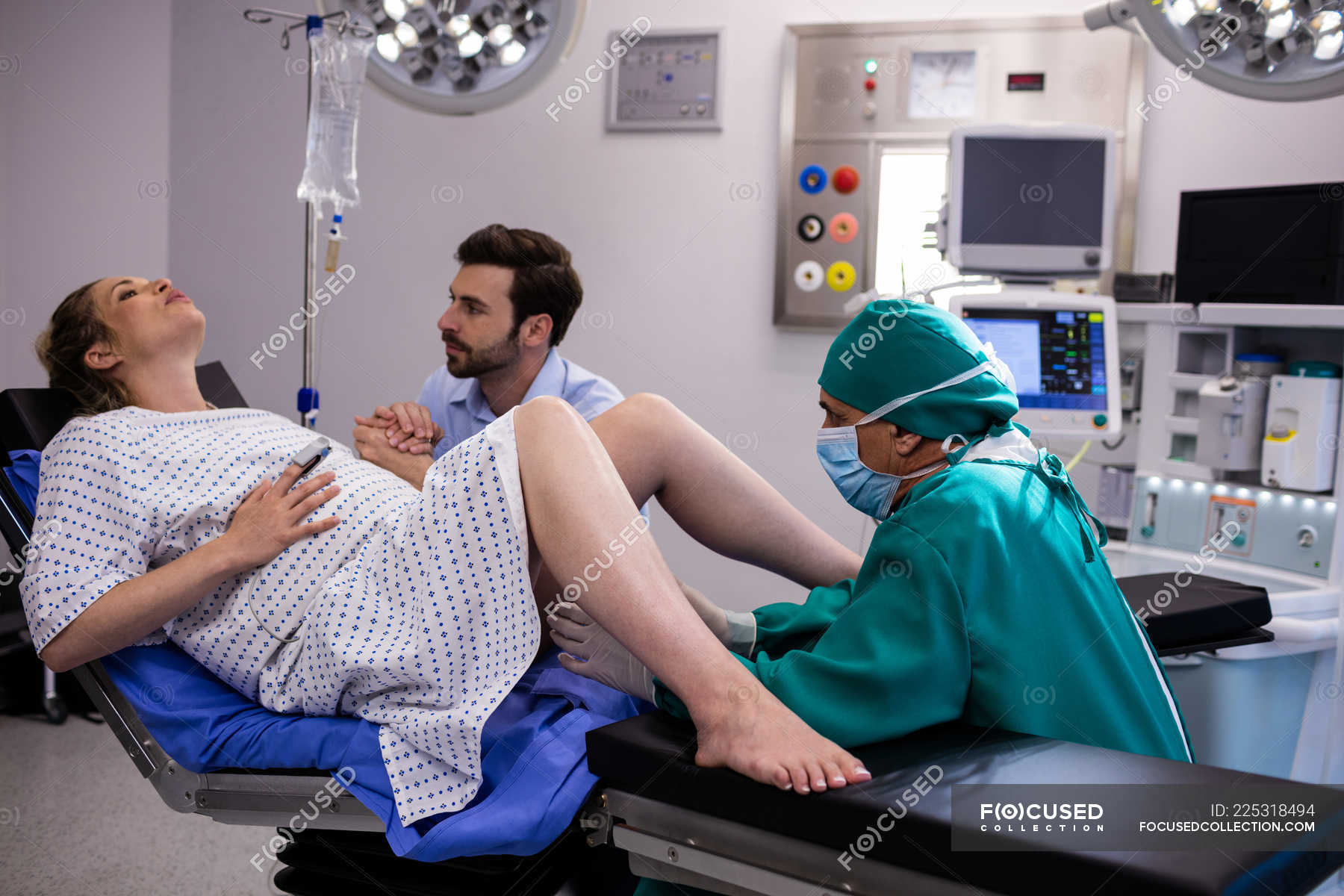
How many months premature can a baby survive
the long-term impacts of being born extremely early
- NEWS FEATURE
Babies born before 28 weeks of gestation are surviving into adulthood at higher rates than ever, and scientists are checking in on their health.
- Amber Dance0
- Amber Dance
-
Amber Dance is a freelance journalist in Los Angeles, California.
View author publications
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
-
They told Marcelle Girard her baby was dead.
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
199,00 € per year
only 3,90 € per issue
Learn more
Rent or buy this article
Get just this article for as long as you need it
$39.95
Learn more
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 582, 20-23 (2020)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-01517-z
References
Soll, R. & Özek, E. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000511 (1997).
Article Google Scholar
Soll, R. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001149 (1998).
Article Google Scholar
British Association of Perinatal Medicine. Perinatal Management of Extreme Preterm Birth Before 27 Weeks of Gestation: A BAPM Framework for Practice (BAPM, 2019).
Google Scholar
Crump, C., Winkleby, M. A., Sundquist, J. & Sundquist, K. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 322, 1580–1588 (2019).
Article Google Scholar
O’Reilly, H., Johnson, S., Ni, Y., Wolke, D. & Marlow, N. Pediatrics 145, e20192087 (2020).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Garfield, C. F. et al. JAMA Pediatr. 171, 764–770 (2017).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Saigal, S. et al. Pediatrics 118, 1140–1148 (2006).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gire, C. et al. Arch. Dis. Child. 104, 333–339 (2018).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bolton, C. E. et al. J. Pediatr. 161, 595–601.e2 (2012).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Doyle, L. W. et al. Thorax 72, 712–719 (2017).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Halkerwal, A. et al. Hypertension 75, 211–217 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Flahault, A. et al. Hypertension 75, 796–805 (2020).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ley, D. et al. J. Pediatr.
 206, 56–65.e8 (2019).
206, 56–65.e8 (2019).Article PubMed Google Scholar
Stalh, A. et al. Lancet 394, 1551–1559 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Härkin, P. et al. J. Pediatr. 177, 72–77.e2 (2016).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Vohr, B. et al. J. Pediatr. 185, 42–48.e1 (2017).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Liu, Y. et al. J. Pediatr. 200, 91–97.e3 (2018).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Download references
-
Could baby’s first bacteria take root before birth?
-
The brain, interrupted
-
Insomnia linked to premature birth in study of 3 million mothers
Subjects
- Medical research
- Health care
- Physiology
Latest on:
Jobs
-
Postdoctoral Research Scientist
The Vasan Lab at the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center seeks a postdoctoral candidate.
