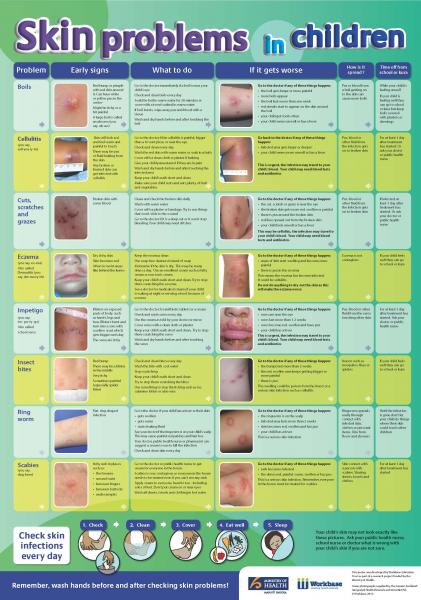
Rash types in children
Skin rashes in children - Injuries & first aid
Childhood rashes are common and aren't usually a cause for concern. Most rashes are harmless and disappear without the need for treatment.
However, see your GP if your child has a rash and seems unwell, or if you're worried. They'll be able to investigate the cause and recommend any necessary treatment.
This page may give you a better idea about what could be causing the rash, but don't use this to self-diagnose your child's condition – always see a GP for a proper diagnosis.
The most common causes of rashes in children are:
- cellulitis
- chickenpox
- eczema
- erythema multiforme
- hand, foot and mouth disease
- impetigo
- keratosis pilaris ("chicken skin")
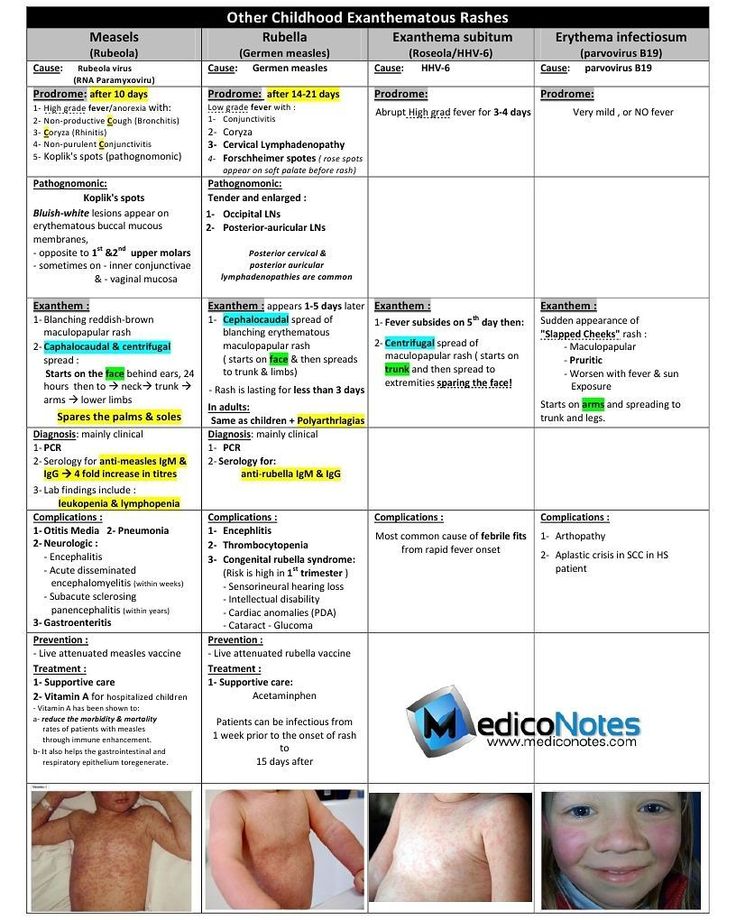
- measles
- molluscum contagiosum
- pityriasis rosea
- prickly heat
- psoriasis
- ringworm
- scabies
- scarlet fever
- slapped cheek syndrome
- urticaria (hives)
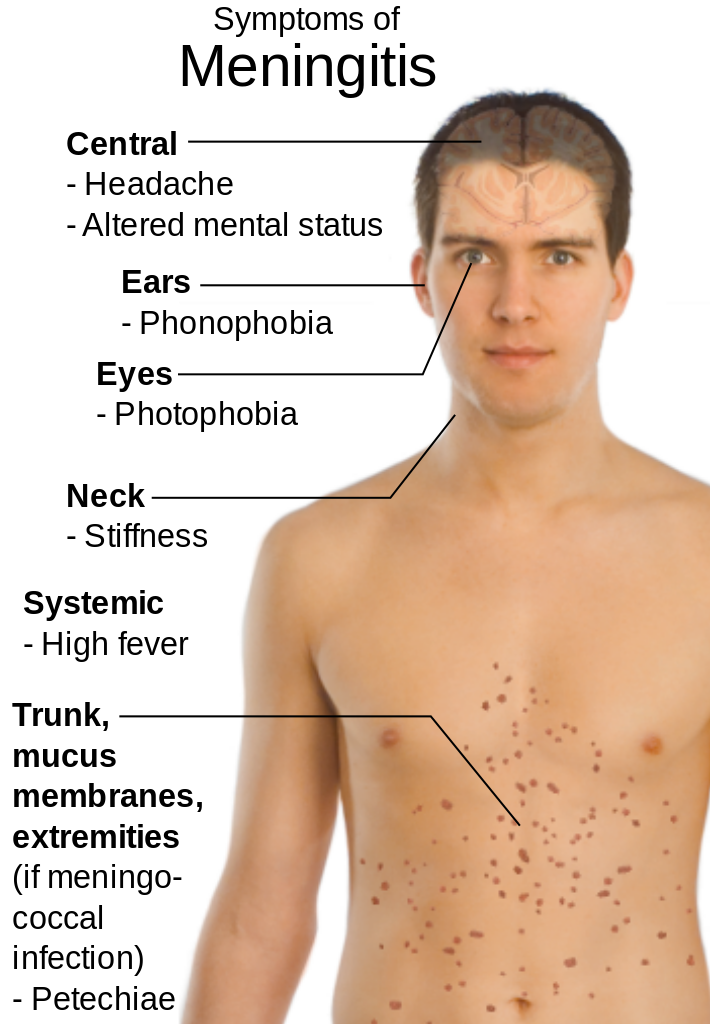
Although meningitis has become less common over recent years, it's important to be aware of the rash and the other signs and symptoms of meningitis.
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is an infection of the deeper layers of skin and underlying tissue. The affected area will be red, painful, swollen and hot. It often affects the legs, but can occur anywhere on the body. Your child will probably also have a fever.
See your GP immediately if an area of your child's skin suddenly turns red, hot and tender. If you can't see your GP on the same day, go to a walk-in centre or minor injuries unit.
Cellulitis can usually be diagnosed by assessing the symptoms and examining the skin. It usually responds well to treatment with antibiotics.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox is a viral illness that most children catch at some point. It most commonly affects children under 10 years of age.
A rash of itchy spots turns into fluid-filled blisters. They crust over to form scabs, which after a while drop off. Some children only have a few spots, whereas others have them over their entire body. The spots are most likely to appear on the face, ears and scalp, under the arms, on the chest and belly, and on the arms and legs.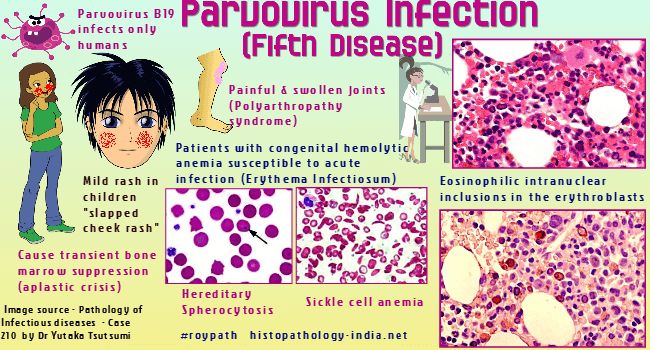
There's no specific treatment for chickenpox, but you can take steps to relieve the symptoms. For example, paracetamol can help relieve fever (don't give aspirin to children under 16), and calamine lotion and cooling gels can be used to ease itching.
Read more about treating chickenpox.
Eczema
Eczema is a long-term condition that causes the skin to become itchy, red, dry and cracked. The most common type is atopic eczema, which mainly affects children but can continue into adulthood.
Atopic eczema commonly develops behind the knees or on the elbows, neck, eyes and ears. It isn't a serious condition, but if your child later becomes infected with the herpes simplex virus, it can cause the eczema to flare up into an outbreak of tiny blisters called eczema herpeticum, and will cause a fever.
About one in five children in the UK has eczema, and in eight out 10 cases it develops before the age of five, often before a child's first birthday.
Read about treating atopic eczema.
Erythema multiforme
Erythema multiforme is a skin rash (usually mild) that's caused by an allergic reaction to the herpes simplex virus.
The spots look like targets, with a dark red centre and paler ring around the outside. The hands or feet tend to be affected first, followed by the limbs, upper body and face.
Your child will probably feel unwell and may have a fever, which you should be able to treat with over-the-counter medicine. It may take from two to six weeks before they feel better. See your GP if your child has a rash and seems unwell.
In rare cases, erythema multiforme can be triggered by a reaction to certain medications, such as an antibiotic or anticonvulsant. This more severe form is called Stevens-Johnson syndrome and it can be life-threatening.
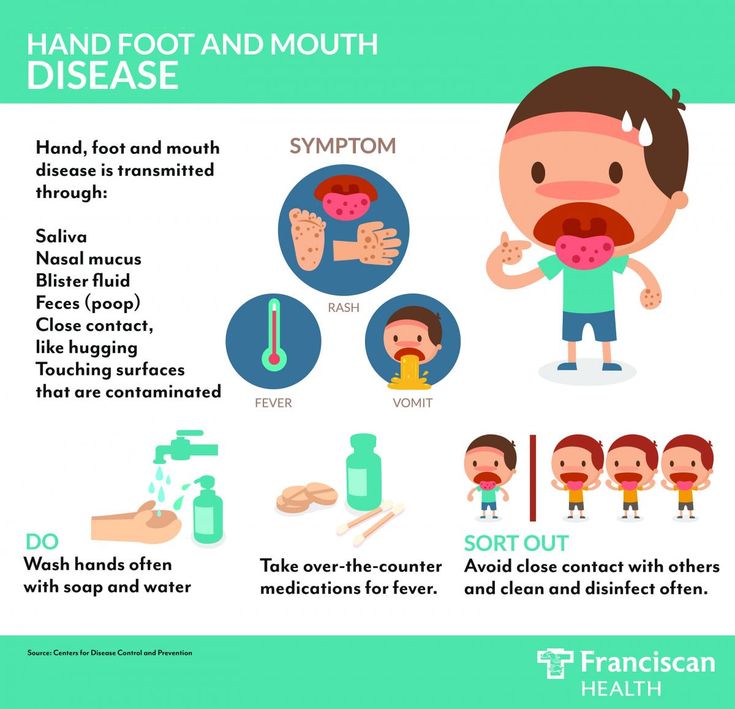
Hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease is a common, contagious infection that causes mouth ulcers and spots and blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
It's most common in young children (particularly those under 10), but it can also affect older children and adults.
