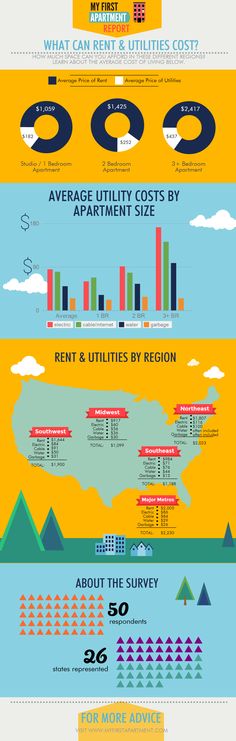
Tubal pregnancy miscarriage
Ectopic Pregnancy | Tubal Pregnancy
Also called: Abdominal pregnancy, Tubal pregnancy
On this page
Basics
- Summary
- Start Here
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis and Tests
- Treatments and Therapies
Learn More
- Related Issues
See, Play and Learn
- No links available
Research
- Clinical Trials
- Journal Articles
Resources
- Find an Expert
For You
- Teenagers
- Patient Handouts
The uterus, or womb, is the place where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant. If you have an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg grows in the wrong place, outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes. The result is usually a miscarriage.
Ectopic pregnancy can be a medical emergency if it ruptures. Signs of ectopic pregnancy include:
- Abdominal pain
- Shoulder pain
- Vaginal bleeding
- Feeling dizzy or faint
Get medical care right away if you have these signs. Doctors use drugs or surgery to remove the ectopic tissue so it doesn't damage your organs. Many women who have had ectopic pregnancies go on to have healthy pregnancies later.
Dept. of Health and Human Services Office on Women's Health
- Ectopic Pregnancy (Nemours Foundation) Also in Spanish
- Ectopic Pregnancy (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists)
- Ectopic Pregnancy (Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research)
- Common Discomforts of Pregnancy (March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation)
- Obstetrical Ultrasound (American College of Radiology; Radiological Society of North America) Also in Spanish
- Pregnancy Test (National Library of Medicine) Also in Spanish
- Progesterone Test (National Library of Medicine) Also in Spanish
- Dilation and curettage (D&C) (Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research)
- Diethylstilbestrol (DES) Exposure and Cancer (National Cancer Institute) Also in Spanish
- ClinicalTrials.
 gov: Pregnancy, Abdominal (National Institutes of Health)
gov: Pregnancy, Abdominal (National Institutes of Health) - ClinicalTrials.gov: Pregnancy, Ectopic (National Institutes of Health)
- ClinicalTrials.
 gov: Pregnancy, Tubal (National Institutes of Health)
gov: Pregnancy, Tubal (National Institutes of Health)
- Article: Tubal ectopic pregnancy in acute abdominal presentation: A case control analysis.

- Article: Endometrial compaction after human chorionic gonadotrophin administration reduces ectopic pregnancy rate...
- Article: Experience in management of cesarean scar pregnancy and outcomes in a.
 ..
.. - Ectopic Pregnancy -- see more articles
- Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Also in Spanish
- Find an Ob-Gyn (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists)
- March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation Also in Spanish
- Ectopic/Tubal Pregnancy and Miscarriage (Boston Children's Hospital)
Ectopic pregnancy
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilised egg implants outside the uterus (womb).
In a normal pregnancy, the fertilised egg spends 4 to 5 days travelling down the fallopian tube before moving to the cavity of the uterus where it implants about 6 to 7 days after being fertilised.
Most, but not all, ectopic pregnancies take place in the fallopian tube. Early detection of an ectopic pregnancy can prevent serious medical complications and may save the fallopian tube from permanent damage.
Cause of ectopic pregnancies
There are several conditions that can cause an ectopic pregnancy.
Any damage to the fallopian tube can block or narrow the fallopian tube. There could also be problems with the tube walls, which should normally tighten and carry the fertilised egg into the uterus.
Hormonal imbalance, infection or malfunction of the uterus or tube can all impair the tube’s normal function and result in an ectopic pregnancy.
Who is most at risk?
