7 month old sick with a cold
Common cold in babies - Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis
If your baby is younger than 3 months of age, call his or her doctor early in the illness. In newborns, it's especially important to make sure that a more serious illness isn't present, especially if your baby has a fever.
In general, you don't need to see the doctor if your older baby has a common cold. If you have questions or if your baby's symptoms worsen or don't go away, it might be time to see the doctor.
Your baby's doctor can generally diagnose a common cold by your baby's signs and symptoms. If your doctor suspects your baby has a bacterial infection or other condition, he or she may order a chest X-ray or other tests to exclude other causes of your baby's symptoms.
Treatment
There's no cure for the common cold. Most cases of the common cold get better without treatment, usually within a week to 10 days, but a cough may linger for a week or more. Antibiotics don't work against cold viruses.
Try to make your baby more comfortable with measures such as making sure he or she drinks enough fluids, suctioning nasal mucus and keeping the air moist.
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications generally should be avoided in babies.
Fever-reducing medications
You can use OTC fever-reducing medications if a fever is making your child uncomfortable. However, these medications don't kill the cold virus. Fever is a part of your child's natural response to the virus, so it may help to allow your child to have a low-grade fever.
For treatment of fever or pain in children, consider giving your child infants' or children's over-the-counter fever and pain medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, others). These are safer alternatives to aspirin.
For children younger than 3 months old, don't give acetaminophen until your baby has been seen by a doctor. Don't give ibuprofen to a child younger than 6 months old or to children who are vomiting constantly or are dehydrated. Use these medications for the shortest time. If you give your child a pain reliever, follow the dosing guidelines carefully. Call your doctor if you have questions about the right dosage for your baby.
Use these medications for the shortest time. If you give your child a pain reliever, follow the dosing guidelines carefully. Call your doctor if you have questions about the right dosage for your baby.
Children and teenagers recovering from chickenpox or flu-like symptoms should never take aspirin. This is because aspirin has been linked to Reye's syndrome, a rare but potentially life-threatening condition, in such children.
Cough and cold medications
Cough and cold medications aren't safe for infants and young children. OTC cough and cold medicines don't treat the underlying cause of a child's cold and won't make it go away sooner ⸺ and they can be dangerous to your baby. Cough and cold medications have potentially serious side effects, including fatal overdoses in children younger than 2 years old.
Don't use over-the-counter medicines, except for fever reducers and pain relievers, to treat coughs and colds in children younger than 6 years old. Also consider avoiding use of these medicines for children younger than 12 years old.
Also consider avoiding use of these medicines for children younger than 12 years old.
Request an appointment
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free, and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips and current health topics, like COVID-19, plus expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Most often, you can treat an older baby's cold at home. To make your baby as comfortable as possible, try some of these suggestions:
- Offer plenty of fluids. Liquids are important to avoid dehydration. Formula or breast milk is the best choice. Encourage your baby to take in the usual amount of fluids. Extra fluids aren't necessary. If you're breastfeeding your baby, keep it up. Breast milk offers extra protection from cold-causing germs.
-
Suction your baby's nose. Keep your baby's nasal passages clear with a rubber-bulb syringe. Squeeze the bulb syringe to expel the air. Then insert the tip of the bulb about 1/4 to 1/2 inch (about 6 to 12 millimeters) into your baby's nostril, pointing toward the back and side of the nose.
Release the bulb, holding it in place while it suctions the mucus from your baby's nose.
 Remove the syringe from your baby's nostril and empty the contents onto a tissue by squeezing the bulb rapidly while holding the tip down. Repeat as often as needed for each nostril. Clean the bulb syringe with soap and water.
Remove the syringe from your baby's nostril and empty the contents onto a tissue by squeezing the bulb rapidly while holding the tip down. Repeat as often as needed for each nostril. Clean the bulb syringe with soap and water. - Try nasal saline drops. Your baby's doctor may recommend saline nasal drops to moisten nasal passages and loosen thick nasal mucus. Look for these OTC drops in your local pharmacy. Apply saline nasal drops, wait for a short period, and then use a suction bulb to draw mucus out of each nostril.
