Sharp pain groin pregnant
Round Ligament Pain During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Written by Kelli Miller
In this Article
- Causes of Round Ligament Pain
- Symptoms of Round Ligament Pain
- Treatment of Round Ligament Pain
- When to Call the Doctor
Round ligament pain is a sharp pain or jabbing feeling often felt in the lower belly or groin area on one or both sides. It is one of the most common complaints during pregnancy and is considered a normal part of pregnancy. It is most often felt during the second trimester.
Here is what you need to know about round ligament pain, including some tips to help you feel better.
Causes of Round Ligament Pain
Several thick ligaments surround and support your womb (uterus) as it grows during pregnancy. One of them is called the round ligament.
The round ligament connects the front part of the womb to your groin, the area where your legs attach to your pelvis. The round ligament normally tightens and relaxes slowly.
As your baby and womb grow, the round ligament stretches. That makes it more likely to become strained.
Sudden movements can cause the ligament to tighten quickly, like a rubber band snapping. This causes a sudden and quick jabbing feeling.
Symptoms of Round Ligament Pain
Round ligament pain can be concerning and uncomfortable. But it is considered normal as your body changes during pregnancy.
The symptoms of round ligament pain include a sharp, sudden spasm in the belly. It usually affects the right side, but it may happen on both sides. The pain only lasts a few seconds.
Exercise may cause the pain, as will rapid movements such as:
- sneezing
- coughing
- laughing
- rolling over in bed
- standing up too quickly
Treatment of Round Ligament Pain
Here are some tips that may help reduce your discomfort:
Pain relief. Take over-the-counter acetaminophen for pain, if necessary.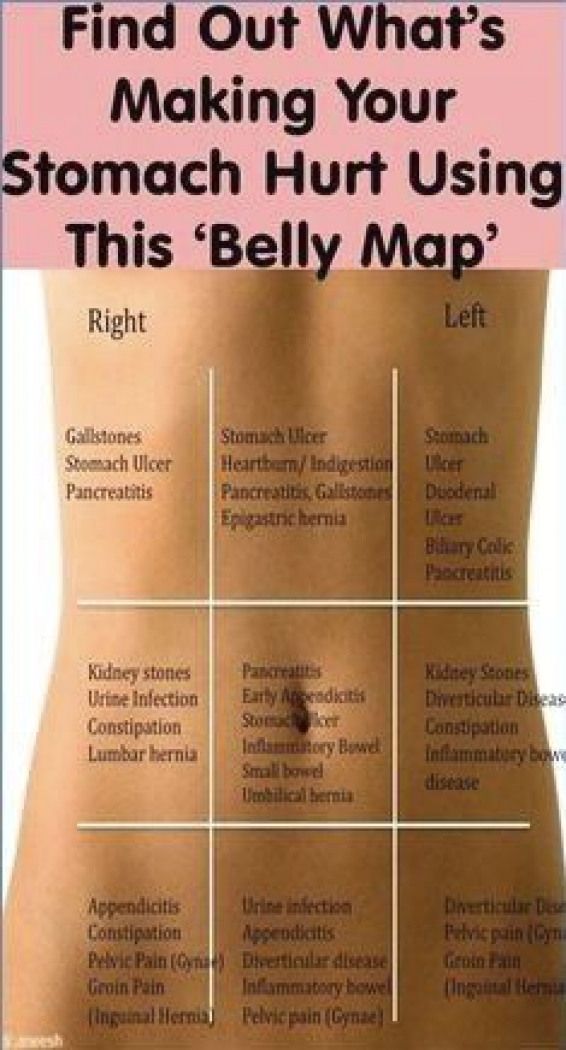 Ask your doctor if this is OK.
Ask your doctor if this is OK.
Exercise. Get plenty of exercise to keep your stomach (core) muscles strong. Doing stretching exercises or prenatal yoga can be helpful. Ask your doctor which exercises are safe for you and your baby.
A helpful exercise involves putting your hands and knees on the floor, lowering your head, and pushing your backside into the air.
Avoid sudden movements. Change positions slowly (such as standing up or sitting down) to avoid sudden movements that may cause stretching and pain.
