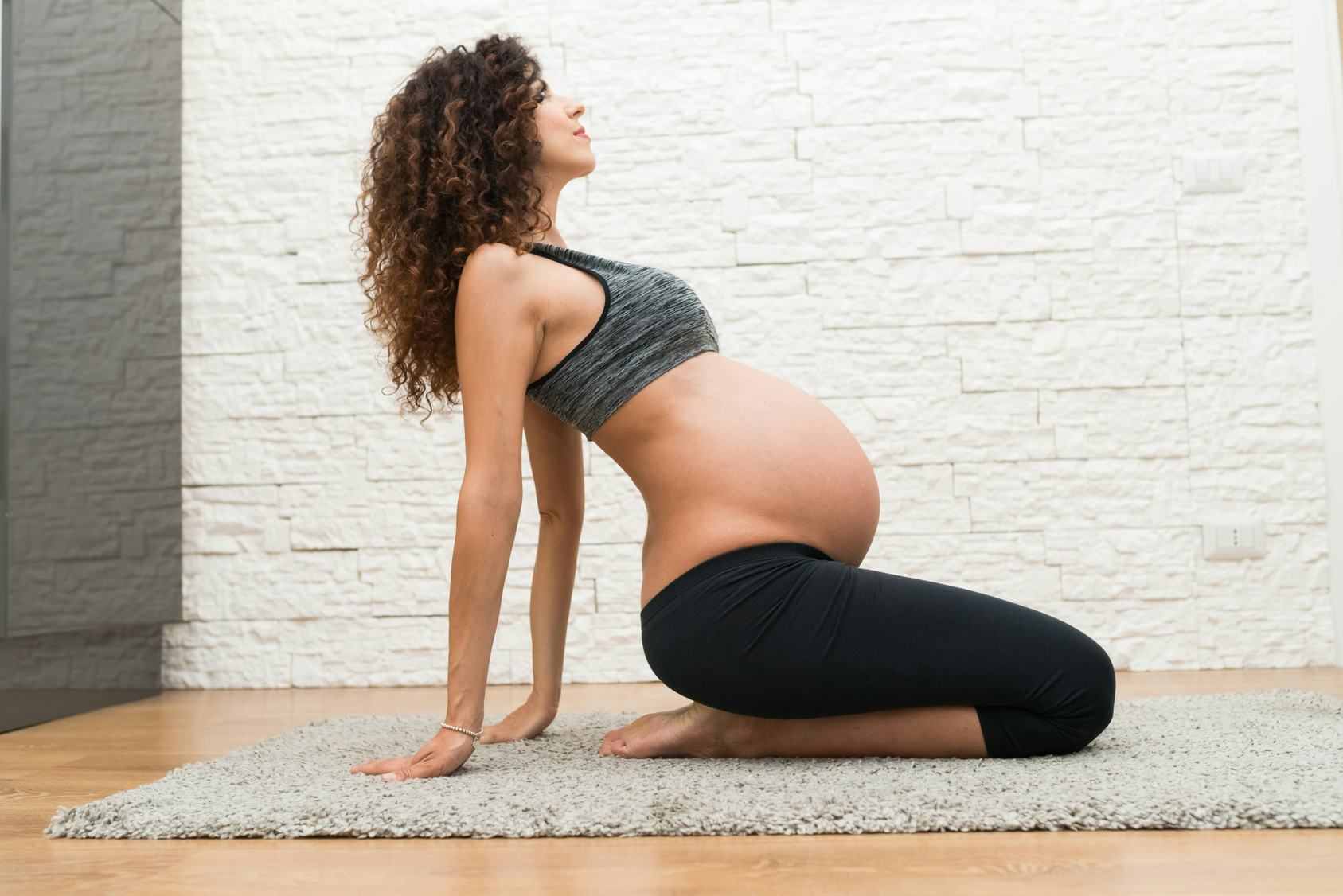
Spina bifida 20 week scan
What is spina bifida? - Shine
Spina bifida literally means ‘split spine’. A fault in the development of the spinal cord and surrounding bones (vertebrae) can leave a gap or split in the spine. The spinal cord does not form properly, and may also be damaged. To help understand what spina bifida is, it is useful to explain the composition of the nervous system.
- The central nervous system
- The spine
- Why does spina bifida happen?
- How is spina bifida diagnosed?
- How is open spina bifida treated?
- What are the effects of spina bifida?
- Genetic Counselling
- MTHFR Gene
The central nervous system
The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. Everything we do, is controlled by the brain, including breathing and maintaining our body temperature. Our senses send information to our brain, which deliver messages to different parts of the body via the spinal cord and pairs of nerves that emerge at each vertebra.
The spine
The spine is made up of 33 bones or vertebrae. The vertebrae have two main functions - to protect our spinal cord, and to provide anchorage to our muscles.
The central nervous system and spine develop very early in the pregnancy, between the 14th and 23rd day after conception. Spina bifida occurs when the neural tube, the structure in the embryo that becomes the brain and spinal cord, fails to close correctly. The vertebrae also fail to form complete rings around the affected portion of the spinal cord. This leaves a gap at the back, involving one or more vertebrae, most commonly around waist-level.
How is spina bifida diagnosed?Open spina bifida, is usually detected at the antenatal mid-term ultrasound (20 week) scan. The appearance of the skull bones and cerebellum - part of the back of the brain - show distinct signs that lead the sonographer to look for tiny changes in the spine. For example, the bones to the sides of the head can look pinched, and the cerebellum looks long, thin and wrapped around the spinal cord, instead of being round (Chiari II).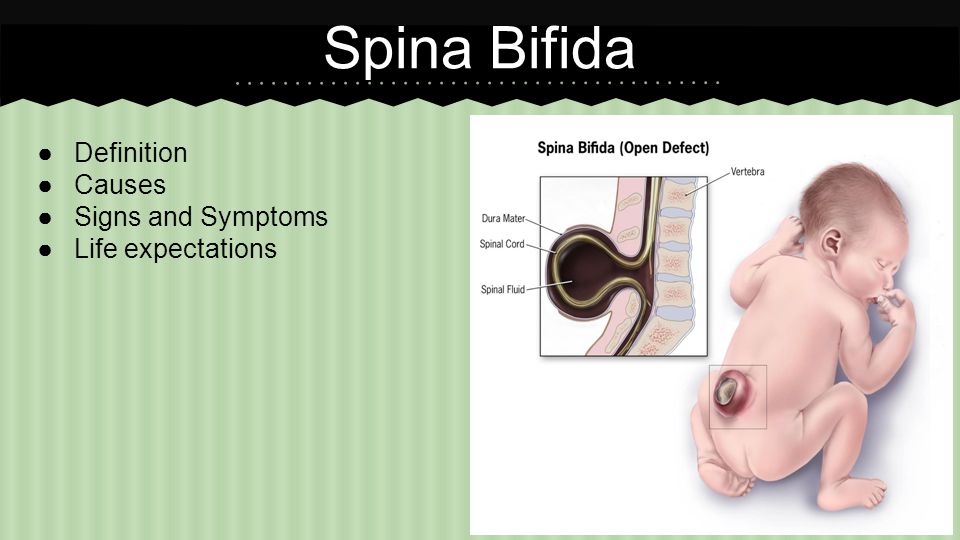
Closed spinal lesions such as lipomyelomeningocele are often not detected at the antenatal mid-term ultrasound scan: the brain and skull will usually look normal so the changes to the spine may not be detected. Often people only become aware that they have it after having a back x-ray for an unrelated problem.
