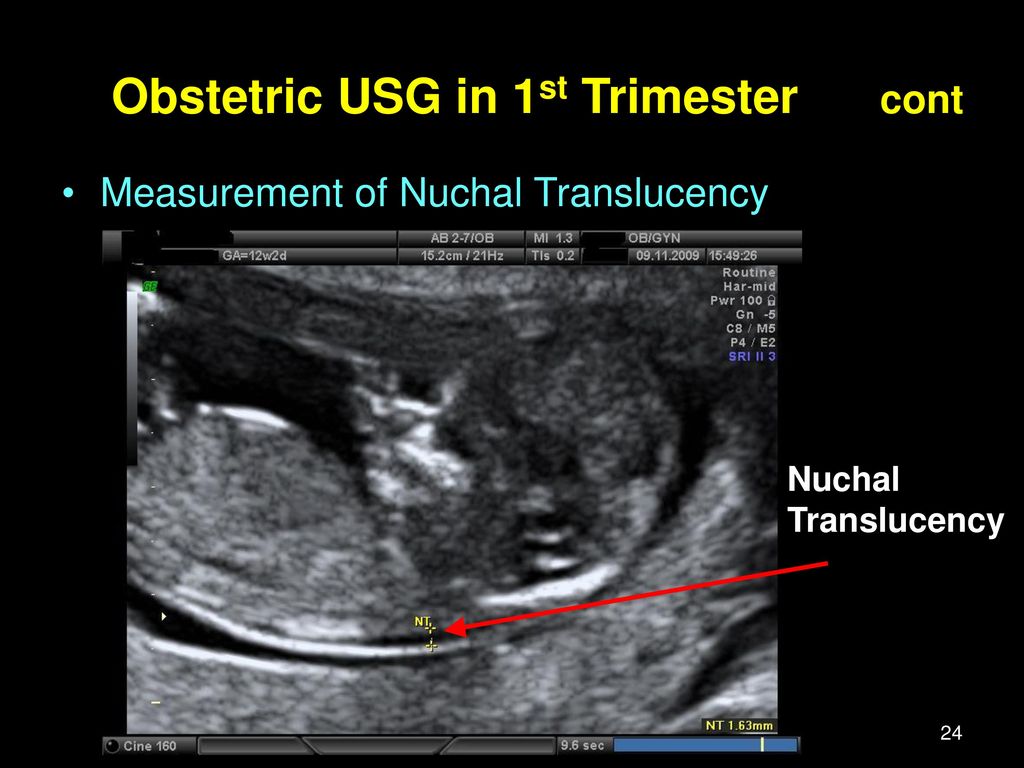
Nuchal translucency scanning
Nuchal translucency test Information | Mount Sinai
Nuchal translucency screening; NT; Nuchal fold test; Nuchal fold scan; Prenatal genetic screening; Down syndrome - nuchal translucency
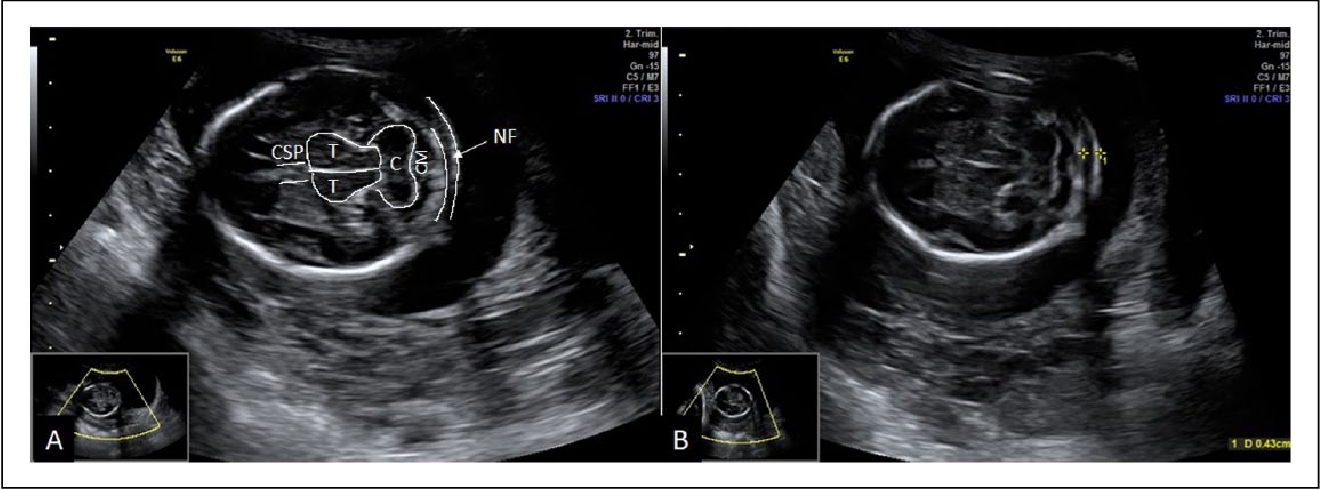
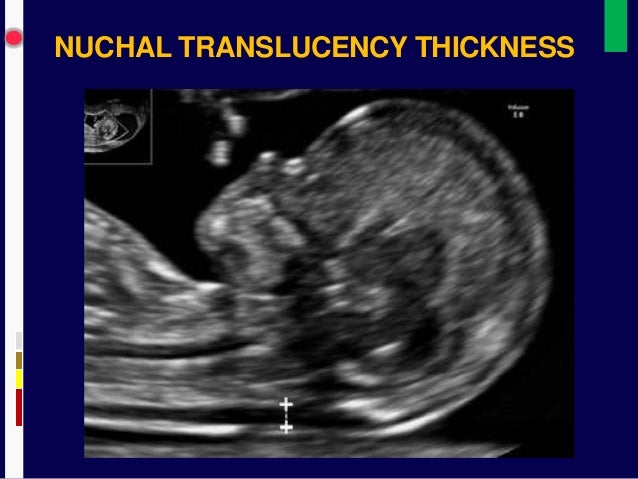
The nuchal translucency test measures the nuchal fold thickness. This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down syndrome and other genetic problems in the baby.
