Stages of first trimester
Stages of pregnancy | Office on Women's Health
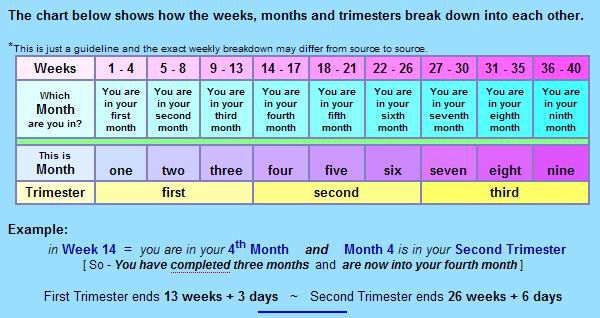
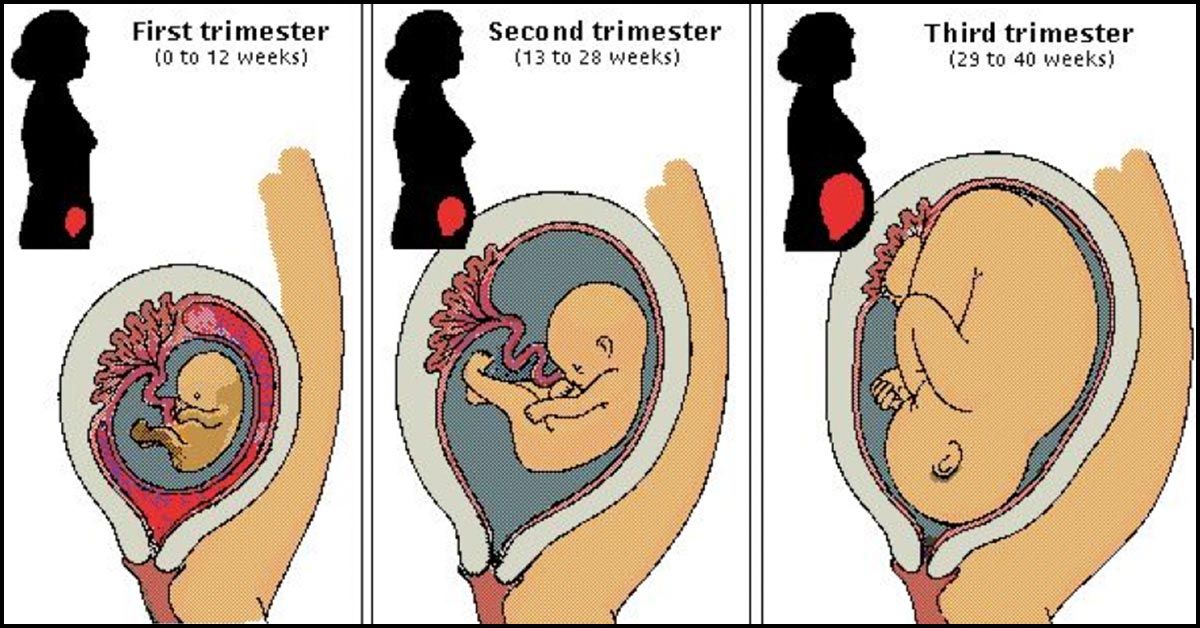
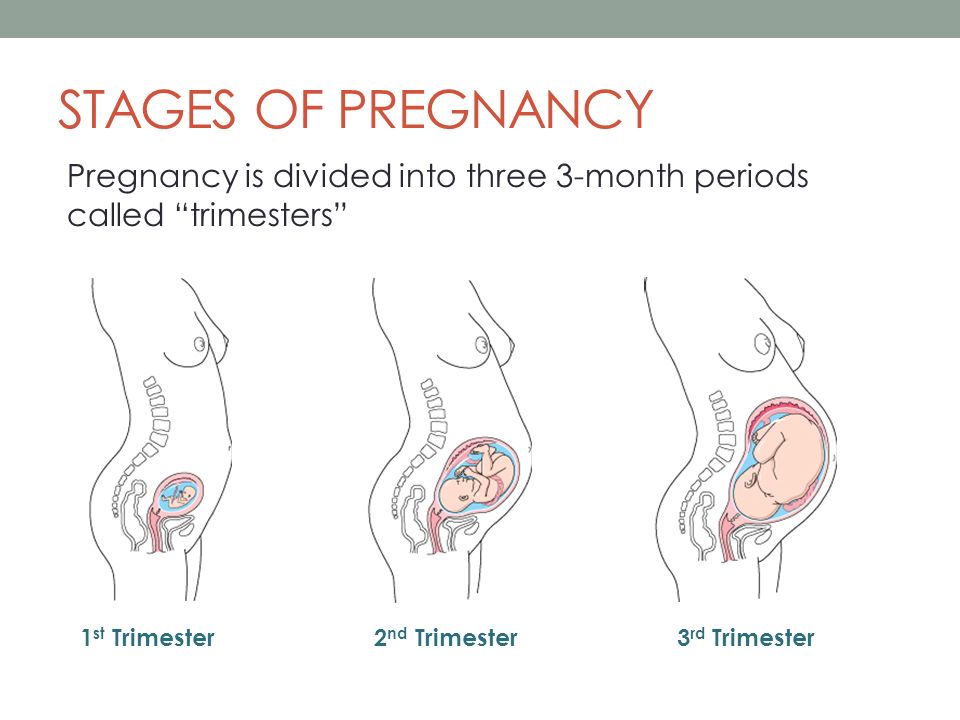
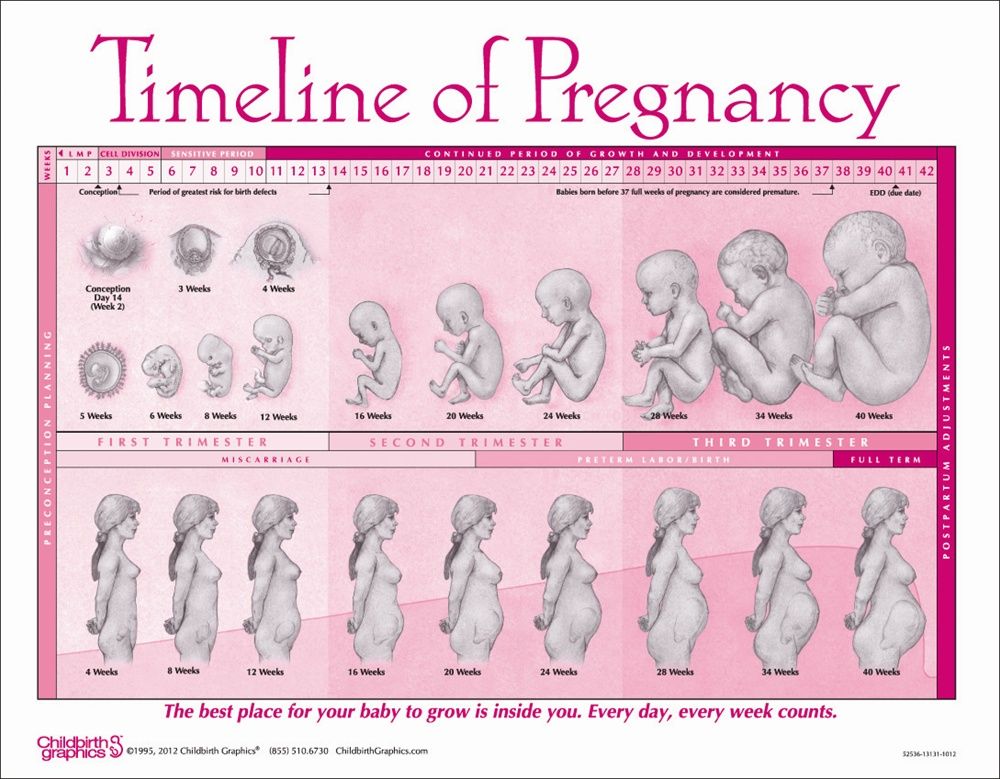
Pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks, counting from the first day of your last normal period. The weeks are grouped into three trimesters.(TREYE-mess-turs) Find out what's happening with you and your baby in these three stages.
