Normal newborn head shape
Newborn Head Shape – What is Normal?
Posted on July 15, 2018 by Sydney West Physio - Paediatric Physiotherapy
It’s very common for a newborn’s head to be elongated or have an odd shape. Babies may have an uneven head shape at birth, however this should remould to a normal, more symmetrical shape within 6 weeks after birth.
When babies are born, the bones of their skull are thin and flexible, meaning the head is soft and may change shape easily. All babies should have two soft areas at the top of their head (fontanelles). These fontanelles allow for your baby’s rapidly growing brain during infancy and usually closes around 12 months of age.
Positional plagiocephaly describes a condition where your baby’s head is not symmetrical but the fontanelle remains open. Positional plagiocephaly does not affect the development of your baby’s brain however; it may alter your baby’s physical appearance as it can cause uneven growth of their head or face. Positional plagiocephaly is a relatively common condition occurring in an estimated 10-50% of newborns.
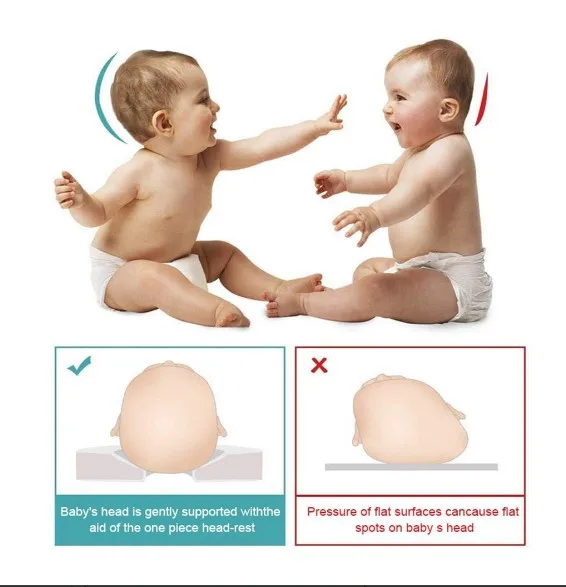
Flattening of your baby’s head can occur when constant pressure is applied to one part of a baby’s head.
Studies have found babies to be more likely to have positional plagiocephaly if they have the following characteristics:
- First born
- Premature
- Male
- Difficult or assisted birth
- Breech positioning during the last trimester
- Other neck problems e.g. congenital muscular torticollis
- Lack of supervised tummy time when awake i.e. less than 3 times per day
- Always positioned to the same side when feeding or sleeping
If your baby has positional plagiocephaly, it is important to determine if the fontanelles have closed too early. This is a condition called craniosynostosis. It is estimated to occur in 1 /2500 live births and should be reviewed by a doctor.
Positional plagiocephaly: What can you do?
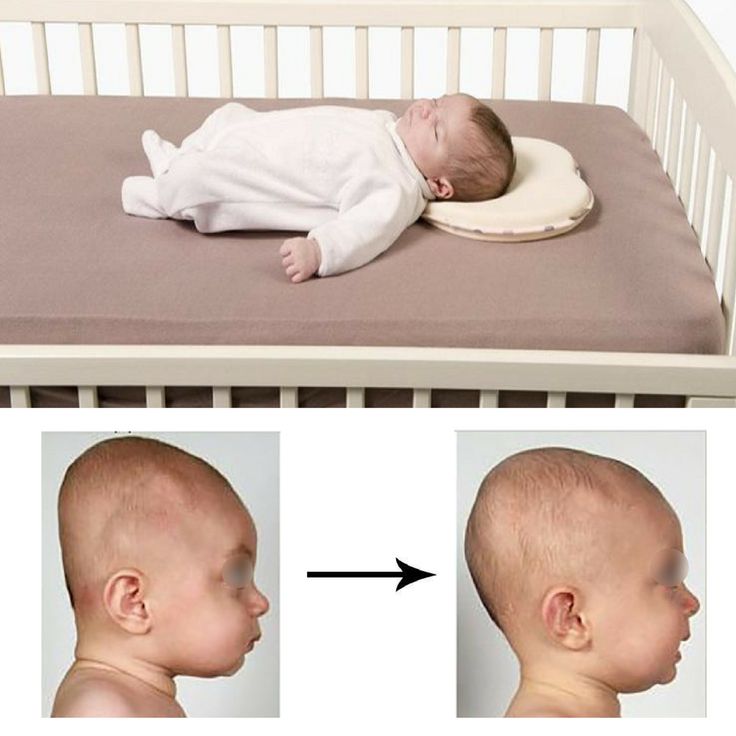
For the majority of children, positional plagiocephaly is a correctable condition. For most babies, regular repositioning of your baby’s head before they are 4 months old will result in optimal outcomes. If your baby has a flat spot, alternating their head position can improve this.