How the Test is Performed
Your health care provider uses abdominal ultrasound (not vaginal) to measure the nuchal fold. All unborn babies have some fluid at the back of their neck. In a baby with Down syndrome or other genetic disorders, there is more fluid than normal. This makes the space look thicker.
A blood test of the mother is also done. Together, these two tests will tell if the baby could have Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.
How to Prepare for the Test
Having a full bladder will give the best ultrasound picture. You may be asked to drink 2 to 3 glasses of liquid an hour before the test. DO NOT urinate before your ultrasound.
How the Test will Feel
You may have some discomfort from pressure on your bladder during the ultrasound. The gel used during the test may feel slightly cold and wet. You will not feel the ultrasound waves.
The gel used during the test may feel slightly cold and wet. You will not feel the ultrasound waves.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may advise this test to screen your baby for Down syndrome. Many pregnant women decide to have this test.
Nuchal translucency is usually done between the 11th and 14th week of pregnancy. It can be done earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis. Amniocentesis is another test that checks for birth defects.
Normal Results
A normal amount of fluid in the back of the neck during ultrasound means it is very unlikely your baby has Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.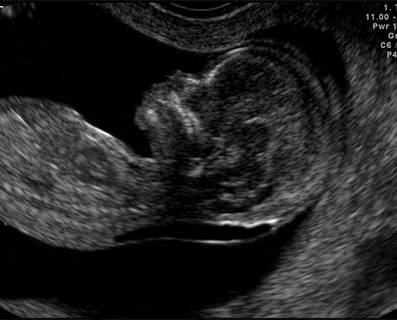
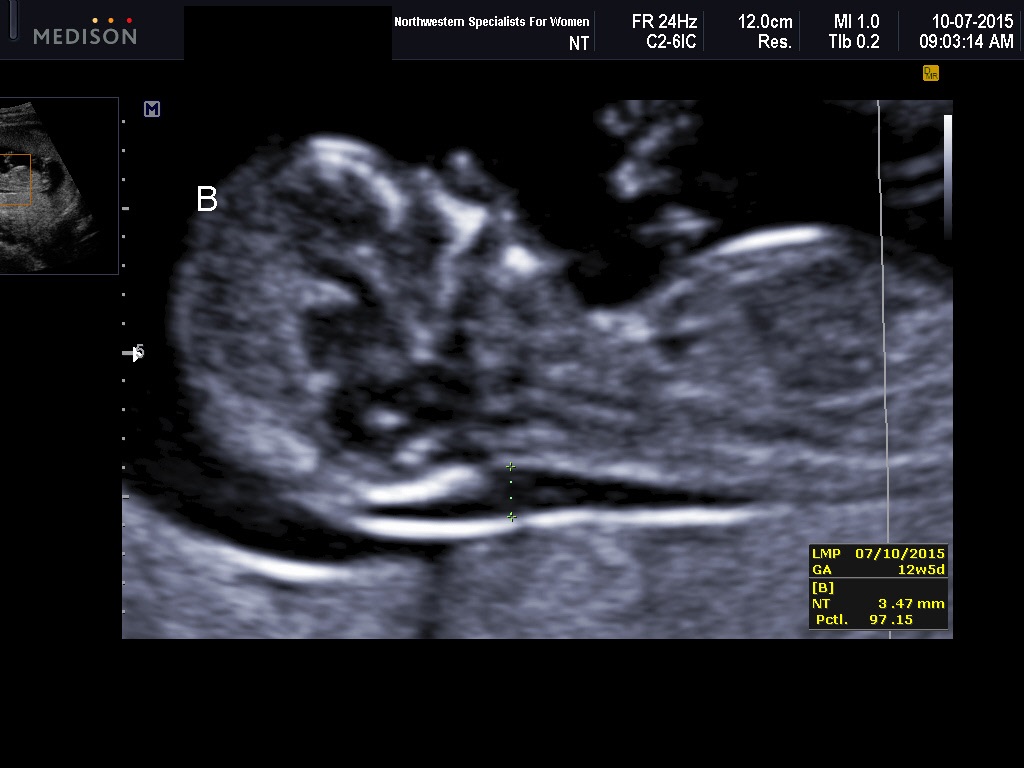
Nuchal translucency measurement increases with gestational age. This is the period between conception and birth. The higher the measurement compared to babies the same gestational age, the higher the risk is for certain genetic disorders.