First trimester (week 1–week 12)
During the first trimester your body undergoes many changes. Hormonal changes affect almost every organ system in your body. These changes can trigger symptoms even in the very first weeks of pregnancy. Your period stopping is a clear sign that you are pregnant. Other changes may include:
- Extreme tiredness
- Tender, swollen breasts. Your nipples might also stick out.
- Upset stomach with or without throwing up (morning sickness)
- Cravings or distaste for certain foods
- Mood swings
- Constipation (trouble having bowel movements)
- Need to pass urine more often
- Headache
- Heartburn
- Weight gain or loss
As your body changes, you might need to make changes to your daily routine, such as going to bed earlier or eating frequent, small meals. Fortunately, most of these discomforts will go away as your pregnancy progresses. And some women might not feel any discomfort at all! If you have been pregnant before, you might feel differently this time around. Just as each woman is different, so is each pregnancy.
Second trimester (week 13–week 28)
Most women find the second trimester of pregnancy easier than the first. But it is just as important to stay informed about your pregnancy during these months.
You might notice that symptoms like nausea and fatigue are going away. But other new, more noticeable changes to your body are now happening. Your abdomen will expand as the baby continues to grow. And before this trimester is over, you will feel your baby beginning to move!
As your body changes to make room for your growing baby, you may have:
- Body aches, such as back, abdomen, groin, or thigh pain
- Stretch marks on your abdomen, breasts, thighs, or buttocks
- Darkening of the skin around your nipples
- A line on the skin running from belly button to pubic hairline
- Patches of darker skin, usually over the cheeks, forehead, nose, or upper lip.
 Patches often match on both sides of the face. This is sometimes called the mask of pregnancy.
Patches often match on both sides of the face. This is sometimes called the mask of pregnancy. - Numb or tingling hands, called carpal tunnel syndrome
- Itching on the abdomen, palms, and soles of the feet. (Call your doctor if you have nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting, jaundice or fatigue combined with itching. These can be signs of a serious liver problem.)
- Swelling of the ankles, fingers, and face. (If you notice any sudden or extreme swelling or if you gain a lot of weight really quickly, call your doctor right away. This could be a sign of preeclampsia.)
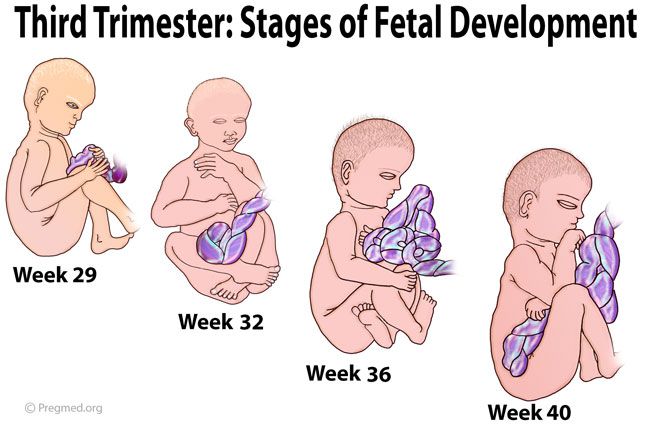
Third trimester (week 29–week 40)
You're in the home stretch! Some of the same discomforts you had in your second trimester will continue. Plus, many women find breathing difficult and notice they have to go to the bathroom even more often. This is because the baby is getting bigger and it is putting more pressure on your organs. Don't worry, your baby is fine and these problems will lessen once you give birth.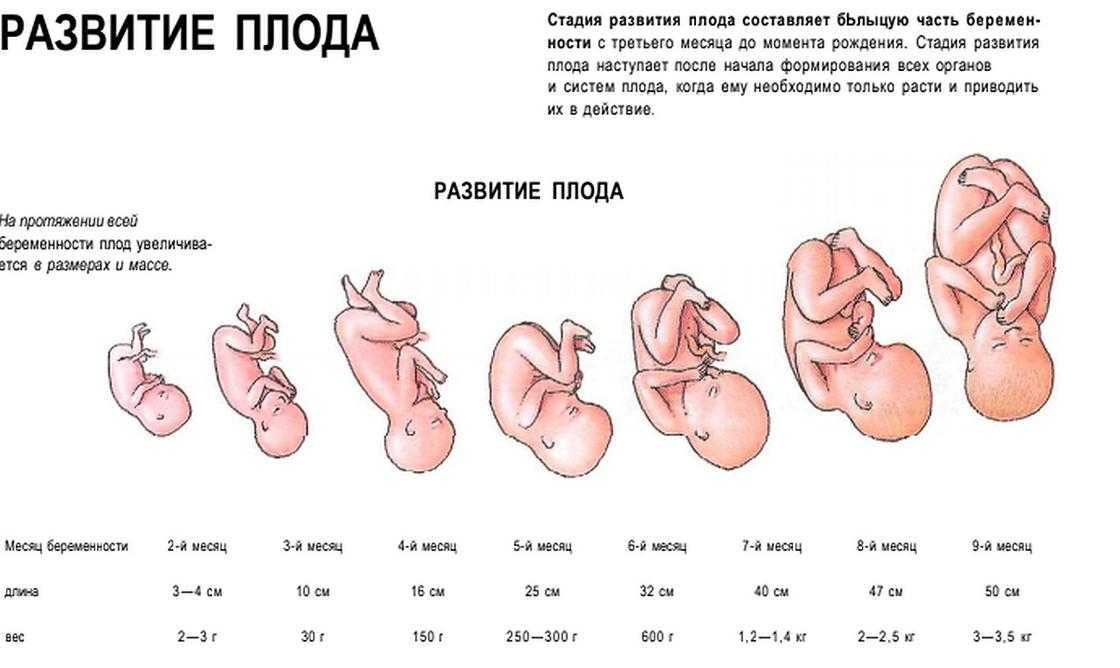
Some new body changes you might notice in the third trimester include:
- Shortness of breath
- Heartburn
- Swelling of the ankles, fingers, and face. (If you notice any sudden or extreme swelling or if you gain a lot of weight really quickly, call your doctor right away. This could be a sign of preeclampsia.)
- Hemorrhoids
- Tender breasts, which may leak a watery pre-milk called colostrum (kuh-LOSS-struhm)
- Your belly button may stick out
- Trouble sleeping
- The baby "dropping", or moving lower in your abdomen
- Contractions, which can be a sign of real or false labor
As you near your due date, your cervix becomes thinner and softer (called effacing). This is a normal, natural process that helps the birth canal (vagina) to open during the birthing process. Your doctor will check your progress with a vaginal exam as you near your due date. Get excited — the final countdown has begun!