How is open spina bifida treated?Most commonly the baby will be seen by a paediatric neurosurgeon shortly after birth. The surgeon will then decide whether the baby should have surgery to repair the defect in the back: this surgery will take place in a specialist unit usually within 48 hours. Sometimes, in large lesions or premature babies, there may not be enough skin available to close the lesion right away, and the Plastic Surgery Team may be involved.
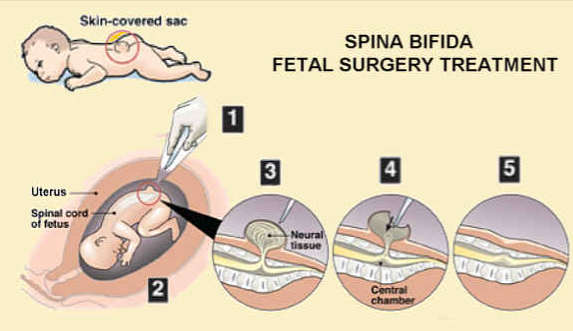
It may be possible, under certain circumstances, to operate on the baby’s lesion in the womb, before 26 weeks of pregnancy. See Shine’s information on prenatal surgery, and talk to your Fetal Medicine clinicians urgently if you are pregnant and would like to know more.
These vary greatly. Even people with a lesion of similar size and position may experience different impairments to varying degrees. Generally, people with lesions at waist level (L1 or above) will use wheelchairs full-time, while most people with lesions at the bottom of the spine (sacral) will be able to walk as adults.
Many children with lesions in the mid lumbar area walk during childhood, but choose to use a wheelchair for longer distances, sports, or as they get older. Splints often help support the feet and ankles.
Loss of skin sensation can lead to sores, especially on the feet, through injury or shoes that rub, and sometimes burns to the feet and legs are also common. It’s important to protect the feet, by having correctly fitting shoes or splints, covering hot pipes and carefully checking the bathwater before getting in.
Bladder and bowels are very often affected, even in people with sacral lesions.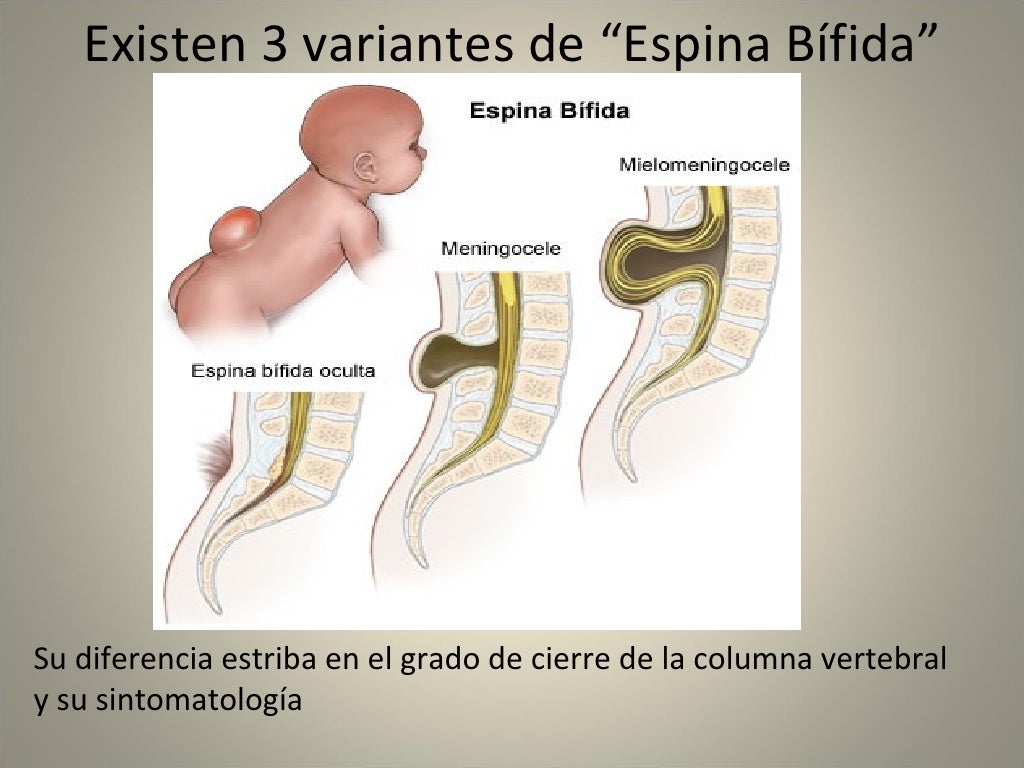 Loss of sensation, and lack of coordination between the bladder muscle and the outlet (bladder neck) can lead to difficulty filling and emptying the bladder. Infections, leaking and frequency of passing urine can occur, but intermittent catheterisation, and medication to relax the bladder can be a big help. Bowel issues such as constipation or leakage can often be helped with irrigation and/or medication.
Loss of sensation, and lack of coordination between the bladder muscle and the outlet (bladder neck) can lead to difficulty filling and emptying the bladder. Infections, leaking and frequency of passing urine can occur, but intermittent catheterisation, and medication to relax the bladder can be a big help. Bowel issues such as constipation or leakage can often be helped with irrigation and/or medication.
Because spina bifida changes the way the brain develops, there can be an impact on learning and behaviour.
NB Children with spina bifida should have their childhood vaccinations just like other children.
Genetic CounsellingProspective parents who have had a baby with a neural tube defect, or who have a close relative with a neural tube defect, should be referred to a genetic counsellor for advice. This referral can be made through a GP.
Why does spina bifida happen?
At present we don’t know exactly why spina bifida develops, and research continues.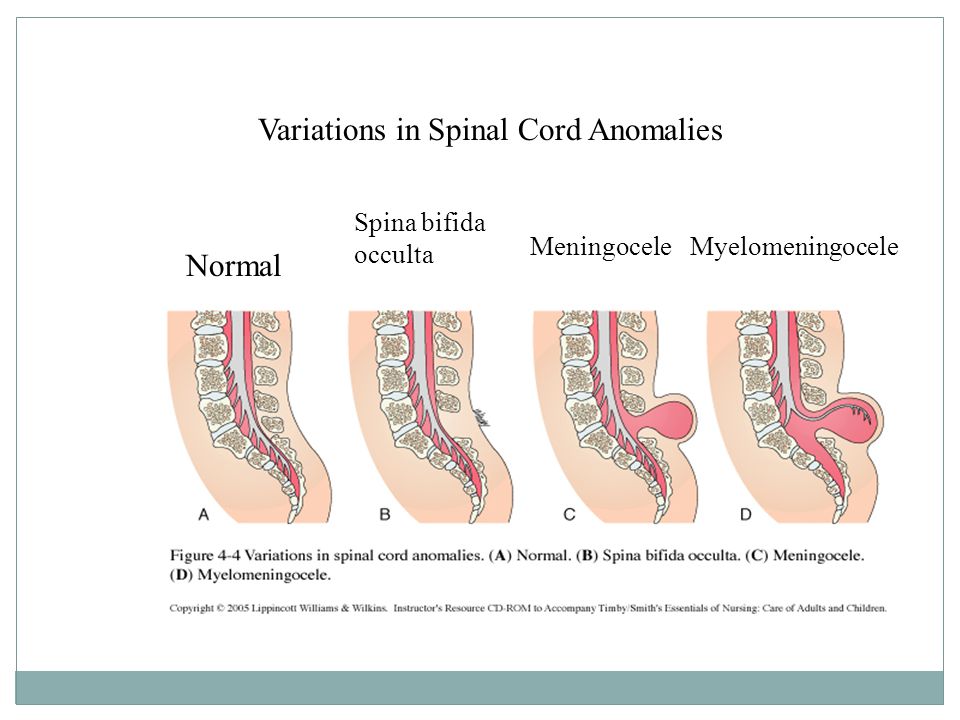
However, we do know that taking folic acid supplements before getting pregnant can reduce the risk of spina bifida in unborn babies. For families with no history of spina bifida the Department of Health recommends women take an ‘over the counter’ dose of 400mcg daily. For families where there is a history of spina bifida, or other neural tube defects, a prescription dose (5mg) of folic acid is needed.
