Signs of early missed miscarriage
Missed Abortion: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Outlook
A missed abortion is also known as a missed miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. It’s a miscarriage in which the fetus didn’t form or is no longer developing, but the placenta and embryonic tissues are still in your uterus.
A missed abortion is not an elective abortion. Medical professionals use the term “spontaneous abortion” to refer to miscarriage.
A missed abortion gets its name because this type of miscarriage doesn’t cause symptoms of bleeding and cramps that occur in other types of miscarriages. It’s common to have no symptoms during a missed abortion. This can make it difficult for you to know that the loss has occurred.
In this article, we’ll cover the causes of missed abortion, as well as how its diagnosed, treated, and more.
On June 24, 2022, the Supreme Court of the United States overturned Roe v. Wade, the landmark 1973 ruling that secured a person’s constitutional right to an abortion.
This means that individual states are now able to decide their own abortion laws. As a result, many states will ban or severely restrict abortion access.
The information in this article was accurate and up to date at the time of publication, but the facts may have changed since. Anyone looking to learn more about their legal rights can message the Repro Legal Helpline via a secure online form or call 844-868-2812.
It’s common to have no symptoms with a missed miscarriage. You may also notice:
- brownish discharge
- lessening or disappearing early pregnancy symptoms like nausea and breast soreness
This is different from a typical miscarriage, which can cause:
- vaginal bleeding
- abdominal cramps or pain
- discharge of fluid or tissue
- lack of pregnancy symptoms
The causes of missed abortion are not fully known. About 50% of miscarriages happen because the embryo has the wrong number of chromosomes.
Sometimes, miscarriage may be caused by a uterine problem like scarring.
You may be at higher risk for missed miscarriage if you have an endocrine or an autoimmune disorder, or are a heavy smoker. Physical trauma can cause a missed miscarriage as well.
If you have a missed miscarriage, your doctor likely won’t be able to pinpoint a reason. In a missed miscarriage, the embryo stops developing, and there’s usually no clear explanation.
Stress, exercise, sex, and travel do not cause miscarriage, so it’s important not to blame yourself.
You should always see a doctor if you suspect any kind of miscarriage. Call your doctor if you have any miscarriage symptoms, including:
- vaginal bleeding
- abdominal cramps or pain
- discharge of fluid or tissue
With a missed miscarriage, a lack of pregnancy symptoms may be the only sign.
For example, if you were feeling very nauseated or fatigued and you suddenly don’t, call the doctor. Most people likely won’t be aware of a missed miscarriage until their doctor detects it during an ultrasound.
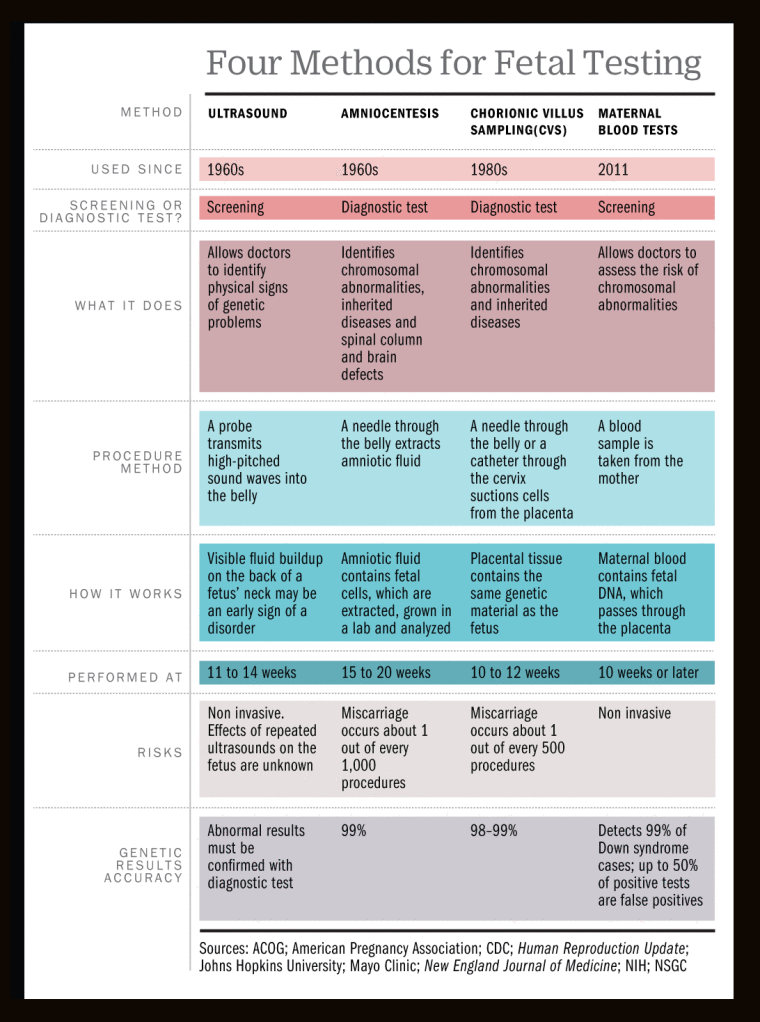
A missed miscarriage is most often diagnosed by ultrasound before 20 weeks of gestation. Usually, the doctor diagnoses it when they can’t detect a heartbeat at a prenatal checkup.
