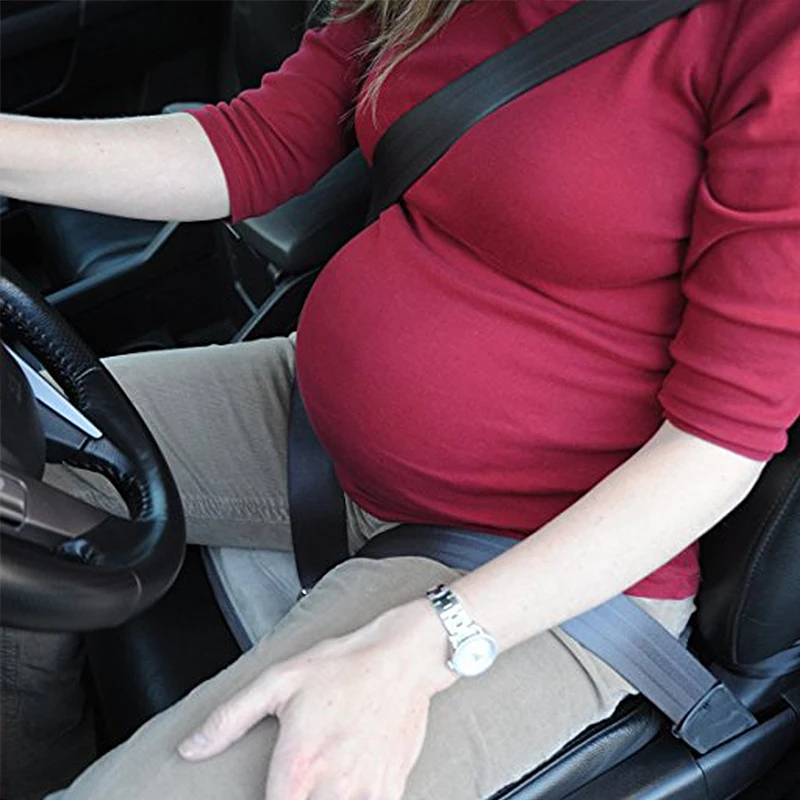
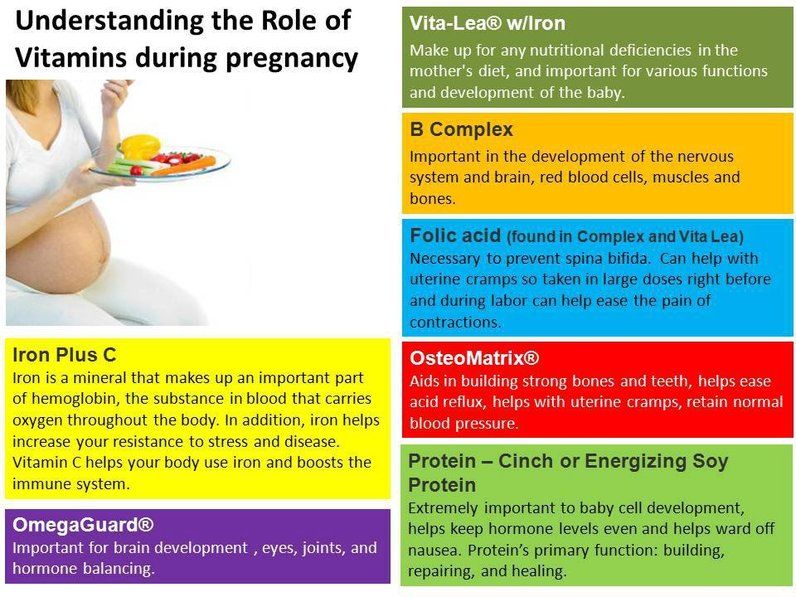
Car sick pregnancy
What if pregnant women get motion sickness?
This is an automatically translated article.
It has been found that pregnant women are more prone to motion sickness. They feel nauseous and vomit when they move. Some women only experience this during pregnancy. In others, motion sickness is present before pregnancy and increases during pregnancy.