Folic acid should be taken daily for at least 8 weeks prior to conception and through to the 12th week of pregnancy.
The exact reasons why the neural tube develops incorrectly are not yet known but it is probably connected with both genetic and environmental factors are known to contribute. Shine also recommends taking a supplement of B12 (2.5mcg or more) for three months before pregnancy. For more information, please visit www.folicforlife.com
Types of spina bifida
You may not know, but there are a number of different types of spina bifida. We’ve listed them here along with an explanation of what each one means.
We’ve listed them here along with an explanation of what each one means.
Learn more about the condition
Need more help?
If you need to speak with one of Shine’s specialist advisers about spina bifida or hydrocephalus, call us on 01733 555988 or click here to email us.
Our office hours are Monday to Friday, 9am to 5pm. We aim to respond to all enquiries as quickly as possible!
Reviewed 31/03/21
Neural tube defects | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Neural tube defects | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
Neural tube defects are abnormalities that occur in the development of the spinal cord and brain of some babies. The most common defects are spina bifida (abnormal development of part of the spine and spinal cord) and anencephaly (severely abnormal development of the brain).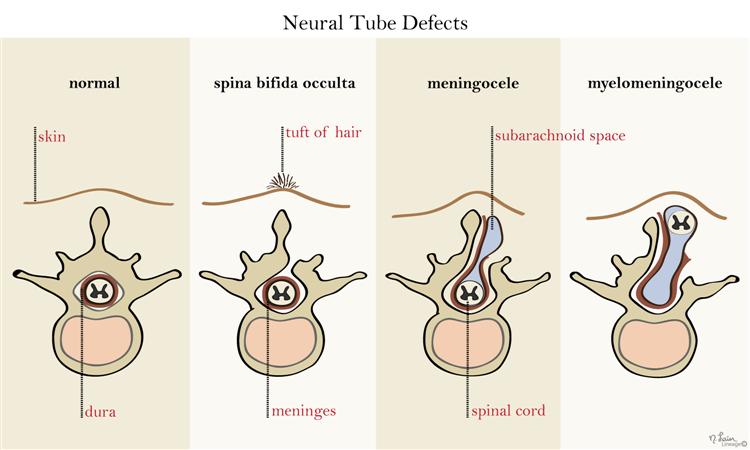
What are neural tube defects?
During the first month of life, an embryo (developing baby) grows a primitive tissue structure called the ‘neural tube’. As the embryo develops, the neural tube begins to change into a more complicated structure of bones, tissue and nerves that will eventually form the spine and nervous system.
However, in cases of spina bifida, something goes wrong with the development of the neural tube and the spinal column (the ridge of bone that surrounds and protects the nerves) does not fully close. Spina bifida is a Latin term that means ‘split spine’.
The chance that a pregnancy will be affected by a neural tube defect is less than one in 1,000.
What causes neural tube defects?
The cause of neural tube defects is not certain, but it appears to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Women are at increased risk of having a baby with a neural tube defect if:
- they have already had a baby with a neural tube defect
- they or their partner have a close relative born with a neural tube defect
- they have type 1 (insulin dependent) diabetes (not gestational diabetes)
- they are obese, or take certain anti-epileptic medications, especially those containing sodium valproate or valproic acid
Prevention
About 2 in 3 neural tube defects can be prevented through increasing folate (folic acid) intake at least a month before pregnancy and during the first 3 months of pregnancy. Adequate folate levels are critical during the early days of the developing embryo, particularly the 3rd and 4th week, the period in which neural tube defects occur and when many women won't know they are pregnant.
Adequate folate levels are critical during the early days of the developing embryo, particularly the 3rd and 4th week, the period in which neural tube defects occur and when many women won't know they are pregnant.
You can increase your folate intake by eating folate-rich foods, including folate-fortified foods in your daily diet, or by taking a folic acid supplement. Good sources of folate include green leafy vegetables, fruit (citrus, berries and bananas), legumes and some cereals (bread and many breakfast cereals now have added folate).
Women who take medicines to control epilepsy, seizures or psychiatric disorders should talk to their doctor before taking folate because it can interfere with how their medications work.
For more information see folate and pregnancy.
Diagnosis
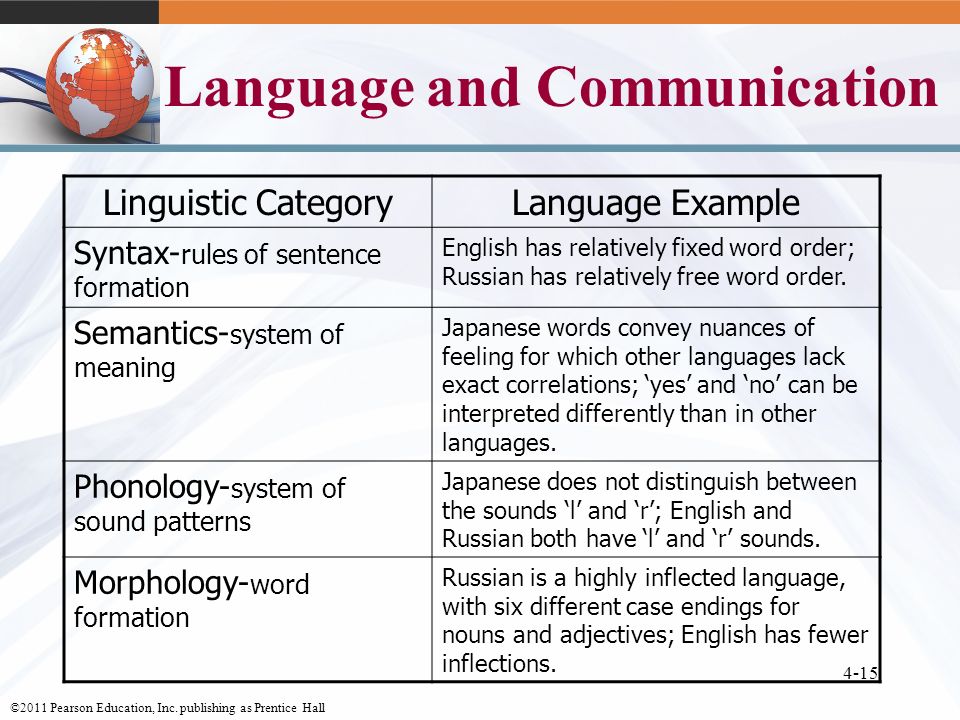
Neural tube defects may be diagnosed during the ultrasound scan that is carried out around week 12 of the pregnancy or, more likely, during the anomaly scan that is carried out at around weeks 18 to 20.