Flex your hips. Bend and flex your hips before you cough, sneeze, or laugh to avoid pulling on the ligaments.
Apply warmth. A heating pad or warm bath may be helpful. Ask your doctor if this is OK. Extreme heat can be dangerous to the baby.
You should try to modify your daily activity level and avoid positions that may worsen the condition.
When to Call the Doctor
Always tell your doctor about any type of pain you have during pregnancy.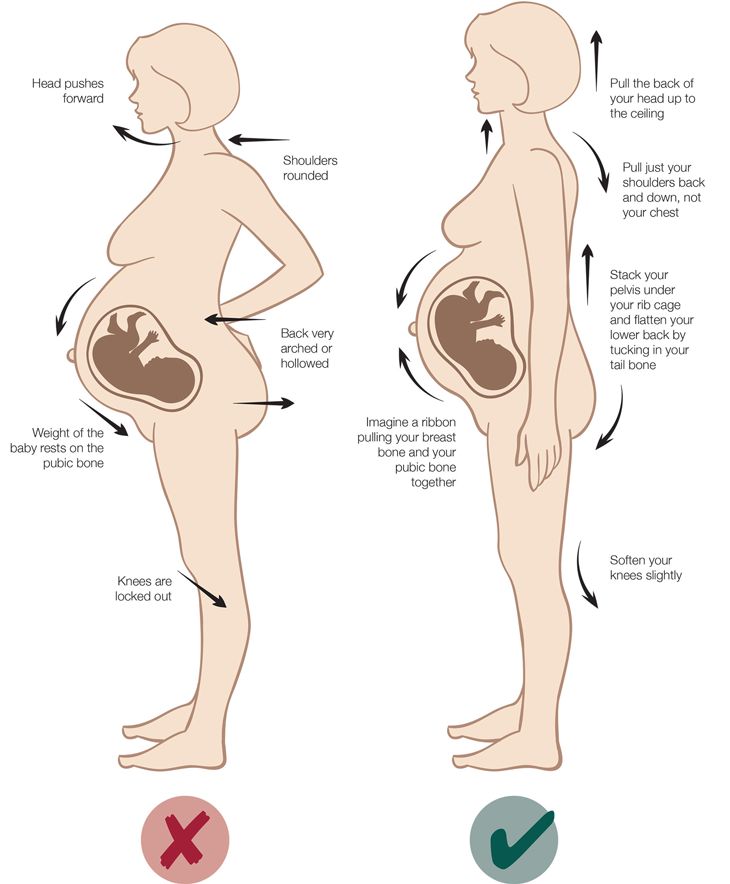 Round ligament pain is quick and doesn't last long.
Round ligament pain is quick and doesn't last long.
Call your health care provider immediately if you have:
- severe pain
- pain that lasts for more than a few minutes
- fever
- chills
- pain on urination
- difficulty walking
Belly pain during pregnancy can be due to many different causes. It is important for your doctor to rule out more serious conditions, including pregnancy complications such as placenta abruption or non-pregnancy illnesses such as:
- inguinal hernia
- appendicitis
- stomach, liver, and kidney problems
Preterm labor pains may sometimes be mistaken for round ligament pain.
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
Causes, remedies, and how it feels
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Read more about our vetting process.Pregnancy can cause several uncomfortable symptoms. While many people are aware of the possibility of morning sickness and Braxton-Hicks contractions, they may not be as familiar with lightning crotch.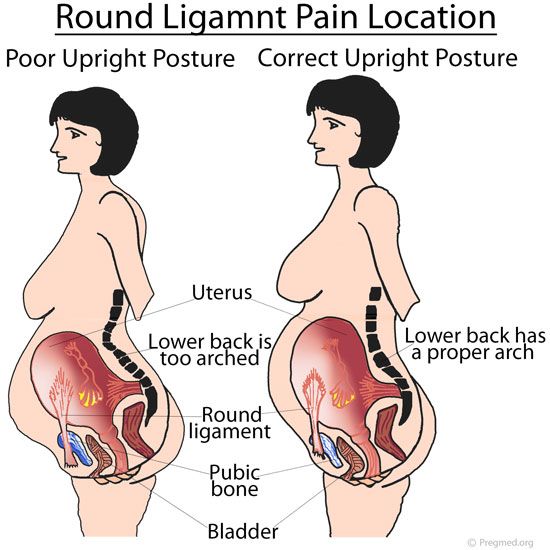
Lightning crotch is the colloquial term for shooting pain in the crotch, which is most likely to occur during pregnancy. It can also occur if a person is not pregnant, but will then have different causes.