- Moisten the air. Running a cool-water humidifier in your baby's room can ease nasal congestion. Change the water daily and follow the manufacturer's instructions for cleaning the unit.
Preparing for your appointment
If you need to see your baby's pediatrician or family doctor, here's some information to help you get ready for your baby's appointment.
What you can do
Make a list of:
- Symptoms you've noticed in your baby, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment.
- Key personal information, such as whether your baby goes to child care or has otherwise been exposed to someone with a common cold. Include how many colds your baby has had, how long they lasted and whether your baby is exposed to secondhand smoke. It might help to make a note on your calendar the day you realize your baby has a cold.
- All medications, vitamins or supplements your baby is taking, including dosages.
- Questions to ask your doctor.
For a common cold, some questions to ask the doctor include:
- What is likely causing my baby's symptoms?
- Are there other possible causes?
- What tests are needed?
- What's the best course of action?
- My baby has other health conditions.
 How can I best manage them together?
How can I best manage them together? - Are there restrictions we need to follow?
- Are there over-the-counter medications that aren't safe for my child at this age?
Don't hesitate to ask other questions you have.
What to expect from your doctor
Your baby's doctor is likely to ask you questions, including:
- When did your baby's symptoms begin?
- Have they been continuous or occasional?
- How severe are they?
- What, if anything, seems to improve them?
- What, if anything, appears to worsen them?
- Has the nasal congestion caused your baby to eat or drink less?
- Is your baby having as many wet diapers as usual?
- Has there been a fever? If so, how high?
- Are your child's vaccinations up to date?
- Has your child taken antibiotics recently?
Your doctor will ask additional questions based on your responses and your baby's symptoms and needs. Preparing and anticipating questions will help you make the most of your time with the doctor.
Preparing and anticipating questions will help you make the most of your time with the doctor.
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Products & Services
Colds (0-12 Months)
Is this your child's symptom?
- Runny nose and sore throat caused by a virus
- You think your child has a cold. Reason: family members, friends or other children in child care have same symptoms.
- Also called an Upper Respiratory Infection (URI).
Symptoms of a Cold
- Runny or stuffy nose
- The nasal discharge starts clear but changes to gray. It can also be yellow or green.
- Most children have a fever at the start.
- At times, the child may also have a cough and hoarse voice. Sometimes, watery eyes and swollen lymph nodes in the neck also occur.
Cause of Colds
- Colds are caused by many respiratory viruses. Healthy children get about 6 colds in the first year.
- Influenza virus causes a bad cold with more fever and muscle aches.
- Colds are not serious. With a cold, about 5 to 10% of children develop a complication. Most often, this is an ear or sinus infection. These are caused by a bacteria.
Trouble Breathing: How to Tell
Trouble breathing is a reason to see a doctor right away. Respiratory distress is the medical name for trouble breathing. Here are symptoms to worry about:
- Struggling for each breath or shortness of breath
- Tight breathing so that your child can barely cry
- Ribs are pulling in with each breath (called retractions)
- Breathing has become noisy (such as wheezes)
- Breathing is much faster than normal
- Lips or face turn a blue color
When to Call for Colds (0-12 Months)
Call 911 Now
- Severe trouble breathing (struggling for each breath, can barely cry)
- You think your child has a life-threatening emergency
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Trouble breathing, but not severe.
 Exception: gone after cleaning out the nose.
Exception: gone after cleaning out the nose. - Wheezing (purring or whistling sound) occurs
- Breathing is much faster than normal
- Trouble swallowing and new onset drooling
- High-risk child (such as with chronic lung disease)
- Weak immune system. Examples are sickle cell disease, HIV, cancer, organ transplant, taking oral steroids.
- Fever over 104° F (40° C)
- Fever in baby less than 12 weeks old. Caution: Do NOT give your baby any fever medicine before being seen.