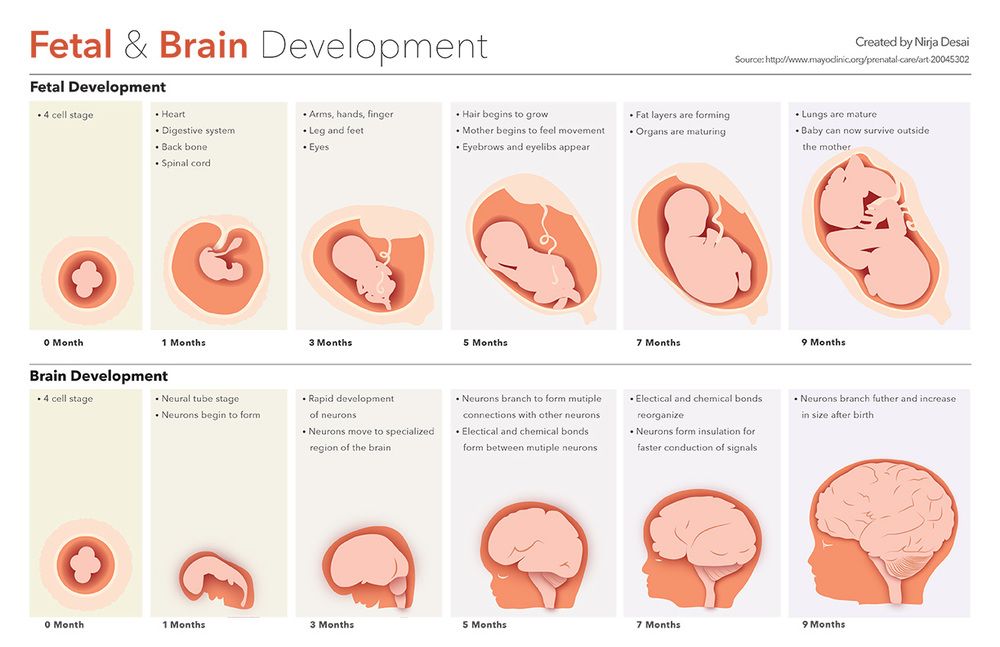
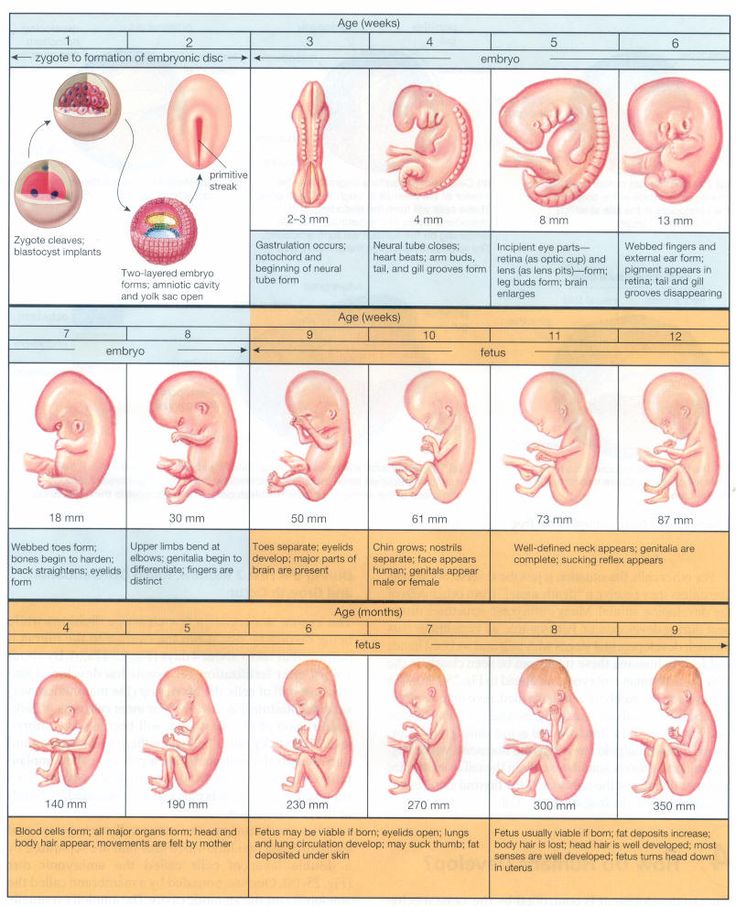
Your developing baby
First trimester (week 1-week 12)
At four to five weeks:
- Your baby's brain and spinal cord have begun to form.
- The heart begins to form.
- Arm and leg buds appear.
- Your baby is now an embryo and one-twenty-fifth inch long.
At eight weeks:
- All major organs and external body structures have begun to form.
- Your baby's heart beats with a regular rhythm.
- The arms and legs grow longer, and fingers and toes have begun to form.
- The sex organs begin to form.
- The eyes have moved forward on the face and eyelids have formed.
- The umbilical cord is clearly visible.
- At the end of eight weeks, your baby is a fetus and looks more like a human. Your baby is nearly 1 inch long and weighs less than one-eighth ounce.
At 12 weeks:
- The nerves and muscles begin to work together. Your baby can make a fist.
- The external sex organs show if your baby is a boy or girl. A woman who has an ultrasound in the second trimester or later might be able to find out the baby's sex.
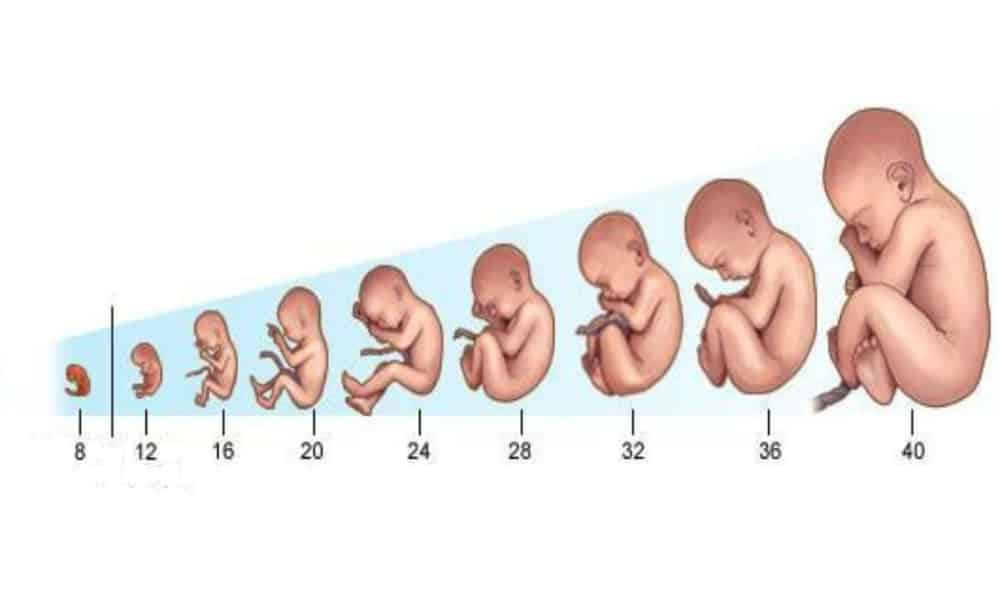
- Eyelids close to protect the developing eyes. They will not open again until the 28th week.