There's no cure for hand, foot and mouth disease and it's easily spread, so you should keep your child away from school or nursery until they're better. Your child's immune system will fight the virus and it should clear up after about seven to 10 days.
Make sure your child drinks plenty of fluid, and if eating and swallowing is uncomfortable, give them soft foods, such as mashed potatoes, yoghurt and soup.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a common and highly contagious skin infection that causes sores and blisters. It isn't usually serious and often improves within a week of treatment. There are two types of impetigo called non-bullous and bullous.
Non-bullous impetigo typically affects the skin around the nose and mouth, causing sores that quickly burst to leave a yellow-brown crust.
Bullous impetigo typically affects the trunk (the area of the body between the waist and neck), and causes fluid-filled blisters that burst after a few days to leave a yellow crust.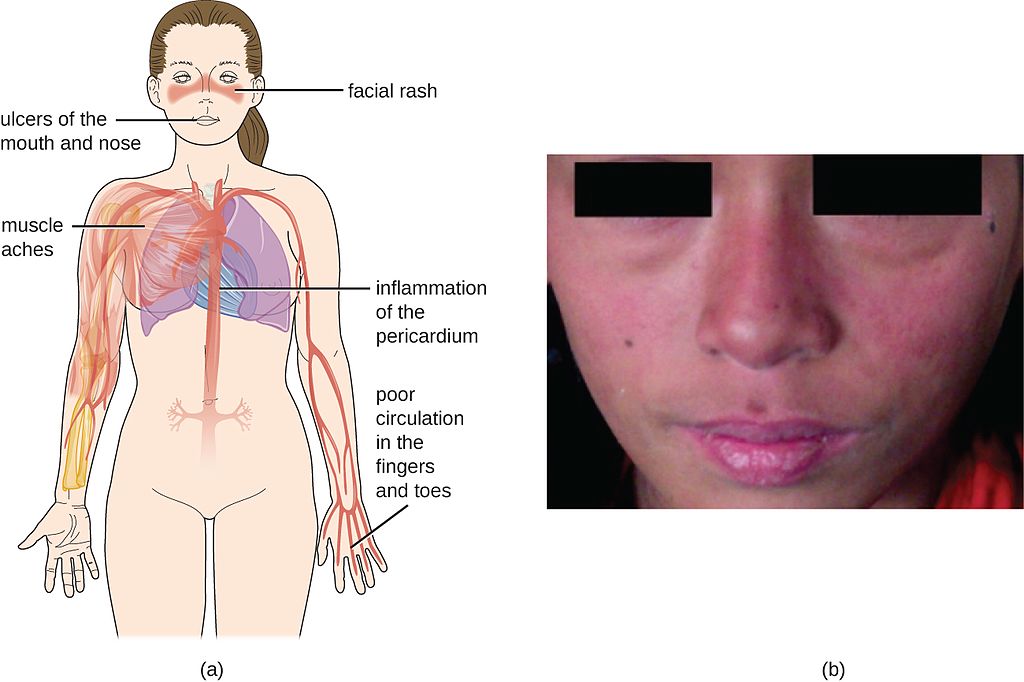
See your GP or pharmacist if you think your child has impetigo. Antibiotics, in the form of a cream or tablets, will be prescribed. This should reduce the length of the illness to around seven to 10 days.
Keratosis pilaris ("chicken skin")
Keratosis pilaris is a common and harmless skin condition. The skin on the back of the upper arms becomes rough and bumpy, as if covered in permanent goose pimples. Sometimes, the buttocks, thighs, forearms and upper back can also be affected.
Keratosis pilaris typically begins in childhood and gets worse during puberty. Some people find it improves after this and may even disappear in adulthood.
There's no cure for keratosis pilaris, and it often gets better on its own without treatment. However, there are some measures you can take that may improve your child's rash, such as using non-soap cleansers rather than soap, and an emollient to moisturise their skin. Your GP or pharmacist will be able to recommend a suitable cream.
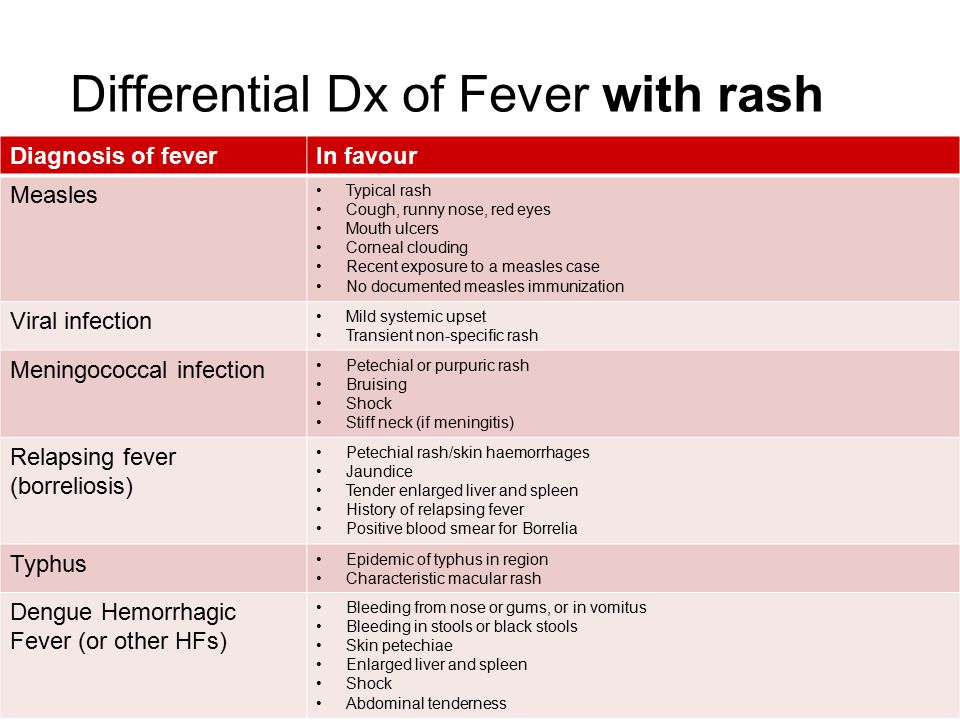
Measles
Measles is a highly infectious illness that most commonly affects young children. It's now rare in the UK because of the effectiveness of the measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
The measles rash is red-brown blotches. It usually starts on the head or upper neck and then spreads outwards to the rest of the body. Your child may also have a fever and cold-like symptoms.
Call your GP surgery immediately if you think your child has measles. It's best to phone before visiting because the surgery may need to make arrangements to reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others.
Measles usually passes in about seven to 10 days without causing further problems. Paracetamol or ibuprofen can be used to relieve fever, aches and pains (don't give aspirin to children under 16). Also, make sure your child drinks plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
Read more about treating measles.
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes clusters of small, firm, raised spots to develop on the skin.
It commonly affects young children aged one to five years, who tend to catch it after close physical contact with another infected child.
The condition is usually painless, although some children may experience some itchiness. It usually goes away within 18 months without the need for treatment.
Molluscum contagiosum is highly infectious. However, most adults are resistant to the virus, which means they're unlikely to catch it if they come into contact with it.
Pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis rosea is a relatively common skin condition that causes a temporary rash of raised, red scaly patches to develop on the body. Most cases occur in older children and young adults (aged between 10 and 35).
The rash can be very itchy. In most cases, it clears up without treatment in 2 to 12 weeks, although in rare cases it can last up to five months.
Emollients, steroid creams and antihistamines can be used to help relieve the itchiness. The rash doesn't usually leave scars, although the skin can sometimes be discoloured afterwards.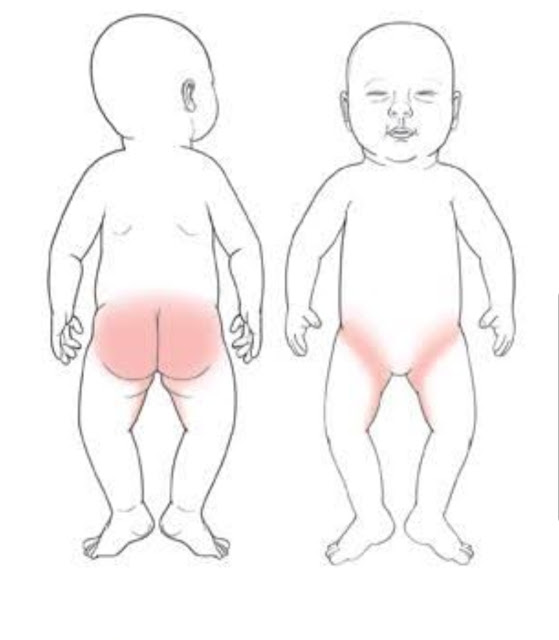
Prickly heat (heat rash)
Prickly heat (heat rash), also known as miliaria, is an itchy rash of small, raised red spots that causes a stinging or prickly sensation on the skin.
It occurs when the sweat ducts in the outer layer of skin (epidermis) are obstructed. You can get a heat rash anywhere on your body, but the face, neck, back, chest or thighs are most often affected.
Infants can sometimes get a prickly heat rash if they sweat more than usual – for example, when it's hot and humid or if they're overdressed. It isn't a serious condition and rarely requires any specific treatment.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting (chronic) skin condition that causes red, flaky, crusty patches of skin covered with silvery scales.
The severity of psoriasis varies greatly from person to person. For some people, it's just a minor irritation, but for others it can have a major impact on their quality of life.
There's no cure for psoriasis, but there are a number of treatments that can help improve the symptoms and appearance of skin patches. For example, topical corticosteroids are creams and ointments that can be applied to the skin.
For example, topical corticosteroids are creams and ointments that can be applied to the skin.
Ringworm
Ringworm is a highly infectious fungal skin infection that causes a ring-like red or silvery patch on the skin that can be scaly, inflamed or itchy.
Ringworm often affects the arms and legs, but it can appear almost anywhere on the body. Other similar fungal infections can affect the scalp, feet, groin and nails.
Ringworm can usually be easily treated with antifungal medicines, which are available from a pharmacy. Ringworm of the scalp can cause scaling and patches of hair loss. It's treated with antifungal tablets, often combined with antifungal shampoo.
Scabies
Scabies is a contagious skin condition that's intensely itchy. It's caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin.