1. Causes of motion sickness during pregnancy
Motion sickness often occurs when you travel long distances. This can increase during pregnancy due to one of the following reasons:
When the car moves continuously at a relatively slow speed, it will upset the balance inside your ears causing motion sickness. After eating a full meal. You feel heavy and nauseous from the constant movement. The air around you is stuffy or full of smoke. When the brain receives the wrong signals. This is mainly due to an inconsistency between the expected motion and the actual motion sensed by the balancer. When two neurotransmitters are inactive.
2. Symptoms of motion sickness in pregnant women
Các triệu chứng say tàu xe phụ thuộc vào mức độ chuyển động
The symptoms of motion sickness depend on the degree of motion. Some common symptoms include:
Mild headache, you may feel slightly uncomfortable and nauseated. Fatigue, dizziness, and feeling weak are also common. In severe cases, you may feel extremely anxious, have increased salivation, sweat a lot, be nauseous or pale, and start vomiting. You may become dehydrated if you vomit continuously. Symptoms of motion sickness go away after stopping movement, but in some cases it can take up to three days to go away completely.
3. Does motion sickness affect the baby during pregnancy?
If vomiting during pregnancy is to the extent that the pregnant woman can still eat and drink even if she has a slight weight loss, and can still walk and carry out daily activities, the pregnant mother only needs to rest reasonably and not affect the fetus.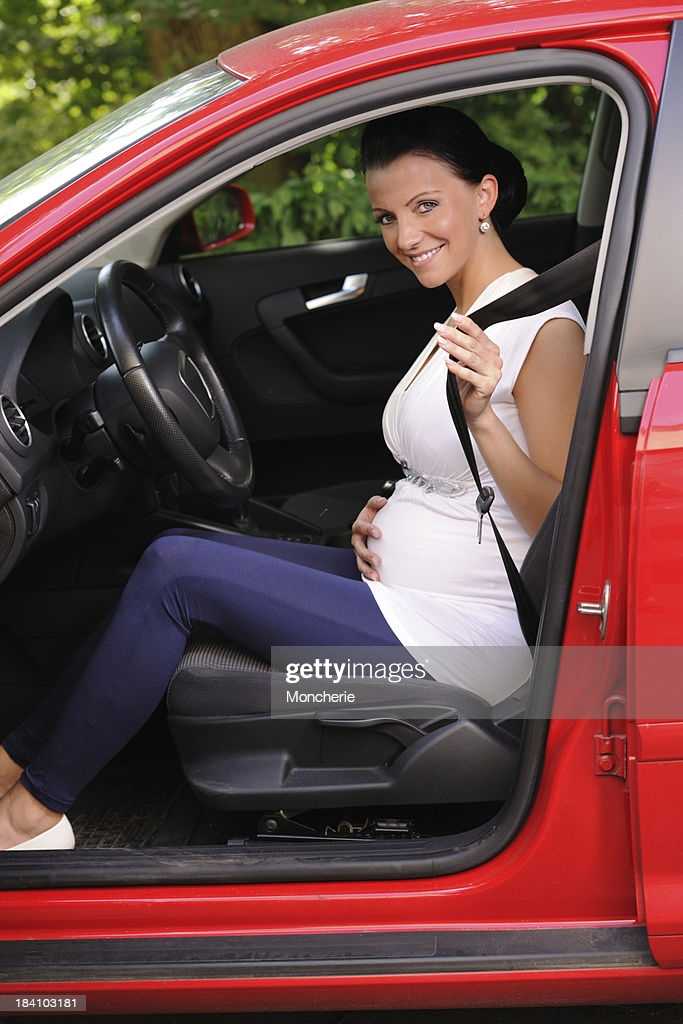
If excessive vomiting disrupts electrolytes and interferes with daily activities, medical intervention is required. When tired and vomiting due to traveling by car, pregnant women should consider which trips are necessary.
