Severe edema pregnancy
Swelling during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
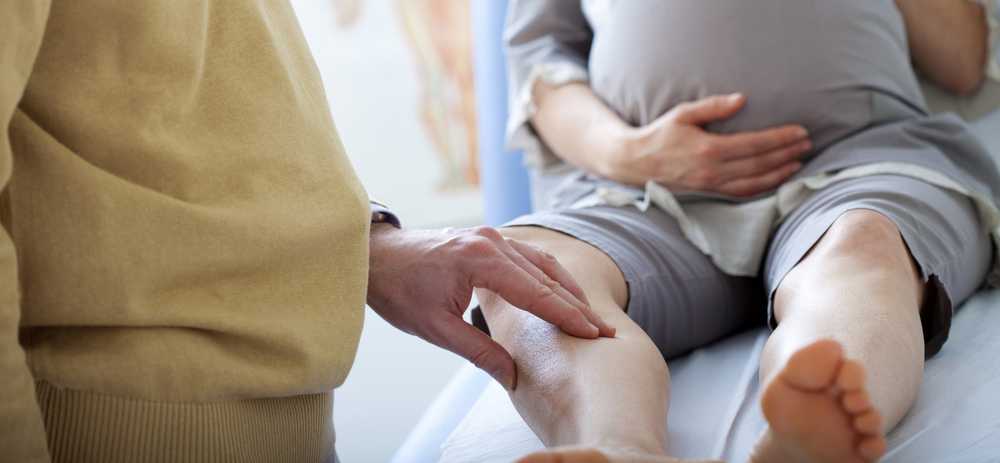
Most women get swollen ankles and feet while pregnant. It’s natural to have concerns about swelling since it can be uncomfortable, make your shoes tighter and possibly make you feel embarrassed. Knowing what to look for and how best to manage it can help you stay as comfortable as possible.
Why do women experience swelling during pregnancy?
There are 3 main reasons women experience swelling while pregnant.
- Throughout pregnancy, you produce more blood than usual to help your baby grow.
- As the baby grows, your uterus presses on and slightly blocks the veins that return blood from your legs to your heart.
- Your hormones make the walls of your veins softer, which makes it harder for them to work properly.
For these reasons, your blood tends to pool in your legs. There, a small amount of blood leaks through tiny blood vessels into the tissues and produces the swelling you can see and feel.
Where and when will I get swelling?
The swelling should be only in your feet and ankles. Your fingers might get a little larger — enough to make any rings feel tight — but they shouldn't be obviously swollen.
Your feet and ankles are likely to swell later in the day. This is mainly due to gravity — any extra fluid in your body will sink to your feet and ankles, especially if you spend a lot of time on your feet.
Swelling is also more likely to happen later in your pregnancy.
Gradual swelling isn't harmful to you or your baby, but it can feel uncomfortable.
How can I reduce swelling?
Some simple things can help you feel more comfortable and can also aid in preventing swelling.
Try to:
- avoid standing for long periods without moving
- wear comfortable shoes (avoid tight straps or anything that might pinch if your feet swell)
- put your feet up as much as you can
- limit salty foods and excessive salt in your diet
- sleep on your left side, which will help blood return to the heart
- exercise regularly by walking or swimming — this helps keep your circulation going
If you need to stand for long periods, try to move around and change position regularly.
Compression stockings can help the blood flow back to the heart and limit how much swelling you get. Massage and reflexology might also help reduce swelling and associated symptoms.
Even if your swelling is bothering you, remember to still drink plenty of water. Keeping your fluids up is important to avoid dehydration and stay healthy.
Normal or abnormal swelling?
Most pregnant women have swollen feet and ankles at some point, and this is perfectly normal. However, there are times when swelling could indicate something more serious.
Contact your midwife, doctor or hospital immediately if:
- swelling is there at the start of the day or doesn't go down when you rest
- your face or hands are swollen
- the swelling is more than you have had before
These are warning signs for pre-eclampsia, which is high blood pressure caused by pregnancy. This is a very serious condition both for you and your baby, so call your doctor or midwife as soon as possible. Don't wait for your next regular appointment.
Don't wait for your next regular appointment.