- Head growth has slowed, and your baby is much longer. Now, at about 3 inches long, your baby weighs almost an ounce.
Second trimester (week 13-week 28)
At 16 weeks:
- Muscle tissue and bone continue to form, creating a more complete skeleton.
- Skin begins to form. You can nearly see through it.
- Meconium (mih-KOH-nee-uhm) develops in your baby's intestinal tract. This will be your baby's first bowel movement.
- Your baby makes sucking motions with the mouth (sucking reflex).
- Your baby reaches a length of about 4 to 5 inches and weighs almost 3 ounces.
At 20 weeks:
- Your baby is more active. You might feel slight fluttering.
- Your baby is covered by fine, downy hair called lanugo (luh-NOO-goh) and a waxy coating called vernix. This protects the forming skin underneath.

- Eyebrows, eyelashes, fingernails, and toenails have formed. Your baby can even scratch itself.
- Your baby can hear and swallow.
- Now halfway through your pregnancy, your baby is about 6 inches long and weighs about 9 ounces.
At 24 weeks:
- Bone marrow begins to make blood cells.
- Taste buds form on your baby's tongue.
- Footprints and fingerprints have formed.
- Real hair begins to grow on your baby's head.
- The lungs are formed, but do not work.
- The hand and startle reflex develop.
- Your baby sleeps and wakes regularly.
- If your baby is a boy, his testicles begin to move from the abdomen into the scrotum. If your baby is a girl, her uterus and ovaries are in place, and a lifetime supply of eggs have formed in the ovaries.
- Your baby stores fat and has gained quite a bit of weight. Now at about 12 inches long, your baby weighs about 1½ pounds.
Third trimester (week 29-week 40)
At 32 weeks:
- Your baby's bones are fully formed, but still soft.
- Your baby's kicks and jabs are forceful.
- The eyes can open and close and sense changes in light.
- Lungs are not fully formed, but practice "breathing" movements occur.
- Your baby's body begins to store vital minerals, such as iron and calcium.
- Lanugo begins to fall off.
- Your baby is gaining weight quickly, about one-half pound a week. Now, your baby is about 15 to 17 inches long and weighs about 4 to 4½ pounds.
At 36 weeks:
- The protective waxy coating called vernix gets thicker.
- Body fat increases. Your baby is getting bigger and bigger and has less space to move around. Movements are less forceful, but you will feel stretches and wiggles.
- Your baby is about 16 to 19 inches long and weighs about 6 to 6½ pounds.
Weeks 37–40:
- At 39 weeks, your baby is considered full-term. Your baby's organs are ready to function on their own.
- As you near your due date, your baby may turn into a head-down position for birth.
 Most babies "present" head down.
Most babies "present" head down. - At birth, your baby may weigh somewhere between 6 pounds 2 ounces and 9 pounds 2 ounces and be 19 to 21 inches long. Most full-term babies fall within these ranges. But healthy babies come in many different sizes.
All material contained on these pages are free of copyright restrictions and maybe copied, reproduced, or duplicated without permission of the Office on Women’s Health in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Citation of the source is appreciated.
Page last updated: February 22, 2021
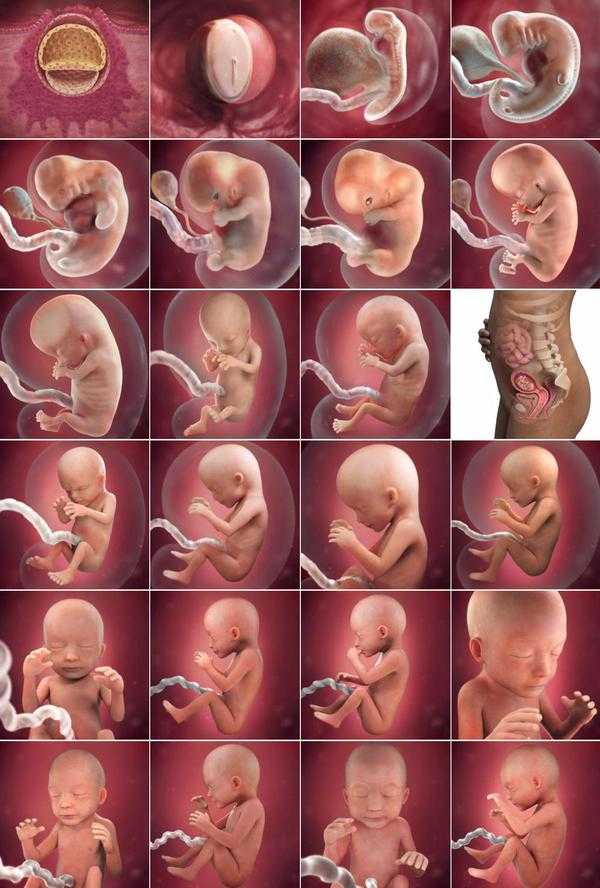
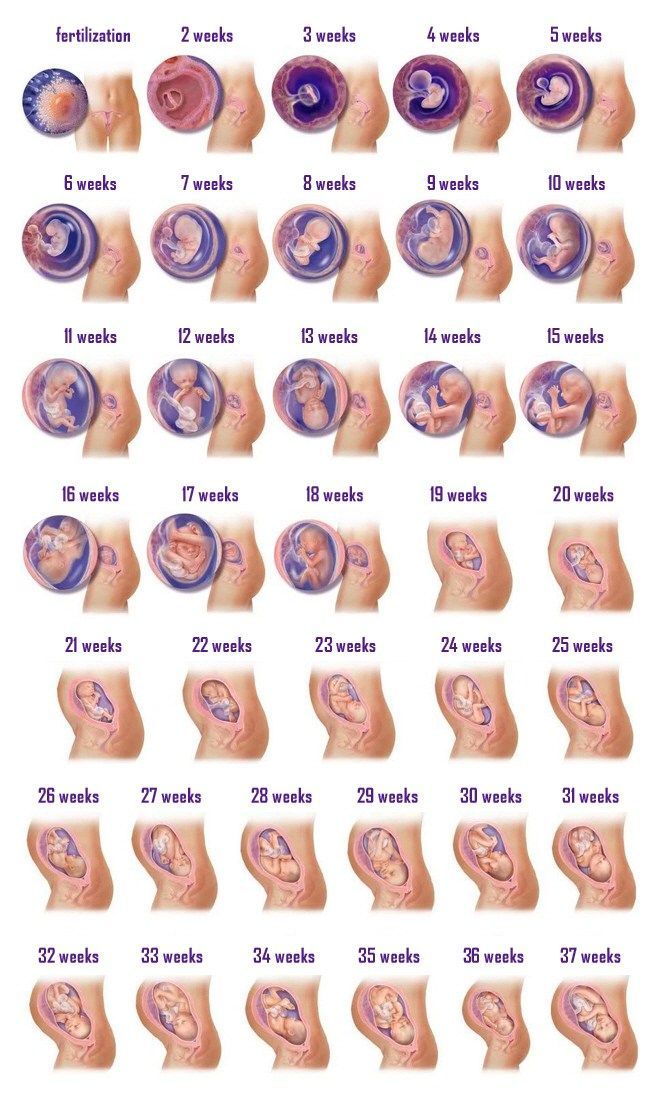
Stages of Fetal Development - First Trimester
Stages of Fetal Development - First TrimesterStages of Fetal Development - First Trimester
One - 13 Weeks
| FERTILIZATION Biologically speaking, fertilization (or conception) is the beginning of human development. | |
| WEEK 2
| |
| WEEK 4
| |
| WEEK 6
| |
| WEEK 8
| |
| WEEK 10
| |
| WEEK 12
| |
1st trimester of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus
1st trimester of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus - Private maternity hospital Ekaterininskaya Clinics1st trimester: 1st-12th weeks
The gestational age is calculated from the first day of the last menstruation, since it is difficult to determine the exact day of conception. Since conception usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle, you are not actually pregnant during the first two weeks, but this period is counted as the beginning of pregnancy.