Ultrasound scans
An ultrasound scan is a safe procedure that uses sound waves to create an image of the inside of your body. Most hospitals will offer women at least 2 ultrasound scans during their pregnancy. The first is usually at around 8 to 14 weeks and is sometimes called the ‘dating scan’ because it can help to determine when the baby is due. This first scan may be able to detect problems with your baby’s spine that could indicate spina bifida if the condition is severe. If a dating scan is done earlier than 12 weeks, another ultrasound called the nuchal translucency scan is done at 12 weeks to check amongst other things for signs of Down Syndrome, and if a dating scan is not done prior to this then this scan can be used as the dating scan.
Morphology scan
The morphology or anomaly scan is an ultrasound scan that is carried out around weeks 18 to 20 of your pregnancy. This scan aims to identify any physical problems with your baby. It is usually during this scan that spina bifida is diagnosed.
Coping with the results
If tests confirm that your baby has spina bifida, the implications will be fully discussed with you. You will need to consider your options carefully. Your options are to:
- continue with your pregnancy while getting information and advice so that you are prepared for caring for your baby
- end your pregnancy
If you are considering ending your pregnancy, you should talk to your doctor or midwife. They will be able to provide you with important information and advice.
Your options for ending your pregnancy will depend on how many weeks pregnant you are when you make the decision. If you decide to end your pregnancy, you may wish to talk to a counsellor afterwards. Your doctor or midwife will be able to arrange this for you.
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to discuss your options regarding your pregnancy with a maternal child health nurse.
Sources:
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (Neural tube defects in Australia), The Centre for Genetics Education (Neural tube defects – spina bifida and anencephaly), RANZCOG (Planning for pregnancy), Women's and Children's Health Network (Screening tests for neural tube defects), Sydney Children's Hospital Network (Factsheet: What is spina bifida?)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.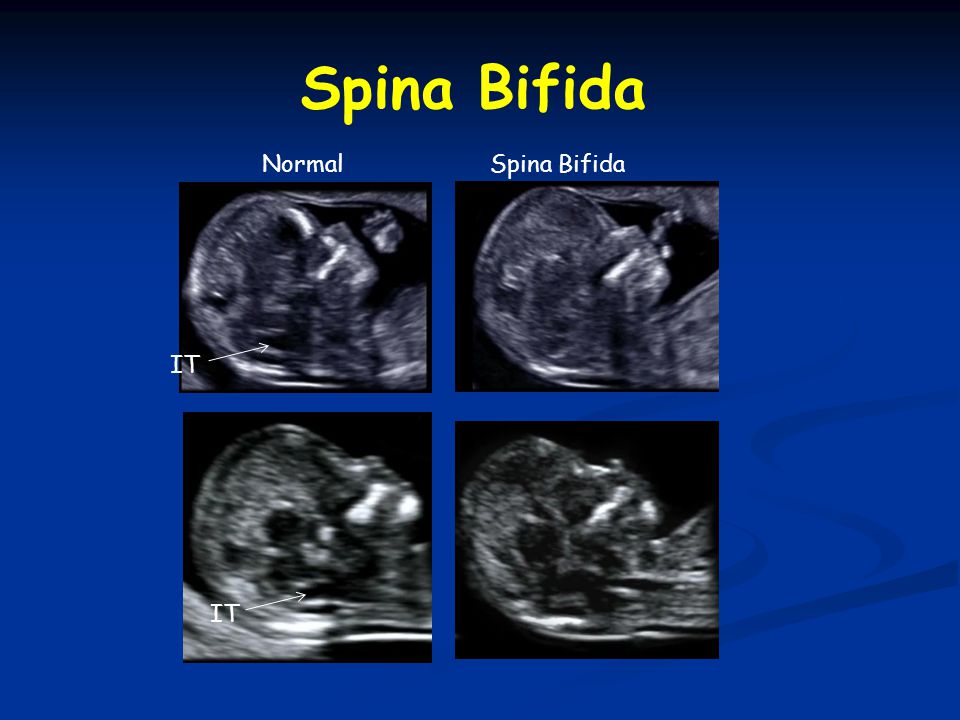
Last reviewed: March 2020
Back To Top
Need more information?
Pregnancy checkups, screenings and scans
Knowing what check-ups, screenings and scans to have and when to have them during your pregnancy is important information for every pregnant woman.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Neural tube defects: children & teens | Raising Children Network
Neural tube defects are brain and spinal cord abnormalities, including spina bifida, encephalocele and anencephaly. Read how they affect children.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Folate and pregnancy
Folate and folic acid are important for pregnancy since they can help prevent birth defects known as neural tube defects, such as spina bifida.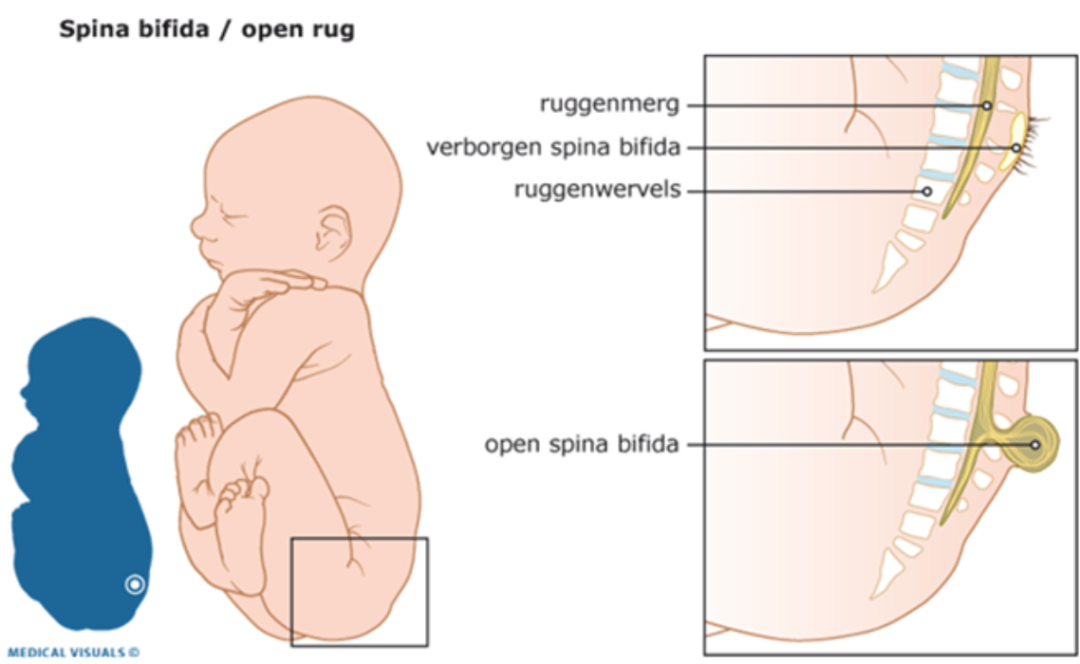
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Spina bifida
Spina bifida is a condition that affects the normal development of a baby’s spine early in pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Spina Bifida | Sydney Children's Hospitals Network
Spina Bifida comes from a latin term which means “split spine”
Read more on Sydney Children's Hospitals Network website
Maternal screening - Pathology Tests Explained
Why and when to get tested for maternal screening
Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website
Folic acid & iodine fortification, Summary - Australian Institute of Health and Welfare
Mandatory folic acid and iodine fortification of bread resulted in increased levels of folic acid and iodine in the food supply, increased folic acid and iodine intakes, a decreased rate of neural. ..
..
Read more on AIHW – Australian Institute of Health and Welfare website
Folate | Jean Hailes
Folate is a B vitamin needed for healthy growing, in particular for the nervous system.