For most babies, regular repositioning of your baby’s head before they are 4 months old will result in optimal outcomes. If your baby has a flat spot, alternating their head position can improve this.
Tummy Time:
- Provide supervised “tummy time” when you baby is awake
- “Tummy time” promotes normal shaping of the back the head, it also helps babies to strengthen their neck muscles and learn to push up on their arms, which helps develop the muscles needed for crawling and sitting up.
- Looking around from a new perspective encourages your baby’s learning and discovery of the world. Move toys around to keep your baby active and stimulated.
Side Positioning for Play:
- When awake and you are supervising them, place your baby on their side to play
Hold your baby more often or consider an appropriate sling
- Pick up and hold your baby in an upright position.
 This will take pressure off the head and may help with development of neck muscle strength and head control. By reducing the amount of time your child spends lying in a position where the head is resting against a flat surface (such as in car seats, strollers, swings and bouncy seats). For instance, if your baby has fallen asleep in a car seat during travel, take your baby out of the seat when you get home rather than leaving your little one snoozing in the seat.
This will take pressure off the head and may help with development of neck muscle strength and head control. By reducing the amount of time your child spends lying in a position where the head is resting against a flat surface (such as in car seats, strollers, swings and bouncy seats). For instance, if your baby has fallen asleep in a car seat during travel, take your baby out of the seat when you get home rather than leaving your little one snoozing in the seat.
Sleeping Position
- Sleeping on the back is the best position for babies to reduce the risk of SIDS. There has been an 80 per cent reduction in SIDS deaths since the introduction of prevention campaigns in 1997 that encouraged parents to place sleeping infants on their back.
- Although your baby is on their back try to alternate your baby’s head position for each sleep: for one sleep turn your baby’s head to their left side and then the next sleep turn your baby’s head to their right side.
- Whichever side of your infant’s head is flattened, you will want to position your baby to encourage active turning of the head to the other side.
- Scientific evidence and SIDS do NOT approve of wedge pillows and other devices to keep your baby in one position as per the guidelines athttps://rednose.com.au/article/pillow-use
- The Australian government states it is safer not to use a pillow at all for children under two15.
- More information on SIDS guidelines can be found at https://rednose.com.au/section/safe-sleeping
Corrective Helmet
- Sometimes when the uneven head shape is more severe or where counter positioning did not work, a cranial remodelling helmetmay help. For children where this treatment is necessary, it is important to see a craniofacial specialist team through your local Childrens Hospital. Treatment is provided by a team specialising in this service, helmets are custom made and adjusted by the orthotist every one to two weeks and treatment usually takes between two to six months.
- Neverpurchase or use any helmet or head shaping devices without first having your child seen by a doctor. Only a small percentage of babies wear helmets. The decision to use helmet therapy is made on an individual assessment and case-by-case basis by the team and child’s family.
Key Points to Remember
- Babies may have an uneven head shape at birth however this should remould to a normal more symmetrical shape within 6 weeks after birth.
- Positional plagiocephaly will not affect the development of your baby’s brain.
- If you are concerned about your baby’s head shape, talk to your Child Health Nurse, GP, paediatrician or paediatric physiotherapist.
- A paediatric physiotherapist can assess your child and assist with planning a home program which may include specific exercises, stretches and promotion of a variety of positions during awake, sleep and play time.
- Few baby’s require helmet therapy.