The measurements below are considered low risk for genetic disorders:
- At 11 weeks -- up to 2 mm
- At 13 weeks, 6 days -- up to 2.8 mm
What Abnormal Results Mean
More fluid than normal in the back of the neck means there is a higher risk for Down syndrome, trisomy 18, trisomy 13, Turner syndrome, or congenital heart disease. But it does not tell for certain that the baby has Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.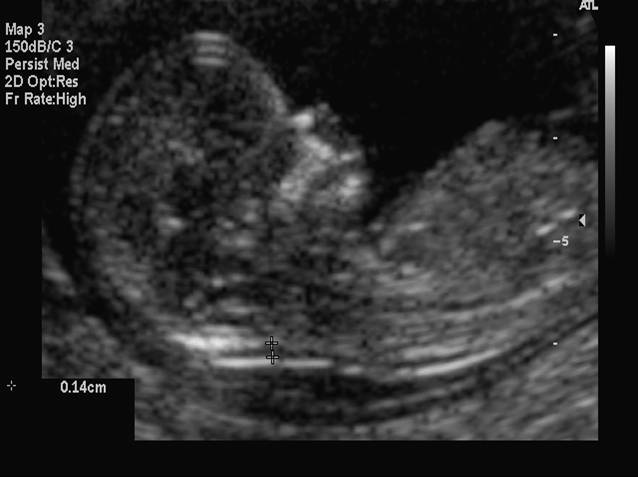
If the result is abnormal, other tests can be done. Most of the time, the other test done is amniocentesis.
Risks
There are no known risks from ultrasound.
Driscoll DA, Simpson JL. Genetic screening and diagnosis. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 10.
Walsh JM, D'Alton ME. Nuchal translucency. In: Copel JA, D'Alton ME, Feltovich H, et al, eds. Obstetric Imaging: Fetal Diagnosis and Care. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 45.
2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 45.
Wapner RJ, Dugoff L. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital disorders. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 32.
Last reviewed on: 4/19/2022
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
First Trimester Screening, Nuchal Translucency and NIPT
First trimester screening (FTS), nuchal translucency (NT) and noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) are prenatal tests that provide information on a developing baby’s risk for certain chromosomal differences (anomalies).
The screening is a blood test that evaluates substances in the blood (analytes), and NT is a sonogram that looks at nuchal translucency in the back of the fetal neck.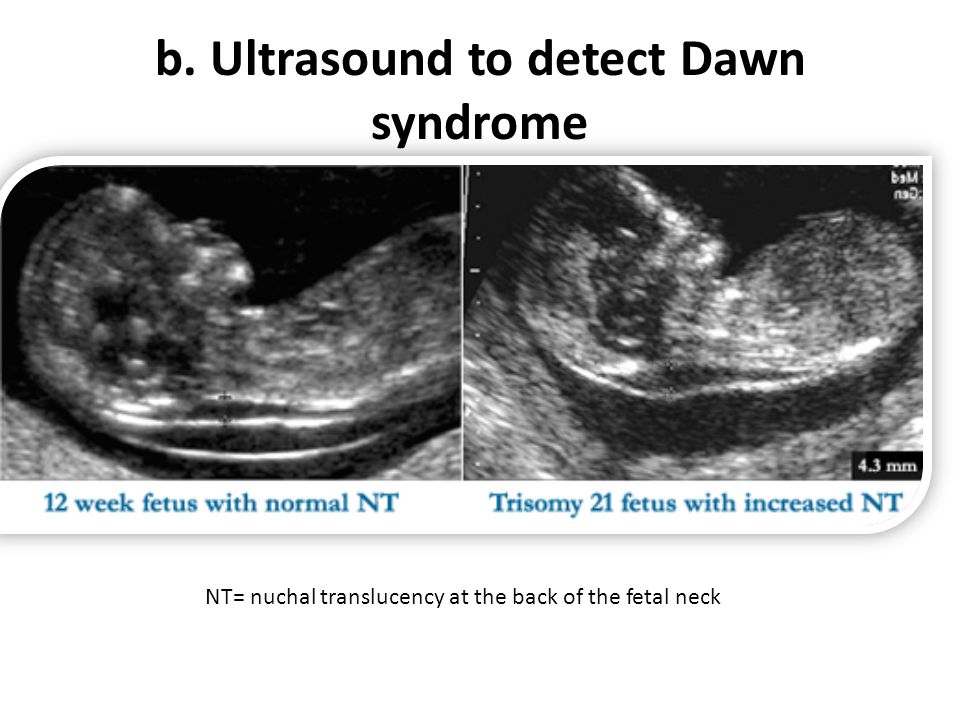 Noninvasive perinatal testing (NIPT) is a newer method that provides a result with a blood test only; a first trimester ultrasound is still recommended.
Noninvasive perinatal testing (NIPT) is a newer method that provides a result with a blood test only; a first trimester ultrasound is still recommended.
FTS, NT and NIPT provide data that can help assess if a fetus (developing baby) has one of three genetic anomalies:
- Down syndrome
- Trisomy 13
- Trisomy 18
These tests cannot diagnose these anomalies. But the data they provide help assess the likelihood that a fetus may have one of these conditions.
What You Need to Know
- The first trimester screening test (FTS) is blood work, and the nuchal translucency test is specialized imaging of the fetus using ultrasound.