Since conception usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle, you are not actually pregnant during the first two weeks, but this period is counted as the beginning of pregnancy.
As soon as the fertilization of the egg takes place around the 3rd week, the hormones begin to produce changes in your body little by little. As a result, you may experience some of the following symptoms:
- Morning sickness. As a result of rising levels of hormones characteristic of pregnancy, up to 80% of women in the 1st trimester experience morning sickness with symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. The idea that such malaise is observed only in the morning is a common misconception. In fact, symptoms can appear at any time of the day or night. Up to 1 in 5 women experience morning sickness in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and can sometimes persist throughout pregnancy.
If you experience morning sickness, avoid foods that make you sick, eat little and often, avoid fatty and spicy foods, drink more water.
 If you experience severe symptoms or symptoms that bother you, see your doctor.
If you experience severe symptoms or symptoms that bother you, see your doctor. - Breast changes. The mammary glands will begin to increase in size, soreness may appear. The nipples will increase in size, become darker and more protruding.
- Fatigue. High levels of the hormone progesterone can make you feel tired and sleepy. Rest as often as possible in a horizontal position with your legs up and eat as well as possible, which is not easy if you are experiencing morning sickness!
- Increased emotionality. A higher level of emotionality, manifested as a result of an increase in hormone levels, is normal. Understanding and patience on the part of your partner and loved ones is very important here.
- Food likes and dislikes. You may find yourself intolerant of one food and addicted to another. This is usually not a problem, unless you feel like eating weird foods like chalk.
 If you are concerned about the situation, contact your doctor.
If you are concerned about the situation, contact your doctor. - Frequent urination. As your fluid levels increase and your uterus puts pressure on your bladder, you will become more likely to visit the toilet. Go to the toilet as soon as you feel the need - this minimizes the pressure on the bladder.
- Feeling of dizziness. Sometimes you may feel a little dizzy (this is due to hormonal changes). Try not to stay on your feet for a long time and slowly rise from a sitting or lying position. If you experience severe dizziness, contact your doctor immediately.
- Heartburn and constipation. Your digestive system will slow down to give you more time to digest your food. This can lead to heartburn and constipation. To help manage heartburn, try to eat small meals at regular intervals and avoid fried or spicy foods and carbonated drinks. Constipation is helped by eating a diet rich in fiber, maintaining physical activity and drinking plenty of water.
1st trimester milestones
- Approximately 7 days after fertilization, the embryo implants in the uterine wall. The placenta, umbilical cord and amniotic sac will begin to form to provide nourishment and protection to the embryo.
- By the end of the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, the uterus is palpable through the wall of the abdomen, the abdomen will begin to grow.
Child development in the 1st trimester of pregnancy
By the end of the 1st trimester:
- All the main organs of the baby are formed, the circulatory system works.
- The development of the sexual organs has begun.
- Fingers are formed on the hands and feet, nails have appeared.
- Facial features have formed.
- The length of the baby's body is about 6 cm from the head to the lower part of the body, he is already recognizable. The baby moves in the amniotic sac, but you don't feel it move yet.

Clinic mobile app
You can make an appointment with a doctor, get tests
and much more...
Fill out the form to make an appointment or order a call back
I agree with personal data processing policy and user agreement I also give my consent to the processing of personal data.
Sign up for a consultation
I agree with personal data processing policy and user agreement I also give my consent to the processing of personal data.
By continuing to use rd.clinic23.ru, you agree to the use of cookies. How to ban the use of certain cookies can be found in Politics
Pregnancy management: 1st trimester
The first 12 weeks after the conception of a baby is a period of active growth and development of the embryo, so managing a pregnancy in the 1st trimester under the supervision of a qualified and caring obstetrician can be the best solution for parents and baby.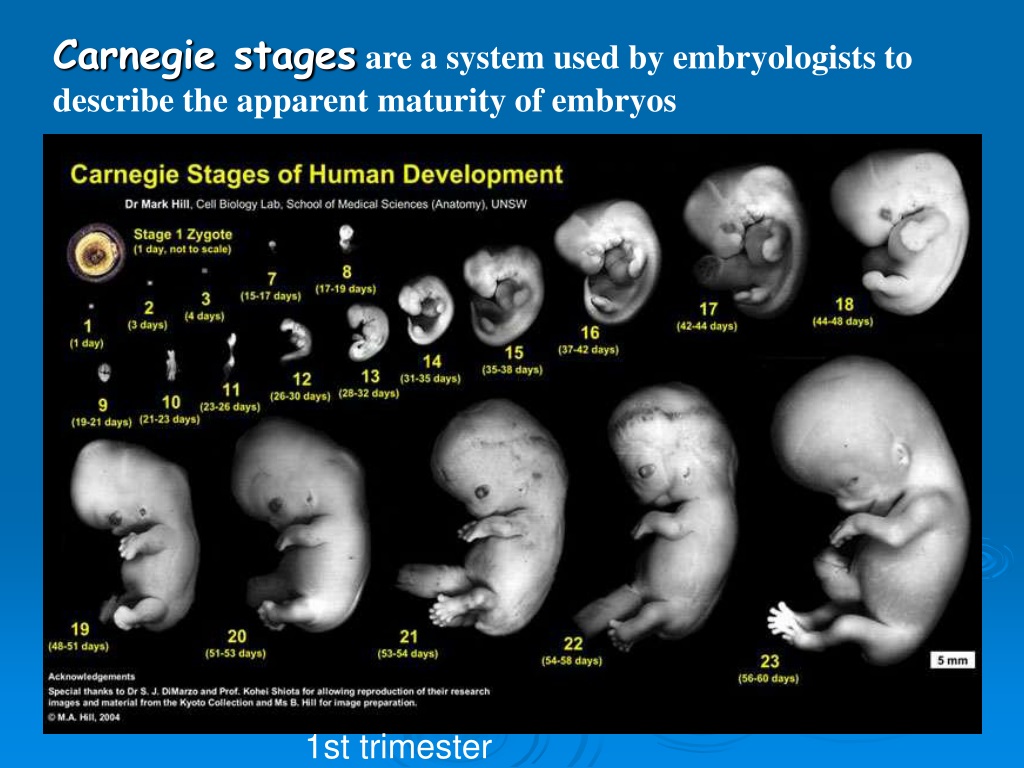 In this article, we will consider in detail what is the peculiarity of this period, why it is very important to take care of the health of mother and child now, and what is included in the program of professional pregnancy management in the 1st trimester in our clinic.
In this article, we will consider in detail what is the peculiarity of this period, why it is very important to take care of the health of mother and child now, and what is included in the program of professional pregnancy management in the 1st trimester in our clinic.