References:
- http://www.essentialbaby.com.au/baby/baby-sleep/sids-safe-sleeping-guidelines-20081201-6oek#ixzz4hOfggbXn
Australian Competition and Consumer Commission. (2007) Cots. Safety Alert Brochure. Retrieved from http://bit.ly/RpYpA1. - https://rednose.com.au/section/safe-sleeping
- https://www.physiotherapy.asn.au/APAWCM/Physio_and_You/Infants.aspx
- http://www.rch.org.au/kidsinfo/fact_sheets/Plagiocephaly_misshapen_head/
- https://www.schn.health.nsw.gov.au/parents-and-carers/our-services/craniofacial/chw
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/craniosynostosis/symptoms-causes/dxc-20256926
Tags: Baby Brain, Newborn Head Shape, Paediatrics
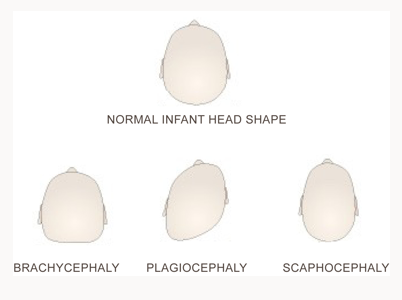
Plagiocephaly, Brachycephaly, Scaphocephal Baby Head Shape
Sometimes known as “flat head syndrome,” plagiocephaly (pronounced play-jee-oh-sef-uh-lee) is a relatively common condition where an infant develops a flat spot on the back or backside of the head.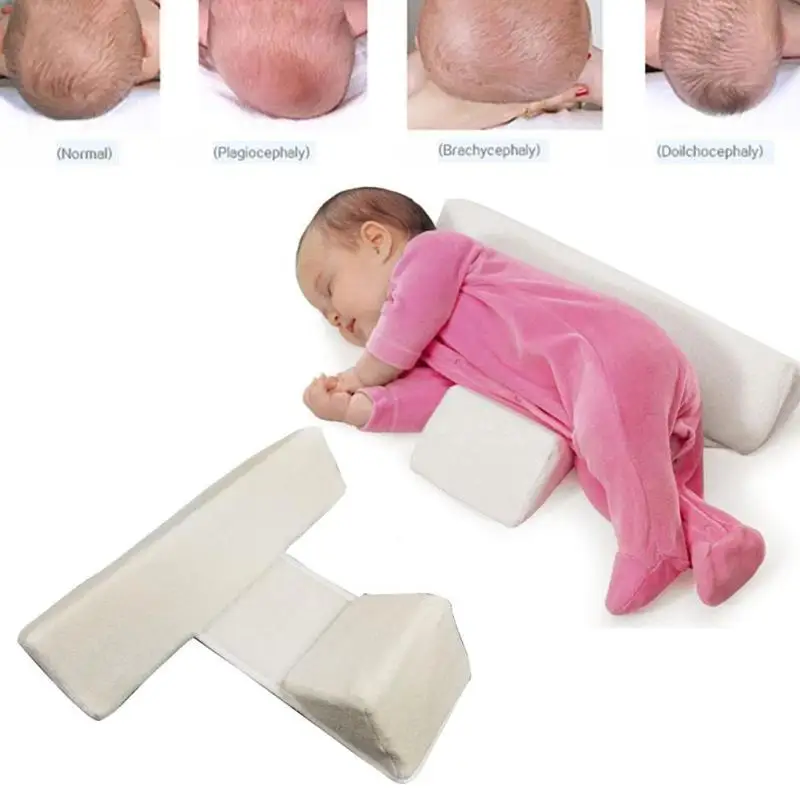 Many factors can cause flat spots. A baby’s skull is very soft and pressure from everyday surfaces, such as beds or car seats, can cause flattening.
Many factors can cause flat spots. A baby’s skull is very soft and pressure from everyday surfaces, such as beds or car seats, can cause flattening.
No two cases of plagiocephaly are alike.
What is Normal?
Parents spend so much time with their baby, recognizing an abnormal head shape can sometimes be difficult. We’ve found it can be helpful to see examples of a normal head shape before looking at abnormal ones. Normally, the head is about 1/3 longer than it is wide and rounded at the back. Below are some examples of a normal head shape at three months, six months and nine months old.
Head Shape Comparisons
Normal Head Shape– 3 month old
Normal Head Shape– 6 month old
Normal Head Shape– 9 month old
Hide All | Show All
What does plagiocephaly look like?