Sometimes, it’s simply too early in the pregnancy to see a heartbeat. If you’re less than 10 weeks pregnant, your doctor may monitor the level of the pregnancy hormone hCG in your blood over a couple of days. If the hCG level doesn’t rise at a typical rate, it’s a sign the pregnancy has ended.
They may also order a follow-up ultrasound a week later to see if they can detect the heartbeat then.
There are several different ways to treat a missed miscarriage. You may be able to choose, or your doctor may recommend a treatment they feel is best for you.
Expectant management
This is a wait-and-see approach. Usually, if a missed miscarriage is left untreated, the embryonic tissue will pass and you’ll miscarry naturally. This is successful in more than 65% of women experiencing a missed miscarriage.
If it’s not successful, you may need medication or surgery to pass the embryonic tissue and placenta.
Medical management
Your healthcare professional may prescribe a medication called misoprostol. This medication helps trigger your body to pass the remaining tissue to complete the miscarriage. This means it will cause cramping, bleeding, and possibly blood clots.
You’ll take the medication at the doctor’s office or hospital and then return home to complete the miscarriage. It usually takes about 4-5 hours for most people to pass the remaining pregnancy tissue.
Surgical management
Dilation and curettage (D&C) surgery may be necessary to remove the remaining tissue from the uterus.
Your doctor may recommend a D&C immediately following your diagnosis of a missed miscarriage. They could also recommend it later if the tissue doesn’t pass on its own or with the use of medication.
Physical recovery time after a miscarriage can vary from a few weeks to a month, sometimes longer. Your period will most likely return in 3 to 6 weeks.
Your period will most likely return in 3 to 6 weeks.
Emotional recovery can take longer. Grief can be expressed in a variety of ways. Some people choose to perform religious or cultural memorial traditions, for example. Talking with a counselor may help as well.
Talking with other people who’ve experienced pregnancy loss is important. You can find a support group near you through Share Pregnancy & Infant Loss Support at NationalShare.org.
If your partner, friend, or family member has a miscarriage, understand that they may be going through a tough time. Give them time and space if they say they need it, but always be there for them as they grieve.
Try to listen. Understand that being around babies and other pregnant people might be difficult for them. Everyone grieves differently and at their own pace.
Having one missed miscarriage doesn’t increase your odds of having a future miscarriage.
If this is your first miscarriage, the rate of having a second miscarriage is between 14-21%, which is about the same as the overall miscarriage rate. But having multiple miscarriages in a row increases your risk for a subsequent miscarriage.
But having multiple miscarriages in a row increases your risk for a subsequent miscarriage.
If you’ve had two miscarriages in a row, your doctor might order follow-up testing to see if there’s an underlying cause. Some conditions that cause repeated miscarriages can be treated.
In many cases, you may be able to try to get pregnant again after you’ve had a regular period. Some doctors recommend waiting at least 3 months after the miscarriage before trying to conceive again.
But one 2017 study suggests that trying again before 3 months may give you the same or even increased odds of having a full-term pregnancy. If you’re ready to try to become pregnant again, ask your doctor how long you should wait.
In addition to being physically ready to carry another pregnancy, you’ll also want to make sure that you feel mentally and emotionally ready to try again. Take more time if you feel you need it.
Missed miscarriage - The Miscarriage Association
A missed (or silent) miscarriage is one where the baby has died or not developed, but has not been physically miscarried. In many cases, there has been no sign that anything was wrong, so the news can come as a complete shock.
In many cases, there has been no sign that anything was wrong, so the news can come as a complete shock.
Why does it happen?
It’s not at all clear why some miscarriages happen within days of a baby dying and others take much longer before the pregnancy hormone levels drop and the physical miscarriage begins. Sometimes that delay may be a matter of days, but it might take several weeks.
Why didn’t I know?While many miscarriages begin with symptoms of pain and bleeding, there are often no such signs with a missed miscarriage. Pregnancy hormones may continue to be high for some time after the baby has died, so you may continue to feel pregnant and a pregnancy test may well still show positive.
In the first few weeks of the second trimester, it may be too early to feel the baby kick so without any bleeding or pain, you are likely to assume all is well.
There often is no way you could know, except by having an ultrasound scan.
The scanNurses told me the baby probably died around seven weeks, four weeks before I realised anything was wrong. Four weeks in which I was marching around with a big smile on my face.
A missed miscarriage is often diagnosed at a routine ultrasound scan, whether around 12 weeks or at the 20 week ‘anomaly’ scan. However it might also be seen at a non-routine scan, NHS or private, whether or not there are any symptoms.
With a missed miscarriage, the scan picture usually shows a pregnancy sac with a baby (or fetus or embryo) inside, but there is no heartbeat and the pregnancy looks smaller than it should be at this stage.
After taking lots of pictures I was told ‘I’m sorry there is no heartbeat, the baby died at 9.5 weeks’, so it was a missed miscarriage and my body thought I was still pregnant. It hit me hard.