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Age less than 6 months old
- Earache or ear drainage
- Yellow or green pus from eyes
- Fever lasts more than 3 days
- Fever returns after gone for more than 24 hours
- You think your child needs to be seen, but the problem is not urgent
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- Blocked nose wakes up from sleep
- Yellow scabs around the nasal openings.
 Use an antibiotic ointment.
Use an antibiotic ointment. - Nasal discharge lasts more than 2 weeks
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Mild cold with no other problems
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
- Virtual Urgent Care
Care Advice for a Cold
- What You Should Know About Colds:
- It's normal for healthy children to get at least 6 colds a year.
 This is because there are so many viruses that cause colds. With each new cold, your child's body builds up immunity to that virus.
This is because there are so many viruses that cause colds. With each new cold, your child's body builds up immunity to that virus. - Most parents know when their child has a cold. Sometimes, they have it too or other children in child care have it. Most often, you don't need to call or see your child's doctor. You do need to call your child's doctor if your child develops a complication. Examples are an earache or if the symptoms last too long.
- The normal cold lasts about 2 weeks. There are no drugs to make it go away sooner.
- But, there are good ways to help many of the symptoms. With most colds, the starting symptom is a runny nose. This is followed in 3 or 4 days by a stuffy nose. The treatment for each symptom is different.
- Here is some care advice that should help.
- It's normal for healthy children to get at least 6 colds a year.
- For a Runny Nose with Lots of Discharge: Suction the Nose
- The nasal mucus and discharge are washing germs out of the nose and sinuses.

- For younger children, gently suction the nose with a suction bulb.
- Put petroleum jelly on the skin under the nose. Wash the skin first with warm water. This will help to protect the nostrils from any redness.
- The nasal mucus and discharge are washing germs out of the nose and sinuses.
- Nasal Saline to Open a Blocked Nose:
- Use saline (salt water) nose spray to loosen up the dried mucus. If you don't have saline, you can use a few drops of water. Use distilled water, bottled water or boiled tap water.
- Step 1. Put 1 drop in each nostril.
- Step 2. Suction each nostril out while closing off the other nostril. Then, do the other side.
- Step 3. Repeat nose drops and suctioning until the discharge is clear.
- How Often. Do nasal saline rinses when your child can't breathe through the nose.
- Limit to no more than 4 times per day. Before breast or bottle feedings are a good time.
- Saline nose drops or spray can be bought in any drugstore. No prescription is needed.
- Reason for nose drops: Suction alone can't remove dried or sticky mucus.
 Also, babies can't nurse or drink from a bottle unless the nose is open.
Also, babies can't nurse or drink from a bottle unless the nose is open. - Other option: use a warm shower to loosen mucus. Breathe in the moist air, then suction each nostril.
- For young children, can also use a wet cotton swab to remove sticky mucus.
- Fluids - Offer More:
- Try to get your child to drink extra formula or breastmilk.
- Goal: Keep your child well hydrated.
- It also will thin out the mucus discharge from the nose.
- It also loosens up any phlegm in the lungs. Then it's easier to cough up.
- Humidifier:
- If the air in your home is dry, use a humidifier.
- Reason: Dry air makes nasal mucus thicker.
- Drugstore Medicines for Colds:
- Cold Medicines. Don't give any drugstore cold or cough medicines to young children. They are not approved by the FDA under 6 years. Reasons: not safe and can cause serious side effects.
 Also, they are not helpful. They can't remove dried mucus from the nose. Nasal saline works best.
Also, they are not helpful. They can't remove dried mucus from the nose. Nasal saline works best. - No Antibiotics. Antibiotics are not helpful for colds. Antibiotics may be used if your child gets an ear or sinus infection.
- Cold Medicines. Don't give any drugstore cold or cough medicines to young children. They are not approved by the FDA under 6 years. Reasons: not safe and can cause serious side effects.
- Other Symptoms of Colds - Treatment:
- Pain or Fever. Use acetaminophen (such as Tylenol) to treat muscle aches, sore throat or headaches. Another choice is an ibuprofen product (such as Advil). Caution: avoid ibuprofen until 6 months or older. You can also use these medicines for fever above 102° F (39° C).
