Pelvic pressure 30 weeks pregnant
Pelvic pain in pregnancy - NHS
Some women may develop pelvic pain in pregnancy. This is sometimes called pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain (PGP) or symphysis pubis dysfunction (SPD).
PGP is a collection of uncomfortable symptoms caused by a stiffness of your pelvic joints or the joints moving unevenly at either the back or front of your pelvis.
Symptoms of PGP
PGP is not harmful to your baby, but it can be painful and make it hard to get around.
Women with PGP may feel pain:
- over the pubic bone at the front in the centre, roughly level with your hips
- across 1 or both sides of your lower back
- in the area between your vagina and anus (perineum)
- spreading to your thighs
Some women may feel or hear a clicking or grinding in the pelvic area.
The pain can be worse when you're:
- walking
- going up or down stairs
- standing on 1 leg (for example, when you're getting dressed)
- turning over in bed
- moving your legs apart (for example, when you get out of a car)
Most women with PGP can have a vaginal birth.
Non-urgent advice: Call your midwife or GP if you have pelvic pain and:
- it's hard for you to move around
- it hurts to get out of a car or turn over in bed
- it's painful going up or down stairs
These can be signs of pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain.
Treatments for PGP
Getting diagnosed as early as possible can help keep pain to a minimum and avoid long-term discomfort.
You may be referred to a physiotherapy service that specialises in obstetric pelvic joint problems.
Physiotherapy aims to relieve or ease pain, improve muscle function, and improve your pelvic joint position and stability.
This may include:
- exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor, stomach, back and hip muscles
- equipment, if necessary, such as crutches or pelvic support belts
These problems tend not to get completely better until the baby is born, but treatment from an experienced practitioner can improve the symptoms during pregnancy.
Coping with pelvic pain in pregnancy
Your physiotherapist may recommend a pelvic support belt to help ease your pain, or crutches to help you get around.
It can help to plan your day so you avoid activities that cause you pain. For example, do not go up or down stairs more often than you have to.
For example, do not go up or down stairs more often than you have to.
The Pelvic, Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy (POGP) network also offers this advice:
- be as active as possible within your pain limits, and avoid activities that make the pain worse
- rest when you can
- ask your family, friends or partner, if you have one, to help with everyday activities
- wear flat, supportive shoes
- sit down to get dressed – for example, do not stand on 1 leg when putting on jeans
- keep your knees together when getting in and out of the car – a plastic bag on the seat can help you swivel
- sleep in a comfortable position – for example, on your side with a pillow between your legs
- try different ways of turning over in bed – for example, turning over with your knees together and squeezing your buttocks
- take the stairs 1 at a time, or go upstairs backwards or on your bottom
- if you're using crutches, have a small backpack to carry things in
- if you want to have sex, consider different positions, such as kneeling on all fours
POGP suggests that you avoid:
- standing on 1 leg
- bending and twisting to lift, or carrying a baby on 1 hip
- crossing your legs
- sitting on the floor, or sitting twisted
- sitting or standing for long periods
- lifting heavy weights, such as shopping bags, wet washing or a toddler
- vacuuming
- pushing heavy objects, such as a supermarket trolley
- carrying anything in only 1 hand (try using a small backpack)
The physiotherapist should be able to provide advice on coping with the emotional impact of living with chronic pain, such as using relaxation techniques. If your pain is causing you considerable distress, then you should let your GP or midwife know. You may require additional treatment.
If your pain is causing you considerable distress, then you should let your GP or midwife know. You may require additional treatment.
Find out more on the Pelvic, Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy (POGP) website.
Labour and birth with pelvic pain
Many women with pelvic pain in pregnancy can have a normal vaginal birth.
Plan ahead and talk about your birth plan with your birth partner and midwife.
Write in your birth plan that you have PGP, so the people supporting you during labour and birth will be aware of your condition.
Think about birth positions that are the most comfortable for you, and write them in your birth plan.
Being in water can take the weight off your joints and allow you to move more easily, so you might want to think about having a water birth. You can discuss this with your midwife.
You can discuss this with your midwife.
Who gets pelvic pain in pregnancy?
It's estimated that PGP affects up to 1 in 5 pregnant women to some degree.
It's not known exactly why pelvic pain affects some women, but it's thought to be linked to a number of issues, including previous damage to the pelvis, pelvic joints moving unevenly, and the weight or position of the baby.
Factors that may make a woman more likely to develop PGP include:
- a history of lower back or pelvic girdle pain
- previous injury to the pelvis (for example, from a fall or accident)
- having PGP in a previous pregnancy
- a physically demanding job
- being overweight
Further information
Find support and advice from other women with PGP at the Pelvic Partnership.
Listen to women’s experiences of pain and discomfort in pregnancy, including PGP, on healthtalk.org.
Read more about coping with common health problems in pregnancy, including nausea, heartburn, tiredness and constipation.
Find maternity services or physiotherapy services near you.
Community content from HealthUnlockedPelvic Pressure & Symptoms • Kopa Birth®
You’ve arrived at week 30 in your pregnancy — 28 weeks from conception. Only 10 weeks left to go! Let’s talk about baby’s weight gain, pelvic pressure, carpal tunnel syndrome, and other pregnancy symptoms that you might experience at week 30.
