Constant itching on body
10 reasons your skin itches uncontrollably and how to get relief
Diseases & conditions
- Coronavirus Resource Center
- Acne
- Eczema
- Hair loss
- Psoriasis
- Rosacea
- Skin cancer
- A to Z diseases
- A to Z videos
- DIY acne treatment
- How dermatologists treat
- Skin care: Acne-prone skin
- Causes
- Is it really acne?
- Types & treatments
- Childhood eczema
- Adult eczema
- Insider secrets
- Types of hair loss
- Treatment for hair loss
- Causes of hair loss
- Hair care matters
- Insider secrets
- What is psoriasis
- Diagnosis & treatment
- Skin, hair & nail care
- Triggers
- Insider secrets
- What is rosacea
- Treatment
- Skin care & triggers
- Insider secrets
- Types and treatment
- Find skin cancer
- Prevent skin cancer
- Raise awareness
- Español
Featured
How Natalie cleared her adult acneNatalie tried many acne products without success. Find out how a board-certified dermatologist helped Natalie see clear skin before her wedding.
JAK inhibitors are helping patients with alopecia areata, eczema/atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and vitiligo. Here’s what you need to know.
Everyday care
- Skin care basics
- Skin care secrets
- Injured skin
- Itchy skin
- Sun protection
- Hair & scalp care
- Nail care secrets
- Basic skin care
- Dry, oily skin
- Hair removal
- Tattoos and piercings
- Anti-aging skin care
- For your face
- For your skin routine
- Preventing skin problems
- Bites & stings
- Burns, cuts, & other wounds
- Itch relief
- Poison ivy, oak & sumac
- Rashes
- Shade, clothing, and sunscreen
- Sun damage and your skin
- Aprenda a proteger su piel del sol
- Your hair
- Your scalp
- Nail care basics
- Manicures & pedicures
Featured
Practice Safe SunEveryone's at risk for skin cancer. These dermatologists' tips tell you how to protect your skin.
These dermatologists' tips tell you how to protect your skin.
Find out what may be causing the itch and what can bring relief.
Darker Skin Tones
- Skin care secrets
- Hair care
- Hair loss
- Diseases & Conditions
- Acne
- Dark spots
- Dry skin
- Light spots
- Razor bumps
- Caring for Black hair
- Scalp psoriasis
- Weaves & extensions
- Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia
- Hairstyles that pull can cause hair loss
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Acne keloidalis nuchae
- Hidradenitis suppurativa
- Keloid scars
- Lupus and your skin
- Sarcoidosis and your skin
- Skin cancer
- Vitiligo
- More diseases & conditions
Featured
Fade dark spotsFind out why dark spots appear and what can fade them.
If you have what feels like razor bumps or acne on the back of your neck or scalp, you may have acne keloidalis nuchae. Find out what can help.
Cosmetic treatments
- Your safety
- Age spots & dark marks
- Cellulite & fat removal
- Hair removal
- Scars & stretch marks
- Wrinkles
- Younger-looking skin
Featured
Laser hair removalYou can expect permanent results in all but one area. Do you know which one?
Do you know which one?
If you want to diminish a noticeable scar, know these 10 things before having laser treatment.
BotoxIt can smooth out deep wrinkles and lines, but the results aren’t permanent. Here’s how long botox tends to last.
Public health programs
- Skin cancer awareness
- Free skin cancer screenings
- Kids' camp
- Good Skin Knowledge
- Shade Structure grants
- Skin Cancer, Take a Hike!™
- Awareness campaigns
- Flyers & posters
- Get involved
- Lesson plans and activities
- Community grants
Featured
Free materials to help raise skin cancer awarenessUse these professionally produced online infographics, posters, and videos to help others find and prevent skin cancer.
Free to everyone, these materials teach young people about common skin conditions, which can prevent misunderstanding and bullying.
Find a dermatologist
- Find a dermatologist
- What is a dermatologist?
- FAAD: What it means
- How to select a dermatologist
- Telemedicine appointments
- Prior authorization
- Dermatologists team up to improve patient care
Featured
Find a DermatologistYou can search by location, condition, and procedure to find the dermatologist that’s right for you.
A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating the skin, hair, and nails. Dermatologists care for people of all ages.
How to relieve itchy skin
Diseases & conditions
- Coronavirus Resource Center
- Acne
- Eczema
- Hair loss
- Psoriasis
- Rosacea
- Skin cancer
- A to Z diseases
- A to Z videos
- DIY acne treatment
- How dermatologists treat
- Skin care: Acne-prone skin
- Causes
- Is it really acne?
