The top of my head is changing shape
Dent in Head: Causes and Treatment
Overview
Dents and irregularities in the shape of your skull are usually simple variations in anatomy. Everyone has variations in bone structure — just consider how very different people’s faces can look from each other as evidence.
But there are some instances where a new dent or bump you notice in your skull can indicate a serious medical condition. This is the type of symptom that should be checked out by a doctor, especially if the shape of your skull appears to change suddenly.
A dent in your head (also known as a skull depression) can indicate several medical conditions. It can also be genetic or happen because of an injury.
Trauma
Car accidents, falls, or severe blows to the head can cause what’s called a depressed fracture in your skull. A depressed fracture means that a part of your skull has been crushed in toward your brain. This kind of injury requires emergency medical treatment.
Any significant head injury should be immediately evaluated by a doctor.
Gorham’s disease
Gorham’s disease is a rare condition that leads your bone mass to be replaced by other kinds of tissue. Gorham’s disease can cause bone loss in your skull, leading to a visible dent in some cases.
Paget’s disease of bone
Paget’s disease interferes with your body’s ability to replace old bone tissue with healthy new bone tissue. This can lead to an overgrowth of bone in your skull, leading to headaches and other symptoms. Sometimes the overgrowth can make your skull appear irregular or dented.
Cancer
There are case reports of skull depressions that have led doctors to discover cancer in a person. These cases are rare, but “bone-destructive” cancers (such as multiple myeloma) can cause skull depressions and skull irregularities.
Congenital skull indentation
Sometimes babies are born with an indentation in their skull. These indentations can be caused by the birth process or by the way the baby was positioned in their mother’s womb. If the bones in a baby’s skull fuse prematurely, the baby’s head may appear dented or misshapen — a condition called craniosynostosis.
If the bones in a baby’s skull fuse prematurely, the baby’s head may appear dented or misshapen — a condition called craniosynostosis.
Craniosynostosis can happen by itself, or it can be caused by genetic syndromes, including Apert syndrome and Pfeiffer syndrome.
If you’re concerned about a dent in your skull, your doctor will evaluate your skull’s shape. Your doctor may also ask questions about family history and other symptoms you might be having.
Often, nothing more than a thorough history and physical exam is needed, but your doctor may recommend further testing to reveal what is causing your skull depression. These tests could include:
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- PET scan
- X-ray
- Bone scan
The risk factors for developing dents in your skull depend on the underlying cause. It’s difficult to nail down who would be more “at-risk” to develop a head dent as a symptom or condition.
There is some research to suggest that men are at a higher risk than women for developing Gorham’s disease.
Genetics can play a role in some of the syndromes that can cause skull depressions in newborns, but often there is no genetic cause. In Apert syndrome, for instance, a parent can pass on the gene for the syndrome to their child, or the child can develop it spontaneously while in utero.
Risk factors for different kinds of cancers can include lifestyle factors (such as smoking), environmental triggers, and family history.
The treatments for a dent in your skull vary widely, depending on the underlying cause.
Treatment for depressed skull fractures
Depressed skull fractures often require surgery. Bone fragments will need to be removed from the area around your brain to prevent brain damage. These types of fractures are also treated with medication for pain relief and antibiotics to prevent infection.
Treatment for cancerous tumors
In the rare case that the irregular shape of your skull reveals a malignant tumor, you will need cancer treatment. Surgery will likely be required to get rid of the cancerous tumor. The treatment you need after surgery will depend on what kind of cancer you have and how aggressive the treatment needs to be.
Surgery will likely be required to get rid of the cancerous tumor. The treatment you need after surgery will depend on what kind of cancer you have and how aggressive the treatment needs to be.
Treatment for bone diseases
If you have Paget’s disease of bone, Gorham’s disease, or another rare bone disease that’s causing your skull dent, your doctor may prescribe bisphosphonates — drugs that keep your body from absorbing your bone tissue. Alendronate (Fosamax) and ibandronate (Boniva) are examples of these drugs.
Some people may need bone grafts to surgically correct the loss of bone mass in their skull.
Treatment for babies with skull dents
When a baby is born with a head dent or skull abnormality, the symptoms will usually resolve on their own within 6 months.
In some cases, helmet therapy may be recommended. There are also cases when surgery is required to correct the skull shape and make sure that the baby’s brain has enough room to develop as it grows.