If one leg is more swollen than the other, this could suggest a more serious problem with one of your veins, such as deep vein thrombosis. Again, contact your doctor or midwife as soon as possible.
Most swelling is a normal part of pregnancy and will usually go away after you've given birth. However, if you're concerned about anything, no matter how small or seemingly insignificant, talk to your doctor or midwife.
You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to talk to a maternal child health nurse.
Sources:
NSW Health (Having a baby), The Royal Women's Hospital (Active pregnancy), The Royal Women's Hospital (Common concerns in early pregnancy), Cochrane (Interventions for varicose veins and leg oedema in pregnancy), King Edward Memorial Hospital (Pregnancy, birth and your baby), Department of Health (Clinical practice guidelines: Pregnancy care), King Edward Memorial Hospital (Minor Symptoms or Disorders in Pregnancy King Edward Memorial Hospital Clinical Guidelines: Obstetrics & Midwifery), The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists - Pre-eclampsia and high blood pressure during pregnancy (The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists - Pre-eclampsia and high blood pressure during pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: February 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Common discomforts during pregnancy
- Varicose veins
- Leg cramps during pregnancy
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
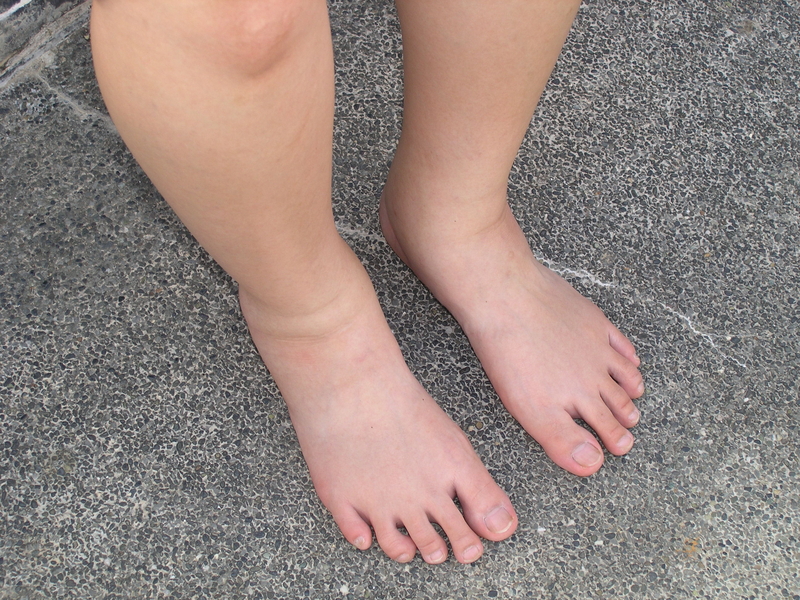
Swollen ankles, feet and fingers in pregnancy
It's normal to get some swelling in pregnancy, particularly in your legs, ankles, feet and fingers.
It's often worse at the end of the day and further into your pregnancy.
Swelling that comes on gradually is not usually harmful to you or your baby, but it can be uncomfortable.
A sudden increase in swelling can be a sign of pre-eclampsia, a condition that needs to be monitored as soon as possible.
Non-urgent advice: Call your midwife, GP or labour ward immediately if you have:
- a sudden increase in swelling in your face, hands or feet
- a very bad headache
- problems with your vision, such as blurring or flashing lights in your eyes
- severe pain just below your ribs
- vomiting with any of these symptoms
These could be symptoms of pre-eclampsia, which can lead to serious complications if it's not monitored and treated.
Normal pregnancy swelling
Swelling is caused by your body holding more water than usual when you're pregnant.
Throughout the day the extra water tends to gather in the lowest parts of the body, especially if the weather is hot or you have been standing a lot.
The pressure of your growing womb can also affect the blood flow in your legs. This can cause fluid to build up in your legs, ankles and feet.