 Our laboratory specializes in breast cancer, with a...
Our laboratory specializes in breast cancer, with a...New York City, New York (US)
Columbia University Irving Medical Center
-
Director of Research in Photon Science
For our location in Hamburg we are seeking: Director of Research in Photon Science Starting date: prefered January 2024 | ID: FSDIR/2023 | Deadline...
Hamburg (DE)
DESY
-
Organoid Director, Assistant Professor of Research
Weill Cornell Medicine is actively seeking an Assistant Professor of Research. In this position, you will lead the Organoid team.
New York City, New York (US)
Weill Cornell Medicine
Premature birth statistics | Tommy's
Tommy's PregnancyHub
A preterm birth is one that happens before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Globally, more than 1 in 10 pregnancies will end in preterm birth.
Globally, more than 1 in 10 pregnancies will end in preterm birth.
A preterm birth is one that happens before 37 completed weeks of pregnancy.
The World Health Organisation gives the following definitions for the different stages of preterm birth:
- Extremely preterm: before 28 weeks
- Very preterm: from 28 to 31 weeks
- Moderate to late preterm: from 32 to 37 weeks.
General UK premature birth statistics
- Around 8% of births in the UK are preterm. That is around 60,000 babies each year.
- This is higher than many countries in Europe and higher than Cuba and Iran
Of the births that were preterm in the UK:
- 5% were extremely preterm (before 28 weeks)
- 11% were very preterm (between 28 and 32 weeks)
- 85% were moderately preterm (between 32 and 37 weeks).
In 2019, live births where gestational age was under 24 weeks increased to 0. 15% compared with 0.13% in 2018 and 0.11% in 2010.
15% compared with 0.13% in 2018 and 0.11% in 2010.
Chances of survival following preterm birth
Medical advances mean that we are getting better at treating preterm babies but the chances of survival still depend on gestational age (week of pregnancy) at time of birth.
- Less than 22 weeks is close to zero chance of survival
- 22 weeks is around 10%
- 24 weeks is around 60%
- 27 weeks is around 89%
- 31 weeks is around 95%
- 34 weeks is equivalent to a baby born at full term.
Preterm birth and neonatal death
Complications arising from premature birth is the leading cause of neonatal death (death in the first few weeks after birth) in the UK.
Preterm birth and multiple pregnancies
Having more than one baby is a risk factor for preterm birth. On average, most singleton pregnancies last 39 weeks, twin pregnancies 37 weeks and triplets 33 weeks.
- Risk of prematurity with singleton pregnancy: 7%
- Risk of prematurity with multiple pregnancy: 57%
Risk of disability in preterm children
Generally, the earlier the birth, the higher the risk of problems. However these are only statistics and cannot predict how an individual child will do; some extremely premature babies do very well and develop into healthy children.
However these are only statistics and cannot predict how an individual child will do; some extremely premature babies do very well and develop into healthy children.
- 1 in 10 of all premature babies will have a permanent disability such as lung disease, cerebral palsy, blindness or deafness.
- 1 in 2 of premature babies born before 26 weeks of gestation will have some sort of disability (this includes mild disability such as requiring glasses).
In one study of 241 children born before 26 weeks' gestation the following was found:
- 22% severe disability (eg cerebral palsy + not walking, low cognitive scores, blindness, profound deafness)
- 24% moderate disability (eg cerebral palsy + walking, IQ/cognitive scores in the special needs range, lesser degree of visual or hearing impairment)
- 34% mild disability (defined as low IQ/cognitive score, squint, requiring glasses)
- 20% no problems.
Preterm birth by ethnicity
The risk of preterm birth is highest for Black Caribbean women and lowest for White British and White Other.
- Bangladeshi: 8%
- Indian: 7%
- Pakistani:7%
- Black African: 8%
- Black Caribbean: 10%
- White British: 7%
- White Other: 6%
Causes of preterm birth
In some cases a cause of preterm birth can be shown but more often it is unknown or unclear.
In 1 in 4 preterm births, the birth is planned (induced labour or c-section) to save the life of mother or baby from pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia, fetal growth restriction, waters breaking early (PPROM) or infection
Preventing premature birth
Too often health professionals are not able to tell women why they have had a premature birth. This area of research is underfunded, with many taking an unhelpful (and unique to pregnancy) approach of ‘It was not meant to be’.
Research into why premature birth happens is the only way we can save lives and prevent future loss. Tommy's funds more than £400k of research into premature birth every year. We are focused on predicting early which women will have a premature birth and treating them to prevent it happening.
We are focused on predicting early which women will have a premature birth and treating them to prevent it happening.
Read about our research into prematurity here.
Back to top
Can a premature baby grow up healthy? Who is to blame for preterm birth? And what do you need to know about vaccinating such children? Answering important questions about preterm babies
Fetus at 8 weeks
BSIP / UIG / Getty Images
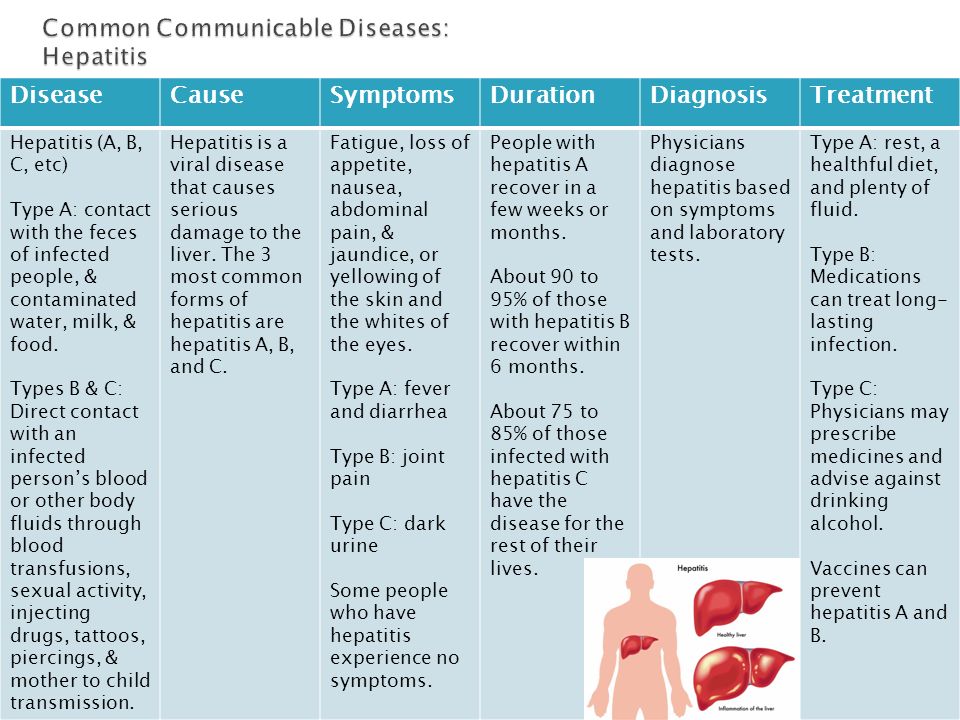
Premature babies weighing over 500 grams are being nursed in Russia. Their parents are often very worried: whether the child will be healthy, what is happening in general, what to look for after discharge, and what are the restrictions. At the same time, people around may not support their parents at all and even condemn the mother for the fact that she is supposedly to blame for what happened. We decided to help such parents and their loved ones by answering important questions about premature babies.
