.
-
External ears, eyes, eyelids, liver, and upper lip begin forming.
-
The sex organs are the same — neither female nor male — in all embryos until the 7th or 8th week. If a gene triggers the development of testes, the embryo develops as a biological male. If there isn’t a trigger, the embryo develops ovaries and becomes biologically female.
What are the symptoms of pregnancy in the second month?
Pregnancy symptoms often become very noticeable when you’re 2 months pregnant. Common discomforts like breast tenderness, feeling very tired, peeing more often, heartburn, nausea, and vomiting usually get worse. Your body produces extra blood during pregnancy, and your heart beats faster and harder than usual to carry the extra blood.
Was this page helpful?- Yes
- No
Help us improve - how could this information be more helpful?
How did this information help you?
Please answer below.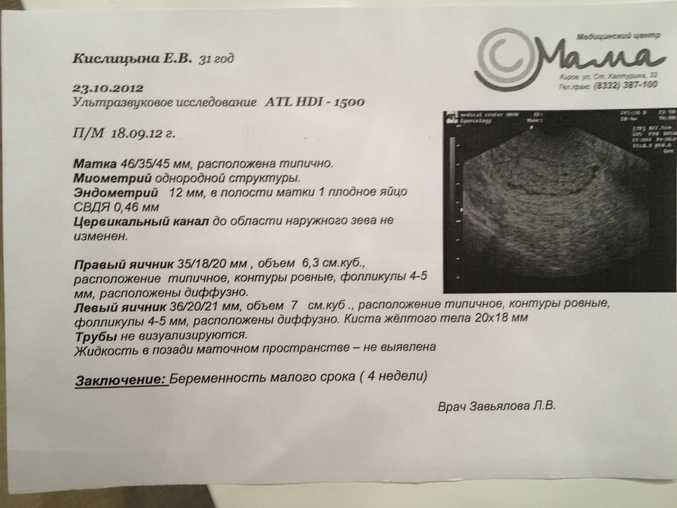
Are you human? (Sorry, we have to ask!)
Please don't check this box if you are a human.
You’re the best! Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.
Back to top
We couldn't access your location, please search for a location.
Zip, City, or State
Please enter a valid 5-digit zip code or city or state.
Please fill out this field.
Service All Services Abortion Abortion Referrals Birth Control COVID-19 Vaccine HIV Services Men's Health Care Mental Health Morning-After Pill (Emergency Contraception) Pregnancy Testing & Services Primary Care STD Testing, Treatment & Vaccines Transgender Hormone Therapy Women's Health Care
Filter By All Telehealth In-person
Please enter your age and the first day of your last period for more accurate abortion options.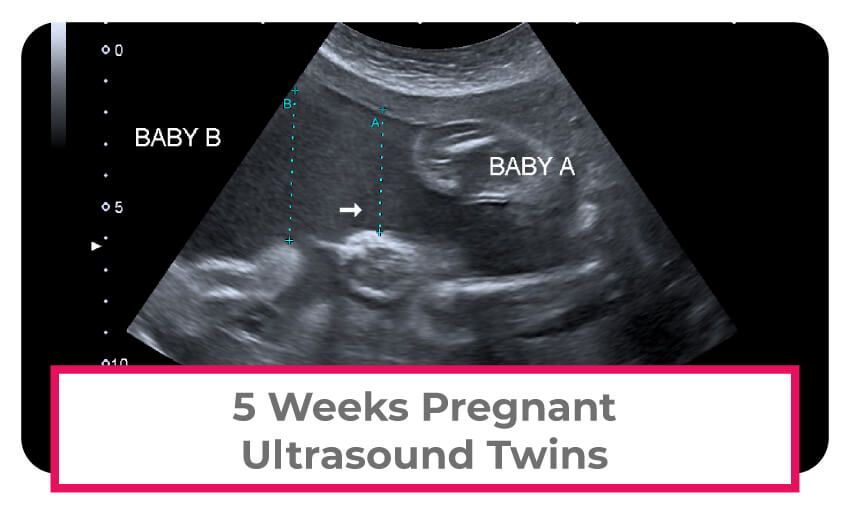 Your information is private and anonymous.
Your information is private and anonymous.
AGE This field is required.