In some cases, the scan shows an empty pregnancy sac or no clear sac at all. The embryo has either not developed or it stopped developing at a very early stage and been reabsorbed by the body. You might hear that called ‘early embryonic demise’ or the old-fashioned term ‘blighted ovum’.
The embryo has either not developed or it stopped developing at a very early stage and been reabsorbed by the body. You might hear that called ‘early embryonic demise’ or the old-fashioned term ‘blighted ovum’.
The diagnosis of a missed miscarriage can be very shocking, especially if you had no indication at all that anything was wrong.
You might have been full of excitement about seeing your baby and looking forward to sharing your news, as Tina was:
As we got to the 12 week scan, I was looking forward to it. I wanted that to be the benchmark when I could tell everybody.
Perhaps you had an early or additional scan because of spotting, pain or bleeding, or just a sense that something wasn’t right. The diagnosis might have confirmed your worst fears but it might still have come as a real shock, perhaps especially if it was some time since the baby had died.
On the other hand, you may have had several scans before the miscarriage was confirmed, and this can be a very stressful time.
The scan showed the “baby” was only the size of a 5 week pregnancy and there was no heartbeat. We were told we would have to wait a week to see if there was any growth and if there had been, then the baby might be big enough to have a detectable heartbeat. That was one of the longest weeks of my life.
This period of waiting can feel like you’re ‘in limbo’, whether you try to be positive, as in this story, or you prepare for the worst. You might move between the two.
Being faced with decisionsAt the same time as dealing with the news that you have a missed miscarriage, you may also be asked to make some difficult decisions about how to manage the miscarriage process. (We write about this here.)
You might feel ready to make that decision very quickly, or you might need a few days to take everything in before making a decision. You are very welcome to contact us if you’d like to talk things through.
What about work?
Work may be the last thing on your mind right now. But if you need more information about your rights and support for you and your employer, our Miscarriage and the Workplace hub has more information for everyone.
But if you need more information about your rights and support for you and your employer, our Miscarriage and the Workplace hub has more information for everyone.
You might also find it helpful to read some of the following stories:
- Jennifer’s story
- Hayley’s story
- Little sesame
- Never thought it would happen to me
- Amy Abrahams writes about her experience (originally published by The Pool), ‘Breaking the silence of a missed miscarriage’
Our animation ‘Helping people through’ shares one couple’s experience of a missed miscarriage:
You might also want to talk with others who have been through something similar:
- by phone (contact us for details of a support volunteer)
- in a support group, or
- through our online forum.
You don’t need to go through this alone.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage is a spontaneous premature termination of pregnancy for a period of less than 20 weeks, that is, during the period when the embryo or fetus cannot yet survive on its own outside the female body. This is the most common complication of the first trimester of pregnancy.
Approximately 10-20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. Most often, spontaneous abortion occurs in the first 12 weeks. In some cases, the pregnancy is terminated before the woman even knows about its existence.
The risk of miscarriage increases with age: in women younger than 35 years old it is 15%, from 35 to 45 years old - 20-35%, over 45 years old - more than 50%. Women who have had a miscarriage in the past have an increased risk of spontaneous abortion. However, if a woman is healthy and re-pregnancy occurs 2-3 months after a spontaneous abortion, then it most often ends safely.
If a woman experiences three or more spontaneous abortions, then this condition is called recurrent miscarriage.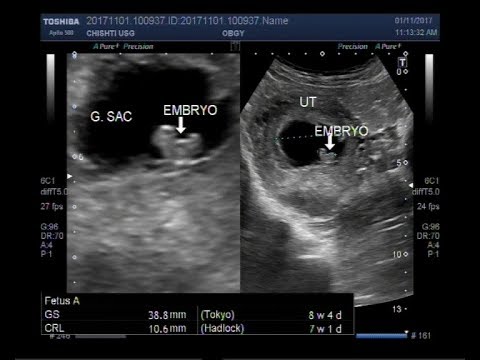 It is diagnosed in approximately 1% of women who have had a spontaneous abortion. Identification of the immediate cause of recurrent miscarriage and appropriate treatment allows most patients to subsequently become pregnant and give birth to a healthy child.
It is diagnosed in approximately 1% of women who have had a spontaneous abortion. Identification of the immediate cause of recurrent miscarriage and appropriate treatment allows most patients to subsequently become pregnant and give birth to a healthy child.
Russian synonyms
Spontaneous abortion, spontaneous abortion.
Synonyms English
Miscarriage, early miscarriage, recurrent miscarriage, spontaneous abortion.
Symptoms
Symptoms of miscarriage can be both almost imperceptible and pronounced. The duration of manifestations can also vary. In some cases, the main symptoms are preceded by a period of non-specific manifestations: there may be weight loss, weakness, back pain, bloody or mucous discharge from the genitals.
The main symptoms of miscarriage are:
- bleeding from the genitals;
- abdominal pain;
- contractions.

Other complications of pregnancy, such as ectopic pregnancy, may have similar symptoms. Therefore, in case of any violations, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible to identify the cause of the pathology and timely treatment.