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Table of contents
- Week 30 Pregnancy: Baby’s Growth and Yours
- Baby’s Development
- Week 30 Pregnancy: Pelvic Pressure
- Week 30 Pregnancy: Symptoms
- Swelling
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Week 30 Pregnancy: Baby’s Growth and Yours
At week 30 in your pregnancy, your little weighs about 3 pounds. His total length, from crown to heel, is about 15 3/4 inches.
His total length, from crown to heel, is about 15 3/4 inches.
You’re also gaining about 1 pound each week. Most of that weight is concentrated on the growth of the uterus, baby, placenta, and amniotic fluid. The top of your uterus (the fundal height) is now about 4 inches above your belly button — 12 inches above the pubic symphysis (2). Total weight gain by week 30 should be around 19 to 26 pounds if your weight was in the normal range before pregnancy. You may have gained a bit more than that if you were underweight before you became pregnant, and a little less if you entered pregnancy overweight.
Baby’s Development
Your baby is fully developed now, and her body is working to fine-tune the details in preparation for birth! Developmental changes at week 30 include:
- Baby gains about a half pound each week from now until birth.
- The surface of baby’s brain is developing wrinkly grooves as the amount of brain tissue increases.
- Baby’s bone marrow is now starting to produce the red blood cells.
 (Prior to this, the spleen produced the red blood cells.)
(Prior to this, the spleen produced the red blood cells.)
Week 30 Pregnancy: Pelvic Pressure
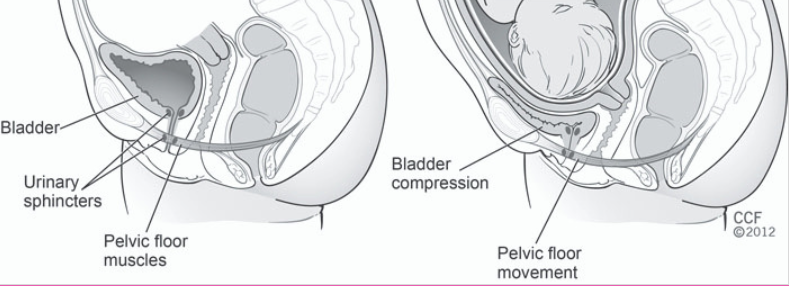
Within 2 to 4 weeks of your due date, the baby will settle deeper into your pelvis to get ready for birth. This is known as the baby dropping, or lightening. The weight of the baby often puts extra pressure on the pelvis, bladder, and hips. Because of your baby sitting lower in your pelvis, you might experience swelling in your legs, uncomfortable pelvic pressure, or the feeling that you have to pee all the time.
While the best way to ease the discomfort of pelvic pressure is to stay off your feet, this is rarely possible for most women. Pregnancy support belts are a great option to help brace some of baby’s weight. If you feel throbbing pressure in your perineum (vulva and vaginal area), consider a perineal support belt like the V2 supporter.
Week 30 Pregnancy: Symptoms
Swelling
During pregnancy, women often retain extra fluid. You not only have an increased volume of blood, but your tissues tend to retain more fluid as well. This swelling may be especially evident in your face seeming a little puffier (because it’s easier to notice in the fine details of your face,) your fingers (because you may notice things like rings not fitting anymore,) or in your feet, ankles, or lower legs (because fluid tends to pool in the lower extremities when you’re on your feet a lot.)
This swelling may be especially evident in your face seeming a little puffier (because it’s easier to notice in the fine details of your face,) your fingers (because you may notice things like rings not fitting anymore,) or in your feet, ankles, or lower legs (because fluid tends to pool in the lower extremities when you’re on your feet a lot.)
Don’t restrict fluid intake. You need to stay hydrated for yourself and your baby. If your rings can’t be comfortably worn, take them off and stash them somewhere safe for now. If your feet swell uncomfortably, try periods of rest with your feet elevated, and if necessary, consider compression socks.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The swelling of tissues can sometimes cause pressure on the nerves. Carpal tunnel syndrome, which occurs in 25% of pregnant women, is caused by the compression of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel in your wrist. Basically, there’s a hole in the bones of your wrist, and a nerve that runs through it, and when your tissues swell, it may put uncomfortable pressure on that nerve. Carpal tunnel syndrome is characterized by numbness and tingling in the hand, near the thumb (1, 3).
Carpal tunnel syndrome is characterized by numbness and tingling in the hand, near the thumb (1, 3).
To decrease symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, try to avoid repetitive movements that require an angle in the wrist, such as typing. If this doesn’t help, your provider may recommend splinting your wrists. Fortunately, the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome usually go away after you give birth and your fluid levels go back to normal.
Drop by again next week to learn all about what you can expect at week 31 of your pregnancy! And if you haven’t yet, check out our guide to what to expect and do in this trimester and as you prepare for birth: Third Trimester Pregnancy & Symptoms: The Ultimate Guide.
Kopa Birth’s online birthing classes allow you to prepare for natural childbirth in the comfort of your own home, 24/7. Enroll today in our free online childbirth class to learn more about preparing for natural childbirth.
References:
- Ladewig, P.
 A., London, M.L., Davidson, M.R. (2006). Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care, 6th edition. Pearson Prentice Hall. Upper Saddle River, NJ.