What can help to reduce swelling
Try to:
- avoid standing for long periods
- wear comfortable shoes and socks – avoid tight straps or anything that might pinch if your feet swell
- try to rest with your feet up as much as you can
- drink plenty of water – this helps your body get rid of excess water
- exercise – try to take regular walks during the day or doing foot exercises
Foot exercises
You can do foot exercises sitting or standing.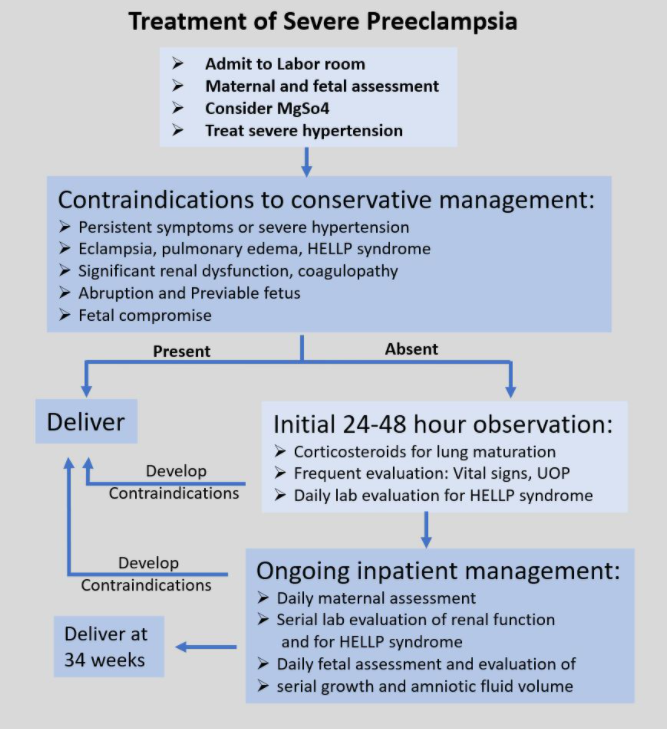 They improve blood circulation, reduce swelling in the ankles, and prevent cramp in the calf muscles:
They improve blood circulation, reduce swelling in the ankles, and prevent cramp in the calf muscles:
- bend and stretch your foot up and down 30 times
- rotate each foot in a circle 8 times one way and 8 times the other way
Get more tips on exercising in pregnancy.
Page last reviewed: 10 March 2021
Next review due: 10 March 2024
Edema during pregnancy | Avanta-Med Medical Center
Updated: 10/31/2022
In the initial months of pregnancy, as a rule, edema in the body of a pregnant woman is either absent or invisible. And this is quite natural. The process of water retention does not begin immediately.
With the passage of time, a woman herself begins to notice that the skin on her arms, legs, and abdomen loses firmness and elasticity. For some, the circumference of the face may increase in later periods. And in the last months of pregnancy, many have swelling of the legs and arms, face and lower back, and abdomen. A clear sign of edema is finger pressure on the skin of the lower leg in front, where there is almost only skin on top of the bone. With this symptom, pressure leaves a hole that does not immediately fill. In addition, a clear increase in body weight can also indicate an increase in edema. With a normal pregnancy, body weight increases gradually.
And in the last months of pregnancy, many have swelling of the legs and arms, face and lower back, and abdomen. A clear sign of edema is finger pressure on the skin of the lower leg in front, where there is almost only skin on top of the bone. With this symptom, pressure leaves a hole that does not immediately fill. In addition, a clear increase in body weight can also indicate an increase in edema. With a normal pregnancy, body weight increases gradually.
Physiological edema
Physiological edema - develops in approximately 70-80% of pregnant women and usually does not require special treatment. Their development occurs as a result of sodium retention in the body, both in the blood and in soft tissues. Due to the tendency of pregnant women to retain sodium in their body, which in turn is necessary for a normal pregnancy, there is the possibility of edema formation, since sodium attracts water. With the abuse of salty foods, physical exertion, the presence of hot weather, the possibility of physiological edema increases. Such edema, as a rule, does not pose a danger to the health of a woman and a baby, and goes away after the elimination of provoking factors.
Such edema, as a rule, does not pose a danger to the health of a woman and a baby, and goes away after the elimination of provoking factors. Pathological edema
In turn, pathological edema can bring quite a few problems during pregnancy.Pathological edema are symptoms of various diseases - cardiovascular, endocrine systems. Manifestation of kidney pathology. With an excessive increase in body weight, persistent edema appears, which can be expressed very sharply, manifested by massive swelling of the legs, face, arms, lower back, and abdominal wall. It becomes difficult for a woman to dress, put on shoes, bend down, clench her fingers into a fist. With the initial form of histosis, this condition is reversible, and as a rule, the fetus practically does not suffer. In more severe forms, manifested not only by massive edema, but also by an increase in blood pressure and protein excretion in the urine, an intrauterine pathological effect on the fetus is noted.