Or call 1-800-230-7526
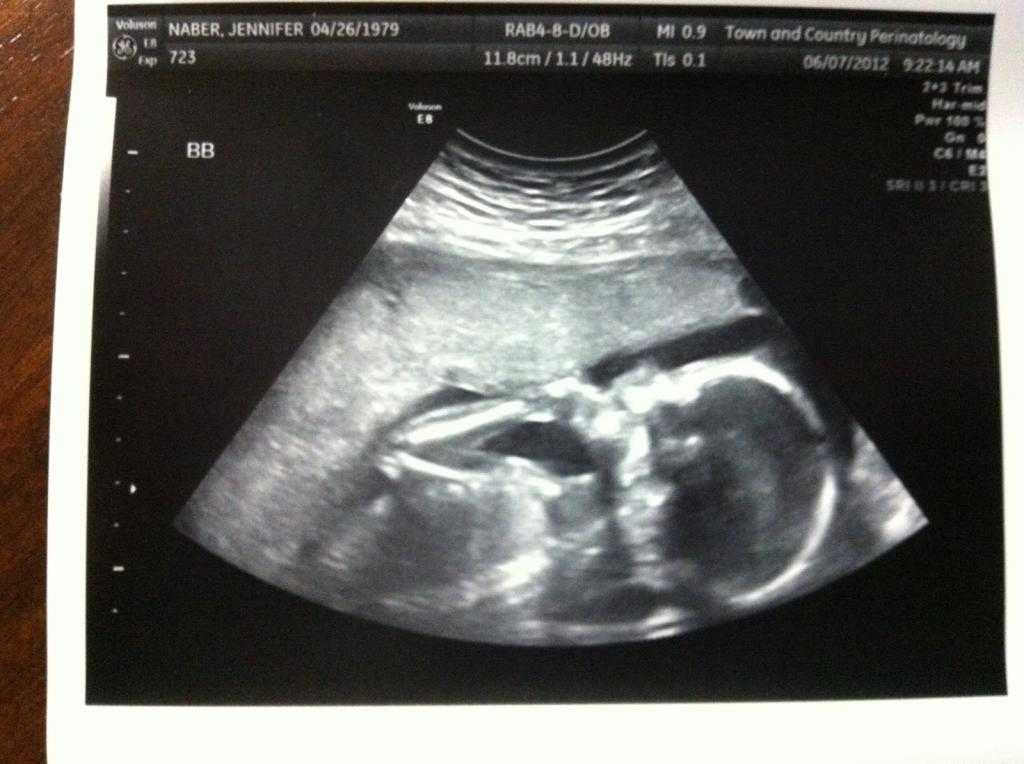
Ultrasound in the second month of pregnancy at the Medical Center "Medicentr"
Usually only by the second month of pregnancy a woman realizes that she is expecting a baby. At this time, ultrasound can be done both to confirm pregnancy, if you have not done this before, and to exclude pathologies and control the development of the child.
During the second month of pregnancy, the embryo continues to develop. Limbs are formed, the nervous system develops, the brain is formed, the rudiments of internal organs appear. At this interesting stage, the baby goes through the stages of development that the embryos of other vertebrate species go through. So, in the middle of the second month, two chambers of the heart are transformed into four, which in the process of evolution appear only in birds and mammals. At the end of the second month, the baby is already moving, ears and rudiments of teeth appear.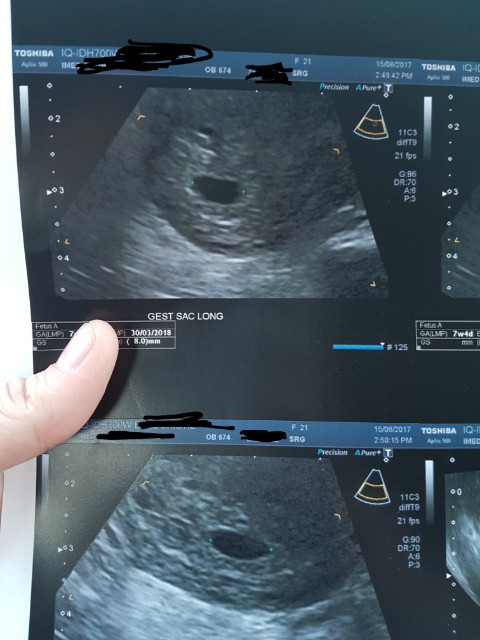 nine0003
nine0003
Ultrasound examination in the second month of pregnancy?
There are two methods of performing ultrasound during pregnancy:
- transvaginal - using a narrow probe that the doctor inserts into the vagina;
- transabdominal - through the abdominal wall.