4. What to do when motion sickness?
Bổ sung Vitamin B6 sẽ giúp giảm say tàu xe do mang thai
What to do with motion sickness while pregnant? Motion sickness can be treated with medication or natural methods. Treatment includes:
Take Diphenhydramine or Dimenhydrinate as an antihistamine 30 minutes before the trip. These drugs are available in all pharmacies without a prescription. If you are planning a long trip, take medicines such as Scopolamine or Meclizine which have long-acting and prevent motion sickness. car. Scopolamine patches should be taken 12 hours before travel. Vitamin B6 supplements will help reduce motion sickness caused by pregnancy. To date, there are no studies that prove that taking motion sickness pills during pregnancy can have an effect bad for the unborn baby. However, all medications used during pregnancy must be carefully considered, especially during the first trimester.
However, all medications used during pregnancy must be carefully considered, especially during the first trimester.
Other measures to avoid motion sickness People with motion sickness should sit in the front seat of the car, behind the wing of the plane or in the center of the boat when traveling, or pregnant women often use motion sickness patches quite effective. Mothers can even wear special bracelets called acupressure bracelets to avoid this discomfort.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and receive 15% off for consultation fee at the first appointment (applied from 17th October to 31th December, 2022). MyVinmec app is also available and convenient for your bookings management and Telehealth service with Vinmec doctors all in one.
XEM THÊM:
- Note the use of motion sickness stickers
- Why do you get motion sickness?
- Why car sickness? Who is prone to motion sickness?
Motion sickness during pregnancy | BabyCenter
Yes, you're more likely to suffer from motion sickness when you're pregnant. But if you're experiencing nausea and vomiting now and it's never been a problem before, it could just as easily be morning sickness, particularly if it's early in your pregnancy. With similar symptoms, the two are very difficult to tell apart.
Interestingly, if you suffered from motion sickness before becoming pregnant, you're more likely to experience morning sickness during pregnancy. If you've started feeling nauseated a lot of the time, but vomit only when you travel, you may have a combination of the two.
Motion sickness is a relatively common problem encountered when people travel by car, by airplane, and particularly by boat. It occurs when your body's balance-sensing system – which includes your inner ear, your eyes, and the sensory nerves in your skin, muscles, and joints – sends conflicting messages to the brain. If your inner ear senses motion, for instance, but your eyes don't, the result is a queasy feeling that may have you reaching for an airsickness bag.
To help ward off motion sickness in a car, sit in the front seat, open the window for fresh air, and focus on the horizon or a distant object. In an airplane, ask for a seat over the wing, where the ride will be smoothest. On a boat, stay on deck and gaze at the horizon.
Frequent light, non-greasy snacks may help soothe a queasy stomach, and it's probably best to avoid having a large, heavy meal just before traveling.
Though research is scant and results are conflicting, some women say that wearing an acupressure wristband helps with motion sickness as well as morning sickness.
To get relief from motion sickness, you can use over-the-counter drugs that contain dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) or diphenhydramine (Benadryl). These are low-risk for pregnant women, though it's always wise to check with your doctor or midwife before taking any medications during pregnancy.
Although Benadryl is best known as an antihistamine taken for allergies, it's also used to reduce nausea. Because both Dramamine and Benadryl can make you drowsy, don't take either medication if you're driving.
Don't combine Dramamine and Benadryl – take one or the other, because taking them together could compound your drowsiness.
Also, if you're already taking prescription Bonjesta or Diclegis (vitamin B6 and doxylamine) for morning sickness, don't add Dramamine or Benadryl to your regimen.
Talk to your provider before using the prescription drug scopolamine (Scopace) during pregnancy. It's not dangerous for your baby, but your response to it can be different while you're pregnant. It can cause side effects such as dry mouth, dizziness, and fatigue.