You are most at risk of having an ectopic pregnancy if you have a previous history of:
- ectopic pregnancy
- salpingitis (pelvic infection)
- damage to your fallopian tube
- infertility
- pelvic surgery including tubal ligation (having your fallopian tubes’ tied or clamped to prevent pregnancy).

Other risk factors include:
- using an intra-uterine device (IUD), also known as a coil
- using a progesterone-only oral contraceptive pill (minipill)
- undergoing fertility treatment (IVF).
In some cases the cause of an ectopic pregnancy may never be known.
Possible outcomes
In many cases of ectopic pregnancy, the fertilised egg dies quickly and is broken down by your system before you miss your period or after you experience some slight pain and bleeding.
In these cases an ectopic pregnancy is rarely diagnosed and it is assumed to be a miscarriage. Nothing needs to be done in these circumstances.
If the fertilised egg continues to grow, the thin wall of your fallopian tube will stretch, causing you pain in your lower abdomen. You may also experience vaginal bleeding. As the egg grows, the tube may rupture, causing you severe abdominal (stomach) pain, internal bleeding and possible collapse.
Signs and symptoms
Women who experience an ectopic pregnancy have all the signs of a normal pregnancy, in the beginning. Most symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy occur between the fourth and tenth week of pregnancy. These include:
- vaginal bleeding
- lower left or right side abdominal (stomach) pain
- feeling light-headed or faint.
If you experience these symptoms you should see your doctor or visit your local hospital immediately.
Managing an ectopic pregnancy
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, your doctor will perform an ultrasound scan and a pregnancy test.
If the ultrasound scan shows an empty uterus but the pregnancy test comes back positive, then it is likely you have an ectopic pregnancy.
These signs may also indicate that you are in very early stages of pregnancy or that you have already miscarried.
While an ultrasound using a transvaginal probe provides the best quality scan, it is not always possible to see an ectopic pregnancy.
If you are well and not in severe pain, you may have a blood hormone test each day for up to 2 to 3 days to help diagnose if you have an ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
Currently there are 3 different treatments available for an ectopic pregnancy.
Your doctor will discuss the most appropriate one for you, however, your doctor may also find it necessary to proceed from one method to another.
Laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery to remove fertilised egg from fallopian tubes
A telescopic device (the laparoscope) is inserted through a small cut below your navel (belly button). To help identify your organs, carbon dioxide gas is blown into your stomach through a needle.
A couple of small incisions are also made in your lower abdomen to manipulate and if necessary remove the ectopic pregnancy tissue.
The surgery may involve removing your fallopian tube (salpingectomy) or opening your fallopian tube (salpingostomy) to remove the ectopic pregnancy tissue.
Laparotomy to remove the ectopic pregnancy
If the pregnancy is advanced or there has been significant associated haemorrhaging (bleeding) then your doctor may perform a laparotomy, a type of surgery involving a much larger incision.
Intramuscular injection of the drug methotrexate
A medication called methotrexate is used to dissolve the pregnancy tissue. It is given by injection in the leg or bottom and is suitable for women without pain or those with minimal pain.
This type of treatment was introduced to avoid surgery but needs careful follow-up.
The follow-up requires blood tests after the first week and then once or twice a week until tests show that you are no longer pregnant. The schedule of blood tests will be explained to you by your doctor. The treatment has a 90 per cent success rate. If it is not successful your doctor may have to reconsider medical treatment or surgery.
Recovery after treatment
After laparoscopic surgery or a methotrexate injection most women recover and are ready to leave hospital within 24 hours.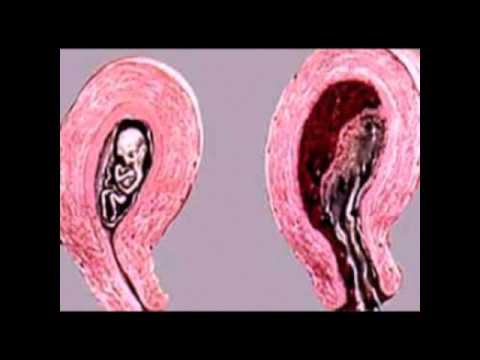
After a laparotomy it is more common to stay in hospital for 2 to 3 days.