In this article, learn about the causes and symptoms of lightning crotch, as well as when to see a doctor.
Share on PinterestLightning crotch feels like an electrical bolt of pain in the vagina, rectum, or pelvis.Lightning crotch refers to sharp or shooting pain in the vagina, rectum, or pelvis. It usually occurs during pregnancy.
The pain comes on suddenly and can stop someone in their tracks.
Some people describe the pain as feeling like an electrical bolt or zap from the inside, which is where the condition gets its name.
The pain can be sporadic and varies between individuals. Many people do not experience this symptom at all during pregnancy. For those who do, lightning crotch seems to occur more often toward the end of pregnancy.
Doctors are unsure why lightning crotch develops in some people but not others.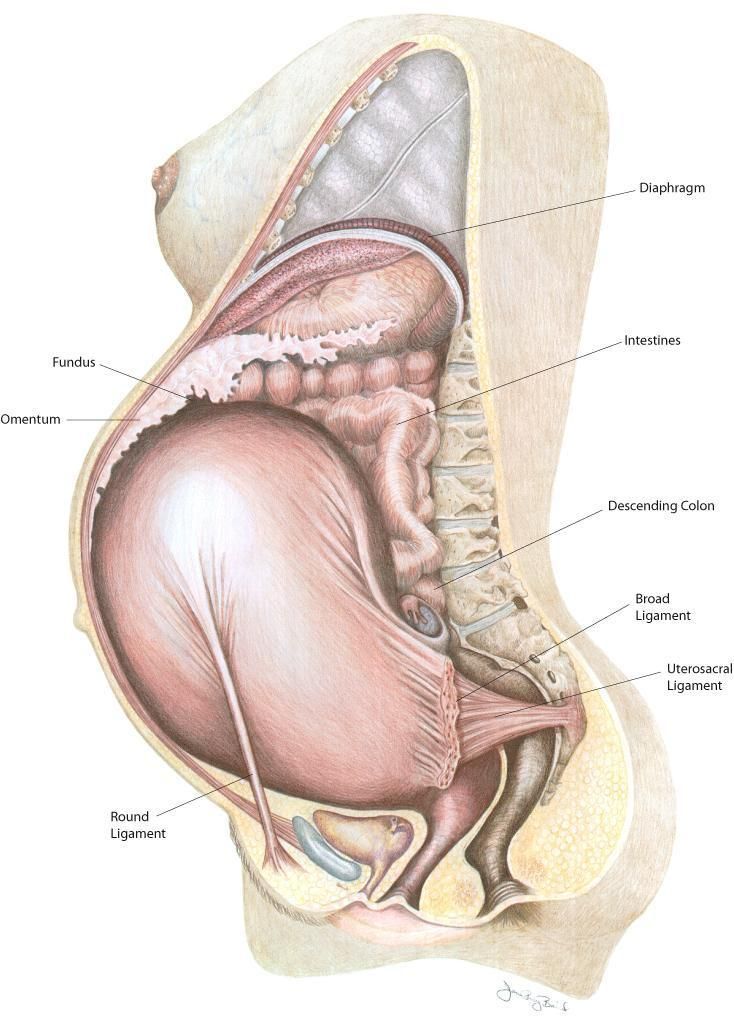 However, some potential causes include:
However, some potential causes include:
Baby movement
The movement of a baby stretching, turning, or kicking during pregnancy can put pressure on a nerve.
This can cause sudden, sharp pain in the pelvis, vagina, or rectum.
As the baby grows, the force behind the movements gets stronger, which may cause an increase in pain.
Dropping
Dropping is when the baby moves into the lower part of the uterus in preparation for labor.
The baby’s head may push on the pelvic floor and bladder, putting pressure on the nerve endings. The pressure on the nerves can cause sharp twinges of pain.