Accordingly, a woman planning a pregnancy needs to know how to avoid edema.
 First of all, you should regulate the intake of salt in the body. During pregnancy, the average volume of fluid consumed per day is about 2 liters, and accordingly, if the amount of fluid consumed is normal and body weight increases evenly, then all processes are balanced and there is nothing to worry about. But with the appearance of uneven edema, edema that does not disappear overnight, or with excessive weight gain, the diet should be adjusted. First of all, you should deal with the amount of sodium consumed, which is contained in table salt, sauerkraut, pickles, herring, black bread, and, if necessary, reduce the amount of its consumption. In addition, you should reduce the amount of fluid consumed, but not less than 1 liter. Do not forget that the liquid in the body comes in the form of drinks, juices, tea and coffee. A large amount of liquid is found in apples, pears, grapes, etc. Accordingly, adjusting the diet should not forget about this. You should definitely inform your attending physician about the appearance of edema, who is observing you and, together with him, adjust the diet, and, if necessary, treatment.
First of all, you should regulate the intake of salt in the body. During pregnancy, the average volume of fluid consumed per day is about 2 liters, and accordingly, if the amount of fluid consumed is normal and body weight increases evenly, then all processes are balanced and there is nothing to worry about. But with the appearance of uneven edema, edema that does not disappear overnight, or with excessive weight gain, the diet should be adjusted. First of all, you should deal with the amount of sodium consumed, which is contained in table salt, sauerkraut, pickles, herring, black bread, and, if necessary, reduce the amount of its consumption. In addition, you should reduce the amount of fluid consumed, but not less than 1 liter. Do not forget that the liquid in the body comes in the form of drinks, juices, tea and coffee. A large amount of liquid is found in apples, pears, grapes, etc. Accordingly, adjusting the diet should not forget about this. You should definitely inform your attending physician about the appearance of edema, who is observing you and, together with him, adjust the diet, and, if necessary, treatment.
Much more difficult with pathological edema. The most common are cardiac and renal. With heart disease, edema occurs as a result of heart failure and spreads to the underlying parts of the body, legs and lower back. With renal edema, puffiness of the face, bags under the eyes, swelling of the arms and legs appear. Appear with certain pathologies of the kidneys with glomerolonephritis, inflammatory diseases of the kidneys, immuno-allergic nature. These conditions require specialized monitoring and treatment by appropriate specialists - a cardiologist and a nephrologist. And if complications occur during pregnancy with these diseases, hospitalization may be required. Therefore, given the above, it is worth paying attention to the appearance of edema, especially if there is a history of diseases of the cardiovascular system and kidneys, since timely assistance will help you and your baby avoid possible unpleasant complications.
what to do if legs and arms swell during pregnancy
Edema during pregnancy, few people manage to avoid. According to various sources, only a fifth of future mothers are lucky. For the rest, this unpleasant phenomenon causes a lot of moral and physical suffering. What to do? Let's try to explain.
According to various sources, only a fifth of future mothers are lucky. For the rest, this unpleasant phenomenon causes a lot of moral and physical suffering. What to do? Let's try to explain.
What is edema?
Edema is an excess of fluid in the tissues. The place where it accumulates looks swollen, puffy. In the early stages, the problem is almost imperceptible or it does not exist at all, which cannot be said about edema during pregnancy in the second and third trimesters.
Pay attention! Hot flashes during early or late pregnancy and swelling are two different things! In the first case, we are talking about a sudden fever (less often chills), and not about the accumulation of fluid.
Why pregnant women have swollen legs
In fact, understanding the cause of edema is very important, because they are both natural and pathological. The latter are quite rare, but are the causes of severe violations.
Natural or physiological edema during pregnancy begins due to a changing hormonal background, when sodium salts linger in the tissues and do not go away. In another version, the growing uterus, while the woman is lying down, occludes the inferior vena cava and does not allow blood to escape from the femoral veins.