While it’s common for the shape of people’s skulls to vary, a new dent or irregularity in your skull can occasionally indicate a serious health condition. Dents in your skull can be caused by trauma, cancer, bone diseases, and other conditions.
If you notice a change in your skull shape, you should make an appointment with your doctor. Take note of any other symptoms, like headaches, memory loss, and vision difficulties, that could be connected to a dent in your skull.
Causes and when to see a doctor
Not everyone has the same skull shape, and normal variations exist among individuals. The skull is not perfectly round or smooth, so it is normal to feel slight bumps and ridges.
However, a dent in the head, especially if it is new, requires a trip to the doctor to determine the cause.
In this article, we examine the possible causes and symptoms of a dent in the head. We also explain when a person should see a doctor and the possible treatment options.
A dent in the head may have a variety of causes. It could result from an injury, be genetic, or indicate a medical condition.
Skull fracture
Skull fractures occur as a result of a blow or impact to the head. Injury to the skull can occur after any direct force, such as a car accident, fall, or physical assault.
An injury to the brain, known as a traumatic brain injury (TBI), can sometimes accompany a skull fracture, but that is not always the case. In the United States, there are about 1.7 million cases of TBI each year.
There are four major types of skull fracture, including:
- open fracture
- closed fracture
- depressed fracture
- basal fracture
Of the four types, a depressed fracture is the most likely to look like a dent in the head. The dent occurs due to the displacement of the bone toward the brain.
In addition to displaced bone, the symptoms of a skull fracture may include:
- headaches
- impaired vision
- balance problems
- nausea
- dizziness
- confusion
Brain surgery
Certain types of brain surgery may leave a small dent in the skull.
For example, a craniectomy involves removing a piece of the skull bone. This removal might be necessary to reduce pressure on the brain from conditions that cause swelling.
Surgeons often restore the removed portion of the skull once the swelling has gone down, which usually resolves the dent.
Additional side effects following brain surgery vary depending on the reason for the operation.
Congenital skull depression
A congenital skull depression is a dent in the head that is present from birth.
In Western countries, the condition is uncommon, with experts estimating that it occurs in 1 in 10,000 newborn babies.
A congenital skull depression is usually due to trauma to the head during delivery. For example, the use of forceps or a suction device to help deliver the baby may result in trauma.
The main sign of a congenital skull dent is the depression in the bone. However, the trauma may also cause a brain injury in some babies.
When a brain injury occurs, symptoms may include:
- trouble breathing
- feeding difficulties
- seizures
Tumors
Although uncommon, different types of bone tumor may cause bone deformity and a dent in the head.
According to research in the journal Surgical Neurology International, tumors in the skull represent about 1–4% of all bone tumors.
Even benign tumors, such as fibrous dysplasia and ossifying fibroma, may cause an indentation of the skull.
Symptoms of a skull tumor may include:
- bone pain
- swelling
- bone deformity
- a painless mass
Gorham’s disease
Gorham’s disease is a condition that involves bone loss and abnormal blood vessel development. The loss of bone can lead to an indentation in the skull.
According to the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, Gorham’s disease is very rare.
Although it can occur at any age, it is most common in young adults and children.
Gorham’s disease can affect any of the bones in the body. Typically, though, the condition involves the skull, ribs, or pelvis.
Gorham’s disease causes symptoms in the affected area, including:
- bone pain
- swelling
- decreased range of motion
- generalized weakness
Vitamin A toxicity
Vitamin A is an essential nutrient that is necessary for a healthy immune system. It is also vital for organs, such as the lungs and heart, to function normally. Too much vitamin A can have adverse effects.
It is also vital for organs, such as the lungs and heart, to function normally. Too much vitamin A can have adverse effects.
Vitamin A toxicity occurs when there is too much vitamin A in the body. It is rarely due to a person eating too many foods high in vitamin A. Instead, it typically occurs as a result of taking an excessively high dosage of vitamin A supplements.
Vitamin A toxicity can cause softening of the bones, including the skull, which can lead to an indentation.
Additional symptoms of vitamin A toxicity include:
- dizziness
- a headache
- nausea
A dent in the head may be alarming, and it can occur for different reasons, some of which are serious. If a person develops a new dent in their head, they should see a doctor as soon as possible.
If an indentation develops after trauma to the head, immediate evaluation is necessary. Some head injuries, including skull fractures, can be life threatening.