If you had a salpingostomy or methotrexate injection you will need to have regular tests at hospital to ensure all the pregnancy cells are gone. This usually involves another blood hormone test.
A discharge summary will be sent to your doctor describing the treatment you have received and any further care you may need.
See your doctor if:
- you have a high temperature or feel feverish
- your surgical cuts become red, swollen or contain pus
- your vaginal discharge has a strong, unpleasant odour
- you have heavy, bright red vaginal blood loss or blood clots
- you feel unwell or worried about an unusual symptom.
Future pregnancies
If you have had an ectopic pregnancy then you have a slightly higher risk of having another ectopic pregnancy in the future.
The risk of ectopic pregnancy in the general population is 1 in 50 to 80 women. The risk of a repeat ectopic pregnancy is 1 in 10.
The risk of a repeat ectopic pregnancy is 1 in 10.
See your doctor immediately if you:
- think you might be pregnant
- have a late period
- have abnormal abdominal pain
- have menstrual bleeding that is different to normal.
You should ask to be examined, reminding your doctor of the previous ectopic pregnancy.
Contraception
If you have had an ectopic pregnancy, some contraception methods may no longer be suitable. It is best to discuss your medical history and options with your doctor or at a family planning clinic.
Your emotions
An ectopic pregnancy can be a devastating experience.
You may be recovering from major surgery while at the same time trying to cope with the loss of your pregnancy and possibly the loss of part of your fertility. You may be worried about whether you can have a baby in the future.
You may also be dealing with the shock of finding out you were pregnant just as your pregnancy is ending.
It’s normal for your emotions to be up and down for weeks and even months after your loss. You may feel utterly relieved to be pain free and profoundly grateful to be alive, while feeling sad about your loss.
If you didn’t have much time to mentally prepare for your treatment, you may feel that you lost control of the decision-making process.
These emotional reactions that you and your partner may experience can test your own relationship and your relationships with others, such as family and friend. You both may find it hard to understand or meet each other’s emotional needs.
Many people, especially men, may find it difficult to express their feelings. They may feel powerless to help. During this time it’s important to talk to each other about how you both feel and share your grief.
After experiencing an ectopic pregnancy your feelings can vary. Some women want to get pregnant again immediately while others are terrified at the thought and cannot cope with another anxious pregnancy.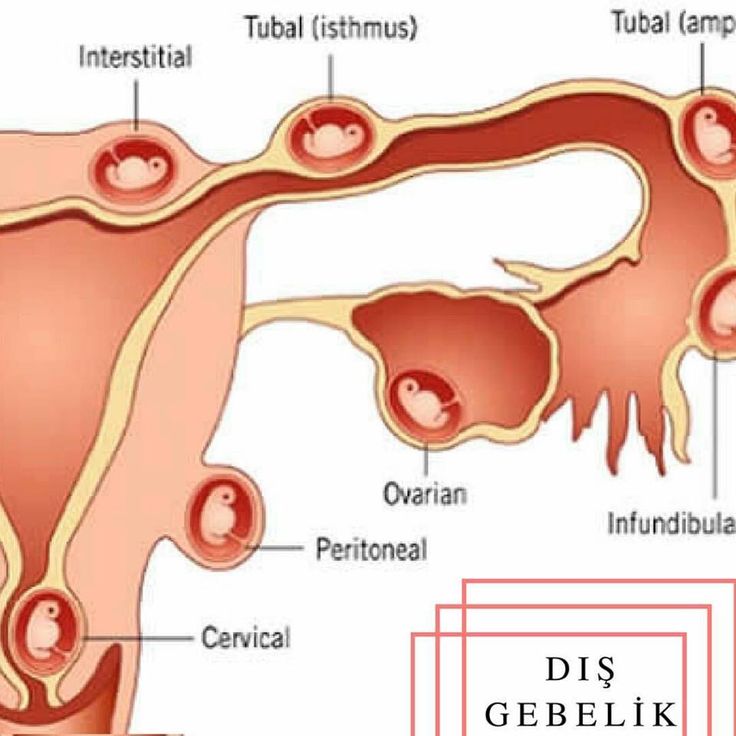
Allow yourself time to recover physically and emotionally before trying to get pregnant again. It is recommended that you wait for at least 3 months for your body to recover. You are the best judge of the time needed for your emotional healing.