Plagiocephaly means “oblique head” (from Greek “plagio” meaning oblique and “cephale” meaning head).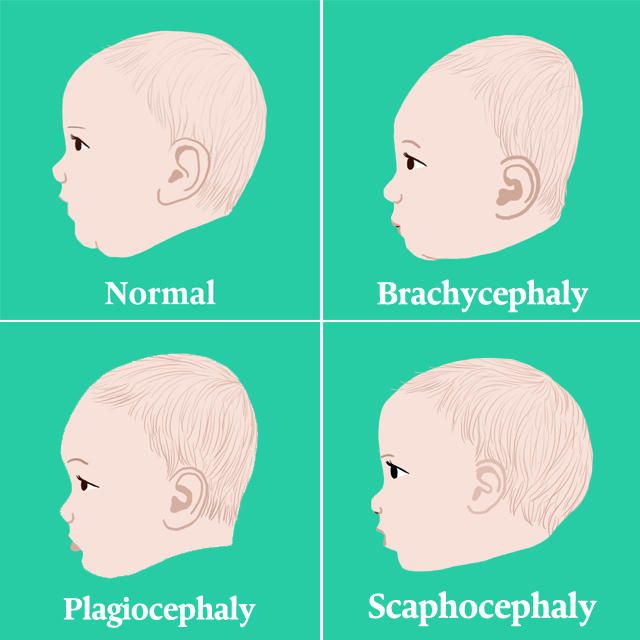 The baby’s head shape resembles a parallelogram from above. Parents and medical professionals can look for these characteristics:
The baby’s head shape resembles a parallelogram from above. Parents and medical professionals can look for these characteristics:
- Head is flat on one side
- One ear is more forward than the other
- One eye is smaller than the other
- One cheek is fuller than the other
- Top of the head is not level
- Head shape resembles a parallelogram from above
Plagiocephaly head shapes, ranging from normal to severe.
What does brachycephaly look like?
Brachycephaly is rooted in Latin, “brachy” meaning short and “cephaly” meaning head. The back of the head becomes flat, causing an abnormally wide, tall head shape. Parents and medical professionals should look for these characteristics:
- Head is wider than normal
- Head is abnormally tall
- Back of head is flat rather than curved
- Face appears small relative to the size of the head
- Widest part of the head is just above the ears
- Tips of ears protrude
- Head shape resembles a trapezoid from above
Brachycephaly head shapes, ranging from normal to severe.
What does brachycephaly with plagiocephaly look like?
As you might expect, babies with brachycephaly and plagiocephaly share characteristics of both head shapes. In these cases, the head is abnormally tall and wide and resembles a distorted trapezoid from above. These are the traits parents and doctors can look for:
- A combination of plagiocephaly and brachycephaly traits
- Head is wider and taller than normal
- Forehead is sloped
- Ears and eyes appear misaligned
- Head shape resembles a distorted trapezoid from above
Brachycephaly with plagiocephaly head shapes, ranging from normal to severe.
Testimonials
“
They are amazing! Honest and up front about everything in the process. Got us booked quickly if we needed to come in for something and my sons head looks great. We live far but it was 100% worth the drive to get there. I tell everyone that if they were a pediatricians office we’d continue to go because we loved the staff that much. Thank you for everything!
Thank you for everything!
- Ashleah F., Parent
They are absolutely amazing! The insurance part of the company worked with me to get insurance coverage for the second band my son is in, and the staff is outstanding, super friendly and make sure everything with the band and baby is spot on. They have been such a blessing, and honestly, I will be sad to stop going when treatment is done, but glad that my son has been so well taken care of!! I highly recommend them, and have already recommended them to family.
- Amanda Crawford, Parent
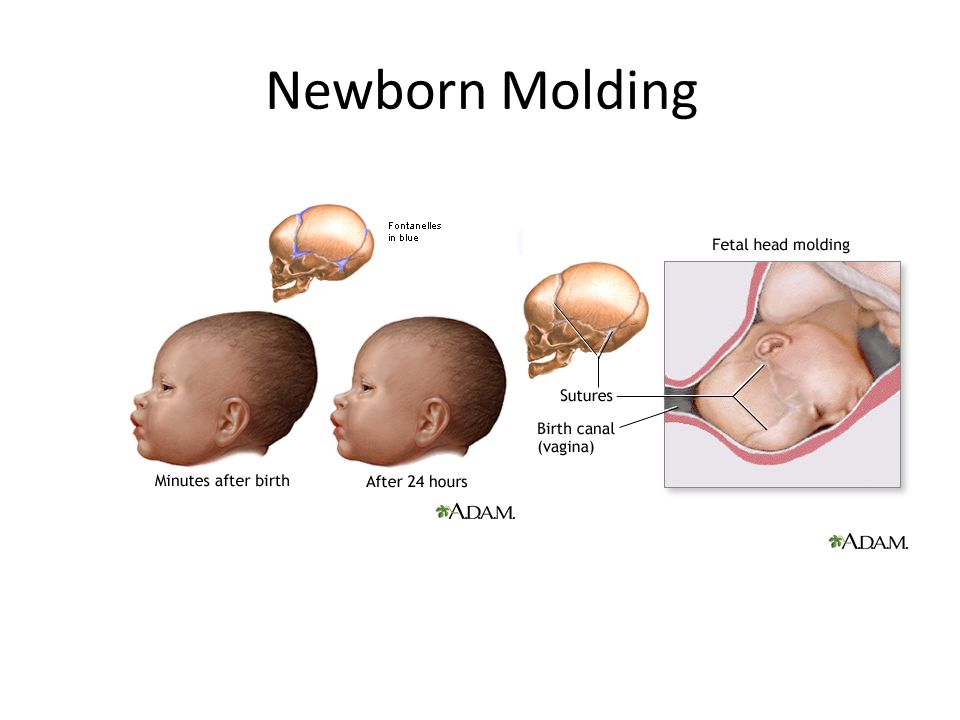
Head shape in a newborn: what options are considered normal loose (they will have to completely harden in the first year), and the seams between them have not yet had time to overgrow. During childbirth, the bones overlap each other, allowing the baby to move out more easily. That is why, after natural childbirth, the shape of the head is slightly elongated, while in small "caesareans" it is even and rounded.