Keep in mind that few studies test drugs in pregnant women, which means there's not enough data to completely rule out risk, even for over-the-counter medications. That's why it's important to check with your healthcare provider before taking any medicines while pregnant.
advertisement | page continues below
The Ministry of Health gave recommendations on the treatment of pregnant women and women in childbirth from coronavirus - RBC
www.adv.rbc.ru
www.adv.rbc.ru
www.adv.rbc.ru
Hide banners
What is your location ?
YesChoose other
Categories
Euro exchange rate on November 8
EUR Central Bank: 60. 9 (+0.29) Investments, 16:33
9 (+0.29) Investments, 16:33
Dollar exchange rate on November 8
USD Central Bank: 61.24 (-0.86) Investments, 16:33
The former president of South Korea will refuse dogs donated by Kim Jong-un Politics, 22:15
Mania Prevention: How to Reduce Gambling Addiction Partner project, 21:59
Averbukh criticized Valieva for jumping for an encore after a performance in Kazan Sports, 21:51
www.adv.rbc.ru
www.adv.rbc.ru
Iran announced the interception of cargo from Saudi Arabia for protesters Politics, 21:40
Serebrennikov's name was removed from the website of the Moscow Art Theater. Chekhov Society, 21:33
Chekhov Society, 21:33
Kokorin scored the third goal in five matches of the Cypriot championship Sport, 21:26
An unnamed trader bet almost $1 million on oil rising to $200/bbl Investments, 21:07
Explaining what the news means
RBC Evening Newsletter
Subscribe
Prime Minister of Kazakhstan said that the number of incoming Russians returned to normal Politics, 21:05
Military operation in Ukraine. The main thing Politics, 21:00
Indonesian President admitted that Putin will not go to the G20 summit in Bali Politics, 20:50
Seven killed in bus crash in eastern Turkey Society, 20:38
Conclusion, a fine and a trip to the morgue: how to deal with drunk driving Partner project, 20:37
The first span of the Crimean bridge was sent to the place of repair Politics, 20:34
Turkey will offer to extend the grain deal for a year Politics, 20:31
www. adv.rbc.ru
adv.rbc.ru
www.adv.rbc.ru
www.adv.rbc.ru
Patient during a CT scan session (Photo: Alexander Avilov / AGN Moskva)
The Russian Ministry of Health has issued recommendations on how to treat pregnant women, women in childbirth, puerperas and newborns from coronavirus. The document is published on the agency's website.
The document states that antimalarial drugs and recombinant interferon beta-1b should not be used in the treatment of pregnant women. Pregnant women can be prescribed drugs with the active substance lopinavir + ritonavir if the benefit to the mother outweighs the risk to the fetus. “Treatment should be started as early as possible, which ensures recovery to a greater extent,” the recommendations say.
The Ministry of Health noted that the main method of detecting the disease among pregnant women may be computed tomography of the chest. According to the agency, CT provides a low dose of radiation to the fetus, but the abdomen should be covered with a special screen for protection.
According to the agency, CT provides a low dose of radiation to the fetus, but the abdomen should be covered with a special screen for protection.
The ministry also recommended echocardiography for pregnant women, puerperas and women in labor if they have respiratory failure. They “often develop peripartum cardiomyopathy,” the agency said. This disease is characterized by the appearance of heart failure at the end of pregnancy and in the first months after childbirth.
According to the Ministry, complications in pregnant women include preterm birth (39%), fetal growth retardation (10%) and miscarriage (2%). The department noted that in a group of 15 pregnant women with infection and pneumonia, the frequency of caesarean sections increased due to the fact that the child developed distress syndrome - an inflammatory lung lesion.
It is not known whether a pregnant woman can transmit the virus to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth, the Ministry of Health noted. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention also said that during pregnancy, transmission of the virus to the child is unlikely, but the newborn can become infected from contact with a patient with coronavirus.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention also said that during pregnancy, transmission of the virus to the child is unlikely, but the newborn can become infected from contact with a patient with coronavirus.