Read more on Jean Hailes for Women's Health website
What supplements should I take during pregnancy? | Queensland Health
Find out what supplements and vitamins you need to take when trying to get pregnant, during pregnancy, after pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
Read more on Queensland Health website
Pregnancy at weeks 1 to 4
When you conceive, your body’s hormone levels change, but you may not notice any signs that you’re pregnant yet.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Spinal hernia in a newborn child: symptoms, treatment
Spinal hernia in newborns is a fairly rare, but very severe developmental pathology that occurs in only 0.1-0.3% of children. And almost 2/3 of children remain chained to a wheelchair for life. Congenital spina bifida can be determined at the stage of pregnancy.
Causes of spinal hernia in newborns
Why manifestations of spinal hernia in newborns may occur is not well understood.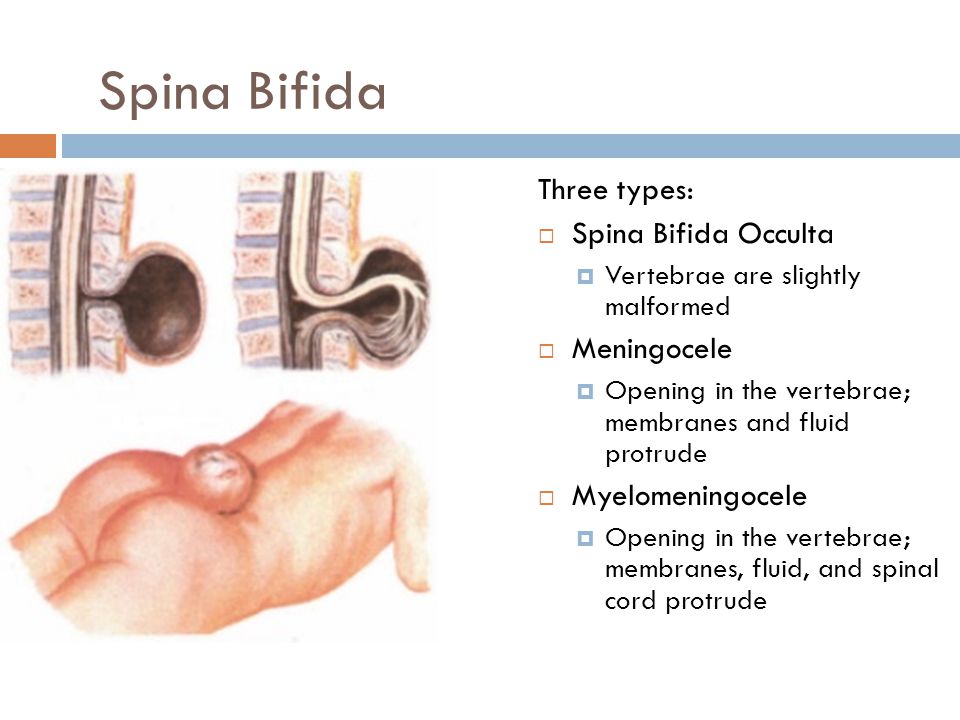 Therefore, one can only name the factors that can influence the development of pathology, based on the opinion of leading professors of medical sciences. Risk factors include:
Therefore, one can only name the factors that can influence the development of pathology, based on the opinion of leading professors of medical sciences. Risk factors include:
- a pregnant woman's lack of adequate amounts of folic acid, also known as vitamin B9, as well as other vitamins, is now recognized as the main cause of spina bifida in infants; nine0016
- pregnancy intoxication;
- early pregnancy;
- hereditary factor.
The formation of the neural tube occurs before the eighth week of gestation, and it is at this time that one or more of the listed factors can provoke the onset of pathology. As a result of this phenomenon, one or more vertebral bodies are separated in the region of the spinous process. The membranes of the spinal cord, fluid and even nerve endings can go into such a gap. nine0003
Forms of spinal hernia in newborns
A spinal hernia in a child can be divided according to its location and structural features.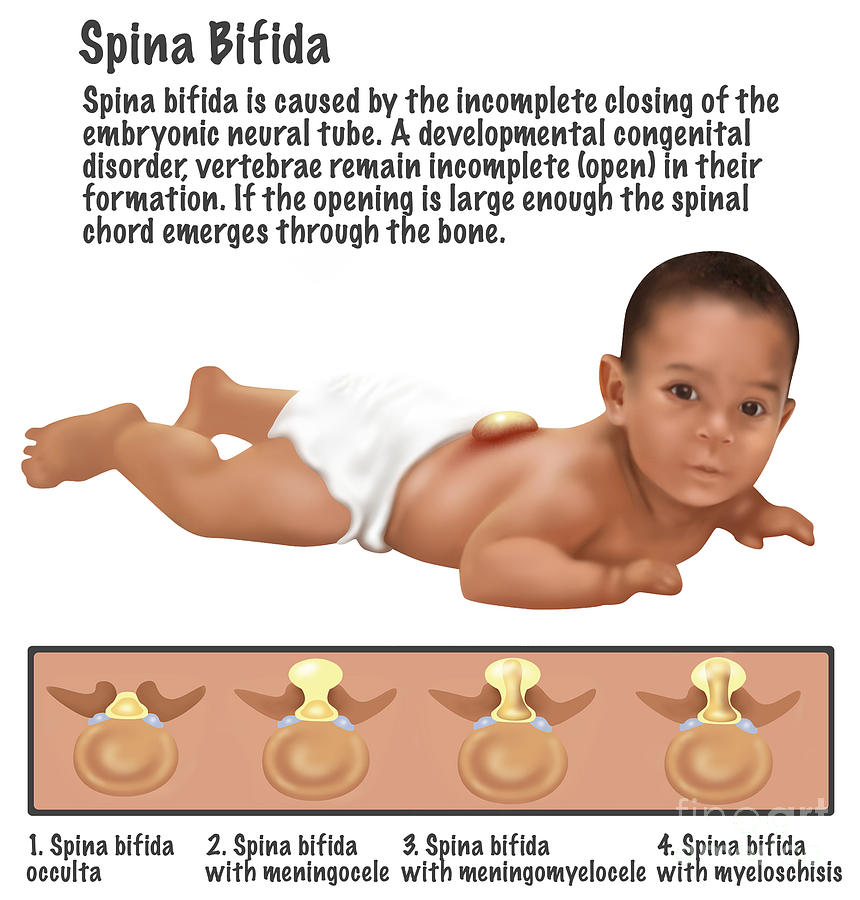 Where the protrusion is located is very important, since further treatment, the complexity of the symptoms and its elimination will depend on this factor. The easiest variety is hidden splitting, when one vertebra is slightly deformed, which will not bring much discomfort to the child. If the defect is more serious, a hernial split occurs when a clearly visible protrusion is detected, which is visible under the skin. In severe cases, the spinal cord itself comes out into this protrusion. If we talk about where the spinal hernia is located in a child, we can distinguish: nine0003
Where the protrusion is located is very important, since further treatment, the complexity of the symptoms and its elimination will depend on this factor. The easiest variety is hidden splitting, when one vertebra is slightly deformed, which will not bring much discomfort to the child. If the defect is more serious, a hernial split occurs when a clearly visible protrusion is detected, which is visible under the skin. In severe cases, the spinal cord itself comes out into this protrusion. If we talk about where the spinal hernia is located in a child, we can distinguish: nine0003
- cervical - the rarest, affects the upper parts of the spinal cord, innervation can occur in the neck and face, respectively, coordination is disturbed, and malfunctions of the lungs and heart occur;
- chest - occurs more often in the neck, but much less often in the lumbar, and the pathology can affect the work of the arms and legs, lungs, heart, stomach, spleen, liver, etc .;
- lumbosacral - occurs most often, affects the functioning of the pelvic organs, kidneys and lower extremities.
 nine0016
nine0016
Whatever the protrusion, the severity of the condition will be determined depending on its size.