In some instances, a doctor may make a diagnosis after performing a physical exam and medical history review.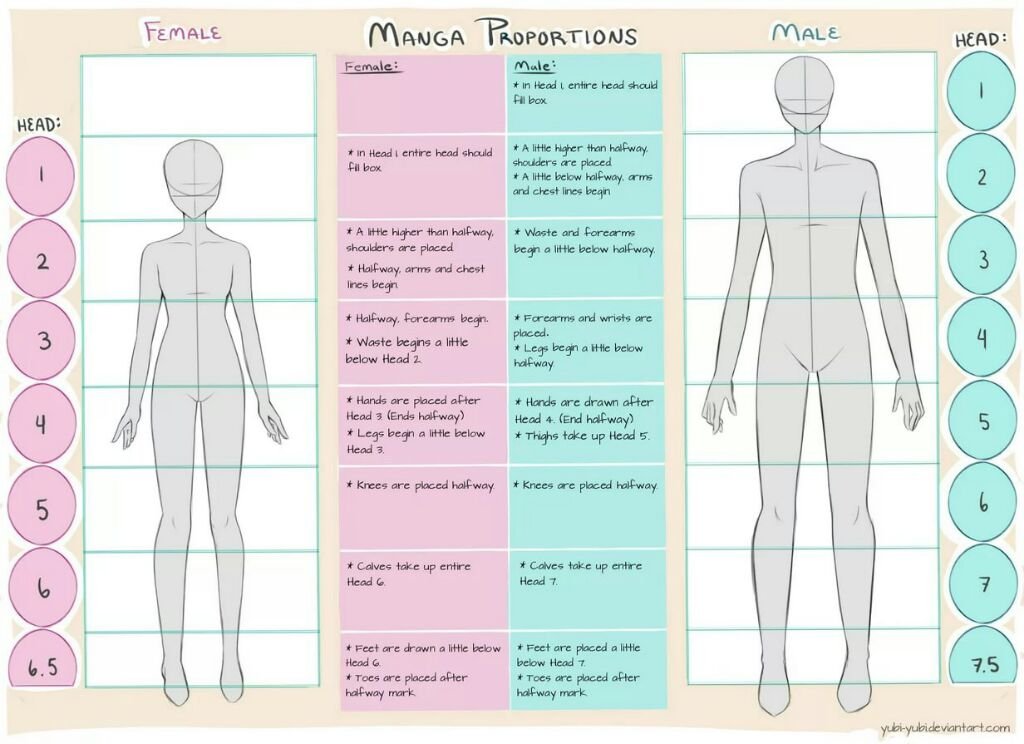 They may also use tests, such as a bone scan, X-ray, and CT scan, to help them make a diagnosis and determine the cause.
They may also use tests, such as a bone scan, X-ray, and CT scan, to help them make a diagnosis and determine the cause.
Treatment for a dent in the head depends on the cause.
In some cases, the condition does not require treatment. For example, if vitamin A toxicity causes a dent in the head, the person will just need to stop taking an excessive number of vitamin A supplements.
Similarly, a congenital skull depression due to a forceps injury during childbirth may not require treatment. According to research in the journal BMJ Case Reports, most congenital skull depressions from a birth injury spontaneously resolve in about 4 months.
In other cases, a dent in the head requires treatment.
For example, a person with a depressed skull fracture will need surgery. Surgery involves removing bone fragments around the brain to decrease the risk of brain damage. The individual will also receive medication, such as antibiotics and pain relievers.
Some people will require treatment to target the underlying condition responsible for a dent in the head. For example, treatment for Gorham’s disease may include radiation therapy and vitamin D supplements. In some circumstances, a doctor might also recommend bone grafting surgery.
For example, treatment for Gorham’s disease may include radiation therapy and vitamin D supplements. In some circumstances, a doctor might also recommend bone grafting surgery.
Skull shape varies naturally from person to person. However, a dent in the head may sometimes develop. This dent can have a variety of causes, including trauma, birth injuries, and some types of bone tumor.
If a person is concerned about a dent in their head, they should see a doctor. It is especially important to seek medical attention if additional symptoms are present, such as nausea, confusion, or dizziness.