Coronavirus
Moscow Mir
0 (per day)
I got infected
0 (per day)
0 (per day)
infected
0 (per day)
died
0 (per day)
Infected
0 (per day)
Died
Research Store Analytics by topic "Medicine"
The case of a traumatic rupture of the bladder in a pregnant woman, complicated by a retroperitoneal phlegmon, the text of a scientific article in the specialty “Clinical Medicine”
UDC: 618.3: 616.62-089: 617.553: 616-002.3
The case of traumatic rupture of the bladder in a pregnant woman, complicated, complicated phlemed phlemed phlegm
U. U.ZHABBAROV, Z.D.KARIMOV, Sh.A.KHUDAYBERGENOV, I.SH.FATTAHOVA
U.ZHABBAROV, Z.D.KARIMOV, Sh.A.KHUDAYBERGENOV, I.SH.FATTAHOVA
The case of traumatic bladder perforation in pregnant female complicated by retroperitoneal phlegmon
U.U.JABBAROV, Z.D.KARIMOV, SH.A.HUDAYBERGENOV, I.SH.FATTAHOVA
Republican Scientific Center for Emergency Medical Care
A case of a severe automobile injury in a pregnant woman is described. The injured woman was found to have an extraperitoneal rupture of the bladder, complicated by suppuration of the urinary leakage of the perivesical tissue and the left parametrium, and a fracture of the pubic pelvic bones. In this case, a diagnostic error was made in the district hospital. This led to infection of the urinary tract, extensive phlegmon of the cellular space of the paravesical and parametrical area. Subsequently, the only correct tactic was chosen in such cases: 1) non-intervention during pregnancy, 2) minimal surgical trauma while maintaining the integrity of the abdominal cavity, 3) adequate drainage of the abscess and bladder was ensured.:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/2785562/original/028627600_1556001360-shutterstock_1019963743.jpg) The patient recovered and delivered successfully.
The patient recovered and delivered successfully.
Key words: pregnancy, accident, bladder rupture, retroperitoneal phlegmon, surgical treatment.
A severe case of motor-vehicle accident in pregnant woman has been described. The patient had retroperitoneal bladder perforation complicated by suppuration of urinous infiltration of paravesical fat and left parametrium, pelvis pubic bone fracture. It has led to ruinous infiltration and to major phlegmon. The following treatment tactics has been chosen: 1) nonintervention into the pregnancy, 2) minimal surgical traumatization with keeping abdominal cavity intactity, 3) providing adequate drainage of the pyogenic abscess and bladder. The patient recovered and delivered.
Keywords: pregnancy, accident, bladder perforation, retroperitoneal phlegmon, surgical treatment.
Recently, severe trauma in pregnant women has ceased to be a casuistry in our region. However, this problem is almost not covered in the domestic literature. More often, researchers from far abroad turn to this issue, since in these countries in the structure of maternal mortality, a large proportion is occupied by cases not related to obstetric causes. Thus, out of 7348 maternal deaths in the United States, 57% were associated with obstetric causes, and 27% with trauma to pregnant women [1]. At 19In 1992 in Chicago (USA), trauma as a cause of maternal death, identified in 46% of pregnant women, came out on top in the structure of maternal mortality [3]. A car injury has become the leading cause in the structure of causes that led to the death of a pregnant woman [2,5]. The available literature covers in detail the issues of resuscitation and intensive care [4,6,7] of injured pregnant women. At the same time, the sporadic nature of observations, as well as the isolation of obstetrician-gynecologists from a systematic analysis of severe trauma in pregnant women, for a long time did not allow us to describe the clinical picture and morphology of the mechanical injury of the pregnant uterus in a real relationship with the emerging substrate of the pathology with the greatest completeness.