In children, scabies is usually spread through prolonged periods of skin-to-skin contact with an infected adult or child – for example, during play fighting or hugging.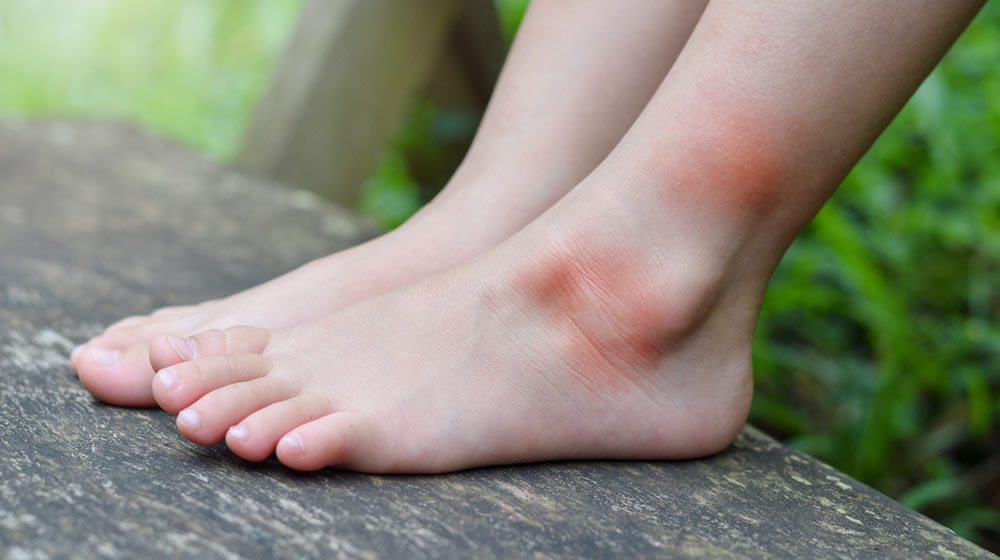
The mites like warm places, such as skin folds, between the fingers, under fingernails, or around the buttock creases. They leave small red blotches, which are often found on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet. In infants, blisters are commonly found on the soles of the feet.
See your GP if you think your child has scabies. It's not usually a serious condition, but it does need to be treated. Your GP will prescribe a lotion or cream. Read more about treating scabies.
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is a highly contagious bacterial infection that usually affects children between two and eight years of age. It causes a distinctive pink-red rash, which feels like sandpaper to touch and may be itchy.
It often starts with a sore throat, fever and headache, with the rash developing two to five days after infection. The rash usually occurs on the chest and stomach before spreading to other areas of the body, such as the ears and neck.
Scarlet fever usually clears up after about a week, but see your GP if you think your child may have it.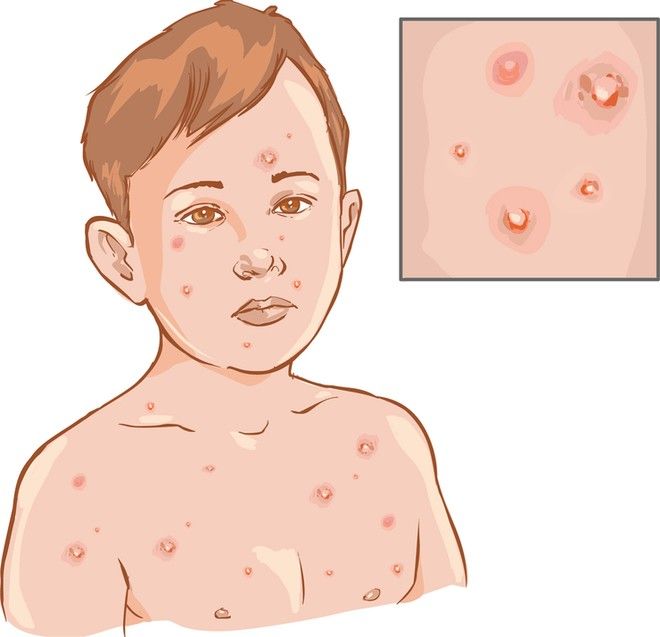 Antibiotics are used to treat it (liquid antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin, are often used to treat children).
Antibiotics are used to treat it (liquid antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin, are often used to treat children).
Slapped cheek syndrome
Slapped cheek syndrome – also known as fifth disease or parvovirus B19 – is a viral infection that's common in children aged six to 10.
It causes a distinctive bright red rash to develop on both cheeks. This can look alarming, but it usually clears up by itself in one to three weeks.
Unless your child is feeling unwell, they don't need to stay away from school. Once the rash appears, the infection is no longer contagious. However, it's a good idea to notify your child's school about the infection.
Urticaria (hives)
Urticaria – also known as hives, weals, welts or nettle rash – is a raised, itchy rash that can affect one part of the body or be spread across large areas. It's a common skin reaction that often affects children.
Urticaria occurs when a trigger causes high levels of histamine and other chemical messengers to be released in the skin.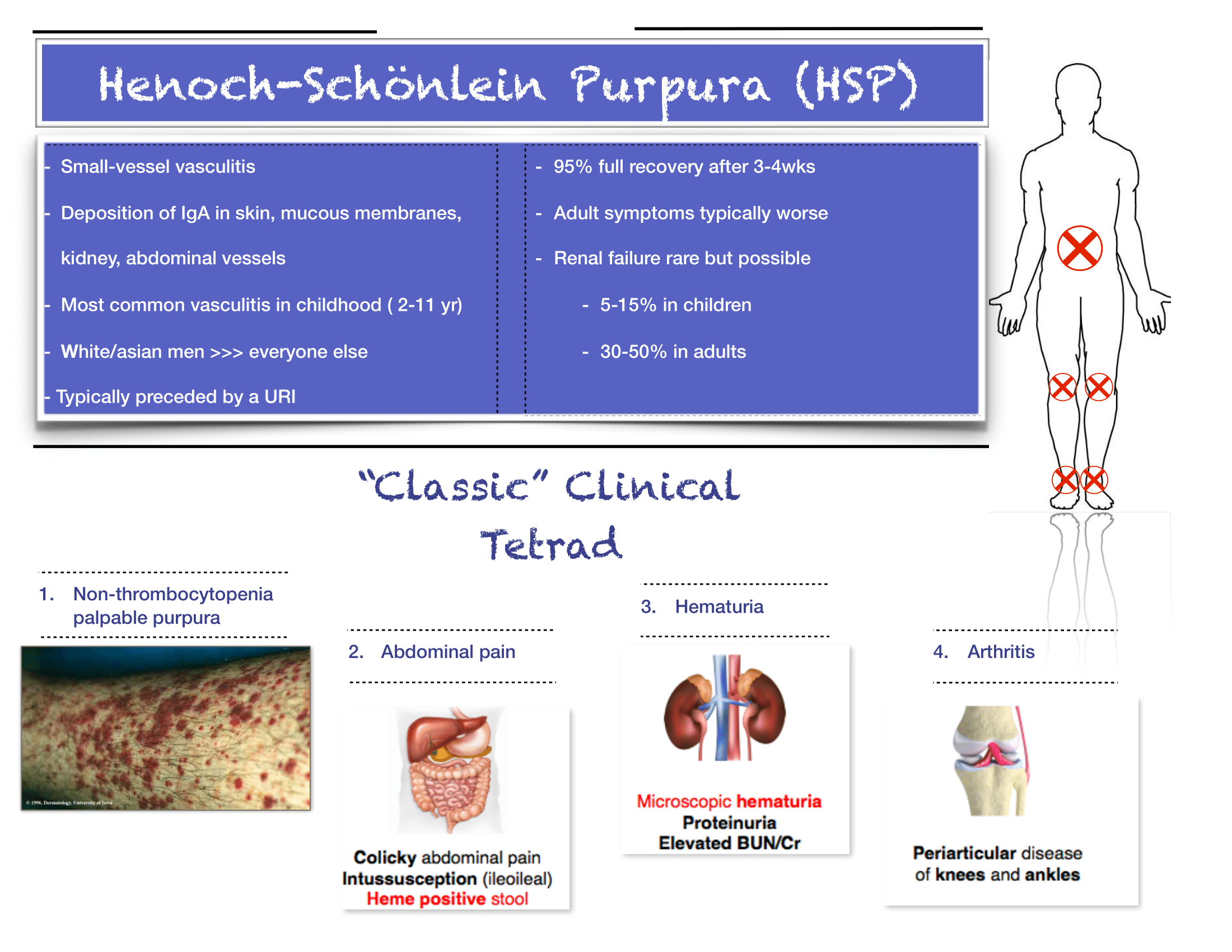 These substances cause the blood vessels in the skin to open up, resulting in redness or pinkness, and swelling and itchiness.
These substances cause the blood vessels in the skin to open up, resulting in redness or pinkness, and swelling and itchiness.
There are many possible triggers of urticaria, including allergens, such as food or latex, irritants, such as nettles, medicines, and physical factors, such as heat or exercise. Sometimes, a cause can't be identified.
The rash is usually short-lived and mild, and can often be controlled with antihistamines.
12 Common Summertime Skin Rashes in Children
Sunny days and starlit evenings spent playing, splashing, and exploring can leave kids with more than warm summertime memories. Balmy weather also can lead to itchy, irritated skin.
Check out the list from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) to see how you can help prevent, identify, and soothe these common summertime skin rashes.
1. Heat Rash
Heat rash (also known as prickly heat or miliaria) is seen most often in babies and young children when sweat gland pores become blocked and perspiration can't escape. The rash looks like patches of small pink or red bumps or blisters under clothing or spots where skin tends to fold—on the neck, elbows, armpits, or thighs—although heat rash can occur on other covered areas.
The rash looks like patches of small pink or red bumps or blisters under clothing or spots where skin tends to fold—on the neck, elbows, armpits, or thighs—although heat rash can occur on other covered areas.
What parents can do:
Keep kids cool. Dress your child in clothing that keeps the skin cool and dry. If possible, use fans and air conditioning to avoid overheating.
Pay attention to hot spots. Wash areas of the skin that stay wet with sweat, urine, or drool with cool water. Pat them dry.
Keep skin bare. Leave areas open to air without clothing. Do not apply skin ointments.
2. Poison Ivy & Other Plant Rashes
Many children get a burning, intensely itchy rash where their skin touches plants—such as poison ivy, poison oak, sumac—containing a sticky oil called urushiol. An allergic skin reaction causes redness, swelling and blisters. Other plants—such as wild parsnip, giant hogweed, and citrus—contain chemicals that make skin hypersensitive to sunlight and cause a phytophotodermatitis rash.
What parents can do:
Prevent exposure. Teach your child what these plants look like and how to avoid them. Both poison ivy and poison oak have shiny green leaves that grow three to a stem, so you might share the rhyme: "Leaves of three, let them be." The sumac shrub has stems that contain 7-13 leaves arranged in pairs, while wild parsnip and giant hogweed have clusters of small, flat-topped yellow and white flowers. If you have younger children, inspect the parks they play in and have rash-causing plants removed.