A., London, M.L., Davidson, M.R. (2006). Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care, 6th edition. Pearson Prentice Hall. Upper Saddle River, NJ. - Glade, B.C., Schuler, J. (2011). Your Pregnancy Week by Week, 7th edition. First Da Capo Press.
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2010). Your Pregnancy and Childbirth Month to Month, 5th edition.
Here are some other birth articles and stories we know you’ll love.
29-32 weeks of pregnancy
29th week
Baby
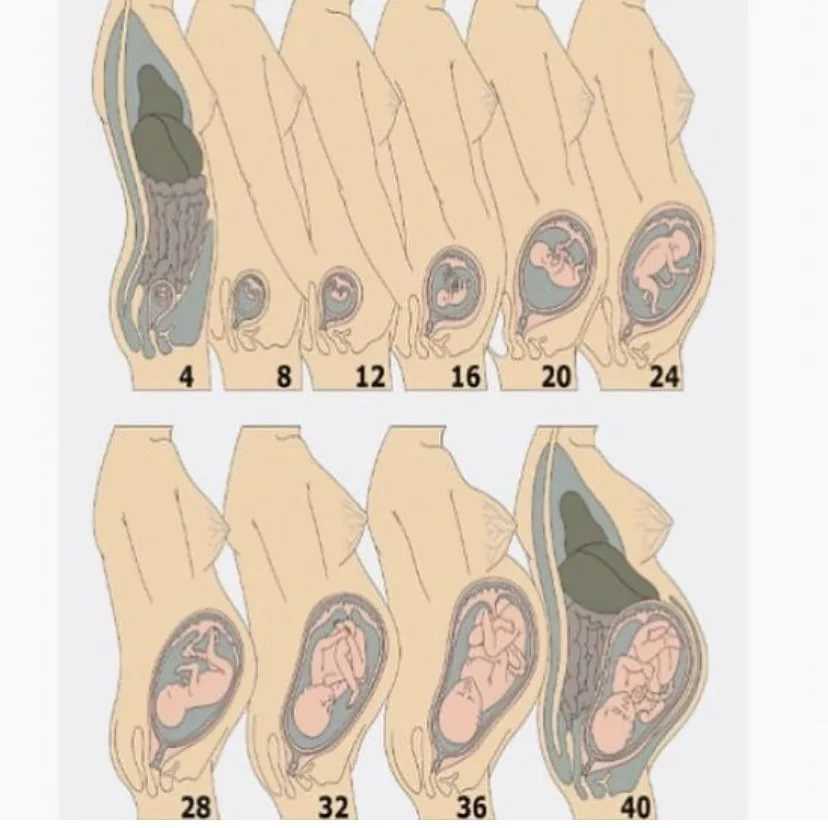
At the 29th week of pregnancy, the baby continues to accumulate fat under the skin, folds and wrinkles are smoothed out, and, as a result, the skin becomes smoother. The body is still completely covered with vellus hair, the amount of which is sharply reduced at this stage. But on the head, hair growth is activated. They become denser, darker and grow back quickly. In the womb, the baby often blinks, moves less actively, the movements become less intense and frequent, but smoother.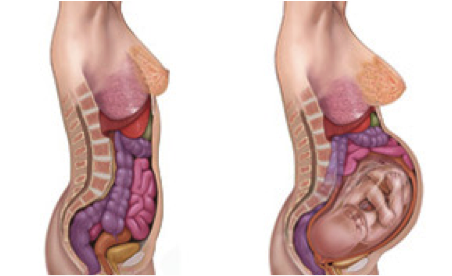 There is less and less space left in the uterus, so the child is most often in the same position, spreading his limbs, exposing his head and pelvic end. His height by this week is 36-37 cm, and his weight is 1,200-1,300 g. At this time, the child takes a head presentation, since his head is heavier than his buttocks. But it is not uncommon for cases when in the body of water at 29week the baby is still in the breech presentation. The expectant mother should not worry about this, because there are still a few weeks for the child to take the correct position. Otherwise, breech presentation will be one of the good reasons for choosing a method of delivery.
There is less and less space left in the uterus, so the child is most often in the same position, spreading his limbs, exposing his head and pelvic end. His height by this week is 36-37 cm, and his weight is 1,200-1,300 g. At this time, the child takes a head presentation, since his head is heavier than his buttocks. But it is not uncommon for cases when in the body of water at 29week the baby is still in the breech presentation. The expectant mother should not worry about this, because there are still a few weeks for the child to take the correct position. Otherwise, breech presentation will be one of the good reasons for choosing a method of delivery.