When should a baby be born to be called premature?
Up to 37 weeks (usually a normal pregnancy lasts 40 weeks). More precisely, up to 36 weeks and 6 days, counting from the first day of the last menstruation.
The lower bound is much more complicated. In Russia, a child can be registered when at the same time:
- the pregnancy is 22 weeks or more;
- The baby's birth weight is 500 grams or more (when weighed within the first hour after birth; this does not apply to multiple births) or if the baby's birth weight is unknown, the body length is 25 centimeters or more.
If one of these criteria is not met, but the child lives 168 hours, then they can also be registered. In other cases, a birth certificate is not issued.
But a child can be born and still not be alive. Therefore, official signs of live birth have also been approved: in addition to the birth itself, the presence of four signs of live birth (heartbeat, spontaneous breathing, umbilical cord pulsation or voluntary movement of the limbs) is important, while the most important sign is the presence of a heartbeat, notes the chief freelance neonatologist of the Ministry of Health in the North Caucasus Federal District Alexey Mostovoy, Head of the Department of Resuscitation and Intensive Care of Newborns of the Kaluga Regional Clinical Hospital. If none of these signs are present, the child can be considered stillborn.
If none of these signs are present, the child can be considered stillborn.
Even if a child does not meet the registration criteria, doctors can still resuscitate and move to an incubator, providing warmth, nutrition, pain relief, mechanical ventilation and other supportive care. Then the child can survive and live those same 168 hours to get a birth certificate. But in reality, such children rarely survive. “If a child who does not meet the criteria for a live birth survives, this is a case that is described in specialized medical publications, and the regular press often writes about this,” says the Deputy Chief Physician for Obstetric and Gynecological Care of the City Clinical Hospital. F. I. Inozemtseva Sergey Apresyan. “That is, it happens, but as an extraordinary event.”
Strict criteria cause problems
Such strict registration criteria and signs of live birth are often criticized. At least because in practice this leads to rather strange situations: “The legal status of such children [who do not meet the signs of live birth] is still not defined - in the first seven days of life, they, according to the letter of the law, are neither live-born nor stillborn, - says the legal adviser on medical law, the founder of the company "Faculty of Medical Law" Polina Gabay. - <...> I read the decision of one court of appeal, which recognized a child who lived for several days in intensive care as unborn, because he, I quote: "Did not meet certain anthropometric parameters." I don’t even know who then, according to the court, was lying in the couveuse? It is known from the circumstances of the case that his weight was 20 grams less than that established by the birth criteria.”
- <...> I read the decision of one court of appeal, which recognized a child who lived for several days in intensive care as unborn, because he, I quote: "Did not meet certain anthropometric parameters." I don’t even know who then, according to the court, was lying in the couveuse? It is known from the circumstances of the case that his weight was 20 grams less than that established by the birth criteria.”
The World Health Organization (WHO) generally does not offer any strict criteria for determining a live birth. Her position is as follows: a child is recognized as live born regardless of the gestational age - the main thing is that he breathes or shows other signs of life, for example, a heartbeat. “The WHO recommendations on keeping statistics, which serve the sole purpose of standardizing data collection around the world, have been turned by officials into legal criteria that determine the status of a newborn child,” writes Diana Mustafina-Bredikhina, Senior Lecturer at Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia. “<...> The presence in the law of the lower limit of the live birth count has a strange effect on the investigative authorities, which have recently begun to initiate criminal cases more often, prosecuting doctors for the “deliberate murder” of premature babies with extremely low body weight.”
“<...> The presence in the law of the lower limit of the live birth count has a strange effect on the investigative authorities, which have recently begun to initiate criminal cases more often, prosecuting doctors for the “deliberate murder” of premature babies with extremely low body weight.”
In the UK and the US, when talking about how doctors should behave, doctors recommend focusing on prognosis. For children born before 22 weeks, it is very bad, so in such cases it is usually not even advised to start resuscitation, believing that it is more humane not to conduct active resuscitation. At a later date, it is advised to discuss this issue with parents. In such cases, the risk of death is also high, as is the risk of serious disorders in the development of the nervous system, so it is important to take their opinion into account. If they refuse resuscitation, then the child is provided with palliative care. In Russia, this is almost impossible: if a live birth is recorded, resuscitation must be carried out, refusing it is contrary to federal law.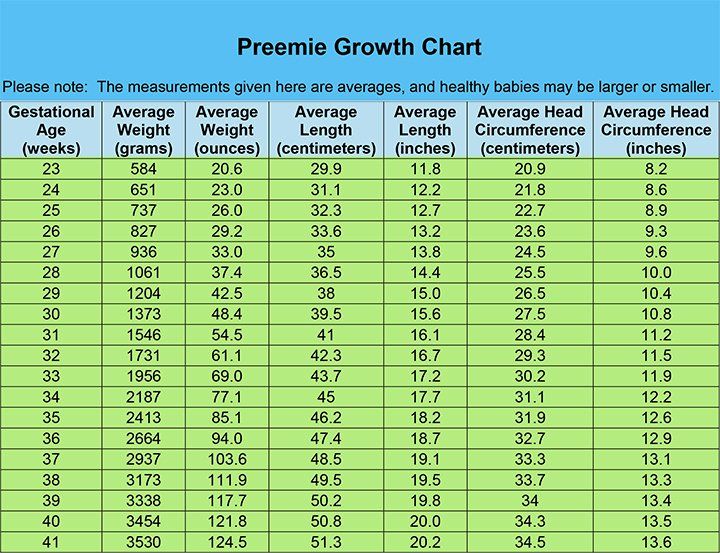
Nine weeks
BSIP / Alamy / Vida Press
What happens to premature babies and their parents immediately after birth?