Round ligament pain
A pair of thick ligaments supports the uterus. During pregnancy, the growing belly puts extra pressure on these ligaments, which causes them to stretch and become thin.
Moving in a certain way may cause the ligaments to stretch too far or too fast, causing sudden, sharp pain.
Stabbing pains in the pelvic area may also be due to:
- menstrual cramps
- endometriosis
- a ruptured cyst
- mittelschmerz, or pain during ovulation
- bladder infections
Share on PinterestA prenatal massage can help relax the muscles and calm aches and pains.
Lightning crotch is not always preventable, especially when the position of the baby in the uterus may be the cause.
Fortunately, several home remedies may help to relieve pelvic pain. It may take some trial and error to determine what works best for each person, especially if the pain comes on suddenly or unexpectedly.
Possible home remedies include the following:
Changing positions
As the baby may be putting pressure on a nerve, it might help to stand up or move.
Changing positions may cause the baby to shift and take pressure off a nerve.
Taking a warm bath
A warm bath can relieve many discomforts during pregnancy, including stress and body aches. The warm water may also help to ease round ligament pain.
It is crucial to ensure that the water is not too hot, as this could raise the body’s core temperature too much.
Having a prenatal massage
Having a prenatal massage may not prevent lightning crotch, but massages can relax the muscles and may ease overall aches and pains during pregnancy.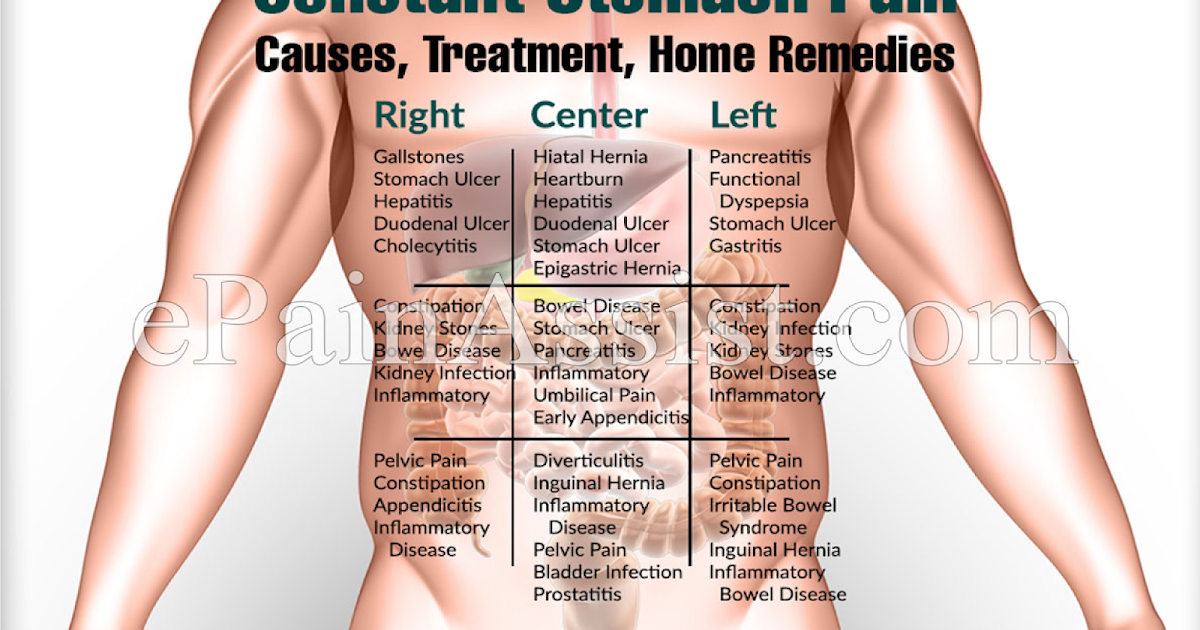
It is essential to go to an experienced, certified massage therapist who specializes in prenatal massage.
Wearing an abdominal support band
Abdominal or belly support garments made especially for pregnancy are available in many stores and online. They help by taking some weight off the pelvis.
They may also relieve some of the pressure on the nerves and ease the sharp, shooting pains of lightning crotch.