Some dents in the head do not require treatment. In other instances, surgery may help treat the indentation.
causes, symptoms, treatment in Moscow - Consultation and examination for hydrocephalus - Neurology at Clinic No. 1
Examination and treatment
Hydrocephalus, or "dropsy of the brain", is a serious and often incurable disease. It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the brain. The lack of fluid outflow negatively affects not only the mental, but also the physical development of the patient, whose appearance becomes specific - the head increases while maintaining the normal parameters of the rest of the body. nine0005
The lack of fluid outflow negatively affects not only the mental, but also the physical development of the patient, whose appearance becomes specific - the head increases while maintaining the normal parameters of the rest of the body. nine0005
Get a diagnosis of cerebral hydrocephalus at Clinic No. 1
- X-ray
- Craniogram
- Ophthalmoscopy (as prescribed by a physician)
- Angiography
With a one-time payment for services - a 20% discount
Call
Classification of hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus can be congenital or acquired. It is generally accepted that the disease is diagnosed in children, but an increase in cases of dropsy in adult patients is increasingly noted. nine0005
Hydrocephalus by the nature of the course can be:
- Acute - this form of the disease is characterized by a rapid course, the symptoms become apparent literally within three days.

- Subacute - symptoms increase and develop within one month.
- Chronic - pathology develops for more than one month.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus
Congenital dropsy is diagnosed much less frequently than acquired. Usually, at the age of six months, pediatricians note that in an infant, the circumference and shape of the head differ from the norm. nine0005
- The circumference of the head is greater than the circumference of the child's chest.
- The head acquires a pear-shaped shape, the elongation of the skull is visually noticeable, while it is expanded, the skin is thinned, the fontanel is enlarged,
- The child does not eat well, is characterized by increased nervousness, often cries. During crying or water procedures, the baby's chin and upper limbs may shake.
- Spasticity of the lower extremities, hyperreflexia and the presence of pathological reflexes. nine0010
- Epileptic seizures.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in children older than 2 years and adult patients are somewhat different:
- Severe headache, up to nausea and vomiting.
 The pain intensifies when the patient changes from horizontal to vertical position.
The pain intensifies when the patient changes from horizontal to vertical position. - Fainting.
- Ophthalmologic examination reveals congestive optic disc.
- Disorders of memory and consciousness, loss of already acquired skills, inability to learn new ones. nine0010
- Optical-spatial agnosia develops - it is difficult for a person to determine which object is closer / farther, lower / higher.
Causes of hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus in the fetus may be associated with problems in the development of the central nervous system, or with intrauterine infection. Therefore, it is so important to undergo a comprehensive examination for various infections - herpetic, cytomegalovirus, before planning pregnancy.
Acquired hydrocephalus in most cases is a consequence or complication of diseases such as: nine0005
- Meningitis - viral or bacterial etiology.
- Meningoencephalitis is an inflammatory process affecting the meninges and medulla.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage is a common consequence of skull trauma or occurs as a result of rupture of an arterial aneurysm.
- Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous lesion of the meninges.
- Intraventricular hemorrhage - a consequence of severe and traumatic obstetrics. nine0010
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus
- The main method of examination is an X-ray, the results of which will confirm the divergence of the sutures of the skull.
- It is also recommended to make a craniogram - X-ray examination of the skull in different projections without contrast. Such a diagnosis will not only identify hydrocephalus, but also determine its type in order to prescribe effective therapy as soon as possible.
- Ophthalmoscopy may be required to detect papilledema. nine0010
- Angiography of cerebral vessels is prescribed for differential diagnosis.
Get a diagnosis of cerebral hydrocephalus at Clinic No. 1
- X-ray
- Craniogram
- Ophthalmoscopy (as prescribed by a physician)
- Angiography
With a one-time payment for services - a 20% discount
Call
Treatment of hydrocephalus
The therapy is based on a set of measures aimed at activating the outflow of pathological fluid accumulation.
If therapeutic agents do not give a positive effect, the patient undergoes surgery. Endoscopic treatment demonstrates the greatest efficiency against the background of low invasiveness:
- endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy of the fundus of the third ventricle,
- aqueductoplasty - the arrangement of a kind of "water pipeline", through which the liquid will be effectively removed from the skull. nine0010
- septostomy - removal of cysts and elimination of occlusion of the Monroe's hole.
- removal of brain tumors by endoscopic method.
After such a surgical intervention, the patient very soon returns to normal life, since his brain is not seriously traumatized. This procedure allows you to regulate the flow of fluid in the cranium, however, after the operation to eliminate hydrocephalus, the patient needs constant monitoring by a specialist and regular monitoring of the state of the brain. nine0005
The prognosis for hydrocephalus depends on the cause and time of diagnosis and the appointment of adequate treatment. Children who receive treatment are able to lead normal lives with few, if any, limitations. In rare cases, speech impairment may occur.