General information about the disease
Miscarriage occurs quite often, and in many cases it is impossible to determine the cause of this pathology. There are several groups of factors that can lead to spontaneous abortion.
- Chromosomal disorders in embryonic cells. Chromosomes are cellular structures that contain genetic information. Chromosomal abnormalities incompatible with life cause spontaneous abortion in the early stages of pregnancy. More than half of the cases of miscarriage in the first trimester is associated with them. The risk of genetic abnormalities increases in proportion to the age of the mother.
- Maternal pathology. Most often, maternal illness leads to miscarriage between the 12th and 20th week of pregnancy.
 Allocate:
Allocate: - Chronic maternal diseases: diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, severe urinary and cardiovascular disorders, autoimmune diseases (antiphospholipid syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus), blood clotting disorders (factor Leiden deficiency), as well as certain chromosomal abnormalities in the mother's body.
- Acute illness of the mother: severe trauma, burns, infections, in particular cytomegalovirus infection, mycoplasma, as well as severe emotional stress.
- Diseases and disorders of the structure of the genital organs of a woman: pathology of the structure of the uterus, cervical insufficiency, uterine fibromyoma. This group also includes anomalies in the structure and position of the placenta, as well as multiple pregnancy, which also increases the risk of miscarriage.
- Use of alcohol, psychoactive substances by a woman.
In the normal course of pregnancy in a healthy woman, moderate physical activity and sex cannot cause miscarriage. However, in some cases, in order to maintain pregnancy, the doctor may advise the patient to limit physical activity and stop sexual intercourse for a while.
However, in some cases, in order to maintain pregnancy, the doctor may advise the patient to limit physical activity and stop sexual intercourse for a while.
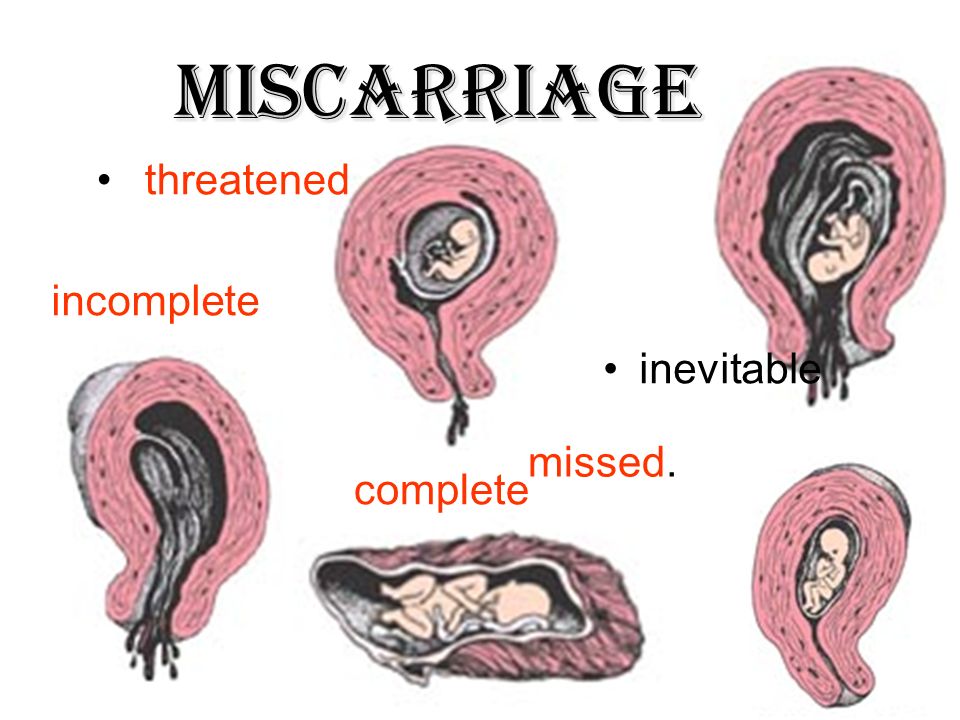
There are the following types of miscarriage:
- Threatened spontaneous abortion. This term is used for any bleeding from the uterine cavity in the first half of pregnancy. At the same time, the external cervical os is closed and there are signs of the vital activity of the embryo.
- Inevitable abortion. It is diagnosed if bleeding from the uterine cavity is accompanied by the opening of the cervix, but the fetus and placenta are still in the uterine cavity.
- Incomplete abortion. A condition in which parts of the embryo or placenta are still in the uterine cavity.
- Complete abortion. With a complete abortion, all components of the fetus, placenta, membranes are completely expelled from the uterine cavity.
- Frozen pregnancy. A condition in which intrauterine fetal death occurs, but neither the fetus nor the placenta is expelled from the uterine cavity.