People can wear these belts under or over their clothes.
Lightning crotch may occur on and off throughout pregnancy, but it appears to be more common in the last trimester.
People who frequently experience the condition may find that their symptoms get worse as the baby’s head drops into the pelvis.
Lightning crotch can be a sign that labor is getting close, but it is not necessarily a sign of active labor.
However, if the condition occurs alongside other signs, it might signify the start of labor. Signs of labor include:
- lower back pain
- nausea
- regular contractions
- blood-tinged vaginal discharge
Share on PinterestLightning crotch occurs more often in the last trimester of pregnancy.
Some aches and pains are common during pregnancy, so it can be hard to know when to see a doctor.
It is essential to see a doctor if sharp, shooting pains occur in the crotch alongside other symptoms, such as vaginal bleeding or fever. The doctor will need to check for infection or other complications.
It is also best to speak to a doctor or midwife if symptoms of lightning crotch occur with other signs of labor.
Usually, lightning crotch pain is brief. If a person’s pain becomes severe or does not go away, they should seek medical advice as soon as possible.
While it is not usually possible to prevent lightning crotch, the pain should be temporary and will resolve following the birth.
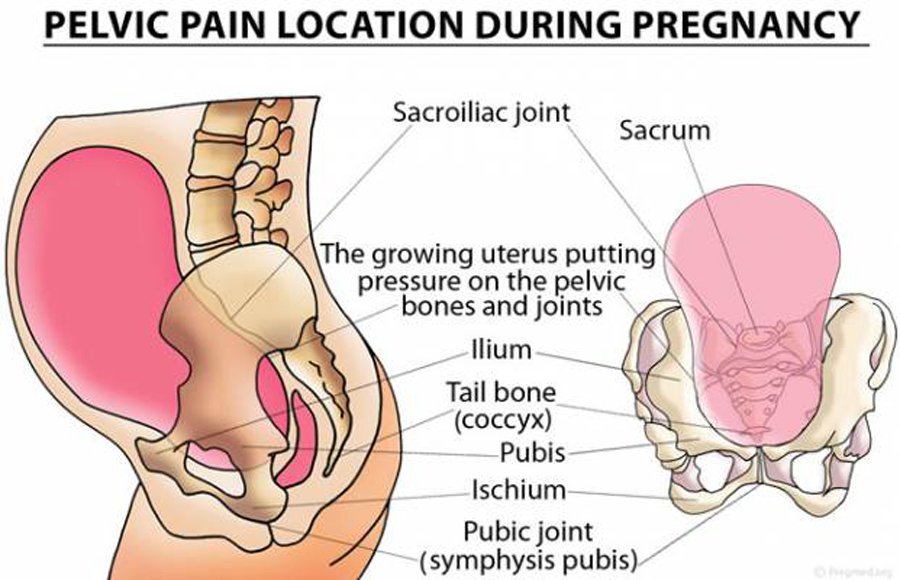
Pregnancy Groin Pain
General
The groin or groin is the part of the lower edge of the abdominal region adjacent to the thigh. Here is the inguinal canal through which the large blood vessels of the thigh and the round ligament of the uterus pass, loops of the intestines can also descend here and form a hernia.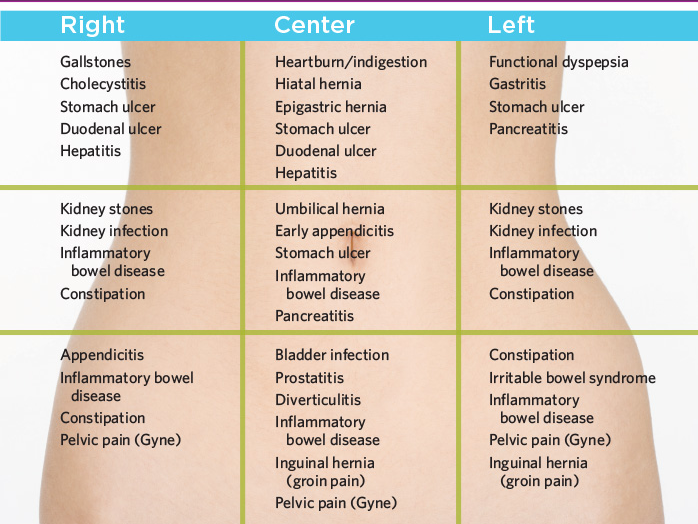
Causes of groin pain during pregnancy
Hernia
If you have groin pain during pregnancy on either side, always think about 9 first0003 hernia . A hernia can occur when local supporting tissues weaken and allow bowel loops to slip out of the abdomen and into the groin. Hernia becomes noticeable as a swelling in the groin, especially when you stand. But you can feel pain without a visible bulge.