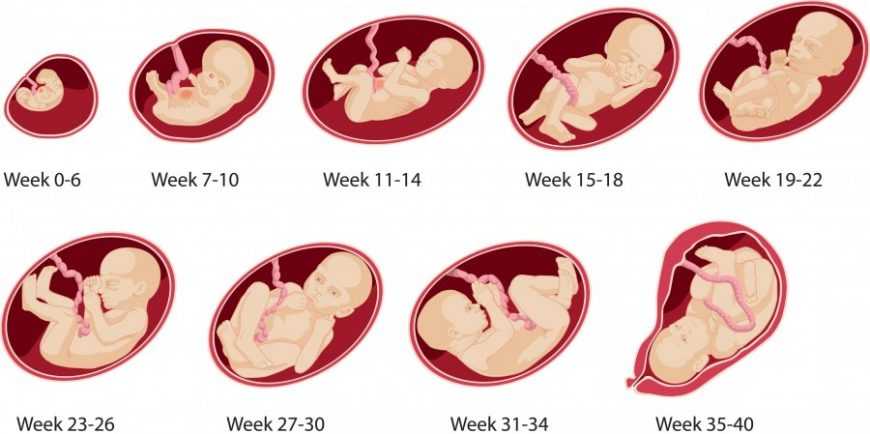
Fetal development in the 1st trimester of pregnancy (weeks 1-12)
Delayed menstruation for 10-14 days - an occasion to consult a gynecologist. Under the 1st trimester of pregnancy, it is customary to consider the period of development of the embryo (fetus) from the moment of fertilization of the egg and the attachment of the zygote (fetal egg) to the wall of the uterus until the 12th week. This stage is characterized by successive changes of blastogenesis, organogenesis, placenta , and also includes the beginning of the fetal period , when the fetus has already formed all organ systems, limbs and even the visual appearance of the baby.
It is the 1st trimester of pregnancy that obstetrician-gynecologists call “critical”, because, on the one hand, during this period the most complex dynamic processes take place in a woman’s body: fertilization, zygote fixation, laying of all systems of the baby’s body. On the other hand, it is at this time that the fetus is most sensitive to damaging factors, so there is a possibility of pregnancy complications and abnormalities in the development of the fetus, if there are prerequisites for this. Moreover, this risk is even higher than in the 2nd or 3rd trimesters of pregnancy. Non-developmental pregnancy is one of the most significant and common risks that can appear already in early pregnancy.
On the other hand, it is at this time that the fetus is most sensitive to damaging factors, so there is a possibility of pregnancy complications and abnormalities in the development of the fetus, if there are prerequisites for this. Moreover, this risk is even higher than in the 2nd or 3rd trimesters of pregnancy. Non-developmental pregnancy is one of the most significant and common risks that can appear already in early pregnancy.
Mothers who have previously faced the problem of infertility, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy should be especially attentive to the development of pregnancy in the 1st trimester. Obstetrician-gynecologists of our clinic will not only conduct prenatal diagnostics themselves as part of the monitoring program for the development of the baby, but also in a hospital will help to correct pathologies in the development of the fetus. We manage pregnancies after IVF and have been helping women experience the joy of motherhood for over 20 years.
How is the 1st-2nd week of pregnancy
The gestational age is calculated from the 1st day of the last menstruation . Pregnancy begins with ovulation and fertilization. At this stage, the zygote is fixed in the uterine cavity. It is extremely important that the anatomy (patency) of the fallopian tubes of a woman is not disturbed. The endometrium should be ready to accept the zygote, and there should be no inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity (its mucous membrane) - this increases the likelihood of low placentation. The movement of the zygote through the fallopian tube takes, on average, 2-3 days. Violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes and, in connection with this, the retention of a fertilized egg can cause an ectopic pregnancy.
As part of the planning and management of pregnancy (in the 1st trimester), a woman undergoes ultrasound diagnostics , and also passes tests aimed at identifying such deviations.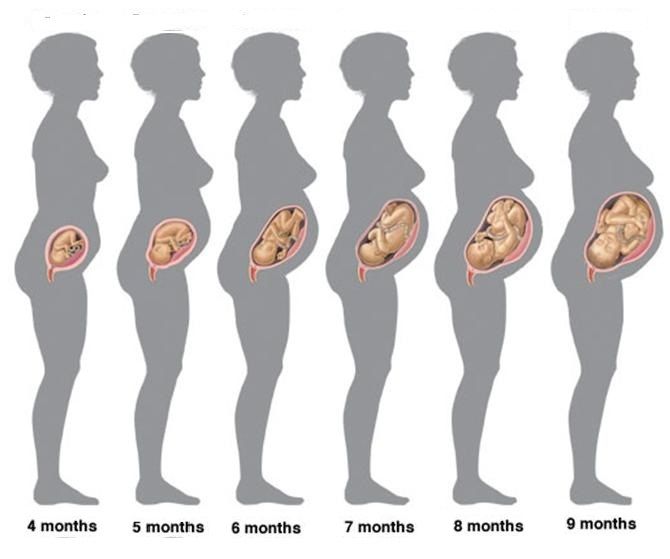 It is at this gestational age that it is already possible to determine the fetal egg in the uterus and, for example, exclude an ectopic pregnancy.
It is at this gestational age that it is already possible to determine the fetal egg in the uterus and, for example, exclude an ectopic pregnancy.
The main indicator by which pregnancy is ascertained and further monitored for its development is level of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in the blood. With a positive pregnancy test result, the hCG level exceeds 30. Pregnancy can be diagnosed by hCG as early as 2-4 days after a missed period.
At the initial stage of pregnancy in the 1st trimester, it is extremely important to compensate for the deficiency of nutrients (iron, magnesium, folic acid), which provide the necessary components for fetal growth, and restore hormonal balance. This must be done strictly under the supervision of a doctor and after passing the tests - the spontaneous intake of medicines, even herbal ones, can cause irreparable damage to the health of the mother and child.*
* An infamous historical example is the thalidomide disaster of 1961.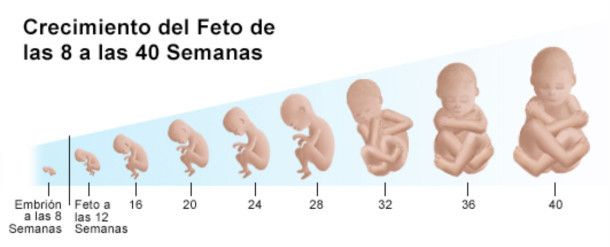
How is the 3rd-8th week of pregnancy
Organs are formed in the embryo: heart, neural tube, intestines, etc. The placenta performs a number of vital functions: nutrition, respiration, excretion, synthesis of hormones and nutrients, blood circulation. The processes of active protein synthesis and embryonic growth factors require a good blood supply from the mother.
Organogenesis from the 3rd week of pregnancy is considered the most important and risky period of development. Any internal failure in the ligament: "mother - placenta - developing organs of the embryo" can lead to fatal malformations.
At 6-7 weeks of pregnancy, ultrasound diagnostics already allows you to fix the baby's heartbeat.
At 7-8 weeks of the 1st trimester of pregnancy, limbs are formed in the fetus, the process of embryogenesis is completed - this means that all organs and tissues have been formed in the embryo in its infancy.