Getting support
Support services at King Edward Memorial Hospital
A range of support services are available at King Edward Memorial Hospital if you have experience a pregnancy loss, including:
- social work
- pastoral care
- counselling and psychiatric services.
Talk to your doctor or midwife, or read more about the support services for pregnancy loss available at King Edward Memorial Hospital.
You may wish to read such resources as:
- Small sparks of life Lysanne Sizoo, Gopher Publishers, 2001
- Hidden Loss: Miscarriage & Ectopic Pregnancy. Contributing editors: Valerie Hey, Catherine Itzen, Lesley Saunders, and Mary Anne Speakman.
 The Women's Press Handbook Series 1989.
The Women's Press Handbook Series 1989.
Where to get help
- Find a GP/doctor
- Search a GP urgent care practice (external site)
- Visit healthdirect (external site) or call 1800 022 222
Remember
- Ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that develops outside of the uterus and usually in the fallopian tubes.
- Symptoms can include vaginal bleeding, stomach pain and cramps.
- Women at high risk should have their pregnancy closely monitored especially during the early stages.
- An ectopic pregnancy is a life-threatening condition.
Acknowledgements
Women and Newborn Health Service
This publication is provided for education and information purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical care. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not imply endorsement and is not intended to replace advice from your healthcare professional. Readers should note that over time currency and completeness of the information may change. All users should seek advice from a qualified healthcare professional for a diagnosis and answers to their medical questions.
Readers should note that over time currency and completeness of the information may change. All users should seek advice from a qualified healthcare professional for a diagnosis and answers to their medical questions.
See also
- Support services for pregnancy loss available at King Edward Memorial Hospital
Ectopic pregnancy - Family clinic
24 July 2016 Gynecology
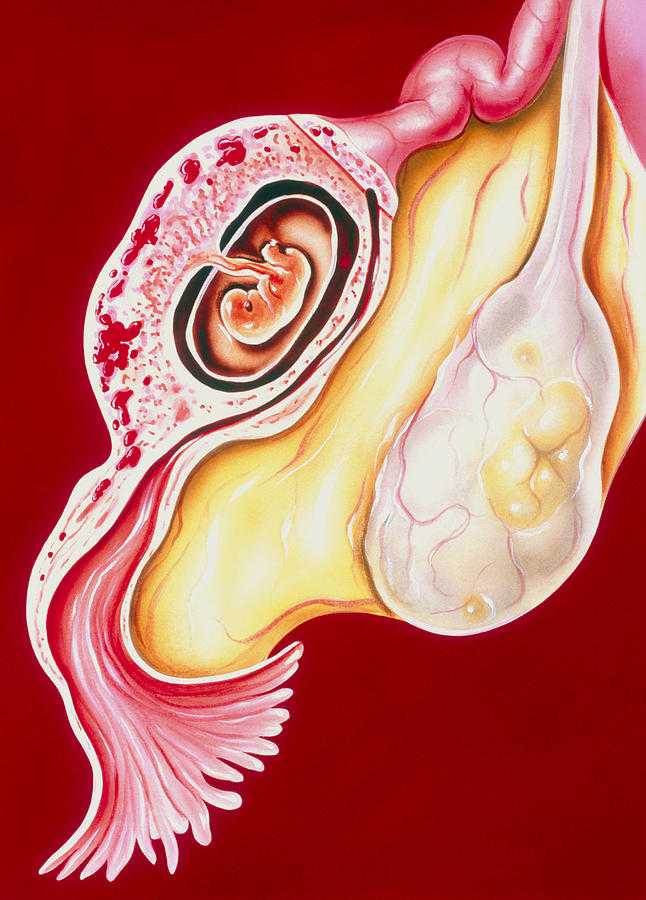
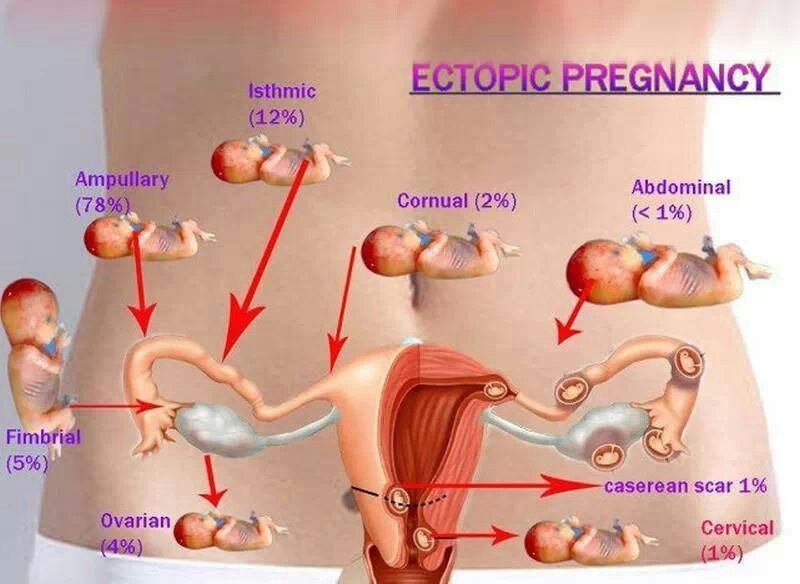
This is the settling and development of the fetal egg outside the uterus. It poses a great danger to the life of a pregnant woman. A fertilized egg can graft on the ovaries, peritoneum, omentum and other abdominal organs, but most often in the tubes (99%).
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