- Red Eyes. Rinse eyelids often with wet cotton balls.
- Return to Child Care:
- Your child can go back to child care after the fever is gone.
- For practical purposes, the spread of colds can't be prevented.
- What to Expect:
- Fever can last 2-3 days
- Nasal drainage can last 7-14 days
- Cough can last 2-3 weeks
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Trouble breathing occurs
- Earache occurs
- Fever lasts more than 3 days or goes above 104° F (40° C)
- Any fever if under 12 weeks old
- Nasal discharge lasts more than 14 days
- Cough lasts more than 3 weeks
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.

Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 04/03/2023
Last Revised: 12/30/2022
Copyright 2000-2023 Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
A cold in a child: how to treat it correctly
Many parents are ready for the fact that babies will catch common, including seasonal infections, which is typical for childhood. Some parents study the methods of treating ARVI and colds in advance, read about it from experienced mothers in blogs and diaries, consult with doctors they know, and watch medical programs. But even despite the fact that the child's body from birth has a powerful immune system, this protection is imperfect. Therefore, no matter how informed the mother is, when the child becomes ill, she has a lot of questions that require qualified answers.
What is ARI and SARS
Most often, children are faced with acute respiratory diseases, abbreviated as acute respiratory infections or colds. This is especially evident when visiting children's groups, where they come into contact with other kids, and actually exchange various pathogens. The mothers of "kindergarten" children are very familiar with the phrase: "We go for 2 days, then 2 weeks - on sick leave."
This is especially evident when visiting children's groups, where they come into contact with other kids, and actually exchange various pathogens. The mothers of "kindergarten" children are very familiar with the phrase: "We go for 2 days, then 2 weeks - on sick leave."
A cold can be both viral and bacterial, even fungal and of a different nature, in 70-80% of cases it is of a viral nature. It is impossible to establish the origin of a cold with accuracy on a pediatric examination, as well as “by eye” to distinguish one infection from another. However, there are certain signs that indicate the action of viruses, harmful bacteria and other pathogens. For example, nasal mucus is indicative of an acute respiratory viral infection, which usually begins with mild malaise, decreased appetite, moodiness, and sleep disturbance in a child. This is a prodromal period, it lasts from several hours to 1-2 days. And such a viral infection as the flu begins acutely, immediately with a very high temperature, intoxication, there is almost no prodromal period, dry cough appears in the late stages of the disease. Often SARS passes with catarrhal symptoms: nasal congestion, change in tone of voice, "circles", "blue" under the eyes, runny nose, discharge from the nose, cough, sore throat and swallowing.
Often SARS passes with catarrhal symptoms: nasal congestion, change in tone of voice, "circles", "blue" under the eyes, runny nose, discharge from the nose, cough, sore throat and swallowing.
What to do?
First of all, you need to remember that parents should not panic if the child has a fever and other unpleasant symptoms of a cold. Any mood of the mother is transmitted to the baby. A cold with a competent approach is simply MUST pass in 5-7 days without complications. And it is important to know that the treatment of a cold is complex, which includes the main drugs - antiviral, antibacterial, etc., as well as symptomatic therapy. You should not rely on just one medicine as a panacea, a magic pill from advertising or the advice of a pharmacy worker.
How to treat?
Antivirals. There is a lot of misinformation about antivirals now. They are credited with mythical side effects and actions. If this comes from a doctor, then he must provide data confirming his point of view in official sources, which are state medical institutions, major scientific journals.
Antibiotics. As for antibiotics, their use is currently limited by very clear indications, contraindications, age of the patient, etc. In addition, antibiotics, especially with uncontrolled, frequent use, contribute to the formation of new strains of harmful bacteria that are difficult to treat. Usually, against the background of antibiotic treatment, it is customary to prescribe biological products - live microbes that make up the human intestinal microflora. But there is an opinion that the antibiotic has a detrimental effect on these bacteria, and such therapy does not bring the desired result.