The term of 7-8 weeks is optimal in order to undergo the first large-scale clinical and laboratory examination and register. You can contact our clinic on the issue of pregnancy management in the 1st trimester - we ourselves will get the expectant mother an exchange card and help her to undergo modern diagnostics in comfortable conditions.
How is the 9th - 12th week of pregnancy
The stage of active growth and complication of the baby's body. The fetus develops a lymphatic system and complex reflexes appear - the child can cover his face with his hands, bring his thumb to his mouth.
Thus, in the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the most important and significant changes occur in a woman's body - it begins to work literally for two, directing resources to the active growth and development of the fetus. To ensure good blood circulation, the work of the heart is enhanced. In order for the baby to receive the necessary amount of oxygen, pulmonary ventilation becomes more intense.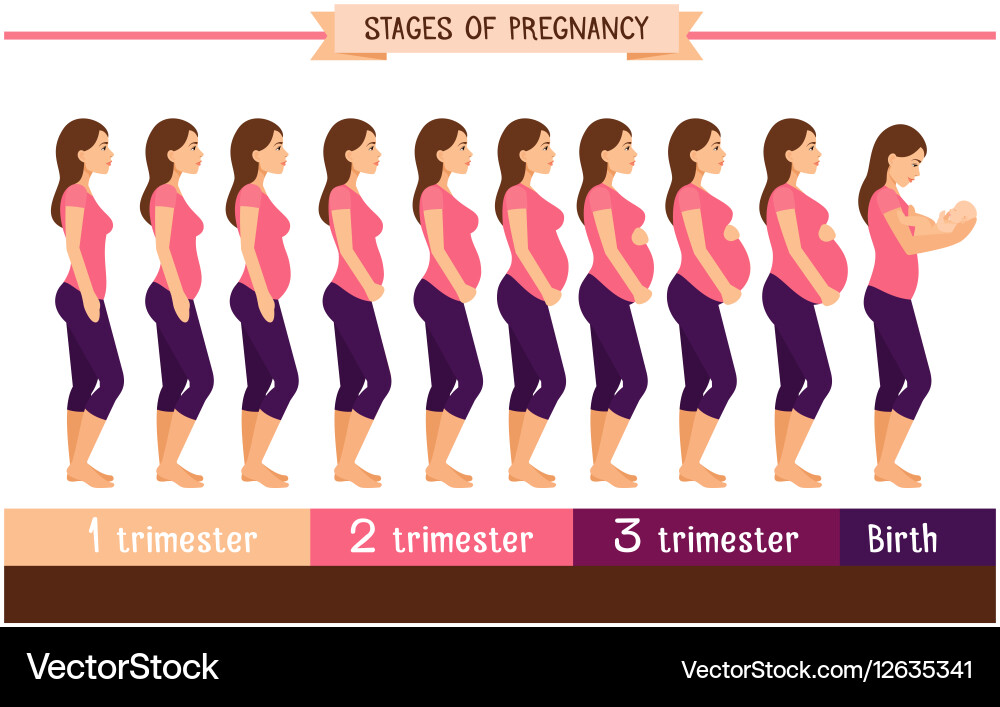 The kidneys are now responsible for the excretion of maternal and fetal metabolic products. The uterus increases in size, which often leads to stagnant movements in the intestines - to constipation. Taste sensations change; a woman may experience nausea and toxicosis in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. A mild degree of toxicosis in early pregnancy is treated with medication. Moderate and severe toxicosis in the 1st trimester of pregnancy is treated in a day hospital (for example, using hormonal infusion therapy).
The kidneys are now responsible for the excretion of maternal and fetal metabolic products. The uterus increases in size, which often leads to stagnant movements in the intestines - to constipation. Taste sensations change; a woman may experience nausea and toxicosis in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. A mild degree of toxicosis in early pregnancy is treated with medication. Moderate and severe toxicosis in the 1st trimester of pregnancy is treated in a day hospital (for example, using hormonal infusion therapy).
It is important that the expectant mother not only undergo examinations according to the program, but also receive support. Turning to the issue of pregnancy management in the 1st trimester in our clinic, you can count on the help of highly professional obstetrician-gynecologists, constant feedback from the doctor, and the European level of medical service.
1st trimester pregnancy management program
The plan of examinations during the 1st trimester of pregnancy was developed strictly in accordance with the regulatory documents of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and does not contain "unnecessary" examinations.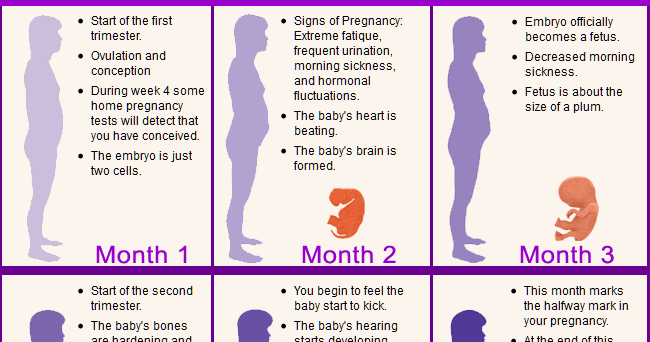
Pregnancy management program includes:
- Primary consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, as well as a follow-up consultation based on the results of examinations passed is your chief doctor and mentor. At the first consultation, the doctor examines the history of the expectant mother, gives a referral for an examination, and helps in solving the most significant issues based on the data obtained about the woman's health. Re-admission is prescribed after prenatal ultrasound and biochemical screening. The obstetrician-gynecologist registers the patient for pregnancy, fills in all the documentation, and gives recommendations.
- Physician's appointment - this doctor will help you assess your general health, predict the risks of developing the most likely diseases during pregnancy and take timely measures. This is very important, because during pregnancy a woman is strictly limited in taking medications and medicines.
- ECG (electrocardiogram) - allows you to assess the condition of the heart and identify pathologies: rhythm disturbance, blood circulation.
- Appointment of an ENT doctor - not a single woman is insured against diseases of the ear, throat and nose (colds, acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis), therefore it is important to carry out sanitation in a timely manner in order to avoid drug treatment during pregnancy.
- Ophthalmological consultation - the doctor checks the eyesight and evaluates the condition of the retina, and determines whether the woman can give birth by herself or by caesarean section. Not only childbirth can affect vision, but toxicosis and other complications of pregnancy.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder - allows you to assess the condition of internal organs, identify hidden diseases (inflammatory, urolithiasis) and neoplasms.
- Pelvic ultrasound - helps to study the anatomy of the pelvic organs, identify gynecological diseases and possible risks of complications.

- Ultrasound of the fetus (performed by a perinatologist at 11-14 weeks of pregnancy) - allows you to see for the first time during pregnancy how the baby is growing and whether everything is fine with him.
- Biochemical blood test — study of more than 15 major indicators (sugar, protein, iron, etc.).
- Complete blood count is the most important analysis, as a result of which the doctor receives the indicators of platelets, hemoglobin, erythrocytes, etc., and then can accurately assess the general condition of the expectant mother's body.
- Urinalysis - allows you to evaluate how the kidneys and urinary system work, as well as identify pathologies such as preeclampsia and eclampsia.
- Blood type - the analysis allows you to answer the question of whether there is a Rh-conflict in the blood type of mother and baby.
- Blood test for hormones is a very important test that gives an understanding of the specifics of metabolism and allows you to predict how the fetus will develop.
- Testing for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B, C is mandatory for a future mother.