More often, researchers from far abroad turn to this issue, since in these countries in the structure of maternal mortality, a large proportion is occupied by cases not related to obstetric causes. Thus, out of 7348 maternal deaths in the United States, 57% were associated with obstetric causes, and 27% with trauma to pregnant women [1]. At 19In 1992 in Chicago (USA), trauma as a cause of maternal death, identified in 46% of pregnant women, came out on top in the structure of maternal mortality [3]. A car injury has become the leading cause in the structure of causes that led to the death of a pregnant woman [2,5]. The available literature covers in detail the issues of resuscitation and intensive care [4,6,7] of injured pregnant women. At the same time, the sporadic nature of observations, as well as the isolation of obstetrician-gynecologists from a systematic analysis of severe trauma in pregnant women, for a long time did not allow us to describe the clinical picture and morphology of the mechanical injury of the pregnant uterus in a real relationship with the emerging substrate of the pathology with the greatest completeness.
In our country, in 1999, a large emergency medical service was created, which is in a single organizational, managerial, scientific and financial system with emergency gynecology units. From that moment on, all pregnant women with trauma of any origin began to concentrate in the head center and its branches. The creation of such a service and the active participation of obstetrician-gynecologists in its work made it possible to gain clinical experience among pregnant women with various injuries and to formulate new clinical and diagnostic provisions associated with trauma to the pregnant uterus. This report is devoted to a severe car injury in a pregnant woman.
Case description
Patient S., 20 years old, case number 11713-1017, is admitted to the Alat sub-branch (Bukhara region) of the RNCEMP on 12.06.2011 by ambulance. assistance immediately after she was hit by a car. A woman considers herself pregnant at 23 weeks. Pregnancy 1, is registered, the date of the last menstruation is 01/17/2011. Upon admission, the general condition of the patient of moderate severity, in a clear mind (did not lose), complained of pain in the lower abdomen, more on the left. Stable hemodynamics was noted: pulse 90 per minute, BP 120/80 mm Hg. After the examination, the diagnosis was made: a closed fracture of the pelvic bones (sciatic and iliac), ber. 1, 23 weeks
Upon admission, the general condition of the patient of moderate severity, in a clear mind (did not lose), complained of pain in the lower abdomen, more on the left. Stable hemodynamics was noted: pulse 90 per minute, BP 120/80 mm Hg. After the examination, the diagnosis was made: a closed fracture of the pelvic bones (sciatic and iliac), ber. 1, 23 weeks
The patient was in the Alat sub-branch for 18 days and was discharged home in a satisfactory condition. 2 days after discharge, the general condition worsened, chills, pain in the left iliac region and lower abdomen, purulent admixture in the excreted urine appeared. On August 3, 2011, the woman was delivered to the Bukhara regional branch of the RNCEMP.
On admission, the patient complained of persistent pain in the lower left abdomen. The patient's condition is moderate, consciousness is clear, body temperature is 38.0°C. Vesicular breathing in the lungs. Heart: muffled tones, tachycardia, blood pressure 100/60 mm Hg, pulse 96 beats. in min. The tongue is moist, the abdomen is enlarged
in min. The tongue is moist, the abdomen is enlarged
U.U. Zhabbarov, Z.D. Karimov, Sh.A. Khudaibergenov, I.Sh. in the left lower half, where a sharply painful tugoelastic formation without clear contours is palpated, approximately 15.0x10.0 cm in size with severe perifocal infiltration. Peritoneal symptoms are negative. The liver and spleen are within normal limits, there is no dullness in the sloping areas of the abdomen. Intestinal peristalsis is auscultated well, there was stool. The symptom of tapping in the lumbar region is negative. Urine through the catheter is cloudy, purulent.
Obstetric status: the uterus is enlarged due to pregnancy, its contours are even, clear, the tone of the uterus is normal, there is no pain. The size of the uterus corresponds to 26 weeks of pregnancy, the fetal heartbeat is heard up to 140 beats per minute, the fetal bladder is intact. During vaginal examination, attention is drawn to a significant deviation of the cervix and body of the uterus up and to the right due to a massive painful tumor-like formation in the left iliac region, described above. There is also massive infiltration of the perivesical tissue and the left parametrium. The vaginal walls were intact, the cervical canal was closed, there was no leakage of amniotic fluid and urine from the vagina.