Symptoms of spinal hernia in newborns
A photo of a spinal hernia in newborns is often found on the Internet, and almost every pregnant woman is afraid of this pathology. To determine if a newborn has such a disease, look for signs of a hernia. These include:
- paralysis of limbs, disorders and nutrition, paresis; nine0016
- pelvic troubles, fecal incontinence;
- malfunctions of the heart, lungs, gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system.
All these symptoms may be accompanied by secondary complications, which include muscle atrophy, edema, trophic ulcers and lack of skin thermoregulation, etc.
Diagnostics
To determine the presence of the disease, the doctor collects an anamnesis of a small patient, and also conducts a complete examination of him. If there were no abnormalities during pregnancy, doctor will determine the health status of the child, taking into account his age. He will check how well the muscles are developed, whether there is any weakness, difficulty in muscle activity, etc. In addition, to determine the presence of the disease and the consequences of spinal hernia in newborns, you will need:
If there were no abnormalities during pregnancy, doctor will determine the health status of the child, taking into account his age. He will check how well the muscles are developed, whether there is any weakness, difficulty in muscle activity, etc. In addition, to determine the presence of the disease and the consequences of spinal hernia in newborns, you will need:
- Visit neurologist .
- Carry out a light scan, called transillumination, to identify the obsession of the protrusion. nine0015 Myelography with contrast - allows you to determine the damage to the spinal cord.
- MRI or CT.
- Visit a neurosurgeon who will determine the need for surgery and give prognosis.
Timely detection of the disease will increase the chances of a successful cure for the baby from the disease.
Treatment
The disease is usually treated with surgery. It can be performed both before and after birth. nine0003
nine0003
Perinatal surgery
It can be prescribed at 19-26 weeks of gestation and is recognized as the most effective method of ridding a child of a hernia. The operation will close the anatomical anomaly in the spinal column, as a result of which the spinal cord returns to its place and is protected from influences. Among the reasons for the appearance of a spinal hernia in newborns in this case may be natural childbirth, therefore, after the operation, the woman will be delivered by caesarean section. This method allows you to ensure the most normal life for the child. Among the shortcomings of the method is that such operations, like those for premature babies, are performed only abroad. At the moment, there are only a few specialists capable of performing such an operation in Russia. nine0003
Postpartum surgery
This type of treatment is possible in the first few days after birth, then it does not make sense. Surgery will remove the growth, but there will be significant developmental problems and additional surgery may be needed.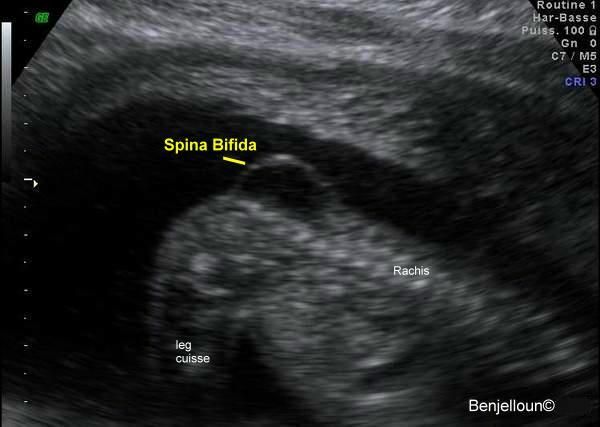 Life expectancy is affected not only by the type of hernia, but also by the presence of hydrocephalus.
Life expectancy is affected not only by the type of hernia, but also by the presence of hydrocephalus.
Rehabilitation
Your healthcare provider will be able to tell if a baby's spinal hernia can be treated with ozone gas, and will also determine what rehabilitation measures are needed. If we are talking about foreign clinics, then often they have sanatorium branches where doctors monitor the child's condition after the intervention. Rehabilitation may include massages and exercise therapy. nine0003
pregnancy bronchi abdomen vagina genitals pituitary eyes eye orbits shin head brain throat larynx rib cage thoracic region diaphragm for kids glands stomach gallbladder stomach retroperitoneum back of the head teeth brush intestines collarbone knee limbs contrast agent coccyx bone sacrum lungs lymph node facial skeleton elbow scapula small pelvis uterus period breast bladder scrotum soft tissues adrenal glands leg nose nasopharynx finger groin liver esophagus pancreas spine penis kidneys small of the back lumbosacral region forearms appendages prostate calcaneus ribs arm sciatic nerve spleen heart vessels joints back foot joints tendon pelvis hip joint trachea Turkish saddle an ear jaw scull cervical cervical region neck thyroid ovaries
Sign up for a consultation or diagnostic today!
You can make an appointment by phone: +7 (812) 901-03-03
Or leave a request
full name
Phone number
By clicking the "Make an appointment" button, I accept the terms of the Personal Data Processing and Security Policy and consent to the processing of my personal data.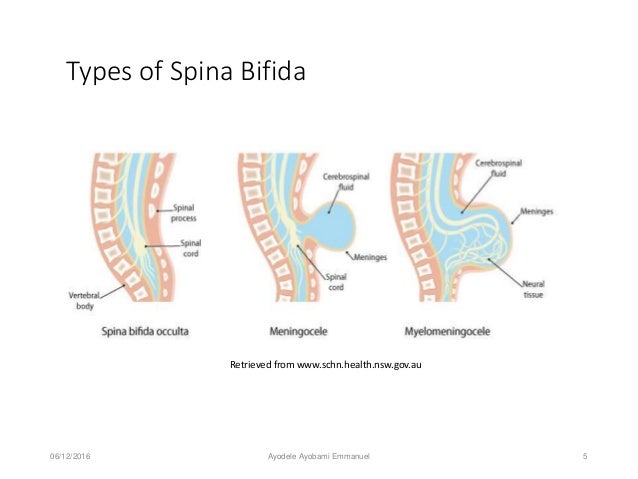 nine0003
nine0003
Our medical centers
Making an appointment
Patient's last name *
Incorrect first name
nine0002 Name *Middle name
nine0002 Contact phone *E-mail *
nine0002 By clicking the "Make an appointment" button, I accept the terms of the Personal Data Processing and Security Policy and consent to the processing of my personal data.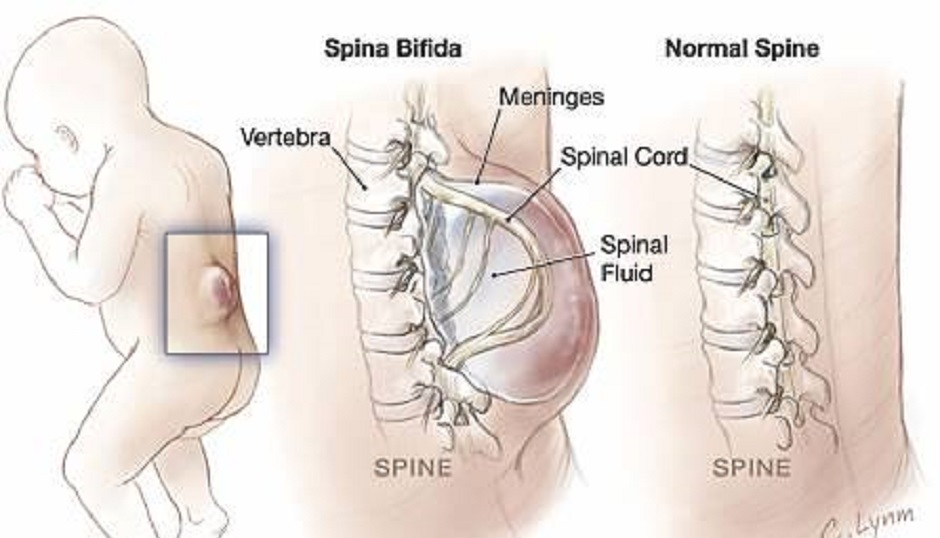
Registration and payment for repeated online appointment
Patient's last name *
Incorrect first name
nine0002 Name *Middle name *
nine0002 Contact phone *E-mail *
nine0002 By clicking the "Submit request" button, I accept the terms of the Personal Data Processing and Security Policy and consent to the processing of my personal data.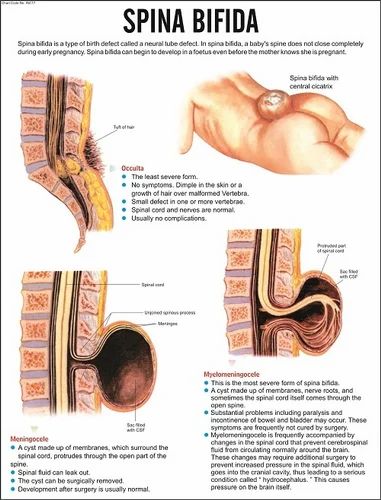
About cookies on this website
We use cookies, IP addresses and device data for analytics to make your visit to the site convenient and personalized. You can disable cookies in your browser settings. By continuing to use our site, you consent to the processing of the listed data and accept the terms of the Privacy Policy. nine0003
Intervertebral disc herniation. Treatment of spinal hernia, symptoms, causes, diagnosis