Unfortunately, this pathology is quite common. During the operation, the couple had to take the fetal egg from anywhere: from the fallopian tubes, ovaries, even from the abdominal cavity. But more often than others, there is still a tubal pregnancy. Why does the attachment of a fertilized egg occur outside the uterus? What makes it go astray and begin to develop in an unintended place? As a rule, the fallopian tubes are to blame, unable to perform their functions.
But more often than others, there is still a tubal pregnancy. Why does the attachment of a fertilized egg occur outside the uterus? What makes it go astray and begin to develop in an unintended place? As a rule, the fallopian tubes are to blame, unable to perform their functions.
Clinical experience shows that ectopic pregnancy is almost always preceded by inflammatory or infectious diseases of the genitals, abortion, difficult childbirth, complicated by the inflammatory process. In this case, the mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes swells, its folds stick together, the tubes are deformed and lose their ability to contract normally. Infantilism also predisposes to ectopic pregnancy.
With this disease, the tubes are excessively elongated, tortuous, their lumen is narrowed, they contract weakly. A healthy tube must contract actively in order to move the egg into the uterus. Moreover, this must be done within strictly defined deadlines, otherwise delay is fraught with disaster. After all, a fertilized egg develops and at a certain stage, villi appear in it, which need to gain a foothold and begin to receive a stable blood supply. If by this time the fetal egg has not been delivered to the uterus, it attaches anywhere, to the wall of the fallopian tube, for example, and begins to grow, unaware that this is the most inappropriate place for the development of the fetus.
After all, a fertilized egg develops and at a certain stage, villi appear in it, which need to gain a foothold and begin to receive a stable blood supply. If by this time the fetal egg has not been delivered to the uterus, it attaches anywhere, to the wall of the fallopian tube, for example, and begins to grow, unaware that this is the most inappropriate place for the development of the fetus.
After all, the lumen of the pipe is in its different sections from 1 mm to 1.5 cm, and a thin and delicate machine is not capable of stretching like a uterus. Therefore, approximately on the 4th-6th week, the chorionic villi “gnaw through” the wall, the tube breaks - and bleeding occurs into the abdominal cavity, accompanied by a sharp cramping pain in the lower abdomen, a feeling of lightheadedness, dizziness, and often loss of consciousness.