You need to prepare for the fact that immediately after the birth, and for a long time after, there will be a lot of uncertainty. It can even shock how a child looks.
“People who have not seen our children sometimes think that these are three-kilogram pink baby dolls, only small ones,” explains Elina Sushkevich, an anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the neonatal intensive care unit of the Regional Perinatal Center of the Kaliningrad Region. In fact, such children have very thin delicate skin through which blood vessels are visible and which poorly performs its barrier functions, that is, it only protects against dangerous bacteria and viruses. These children have little subcutaneous fat, so they look very fragile and emaciated. They lack some reflexes at birth, and it is difficult for a baby born before the 35th week to coordinate sucking and swallowing.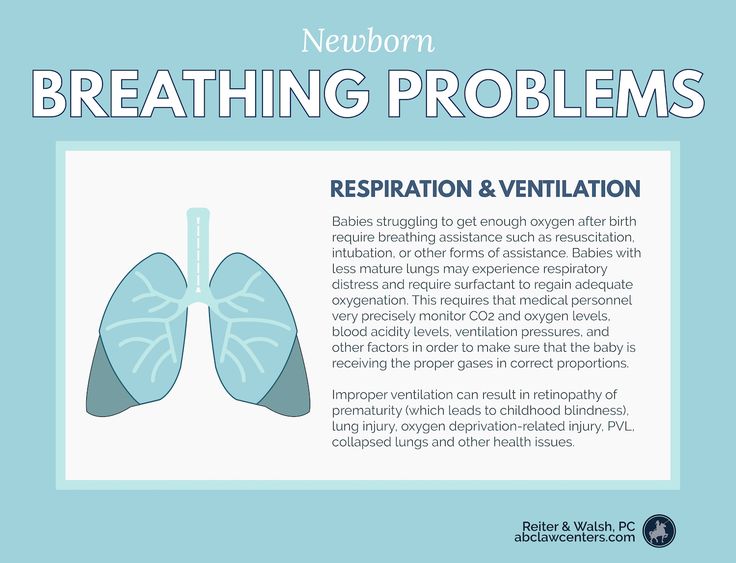 “Anatomically formed organ systems do not have the proper functionality and do not fully cope with the conditions of extrauterine life,” writes Olga Evseichik, a pediatrician at the Rassvet Clinic, in response to a question from Meduza.
“Anatomically formed organ systems do not have the proper functionality and do not fully cope with the conditions of extrauterine life,” writes Olga Evseichik, a pediatrician at the Rassvet Clinic, in response to a question from Meduza.
“I would not recommend looking for any information on the survival rate, disability of a child,” writes Natalya Vasilyeva, a pediatrician and chief physician of the Rassvet children’s clinic, in response to a question from Meduza. “It can turn out to be false both positively and negatively.” “For such children, everything can change at any moment, both for the better and for the worse,” writes Olga Evseichik. “It’s impossible to predict this, and it’s not even always possible to explain changes after the fact.”
“In the first place [among the causes of death of premature babies] are severe congenital infections and related complications: necrotizing enterocolitis, intracranial hemorrhages,” writes Alexey Mostovoy.
Other causes include respiratory distress syndrome and congenital abnormalities.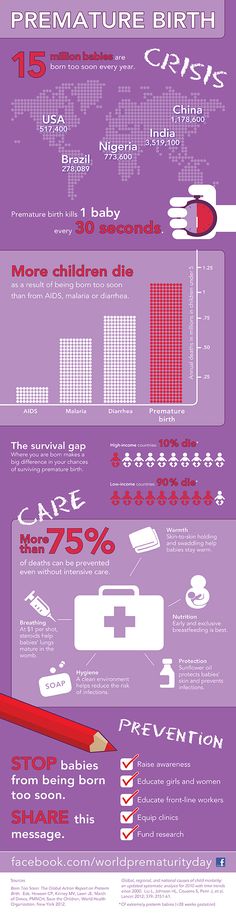 According to American data, out of 1000 children born before the 28th week of pregnancy, 625 will survive, from the 28th to the 31st week - 964, from the 32nd to the 33rd week - 984, from the 34th to the 36th th week - 993. According to Alexey Mostovoy, such all-Russian statistics are not kept. However, on average, as far as is known, the figures are comparable to those in other developed countries. On the other hand, a lot depends on the level of the clinic, and this indicator can vary greatly from region to region.
According to American data, out of 1000 children born before the 28th week of pregnancy, 625 will survive, from the 28th to the 31st week - 964, from the 32nd to the 33rd week - 984, from the 34th to the 36th th week - 993. According to Alexey Mostovoy, such all-Russian statistics are not kept. However, on average, as far as is known, the figures are comparable to those in other developed countries. On the other hand, a lot depends on the level of the clinic, and this indicator can vary greatly from region to region.
However, in order to make a prediction for a particular child, it is not enough to know only the date on which he was born.
If you do not have enough information about what is happening, Natalya Vasilyeva recommends asking questions to doctors. “It often turns out that the words “they don’t tell us anything” mean “yes, we didn’t ask anything,” the expert explains.
Perhaps in this difficult time you should seek support from a psychologist. This can be done online or by phone - for example, by contacting the hotline of the Right to a Miracle charity fund for helping premature babies (8 800 555 2924). On other important issues, for example, regarding financial assistance or legal support, they can also advise there. There are also foreign non-profit organizations whose websites have a lot of supportive and useful materials (for example, Tommyʼs and Bliss).
On other important issues, for example, regarding financial assistance or legal support, they can also advise there. There are also foreign non-profit organizations whose websites have a lot of supportive and useful materials (for example, Tommyʼs and Bliss).
Can a premature baby grow up healthy?
It is possible, but a lot depends on how old he was born, how much he weighed at birth, what diseases he had initially, and also what resources the medical organization he was in had.
The main negative consequences that premature babies have are cerebral palsy, cognitive impairment, visual and hearing impairments. The lower the weight and term of delivery, the more likely such consequences are. Therefore, if there is a threat of preterm birth, they try to push them back by various methods for at least a few days: this in itself improves the prognosis for the child, and makes it possible to use drugs that help the child quickly adapt to life outside the uterus. But even in extremely premature babies (born before the 28th week) there is a chance for the absence of all these disorders.