Video
Title
- Manifestation
- Methods of treatment
Herniated discs are the most common and most severe manifestation of spinal osteochondrosis. At the same time, a pain radicular syndrome develops, which may be accompanied by paresis or paralysis of the muscles of the lower extremities, a sensitivity disorder, and a dysfunction of the pelvic organs. nineteen% of patients with herniated discs need surgical treatment.
nineteen% of patients with herniated discs need surgical treatment.
Dystrophic changes in the lumbosacral spine are most pronounced at the age of 20 to 50 years and are one of the most common causes of temporary disability and often - disability of the patient. Up to 50% of all surgical interventions in neurosurgical hospitals are performed for the pathology of discs at the lumbosacral level.
The disease results from a ruptured intervertebral disc . The resulting spinal hernia , protruding back and to the side, puts pressure on the nerve root at the point of its exit from the spinal canal and causes inflammation, accompanied by edema. This explains why pain and loss of sensation appear only a day after the onset of the disease. The pinched nerve root sends pain impulses to the brain, which are perceived by the patient as if they were coming from the leg. Part of the nerve outside the pressure site hernia almost ceases to function, which leads to a sharp decrease in sensitivity and the appearance of weakness in the leg.
Manifestation
In almost all patients, the main complaint is pain. As a rule, pain occurs in adolescence after moderate physical exertion, an uncomfortable position at the workplace or in bed. As well as with "lumbago", the disease often occurs when tilting with a simultaneous turn to the side, often in combination with heavy lifting. Sudden, not particularly severe pain in the lumbar region is also characteristic. Then, during the day, pain and weakness appear in one of the legs, sometimes with loss of sensation on the inside of the foot and lower leg or on the outside of the foot and the inside of the leg. When moving, coughing, sneezing or straining, the pain in the back and leg intensifies and often becomes so intense that the patient needs bed rest. Some relief can be achieved by lying down, raising your legs or placing them on a pillow. nine0003
There are two stages in the development of the disease. At the first stage, there is pain in the lumbar region, which indicates the beginning of the degenerative-dystrophic process.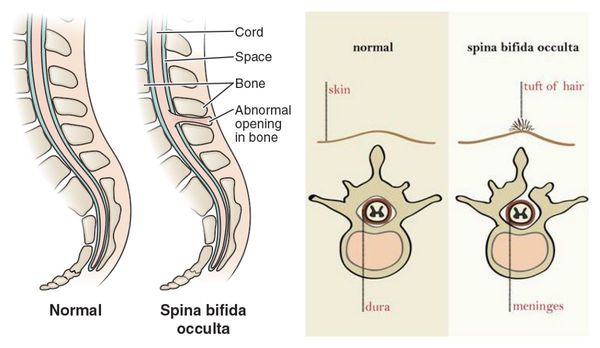 Under the influence of degenerative changes in the spinal motion segments, the rather complex structure of the fibrous ring changes, radial cracks form in it, which reduces its strength. The nucleus pulposus protrudes, the blood circulation of this zone is disturbed, there is swelling of local tissues, hypoxia of the spinal cord root, adhesions. Annulus fibrosus, posterior longitudinal ligament, dura mater, intervertebral joints are well innervated by branches of the sinuvertebral nerve. A pain syndrome occurs, which leads to myopically fixation of the pathological zone due to the tension of the back muscles and, as a result, compensatory curvature of the overlying sections of the spine occurs. Thus, a vicious circle is formed. Subsequently, prolonged pathological impulsation leads to degenerative changes in the articular-ligamentous apparatus.
Under the influence of degenerative changes in the spinal motion segments, the rather complex structure of the fibrous ring changes, radial cracks form in it, which reduces its strength. The nucleus pulposus protrudes, the blood circulation of this zone is disturbed, there is swelling of local tissues, hypoxia of the spinal cord root, adhesions. Annulus fibrosus, posterior longitudinal ligament, dura mater, intervertebral joints are well innervated by branches of the sinuvertebral nerve. A pain syndrome occurs, which leads to myopically fixation of the pathological zone due to the tension of the back muscles and, as a result, compensatory curvature of the overlying sections of the spine occurs. Thus, a vicious circle is formed. Subsequently, prolonged pathological impulsation leads to degenerative changes in the articular-ligamentous apparatus.
And at the second stage, the nature of the pain syndrome changes. There is a compression radicular syndrome, which is caused by mechanical compression and tension of the root. In this case, swelling of the root occurs, its blood supply is disturbed. With direct contact herniated disc with root chemical irritation causes more intense pain. Often, when radicular pain occurs, pain in the lumbosacral region weakens or disappears. Apparently, this is due to a decrease in intradiscal pressure due to rupture of the annulus fibrosus. Vertebrogenic pain syndrome can be caused not only by compression of the root (radiculopathy) or spinal cord (myelopathy), but also by the vessel feeding the root - radiculomyeloishemia. nine0003
In this case, swelling of the root occurs, its blood supply is disturbed. With direct contact herniated disc with root chemical irritation causes more intense pain. Often, when radicular pain occurs, pain in the lumbosacral region weakens or disappears. Apparently, this is due to a decrease in intradiscal pressure due to rupture of the annulus fibrosus. Vertebrogenic pain syndrome can be caused not only by compression of the root (radiculopathy) or spinal cord (myelopathy), but also by the vessel feeding the root - radiculomyeloishemia. nine0003
Distribution and localization of radicular pain generally corresponds to the zone of innervation of the compressed root. Pain is more often "lamp" in nature, may be constant or coming. The disks L4-L5 and L5-S1 are mainly affected. The L3-L4 level suffers only in 2-4% of cases. In addition to pain, sensitivity disorders, such as hypoesthesia and anesthesia, sometimes hyperesthesia, can be determined.