- PRC-diagnostics is a laboratory analysis aimed at identifying many hidden infectious agents (from pneumonia to herpes).
- Laboratory examination of a gynecological smear — analysis of the microflora of the vagina, cervical canal, urethra reveals hidden inflammatory processes and their pathogens (gonococcus, Trichomonas)
- Biochemical screening (PAPP-A, hCG, risk calculation) is a very important examination that allows you to assess the risk of chromosomal pathology, obtain the most important indicators of fetal development, and also answer the question of whether it is advisable to prescribe invasive diagnostic methods.
- Extended coagulogram with the definition of lupus type Ab+ - allows you to assess the risk of thrombosis and bleeding, which can lead to miscarriage.
Find out more about pregnancy management at the Pirogov Clinic (St.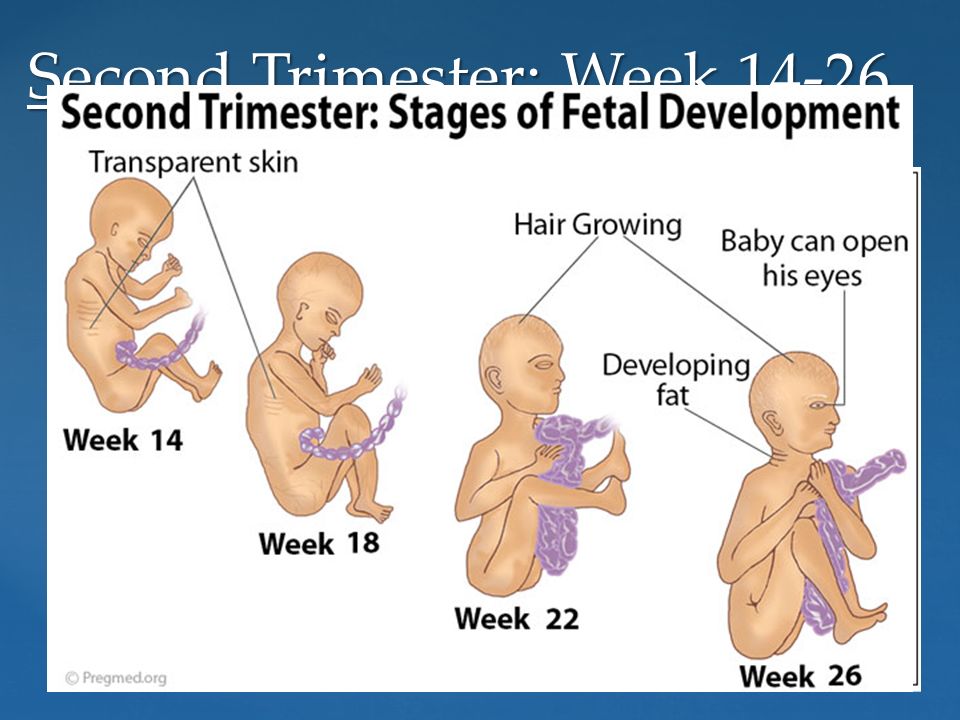 Petersburg)
Petersburg)
Pregnancy management after IVF in the 1st trimester
The pregnancy management program after IVF in the 1st trimester may be slightly different from the usual one. Firstly, the woman continues to be observed at the IVF center by a reproductologist until the period of 6-7 weeks, when the doctor can record the heartbeat of the embryo. Only after that, the expectant mother can turn to an obstetrician-gynecologist. At the first stage, the doctor decides on the advisability of supporting hormone therapy previously prescribed at the IVF center. Whenever possible, we try to either reduce additional hormonal therapy or cancel it.
Thus, monitoring of pregnancy after IVF begins at an earlier date, and the program can be adjusted depending on the characteristics of the individual case: is it a singleton or multiple pregnancy, what problems should be taken into account, etc.
Advantages of pregnancy management in our clinic
The Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics of the Pirogov Clinic on Vasilyevsky Island (St.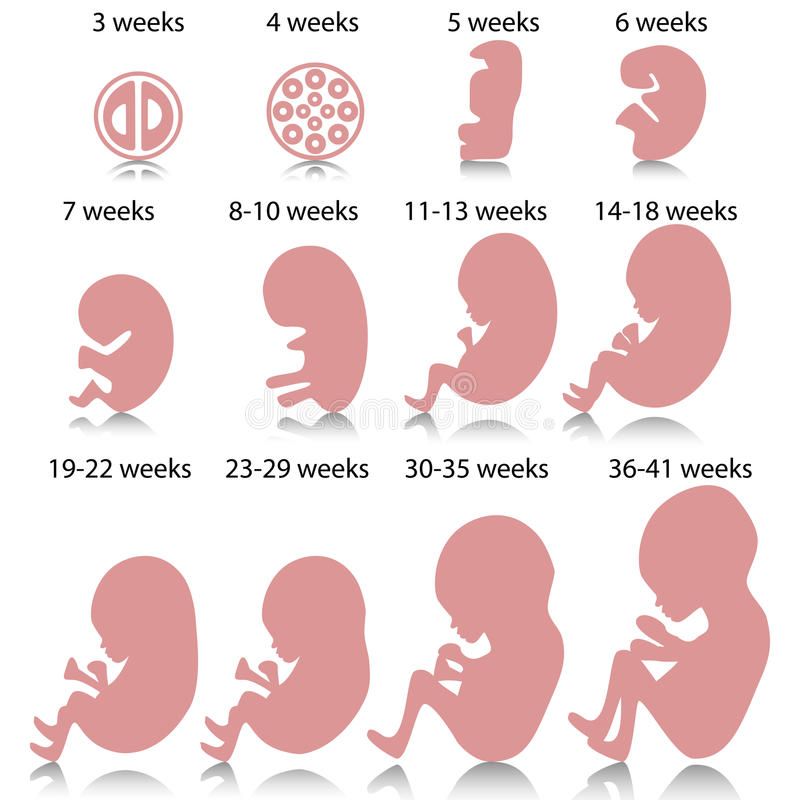 Petersburg) is in the TOP-3 best in the city according to the results of the VIII and IX rating of private clinics (2018-2019). You can view reviews on pregnancy management on our website, as well as on independent sites. Turning to us, you can be sure of the high standards of diagnostics and the professionalism of doctors. We offer our patients:
Petersburg) is in the TOP-3 best in the city according to the results of the VIII and IX rating of private clinics (2018-2019). You can view reviews on pregnancy management on our website, as well as on independent sites. Turning to us, you can be sure of the high standards of diagnostics and the professionalism of doctors. We offer our patients:
- Services of experienced, attentive and caring obstetrician-gynecologists — our specialists worked and improved their skills in clinics in Finland, France, the USA, as well as in maternity hospitals in St. Petersburg.
- Presence of own laboratory and all highly specialized doctors in one place, as well as medical offices equipped with new generation equipment. All examinations you can pass in a comfortable environment and without queues. We guarantee the reliability of the results. You do not need to come for them - we will send everything by e-mail.
- Remote video consultations of gynecologists (online).
 Fertilization normally occurs within several hours of ovulation (some authors report up to 24 hours) when a man's sperm combines with a woman's egg
Fertilization normally occurs within several hours of ovulation (some authors report up to 24 hours) when a man's sperm combines with a woman's egg
 The upper lip and nose have formed.
The upper lip and nose have formed.