Children who receive treatment are able to lead normal lives with few, if any, limitations. In rare cases, speech impairment may occur.
Make an appointment with a neurologist
Experienced specialists invite you to an appointment at the neurological department of the private Multidisciplinary Medical Center in Moscow - "Clinic No. 1". To confirm hydrocephalus or to refute a preliminary diagnosis - we can absolutely accurately, using the progressive capabilities of the diagnostic department of the center. After the diagnosis is clarified, the patient will be prescribed treatment, if necessary, an operation will be performed to remove the pathological accumulation of fluid. nine0005
Information on prices for primary and repeated paid appointments with a neurologist is available on our website. You can make an appointment with a specialist at a convenient time by phone or using the online form on our website.
Moscow, st. Krasnodarskaya, house. 52, bldg. 2
52, bldg. 2
+7 (495) 152-33-19
We work on weekdays and weekends from 8.00 to 21.00
Prices for consultations and appointments with a neurologist
| Service name | Price |
| Free medical consultation after MRI/CT | 0.00 |
| Initial appointment with a neurologist (consultation) | 2200.00 |
| Repeated consultation with a neurologist nine0156 | 1500.00 |
| Calling a doctor at home | 5180.00 |
Got an appointment with Vyacheslav Mazurov. Many thanks to the doctor for the promptness and clear description of the picture! An excellent doctor, he explained everything, showed everything in the picture,...
Came in for an x-ray of the bones of the nose after an injury: a horse hit his head in the nose. Dr. Vyacheslav Mazurov received me well and kindly, escorted me to the X-ray room,...
Dr. Vyacheslav Mazurov received me well and kindly, escorted me to the X-ray room,...
Were at the reception of Mazurov Vyacheslav Vitalievich. I would definitely recommend contacting him. The quality of the examination, the selected treatment, the information content of the reception and...
Rakitina Valentina Nikolaevna
She came to the Clinic with an injury to her right knee joint. I was pleasantly surprised at how attentively they treated my problem. The receptionist is very attentive,...
Tatyana
I often come to the clinic in Lublino, because I live nearby. The manager Olya always greets with a smile. You can consult with her - which doctor is best ...
Tatyana
I have been seeing at the clinic No. 1 in Lyublino for many years. The manager Olya meets me. Always a smile on her face. Everything will tell you, which doctor to go to if you don't know what exactly...
Tatiana
In clinic No. 1 I do periodic gastroscopy with Korolkov Alexei Grigorievich. You can not be afraid for the consequences of this doctor. The doctor is wonderful. Will meet with...
You can not be afraid for the consequences of this doctor. The doctor is wonderful. Will meet with...
Tatyana
Operated on Vyacheslav Valeryevich Samoilov's hip joint. To say that I was afraid is an understatement. This is a business man. On the 4th day I left with crutches already...
Tatyana
I am grateful to Yury Anatolyevich Aksyonov for the operation to strengthen the spine. Kind, caring and knowledgeable doctor. Everything will be told and explained. Very...
Tatyana
All the time I turn to clinic No. 1 in Lyublino, I live nearby. Many thanks to the doctor Ostanina Alla Anatolyevna for sensitivity, responsiveness, professionalism! I got sick...
Ekaterina
I want to express my gratitude to the doctor of functional diagnostics (ultrasound) - Maslova Alla Nikolaevna. A very attentive and knowledgeable professional. Passed ultrasound of organs ...
Sergey Leonidovich
I would like to express my gratitude to Kanevsky Timofey Valerievich. This is not just a doctor, but really a specialist in his hard work! There was an operation on...
This is not just a doctor, but really a specialist in his hard work! There was an operation on...
Olga Evgenievna
I did in the Gastro clinic and colonoscopy under anesthesia. Doctor: A.G. Korolkov, nurse: S.E. Konovalova A big human “THANK YOU”. Everything is tactful and...
Alina
I liked everything in the clinic!
Svetlana
I liked the appointment with cosmetologist Anastasia Kurbatova very much.0005
Svetlana
I liked the appointment with cosmetologist Anastasia Kurbatova very much. October 23, 2018 - surgery: hip arthroplasty. Oct 25 - First steps with a walker. Oct 28 - walking with two French...