Expectant mother
Women at 29 weeks of pregnancy still experience discomfort as the uterus continues to grow rapidly. This is especially felt by the organs that are located next to it - the bladder, stomach, and also the lower part of the large intestine. As the uterus grows, they move and occupy a rather uncomfortable position, which can affect their work in the future. That is why at this time women often complain of a feeling of heaviness after eating, suffer from heartburn. Heartburn occurs as a consequence of throwing stomach contents into the esophagus and is manifested by an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth, as well as a burning sensation inside. During pregnancy, the muscles that separate the esophagus from the stomach become highly hormonal and relax. This creates such a situation. The rebuilt position of the stomach only worsens the situation. It is impossible to completely get rid of this condition. Of course, after childbirth, this problem will be solved by itself, but in order to somehow help herself, a woman should eat often, but in small portions. It is important that you chew your food thoroughly. These simple rules will help reduce the risk of heartburn after eating. nine0007
That is why at this time women often complain of a feeling of heaviness after eating, suffer from heartburn. Heartburn occurs as a consequence of throwing stomach contents into the esophagus and is manifested by an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth, as well as a burning sensation inside. During pregnancy, the muscles that separate the esophagus from the stomach become highly hormonal and relax. This creates such a situation. The rebuilt position of the stomach only worsens the situation. It is impossible to completely get rid of this condition. Of course, after childbirth, this problem will be solved by itself, but in order to somehow help herself, a woman should eat often, but in small portions. It is important that you chew your food thoroughly. These simple rules will help reduce the risk of heartburn after eating. nine0007
In addition, at the 29th week, expectant mothers notice frequent urination, which in most cases will accompany them until the very birth. Frequent urges are due to rapidly progressive pressure on the bladder. False urges are also not uncommon during this period. These are situations when the bladder is not yet full, but the brain has already sent a signal to urinate. In such cases, urination does not occur at all or passes in a minimal amount. During pregnancy, frequent and completely painless urination is not a sign of any disease. However, if symptoms such as pain, the appearance of cloudy urine join this process, you should immediately inform your doctor about this, who will be able to establish the cause of these changes and exclude or confirm pyelonephritis. nine0007
False urges are also not uncommon during this period. These are situations when the bladder is not yet full, but the brain has already sent a signal to urinate. In such cases, urination does not occur at all or passes in a minimal amount. During pregnancy, frequent and completely painless urination is not a sign of any disease. However, if symptoms such as pain, the appearance of cloudy urine join this process, you should immediately inform your doctor about this, who will be able to establish the cause of these changes and exclude or confirm pyelonephritis. nine0007
30th week
Baby
The 30th week is characterized by an intensive growth of the baby's muscle mass. He actively trains the muscles of the limbs, makes frequent movements, because during childbirth all muscle groups of the arms, legs, chest, and back must be prepared. In the second stage of labor or during the immediate birth of a child, there is an active contraction of the uterus, the muscles of the abdominal wall. The child moves independently. In this he is helped by a high tone of the muscles of the body, which greatly facilitates the movement through the birth canal, and also allows you to make translational movements. Also this week, the preparation of the internal organs of the fetus for extrauterine life continues. The baby's chest is actively training, expanding and contracting. Such movements are very similar to breathing. The lungs are washed with amniotic fluid, intensive production of surfactant continues. This substance ensures normal pulmonary respiration. You can also note the development of the alveoli. These vesicles in the lung tissue are necessary for gas exchange, because it is very important for the survival of the fetus to be ready for spontaneous breathing at the time of birth. It is worth noting that childbirth at the thirtieth week, which is due to any reasons, gives a high chance of independent breathing of the newborn, because the lung tissue is already mature and quite ready to perform its functions.
The child moves independently. In this he is helped by a high tone of the muscles of the body, which greatly facilitates the movement through the birth canal, and also allows you to make translational movements. Also this week, the preparation of the internal organs of the fetus for extrauterine life continues. The baby's chest is actively training, expanding and contracting. Such movements are very similar to breathing. The lungs are washed with amniotic fluid, intensive production of surfactant continues. This substance ensures normal pulmonary respiration. You can also note the development of the alveoli. These vesicles in the lung tissue are necessary for gas exchange, because it is very important for the survival of the fetus to be ready for spontaneous breathing at the time of birth. It is worth noting that childbirth at the thirtieth week, which is due to any reasons, gives a high chance of independent breathing of the newborn, because the lung tissue is already mature and quite ready to perform its functions. nine0007
nine0007
The fetus actively swallows the amniotic fluid, thereby contracting the digestive tract and stimulating the liver and pancreas. The liver in the body of any person performs an important function, cleansing the blood, and already at this stage of pregnancy is ready for full functioning. The formation of liver lobules by the thirtieth week is almost complete.
Amniotic fluid constantly flows and stimulates the kidneys to function intensively: the production of urine from the liquid part of the water. The daily rate of urine at this time in a child can reach 0.5 liters. nine0007
Active work is also observed in the pancreas, which produces hormones and enzymes from the amniotic fluid. One of the most important is insulin. Potentially, the pancreas is ready for full-fledged work already at this time and will be able to supply the body of the newborn with everything necessary.
Thus, at the thirtieth week, the internal organs of the fetus will be able to ensure its vital functions in case of childbirth. Although their development actively continues until the very birth.
Although their development actively continues until the very birth.
The height of the baby is 37-38 cm, and the body weight is about 1300-1400 g.
Mother-to-be
The mother-to-be may experience active breast swelling and colostrum production in the thirtieth week. This secret of the mammary gland - "primary milk" - is quite thick, has a white or yellowish tint. The release of colostrum can occur at different times, everything is very individual, but most often this happens after the 30th week of pregnancy. If you find such discharge in yourself, then this means that your body is actively preparing for the upcoming lactation. In the first few days after the birth of a child, colostrum from the woman's body will be released very actively until the appearance of breast milk. nine0007
During pregnancy, the fetus itself stimulates the production of colostrum. His adrenal glands produce a special hormone that, when interacting with placental hormones, activates the production of prolactin. Prolactin is a maternal pituitary hormone that is responsible for milk production after childbirth.