At school age, those who were born prematurely have a higher risk of becoming overweight and obese. In adulthood, the development of insulin resistance, high blood pressure, coronary heart disease and some other diseases. But, in fact, one can talk about some predictions only with the proviso that now the long-term consequences are visible in children who were born prematurely many years ago, when medical specialists had fewer tools. What the exact prognosis for children born now is is unclear.
Is it true that babies are born prematurely because the mother smoked or drank during pregnancy? What generally influences it?
Many circumstances can lead to preterm birth, including uncontrollable, unpredictable and unknown. Unidentified causes are responsible for most preterm births. And far from always, even known risk factors have a significant impact on their own - their combination can lead to preterm birth.
It is now believed that the risk of preterm birth is negatively increased by, for example, the following factors:
- smoking;
- pregnancy as a result of in vitro fertilization.
 This is largely due to the fact that in such cases, pregnancy is more often multiple, and twins and triplets tend to be born prematurely. That is why modern recommendations are changing, and now in most cases it is advised to transfer only one embryo into the uterine cavity at a time;
This is largely due to the fact that in such cases, pregnancy is more often multiple, and twins and triplets tend to be born prematurely. That is why modern recommendations are changing, and now in most cases it is advised to transfer only one embryo into the uterine cavity at a time; - pregnancy within 18 months of childbirth;
- age of mother - risks are higher if the woman is younger than 17 and older than 35;
- diabetes mellitus and certain other chronic diseases;
- preeclampsia. In this condition, a woman's blood pressure rises, which does not cause symptoms, but can be detected at the reception (while, of course, not every increase in pressure is a sign of preeclampsia). The danger is that the condition can be complicated by swelling, severe headache, vision problems, and then, in some women, seizures, stroke, and other severe and life-threatening conditions. In this case, doctors may perform a caesarean section or induce labor even if the pregnancy is less than 37 weeks because it is safer for both mother and baby.

As for stress, it may slightly increase the risk of preterm birth. However, this cannot be said with certainty: conducting research is complicated by the fact that almost everyone experiences stressful events. And at what stage of pregnancy they can at least theoretically have a negative effect, it is not clear.
11 weeks
BSIP / Alamy / Vida Press
How to prevent preterm labor?
In addition to combating the controllable risk factors already listed (smoking, number of embryos transferred), doctors can offer several more tools to delay labor. First of all, it is important that a woman plans a pregnancy, prepares for it and is subsequently observed by a doctor. According to Alexey Mostovoy, this approach has been common for a long time, for example, in Sweden, and as a result, more women are doing just that, as a result of which infant mortality in this country has decreased.
Here's what else you can do besides this.
- Sometimes you can "catch" a dangerous state in time.
 Women with a history of preterm labor and a singleton pregnancy between weeks 16 (some say week 18) to week 24 are advised to have their cervical length scanned by ultrasound (some experts suggest everyone should do this). If it is shorter than expected, then this means that the risk of preterm birth is increased. Then, to reduce the risks, you can prescribe progesterone in the form of a vaginal gel or put stitches on the cervix, or possibly a pessary, although it is getting worse with evidence of effectiveness.
Women with a history of preterm labor and a singleton pregnancy between weeks 16 (some say week 18) to week 24 are advised to have their cervical length scanned by ultrasound (some experts suggest everyone should do this). If it is shorter than expected, then this means that the risk of preterm birth is increased. Then, to reduce the risks, you can prescribe progesterone in the form of a vaginal gel or put stitches on the cervix, or possibly a pessary, although it is getting worse with evidence of effectiveness. - As a prophylaxis for women who have already given birth prematurely, you can immediately prescribe progesterone starting from the 16-20th week of pregnancy (if she is singleton). Also, if the doctor understands that the risk of preterm birth is high, he may prescribe corticosteroids - drugs that accelerate the development of the baby's organs (usually this occurs after the 24th week).

- If the woman is already in labor and her cervix is dilating, you can use tocolytic therapy (such as indomethacin or nifedipine), which can stop the process for at least a few days. This requires hospitalization. However, tocolytic therapy cannot be used for prophylaxis: its safety and effectiveness are best balanced precisely in cases where a woman has started labor. During the time doctors gain in this way, corticosteroids can be administered. And magnesium sulfate, which helps protect the brain from damage and therefore reduces the risk of developing cerebral palsy. Even if tocolytics delay labor by a few hours, that's a good thing: magnesium sulfate and corticosteroids will have more time to work. Also, a woman has the opportunity to go to a more equipped clinic, where premature babies are regularly nursed. “The birth of a premature baby is always a high-risk birth,” explains pediatrician Natalya Vasilyeva. “By all standards, high-risk births in an ideal world should take place in specialized institutions that have all the technical capabilities to save the child.
 ”
”
It must also be remembered that in a third of cases, contractions stop on their own, and a woman gives birth on time.
Does bed rest or lying "on hold" help?
There is no good evidence that bed rest (or lying "on hold") reduces the risk of preterm birth, including in women with a short cervix. Moreover, this practice could theoretically be dangerous due to the increased risk of blood clots. Not to mention that it does not improve the quality of life.
However, there are exceptions. “In some situations, hospitalization makes sense with a very high risk of preterm birth to quickly save a premature baby (not to prevent preterm birth), explains obstetrician-gynecologist, medical director of the Fomin Clinic Tatyana Rumyantseva. “[This happens] is relevant if a woman lives far from a large perinatal center and, theoretically, may not have time to get to it.”
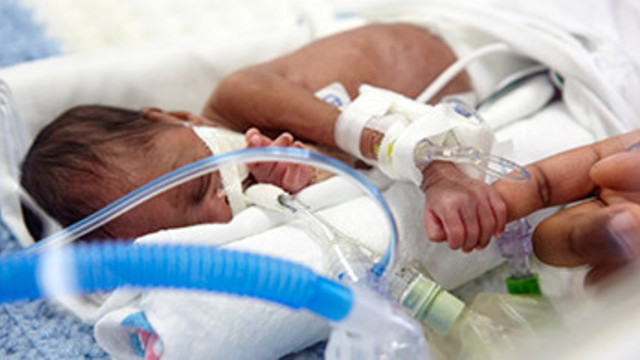
What does it take to have a premature baby?