Many thanks to the doctor Ostanina Alla Anatolyevna for sensitivity, responsiveness, professionalism! And Saving the life and health of the patient. I wish your clinic and...
Lyudmila Grigorievna
I would like to express my deep gratitude to all the staff of the clinic, and especially to the chiropractor Dmitry Veniaminovich Kotlyarov for the treatment. I designed a medical book and did not stop being surprised at how competently the work was organized. No...
I designed a medical book and did not stop being surprised at how competently the work was organized. No...
Symptoms of scleroderma
Typical manifestations of systemic scleroderma are spasm of small vessels of the circulatory system on the extremities (Raynaud's phenomenon) and sclerosis of the skin on the arms, legs, head and sometimes on the upper body. The manifestations of the disease will depend on the stage of its development and severity. As a result of the disease, normal tissue is replaced by coarse connective tissue fibers, which reduce the elasticity of organs, extensibility, disrupting their functionality. nine0005
In addition to the main symptoms, other signs of the disease may appear, depending on which internal organs are affected.
In more than 90% of those affected, systemic scleroderma first manifests itself in the so-called Raynaud's phenomenon. Some authors in these cases speak of prescleroderma. When Raynaud's attack occurs, a sudden spasm of the small arteries of the hands, and less often - the legs, which prevents blood filling and leads to tissue ischemia and skin pallor. Within minutes, the fingers become white, cold, and numb and look "dead". You can usually see a clear dividing line between the physiological coloration of the hand and white fingers. Due to the lack of oxygen, carboxyhemoglobin begins to accumulate in the fingers, which turns the skin blue. nine0005
Within minutes, the fingers become white, cold, and numb and look "dead". You can usually see a clear dividing line between the physiological coloration of the hand and white fingers. Due to the lack of oxygen, carboxyhemoglobin begins to accumulate in the fingers, which turns the skin blue. nine0005
Finally, when the vascular muscles relax, more blood than usual enters the vessels, they overflow, and the fingers or toes become intensely red. Because of the typical sequence of color changes (white, blue, red), many compare this tricolor to the tricolor of the French flag. Raynaud's individual attacks can be triggered by low outdoor temperatures, cold water work, and emotional stress. In addition to discoloration, patients will complain of tingling in the fingers, their numbness. nine0005
Raynaud's phenomenon sometimes appears long (months and even years) before the development of skin changes. It can also occur in the context of other diseases and even without apparent causes. Some experts believe that spasm of the vessels of the fingers, nose, and ears occurs in every tenth inhabitant of the planet, and only 5% of them have connective tissue damage. In general, systemic scleroderma should be ruled out first when a patient reports a tricolor vascular attack.
In general, systemic scleroderma should be ruled out first when a patient reports a tricolor vascular attack.
How does systemic scleroderma affect the skin? nine0007
When vasospasms are repeated over a long period of time, the ends of the fingers eventually become permanently swollen and the skin becomes inflamed. Similarly, the toes and lower legs may be affected. This is the first stage of the disease.
In general, the change in the dermis goes through three successive stages:
- Edema stage. Mediators dilate blood vessels, fluid effusion occurs and edema forms, as a result, the fingers become pasty and swollen. The patient hardly squeezes his fingers into a fist, with pressure on the skin, swelling occurs. The color of the fingers or the entire hand changes color and becomes purple or fiery red. There may be complaints of itching. nine0010
- Stage of sclerosis. Over time (after a few weeks), the skin tightens, becomes hard and thickened. There are phenomena of sclerodactyly - the skin on the fingers looks waxy smooth and pale.
 The fingers are cold to the touch.