If a large vessel is damaged, massive blood loss threatens the woman with death, and only an emergency operation can save her. Sometimes events develop according to a slightly modified "scenario". It is not the tube that breaks, but the wall of the fetal egg, which is then expelled into the abdominal cavity. There is a so-called tubal abortion, also accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes vomiting and dark brown bloody discharge from the vagina. After a while, the pain subsides and the woman begins to reassure herself that everything will be fine. No, it won't! And in this case, surgical intervention is necessary, otherwise peritonitis, a purulent inflammation of the peritoneum, may develop.
Sometimes events develop according to a slightly modified "scenario". It is not the tube that breaks, but the wall of the fetal egg, which is then expelled into the abdominal cavity. There is a so-called tubal abortion, also accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes vomiting and dark brown bloody discharge from the vagina. After a while, the pain subsides and the woman begins to reassure herself that everything will be fine. No, it won't! And in this case, surgical intervention is necessary, otherwise peritonitis, a purulent inflammation of the peritoneum, may develop.
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy
Are there any special signs by which a woman herself can guess about an ectopic pregnancy? Alas, there are no special signs. A catastrophe (ruptures, bleeding) sometimes comes like a bolt from the blue: almost nothing bothers, except for a slight aching pain in the lower abdomen and spotting ...
And suddenly! But more often, an ectopic pregnancy is disguised as a normal one: the same delay in menstruation, the mammary glands are also engorged, sometimes there is slight nausea, taste and olfactory sensations are distorted. Therefore, a woman cannot independently recognize an ectopic pregnancy, but she certainly can prevent trouble without bringing the matter to bleeding, pain, loss of consciousness. How?
Therefore, a woman cannot independently recognize an ectopic pregnancy, but she certainly can prevent trouble without bringing the matter to bleeding, pain, loss of consciousness. How?
Yes, you just need to go to the antenatal clinic on the 4-7th day after the delay in menstruation. And there the experts will determine what it is connected with. Modern diagnostic methods, including ultrasound, allow you to establish pregnancy in the early stages. It is especially desirable to undergo an ultrasound examination for those who have a delay in menstruation accompanied by spotting bloody discharge.
If you don’t feel like going to the clinic, buy any test indicator for early diagnosis of pregnancy at the pharmacy. There are a lot of them, and it’s easy to use them (the instructions indicate how). With the help of the indicator, you can make sure that the pregnancy has occurred, but only a specialist can determine what kind of pregnancy it is - normal or pathological. At the slightest suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy, the doctor suggests that the woman go to the hospital.
At the slightest suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy, the doctor suggests that the woman go to the hospital.
Do not refuse: only in a specialized institution equipped with modern equipment, you can conduct the necessary studies and make an accurate diagnosis, determine where the embryo was implanted - in the uterus or outside it. Please note: the sooner an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed, the more gentle ways doctors will be able to terminate it.
If the pathology is detected when the receptacle of the fetal egg is still intact, a laparoscopic, low-traumatic method is used. The surgeon inserts the instrument through a small incision in the skin; he sees the operating field and the manipulations themselves on the monitor (the laparoscope is equipped with an optical system). With such an intervention, the surrounding organs and tissues are practically not injured, there is no severe bleeding, the risk of adhesions and scarring is much less. Deaths are rare.
Sometimes, with the help of a laparoscope, it is possible to simply "suck" the fetal egg in much the same way as a mini-abortion is done. It is important that during such operations the tube is preserved, it continues to function, and after a while the woman, after undergoing a course of treatment, can become pregnant again.
← All articles
Ectopic pregnancy - signs, symptoms in the early stages, treatment in ON CLINIC Ryazan
Already from the very term "ectopic pregnancy" it is easy to understand that this pathology is the wrong location of the fetal egg. In this case, fertilization occurs, and the pregnancy develops outside the uterus. An egg fertilized by a sperm is able to attach to the inner surface of the fallopian tube, as well as to the ovary, or begin its development somewhere else inside the peritoneum. In principle, history knows cases of the birth of healthy children as a result of an ectopic pregnancy detected in the later stages, but the likelihood of such a development of events is extremely small. An improperly located ovum means that the fetus will not have the space required for its development, and it will not receive the required amount of nutrients for its formation and growth. In addition, if the signs of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages did not lead to its termination, then this is very dangerous - especially for a woman.