Prolactin is a maternal pituitary hormone that is responsible for milk production after childbirth.
At the 30th week of pregnancy, a woman receives a certificate of temporary incapacity for work, and also goes through the procedure for issuing maternity leave, which lasts only 140 days. nine0007
31st week
Baby
At the 31st week of intrauterine life, the fetus weighs 1500-1600 g and has a height of 39-40 cm. This period is characterized by the continuation of the development of the nervous system. The brain grows at a high rate, the convolutions deepen, and the surface area of the cortex increases. The brain, as well as its departments, thanks to nerve connections, function as one. In the baby, periods of sleep and activity are already clearly changing. Sleep, as before, takes up most of the time. It is worth noting that the child closes his eyes during sleep, and opens them during the period of activity. The eyelids are so well developed that the fetus can already blink, open and close its eyes, squint and even squint at this stage.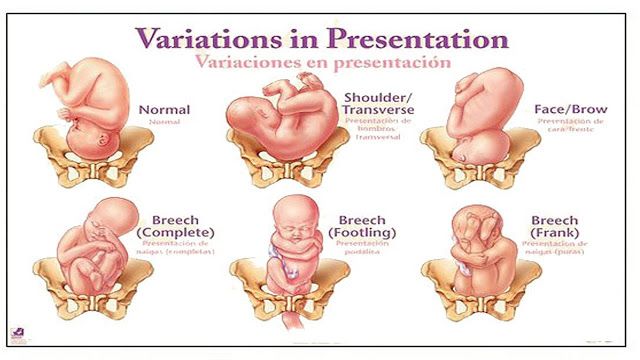 If bright light hits the stomach, it makes the baby close his eyes, which indicates a good level of development of his nervous system. nine0007
If bright light hits the stomach, it makes the baby close his eyes, which indicates a good level of development of his nervous system. nine0007
Expectant mother
By this time, the weight of the expectant mother increases by 7-8 kg. For a woman in position, it is important to monitor the rate of weight gain, because too much weight gain may indicate poor kidney function. So, per week, the weight should increase by no more than 300-400 g. In addition, it is important to monitor the presence of edema on the limbs and notify the doctor if they are found. Fluid retention is a sign of a pregnancy complication. Preeclampsia, which is also called late toxicosis, is characterized not only by swelling, but also by an increase in blood pressure, as well as the appearance of protein in the urine. nine0007
At the initial stages, preeclampsia can be completely asymptomatic, so a pregnant woman may not notice changes at all, feel great. That is why it is important to constantly visit a doctor who can already determine the presence of late toxicosis by analysis. Preeclampsia is one of the main causes of complications in both the mother and her child. It can provoke fetal growth retardation, hypoxia, adversely affect the functioning of the kidneys, the vascular system and the heart, as well as the woman's liver. nine0007
Preeclampsia is one of the main causes of complications in both the mother and her child. It can provoke fetal growth retardation, hypoxia, adversely affect the functioning of the kidneys, the vascular system and the heart, as well as the woman's liver. nine0007
Preeclampsia is mildly manifested in the form of edema. It can be corrected by normalizing the water-salt metabolism. The doctor may prescribe special diets for the pregnant woman, as well as drugs that will help cope with this condition.
Moderate or severe preeclampsia (nephropathy, preeclampsia and eclampsia) requires urgent hospitalization. In a hospital setting, intensive care is provided. Nephropathy in a future mother manifests itself not only in the form of edema, but also in the form of high blood pressure, as well as the appearance of a protein in the urine, which is detected during tests. nine0007
Active progression of gestosis can cause a severe degree of nephropathy, which smoothly flows into preeclampsia. This condition is manifested not only by edema, high blood pressure, protein in the urine, but also by circulatory disorders in the brain. Women note frequent dizziness, pain, as well as nausea, vomiting, and changes in reflexes.
This condition is manifested not only by edema, high blood pressure, protein in the urine, but also by circulatory disorders in the brain. Women note frequent dizziness, pain, as well as nausea, vomiting, and changes in reflexes.
Preeclampsia at the most severe stage (eclampsia) is characterized by the manifestation of convulsive seizures, which can cause coma. That is why it is important for a pregnant woman to detect signs of preeclampsia in the early stages in order to avoid an increase in symptoms, which in the future can lead to irreversible consequences. nine0007
32nd week
Baby
This week of pregnancy is an important stage in the development of fetal immunity, in the blood of which there is a sharp increase in its own immunoglobulins. These substances protect the child from infection. At the time of delivery, the level of immunoglobulins will increase greatly under the influence of the mother's immunoglobulins entering the child's body. The last weeks of pregnancy are characterized by excellent permeability of the placental barrier, so protective cells from the mother's body easily pass into the baby's blood. nine0007
nine0007
In this week of pregnancy, the baby weighs about 1,700-1,800 g, and its body length is 41-42 cm. . The even distribution of fat under the skin allows the baby to change the color of the skin from bright red to pink.