The fingers are cold to the touch. - Atrophy. In severe cases, atrophy of the dermis and underlying layers develops. This is the last stage of the disease. The skin becomes thinner, like parchment, dry to the touch. The terminal phalanges look pointed (the so-called "fingers of the Madonna"). Atrophy is so pronounced that the skin almost envelops the skeleton (legs and arms look like sticks). nine0010
The patient is characterized by the following complaints:
- fine motor skills are lost, it may be difficult or even impossible to button a shirt or blouse;
- Ulcerations appear on the fingers ("rat-bite symptom"), the wounds are very painful, become deeper and more extensive, and can cause suffering without treatment from several months to several years;
- are periodically formed in the skin or in the subcutaneous adipose tissue of the extremities of limestone accumulations (calcinosis cutis), which spontaneously open and ulcerate, causing the patient torment; nine0010
- spider veins appear on the skin - telangiectasias;
- thickening of the skin can limit joint mobility as flexion contractures occur and the fingers are forced into a flexed position
Facial changes
With systemic scleroderma, the skin becomes hard not only on the extremities, but also on the face. Small wrinkles formed in the course of life gradually disappear. The person looks strangely young, the face becomes amimic, he has difficulty expressing his emotions. The slits of the eyes become narrow, the face resembles a mask. The tip of the nose is pointed and may ulcerate. The patient cannot open his mouth in the same way as before (microstomia), it is difficult for him to eat and brush his teeth, it is difficult for him to stick out his tongue and smile. Even the frenulum of the tongue shortens and thickens. Thickening of the skin on the upper body can make breathing difficult. On contact with the skin, there is a sensation of stiffness. nine0005
Small wrinkles formed in the course of life gradually disappear. The person looks strangely young, the face becomes amimic, he has difficulty expressing his emotions. The slits of the eyes become narrow, the face resembles a mask. The tip of the nose is pointed and may ulcerate. The patient cannot open his mouth in the same way as before (microstomia), it is difficult for him to eat and brush his teeth, it is difficult for him to stick out his tongue and smile. Even the frenulum of the tongue shortens and thickens. Thickening of the skin on the upper body can make breathing difficult. On contact with the skin, there is a sensation of stiffness. nine0005
How does SJS affect the digestive system?
Of all the internal organs, the esophagus is the most commonly affected by systemic scleroderma: in more than 60 percent of patients, the esophagus hardens, expands and becomes immobile. Because the muscles of the esophagus are no longer able to move chewed foods to the stomach, sufferers usually suffer from difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
There are also changes in the oral cavity - it shrinks and becomes dry.
The sphincter muscle between the esophagus and stomach becomes atonic and no longer functions properly. As a result, the acidic contents of the stomach can flow into the esophagus. Gastroesophageal reflux, also called reflux disease, occurs. Ulcers appear in the lower part of the esophagus. nine0005
Like the esophagus, the connective tissue in the stomach can harden. Because the stomach wall is then unable to stretch and move enough, this often causes gastric bloating, aerophagia, or nausea after eating. Corresponding changes in the intestines can lead to both constipation and diarrhea. Fecal incontinence may develop. If nutrients through the thickened intestinal wall can no longer be fully absorbed into the bloodstream, unwanted weight loss results. nine0005
How does SJS affect the lungs?
In 80% of patients with scleroderma, lung tissue is involved in the process. Usually, the layer of connective tissue that is located between the air-filled alveoli and the blood vessels of the lungs is very thin so that oxygen molecules can enter the blood through diffusion. When systemic scleroderma accumulates connective tissue fibers (pulmonary fibrosis), the lung tissue becomes stiffer and thicker, and the ability to diffuse is reduced. oxygen saturation drops. The result of impaired gas exchange is shortness of breath, especially during exercise and coughing. nine0005
When systemic scleroderma accumulates connective tissue fibers (pulmonary fibrosis), the lung tissue becomes stiffer and thicker, and the ability to diffuse is reduced. oxygen saturation drops. The result of impaired gas exchange is shortness of breath, especially during exercise and coughing. nine0005
Pathological changes in the lung connective tissue can lead to high blood pressure in the lungs. Pulmonary arterial hypertension provokes a load on the right ventricle of the heart. Physical performance declines as pneumosclerosis progresses, with patients suffering from shortness of breath or even dizziness as soon as they make a small effort.
How does systemic scleroderma affect the heart?
High pressure in the arteries of the lungs stresses the muscles of the right ventricle. In the long term, this direct cardiac stress can lead to weakness of the right ventricle (right heart failure). nine0005
In addition, in the process of systemic scleroderma, collagen fibers increase in all areas of the heart muscle (myocardium) - not only in the right ventricle, but also in the left ventricle and in two atria. Myocardial fibrosis develops. Since the heart muscle is under severe stress, heart failure occurs. Sometimes a heart defect is formed.
Myocardial fibrosis develops. Since the heart muscle is under severe stress, heart failure occurs. Sometimes a heart defect is formed.