When a baby is born prematurely, he may need a variety of assistance to survive: from mechanical ventilation to warming devices and a warm hat (often knitted by volunteers).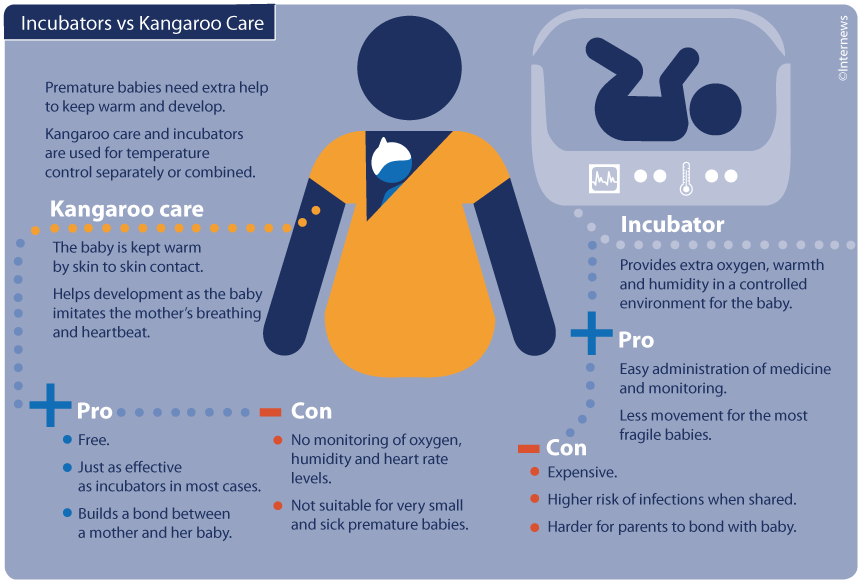 In addition, doctors and nurses are trying to reduce the risks of negative consequences - both in the short term and in the long term. For example, they give oxygen and, with the help of drugs, correct various indicators of the body's functioning so that everything is normal, and this, among other things, reduces the risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
In addition, doctors and nurses are trying to reduce the risks of negative consequences - both in the short term and in the long term. For example, they give oxygen and, with the help of drugs, correct various indicators of the body's functioning so that everything is normal, and this, among other things, reduces the risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
In specialized medical organizations (perinatal centers) there are more opportunities to provide a premature baby with all the necessary care and improve his chances of survival and a healthy life than in ordinary maternity hospitals. Not only experienced specialists are concentrated in perinatal centers, but also modern equipment and drugs, without which it is impossible to provide adequate medical care: “Neonatal resuscitation is expensive, and working with very premature babies is even more expensive,” explains Natalya Vasilyeva. “There is no point in spreading resources around rural maternity hospitals, it makes sense to organize large perinatal centers and establish professional transportation of newborns if high-risk births took place outside their walls. ”
”
Olga Yevseychik explains that such institutions have mobile resuscitation and advisory teams of intensive care units and neonatal intensive care units: “[They] make it possible to bring neonatal resuscitation care as close as possible to babies and ensure their most gentle transportation to the center,” Yevseychik writes.
Both experts provide a long list of what is needed to help premature babies. For example:
- heating systems (incubators). “[It should be] a normal ‘smart’ system that takes into account temperature fluctuations, sound insulation and the possibility of weighing a child without removing him from the incubator,” explains Natalya Vasilyeva. — <…> A premature baby cannot retain heat on its own. The incubator replaces the function of thermoregulation, maintaining the optimal temperature and humidity for the baby. And it also performs one of its most important functions - it protects the baby from loud sounds and bright lights.
 If you look at real photos from neonatal intensive care units, you will notice blankets and covers thrown over the incubators - this is additional protection from sound and light. As soon as the child can retain heat on his own, he can be transferred first to a heating source in a crib, and then to a regular crib without additional heat.
If you look at real photos from neonatal intensive care units, you will notice blankets and covers thrown over the incubators - this is additional protection from sound and light. As soon as the child can retain heat on his own, he can be transferred first to a heating source in a crib, and then to a regular crib without additional heat. - devices for various types of oxygen support: “From a “simple” neonatal ventilator to a high-frequency ventilator,” explains Natalya Vasilyeva;
- a plurality of microfluidizers;
- various types of parenteral nutrition, i.e. nutritional mixtures for intravenous administration;
- modern antibiotics, surfactants, that is, drugs that help the lungs open up, and other expensive medicines.
Various medical organizations, including the World Health Organization, recommend not to separate parents and a premature baby: if possible, establish breastfeeding and practice prolonged skin-to-skin contact - one of the parents sits in a chair, a child is placed under his clothes on his chest without clothes (except perhaps in a diaper), and they can sit like that for many hours. In English, this is called kangaroo care, that is, literally "kangaroo care", because the child is in contact with one of the parents, like a kangaroo in a mother's pouch. “If the baby’s condition allows it to be carried from place to place, then the number of wires and hoses connected to it does not matter — it can be placed on the hands/chest of the parents,” writes Natalya Vasilyeva. - It's just worth remembering that for babies in critical condition, moving can be deadly. There is a so-called "transfer test" - if the baby can tolerate it, then it can be moved.
In English, this is called kangaroo care, that is, literally "kangaroo care", because the child is in contact with one of the parents, like a kangaroo in a mother's pouch. “If the baby’s condition allows it to be carried from place to place, then the number of wires and hoses connected to it does not matter — it can be placed on the hands/chest of the parents,” writes Natalya Vasilyeva. - It's just worth remembering that for babies in critical condition, moving can be deadly. There is a so-called "transfer test" - if the baby can tolerate it, then it can be moved.
According to Olga Evseichik, this practice is not widespread in Russia, although there is evidence of its effectiveness.
When the child can breathe and eat normally on his own, maintain a normal body temperature, and gain stable weight, he or she will be discharged home.
22 weeks
BSIP / Alamy / Vida Press
What do you need to know about raising a premature baby?
Before being discharged, parents should be explained what is normal and what is not normal, and in what cases it is necessary to see a doctor (or even an ambulance). This often depends on the characteristics of the child himself. But in fact, there are fewer features in caring for such children than it might seem.
This often depends on the characteristics of the child himself. But in fact, there are fewer features in caring for such children than it might seem.
A premature baby may need frequent visits to the pediatrician (especially at first) to adjust the treatment of existing diseases, monitor changes and advise on other issues such as sleep and nutrition. All premature babies need to undergo additional screening tests. How often and which ones - depends on the specific situation. But the focus is usually on hearing loss, retinopathy of prematurity and other eye diseases, motor, intellectual and neuropsychiatric development (including autism spectrum disorders, the risk of which is increased in such children). Screening planning takes into account the adjusted age of the child.