 Due to the ups and downs of traveling through the birth canal, a baby may be born with an asymmetrical head, and sometimes also with a bump (cephalohematoma) or edema (the so-called generic). nine0003
Due to the ups and downs of traveling through the birth canal, a baby may be born with an asymmetrical head, and sometimes also with a bump (cephalohematoma) or edema (the so-called generic). nine0003 Mothers often wonder: why do babies have such a large head? Relative to the size of the body, it is indeed much larger than in adults - at birth, the baby's head in a circumference is about 2 cm larger than the chest. But it happens that these dimensions increase even more: this happens if cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the cranial cavity. Then doctors talk about hydrocephalus. This problem can occur if a woman has a severe infection during pregnancy. And it happens the other way around - the head of the newborn is too small (microcephaly). Fortunately, in many cases, the reason for its unusual shape or size is much simpler: a child can inherit all these features from their parents. nine0003
In newborns, the following head shapes are considered normal:
-
Dolichocephalic - in this case, the skull is slightly flattened, elongated from the chin to the back of the head, and has an elongated diagonal shape.

-
Bracheocephalic - the transverse diameter of the head is greater than the longitudinal one, the skull is elongated from the forehead to the back of the head, slightly flattened.
-
Tower - the skull is elongated vertically, the reason is the rapid healing of the sutures of the skull bones. nine0003
When will the baby's head become the correct shape? It begins to level off already in the first days after childbirth, and in total this process can last up to a year. How can you help your baby get back to normal?
-
Caring care. If the baby lies on his back in one position for a long time, his head may become flat. That is why the child's head must be turned from time to time to the left, then to the right, lay the baby on its side, and if necessary, put a roller. nine0003
-
Proper nutrition. The shape of the child's head may change due to rickets, in which calcium metabolism is disturbed in the body.
 In this situation, the baby will need the help of a doctor; he will advise the mother to monitor her diet (for example, eat more dairy products) if she is breastfeeding the baby, and he will prescribe a suitable mixture for the little “artist”.