There is also massive infiltration of the perivesical tissue and the left parametrium. The vaginal walls were intact, the cervical canal was closed, there was no leakage of amniotic fluid and urine from the vagina.
Examined: Hb 68.0g/l, e. 2.3 million, l. 6.1 thousand, ESR 65 mm/h, col. 0.9, M-25%. In urine: protein 0.66 g/l, rel. 1025, leukocytes in large numbers. Blood glucose 5.8 mmol/l; total protein 64.5 g/l; ALT 0.08; total bilirubin 13.8 mmol/l; urea
6.9 mmol/l. PTI 100%, thrombotest grade IV, fibrinogen
3.10 g/l. Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity: signs of a retroperitoneal hematoma of the left iliac region with anechoic turbid contents, 135.0-75.0 mm in size, were found. There was no fluid in the abdominal cavity, there was no intestinal pneumatosis. Ultrasound of the kidneys: on the left, the contours of the kidney are even, the dimensions are 121-53 mm, the CCI is -1.2 cm, the pelvis is moderately expanded to 32 mm, stones are determined with dimensions of 13x11x9mm. On the right, the kidney is 119-54 mm, the CCI is 17 mm, the pelvis is not dilated. Ultrasound of the uterus and fetus: the size of the fetus corresponds to a period of 26 weeks, the s / b of the fetus is up to 140 beats. per minute, placenta along the anterior wall, oligohydramnios. Radiography of the pelvic bones: bilateral fracture of the pubic bones of the pelvis. Computed tomography of a pregnant woman was performed according to vital indications. In the small pelvis and left hypogastric region, a formation with fuzzy contours 15-13 cm in size of low density was revealed.
On the right, the kidney is 119-54 mm, the CCI is 17 mm, the pelvis is not dilated. Ultrasound of the uterus and fetus: the size of the fetus corresponds to a period of 26 weeks, the s / b of the fetus is up to 140 beats. per minute, placenta along the anterior wall, oligohydramnios. Radiography of the pelvic bones: bilateral fracture of the pubic bones of the pelvis. Computed tomography of a pregnant woman was performed according to vital indications. In the small pelvis and left hypogastric region, a formation with fuzzy contours 15-13 cm in size of low density was revealed.
The patient was examined by a surgeon, urologist, traumatologist and obstetrician-gynecologist. Diagnosis: fracture of the pubic bones of the pelvis. Retroperitoneal hematoma of the left iliac region, hematoma of the broad ligament of the uterus. Pregnancy 1, 26 weeks. Urolithiasis, right kidney stones. Acute cystitis. Retroperitoneal rupture of the bladder? Severe anemia.
On August 4, 2011, under general endotracheal anesthesia, a lower median laparotomy was performed. During the operation, after dissection of the aponeurosis, 1000.0 ml of pus with a fetid odor were released. Upon further revision, it was found that the cavity of the large abscess extends from the upper parts of the paravesicular tissue to the left parametrium between the sheets of the broad uterine ligament. At this moment, they refrained from opening the abdominal cavity, because during the revision, a penetrating defect of the upper wall of the bladder with dimensions of 2.0x2.0 cm was established, from which urine began to flow. At this stage of the operation, it became apparent that the abscess was the result of urinary leakage due to an unrecognized rupture of the bladder. Therefore, for obvious reasons, it was decided to refrain from opening the abdominal cavity. Due to the pronounced inflammatory infiltration, as well as due to the presence of pregnancy (accompanied by the expansion of the vascular network in all areas of the small pelvis), tissue bleeding, it was decided to minimize the amount of intervention by installing a Petzer catheter in the bladder cavity through the above defect after additional drainage of the left parametrial abscess.