In addition to heart failure, the deposition of collagen fibers in the heart muscle can cause various types of cardiac arrhythmias. The reconstructed areas of the connective tissue conduct electrical current much worse than a healthy heart muscle and prevent the propagation of electrical impulses in the heart. Damage to the heart is manifested by pain behind the sternum, sudden palpitations, arrhythmia, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, shortness of breath with little physical effort. nine0005
How does SJS affect the kidneys?
If the disease affects the blood vessels in the kidneys, kidney function deteriorates (renal failure occurs): water and mineral salts, as well as metabolic products of the body such as creatinine and urea, accumulate in the body and blood pressure rises. Victims complain of headaches, malaise and accumulation of fluid (edema) in the lower extremities. Chronic renal failure develops with ascites, with impaired consciousness. Sclerosis of the renal vessels can lead to acute nephropathy, which can be fatal. nine0005
Chronic renal failure develops with ascites, with impaired consciousness. Sclerosis of the renal vessels can lead to acute nephropathy, which can be fatal. nine0005
How does systemic scleroderma affect the musculoskeletal system?
Systemic scleroderma sometimes causes inflammation of the tendon sheaths (tenosynovitis), joints (arthritis) of the fingers, or skeletal muscles (myositis). With myositis, the affected muscles hurt, and their strength decreases. Contractures appear that disrupt the function of the joints and limit their mobility. The deformation of the hand with bent fingers makes it look like a bird's foot.
How does the disease progress and does it depend on the type of SJS? nine0303
The disease is classified into four forms according to the nature of skin changes and the degree of involvement of the organ during the course of the disease
- Limited
In the case of localized systemic scleroderma, hardening of the skin on the hands, feet and face is limited. The first sign of the disease is usually an episodic circulatory disorder of the fingers or toes (Raynaud's phenomenon). After Raynaud's first attack, it usually takes several years for the disease to become visible—the skin becomes visibly thick. Then the disease continues to slowly progress: the internal organs are often affected only after years or even decades. This form includes the so-called CREST syndrome (obsolete name). CREST - syndrome is an abbreviation in English, the initial letters of the list of the most common symptoms of scleroderma
The first sign of the disease is usually an episodic circulatory disorder of the fingers or toes (Raynaud's phenomenon). After Raynaud's first attack, it usually takes several years for the disease to become visible—the skin becomes visibly thick. Then the disease continues to slowly progress: the internal organs are often affected only after years or even decades. This form includes the so-called CREST syndrome (obsolete name). CREST - syndrome is an abbreviation in English, the initial letters of the list of the most common symptoms of scleroderma
C- Cutis calcinosis - dense calcifications under the skin in the form of calcium salts, they periodically open up, forming ulcers that become the gates of infection.
R-Raynaud - Raynaud's phenomenon due to sudden spasm of small vessels under the influence of a cold agent.
E - Esophageal dysmotility - inflammation of the esophagus due to damage to smooth muscles, impaired motility with symptoms of dysphagia and heartburn
S - Sklerodaktylie - thickening of the skin of the fingers, swelling of the hand; nine0005
T - Teleangiektasien - dilated capillaries in the form of stars, especially in the face
Skin changes can visually look
- in the form of formation of pink plaques (most often) slightly rising above the level of the skin, they have a rounded shape, are arranged as symmetrically, and asymmetrically; on plaques localized in the scalp area - hair does not grow;
- in the form of the appearance of long stripes (linear form) of brown or yellowish color, "ribbons" are soldered areas of the epidermis, dermis and muscle tissue, several centimeters long, they can be single, usually located on the legs, arms, head and face and resemble the scars that appear from a saber strike; nine0010
- in the form of white spots of various shapes, which can merge and reach up to 15 cm in diameter, the skin in these areas is thin, dry, with an abundance of folds.
Localized scleroderma is considered benign in course, the prognosis is favorable.
- Diffuse
Diffuse systemic scleroderma develops symptoms much faster: after the first Raynaud's attack, less than a year passes before the first hardening of the skin is felt. They occur in reverse order from the limited form, first affecting the upper body, then the face, and finally the arms and legs. The internal organs are often affected several years after the onset of the disease. nine0005
- Undifferentiated
Patients with the undifferentiated form suffer from Raynaud's attacks, persistently swollen fingers, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. This form of the disease may not have the roughening of the skin that is typical of other types of SJS. Scleroderma without scleroderma - a rare form (about 2% of cases)
- Crossed forms of scleroderma.
Cross-forms ("overlap" in English) - when typical signs of systemic scleroderma are combined with symptoms of another autoimmune disease.