The accumulation of subcutaneous fat is very important for thermogenesis. This process is necessary to constantly maintain body temperature at the same level. In an adult, these processes are controlled by special thermoregulation centers in the brain. At the time of birth, the child is not yet able to fully provide thermoregulation, so the presence of subcutaneous fat is so important for him to maintain the required body temperature. nine0007
Expectant mother
The third trimester of pregnancy can be manifested by pain in the back, pubis, as well as knee and hip joints. There may also be a feeling of fullness of the pelvic bones, pain. Such phenomena are present in many pregnant women, since the center of gravity changes, the spine shifts (due to the growth of the abdomen). At week 32, the woman’s body is already actively preparing, the placental hormone, relaxin, is produced, which is responsible for relaxing the ligaments, making the pelvis supple during childbirth and thereby ensuring the easiest and most comfortable movement of the child through the birth canal. Too much of this hormone causes pain and loosening of the ligaments. That is why women in position are recommended regular physical activity in the form of hiking, yoga, fitness, and swimming. Strong muscles will be able to support the spine, and will also reduce discomfort in the lumbar region and pain. Doctors recommend that women wear a bandage, sleep on their side to avoid significant stress on the back. Also, special devices (pillows, rollers) will not be superfluous, which will allow the expectant mother to fully relax at night, take a comfortable position that will help relax the muscles of the back and legs. nine0007
At week 32, the woman’s body is already actively preparing, the placental hormone, relaxin, is produced, which is responsible for relaxing the ligaments, making the pelvis supple during childbirth and thereby ensuring the easiest and most comfortable movement of the child through the birth canal. Too much of this hormone causes pain and loosening of the ligaments. That is why women in position are recommended regular physical activity in the form of hiking, yoga, fitness, and swimming. Strong muscles will be able to support the spine, and will also reduce discomfort in the lumbar region and pain. Doctors recommend that women wear a bandage, sleep on their side to avoid significant stress on the back. Also, special devices (pillows, rollers) will not be superfluous, which will allow the expectant mother to fully relax at night, take a comfortable position that will help relax the muscles of the back and legs. nine0007
what is happening, the development of pregnancy and fetus
Week by week
29 - 32 weeks of pregnancy
Elena Gevorkova
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Moscow
29th week
BABY
The length of the fetus is 36–37 cm, and the body weight is 1200–1300 g. By this time, the baby’s skin becomes smoother, as subcutaneous fat continues to accumulate, smoothing out all wrinkles and folds. The body of the fetus is covered with vellus hair, but their number is already less than in earlier periods. On the contrary, the hair on the head thickens, grows and darkens. The baby blinks frequently, opening his eyes wide. nine0007
By this time, the baby’s skin becomes smoother, as subcutaneous fat continues to accumulate, smoothing out all wrinkles and folds. The body of the fetus is covered with vellus hair, but their number is already less than in earlier periods. On the contrary, the hair on the head thickens, grows and darkens. The baby blinks frequently, opening his eyes wide. nine0007
Fetal movements become less active by this time, frequent and intense shocks are replaced by smoother movements: the baby straightens its arms and legs, protrudes its head and pelvic end. There is little free space in the uterus, and the fetus, which has reached a fairly large size by this time, is forced to be in one position most of the time. Since its head is heavier than the buttocks, in the water space of the uterus, the fetus occupies a head-down position - this is the so-called head presentation. At this time, situations of breech presentation are not uncommon, when the legs and buttocks of the fetus are located at the bottom of the uterus. Most often, in the following weeks, the child rolls over, occupying a physiological head presentation. In some cases, this does not happen, and the baby "sits on the priest" until the full term. Breech presentation will play an important role in choosing the delivery option. nine0007
Most often, in the following weeks, the child rolls over, occupying a physiological head presentation. In some cases, this does not happen, and the baby "sits on the priest" until the full term. Breech presentation will play an important role in choosing the delivery option. nine0007
FUTURE MOTHER
Intensive growth of the uterus continues, and the internal organs located next to the uterus continue to experience discomfort. In the most cramped conditions are the "neighbors" of the uterus - the stomach, bladder and lower part of the large intestine: these are organs that have a cavity inside. They are displaced by the growing uterus and take a forced position, which can affect their work.
"Suffering" of the stomach can be manifested by heartburn, a feeling of heaviness after eating. Heartburn is the discomfort that occurs when the contents of the stomach reflux into the esophagus. This condition is manifested by a burning sensation, an unpleasant taste in the mouth. During pregnancy, the muscle separating the esophagus from the stomach, under the influence of hormones, in particular progesterone, relaxes, which makes it possible to throw the acidic contents of the stomach "from the bottom up" - into the esophagus. Changing the position of the stomach exacerbates this situation. That is why the expectant mother should eat small portions, chewing food thoroughly - this will greatly alleviate her condition. Increasing pressure on the bladder causes frequent urination, which can accompany a pregnant woman until the very birth. False urges are also possible, when the brain sends a signal about the need to urinate, but the bladder is not yet full and there is no urine output at all or it occurs in very small quantities. During pregnancy, the situation of frequent and painless urination is not a sign of any disease. When other symptoms are attached: the appearance of cloudy urine, pain, etc. - you should inform your doctor about this to exclude pyelonephritis and other diseases.