In the second month, gynecologists prefer to use the transvaginal method of examination, because it provides more information about the developing pregnancy and the formation of the embryo. Before the examination, the woman needs to lie on the couch on her back and bend her knees. The doctor will gently insert the ultrasound probe. The procedure usually takes several minutes, during which the doctor will record the main dimensions of the embryo, check the fetus and reproductive organs for abnormalities, and make a conclusion about whether your pregnancy is proceeding normally. nine0003
Ultrasound at the fifth week of pregnancy
If you have not had an ultrasound to confirm pregnancy before, you can do one at the fifth week.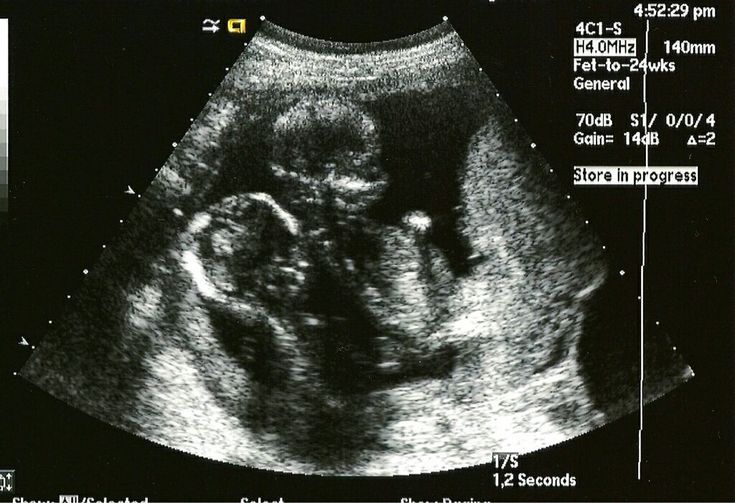 The doctor will be able to find a fetal egg, calculate its size, determine multiple pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, as well as other pathologies, if any.
The doctor will be able to find a fetal egg, calculate its size, determine multiple pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, as well as other pathologies, if any.
Ultrasound at the sixth week of pregnancy
At this time, the fetal egg in the uterus is already clearly visible on the screen of the ultrasound machine. The yolk sac is visible inside, which carries out the metabolism of the embryo before the placenta takes over this function. Modern devices allow you to determine the presence of an embryo, however, if the ultrasound specialist cannot see it for such a short period, this is not a reason to worry. nine0003
Ultrasound at the seventh week of pregnancy
Starting from this week, the embryo should be clearly identified. If the doctor cannot see it, this can mean both an incorrectly set period and pathologies, for example, a missed pregnancy or anembryony. Normally, the doctor can already fix the heart rate (HR) of the fetus (normally 130-150 beats per minute) - this is an important indicator of how the baby is developing.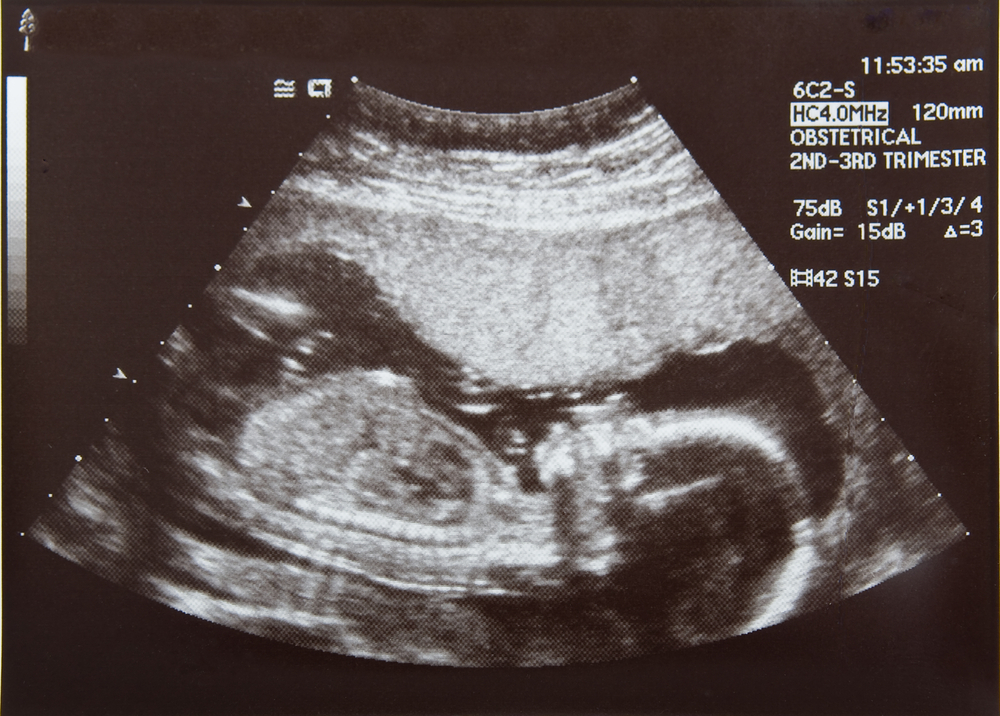 You can also determine the coccyx-parietal size of the embryo (CTE) - usually it is 6-13 mm. The embryo weighs at this moment less than 1 gram. nine0003
You can also determine the coccyx-parietal size of the embryo (CTE) - usually it is 6-13 mm. The embryo weighs at this moment less than 1 gram. nine0003