- When the two tests are performed together, the combined data can help assess the risk of certain genetic conditions, but it cannot diagnose them.
- Noninvasive prenatal testing, or NIPT, is a new option that uses a blood test to look for signs of Down syndrome, trisomy 13 and trisomy 18 by analyzing free fragments of DNA in the bloodstream.

What is combined first trimester screening?
This is available to pregnant people from weeks 11 through 13 of pregnancy. It comprises a maternal blood test and a nuchal translucency test, which is ultrasound imaging of the fetus to look for clues that could affect the chances of certain genetic conditions. The test may be accompanied by genetic counseling.
The nuchal translucency ultrasound portion of combined first trimester screening is performed by specially credentialed sonographers.
FTS is not a diagnostic test, which means it cannot tell you for certain whether the fetus has Down syndrome, trisomy 13 or trisomy 18. Instead, the screening helps measure the probability that a fetus might have one of these conditions. Data from the ultrasound and blood test, together with the mother’s age, can provide information about whether the fetus is at an increased risk for one of these chromosomal disorders.
If the combined first trimester screening data show that there is a 1 in 250 chance ― or greater ― that the developing fetus has one of these conditions, your doctor may recommend further testing to rule them out.
What is noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT)?
NIPT is a different approach for identifying the risk that a fetus is affected by Down syndrome, trisomy 13 or trisomy 18. It consists of a blood test alone. A nuchal translucency ultrasound can still be performed, and it will not affect the NIPT results. Noninvasive prenatal testing can pick up tiny pieces of DNA in the mother’s bloodstream and analyze them for factors that would raise the risk of the fetus having a chromosomal difference.
In addition to Down syndrome and trisomies 13 and 18, NIPT can detect clues associated with other abnormal chromosomes, such as Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome and triple X syndrome. NIPT can also predict the fetus’s sex with high accuracy.
Nuchal translucency and NIPT: Why are they performed?
Down syndrome, trisomy 13 and trisomy 18 are chromosomal disorders that cause intellectual disability and birth defects in children who are born with them. Anyone can have a baby with these chromosomal abnormalities, but the chance increases with the mother’s age.
Babies with Down syndrome (trisomy 21) have an extra 21st chromosome, which may cause a range of signs and symptoms, including intellectual disability and various medical complications involving the heart, digestive tract and other organ systems.
Trisomy 18 (having an extra 18th chromosome) and trisomy 13 (having an extra 13th chromosome) are more severe disorders that cause profound intellectual disability and severe birth defects in many organ systems. Sadly, few babies with trisomies 13 or 18 survive more than a few months.