Auxiliaries . In the treatment of colds of any origin, symptomatic therapy is used, the action of which is directed against the symptoms of the disease. They are called auxiliary, as they help to alleviate the course of a cold. They do not get rid of the cause of ARVI, but the child's own antibodies work against viruses.
How to treat a runny nose? In case of a runny nose, a nasal toilet with saline solutions is performed. The procedure is simple, but requires certain skills and care. To do this, you should seat the child with his back to him, first clean his nose. In babies, this can be done with cotton buds (in children under six months old, only with ordinary cotton turundas), and at an older age, children can already blow their nose. After that, you need to raise the chin, holding the child's face with his palm in a raised position. Using a pipette, drip saline solution into both nasal passages, lower the child's head forward. Part of the medicine may spill out of the nose, but the result of such a procedure will still be achieved. If there are no special recommendations from the pediatrician of the sick child, you can use a pipette and normal saline. But preferably a sterile solution based on sea water. It is a delusion to think that washing a child's nose will be addictive or the snot will flow out on its own. Part, of course, can leak out, but if you do not clean your nose, there is a high risk of infection spreading to the lower respiratory tract, the development of complications such as inflammation of the trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
The procedure is simple, but requires certain skills and care. To do this, you should seat the child with his back to him, first clean his nose. In babies, this can be done with cotton buds (in children under six months old, only with ordinary cotton turundas), and at an older age, children can already blow their nose. After that, you need to raise the chin, holding the child's face with his palm in a raised position. Using a pipette, drip saline solution into both nasal passages, lower the child's head forward. Part of the medicine may spill out of the nose, but the result of such a procedure will still be achieved. If there are no special recommendations from the pediatrician of the sick child, you can use a pipette and normal saline. But preferably a sterile solution based on sea water. It is a delusion to think that washing a child's nose will be addictive or the snot will flow out on its own. Part, of course, can leak out, but if you do not clean your nose, there is a high risk of infection spreading to the lower respiratory tract, the development of complications such as inflammation of the trachea, bronchi, and lungs.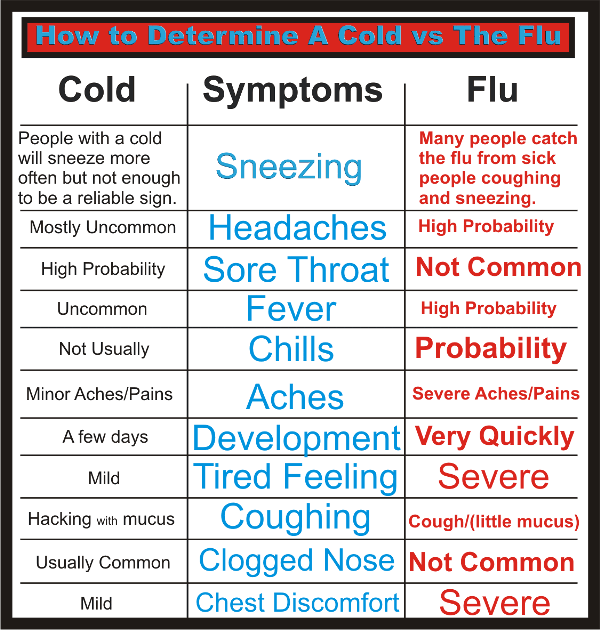
If the runny nose is profuse, watery, painful, accompanied by nasal congestion, vasoconstrictor drugs (based on oxymetazoline, xylometazoline) are used in the form of drops at bedtime, before walking with the child. This helps the baby to have a good rest in a dream without waking up, and on a walk it is normal to breathe through the nose without taking cold air into the mouth. It should not be instilled into the nose of a child in a supine state, since there is a high probability of a change in pressure during such manipulation and there is a risk of otitis media. All instillations must be done while sitting. The use of special preparations in the form of soft (spray with limited jet pressure) should be carried out with great care, since there is also a risk of promoting the spread of infection under pressure.