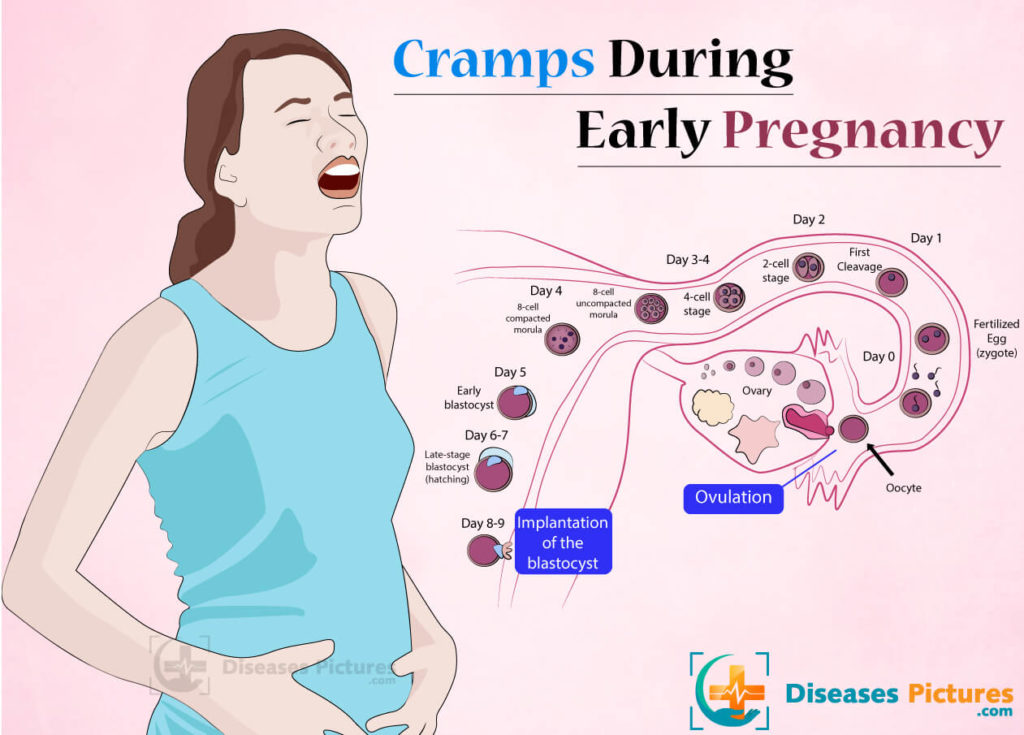
Who is at risk?
- Women over 35
- Women who have had a spontaneous abortion in the past
- Women with chronic diseases
- Women with acute infectious pathology, injuries, exhaustion, exposed to ionizing radiation
- Women who smoke and use alcohol and/or drugs
- Women with multiple pregnancies
Diagnosis
If a spontaneous abortion is suspected, the doctor first of all performs a gynecological examination and ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, which allows assessing the condition of the uterus, its cervix, the presence of elements of the fetus and placenta in its cavity. Sometimes, to monitor the course of pregnancy, as well as to identify the causes of miscarriage, a number of additional laboratory and instrumental studies may be required.
Laboratory diagnostics
- Complete blood count with leukocyte formula, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
 These indicators allow you to assess the general condition of the patient, identify signs of anemia, infection and other diseases that affect the normal course of pregnancy.
These indicators allow you to assess the general condition of the patient, identify signs of anemia, infection and other diseases that affect the normal course of pregnancy. - Urinalysis with microscopy, serum creatinine, serum urea. These studies allow you to evaluate the functioning of the urinary system and identify kidney diseases that can cause spontaneous abortion.
- Hemostasiology studies that assess the activity of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation system, identify diseases that increase the risk of miscarriage:
- D-dimer
- Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT)
- Coagulogram No. 1 (prothrombin (according to Quick), INR)
- Fibrinogen
- Examination of liver functions. Allows you to identify signs of acute or chronic liver pathology:
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Total protein in serum
- Bilirubin total
- Bilirubin direct
- Plasma glucose.
 An increase in blood glucose levels can be a sign of diabetes, one of the main risk factors for miscarriage.
An increase in blood glucose levels can be a sign of diabetes, one of the main risk factors for miscarriage. - Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Allows you to evaluate the activity of the thyroid gland and signs of endocrine diseases that affect the course of pregnancy.
- Diagnosis of infectious diseases. The level of various types of antibodies to certain infections is determined:
- HIV 1, 2 Ag/Ab Combo (determination of antibodies to HIV types 1 and 2 and p24 antigen)
- anti-HCV, antibodies, express, ultra sensitive
- HBsAg, ultra sensitive
- Treponema pallidum, antibodies, hypersensitive
- Toxoplasma gondii, IgM
- Toxoplasma gondii, IgG (quantitative)
- Rubella Virus, IgM
- Rubella Virus, IgG (quantitative)
- Cytomegalovirus, IgM (quantitative)
- Cytomegalovirus, IgG
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2, IgM
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2, IgG
- Beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (beta hCG).
 It is a glycoprotein synthesized by the placenta. A decrease in the level of beta-hCG, which does not correspond to the gestational age, makes it possible to suspect a pathology.
It is a glycoprotein synthesized by the placenta. A decrease in the level of beta-hCG, which does not correspond to the gestational age, makes it possible to suspect a pathology. - Diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome, which can cause miscarriage:
- Antiphospholipid IgG
- Antiphospholipid IgM
- Genetic research. Allow to identify chromosomal abnormalities in the mother, which can cause abnormal gametogenesis and, as a result, genetic abnormalities of the fetus that are incompatible with life. It is also possible to identify a genetic predisposition to early habitual pregnancy loss.