In this situation, the baby will need the help of a doctor; he will advise the mother to monitor her diet (for example, eat more dairy products) if she is breastfeeding the baby, and he will prescribe a suitable mixture for the little “artist”. -
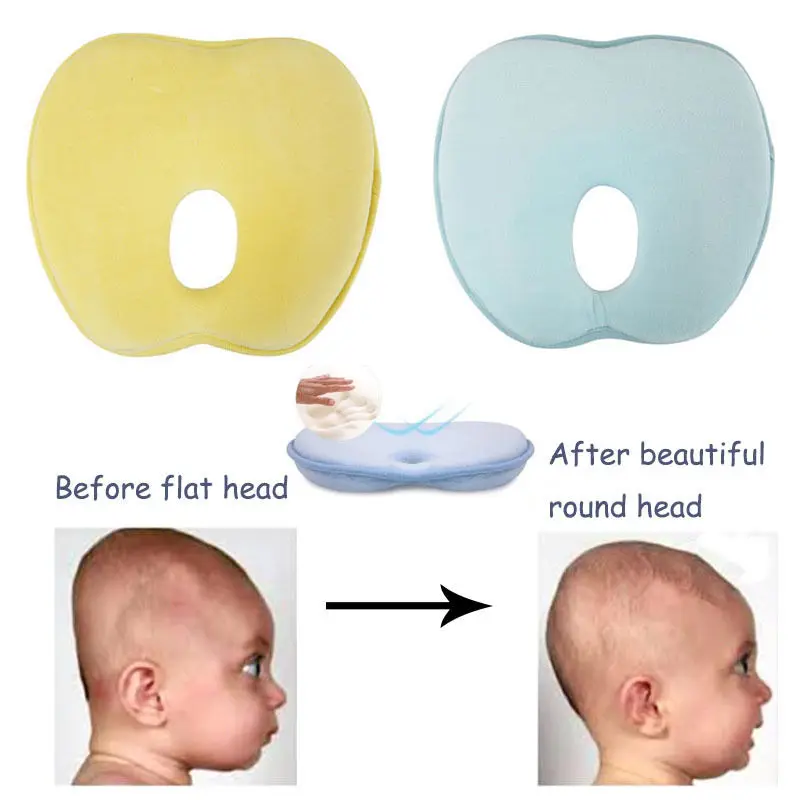
Orthopedic pillows for newborns. These pillows are prescribed by a doctor to correct the shape of the baby's head and prevent deformities in the back of the head and neck. nine0003
More interesting and useful materials for expectant mothers - in our channel on Yandex.Zen.
Lyubov Prishlaya
Reading today
How can you look like that at 53! Incredible Jennifer Lopez in a transparent dress at the premiere of "My Pirate Wedding"
Benefits for pregnant women and parents in 2023: a full list of new payments
Why after 40-45 years, most women begin prolapse of organs0003
Online broadcast and funeral at sunset: 8 features of the burial of Elizabeth II
7 myths about pregnancy that men believe in
shape, size, fontanel.
 Everything is good? Shape and size of a baby's head
Everything is good? Shape and size of a baby's head What can the shape and size of a newborn's head tell parents? What "signals" about the state of the baby does a large fontanel give? We dispel the fears and doubts of mothers.
What should a newborn's fontanel be like
A small dimple on the baby's crown - a fontanel - performs an important task during the birth of a baby. And after birth, she is given a serious role, and along with this, special attention of mothers and doctors. nine0003
Fontanelles are areas at the junctions of cranial bones, covered with soft elastic membranes instead of bone tissue. Thanks to them, the baby's head is plastic and during childbirth can adapt to the curves of the mother's pelvis. The volume and size of the baby's head decrease at the time of birth, which helps protect both the baby's brain and the mother's organs from damage.
There are six fontanels in total, but in full-term babies, by the time of birth, as a rule, only one remains open, in the region of the crown, the so-called large fontanel.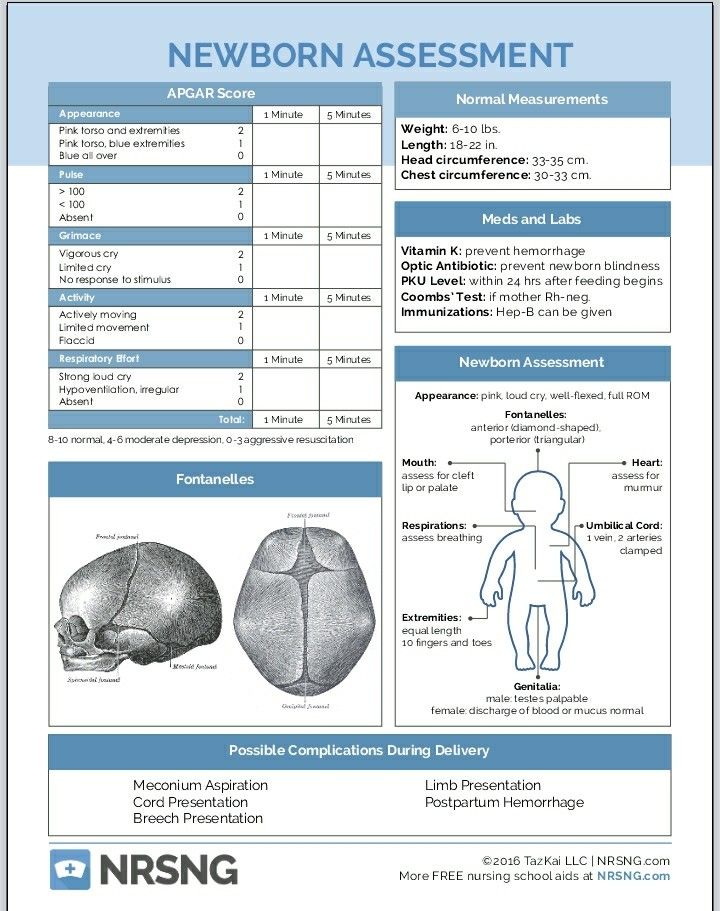 Normally, its size is from 0.5 to 3 cm, and the shape resembles a rhombus. After birth, it helps the baby to adapt to the changing external environment: maintain body temperature, regulate fluctuations in intracranial pressure. nine0003
Normally, its size is from 0.5 to 3 cm, and the shape resembles a rhombus. After birth, it helps the baby to adapt to the changing external environment: maintain body temperature, regulate fluctuations in intracranial pressure. nine0003
We have been trying to get around this big spring for a whole year when we stroke the child’s head, take off his hat, and comb it. Just under the skin, thin and shiny, is a strong but elastic membrane, which will later be replaced by bone, and under it a rather large vein pulsates. It is she who swells, transmitting the vibrations of the arteries and the heart, when the baby cries, screams or takes a deep breath.