Vegetative disorders are observed in the form of hypothermia of the skin, their pastosity, sweating changes, dryness of the skin increases.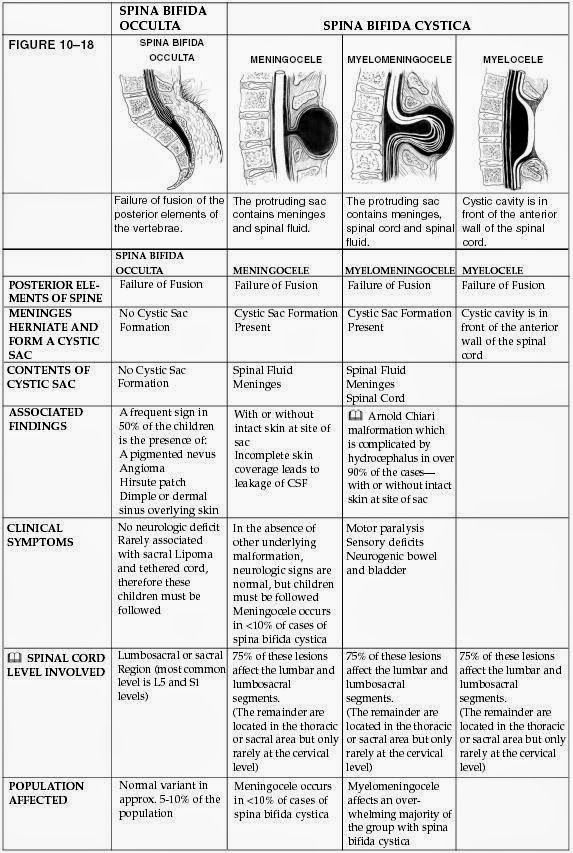 nine0003
nine0003
Quite often, patients are in a forced position. Compensatory postures that reduce the degree of compression and tension of the root are manifested by scoliosis, flattening of the lumbar lordosis, limitation of flexion and extension of the body, and tension of the long back muscles.
Sometimes patients cannot straighten their leg due to pain. Motor disturbances in the form of paresis or paralysis are rarely noted, they are more typical for advanced cases. There may be trophic disorders in the form of "weight loss" due to muscle atrophy. In the early stages of the disease, symptoms of irritation are more pronounced, in the later stages - symptoms of loss of functions. nine0003
Treatment of intervertebral disc herniation.
The human body has a powerful ability to self-heal, which also applies to damaged intervertebral discs . Usually this disease goes away in 2-3 months, subject to bed rest and rest - the best prerequisites for a quick recovery without complications.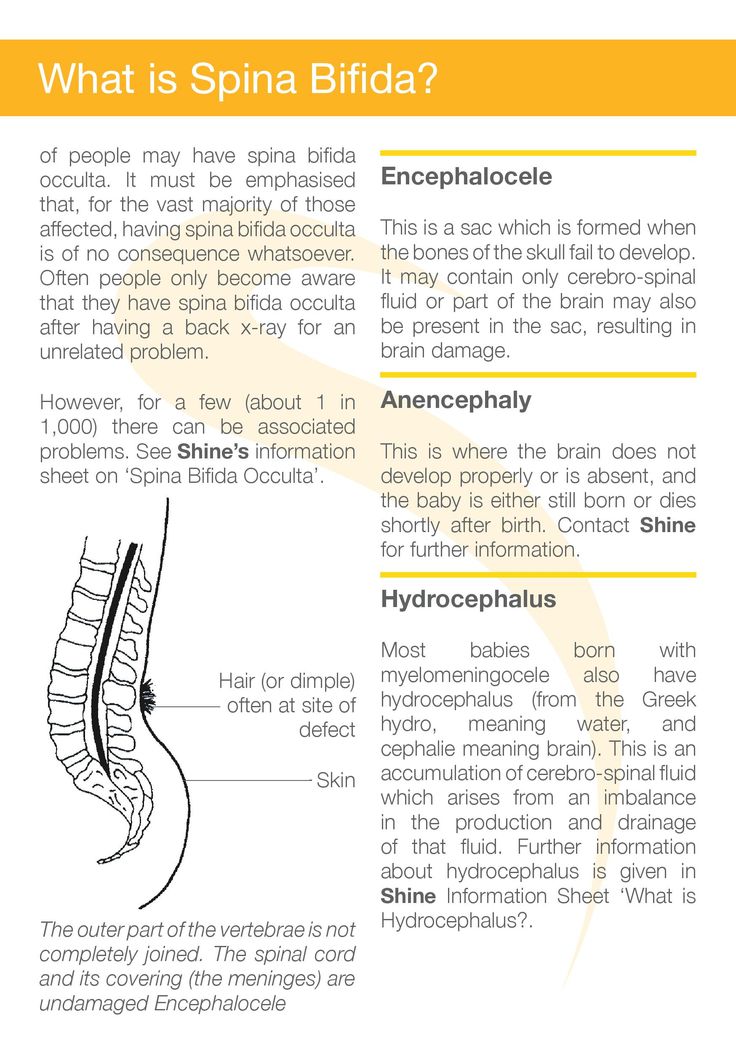 As with other diseases of the lumbar spine, it is recommended to lie on your back with your legs raised or placed on a pillow, changing body position and looking for a comfortable, painless posture. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs can be taken to relieve severe pain, although they do not speed up recovery, they reduce suffering. After 3-4 weeks, the pain usually subsides significantly, but the damage itself disk is not yet healed, therefore, in order to avoid possible complications in the form of chronic back pain, rest for another whole month is necessary.
As with other diseases of the lumbar spine, it is recommended to lie on your back with your legs raised or placed on a pillow, changing body position and looking for a comfortable, painless posture. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs can be taken to relieve severe pain, although they do not speed up recovery, they reduce suffering. After 3-4 weeks, the pain usually subsides significantly, but the damage itself disk is not yet healed, therefore, in order to avoid possible complications in the form of chronic back pain, rest for another whole month is necessary.
Surgical treatment is indicated in the presence of intractable pain syndrome (treatment period from 2 weeks to 3 months), an increase in neurological deficit, cauda equina syndrome (impaired function of the pelvic organs, decreased potency, numbness of the perineum).
Other herniated disc treatment in the acute stage - traction of the spine. This is a very old method, interest in which has recently been increasing. Traction creates a pressure drop in the intervertebral space, which makes it possible to “suck in” a hernia of the spine . In this case, it is necessary to find the correct direction of influence and select the appropriate force so as not to damage the spine even more. Sometimes the patient is recommended to carry out traction himself, in accordance with the pain sensations. With the right procedure, the pain should decrease, not increase. nine0003
Traction creates a pressure drop in the intervertebral space, which makes it possible to “suck in” a hernia of the spine . In this case, it is necessary to find the correct direction of influence and select the appropriate force so as not to damage the spine even more. Sometimes the patient is recommended to carry out traction himself, in accordance with the pain sensations. With the right procedure, the pain should decrease, not increase. nine0003
So, treatment of hernia is as follows:
- If the pain is moderate or tolerable, bed rest and pain medications are recommended until the condition improves or at least for 3-4 weeks.
- The spinal traction method can also be used to quickly relieve pain. If they are still unbearable despite bed rest and drug therapy, mechanical stretching may also be a way out. nine0016
- However, if the pain is unbearable despite repeated traction and complete rest, surgery is not excluded.