Ultrasound at the eighth week of pregnancy
The eighth week is the time of active development of external and internal organs, in boys the external genitalia begin to form. The CTE of the embryo at this time is 13-19 mm, and it weighs about 3 grams. The fetus is already actively moving, but since it is still very small, the expectant mother does not feel any movement.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
For more information and to make an appointment, please call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
Early pregnancy ultrasound
Two stripes on the test is always a complete surprise for a woman, even if she already knows about her position in her soul. After the first confirmation, the girl most often wants to see the baby with her own eyes and make sure that he is developing normally. This can be done using an instrumental method such as ultrasound. Usually, expectant mothers, especially expecting their first child, have a lot of questions. nine0003
This can be done using an instrumental method such as ultrasound. Usually, expectant mothers, especially expecting their first child, have a lot of questions. nine0003
How not to miss ectopic and non-developing pregnancies
Often, pregnant women at the very beginning are afraid of two conditions - an ectopic or missed pregnancy. Especially experienced by those who have already experienced it once.
In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg does not reach the uterus and is implanted in other places - most often these are the fallopian tubes. If nothing is done, the embryo will grow and burst the tube. In this case, the woman can not be saved. Therefore, an ectopic pregnancy should be terminated without hesitation. Since the embryo is not removed separately, the entire tube is cut out. This can be done twice in a lifetime, after which pregnancy occurs only after artificial replanting using IVF. An ectopic pregnancy can be suspected indirectly by the level of β-hCG, but only the presence of a fetal egg in the uterus on ultrasound clearly refutes it.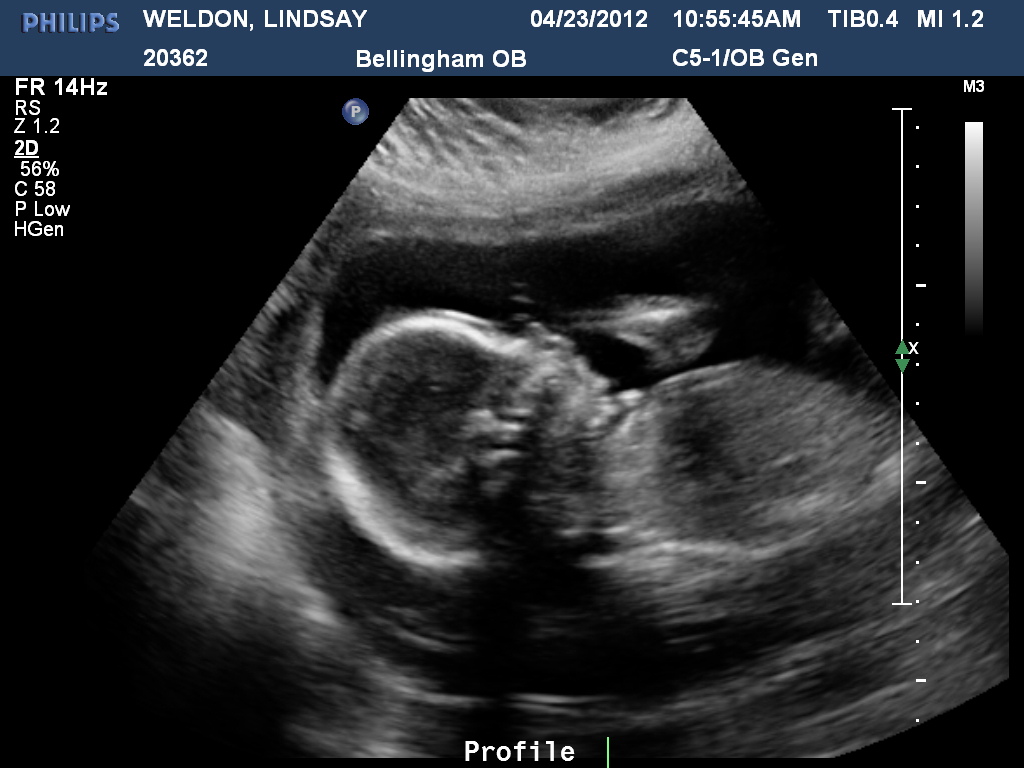 nine0003
nine0003