In another version, the growing uterus, while the woman is lying down, occludes the inferior vena cava and does not allow blood to escape from the femoral veins.
Pathological swelling during pregnancy may indicate the presence of:
| Disease | Description |
| Deep vein thrombosis | Blockage of the vessel, which leads to death. Risk factors: trauma, venous insufficiency, smoking, physical inactivity, oncology. |
| Preeclampsia | It occurs in approximately 2% of pathological edema. It is characterized by increased blood pressure and high levels of protein in the urine. The disease has varying degrees of severity. The most terrible consequences are a stroke, the death of a mother or child, fetal pathology. Risk factors: chronic hypertension, adolescence or women over 35 years of age, hereditary predisposition, first or multiple pregnancies, diabetes mellitus, etc. |
| Phlegmon | Acute infection, usually caused by streptococci; characterized by skin lesions and inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue. |
Types and features of edema
Edema begins in the lower extremities and gradually moves up to the face. We’ll talk about the dangers of edema during pregnancy a little later, but for now it’s worth understanding if there is any difference between them at different times. Note that we will talk about pathological situations when the accumulation of fluid exceeds the norm by 30%.
Early
Edema is not as common in early pregnancy. The weight of the child and the volume of the uterus are not yet so large as to interfere with the full functioning of the body. However, if they occur, then you should pay the attention of your doctor to this, since such deviations may indicate serious illnesses. In particular:
- hypothyroidism - insufficient production of thyroid hormones.

- kidney problems - that is why it is very important to take urine for analysis every two weeks.
Second trimester
In the middle of pregnancy, this pathology can signal the onset of varicose veins, in which case the doctor will send the woman for a consultation with a phlebologist.
Another pathology that causes the disease is heart failure. The disorder is also accompanied by shortness of breath and cyanosis of the mucous membranes. Such problems will have to be treated together with a cardiologist.
But a much bigger problem when carrying a baby is preeclampsia. Its onset can be seen already at 18-20 weeks, although the disease is gaining full strength in the third trimester. It will only have to be treated in a hospital.
Late term
Here it is worth dwelling in more detail on gestosis. So called late toxicosis. Together with edema, a woman is tormented by high blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, convulsions, drowsiness, weakness, fever, or excessive emotional arousal, which affects the physical condition.