Wash and trim. If your child comes into contact with these plants, wash all of his or her clothes and shoes in soap and water. Also, wash the area of the skin that was exposed with soap and water for at least 10 minutes after the plant or the oil is touched. To discourage scratching and further damage to the skin, keep your child's fingernails trimmed. This will also prevent the rash from spreading if there is still a small amount of oil under the fingernails.
Soothing salves. If the rash is mild, apply calamine lotion to cut down on the itching. Avoid ointments containing anesthetics or antihistamines—they can cause allergic reactions themselves. Another good option to reduce skin inflammation is 1% hydrocortisone cream.
Talk with your pediatrician. While mild cases can be treated at home, talk with your pediatrician if your child is especially uncomfortable, the rash is severe and/or isn't going away, if the rash is on your child's face or groin area, or if you notice signs of infection (i.e., fever, redness, swelling beyond the poison ivy or oak lesions).
3. Eczema
Eczema (also called atopic dermatitis or AD) is a chronic condition common in children that causes patches of dry, scaly red skin and tends to flare up during colder months when there's less moisture in the air. But dryness caused by air conditioning and pressurized planes during summer travel can cause problems, too. Overheating, sweating and chlorine in swimming pools also can trigger eczema.
Overheating, sweating and chlorine in swimming pools also can trigger eczema.
What parents can do:
Moisturize. Apply fragrance-free creams or ointments at least once a day or more often if needed. After a bath or swimming, gently pat your child's skin with a towel and then apply moisturizer to his or her damp skin.
Dress wisely. Choose clothing made of soft, breathable fabrics like cotton when possible. Wash clothes in a detergent free of irritants such as perfumes and dyes.
Don't scratch. Keep your child's fingernails short and smooth, and remind him or her not to scratch. Scratching can make the rash worse and lead to infection.
Talk with your pediatrician. Ask your child's pediatrician if allergies, sometimes triggered by trees and plants that bloom during summer, could be a cause of the eczema. Your child's pediatrician may recommend medicines to help your child feel better and to keep the symptoms of eczema under control.

4. Insect Bites & Stings
Insects such as bees, wasps, mosquitos, fire ants, and ticks can cause itching and minor discomfort where they prick the skin. For some children, insect bites and stings can cause a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis—which includes a rash or hives and life-threatening symptoms such as airway swelling. (For children with a known allergy to insect bites and stings, it is important to have anaphylaxis emergency care plan in place). Other times, diseases spread by insects such as Lyme Disease, Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, and Zika Virus can cause rashes and other health problems.
What parents can do:
Avoidance. When spending time outdoors, avoid scented soaps and shampoos and brightly colored clothing—they can attract insects. If possible, steer clear of areas where insects nest and gather (i.e., stagnant pools of water, uncovered food, and blooming flowers).
Use insect repellent. Products with DEET can be used on the skin, but look for family-friendly products that contain concentrations of no more than 30% DEET. Wash the insect repellent off with soap and water when your child returns indoors.
Cover up. When in wooded areas or in or near tall grass, stay on cleared trails as much as possible. Have your child wear a long-sleeved shirt, pants, and hat. Avoid wearing sandals in an area where ticks may live.
Look closely. Wear light-colored clothing to make it easier to spot ticks. After coming indoors, check for ticks on your child's skin—they often hide behind the ears or along the hairline.
Remove stingers and ticks. To remove a visible stinger from skin, gently scrape it off horizontally with a credit card or your fingernail. If you find a tick, gently grasp it with fine-tipped tweezers as close to the skin as possible.
 Without squeezing the tick's body, slowly pull it away from the skin. See How To Remove A Tick for more information.
Without squeezing the tick's body, slowly pull it away from the skin. See How To Remove A Tick for more information. Clean the skin. After the stinger or tick is out, clean the bitten area with rubbing alcohol or other first aid ointment.
Treat swelling. Apply a cold compress or an ice pack to any swelling for at least 10 minutes.
Help relieve the itch. Applying ice, along with calamine lotion or 1% hydrocortisone cream, can also help relieve itching.
5. Impetigo
Impetigo is a bacterial skin infection that's more common during hot, humid weather. It causes a rash that may have fluid-filled blisters or an oozing rash covered by crusted yellow scabs. Impetigo is more likely to develop where there is a break in the skin, like around insect bites.
What parents can do:
Clean and cover. Clean the infected area with soap and water.
 Cover the infected area loosely to help prevent contact that would spread the infection to others or to other parts of the body. Wash your own hands well after treating your child's sores.
Cover the infected area loosely to help prevent contact that would spread the infection to others or to other parts of the body. Wash your own hands well after treating your child's sores. Avoid scratching. Trim your child's fingernails and discourage scratching. A child can spread the infection to other parts of his or her body by scratching. You can cover the rash loosely with a bandage to discourage your child from touching the rash, but make sure air can flow through so the skin can heal.
Talk with your pediatrician. While mild cases may respond to over-the-counter antibiotics such as bacitracin or bacitracin-polymyxin, impetigo is usually treated with prescription antibiotics—either a skin cream or oral medication. Your pediatrician may order a skin culture (test of your child's skin) to determine which bacteria are causing the rash.
6. Swimmer's Itch
Swimmer's itch (also called clam digger's itch or cercarial dermatitis) may appear after playing in lakes, oceans, and other bodies of water. The rash is caused by microscopic parasites found in shallow, warmer water near the shoreline where children tend to stay. The parasites burrow into skin, and cause tiny reddish, raised spots on skin not covered by the swimsuit to appear. Welts and blisters may also form.
The rash is caused by microscopic parasites found in shallow, warmer water near the shoreline where children tend to stay. The parasites burrow into skin, and cause tiny reddish, raised spots on skin not covered by the swimsuit to appear. Welts and blisters may also form.
What parents can do:
Be aware. Don't swim near or wade in marshy areas where snails are commonly found. Try not to attract birds (by feeding them, for example) where your family swims. Birds may eat the snails and spread the parasites in the water.
Shower or towel dry. Shower or briskly rub the skin with a towel immediately after getting out of the water. The parasites start to burrow when the water on skin begins evaporating. If your skin child's skin stings with rubbing—and the rash appears under the swimsuit—he or she may instead have Seabather's Eruption from stinging larvae of sea critters such as jellyfish or sea anemone. Stop rubbing and shower instead.
Don't scratch. Trim your child's fingernails and discourage scratching. Home treatments such cool compresses on the affected areas, Epsom salt or oatmeal baths, or baking soda paste may help to relieve the discomfort. If itching is severe, talk with your child's pediatrician. He or she may suggest prescription-strength lotions or creams to reduce your child's symptoms.
7. Cutaneous Larva Migrans (Sandworms)
Sandworms may be present in sand contaminated with feces from pets or stray animals. When a child stands or sits in contaminated sand on a beach or in a sandbox, the worms may burrow under the skin, usually around the feet or buttocks. Lines of itchy, reddish rash known as a creeping eruption appear as the worms move under the skin, up to a few centimeters a day. The condition is more common subtropical and tropical areas such as the Caribbean, as well as parts of the southwestern United States.
What parents can do:
Keep shoes on.
 Don't let your child play on beaches where people walk their dogs. If your family goes on an outing to a designated pet-friendly beach, make sure your child keeps shoes on and doesn't sit in the sand without a blanket or towel.
Don't let your child play on beaches where people walk their dogs. If your family goes on an outing to a designated pet-friendly beach, make sure your child keeps shoes on and doesn't sit in the sand without a blanket or towel.Talk with your pediatrician. Your pediatrician can prescribe anti-parasitic medications such as albendazole or ivermectin to treat the rash. Without treatment, the larvae usually will die off in 5 to 6 weeks. Your pediatrician may suggest a cream to help relieve itching.
8. Folliculitis (Hot Tub Rash)
Folliculitis (hot tub rash) is an itchy, pimply rash that occurs when bacteria in unclean pools and hot tubs gets into hair follicles on the skin. The area where hairs grow from the skin becomes infected and inflamed, sometimes forming small, pus-filled blisters. A similar rash may come from wearing a damp swimsuit that wasn't washed and dried well after previous use. Hot rub rash typically starts 12-48 hours after being in a hot tub.
What parents can do:
Avoid dirty pools. If you're unsure whether the acid and chlorine levels are properly controlled in a heated pool, don't allow your child to go in.
Don't allow young children in spas or hot tubs. In addition to the risk for drowning and overheating, young children are also at higher risk of bacterial skin infection because they tend to spend more time in the water than teens or adults.
Talk with your pediatrician. Hot tub rash usually clears up without medical treatment. In the meantime, warm compresses and an over-the-counter anti-itch cream recommended by your pediatrician can help your child be more comfortable. If your child's rash lasts more than a few days, talk with your pediatrician.
9. Molluscum Virus
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection that causes pearly bumps on the skin on a child's chest, back, arms or legs. The dome-shaped bumps, also known as "water warts," may have a dimple in the center. The poxvirus that causes the bumps is more common in hot, humid climates. Some studies suggest the infection may spread in contaminated swimming pools.
The poxvirus that causes the bumps is more common in hot, humid climates. Some studies suggest the infection may spread in contaminated swimming pools.
What parents can do:
Wait it out. In most cases, molluscum contagiosum does not need treatment. The bumps usually will go away in 6 to 12 months.
Stop the spread. A child with molluscum contagiosum should not share towels, bedding, or clothing with others to avoid spreading the virus. The bumps are contagious as long as they are present.
Avoid scratching. Scratching the bumps can spread the virus and cause a second, bacterial infection where the skin is open.
10. Juvenile Plantar Dermatosis (Sweaty Sock Syndrome)
A smooth, reddened rash on your child's feet, sometimes with peeling, cracking skin or scaly skin, could be from a condition called Juvenile Plantar Dermatosis (Sweaty Sock Syndrome). It happens when feet get wet and then dry quickly, again and again—like when shoes are taken on and off coming in and out of the house during summer.
What parents can do:
Breathable footwear. Reduce how often the feet go from wet to dry quickly by having your child wear open or more breathable footwear made of materials like mesh or cotton (i.e., water shoes) and/or thicker more absorbent socks.
Apply ointment. Applying moisturizing ointment or an over-the-counter steroid cream to the affected areas of your child's foot immediately after taking shoes off or getting out of water can help. If the condition does not improve, or if you notice any sign of infection where your child's skin is cracking, talk to your pediatrician.