- Types & treatments
- Childhood eczema
- Adult eczema
- Insider secrets
- Types of hair loss
- Treatment for hair loss
- Causes of hair loss
- Hair care matters
- Insider secrets
- What is psoriasis
- Diagnosis & treatment
- Skin, hair & nail care
- Triggers
- Insider secrets
- What is rosacea
- Treatment
- Skin care & triggers
- Insider secrets
- Types and treatment
- Find skin cancer
- Prevent skin cancer
- Raise awareness
- Español
Featured
How Natalie cleared her adult acneNatalie tried many acne products without success. Find out how a board-certified dermatologist helped Natalie see clear skin before her wedding.
Find out how a board-certified dermatologist helped Natalie see clear skin before her wedding.
JAK inhibitors are helping patients with alopecia areata, eczema/atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and vitiligo. Here’s what you need to know.
Everyday care
- Skin care basics
- Skin care secrets
- Injured skin
- Itchy skin
- Sun protection
- Hair & scalp care
- Nail care secrets
- Basic skin care
- Dry, oily skin
- Hair removal
- Tattoos and piercings
- Anti-aging skin care
- For your face
- For your skin routine
- Preventing skin problems
- Bites & stings
- Burns, cuts, & other wounds
- Itch relief
- Poison ivy, oak & sumac
- Rashes
- Shade, clothing, and sunscreen
- Sun damage and your skin
- Aprenda a proteger su piel del sol
- Your hair
- Your scalp
- Nail care basics
- Manicures & pedicures
Featured
Practice Safe SunEveryone's at risk for skin cancer. These dermatologists' tips tell you how to protect your skin.
These dermatologists' tips tell you how to protect your skin.
Find out what may be causing the itch and what can bring relief.
Darker Skin Tones
- Skin care secrets
- Hair care
- Hair loss
- Diseases & Conditions
- Acne
- Dark spots
- Dry skin
- Light spots
- Razor bumps
- Caring for Black hair
- Scalp psoriasis
- Weaves & extensions
- Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia
- Hairstyles that pull can cause hair loss
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Acne keloidalis nuchae
- Hidradenitis suppurativa
- Keloid scars
- Lupus and your skin
- Sarcoidosis and your skin
- Skin cancer
- Vitiligo
- More diseases & conditions
Featured
Fade dark spotsFind out why dark spots appear and what can fade them.
If you have what feels like razor bumps or acne on the back of your neck or scalp, you may have acne keloidalis nuchae. Find out what can help.
Cosmetic treatments
- Your safety
- Age spots & dark marks
- Cellulite & fat removal
- Hair removal
- Scars & stretch marks
- Wrinkles
- Younger-looking skin
Featured
Laser hair removalYou can expect permanent results in all but one area.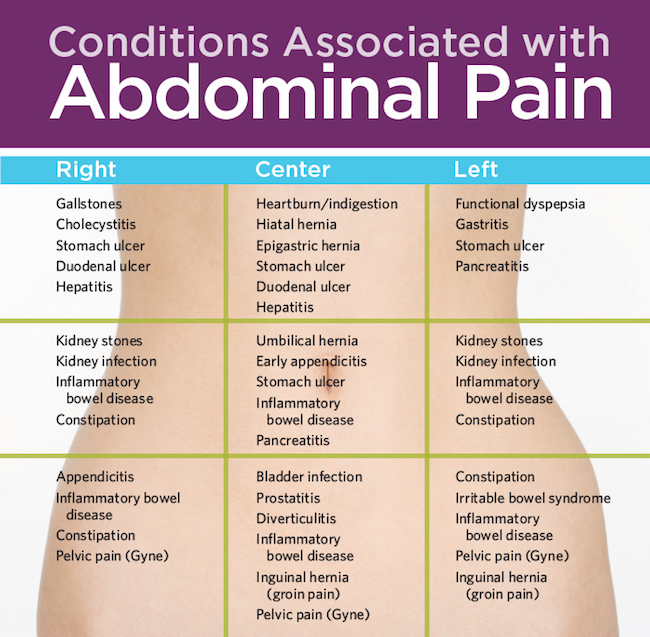 Do you know which one?
Do you know which one?
If you want to diminish a noticeable scar, know these 10 things before having laser treatment.
BotoxIt can smooth out deep wrinkles and lines, but the results aren’t permanent. Here’s how long botox tends to last.
Public health programs
- Skin cancer awareness
- Free skin cancer screenings
- Kids' camp
- Good Skin Knowledge
- Shade Structure grants
- Skin Cancer, Take a Hike!™
- Awareness campaigns
- Flyers & posters
- Get involved
- Lesson plans and activities
- Community grants
Featured
Free materials to help raise skin cancer awarenessUse these professionally produced online infographics, posters, and videos to help others find and prevent skin cancer.
Free to everyone, these materials teach young people about common skin conditions, which can prevent misunderstanding and bullying.
Find a dermatologist
- Find a dermatologist
- What is a dermatologist?