Preparing for First Trimester Screening
These screenings include a simple blood test, with or without ultrasound. Neither the blood test nor the ultrasound is invasive, so no special preparations are necessary.
What happens during combined FTS?
The blood test part of the test takes a sample of the mother’s blood. The sample is analyzed to check levels of three chemicals to see if they are higher or lower than average, which can indicate a higher or lower chance of Down syndrome, trisomy 13 or trisomy 18:
- Free beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
- Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A)
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
The nuchal translucency will examine:
- The progress of your pregnancy
- The fluid underneath the skin along the back of the fetus’s neck, called the nuchal translucency, or nuchal fold.
 In some pregnancies, when the fetus has Down syndrome, trisomy 13 or trisomy 18, there is extra fluid behind the neck. A larger-than-expected nuchal fold is associated with other birth defects such as congenital heart defects and skeletal problems.
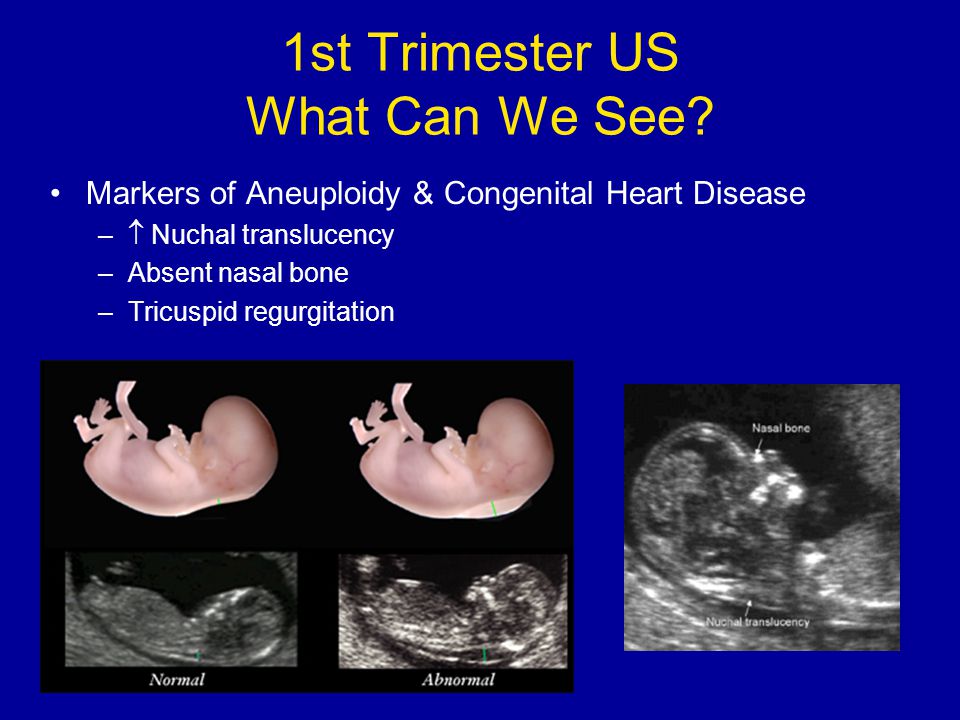
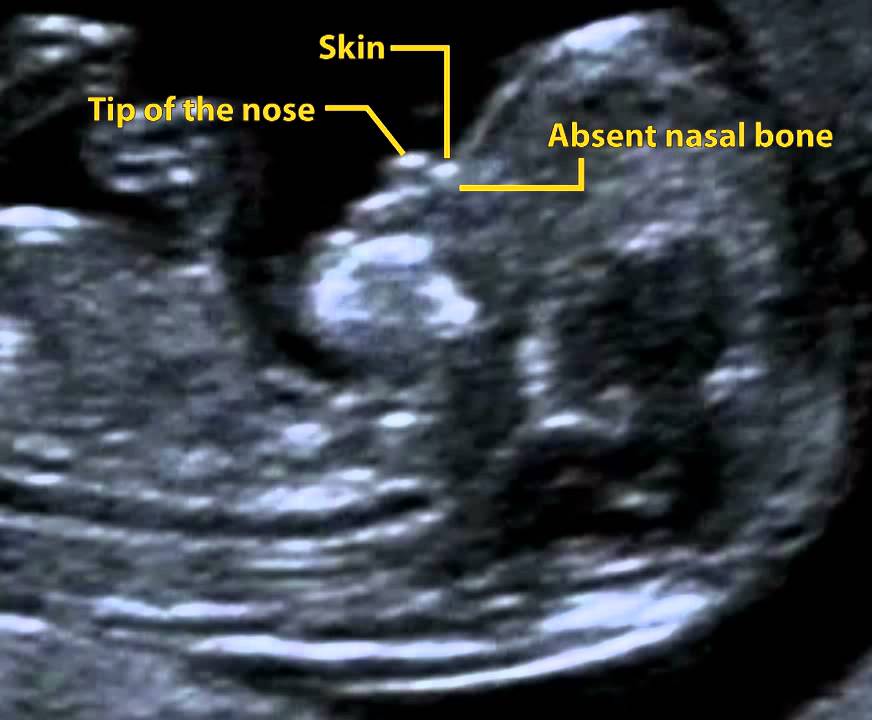
In some pregnancies, when the fetus has Down syndrome, trisomy 13 or trisomy 18, there is extra fluid behind the neck. A larger-than-expected nuchal fold is associated with other birth defects such as congenital heart defects and skeletal problems. - Presence of the fetus’s nasal bone. While a nasal bone may be absent in some fetuses with a chromosomal abnormality, most with this finding are normal.
Combining your age-related risk with the nuchal translucency measurement, nasal bone data and bloodwork provides one risk result for Down syndrome and a separate risk result for trisomy 13 or trisomy 18. Your obstetrician will get your screening results in about one week.
How accurate is FTS?
Because these are screening tests, a positive result (showing an increased risk) does not mean that your baby has one of these conditions. It indicates that further diagnostic tests are options for you to consider. Also, a negative or normal result (one that shows a decreased risk) does not mean a chromosomal abnormality is definitely not present.
The combined first trimester screening’s detection rate is approximately 96% for pregnancies in which the baby has Down syndrome, and it is somewhat higher for pregnancies with trisomy 13 or trisomy 18. A nuchal translucency ultrasound can be performed without the bloodwork, but the detection rate is reduced to about 70%.
This screen is not designed to provide information about the possibility of other chromosomal conditions, but it does have limited utility for screening for some other genetic syndromes, genetic disorders and birth defects.
For NIPT, the detection rate depends on the laboratory, but for high-risk mothers pregnant with one baby, the accuracy rate ranges between 90% and 99%, with false positive rates of less than 1%.
What if the screening shows an increased risk for one of the conditions?