Instrumental methods of examination
Visual examination of the pelvic organs assesses the condition of the uterus, reveals anomalies in its structure, pathology of the reproductive system, establishes the presence or absence of elements of the placenta and embryo in the uterine cavity.
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Hysteroscopy
- Laparoscopy
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of spontaneous abortion, the condition of the woman. With a complete spontaneous abortion, when there are no elements of the fetus and placenta in the uterus, additional intervention is usually not required. In case of incomplete abortion, it is necessary to remove all elements of the membranes, embryo and placenta from the uterine cavity. For this, curettage or, in some cases, drug treatment can be carried out.
With a complete spontaneous abortion, when there are no elements of the fetus and placenta in the uterus, additional intervention is usually not required. In case of incomplete abortion, it is necessary to remove all elements of the membranes, embryo and placenta from the uterine cavity. For this, curettage or, in some cases, drug treatment can be carried out.
If there is a threat of miscarriage and the preservation of signs of fetal vital activity, it is necessary to try to save the pregnancy. Depending on the severity of the condition, a woman may be admitted to a hospital or treated on an outpatient basis. The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor individually, depending on the cause of miscarriage, gestational age, the patient's condition and other factors.
Prevention
Prevention of miscarriage includes both parental care before conception and following certain recommendations after pregnancy. To reduce the risk of pregnancy termination, a pregnant woman should:
- give up alcohol, smoking, limit or stop drinking coffee and caffeinated drinks;
- regularly undergo preventive examinations;
- refrain from extreme sports that could result in serious injury;
- avoid ionizing radiation, contact with sources of infection.

Recommended tests
- CBC
- Leukocyte formula
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- Urinalysis with microscopy
- D-dimer
- Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT)
- Coagulogram No. 1 (prothrombin (quick), INR)
- Fibrinogen
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Plasma glucose
- Serum creatinine
- Serum urea
- Total protein in serum
- Bilirubin total
- Bilirubin direct
- HIV 1, 2 Ag/Ab Combo (determination of antibodies to HIV types 1 and 2 and p24 antigen)
- anti-HCV, antibodies, express, ultra sensitive
- HBsAg, ultra sensitive
- Treponema pallidum, antibodies, hypersensitive
- Toxoplasma gondii, IgM
- Toxoplasma gondii, IgG (quantitative)
- Rubella Virus, IgM
- Rubella Virus, IgG (quantitative)
- Cytomegalovirus, IgM
- Cytomegalovirus, IgG
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2, IgM
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2, IgG
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Pregnancy - I trimester
- Beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (beta hCG)
- Antiphospholipid IgG
- Antiphospholipid IgM
- Predisposition to early habitual pregnancy loss
- Predisposition to early habitual pregnancy loss (extended)
Miscarriage: primary and habitual, why spontaneous abortion occurs
Miscarriage is a pathological condition that consists in the termination of (spontaneous) pregnancy for up to 37 weeks. If after the first miscarriage, appropriate treatment was not carried out, the risk of a second one increases. That is why it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner. This will reduce the risks of recurrent miscarriage, eliminate existing pathologies and become pregnant.
If after the first miscarriage, appropriate treatment was not carried out, the risk of a second one increases. That is why it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner. This will reduce the risks of recurrent miscarriage, eliminate existing pathologies and become pregnant.
It should be understood that there is nothing shameful in the diagnosis of "miscarriage", treatment should be carried out in a timely manner and by professionals!
Miscarriage is a problem that today has affected a huge number of women around the world. It negatively affects the birth rate and is important from the point of view of socio-economic development. Miscarriage, the causes of which are constantly being studied, depending on the time of occurrence, can be classified as spontaneous abortion (early: before 12 weeks, late: before 22 weeks) or preterm birth (early: from 22 to 28 weeks, late: from 28 to 37 weeks ).
Reasons
Miscarriage, the causes and treatment of which are being investigated by specialists, is a complex pathology.
Usually it is provoked by pathological conditions of the woman's body, immunological disorders in the "mother-placenta-fetus", chromosomal and gene disorders, socio-biological (physiological, chemical and other factors).
The causes of the pathological condition include:
- Induced abortions
- Metabolic disorders
- Anomalies in the structure of internal organs (mainly uterus)
- Immune system disorders
- Inflammation of the pelvic organs: gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, etc.
- Impaired blood flow in the uterus or placenta
Often, specialists diagnose not one, but several causes of miscarriage at once.
Early miscarriage
Early termination of pregnancy usually occurs due to pathologies of the endocrine system, genetic factors or inflammatory processes. Miscarriages in the second trimester are rare. If pathology occurs, it is usually under the influence of factors such as violations of blood clotting processes.