During pregnancy, the muscle separating the esophagus from the stomach, under the influence of hormones, in particular progesterone, relaxes, which makes it possible to throw the acidic contents of the stomach "from the bottom up" - into the esophagus. Changing the position of the stomach exacerbates this situation. That is why the expectant mother should eat small portions, chewing food thoroughly - this will greatly alleviate her condition. Increasing pressure on the bladder causes frequent urination, which can accompany a pregnant woman until the very birth. False urges are also possible, when the brain sends a signal about the need to urinate, but the bladder is not yet full and there is no urine output at all or it occurs in very small quantities. During pregnancy, the situation of frequent and painless urination is not a sign of any disease. When other symptoms are attached: the appearance of cloudy urine, pain, etc. - you should inform your doctor about this to exclude pyelonephritis and other diseases.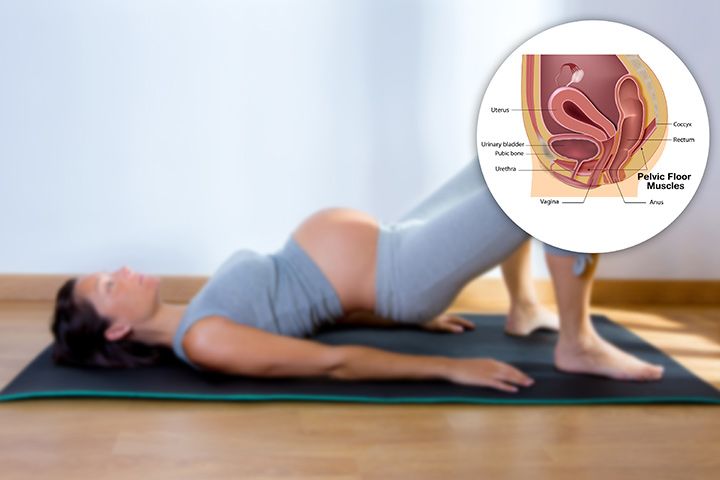 nine0007
nine0007
30th week
BABY
This week baby's height is 37-38 cm, and body weight is about 1300-1400 g. fetus are designed to train the muscles of the limbs, because by the time of birth the baby must have strong muscles of the arms, legs, chest, back. The expulsion of the fetus (the so-called second stage of labor - the immediate birth of a child) is carried out due to the contraction of the uterus, the muscles of the abdominal wall and the independent movements of the baby. The high tone of the muscles of the body of the fetus helps to make translational movements easier, making it easier to move along the birth canal. nine0007
Also during this period, the preparation for the extrauterine life of the internal organs continues. The chest makes movements similar to breathing - it expands and contracts. The lungs are washed by amniotic fluid, the production of surfactant, a special substance that provides pulmonary respiration, continues. Intensively develop alveoli - bubbles of lung tissue, in which gas exchange occurs. Readiness for spontaneous breathing is the most important indicator of fetal survival. If, for some reason, childbirth occurs at this time, then the maturity of the lung tissue is already able to ensure the breathing of the newborn. nine0007
Intensively develop alveoli - bubbles of lung tissue, in which gas exchange occurs. Readiness for spontaneous breathing is the most important indicator of fetal survival. If, for some reason, childbirth occurs at this time, then the maturity of the lung tissue is already able to ensure the breathing of the newborn. nine0007
The fetus constantly swallows amniotic fluid, which causes the organs of the gastrointestinal tract to contract, stimulates the functioning of the liver and pancreas. The liver performs the most important function of cleansing the blood and at this time is already ready to function in full, since the formation of this organ, or rather, the lobules of the liver as a structural unit, is almost completed by this moment. The pancreas produces enzymes and hormones, the most important of which is insulin, in small quantities, since during pregnancy the fetal body only needs to process the amniotic fluid, which requires a small amount of enzymes. But potentially the pancreas at this time is already ready to fully provide the body of the newborn. nine0007
nine0007
The constant supply of amniotic fluid causes the kidneys to function intensively, to produce urine from the liquid part of the amniotic fluid. The amount of urine at this time can reach up to 500 ml per day. Thus, during this period, the internal organs are able to ensure the vital activity of the newborn in the event of childbirth, but the process of their maturation and improvement will continue until the full term.
MOTHER-TO-BE
Pregnant women may notice breast swelling and colostrum secretion from the nipples: this is the name of the secret of the mammary glands, “primary milk”. Colostrum has the appearance of a thick liquid of a whitish or yellowish hue. Its release can begin at different stages of pregnancy, but most often this occurs after the 30th week. The appearance of colostrum indicates the active preparation of a woman for lactation - feeding the baby with breast milk. In the first days after childbirth, colostrum is secreted more intensively and precedes the appearance of breast milk. nine0007
nine0007
During pregnancy, colostrum production is stimulated directly by the fetus. His adrenal glands synthesize a special hormone that interacts with placental hormones and activates the production of prolactin, the mother's pituitary hormone responsible for milk production. It is he who will be responsible for breastfeeding after childbirth.