If the screening results indicate that your baby is at an increased risk for Down syndrome or trisomy 13 or 18, this does not mean that one of these conditions is present, but this information can help your doctor decide whether further testing is right for you.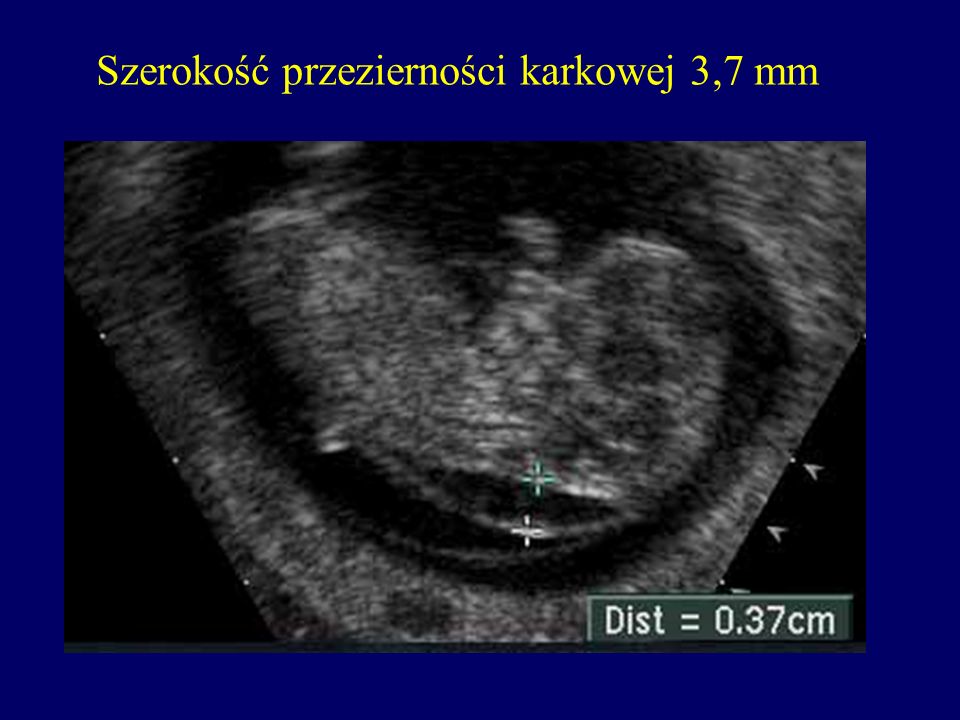
A genetic counselor is available to go over your results and to discuss additional screening and testing options, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis. CVS and amniocentesis are more invasive diagnostic procedures that detect a chromosomal abnormality with greater than 99% accuracy.
What is a quad screen?
The second trimester maternal serum screening test, also known as the quad screen, is performed between 16 and 20 weeks, and measures chemicals in the mother’s blood. Like the first trimester screening, results from a second trimester quad screen can be used to statistically adjust a woman’s age-related risk for Down syndrome and trisomy 18 (but not trisomy 13).
In addition, the alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) portion of the screen in the second trimester can identify pregnancies at an increased risk for open neural tube defects such as spina bifida. Quad screening is not recommended if combined first trimester screening has already been performed. However, AFP can be drawn as an independent test to screen for spina bifida.
However, AFP can be drawn as an independent test to screen for spina bifida.
TKDS of cerebral vessels, prices for transcranial duplex scanning in Moscow at SM-Clinic
Book online Request a call
Medical holding "SM-Clinic" offers the most advanced diagnostic methods, which include the procedure of transcranial duplex scanning. This is the youngest type of ultrasound.
The essence of the method of transcranial duplex scanning of the brain is to visualize the main intracranial arteries, veins, and vessels using color flow mapping. The procedure allows you to determine the state in the brain by the middle, anterior and posterior arteries. According to the obtained indicators, the specialist diagnoses various arterial lesions.
Ultrasound examinations at SM-Clinic
-
Without irradiation
Ultrasound is a non-radiological diagnostic method. It can be carried out by almost everyone - even newborns, pregnant and lactating women.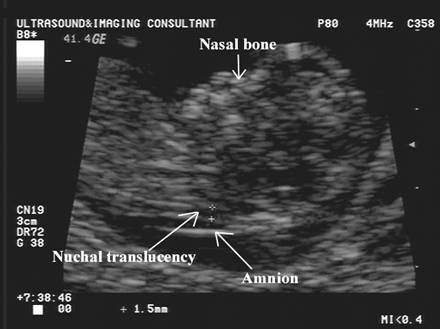 We know how important accessibility and careful attitude to health are for our patients, and we actively use the ultrasound method in carrying out a complex of therapeutic and diagnostic measures.
We know how important accessibility and careful attitude to health are for our patients, and we actively use the ultrasound method in carrying out a complex of therapeutic and diagnostic measures. -
Without pain
If a person does not have a pronounced pain syndrome, then the process of ultrasound diagnostics can be described as delicate stroking: the doctor drives the sensor gently, almost without pressure. Research without stress and inconvenience - you must admit, it is hardly worth being afraid or postponing such a procedure “for later”. -
You will find the research you need
We carry out almost all types of ultrasound diagnostics. Rare or most common - we help to investigate a wide variety of health problems. We can perform eye ultrasound, 3D and 4D ultrasound, stress echocardiography (diagnosis of heart pathologies), intracardiac echocardiography using intracardiac catheters, elastography and many others. -
Affordable price
With all its advantages, ultrasound is also one of the most affordable studies.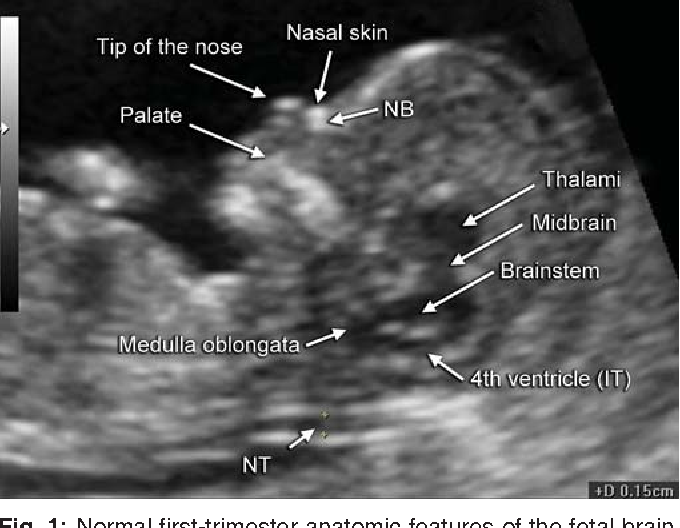 The money you spend on ultrasound diagnostics in our centers will be a smart investment in your health and will help you make an informed decision on further treatment.