Provoke abortion in the early stages can and reasons such as:
- Myoma
- Anomalies in the structure of the uterus
- Placenta previa
Important! The threat of miscarriage exists constantly, not only in the early stages. That is why you should be regularly examined in a antenatal clinic or a doctor in a large clinic. Only timely diagnosis will help to avoid a pathological condition and prevent miscarriage in the early or late stages. For any unusual sensations or signs, you should consult a doctor! So you can keep the pregnancy and bear a healthy baby, even if there is a predisposition to abortion.
Recurrent miscarriage
The diagnosis of "recurrent miscarriage" is made if the interruption occurred more than 2-3 times in a row. A woman needs not only the supervision of a doctor, but also a thorough examination. All therapy is based on the factors and causes of miscarriage. If necessary, the patient is observed not only by a gynecologist, but also by an endocrinologist, geneticist, and other specialists. Particular attention is paid to finding out the main and additional reasons that provoked a miscarriage.
Particular attention is paid to finding out the main and additional reasons that provoked a miscarriage.
Risk of miscarriage
Miscarriage is a pathological condition that can occur today in almost every woman.
This is due to the fact that it is provoked by factors such as:
- Regular strenuous exercise
- Night shift work
- Exposure to stressors
- Smoking and drinking
- Abortion
- Caesarean section and other pelvic surgeries
- Genetics: miscarriage in mother or grandmother
- Age: under 16 and over 35
- Cardiovascular pathologies
- Diabetes mellitus
- Diseases of the kidneys
- Obesity 2-3 degrees
- Diseases of the thyroid gland
- Increased blood clotting, etc.
The cause of abortion (especially in the early stages) in some cases is even a common viral infection.
Pathology diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathology is carried out in the presence of clinical signs of miscarriage (permanent miscarriages, fetal developmental arrest, stillbirths) and symptoms of a threatened abortion, which include bloody discharge from the genital tract and pulling pains in the lower abdomen at any stage of pregnancy.
For the diagnosis of pathology are carried out:
General examination of the patient
The doctor performs it comprehensively, paying attention to:
- Body type
- Height to weight ratio
- Blood pressure readings
- Presence of skin striae
- Liver condition
- Features of the cardiovascular system
- Expression of secondary sexual characteristics
The increased risk of miscarriage may be indicated by such signs as:
- Psycho-emotional instability of the patient
- Excessive sweating
- Paleness or blueness of the skin
- Rapid pulse
Gynecological examination
It consists in:
- Detection of scars on the cervix
- Determination of the dimensions of the external os of the cervical canal
- Neck fixings
- Identification of hair type
During a gynecological examination, a specialist can detect the presence of genital warts and other formations, as well as tumor processes, determine the size of the ovaries, detect inflammation and malformations of internal organs.
Special examinations
Diagnostics is carried out in two stages. At the first, the general condition of the reproductive system of the couple is assessed, at the second, the causes of the pathological condition (if it is detected) are specified.
Hormonal studies
When diagnosing, the causes of hormonal imbalance in the body are determined. Thanks to this study, doctors are able to quickly select the necessary means of therapy.
Analyzes are aimed at studying hormones such as:
- Progesterone
- Testosterone
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone, etc.
The full range of studies is voiced by a specialist.
Immunological testing
With such a diagnosis, indicators of immunoglobulins, growth hormone, thyroid hormones and other parameters are determined that determine the ability of a woman's body to bear a child.
Bacteriological tests
Such a diagnosis consists in the study:
- Vaginal, cervical and uterine materials
- Urine
- Blood
Experts determine not only the causative agents of the infection, but also the presence of antibodies to them.
Genetic research
Diagnostics is carried out at:
- Early termination of pregnancy
- History of stillbirth
- Couple over 35 years of age
The geneticist necessarily studies the pedigree of the couple, receives information that allows us to understand the regularity or randomness of the miscarriage factors.
Important! Diagnosis with suspicion of pathology is not only a woman, but also a man.
What tests and examinations are needed?
Women with suspicions of miscarriage and for an accurate diagnosis pass the following tests:
- Clinical analysis of urine and blood
- Biochemical blood test
- Rh factor and blood group determination
- Hormone profiling
- Virological testing
- Genetic diagnostics
- Immunological study
A pelvic ultrasound is also performed to determine ovulation.
The man will:
- Complete virological and genetic testing
- Take a spermogram
- Visit a urologist-andrologist for a comprehensive examination and consultation
Important! Only a comprehensive examination allows you to find out all the main and concomitant causes of miscarriage, after which you can develop an individual treatment plan, even with a combination of a number of factors that provoke miscarriages.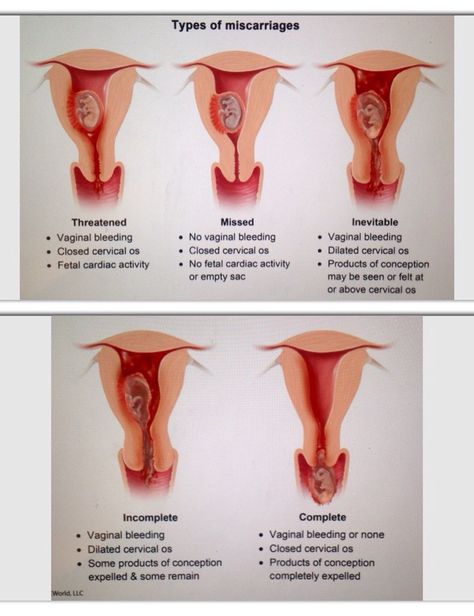
Examination: features of the procedure
With such a pathology as miscarriage, tests are given by the patient and her partner all the time.