For a period of 30 weeks, pregnant women are issued a certificate of temporary disability - maternity leave is issued. Its duration is 140 days - 70 days before and 70 days after childbirth. nine0007
31st week
BABY
The length of the body of the fetus is 39--40 cm, and the weight is 1500--1600 g. During this period, important stages of the formation of the fetal nervous system continue. The brain grows intensively, the convolutions deepen, increasing the surface area of the cerebral cortex. The brain and all its departments function as a single system, such interaction is provided by many neural connections. By this time, the periods of sleep and wakefulness change quite clearly, and sleep still takes a longer time than the period of activity. During sleep, the eyes of the fetus are closed, and during wakefulness, the baby opens them. The eyelids are already very well developed, which makes a variety of movements possible: the fetus can open its eyes wide, squint, squint, blink frequently. As a rule, the fetus's eyes are always open, and it closes its eyes when a bright light hits the mother's stomach or when it touches the surface of the eye: this is another evidence of the high development of the nervous system - the corneal reflex. nine0007
By this time, the periods of sleep and wakefulness change quite clearly, and sleep still takes a longer time than the period of activity. During sleep, the eyes of the fetus are closed, and during wakefulness, the baby opens them. The eyelids are already very well developed, which makes a variety of movements possible: the fetus can open its eyes wide, squint, squint, blink frequently. As a rule, the fetus's eyes are always open, and it closes its eyes when a bright light hits the mother's stomach or when it touches the surface of the eye: this is another evidence of the high development of the nervous system - the corneal reflex. nine0007
FUTURE MOTHER
Weight gain by this time is approximately 7-8 kg. It is necessary to monitor the intensity of weight gain, since its too rapid gain may indicate dysfunctional kidney function. The weekly increase should not exceed 300-400 g per week. You should be very careful about the appearance of edema on the arms and legs and report this to the doctor. Fluid retention in the body of a pregnant woman can be the first step in the complication of the second half of pregnancy - preeclampsia, which is also called late toxicosis. In addition to edema, signs of preeclampsia of mild to moderate severity also include an increase in blood pressure and the appearance of protein in the urine. nine0007
Fluid retention in the body of a pregnant woman can be the first step in the complication of the second half of pregnancy - preeclampsia, which is also called late toxicosis. In addition to edema, signs of preeclampsia of mild to moderate severity also include an increase in blood pressure and the appearance of protein in the urine. nine0007
The initial stages of preeclampsia can proceed without pronounced changes, and the pregnant woman can feel great without complaining. That is why regular visits to the doctor and timely delivery of tests are so important. Preeclampsia is the most common cause of complications for both the fetus and the mother. As a result, a baby may experience developmental delay, hypoxia, etc., and a woman may experience a violation of the function of the kidneys, liver, cardiovascular system, and other dangerous conditions.
Mild preeclampsia, dropsy of pregnancy, characterized by the appearance of edema and can be corrected with the normalization of water-salt metabolism: for this, the expectant mother can be prescribed a diet, herbal preparations, etc.
Moderate and severe degrees of gestosis - nephropathy, preeclampsia and eclampsia - require intensive care in a hospital setting. Nephropathy of pregnant women is characterized by the fact that episodes of increased pressure and the appearance of protein in the general analysis of urine join the edema at the stage of dropsy. nine0007
With further progression of preeclampsia, a severe degree of nephropathy turns into preeclampsia - a condition for which, in addition to pronounced edema, high blood pressure and protein in the urine, signs of cerebral circulation disorders are characteristic: dizziness, headaches, as well as neurological symptoms - changes in reflexes, nausea and vomiting.
The most severe stage of gestosis, eclampsia, is characterized by the presence of convulsive seizures followed by the development of coma.
It is extremely important to detect signs of preeclampsia at an early stage and treat this condition without fail, since the increase in complications can occur quickly and lead to severe, and sometimes irreversible consequences. nine0007
nine0007
32nd week
BABY
The fetus at this time weighs 1700-1800 g, and its body length reaches 41--42 cm. , the hair on the head is markedly pronounced. The skin of the fetus is no longer bright red, but pink due to the even distribution of subcutaneous fat. The accumulation of such fat is essential for the process of thermogenesis - maintaining body temperature at a constant level. In adults, these processes are controlled by the brain - the centers of thermoregulation. By the time the baby is born, these centers are not yet able to fully provide thermoregulation, and that is why the presence of subcutaneous fat is extremely important to maintain the correct body temperature of the fetus. nine0007
The period of 32 weeks is marked by important stages in the functioning of the immune system. In the blood of the fetus, there is a sharp increase in the level of its own immunoglobulins - special proteins that protect the baby from infections. By the time of delivery, the level of immunoglobulins will increase, but this will happen already due to the penetration of the mother's immunoglobulins into the body of the fetus. In the last weeks of pregnancy, the permeability of the placental barrier increases, which allows the protective cells of the mother's body to pass into the blood of the baby. nine0007
By the time of delivery, the level of immunoglobulins will increase, but this will happen already due to the penetration of the mother's immunoglobulins into the body of the fetus. In the last weeks of pregnancy, the permeability of the placental barrier increases, which allows the protective cells of the mother's body to pass into the blood of the baby. nine0007
FUTURE MOTHER
Pain in the back, in the pubic area and large joints, such as hips, knees, a feeling of fullness and pain in the pelvic bones - these phenomena are present to one degree or another in many pregnant women in the third trimester. Changing the center of gravity of a woman's body due to an increase in the volume of the abdomen leads to some displacement of the spine, which entails the above problems. On top of that, the mother's body begins preparing for childbirth by producing the placental hormone - relaxin. It causes relaxation of the ligaments, and during childbirth, the pelvis becomes more pliable, which ensures the free passage of the child through the birth canal.