The large fontanel grows gradually and finally closes between 6 and 18 months. When exactly this happens depends primarily on the characteristics of the baby's body. Although too slow or, conversely, rapid overgrowth of the fontanel is a sign of illness, but not in itself, but along with other symptoms. So, most often the "dent" is tightened too slowly due to rickets.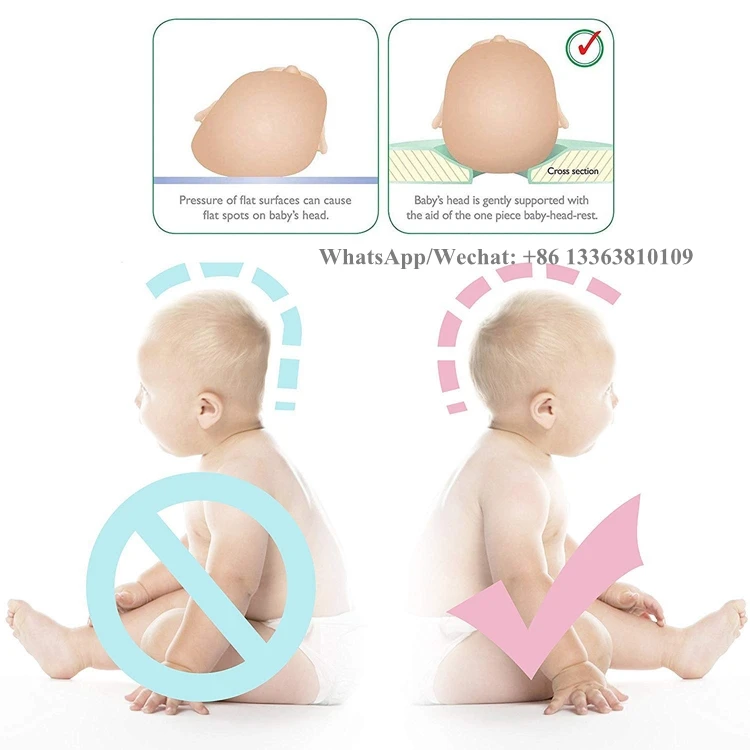 It also happens that the fontanel disappears already in the first six months of a baby's life - the reason for this is a violation of the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body. nine0003
It also happens that the fontanel disappears already in the first six months of a baby's life - the reason for this is a violation of the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body. nine0003
The dimple is low maintenance. You can touch the fontanel with both your hand and a comb - although, of course, you should not put much pressure on it, as, indeed, on any other part of the child's body.
By the appearance of the fontanel, you can assess the condition of the baby. Normally, it should neither swell nor sink; touching the fontanel with your fingers, it is easy to feel the pulsation.