“The task of a pediatrician is to summarize knowledge about the baby in one hand, combine observation plans in different directions into one, control them, change them as the child grows and improves / worsens,” writes Olga Evseichik. - The earlier the child was born, the more such checkpoints are in the list. How much is individual in each case. The expert also points out that such children require consultations of narrow specialists, but the list also depends on the specific situation.
- The earlier the child was born, the more such checkpoints are in the list. How much is individual in each case. The expert also points out that such children require consultations of narrow specialists, but the list also depends on the specific situation.
“The very word “premature” for parents is something like an internal stigma, some kind of seal of guilt that they feel latently at first,” explains Olga Evseichik. - They most often read a lot of different literature, they know how it "should be" and perceive all deviations from the "norm" as a threat. <...> [Parents] are worried about the weight of the child, the increase in his skills, [they] often ask, "when he will catch up." Unnecessary anxieties are similar to those in full-term children, there are just more of them: the chair is not the color, yesterday I added 30 grams in a day, and today only 25, I slept longer than usual, I could not fall asleep longer than usual, etc. ".
This is an understandable relationship, but sometimes it does not lead to very good results. Doctors even singled out such a phenomenon as the “vulnerable child syndrome”, which is caused by excessive protection of the child, in particular, if he was born prematurely. As a result, such children find it difficult to build relationships with peers, they have to miss school more often than they really need to, they develop anxiety and other physical and psychological problems arise.
Doctors even singled out such a phenomenon as the “vulnerable child syndrome”, which is caused by excessive protection of the child, in particular, if he was born prematurely. As a result, such children find it difficult to build relationships with peers, they have to miss school more often than they really need to, they develop anxiety and other physical and psychological problems arise.
Can premature babies be vaccinated?
Premature babies must be vaccinated, and not only according to the general calendar, but also additionally. “It should be taken into account that such children, in case of childhood infections, endure them much harder, it can be fatal for them, because vaccination is even more necessary for them,” Olga Evseichik explains. In addition, babies born before the 28th week do not have protection against certain diseases that should have been transmitted in utero from the mother. And those premature babies who were born after the 28th week will have less of this protection than if they were born at term. Some vaccines may protect these babies a little less because they produce fewer antibodies than full-term babies. But doctors agree that vaccination is still necessary. Sometimes you just need another shot later on over the calendar to get better protection.
Some vaccines may protect these babies a little less because they produce fewer antibodies than full-term babies. But doctors agree that vaccination is still necessary. Sometimes you just need another shot later on over the calendar to get better protection.
The UK recommends that these children be vaccinated eight weeks after birth. In the United States, it is not recommended to wait and is advised to be vaccinated according to chronological (not adjusted) age. In Russia, prematurity itself is not officially a contraindication. However, it is recommended to vaccinate from a month - “according to passport age, with all vaccines in usual doses after stabilization of the condition with adequate weight gain”, as indicated in the methodological recommendations of the Ministry of Health.
There are only a few differences in when certain vaccinations are given.
Hepatitis B virus
Children who weigh from one and a half to two kilograms at birth and who do not have visible diseases can be immediately vaccinated against hepatitis B in Russia. Or postpone vaccination for a month. In the US, the recommendations are similar.
Or postpone vaccination for a month. In the US, the recommendations are similar.
In other cases, if the child weighs less than two kilograms, you need to stabilize his condition or wait until he gains weight - then you can vaccinate against hepatitis B.
If the mother has a positive HBsAg test, regardless of the weight of the child, vaccination is needed on the first day (in the US, it is recommended to meet the first 12 hours).
Rotavirus
The rotavirus vaccine is certainly needed for premature babies (although it is not on the main list of the Russian National calendar approved by the Ministry of Health). However, this is a live vaccine, and there is a theoretical risk that other children who are contraindicated for it and who are in the same intensive care unit may encounter the virus from the vaccine. This could end badly. Therefore, the child should receive the first dose at discharge (but not later than the 15th week of life).
BCG
This vaccination is contraindicated if the child weighs less than two kilograms. This is due to the fact that it is administered intradermally, while in children with low weight the skin is very thin, and it is technically impossible to vaccinate correctly. “Such children should be vaccinated upon discharge from the second stage, however, in practice, we encounter medical challenges in the vast majority of cases,” Olga Evseichik explains.
This is due to the fact that it is administered intradermally, while in children with low weight the skin is very thin, and it is technically impossible to vaccinate correctly. “Such children should be vaccinated upon discharge from the second stage, however, in practice, we encounter medical challenges in the vast majority of cases,” Olga Evseichik explains.
Respiratory syncytial virus
In this case, we are not talking about a vaccine, but about a drug that protects against respiratory syncytial virus in a different way. The drug palivizumab (in Russia it is sold under the sole commercial name Synagis) is a monoclonal antibody, that is, an antibody created using gene technology. When a conventional vaccine is administered, the body must develop antibodies to the virus or bacteria so that the next time it encounters a pathogen, the immune system responds quickly. Here, antibodies are introduced from the outside.
The Union of Pediatricians of Russia recommends using this drug in premature babies in the first year of life and in some cases up to two years, and at the beginning of the seasonal spread of the respiratory syncytial virus (usually this is the cold season - in Russia they say that palivizumab should be administered every month from November to March). In some regions, the drug is administered free of charge.
In some regions, the drug is administered free of charge.
In the United States and Canada, recommendations for the use of palivizumab are narrower. This is probably due to its high cost.
Other dangerous viruses and bacteria
In many countries, all children, including premature babies, are recommended to be vaccinated against more diseases than indicated in the official Russian vaccination calendar. There are several reasons for this, and financial is one of them: what is included in the calendar should be provided "for free". However, the Union of Pediatricians of Russia has compiled an expanded “ideal vaccination schedule”, which includes everything an average child needs. In general, you can rely on these recommendations, however, the pediatrician is likely to make some adjustments depending on the individual characteristics of the child and the local epidemiological situation. Most likely, additional vaccines will be paid, however, in different regions, the calendar may be wider than the national one. In addition, even according to the general National calendar, premature babies need to be vaccinated against hemophilic infection, that is, this should happen at no additional charge.
In addition, even according to the general National calendar, premature babies need to be vaccinated against hemophilic infection, that is, this should happen at no additional charge.