The money you spend on ultrasound diagnostics in our centers will be a smart investment in your health and will help you make an informed decision on further treatment. -
Latest generation equipment
Our devices allow you to obtain high-resolution images: the smallest details and tissue changes are displayed on the screen during the study. The capabilities of our equipment allow, for example, to visualize blood vessels and blood flow, which helps to detect blood clots, diagnose varicose veins and understand the causes of other problems of the cardiovascular system. -
3D and 4D ultrasound
3D (3D) and 4D (3D in motion) examinations provide more information and, as a result, allow you to get a more complete picture and make an accurate diagnosis. In our centers, you can choose different types of diagnostics, depending on the indications that led you to the doctor.
Purpose of transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS)
Duplex scanning of the main arteries of the head is indispensable for choosing effective therapy and monitoring the condition in a number of confirmed diagnoses.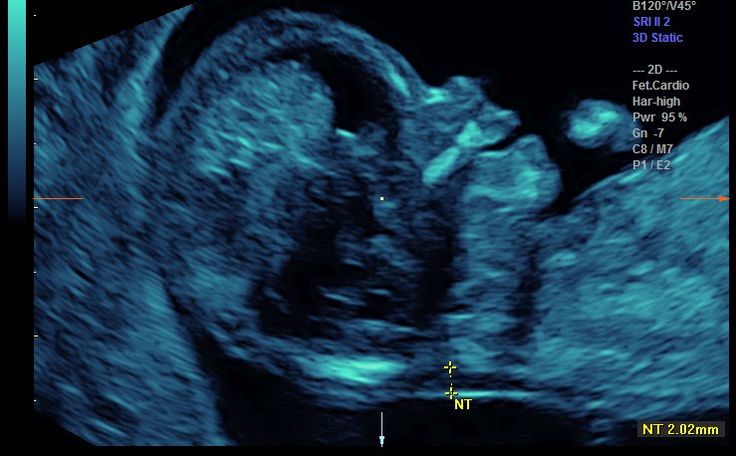
These include atherosclerosis, aortic aneurysm, vegetative dystonia, traumatic brain injury, arterial hypertension, systemic vasculitis, and others.
This study also allows the specialist to monitor the patient's condition after surgery, stroke or injury. In addition, ultrasound diagnostics of blood vessels is carried out directly during the treatment itself.
The method allows the doctor to track the dynamics of changes in blood circulation. Thus, it can be determined whether the chosen therapy is effective, whether it brings the desired results.
Indications for transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS)
TCDS of cerebral vessels is used as a diagnostic tool for routine preventive examinations. Also, this informative method is used to clarify the diagnosis.
The main indications for the procedure are:
- pain syndrome in the neck-collar area and head;
- dizziness;
- tinnitus;
- decreased vision;
- panic attacks;
- cases of loss of consciousness;
- osteochondrosis;
- unexplained bleeding from the nose;
- diabetes mellitus;
- changes in the cervical spine;
- previous stroke;
- Suspicion of vascular anomalies of the brain.
How transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS) works
Duration of the examination
20-30 minutes
Preparation of the report
10 minutes
Results of the procedure:
images and a detailed conclusion of a diagnostician describing the state of the cerebral vessels
In the medical center "SM-Clinic" the procedure for TKDS is carried out as follows:
- The patient must alternately lie on his back and on his stomach.
- The specialist applies a special gel to the skin of the examined area, which improves the conduction of ultrasonic waves. The tool also improves the quality of the image displayed on the monitor during manipulation.
- A phased study is being carried out: arteries, vessels and veins of the brain. The diagnostician performs transtemporal (temporal area), transoccipital (occipital area) and transorbital (through the orbit) analysis.
 The procedure is carried out using Doppler diagnostic modes and functional techniques. The spectral characteristics of blood flow are examined.
The procedure is carried out using Doppler diagnostic modes and functional techniques. The spectral characteristics of blood flow are examined.
If pathological changes are detected, the specialist conducts a more thorough examination of all vessels extending from these branches. If necessary, functional tests can be carried out. They allow us to evaluate changes in indicators in various positions of the body - not only lying down, but also sitting and standing.
Results of transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS)
The device displays and records the necessary indicators. Deciphering the results takes no more than 10 minutes. It is a printed sheet with a list of examined vessels, veins and arteries of the brain and a description of their size and condition.
Deciphering allows you to determine whether they correspond to the anatomical norm, and makes it possible to identify pathology. On its basis, the attending physician prescribes treatment.
Enroll
for a consultation with a neurologist
Preparation for transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS)
The research methodology does not require special preliminary preparation. Before proceeding with the procedure, the patient must remove headgear, jewelry, hairpins and hair bands and other unnecessary items from the head and neck. According to the sensations, the procedure is no different from the usual ultrasound familiar to everyone, therefore, as a rule, patients do not experience discomfort. In all branches of the SM-Clinic medical holding, the procedure is carried out in conditions that are comfortable for patients, using modern devices.