An improperly located ovum means that the fetus will not have the space required for its development, and it will not receive the required amount of nutrients for its formation and growth. In addition, if the signs of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages did not lead to its termination, then this is very dangerous - especially for a woman.
What threatens the patient with this condition? It is easy to guess that, unlike the uterus, neither the ovaries nor the fallopian tubes are designed by nature to bear offspring. The tissues that form them do not have the strength and elasticity necessary for this. This means that an increase in the size of the fetus to critical values is fraught with a rupture of the organ inside which the embryo develops. It is for this reason that the correct development of the child and his birth at the appointed time is possible only with a normal - uterine - pregnancy.
According to statistics, a woman's risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy increases the older she is. Most often, this pathology develops in the fair sex over the age of 35 years. If the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy were not detected in the early stages, then a rupture of the internal organ in the absence of qualified medical care can be fatal. The risk of death for a patient with an ill-located embryo is approximately 10 times higher than during childbirth and 50 times higher than during abortion. Also, 5 to 9women out of 100 who were not lucky enough to avoid an ill-localized pregnancy are subsequently registered with a gynecologist with a diagnosis of "Infertility".
Most often, this pathology develops in the fair sex over the age of 35 years. If the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy were not detected in the early stages, then a rupture of the internal organ in the absence of qualified medical care can be fatal. The risk of death for a patient with an ill-located embryo is approximately 10 times higher than during childbirth and 50 times higher than during abortion. Also, 5 to 9women out of 100 who were not lucky enough to avoid an ill-localized pregnancy are subsequently registered with a gynecologist with a diagnosis of "Infertility".
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
The most frequently asked question, which concerns the signs of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages, is as follows: “Is it possible to independently determine this pathology in yourself, and what will a pregnancy test show if it is abnormally localized?” To date, no special test has been developed to determine whether the pregnancy is uterine or not, and the period at which it is now has not been developed. However, you can use the usual pregnancy test. Regardless of the location of the fetal egg, it should show a positive result.
However, you can use the usual pregnancy test. Regardless of the location of the fetal egg, it should show a positive result.
Many women with a history of a pregnancy localized outside the uterine cavity claim that the second strip on the test was fuzzy. Moreover, they assure that every day the color of this strip became less and less saturated. This statement can be associated with the opinion of experts that the concentration of chorionic gonadotropin - a hormone that is secreted in the body of a pregnant woman - in the early stages of an ectopic pregnancy is much lower than in cases where the embryo is located correctly inside the uterus. However, this information has not been documented and cannot be a decisive argument in determining the location of a fertilized egg.
Other indirect symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include:
- discharge from the genital tract, having a pale brown hue and a watery-mucous consistency;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
 They are associated with an increase in the size of the embryo, which provokes the deformation of the internal organs directly in contact with it.
They are associated with an increase in the size of the embryo, which provokes the deformation of the internal organs directly in contact with it.
The presence of these alarming signs in a woman is not at all a guarantee that she is pregnant and that the embryo has attached to the inner surface of the fallopian tube. Another thing is that you can not leave them unattended in any case. With such symptoms, you should immediately consult a gynecologist! In our private clinic in Ryazan, patients of all ages are treated by the best specialists in the city. As for the equipment of our medical center, there is everything that can be needed to detect an ectopic pregnancy at an early stage. Ultrasound of the pelvis and other studies - including a blood test for the hCG hormone - if necessary, can be done right on the day you contact us!
If we talk about the obvious signs that may accompany this pathology, then among them may be:
- severe nausea and vomiting, dizziness and low blood pressure up to fainting;
- acute pain in the abdomen - in its lower part, which can "give" to the anus;
- Ultrasound of the uterus shows that there is no fetal egg inside this hollow organ.
Remember that an ectopic pregnancy that is not detected and terminated at an early stage can lead to spontaneous miscarriage. Auto-termination of pregnancy in this case is not the biggest problem. The entire reproductive system of a woman can be severely affected by the development of an embryo in the wrong place. Violation of the integrity of the internal genital organs with strong - sometimes indomitable - bleeding can not only greatly harm the health of the patient, but also lead to her death.