But the experiences of the expectant mother do not end there. Frozen pregnancy is impossible to predict. In some cases, doctors shrug their shoulders, and why this happened remains unknown. It is dangerous to wait for a non-developing egg to come out by itself for a long time, since it can begin to decompose, and the uterus can become inflamed. Up to 6 weeks, the gynecologist can offer a less traumatic medical interruption, and after - classic abortive methods. It is possible to unambiguously identify a frozen one only by ultrasound - it shows that the fetal egg is smaller than it should be for its term or a heartbeat is not heard. At random, such a diagnosis is never made, because the life of the unborn child depends on it, and most often an ultrasound is prescribed again after a few days. If it turns out that the dimensions have not changed, and there is still no heartbeat, then - alas! nine0003
Why early ultrasound is needed
Ultrasound diagnostics is a safe method that has no contraindications.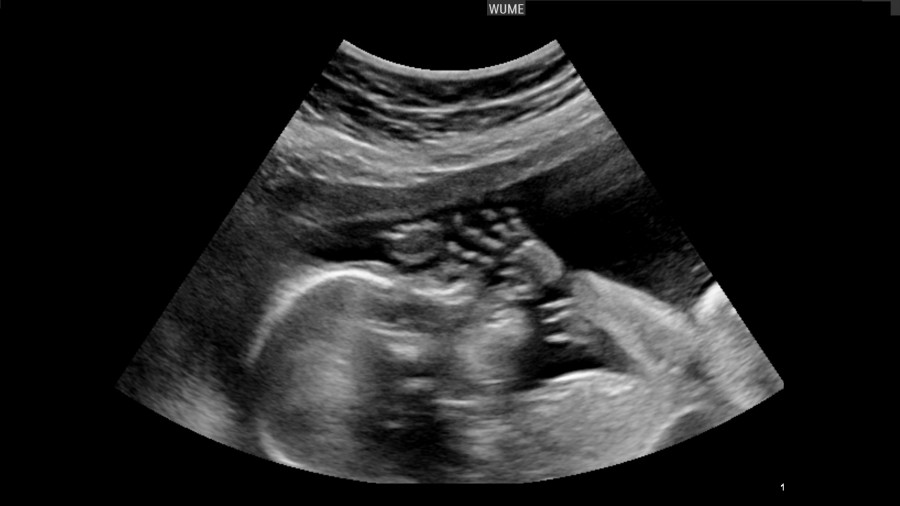 But it is pointless to do it before 4-5 weeks, the fetal egg cannot be seen so early. In this case, a transvaginal probe is used for ultrasound. In public clinics, the first ultrasound diagnosis is carried out as part of the first screening at 12 weeks, and earlier it is prescribed only if the woman herself or her doctor is worried about something:
But it is pointless to do it before 4-5 weeks, the fetal egg cannot be seen so early. In this case, a transvaginal probe is used for ultrasound. In public clinics, the first ultrasound diagnosis is carried out as part of the first screening at 12 weeks, and earlier it is prescribed only if the woman herself or her doctor is worried about something:
- a woman complains of pain in the lower part of the abdominal region and bloody “daub”;
- expectant mother has serious chronic diseases;
- pregnancy occurred, although the couple was protected by a spiral;
- the patient took dangerous and heavy drugs, had an infection, was irradiated. Although the principle of “all or nothing” usually works up to 4 weeks, doctors recommend being examined;
- in the anamnesis, the future mother herself and her relatives had multiple pregnancies; nine0012
- Embryo implanted with IVF;
- physician suspects hydatidiform mole, ectopic or miscarriage;
- the patient was diagnosed with various formations in the uterus and ovaries;
- if there is a risk of developing genetic abnormalities (for example, there have already been interrupted pregnancies due to malformations, chromosomal disorders).