During the operation, after dissection of the aponeurosis, 1000.0 ml of pus with a fetid odor were released. Upon further revision, it was found that the cavity of the large abscess extends from the upper parts of the paravesicular tissue to the left parametrium between the sheets of the broad uterine ligament. At this moment, they refrained from opening the abdominal cavity, because during the revision, a penetrating defect of the upper wall of the bladder with dimensions of 2.0x2.0 cm was established, from which urine began to flow. At this stage of the operation, it became apparent that the abscess was the result of urinary leakage due to an unrecognized rupture of the bladder. Therefore, for obvious reasons, it was decided to refrain from opening the abdominal cavity. Due to the pronounced inflammatory infiltration, as well as due to the presence of pregnancy (accompanied by the expansion of the vascular network in all areas of the small pelvis), tissue bleeding, it was decided to minimize the amount of intervention by installing a Petzer catheter in the bladder cavity through the above defect after additional drainage of the left parametrial abscess. The operation ended with the installation of a Foley catheter into the bladder. Blood loss was 300.0 ml.
The operation ended with the installation of a Foley catheter into the bladder. Blood loss was 300.0 ml.
Postoperative diagnosis: extraperitoneal rupture of the bladder, complicated by suppuration of the urinary leakage of the perivesical tissue and the left parametrium. Fracture of the pubic bones of the pelvis. Pregnancy 1, 26 weeks, oligohydramnios. Urolithiasis, right kidney stones. Severe anemia.
The postoperative period was uneventful. The patient was discharged on 15.08.2011 in a satisfactory condition, with a recommendation to be registered with a traumatologist and gynecologist at the place of residence.
On September 25, 2011, a woman is admitted to the maternity ward of the regional perinatal center, where a premature birth occurs in a foot presentation at 35 weeks of gestation with a live, premature female fetus weighing 1800.0 g, 42 cm tall, with an Apgar score of 6 -7 points. The postpartum period proceeded without complications. They were discharged home with the child on 10. 10.2011 in a satisfactory condition.
10.2011 in a satisfactory condition.
Conclusion
According to the Department of Emergency Gynecology of the RNCEM (headed by Prof. ZD Karimov), bladder ruptures and urethral injuries in pregnant women as a result of traffic accidents and catatraumas are observed with the same frequency - 2.3%. Examination standards make it possible to timely identify this nature of the injury: assessment of outflowing urine (gross hematuria), Zeldovich test, ultrasound of the bladder with assessment of the state of the paravesical tissue, cystoscopy, contrast cystography. The described case is interesting in that a diagnostic error was made due to non-compliance with the fundamental requirements of the standard and algorithm for examining patients after an accident in the Alat sub-branch of RRCEM. This led to infection of the urinary tract, extensive phlegmon of the cellular space of the paravesical and parametrical area.
in the focus with the installation of a Petzer catheter through an additional incision in the wall of the bladder, 4) adequate drainage is provided. Any other increase in the volume of intervention could lead to the most serious complications associated with bleeding and the development of severe sepsis.
Any other increase in the volume of intervention could lead to the most serious complications associated with bleeding and the development of severe sepsis.
Literature
1. Chang J. et al. Homicide: a leading cause of injury deaths among pregnant and postpartum women in the United States, 1991-1999. Amer J Public Health 2005; 95(3): 471-477.
2. El Kady D. Perinatal outcomes of traumatic injuries during pregnancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol 2007; 50(3): 582-591.
3. Fildes J. et al. Trauma: the leading cause of maternal death. J Trauma 1992; 32(5): 643-645.
4. Fujitani S., Baldisseri M.R. Hemodynamic assessment in a pregnant and peripartum patient. Crit Care Med 2005;33(10 Suppl):S354-S361.
5. Ikossi D.G. et al. Profile of mothers at risk: an analysis of injury and loss of pregnancy in 1,195 trauma patients. J Amer Coll Surg 2005;200(1):49OLATI
UU Zhabbarov, ZD Karimov, Sh.A. Khudaibergenov, I.Sh. Jabrlangan ayolda sidik pufa-gining korin parda ortida yorilishi wa uning pufak atrophy tukimashiga hamda chap parametriyga singigan sidikning yiringlashi, tosning kov suyaklari sini-shi aniklangan.