Why do some women have an ectopic pregnancy?
Here are the most common reasons that the embryo is attached not to the inner wall of the uterus, but to some other organ:
- complete or partial obstruction of the fallopian tubes, the cause of which may be the presence of adhesions or scars after them in a woman, as well as narrowing of the lumen of this paired organ of the small pelvis;
- indolent prolonged inflammation affecting the female reproductive system;
- a woman has a history of abortion.
 Especially dangerous in this sense is the termination of the first pregnancy;
Especially dangerous in this sense is the termination of the first pregnancy; - underdevelopment of the internal genital organs of the patient. What it is? This means that the woman's fallopian tubes are too thin and tortuous, making it difficult for a normal pregnancy to occur;
- one of the risk factors is insufficiently motile spermatozoa of the patient's partner. For this reason, a fertilized egg simply “does not have time” to get into the uterine cavity and gain a foothold inside it, remaining inside organs that are not adapted for carrying a pregnancy.
There is also a widespread - however, not scientifically substantiated - opinion that the unstable state of the woman's psyche at the time of conception, as well as in the first days and weeks of pregnancy, can become the cause of an ectopic pregnancy. The correctness of this hypothesis has not been documented, which, however, is not an argument in favor of its failure.
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
Currently, laparoscopy will help to get rid of such a pregnancy quickly and with minimal interference in the functioning of the body.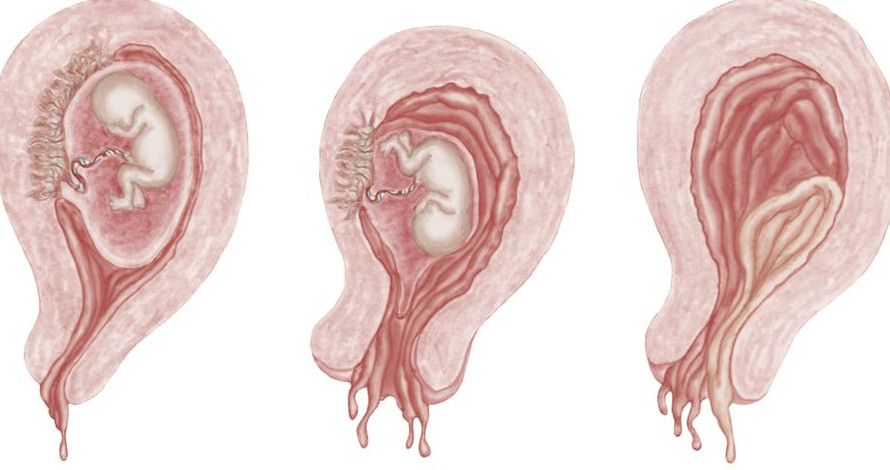 In medical centers equipped with modern equipment for surgical interventions - for example, ON CLINIC Ryazan - such interventions are performed using a flexible endoscope. To introduce it into the patient's abdominal cavity, it is not necessary to make an incision on her anterior abdominal wall: two or three punctures with a diameter of no more than 10 mm each are enough. This removal of the embryo allows you to save the fallopian tubes.
In medical centers equipped with modern equipment for surgical interventions - for example, ON CLINIC Ryazan - such interventions are performed using a flexible endoscope. To introduce it into the patient's abdominal cavity, it is not necessary to make an incision on her anterior abdominal wall: two or three punctures with a diameter of no more than 10 mm each are enough. This removal of the embryo allows you to save the fallopian tubes.
Laparoscopy is good because a few hours after the operation, after a medical examination, the patient can go home. Full recovery after laparoscopic treatment of ectopic pregnancy takes much less time than after abdominal surgery.
How to prevent an ectopic pregnancy? First of all, its prevention is the same as protection against unwanted pregnancy and STDs. Regarding which method of contraception to choose, consult with a reputable gynecologist - for example, in ON CLINIC Ryazan, patients are treated daily by highly qualified specialists with vast experience! If you are planning a pregnancy, then after the appearance of the coveted second strip on the test, pay attention to your well-being.