- FAAD: What it means
- How to select a dermatologist
- Telemedicine appointments
- Prior authorization
- Dermatologists team up to improve patient care
Featured
Find a DermatologistYou can search by location, condition, and procedure to find the dermatologist that’s right for you.
A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating the skin, hair, and nails. Dermatologists care for people of all ages.
Skin itching as a symptom of diseases of internal organs and skin
Types of itching
In the literature, the term “itch” is understood as a sensation that causes a purposeful scratching reflex. In the scientific literature, itching is also referred to by the term "pruritus" (from the Latin prūrio - to scratch). Often, this phenomenon is one of the first symptoms of not only skin, but also internal diseases, diseases of the nervous system, hormonal disorders, and even tumors. That is why itching is currently regarded as an "interdisciplinary symptom" and in some cases even isolated as a separate disease.
Allocate general (generalized) and local (localized) pruritus. Acute generalized - more often it is a consequence of food, drug allergies, reactions to cold, heat, etc. Often, generalized pruritus is a symptom of serious illnesses: diabetes mellitus, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, malignant neoplasms, etc.
Often, generalized pruritus is a symptom of serious illnesses: diabetes mellitus, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, malignant neoplasms, etc.
Localized itching occurs most often in the scalp and anogenital zone and is paroxysmal in nature. The reasons for the development of this phenomenon in the anal region, as a rule, are considered chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, infections, incl. helminthic invasions, etc. Long-term sensations are often complicated by the development of a bacterial infection, candidiasis. Localized itching is also observed in the area of rashes in various skin diseases: psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, etc.
Frequency of pruritus in skin and systemic diseases
| Diagnosis | Frequency | |
| Atopic dermatitis | main symptom, in 100% of cases | |
| Psoriasis | 77-84% | |
| Herpes zoster/postherpetic neuralgia | 58%/30% | |
| Chronic kidney disease/dialysis | 22% | |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | 80% | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 3% | |
| Hyperthyroidism | 4-7. 5% 5% | |
| Anorexia | 58% | |
| Polycythemia vera | 48% | |
| Hodgkin's lymphoma | 25-35% |
Itching that persists for more than 6 weeks is defined as chronic. Its frequency among the adult population is, according to studies, 8-9%. Chronic phenomena are observed in various skin diseases (atopic dermatitis / neurodermatitis, eczema, prurigo, psoriasis, etc.) and systemic diseases.
Itching in various skin diseases
| Diseases often accompanied by itching | Diseases rarely associated with itching | |
| Inflammatory dermatoses: atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, eczema, lichen planus, prurigo, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, mastocytosis, Gibert's lichen, urticaria | Inflammatory dermatoses: scleroderma and lichen sclerosus, Devergy's disease | |
| Infectious dermatoses: viral infections, impetigo, pediculosis, scabies | Genodermatoses: Darier disease, Hailey-Hailey disease | |
Autoimmune dermatoses: bullous dermatoses, incl. dermatitis herpetiformis Dühring dermatitis herpetiformis Dühring | Tumors: B-cell lymphoma of the skin, basalioma, squamous cell skin cancer | |
| Tumors: T-cell lymphoma of the skin | Other conditions: scars |
Mechanism of pruritus development
Mechanisms of pruritus development in chronic kidney disease are not fully understood. The role of metabolic disorders is assumed, as well as the involvement of opioid receptors in the process and increased dryness of the skin. Itching develops, as a rule, after 2-3 months. after the start of hemodialysis, in 25-50% of cases it is generalized, in other cases it is localized. As a rule, itching is most pronounced in the back and face.
In diseases of the liver, itching is a very common symptom (observed in 80% of cases of cirrhosis of the liver, in 15% of all cases of viral hepatitis C). As a rule, it begins in the area of the palms and soles, as well as in the area of \u200b\u200bfriction of clothing. It is characterized by its intensification at night. Over time, itching takes on a generalized character, while scratching the skin brings almost no relief.
It is characterized by its intensification at night. Over time, itching takes on a generalized character, while scratching the skin brings almost no relief.
In case of endocrine pathology, such as diabetes mellitus and hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands, itching may be accompanied by a burning sensation, stinging, “crawling”. The lack of vitamin D, minerals, iron also in some cases leads to the development of this phenomenon. With iron deficiency, “aquagenic itching” (on contact with water) is often observed. As a rule, the restoration of normal levels of iron and minerals leads to the disappearance of any sensations within 2 weeks from the start of therapy.
Itching can be one of the symptoms of tumors and blood diseases. As possible mechanisms of its occurrence, toxic effects, allergic reactions to tumor components, as well as a direct irritant effect on the nerves and the brain (in case of brain tumors) are assumed.