11. Tinea (Ringworm)
Despite having "worm" in its misleading name, tinea (ringworm) is an infection caused by a fungus that thrives in warm, damp conditions. It is similar to athlete's foot and jock itch and can appear on a child's scalp or other parts of the body. It's called ringworm because the rash from the infection tends to form round or oval spots that become smooth in the center as they grow while the border remains red and scaly. The fungus can spread quickly among student athletes, especially during sweaty, summertime practices and games, when they share sports equipment and locker rooms.
The fungus can spread quickly among student athletes, especially during sweaty, summertime practices and games, when they share sports equipment and locker rooms.
What parents can do:
Stop the spread. Check and treat any pets that may have the fungus—look for scaling, itchy, hairless areas on their fur. Family members, playmates, or schoolmates who show symptoms also should be treated. Do not allow your child to share combs, brushes, hair clips, barrettes, or hats. Make sure mats used in sports like wrestling and gymnastics are properly disinfected after use.
Talk with your pediatrician. A single ringworm patch on the body can be treated with an over-the-counter cream recommended by your pediatrician. If there are any patches on the scalp or more than one on the body, or if the rash is getting worse while being treated, your pediatrician may prescribe a stronger medication and special shampoo.
12.
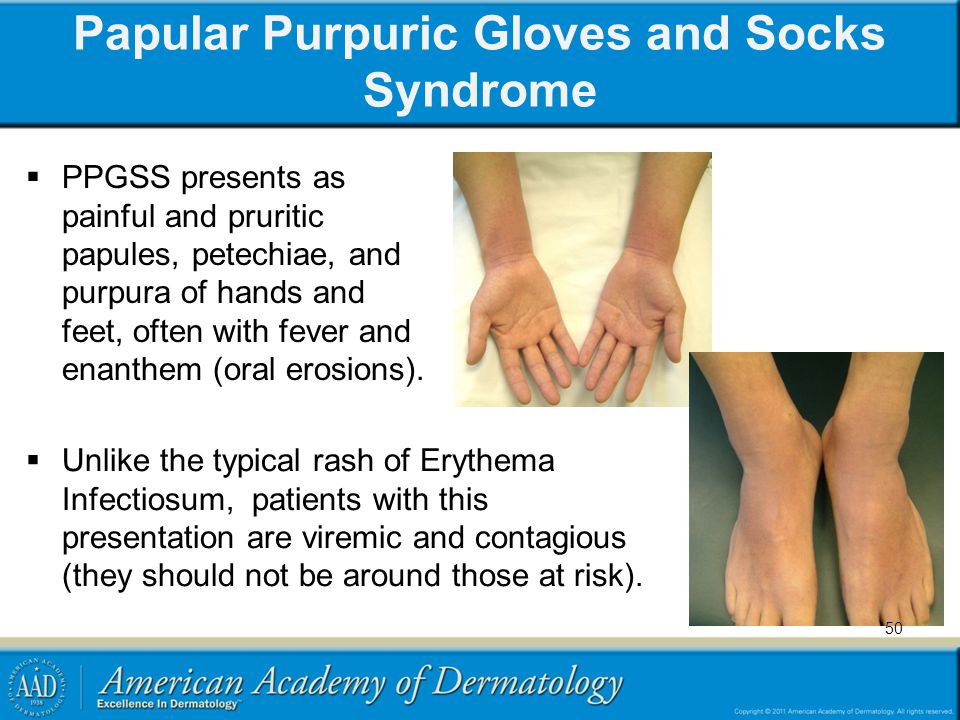 Hand, Foot & Mouth Disease
Hand, Foot & Mouth DiseaseMany parents assume virus season winds down after winter. But some viral illnesses, such as hand, foot, and mouth disease, are more common during summer and early fall. Outbreaks are most common in younger children and can spread in child care centers, preschools, and summer camps. Caused by Enterovirus coxsackie, the illness starts with a fever, sore throat, and runny nose—much like the common cold—but then a rash with tiny blisters may appear on any or all the following places on the body:
In the mouth (inner cheeks, gums, sides of the tongue or back of the mouth)
Fingers or palms of hands
Soles of feet
Buttocks
Symptoms are the worst in the first few days, but they are usually gone within a week. Peeling skin on the fingers, toes, and nails may begin after a week or two, but it is harmless. Parents of children with a history of atopic dermatitis or eczema should be aware that their children may be prone to a more severe outbreak.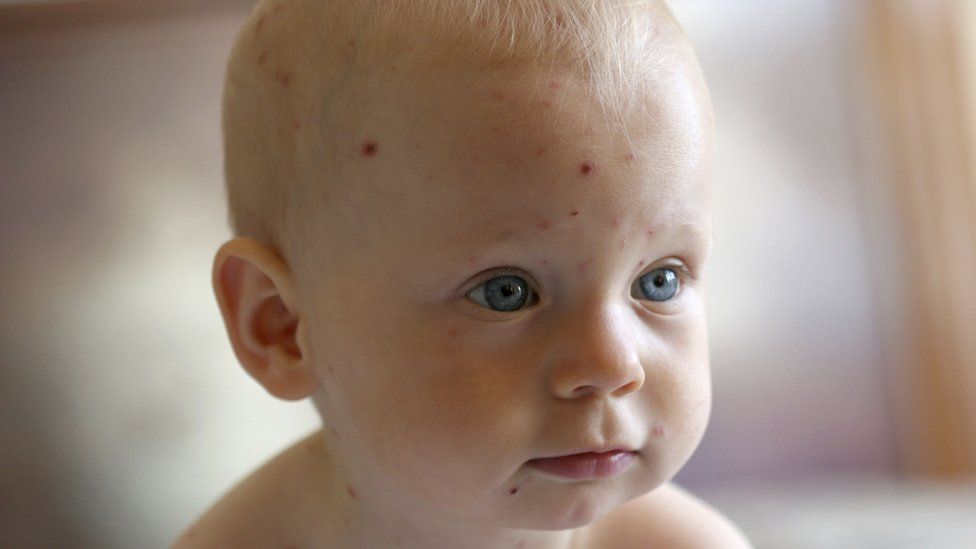
What parents can do:
Monitor symptoms. Be sure to call your pediatrician if your child's fever lasts more than 3 days or if he or she is not drinking fluids. If symptoms are severe, your pediatrician may collect samples from your child's throat for lab testing.
Ease the pain. For fever and pain, the pediatrician may also recommend acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Liquid mouth-soothing remedies may be useful to alleviate mouth ulcer pain. Do not use regular mouthwashes, because they sting.
Avoid dehydration: Children with hand, foot, and mouth disease need to drink plenty of fluids. Call your pediatrician or go to the ER if you suspect your child is dehydrated. See Signs of Dehydration in Infants & Children for more information.
Inform others. Tell child care providers and playmates' parents to watch for symptoms of the illness.
 Children with hand, foot, and mouth disease may spread the virus through the respiratory tract (nose, mouth and lungs) for 1-3 weeks, and in the stool for weeks to months after the infection starts. Once a child's fever has gone away and he or she is feeling better, there is no need to keep him or her home unless there are still open and oozing blisters. See When to Keep Your Child Home from Child Care for more information.
Children with hand, foot, and mouth disease may spread the virus through the respiratory tract (nose, mouth and lungs) for 1-3 weeks, and in the stool for weeks to months after the infection starts. Once a child's fever has gone away and he or she is feeling better, there is no need to keep him or her home unless there are still open and oozing blisters. See When to Keep Your Child Home from Child Care for more information.
Remember…
Protecting your child's skin is a year-round concern, but it's especially important in the summer months when so much skin is exposed and vulnerable. Fortunately, many summertime rashes clear up quickly on their own. Be sure to talk with your pediatrician about any rash that you're unsure about—especially if you don't know what caused it, if it is making your child feel miserable or doesn't clear up quickly, or if it shows signs of infection or is accompanied by any shortness of breath.
Additional Information:
- Summer Safety Tips: Staying Safe Outdoors
- Antibiotic Prescriptions for Children: 10 Common Questions Answered
- American Academy of Dermatology
- American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology
- Society for Pediatric Dermatology
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Skin rash in children: analyze the causes
Features of children's skin
The skin, like most other organs and systems, gradually develops until puberty. In a child, it is functionally and structurally more sensitive to external influences and allergic reactions. At the same time, the sweat and sebaceous glands do not yet work properly, which is associated with insufficient development of skin innervation.
At the same time, the skin from birth takes an active part in metabolism and respiration due to the many superficially located vessels. Because of this, skin diseases often greatly affect the general condition of the child. nine0005
Types of rash in children
Skin rash caused by a particular disease usually has its own characteristics. The most common types of rashes include:
- Papules. These are volumetric formations of a small size (up to 10 mm), which rise above the skin.
 The main color is red and pink. Occurs with lichen planus, roseola infantum, atopic dermatitis, etc.
The main color is red and pink. Occurs with lichen planus, roseola infantum, atopic dermatitis, etc. - Vesicles. They are bubbles up to 5 mm in diameter, filled with a cloudy liquid. After opening, erosion is often left behind. May be a sign of chickenpox and other herpes infections. nine0014
- Petechiae. A purplish skin eruption that does not go away with pressure. Its elements do not exceed 3 mm in diameter, do not rise above the skin and are not felt to the touch. As a rule, they indicate meningococcal infection, vascular damage (vasculitis), platelet deficiency.
- Erosion. This is a skin defect that does not penetrate deeper than the epidermis. It has the appearance of a rounded, somewhat in-depth formation of red color with a weeping surface.
- Peel. A secondary element formed by the drying of secretions from vesicles, erosions, or blood. Solid, has a dark red, brown color. nine0014
- Macula or spot. This is an area of discoloration that is on the same level as adjacent areas of the skin.
 It can be both an independent element in rubella, measles, roseola, and a residual phenomenon after papules, vesicles or erosions.
It can be both an independent element in rubella, measles, roseola, and a residual phenomenon after papules, vesicles or erosions. - Wheals or urticaria. A rounded element of a rash of pale pink, red or purple-white color, the size of which varies from 1-2 mm to tens of centimeters. Leaves no secondary elements behind. Meet with allergic reactions, urticaria. nine0014
- Lichenification. These are areas of excessive thickening of the skin with increased skin pattern. Often a secondary element.
Diseases that cause skin rashes in children
Baby skin rashes can indicate various diseases, most often infections and allergic reactions.