Before proceeding with the procedure, the patient must remove headgear, jewelry, hairpins and hair bands and other unnecessary items from the head and neck. According to the sensations, the procedure is no different from the usual ultrasound familiar to everyone, therefore, as a rule, patients do not experience discomfort. In all branches of the SM-Clinic medical holding, the procedure is carried out in conditions that are comfortable for patients, using modern devices. Would you like us to call you back?
Leave a request and we will answer all your questions in detail!
Name
Telephone *
Ultrasound Photo Gallery
Useful information
The equipment used for TCDS of cerebral vessels combines the acquired images and outputs data. The display of results in multiple colors allows the physician to conduct an accurate analysis.
Manipulation is carried out in two modes:
- Two-dimensional (B-mode).
 Views blood vessels and adjacent tissues. Does not provide complete information about the blood supply.
Views blood vessels and adjacent tissues. Does not provide complete information about the blood supply. - Duplex (Doppler). In this mode, a two-dimensional color drawing is created, which allows for an in-depth analysis of the state of the vessels.
Ultrasound reflects off the blood cells, allowing the route of blood flow to be estimated and its velocity and dynamics to be calculated. The occurrence of retrograde movement, slowing down and turbulence indicate the presence of pathology.
Despite the fact that this method is the youngest method of ultrasound diagnostics, it has already gained wide popularity. Diagnostic doctors of the medical holding "SM-Clinic" use this study when working with patients of different age groups.
The main advantage of the technique is absolute safety. TKDS does not create a radiation or magnetic load on the body. The method is applicable when examining children, pregnant and lactating women. Being the most modern research, at the same time it remains one of the most accessible, in comparison with alternative diagnostic methods.
Other advantages include:
- high information content - the image formed on the monitor during the study is similar to conventional ultrasound, but the vessel is clearly visible;
- painless - the procedure does not bring pain;
- no prior preparation - does not require the administration of drugs or contrast agents, diet or enema;
- visualization of the results - patients of the medical center "SM-Clinic" receive not only a conclusion, but also a graphical report.
The shortcomings of diagnostics include a narrow area of interest due to poor transmission of ultrasonic waves through the bones of the skull. There are also difficulties in the study of small vessels.
The quality of the equipment and the doctor's professionalism play an important role in TKDS diagnostics. Choosing a clinic for duplex scanning should be especially careful. "SM-Clinic" uses modern devices that meet current WHO requirements. The procedure is performed by highly qualified specialists with extensive experience in various types of diagnostics.
The procedure allows to evaluate:
- the elasticity of the vascular walls;
- correctness and level of blood flow;
- quality of vascular tone regulation;
- functional reserves of the brain blood supply system.
The technique allows solving a number of problems. The study reveals the presence of cholesterol plaques that cause atherosclerosis and are the cause of narrowing of the vascular lumens. All this leads to a violation of blood circulation. Also, this procedure indicates the development of vascular pathology, helps to track its dynamics. The study allows to reveal the symmetry and adequacy of the blood supply to the brain in atherosclerotic lesions. In addition, the manipulation fixes the change in the rate of blood flow and the difference in the blood supply to the cerebral hemispheres.
The most frequently detected pathologies in TCDS of the brain are:
- angiospasm;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- hypoplasia, aplasia of the artery;
- stenosis of the artery with determination of the hemodynamic significance of the stenosis;
- cerebral artery aneurysm;
- vascular malformations;
- venous discirculation.
Based on the principle of the study, it can be directed both to the extracranial sections of the vessels of the head, and to the intracranial ones. In the first case, the state of the common carotid arteries and their branches is analyzed, and in the second case, the arteries and veins located inside the skull are scanned. A combination of varieties of this diagnostic method is also used.
Booking for transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS)
Early detection of serious violations of the blood supply to the brain will give you the opportunity to get rid of the disease in a short time, and in many cases without surgical intervention.
You can find out the details of the procedure, the price of transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS) and sign up for an examination by calling:
+7 (495) 292-39-72
Request a call back Book online
Prices for transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS)
| Transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS) of cerebral vessels | 4 500 rub | +7 (49)5) 292-39-72. The posted price is not an offer. Medical services are provided on the basis of a contract.
 Clara Zetkin, 33 bldg. 28
Clara Zetkin, 33 bldg. 28 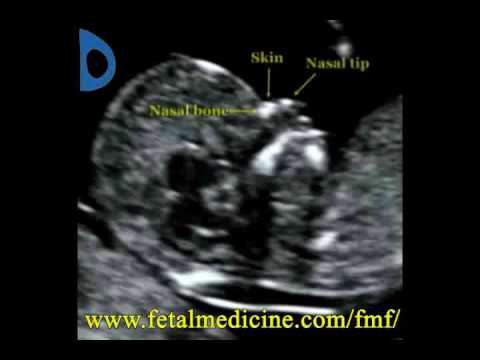
 Duplex scanning can reveal even the slightest abnormalities at the initial stage, therefore, treatment will be started in a timely manner
Duplex scanning can reveal even the slightest abnormalities at the initial stage, therefore, treatment will be started in a timely manner