Antipyretics . Often there are questions about the use of antipyretics, for children - these are drugs based on paracetamol or ibuprofen, for babies - in syrup, suppositories. It should be noted that if there are no special recommendations in this regard, it is necessary to reduce the temperature above 38.3 - 38.5 ° С. If the child feels well, plays, has an appetite, and, in general, tolerates temperature well, antipyretic drugs can not be used. If the parents see that the child's condition is bad, he refuses to eat and drink, becomes lethargic, vomiting occurs, headache, the temperature rises further, you can start giving antipyretics even at a low temperature.
It should be noted that if there are no special recommendations in this regard, it is necessary to reduce the temperature above 38.3 - 38.5 ° С. If the child feels well, plays, has an appetite, and, in general, tolerates temperature well, antipyretic drugs can not be used. If the parents see that the child's condition is bad, he refuses to eat and drink, becomes lethargic, vomiting occurs, headache, the temperature rises further, you can start giving antipyretics even at a low temperature.
How to treat a cough? Questions about cough are the most frequent and sometimes the most difficult at pediatric appointments for SARS. It is best if the doctor dynamically observes the coughing child. In this case, the specialist can distinguish changes in the tone of the voice, a barking component, a dry or wet cough, wheezing, localization of wheezing. If the pediatrician recommends taking an x-ray, you should not refuse such an examination, this will help to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.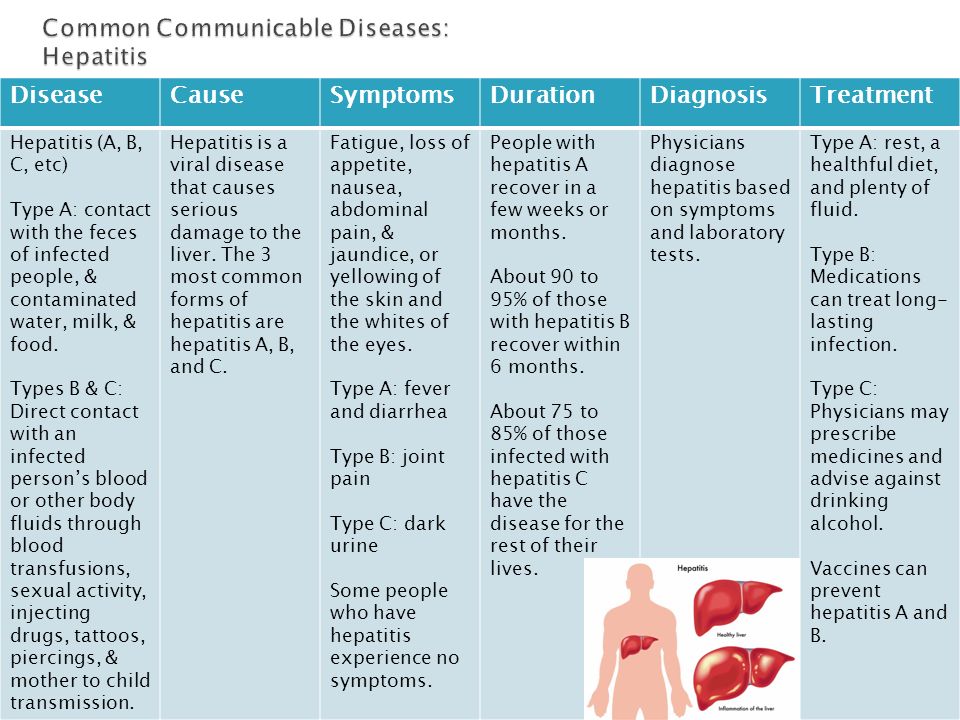 Currently, in the treatment of cough, inhalation drugs are widely used - through a special device - an inhaler. This tactic reduces the systemic effect of the drug on the child's body, where the drug reaches the point of its application - large and medium bronchi, and even alveoli. Inhalers can be used from the very birth of a child, but it is necessary to pay attention to the type of device, the medicinal substances recommended for it, their dosages and the frequency of use.