Roseola infantum
Roseola infantum or sudden exanthema is a childhood infectious disease that occurs when infected with human herpesviruses type 6 or 7. Most often observed between the ages of 6 months and 2 years. nine0005
Sudden exanthema is accompanied by an increase in body temperature up to 39-40°C, which persists for 3-5 days, after which a bright red maculopapular rash appears on the child's skin.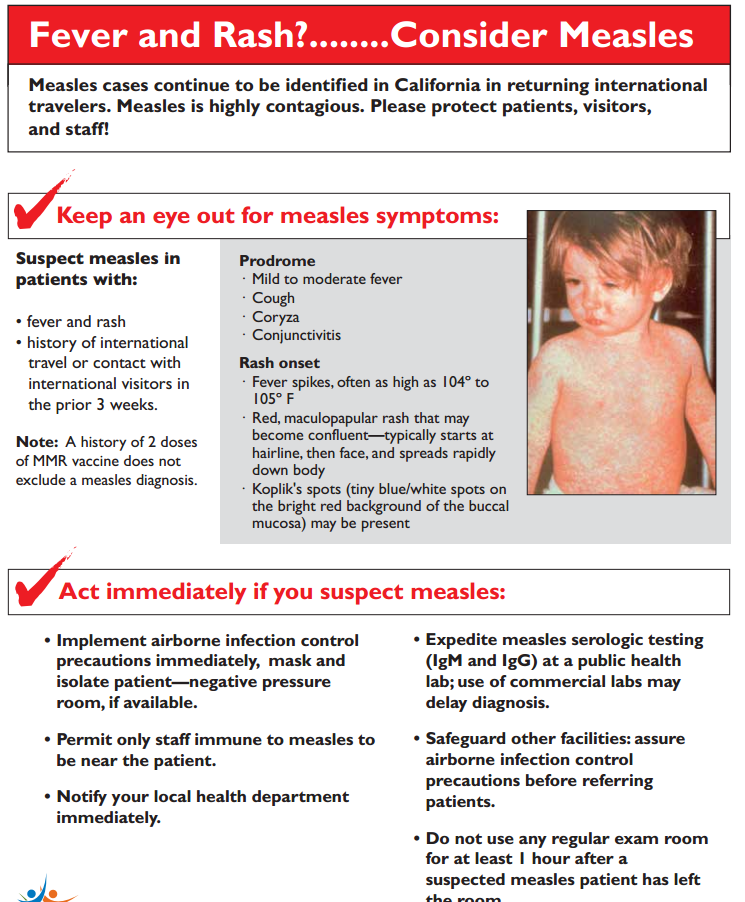 It occurs on the surface of the chest and abdomen, spreading throughout the body (Fig. 1). The elements of the rash, as a rule, are not felt by the fingers, but sometimes they can be raised. They disappear when the skin is stretched or when the glass of a glass is pressed on them.
It occurs on the surface of the chest and abdomen, spreading throughout the body (Fig. 1). The elements of the rash, as a rule, are not felt by the fingers, but sometimes they can be raised. They disappear when the skin is stretched or when the glass of a glass is pressed on them.
In roseola infantum there may be white rings around some elements of the rash. Often the rash is limited only to the trunk and, not having time to reach the face and limbs, disappears. The rash does not cause discomfort or itching, but children usually become sharply capricious and "unbearable" during this time; the rash lasts from several hours to several days, and then disappears, leaving no pigmentation or peeling. An excerpt from the book by Sergei Butriy “Child health: a modern approach. how to learn to cope with illness and your own panic. nine0005
Roseola infantum should be treated symptomatically, preferably with antipyretics and plenty of fluids. In immunodeficiency states (HIV infection, congenital disorders of the immune system), antiherpetic drugs are additionally prescribed.
Figure 1. Rash in roseola infantum. Source: WikipediaNo matter how hard baby roseola flows, it is perfectly safe. Complications are extremely rare and are usually limited to febrile convulsions. An excerpt from the book by Sergei Butriy “Child health: a modern approach. how to learn to cope with illness and your own panic. nine0005
Enteroviral exanthems: chicken pox and enteroviral pharyngitis
The viral pemphigus, also known as turkish varicella, is caused by enterovirus 71 (EV-71). Enteroviral pharyngitis is caused by Coxsackie A16, B2, B5 viruses. They occur mainly among children under the age of 10 years, infection often occurs during holidays in southern countries.
The primary signs of pathologies are pain in the mouth and throat, because of which the child refuses to eat and does not even swallow saliva, but spits it out. Then the body temperature rises to 39°C. The fever persists for about 4 days and is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite and excessive irritability.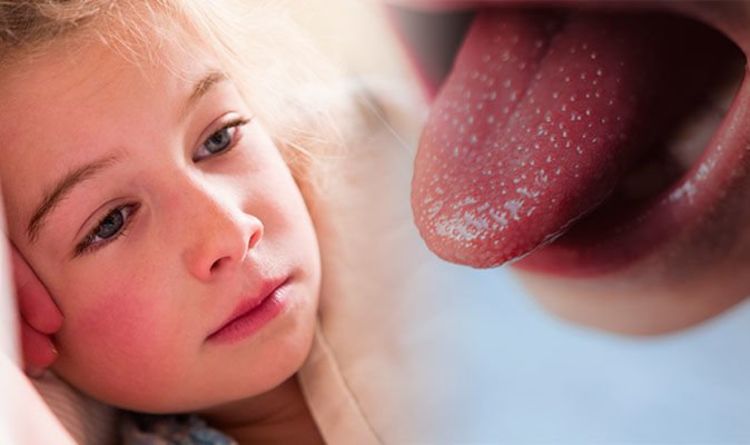 With enteroviral pharyngitis, small white sores usually occur only on the palatine arches (Fig. 2), but Turkish chickenpox is a rash throughout the mouth, including the tongue, around the mouth, on the palms and feet. The rash on the skin may resemble chickenpox - red spots or blisters.
With enteroviral pharyngitis, small white sores usually occur only on the palatine arches (Fig. 2), but Turkish chickenpox is a rash throughout the mouth, including the tongue, around the mouth, on the palms and feet. The rash on the skin may resemble chickenpox - red spots or blisters.
Symptomatic treatment:
- Oral hygiene and rinsing with antiseptic solutions.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that help control pain while lowering body temperature.
- Plentiful warm drinks to prevent dehydration, cold drinks and ice cream may be given (these are more easily tolerated by sick children).
- Diet with the exception of mechanically hard, sour and salty foods. nine0014
- Enteroviral exanthems are self-limiting, the disease usually recedes after 3-7 days. However, the condition of the child during the illness must be monitored in order to consult a doctor in time in case of complications.
 The most common are dehydration and secondary bacterial infections. In the latter case, abscesses, yellow crusts appear on the skin, the skin swells. Rarely enterovirus infection leads to serous meningitis.
The most common are dehydration and secondary bacterial infections. In the latter case, abscesses, yellow crusts appear on the skin, the skin swells. Rarely enterovirus infection leads to serous meningitis.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox or chickenpox is an infectious disease caused by the human herpesvirus type 3 (Varicella Zoster). People of any age get sick with it, but mostly it is children 5-9years.
The main symptom is skin rashes that have a certain sequence of development. Small pink spots appear first, quickly transforming into papules, and then into vesicles (Fig. 3) with reddening around. After a couple of days, they open or dry out, forming crusts of dark red, brown color on their surface. A characteristic feature is severe itching.
Figure 3. Development of a skin rash in chickenpox. Source: SlideToDoc
The total period of rashes lasts from 2 to 9days. At the same time, the general condition practically does not suffer, but fever may occur.
There are no drugs that can completely eliminate the virus, so the treatment tactics are aimed at eliminating the symptoms and normalizing the child's condition:
- Bed rest in the presence of fever.
- Treatment of elements of the rash with a solution of manganese, methylene blue or brilliant green (brilliant green).
- Antihistamines for itching. nine0014
- Antipyretics.
- Taking regular warm showers without using a washcloth or brush.
Complications of chickenpox occur against the background of suppression of the body's immune system. These include: inflammation of the lungs (pneumonia), lesions of the nervous system (neuralgia, meningitis, encephalitis, damage to the facial nerve), eyes (keratitis, conjunctivitis, uveitis), etc.
Important ! For the prevention of chickenpox, especially for adults, against the background of a weakened immune system and a high risk of complications, vaccination is recommended. It can also be carried out as an emergency prophylaxis up to 2 days from the moment of contact with a sick person. nine0005
It can also be carried out as an emergency prophylaxis up to 2 days from the moment of contact with a sick person. nine0005
Measles
Measles is a viral infectious disease. Often it occurs in unvaccinated children from 2 to 5 years and older.
Measles debuts with a sharp rise in temperature to 39-40°C, dry cough, runny nose, headache, hoarseness. Characteristic features are swelling and redness of the eyelids, pharynx and red spots in the sky. On the 2-3rd day of development, a symptom specific to measles occurs - Filatov-Belsky-Koplik spots. These are white spots with a red border, observed on the inner surface of the cheeks near the molars. On the 4-5th day from the appearance of the first signs of the disease, these spots disappear, and they are replaced by a skin rash. nine0005
The primary localization of measles papular rash is the outer surface of the elbow, knees, fingers. Further, it spreads throughout the body (Fig. 4). The elements of the rash are surrounded by red spots and tend to merge with each other. After 4 days from the moment they appear, the child's condition returns to normal, and the elements of the rash become darker and peel off. Residual effects and pigmentation disappear after 7-10 days.
After 4 days from the moment they appear, the child's condition returns to normal, and the elements of the rash become darker and peel off. Residual effects and pigmentation disappear after 7-10 days.
There is no specific treatment for measles; helping a child involves managing individual symptoms:
- NSAIDs to reduce body temperature.
- Expectorants for relief of coughs.
- Antiseptic mouth rinses.
- Topical treatment of rash elements with astringents or tea to relieve itching and soreness.
Measles is very dangerous. Possible complications of measles:
- Stenosis of the larynx - croup.
- Primary measles or secondary bacterial pneumonia. nine0013 Inflammation of the respiratory tract - bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis.
- Otitis media.
- Hepatitis.
- Encephalitis and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis.
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is a bacterial infection caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Most cases occur in children between 3 and 7 years of age.
The first manifestation of scarlet fever is an intoxication syndrome - an increase in body temperature up to 38-39°C, headache, general weakness and loss of appetite. On the 2-4th day from the moment the first signs of the disease appear, one of the characteristic symptoms appears - "crimson tongue" (Fig. 5). It is manifested by pronounced graininess and bright red color of the surface. Angina also occurs - inflammation of the palatine tonsils.
Figure 5. Crimson tongue in scarlet fever. Source: ResearchGate
From the first days of scarlet fever, a characteristic red punctate rash appears, which does not disappear when pressed with glass, but becomes yellowish with effort. It is located on the flexion surfaces: the inner parts of the elbows, under the knees, in the inguinal pits, on the cheeks and sides of the body. It lasts up to 1 week, after which it disappears, leaving no pigmentation behind. A specific sign is the pallor of the nasolabial triangle. nine0005
It lasts up to 1 week, after which it disappears, leaving no pigmentation behind. A specific sign is the pallor of the nasolabial triangle. nine0005
Another characteristic feature of scarlet fever is the peeling of the skin that occurs after the rash has disappeared. At the same time, the skin "moves away" in whole layers in the area of the palms and feet, while in other areas - in small fragments.