The condition has four levels of severity:
| Severity | Description |
| 1 degree | edema directly |
| 2 degree | protein in the urine and problems with pressure are added to them |
| 3 degree | preeclampsia |
| 4 degree | eclampsia, in which strokes and placental abruption are possible |
Case study:
A woman was observed in our hospital with complaints of severe swelling of the legs during pregnancy. The lower limbs were indeed swollen, which was noticeable to the naked eye. During the survey, it turned out that the woman's blood pressure began to rise regularly. Since she was already in her 3rd trimester, the patient was recommended to immediately go to the hospital for preservation and additional examination.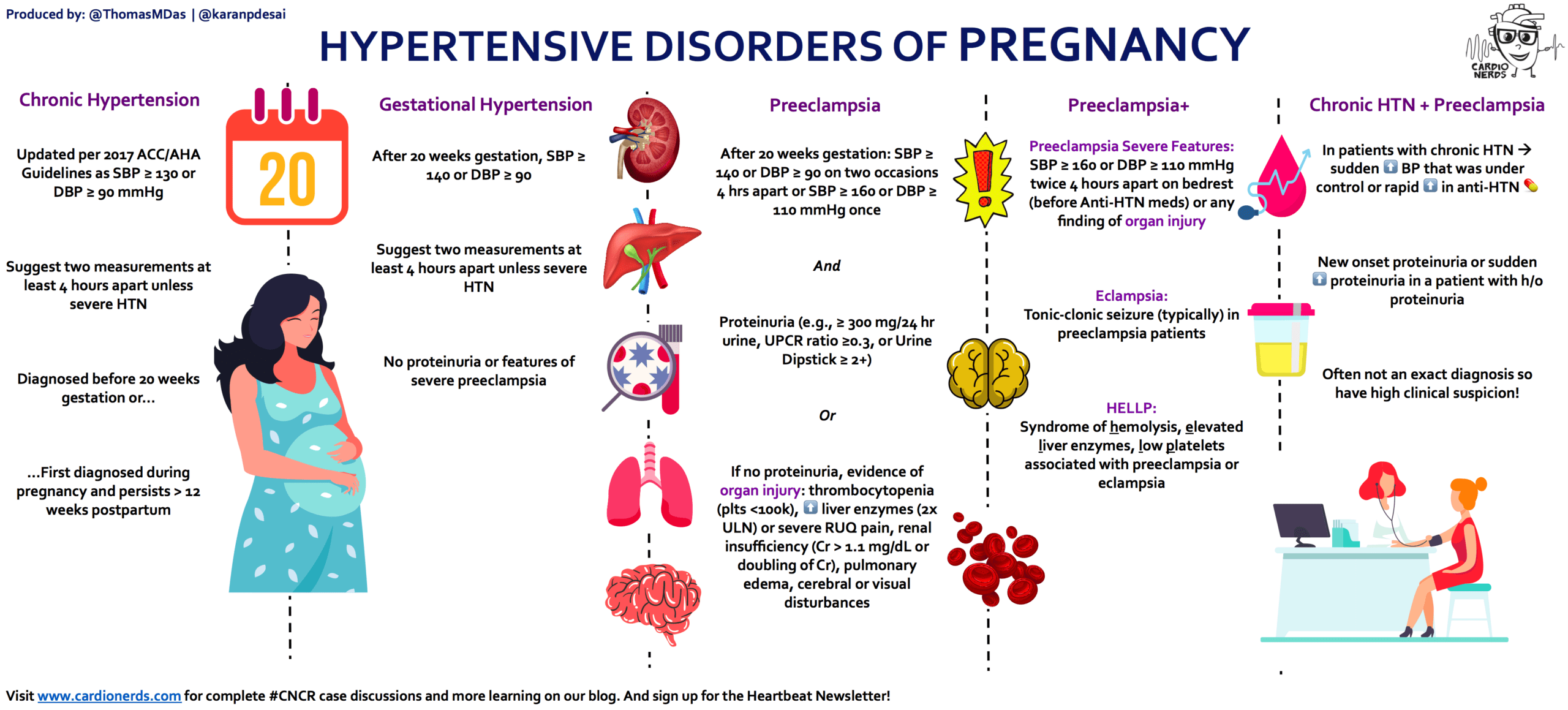 As a result, the patient was diagnosed with preeclampsia.
As a result, the patient was diagnosed with preeclampsia.
How to get rid of swelling during pregnancy
Physiological edema can be prevented or at least reduced. For this you need:
- reconsider your diet - there should not be fried, smoked, salty or spicy.
- treat water more carefully - drink only clean, non-carbonated and, preferably, most of it before lunch.
- less to be in the heat and in stuffy rooms - you will certainly want to drink.
- wear comfortable shoes.
- lie down daily for about half an hour so that the legs are located above the head.
- walk more - light physical activity is good for everyone, but in this case there is a need for the approval of a doctor.
Your doctor may give other recommendations. It is important to take into account all the factors of pregnancy and choose the most effective therapy within the given framework. Our doctors can advise you remotely and draw up the right treatment regimen.
FAQ
Swollen legs during pregnancy - how to fix?
+
You need to discuss this with the doctor who manages the pregnancy. Edema can be both physiological - then you will simply be given a number of recommendations for their elimination, and pathological - when it comes to certain disorders in the body.
What is "internal edema" during pregnancy?
+
Internal or hidden edema during pregnancy is invisible externally. Here we are talking about swelling of the internal organs. A violation is calculated by exceeding the norm of weight gain in the last terms.
How to eliminate swelling at 37-39 weeks of pregnancy?
+
Follow the recommendations of the doctor and, if necessary, undergo a course of treatment. In any case, your doctor will answer all questions in more detail. Do not self-medicate.
Do not self-medicate.
We publish only verified information
Article author
Menshikova Maria Viktorovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Experience 38 years
Consultations 1816
Articles 46
Specialist with extensive practical experience. He has a certificate of a mammologist, a certificate of professional certification.