Currently, in the treatment of cough, inhalation drugs are widely used - through a special device - an inhaler. This tactic reduces the systemic effect of the drug on the child's body, where the drug reaches the point of its application - large and medium bronchi, and even alveoli. Inhalers can be used from the very birth of a child, but it is necessary to pay attention to the type of device, the medicinal substances recommended for it, their dosages and the frequency of use.
Activities before the doctor arrives
Sometimes, especially during the season of high incidence of flu and colds, there are difficulties with a doctor's visit, you have to wait for an appointment, the doctor does not have time to come as quickly as parents would like. There are steps that can be taken before the arrival of a specialist. It is necessary to measure the temperature of the child and write down the data on the thermometry performed in a diary, which is then shown to the doctor. If the temperature is high, do not wrap or even dress the child warmly. At home, you can generally strip to your underwear. Disposable diapers are also recommended to be removed from babies. Do not forget about physical methods of cooling - you can wipe it with cool water, you can put a cloth moistened with water on the head, stomach, places of the main vessels. A sick child should be given plenty of fractional water, even if he refuses to drink, it is necessary to constantly offer from a teaspoon, moisten his lips.
If the temperature is high, do not wrap or even dress the child warmly. At home, you can generally strip to your underwear. Disposable diapers are also recommended to be removed from babies. Do not forget about physical methods of cooling - you can wipe it with cool water, you can put a cloth moistened with water on the head, stomach, places of the main vessels. A sick child should be given plenty of fractional water, even if he refuses to drink, it is necessary to constantly offer from a teaspoon, moisten his lips.
There are no children who do not get sick. Everyone gets sick, only some often, while others not so much. The main thing to remember is that any medicines should be prescribed by a doctor at an internal appointment, after examination.
If a child falls ill - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Archegova Galina Altafovna
Gastroenterologist, Gastroenterologist for children, Nutritionist
Clinical Hospital MD GROUP
It is known that children in the first months of life rarely get sick, for example, SARS. This is due not only to the fact that they do not visit public places, but also to the fact that there are protective factors in their blood that were passed on to them by their mothers. Gradually, the level of these factors decreases, and the likelihood of respiratory disease, respectively, increases.
This is due not only to the fact that they do not visit public places, but also to the fact that there are protective factors in their blood that were passed on to them by their mothers. Gradually, the level of these factors decreases, and the likelihood of respiratory disease, respectively, increases.
If a child of the first 6 months of life gets sick with a viral infection, which theoretically should be protected by immunity inherited from the mother, then this is a situation that goes beyond the norm. Therefore, in this case, you should immediately consult a doctor. Even if the disease is mild, only in the form of a runny nose and sneezing.
If a child of the second half of life who already “has the right” to get sick falls ill, then in cases of a mild form of the disease with a temperature within 38 °, with minor symptoms of a cold, one can independently, based on one’s own experience, begin treatment using certain means.
It has been known for many years that one of the protective factors, interferon, is weakly secreted at temperatures below 38°C, which can weaken the immune response in general. Therefore, there is no reason to consider a decrease in temperature in all cases as necessary. In addition, the use of antipyretics can lead to side effects.
Therefore, there is no reason to consider a decrease in temperature in all cases as necessary. In addition, the use of antipyretics can lead to side effects.
When the temperature rises, the skin vessels dilate, which allows the body to balance heat production and heat loss. Therefore, it is not necessary to wrap up a feverish child, to cover him with blankets, this can only impede heat transfer. There is no need to be afraid that the temperature will “roll over the top”, will rise indefinitely. In the vast majority of patients, the temperature does not exceed 39 °. However, at higher temperatures, the heat output may not match its products.
Such a situation - it is called a malignant temperature - is extremely dangerous. It is not difficult to recognize it - while the surface of the child's body acquires a motley "marble" color, the skin, especially the hands and feet, remains cold despite the fever. In these cases, it is necessary to rub the skin vigorously until it turns red and give an antipyretic. A child with a fever should be put to bed and provided with plenty of fluids to prevent excessive fluid loss.