Daria Sargsyan
The editors would like to thank the Vera Hospice Fund for help in preparing the material
Premature baby: development by months It happens that babies are born with a weight of 500 grams. How do doctors assess their condition? What indicators of development should be guided by in order to understand whether everything is normal for the baby?
In the official language
Russia switched to the medical birth criteria approved by the World Health Organization in 2012. They are determined by the presence of the following signs in a newborn: breathing, heartbeat, pulsation of the umbilical cord, or voluntary muscle movements.
According to these parameters, a premature newborn is an infant weighing over 500 grams, over 25 centimeters tall, born at 22 weeks of gestation. Every year, 5-10% of such children are born from the total number of newborns around the world.
Every year, 5-10% of such children are born from the total number of newborns around the world.
Today there are all conditions for nursing "early" children.
Early help
A 500g baby is not just very small. In such babies, the organs and systems are immature, the immune system does not work at full strength, so the body of prematurely born children is very vulnerable and susceptible to the effects of various adverse factors. What does not harm the health of full-term babies may affect a child with extremely low body weight.
Children weighing 1000-1499 g and less than 1000 g are most at risk of developing various diseases. Moreover, the shorter the gestation period, the higher the risk that the baby may have several problems at once.
The sooner doctors can identify possible pathologies and disorders, the sooner it will be possible to start adequate treatment, facilitate the adaptation of the baby to the air environment and provide him with the most favorable opportunities for development.
Three ages of premature baby
Usually a person's age is calculated from the moment of his birth. But for each premature baby, doctors determine three ages at once.
Chronological
This is a familiar indicator for everyone. It is counted from the moment the child is born. If the baby was born on December 1, then on January 1 he will be 1 month old.
Gestational
This is the age that is equal to the number of completed weeks of pregnancy at the time of delivery. It is counted in weeks and days. For example, a child was born on January 1 at 25 weeks and 5 days. In this case, his age is 25 weeks, rounding up does not occur.
Corrected
This is the child's age minus the "missing" weeks. It is considered relative to 40 weeks.
Corrected age = chronological age - (40 weeks - gestational age)
For example, the child's chronological age is 4 months (i.e. 16 weeks). The baby was born at the 28th week of gestation, that is, 12 weeks earlier (term delivery = 40 weeks). Corrected age of the child: 16-12 = 4 weeks (or 1 month).
Corrected age of the child: 16-12 = 4 weeks (or 1 month).
This means that if a full-term baby usually starts crawling around the age of 9months, then for a child born 3 months premature, it is permissible to start crawling at the age of up to 12 months. This is by no means considered a pathology. In addition, if a premature baby was sick after birth and, for example, was connected to a ventilator, this period will affect its development. In this case, such a baby will learn everything a little later.
The most commonly used skill scale for preterm infants, adjusted for age.
Peculiarities of psychomotor development
Each child is individual, and one should not compare different children with each other. It is quite natural that a baby born at 34 weeks is more likely to catch up with his full-term peers than a baby born at 27 weeks. What indicators do doctors focus on? What should parents pay attention to?
Pediatrician Natalya Maykova tells about what scientists know today.
- The child develops gradually and progressively.
- In premature babies, skills are formed in approximately the same sequence as in full-term babies, but adjusted for corrected age.
- Individual characteristics of a child's development are related to his gestational age (gestational age at which he was born) and his condition at the time of birth. That is, the more problems the baby experienced in the first months of his life, the longer it will take him to acquire new skills.
- For an adequate assessment of the pace and level of development of the baby, dynamic monthly monitoring of the child is necessary.
Development by month
There is a rough list of skills and abilities that can be expected from a premature baby in the first 18 months of his life. However, it is worth remembering that one should focus not on the chronological age, but on the corrected one.
Of course, conditional standards cannot be applied to absolutely all premature babies, but they can serve as a guideline for both doctors and parents.
Only prematurely born children, as a rule, need special conditions and constant medical supervision. Often these babies are fed through a food tube and supported by their breathing through artificial oxygen supply.
2 months of corrected age
The baby holds his head well, his first coos, smiles appear. The child begins to listen, recognize native people and rejoice when communicating with them.
4 months
The child lies confidently on his tummy, raises his head, looks around. He watches over objects and people. Some babies are already well rolled over on their stomach and back.
6 months
The child learns several skills at once: he learns to sit down, crawl, stand on all fours. Babble appears in the baby’s speech when he repeats the same simple syllables: “ma-ma-ma”, “yes-yes-yes”, etc. He enthusiastically plays with toys and various objects. He is interested in those that are out of his reach, and tries to crawl up to them or reach out to them.
9 months
Baby crawls everywhere, gets up, reaches for objects, plays with them. More and more new syllables appear in his "lexicon", he tries to imitate new sounds. At this time, the child begins to understand the word "no" well.
12 months
By the age of one, children, as a rule, are already completely catching up with their peers who were born on time, both physically and psycho-emotionally. They already know a lot: they take their first steps, walk holding on to walls and furniture, bend down and pick up objects from the floor. The speech of a one-year-old child is actively developing: the baby consciously pronounces new words, enters into communication, answering the questions posed. He likes to communicate with the help of gestures: he waves his hand, shakes his head, nods. During this period, the child begins to get upset at the moments of the absence of a close adult nearby.
15 months
The child's vocabulary grows quickly. He can, upon request, point his finger at objects, animals, body parts. The coordination of movements improves, the gait becomes confident, the child knows how to squat. The kid's games with simple educational toys (cubes, pyramid) become conscious. He learns to sort objects, to solve simple puzzles.
He can, upon request, point his finger at objects, animals, body parts. The coordination of movements improves, the gait becomes confident, the child knows how to squat. The kid's games with simple educational toys (cubes, pyramid) become conscious. He learns to sort objects, to solve simple puzzles.
18 months
At this age, the child can confidently use a spoon and drink from a cup. He knows how to go up and down the stairs, tries to dress and undress on his own. The child communicates emotionally, uses more and more words in speech.
Specialists: a pediatrician and a neurologist can help parents assess the harmonious development of their baby. Doctors will notice “weak points” in the development of the child in time and help develop a plan for his further observation and, if necessary, treatment, which includes not only drugs, but also massage, physiotherapy exercises, kinesitherapy and other modern methods.
It is important to remember that the development of a premature baby largely depends on the care and responsible attitude of parents to the recommendations of doctors.