Systemic diseases that may be accompanied by itching
- Metabolic and endocrinological disorders: chronic renal failure, liver disease, diseases of the thyroid and parathyroid glands, iron deficiency.

- Infectious diseases: HIV infection, parasitosis and helminthic infestations.
- Blood diseases: polycythemia vera, myelodysplastic syndrome, lymphoma.
- Neurological diseases: multiple sclerosis, neuropathy, tumors of the brain and spinal cord, postherpetic neuralgia.
- Psychosomatic and psychiatric disorders: depression, eating disorders, bipolar disorders.
Itching, its causes and treatments
Itching often becomes one of the main symptoms of many diseases - sometimes ordinary dry skin, or - a symptom of severe oncological diseases, often causing insomnia and psycho-emotional discomfort of a person.
Many patients evaluate the severity of their disease by the intensity of itching, and not by the severity of skin manifestations.
Despite numerous studies, the mechanisms of pruritus remain largely unclear. Previously, itching was considered as a special form of pain, but at present, most scientists are of the opinion that itching is an independent sensation. This is supported, for example, by the fact that itching can be caused only in the superficial layers of the skin, corneal mucosa and mucous membranes bordering the skin, while pain occurs in various organs and parts of the body. In addition, you can cause any degree of itching without pain and vice versa.
This is supported, for example, by the fact that itching can be caused only in the superficial layers of the skin, corneal mucosa and mucous membranes bordering the skin, while pain occurs in various organs and parts of the body. In addition, you can cause any degree of itching without pain and vice versa.
Types of itching
Based on modern concepts of the mechanisms of itching, 4 types of itching are distinguished:
-
Pruritoceptive pruritus occurs when the skin becomes inflamed, damaged, or dry (itching from scabies, urticaria, insect bites).
-
Neuropathic pruritus occurs with damage to the nervous system and is often associated with sensory disorders (eg, brain tumors).
-
Neurogenic is called itching that occurs without signs of damage to the structures of the nervous system (for example, itching with bile stasis).
-
A special form is psychogenic itching - severe, prolonged, not accompanied by any skin diseases.
 The basis of this state is, as a rule, a depressed emotional state.
The basis of this state is, as a rule, a depressed emotional state.
It should be noted that the nature of itching in different diseases is different. So, for example, with atopic dermatitis, numerous scratching is formed, and with urticaria, on the contrary, despite intense itching, scratching is usually not observed. Itching with scabies tends to get worse in the evening and at night. Herpes patients describe their itching as a burning sensation, and aquatic itching (on contact with water) is characterized by a tingling sensation.
Treatments for pruritus
General recommendations for patients with pruritus include a diet free from spicy, salty foods, coffee and alcohol, avoidance of overheating and contact with hot water, irritating fabrics and chemicals (washing powders, cleaning products, etc.) , as well as alkaline soaps that increase dryness of the skin. Regularly (up to several times a day) it is recommended to apply moisturizers (based on petroleum jelly or glycerin) and coolants (for example, menthol cream) to itchy areas. In inflammatory processes of the skin, local steroids are used, as well as the latest non-hormonal agents - calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus), which have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effect and, unlike hormonal agents, do not cause such undesirable side effects as, for example, atrophy ( thinning) of the skin.
In inflammatory processes of the skin, local steroids are used, as well as the latest non-hormonal agents - calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus), which have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effect and, unlike hormonal agents, do not cause such undesirable side effects as, for example, atrophy ( thinning) of the skin.
However, the success of itch therapy largely depends on the ability to eliminate the conditions that caused it. Specialists of the Department of Dermatovenereology of EMC pay special attention to this problem. During the treatment, the patient is offered a detailed examination according to the protocol of the AWMF-Leitlinie (Association of Scientific Medical Societies in Germany e.V.). The experience of highly qualified doctors helps to identify the causes of itching, which, combined with a comprehensive, individually selected treatment, allows you to achieve maximum results in therapy; an important factor is also the use of a wide range of possibilities and methods of examination - both laboratory and instrumental.
In case of intense itching, specialists prescribe oral antihistamines. They reduce the increase in capillary permeability caused by histamine, tissue swelling and itching. The most modern drugs - II and III generations - have a long-term effect and almost do not cause side effects from the nervous system (lethargy, drowsiness, etc.).
Antihistamines are most effective for urticaria, atopic dermatitis, but they can also be used for itching of other origins. In severe cases that cannot be treated with antihistamines, drugs are used to reduce nervous excitability - antidepressants, neuroleptics, etc.
In recent years, a large number of reports have appeared in foreign literature about the successful use of anticonvulsants (gabapentin, pregabalin) in chronic itching. The most effective use of this group of drugs for brachioradial, senile (senile) and neuropathic itching.
For cholestatic pruritus resulting from bile stasis, cholestyramine is used, the action of which is to absorb bile acids.