A child with a fever should be put to bed and provided with plenty of fluids to prevent excessive fluid loss.
If a child is ill, the first thing to do is DON'T PANIC. Most problems are born out of panic. Call your pediatrician immediately.
Before he arrives, take a temperature measurement.
Make sure that the room where the child is is ventilated and the air is fresh. Don't forget to increase your drinking. Experts note that if the child drinks enough, then you can not be afraid that the temperature will pose a danger to him.
There is a very small group of children who, in response to any infection, overreact, that is, they immediately develop a high temperature, heart and lung failure, loss of consciousness, convulsions immediately occur. Therefore, if a child's temperature creeps up, despite the measures you take, the bill goes to hours and minutes.
The easiest and best way out in this situation is to call an emergency or a pediatrician and hospitalize the baby in a hospital, where all the necessary examinations will be performed and treatment prescribed, and, most importantly, the child will be under the supervision of a doctor around the clock, since the children have a condition can get heavy in a matter of hours.
As the head of the children's consultative and diagnostic center of the Perinatal Medical Center, which includes not only a polyclinic, but also a boxed department for infants and older children, I categorically do not advise you to go to hospitals yourself, “choosing” a hospital. For this, there is emergency care, which, in accordance with the diagnosis, will take the child to a specialized medical institution, depending on the availability of vacant places in it.
I would like to note that the conditions of his stay in the hospital are of great importance for a child, especially at an early age. Individual wards - boxes, round-the-clock stay of a mother with a child, everything necessary for a comfortable stay, modern materials in interior decoration, colors of walls and floors - taking into account the favorable psychological impact on the child - all this is available in the rehabilitation department of the Perinatal Medical Center. In addition, the uniqueness of this department for Moscow lies in the fact that the Center has not only a children's hospital, but also a polyclinic children's department, and specialized traveling children's teams. Thus, the principles of continuity and phasing are fully respected. In the event of a critical situation, a team of pediatricians goes to provide medical assistance and, if necessary, the child is transported to the children's boxed department. Therefore, it is not for nothing that the medical staff of the PMC departments is considered one of the most qualified, because they have to deal with the most difficult situations.
Thus, the principles of continuity and phasing are fully respected. In the event of a critical situation, a team of pediatricians goes to provide medical assistance and, if necessary, the child is transported to the children's boxed department. Therefore, it is not for nothing that the medical staff of the PMC departments is considered one of the most qualified, because they have to deal with the most difficult situations.
Of course, a child's illness is a misfortune. But faith in the successful resolution of the situation, in the child’s own strengths and strengths, and the professionalism of doctors can work wonders. The purpose of our article is not to intimidate future and current parents, but to warn. Convince to be as attentive as possible to the health of the child. After all, as you know, forewarned is forearmed. So, if you notice even minimal deviations in the condition of the baby, then do not treat yourself, consult your doctor.
For every family, the most important thing in life is the happiness and health of their child. But, unfortunately, children often get sick. We sincerely wish you and your children good health, but if the child gets sick, try to "pull yourself together" and do not panic! Your task is to help your child as much as possible! Emotions should fade into the background.
But, unfortunately, children often get sick. We sincerely wish you and your children good health, but if the child gets sick, try to "pull yourself together" and do not panic! Your task is to help your child as much as possible! Emotions should fade into the background.
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Archegova Galina Altafovna
Clinical Hospital MD GROUP
GastroenterologyPediatric gastroenterology
By clicking on the send button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select the clinic
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to update the prices for programs in a timely manner, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we recommend that you check the cost of services by phone / with the managers of the clinic
Clinical Hospital MD GROUPClinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child"Children's Clinic KG "Lapino" in New Riga (branch)Clinic "Mother and Child" KuntsevoClinic "Mother and Child" SavelovskayaClinic "Mother and Child" South-WestClinic "Mother and child" Novogireevo
All directionsKinesiotherapy for childrenSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Massage / manual therapy for childrenTherapeutic research
01.