Treatment is based on antibiotics from the penicillin group. Vitamin C and B vitamins, symptomatic preparations are used as adjuvants. Plentiful warm drink and bed rest are recommended. In severe cases, glucocorticosteroids and intravenous drip of glucose solutions and plasma substitutes are used. nine0005
The most common complications of scarlet fever: otitis media, sinusitis and frontal sinusitis (inflammation of the maxillary and frontal paranasal sinuses, respectively), cervical lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes of the cervical region).
Rubella
Rubella is caused by Rubella virus.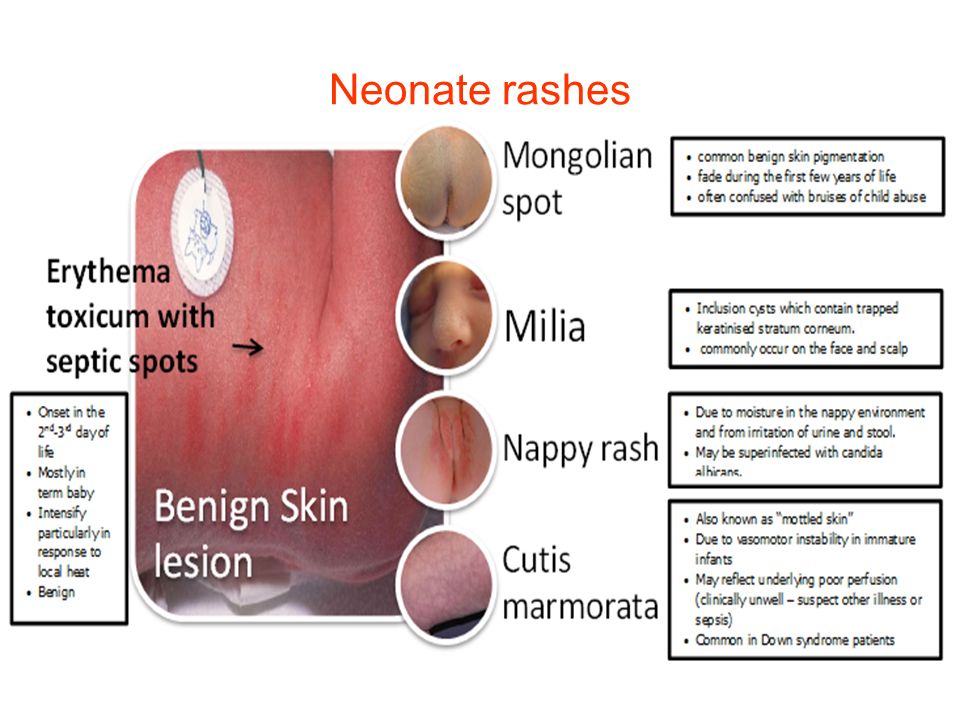 The majority of patients are children aged 3 to 9 years.
The majority of patients are children aged 3 to 9 years.
Rubella begins with an intoxication syndrome of moderate severity: fever up to 38-38.5°C, headache and fatigue, signs of pharyngitis and conjunctivitis, marked enlargement of the lymph nodes of the cervical and occipital region. nine0005
After 1.5-2 days from the onset of the disease, a skin rash appears in the form of spots, which spreads downward over several hours - appearing on the face, gradually moving to the trunk and limbs. Outwardly, the rash initially resembles measles, then scarlet fever. Itching and peeling are absent, and the spots, unlike measles, do not merge with each other. The bulk of the spots are located on the buttocks and lower back, the outer surface of the elbows and knees. After 3-5 days, the rash disappears without a trace. nine0005
There is no specific treatment for rubella, and the main actions are aimed at eliminating individual symptoms of the disease. Complications are very rare, as a rule - against the background of disorders of the immune system.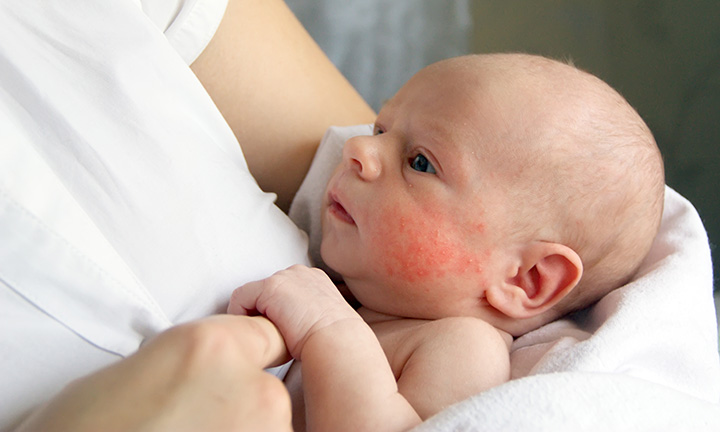 In such cases, the development of pneumonia, arthritis, otitis media is possible.
In such cases, the development of pneumonia, arthritis, otitis media is possible.
Important ! Rubella is especially dangerous for pregnant women, as it causes problems in the fetus, so when planning a pregnancy, all unvaccinated people should be vaccinated against this infection. nine0005
Urticaria
Urticaria or urticaria is a type of dermatitis caused by allergies. The disease is very common among both children and adults. In total, about 20% of the adult population and 2-7% of children suffer from it.
Medications (most often antibiotics), various foods, vaccines and physical influences: cold, sunlight, mechanical pressure can provoke the development of urticaria.
The leading symptom of the pathology is a skin rash in the form of dense red or pink vesicles or nodules 2-10 mm in diameter with clear edges, which become pale when pressed (Fig. 6). A characteristic feature is the sudden appearance and equally rapid disappearance of the elements of the rash without a trace, as well as severe itching. nine0005 Figure 6. Urticaria rash. Source: James Heilman, MD/Wikipedia
nine0005 Figure 6. Urticaria rash. Source: James Heilman, MD/Wikipedia
Treatment, depending on the form of the disease, is represented by antihistamines, histamine receptor blockers or glucocorticosteroids.
Complications occur in the absence of treatment and include angioedema, anaphylactic shock, heart and kidney damage in the form of myocarditis or glomerulonephritis, respectively.
Lichen planus
Lichen planus is a chronic dermatitis of unknown origin. Most of the patients are people aged 30 to 60 years. However, about 5% of the total number of patients are children.
A typical form of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of gray-white papules up to 2 mm in diameter on the oral mucosa, namely: the inner surface of the cheeks behind the molars, on the lateral parts of the tongue and on the palate. Sometimes the rashes can merge, forming patterns.
In some patients, a rash also appears on the skin of the flexor surfaces of the limbs of the arms and legs, the inner thighs.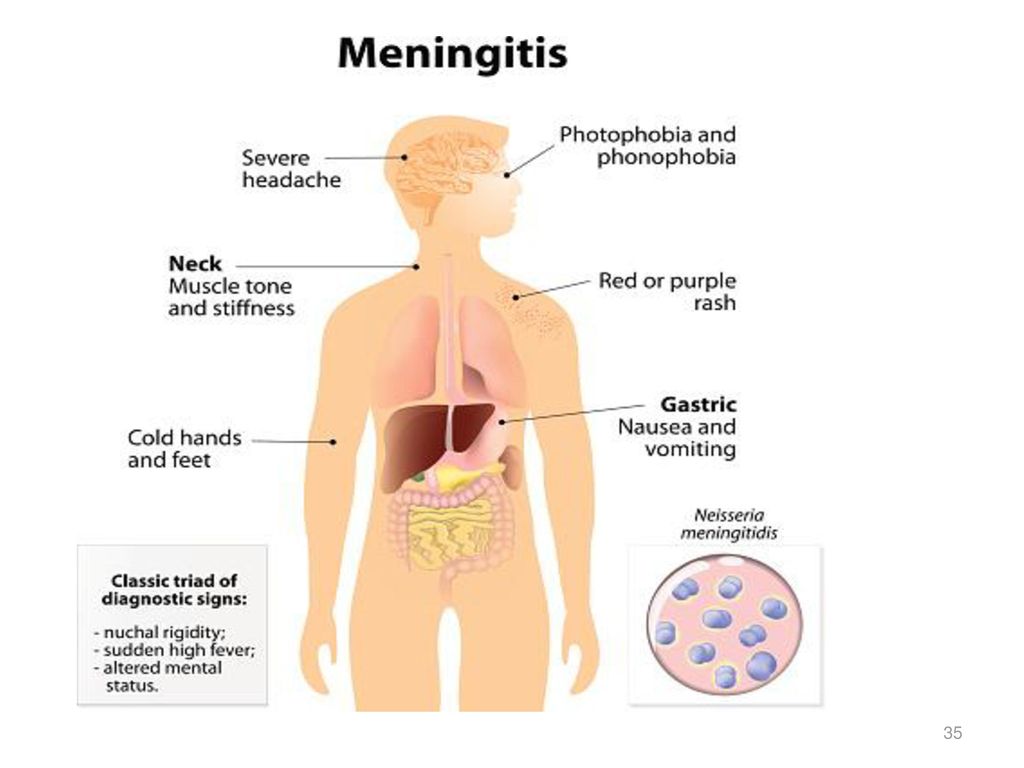 It has the appearance of small papules of various shapes and pinkish-purple color with a shiny surface and a depression in the center. nine0005
It has the appearance of small papules of various shapes and pinkish-purple color with a shiny surface and a depression in the center. nine0005
Treatment includes diet with restriction of salt, smoked and fried foods, coarse food that irritates the mucous membranes. Glucocorticosteroids are prescribed as medical support.
Pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis rosea or Gibert's versicolor is a variant of a skin lesion whose cause has not been clearly identified. Exacerbations occur against the background of immune suppression - colds, hypothermia, chronic stress, etc. Most cases of this pathology are observed in people aged 20 to 40 years, as well as in adolescents. nine0005
The disease begins with the formation of a primary scaly focus of pinkish or yellowish color from 1 to 10 cm in diameter with a clear rim. After 1-2 weeks, secondary plaques and smaller papules appear on the body and limbs - up to 2 cm (Fig. 7). Gradually, the elements of the rash turn pale, and the outer edge becomes rougher. The rash may be accompanied by itching, fever and other manifestations of the intoxication syndrome.
The rash may be accompanied by itching, fever and other manifestations of the intoxication syndrome.
The disease tends to self-heal within 4-5 weeks. Treatment is mainly local in the form of ointments based on glucocorticosteroids, and antihistamines and NSAIDs are prescribed to combat itching and fever. nine0005 Figure 7. Skin rash with rosacea. Source: James Heilman, MD/Wikipedia
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis or eczema is a genetically determined inflammatory skin lesion of an autoimmune nature. Most often, children under 14 years of age living in large, industrial cities get sick.