It is worth consulting a doctor if the fontanel becomes hard to the touch, there is no pulsation inside it, it swells or sinks, and the baby is worried or, on the contrary, looks lethargic (normally, the fontanel can swell when the baby cries, but then quickly returns to its previous form). When the fontanel is pulled inward, this may indicate severe dehydration of the child: it must be urgently shown to the doctor.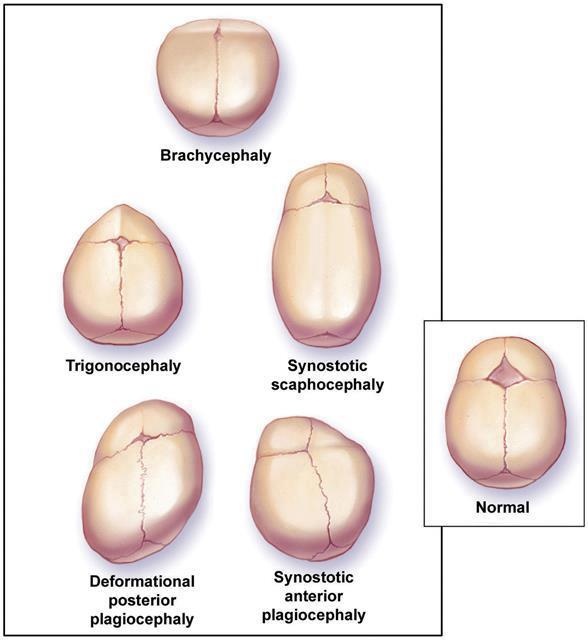 nine0003
nine0003
The speed of overgrowth of a large fontanel is different for each baby - this is normal if the head circumference increases both smoothly and on time. This phenomenon can be explained as follows: if, due to some kind of stress received during childbirth, the child’s brain “lives” better in the conditions of a “spacious” skull, it will retain a large fontanelle and open sutures for a long time, and if mobility harms the brain, the wise the body will overgrow it in 3 months.
Newborn head shape and size
The shape of the head in newborn babies can be not only round, but also elongated, flattened, ovoid - and all these options are considered the norm. Why it happens?
By the time of birth, the bones of the skull in babies are not yet too dense (they will have to completely harden during the first year of life), and the seams between them have not yet managed to heal. During childbirth, the bones overlap each other, allowing the baby to move out more easily.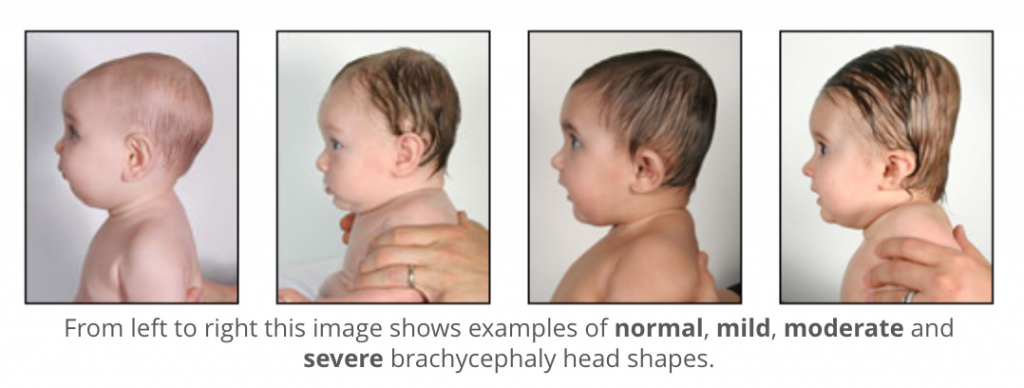 That is why, after natural childbirth, the shape of the head, as a rule, is slightly elongated, while in small "cesareans" it is even and rounded. Due to the ups and downs of traveling through the birth canal, a baby may be born with an asymmetrical head, and sometimes also with a bump (cephalohematoma) or edema (the so-called generic). nine0003
That is why, after natural childbirth, the shape of the head, as a rule, is slightly elongated, while in small "cesareans" it is even and rounded. Due to the ups and downs of traveling through the birth canal, a baby may be born with an asymmetrical head, and sometimes also with a bump (cephalohematoma) or edema (the so-called generic). nine0003
At birth, the baby's head is approximately 2 cm larger than the chest. But it happens that these dimensions increase even more: this happens if cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the cranial cavity. Then the upper part becomes larger than the lower one, a heavy forehead hangs over the eyes and nose, and doctors talk about hydrocephalus. This problem can occur if, during pregnancy, a woman suffered a severe infection that affected the unborn baby. In this case, doctors will immediately start treating the child, and after a few months, his head may approach normal size. nine0003
A more serious situation is when a newborn, on the contrary, has a too small head (microcephaly).