At the first visit to a pregnant gynecologist and registration, the following are carried out:
- History taking
- Gynecological examination
- ultrasound
- Laboratory tests (blood and urine tests)
When diagnosing thrombopholia (blood clotting disorders), the causes of the pathology are identified. Immediately after this, the necessary therapy is carried out. Be sure to study the indicator of TBG (marker of placental insufficiency). If the rate is reduced in the first trimester, the doctor may judge the risk of miscarriage.
At 15-20 weeks of pregnancy are carried out:
- Cervical examination
- ultrasound
- Vaginal and cervical swabs (for elevated leukocyte counts)
- Specialized tests to rule out Down's disease and other genetic abnormalities
At the 24th week of pregnancy, the following are performed:
- Glucose tolerance tests
- Transviganile Ultrasound
- Manual examination of the cervix
- Cervical swabs
- Doppler study to determine placental and uterine blood flow
At week 32, the following are evaluated:
- Fetal activity
- Absence of antibodies in the blood (with negative Rh)
- Contractile activity of the uterus
- Bacteriological status (presence of infections in the vagina)
- Preterm markers
If necessary, the woman is hospitalized. It is aimed at the prevention of miscarriage and treatment in case of detection of pathological processes.
It is aimed at the prevention of miscarriage and treatment in case of detection of pathological processes.
At 37 weeks:
- Blood sugar test is taken
- WBC and total protein are assessed
- Determine the contractile function of the uterus
- Fetal assessment
- Smears being examined
- Hepatitis, HIV and AIDS tests are taken
Preparation for pregnancy in case of miscarriage and treatment
Preparation for pregnancy with a diagnosis of "miscarriage" is always carried out according to an individual scheme, which is developed in accordance with the patient's condition and the results of the diagnosis.
Preparation may include:
- Elimination of inflammatory processes
- Restoration of immune status
- Correction of comorbidities
- Restoration of hormonal status
- Elimination of metabolic disorders, etc.
It usually takes at least 2-3 months to prepare for pregnancy.
The psychological support of the woman becomes obligatory.
It is important for specialists:
- Remove all psychological barriers
- Teach a woman to talk about a problem
- Set up the patient for a successful pregnancy
Preparation is impossible without the support of loved ones. In no case should you brush aside the problems of a woman who cannot bear a child. You should devote time to her problem, talk to her, tune in to a positive outcome of the upcoming pregnancy. Do not forget that one of the causes of the pathological condition is stress.
The treatment of miscarriage largely depends on the causes that provoked the difficulties.
Patients may be given:
- Herbal sedatives
- Antispasmodics
- Hormonal preparations
- Immunoglobulins
Treatment is possible with placental insufficiency, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, inflammatory and other negative and aggressive processes.
In some cases, partner treatment is also carried out.
Today, special attention is paid to the prevention of pathological conditions.
It is aimed at:
- Determination of factors provoking miscarriage
- Comprehensive couple examination
- Preparation for a successful pregnancy
- Mandatory control over the occurrence of complications during childbearing
- Taking special drugs
Prevention in a condition such as miscarriage can reduce complications (risks of their occurrence) by several times.
With the right approach, you can:
- Reduce the chances of miscarriage
- Prevent purulent infections, heavy bleeding, spread of infection during miscarriage
- Reduce the risk of preterm birth and neonatal death
Of course, in such a condition as miscarriage, rehabilitation after a miscarriage should be carried out only under the supervision of experienced professionals. A woman can undergo recovery both in a hospital and at home. The decision on hospitalization is made by the patient together with the doctor.
A woman can undergo recovery both in a hospital and at home. The decision on hospitalization is made by the patient together with the doctor.
Factors such as:
- Need for ongoing medical support
- Psychological status of the patient
- Presence of comorbidities
Benefits of treatment in MEDSI clinics
- Assistance to patients with primary and recurrent miscarriage at various times. Support is provided by experienced professionals who improve their skills
- Availability of facilities for comprehensive diagnostics of a woman and her partner. For examinations, modern installations of well-known manufacturers are used. Availability of own laboratory allows to carry out analyzes in the CITO mode (urgently)
- Use in diagnosis, treatment, prevention and rehabilitation of classical and modern methods
- Expert gynecological consultations providing a second opinion on your situation
- Opportunities for conservative and surgical treatment using modern drugs and innovative techniques and equipment
- Reproductive hemostasiologist appointment for bleeding disorders, which in some cases is the cause of miscarriage
- Providing a full service to a woman and her partner
- Pre-pregnancy programs to reduce the risk of miscarriage
- Comfortable conditions and pleasant psychological atmosphere in clinics
- Opportunities for psychotherapeutic support
- Involvement of several doctors in the work with a patient
Make an appointment by calling +7 (495) 7-800-500.