Atopic dermatitis develops with a probability of 80% if both parents have a history of this pathology, and with a 50% probability if only one of them. nine0005
The first symptoms occur before the age of 2 years due to exposure to allergens, which can be food, plant pollen, dust and mold, cosmetics.
Typical symptoms are skin rashes, which vary depending on the stage of the disease.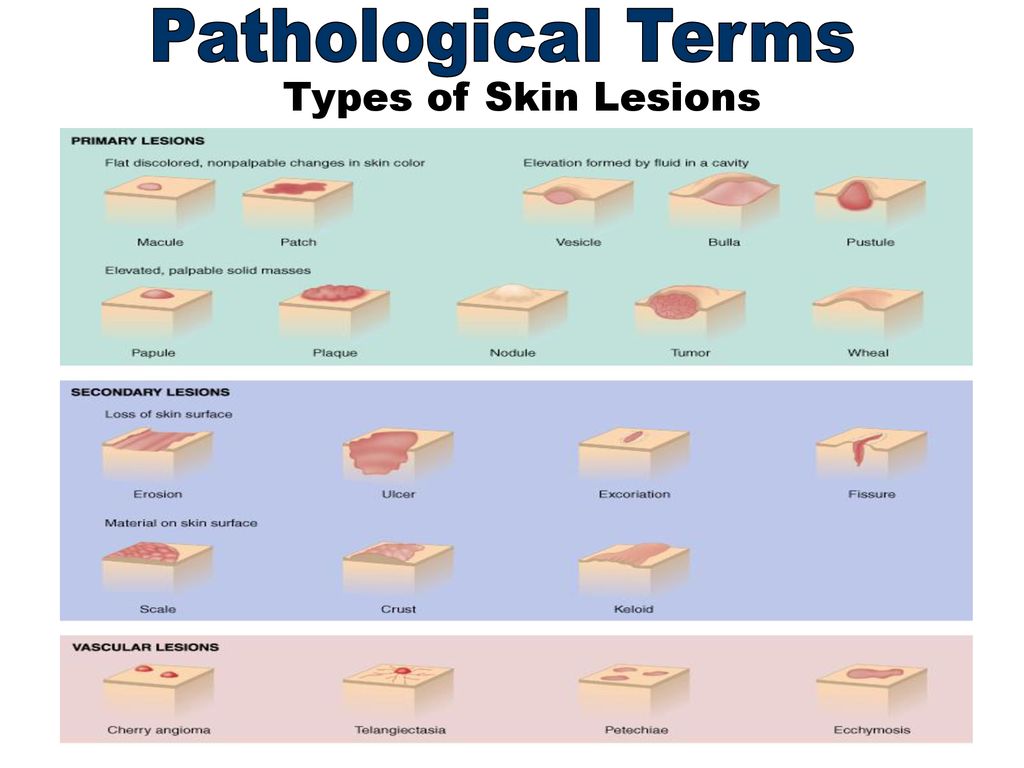 When exacerbated, red spots, papules and small vesicles appear, accompanied by severe itching. In infants, the typical site is the face, scalp, and neck. At an older age, the flexion surfaces of the limbs and the neck are affected. In the remission stage, they are replaced by foci of increased dryness of the skin, peeling and lichenification. During the year, on average, there are 2-4 exacerbations. nine0005
When exacerbated, red spots, papules and small vesicles appear, accompanied by severe itching. In infants, the typical site is the face, scalp, and neck. At an older age, the flexion surfaces of the limbs and the neck are affected. In the remission stage, they are replaced by foci of increased dryness of the skin, peeling and lichenification. During the year, on average, there are 2-4 exacerbations. nine0005
Ointments and creams based on glucocorticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and zinc are used in the treatment. In severe cases, hormonal drugs are used in the form of tablets or intravenous injections. Antihistamines are also used to combat itching.
Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis is the result of infection with human herpesvirus type 4 (Epstein-Barr virus). It is believed that already before the age of 5, about 50% of children become infected with this virus, and its prevalence among adults reaches 95% of the population. Most often, clinical signs of pathology occur at the age of 14-18 years.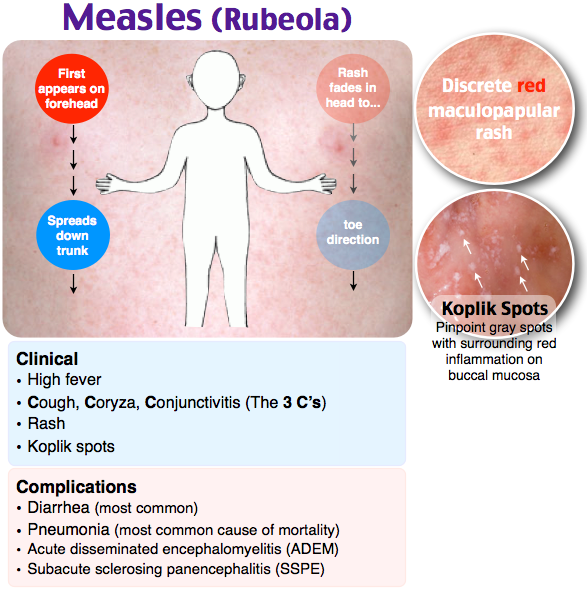
Typical symptoms of infectious mononucleosis include:
- General weakness and malaise.
- Sore throat and pain when swallowing
- Headache.
- Slight increase in body temperature.
- Sensation of aching in muscles and joints.
- Enlargement and soreness of the lymph nodes in the region of the lower jaw and neck. nine0014
Skin rash occurs in less than ¼ of patients. Most often, they occur on the 5th-10th day of the course of the disease against the background of the erroneously prescribed antibiotics ampicillin or amoxicillin. The rash is represented by spots and papules and is located in the face, trunk, thighs and shoulders. It is accompanied by swelling of the skin and itching, sometimes peeling. The rash disappears within 5-7 days.
Since mononucleosis is of viral origin, antibiotic therapy is not used against it. Treatment of the disease involves the elimination of individual symptoms. In severe cases and with concomitant immunodeficiency, antiherpetic drugs are prescribed: ganciclovir, valaciclovir.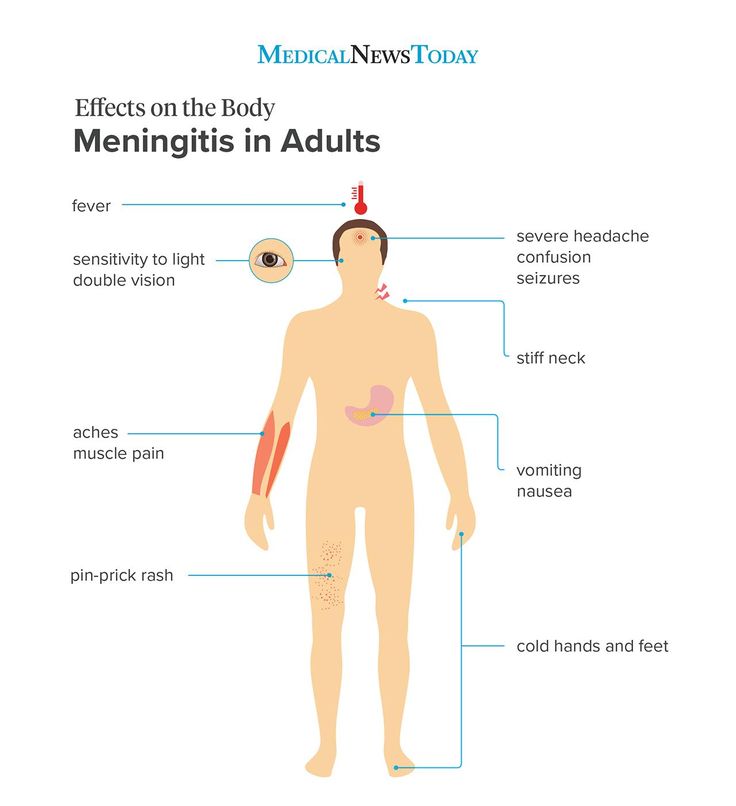 nine0005
nine0005
Prevention of rashes
In cases of infectious diseases, the only way to avoid rashes is to prevent infection, namely by limiting contact with sick people and practicing basic personal hygiene.
In case of allergic pathologies, it is important to exclude contact with triggers, and if this is not possible, take antihistamines or corticosteroids previously agreed with the attending physician in advance.
A series of recommendations to help avoid skin rashes of other origin for people with sensitive skin:
- Avoid direct skin contact with aggressive, irritating substances such as household chemicals.
- Limit skin exposure to sunlight, cold.
- Give preference to clothing and underwear made from natural fabrics.
- Avoid tight, uncomfortable clothing and mechanically rough objects such as washcloths.
- Use ointments or other skin care products recommended by a dermatologist or esthetician. nine0014
Conclusion
Skin rash is an important symptom of many diseases. She can tell you exactly what kind of disease you have to deal with. This, in turn, makes it possible to provide the right assistance before contacting a doctor, avoiding mistakes or even coping with the problem on your own.
She can tell you exactly what kind of disease you have to deal with. This, in turn, makes it possible to provide the right assistance before contacting a doctor, avoiding mistakes or even coping with the problem on your own.
References
- Federal Clinical Guidelines. Dermatovenereology 2015. Skin diseases. Sexually transmitted infections. - 5th ed. revised and additional - M: Business Express, 2016. - 768 p. nine0014
- V.M. Kozin, Yu.V. Kozina, N.N. Yankovskaya "Dermatological diseases and sexually transmitted infections: Educational and methodological manual" - Vitebsk: VSMU, 2016. - 409 p.
- P.D. Walk. "Skin and venereal diseases: Textbook" - Grodno: Grodno State Medical University, 2003. - 182 p.
- Yu.V. Odinets, M.K. Biryukova “Atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, urticaria in children: method. decree. for stud. and interns" - Kharkiv: KhNMU, 2015. - 52 p. nine0014
- S. A. Butriy “Child health: a modern approach. How to learn to cope with diseases and your own panic ”-“ Eksmo ”, 2018.
Rash in a child on body, legs, back
We treat children according to the principles of evidence-based medicine: we choose only those diagnostic and treatment methods that have proven their effectiveness. We will never prescribe unnecessary examinations and medicines!
Make an appointment via WhatsApp
Prices Doctors nine0005
The first children's clinic of evidence-based medicine in Moscow
No unnecessary examinations and drugs! We will prescribe only what has proven effective and will help your child.
Treatment according to world standards
We treat children with the same quality as in the best medical centers in the world.
The best team of doctors in Fantasy!
Pediatricians and subspecialists Fantasy - highly experienced doctors, members of professional societies. Doctors constantly improve their qualifications, undergo internships abroad. nine0005
Ultimate safety of treatment
We have made children's medicine safe! All our staff work according to the strictest international standards JCI
We have fun, like visiting best friends
Game room, cheerful animator, gifts after the reception.