Hernia can cause unpleasant complications. If the opening is relatively small and the intestinal loop is relatively large, then the latter may be trapped or strangulated in it. When this happens, it is called a "strangulated hernia." A strangulated hernia requires immediate surgery, as the blood supply to the strangulated intestine is disrupted, which leads to its destruction. nine0009
Infection in the pelvic region
• infections in the pelvic region:
• adnexitis;
• endometritis;
• proctitis;
• parametritis
Infections can cause swelling and tenderness of the lymph nodes in the groin.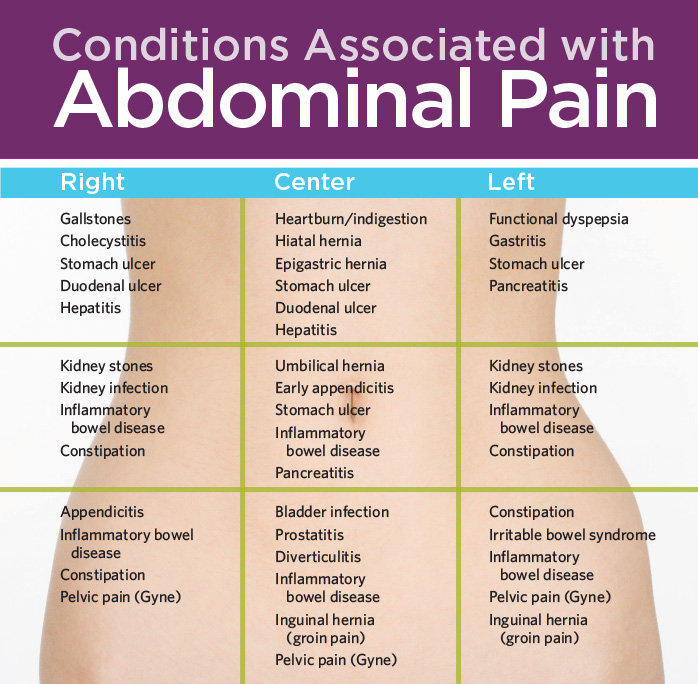
With tumors of lymph nodes in the groin, there is a possibility of cancer or benign tumor . It may also be a manifestation of an early (primary stage) syphilis.
Kidney stones
A low-lying kidney stone, ureteral stone will also cause pain in the groin. An attack of renal colic occurs suddenly, can last several minutes, hours or even days. It is characterized by the following symptoms: acute pain in the lower back or hypochondrium with irradiation along the ureter to the inguinal region, bladder, external genitalia. Frequent urination and blood in the urine will help in determining the correct diagnosis. nine0009
If the pain in your groin is not associated with enlarged lymph nodes or kidney stones, then it may be due to the fact that the spinal disc is compressing the nerves that go to this area. The reason for this may be osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
Infections and injuries
Pain in the groin during pregnancy may indicate genitourinary infections and inflammation, which lead to enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes in the groin.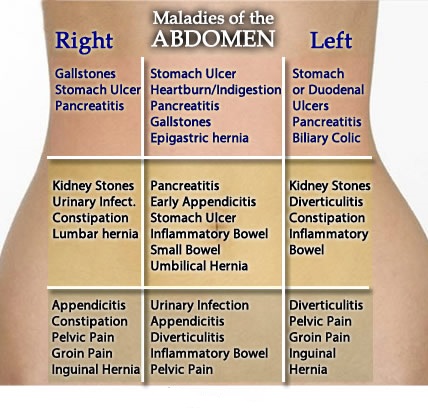 nine0009
nine0009
Other causes of groin pain during pregnancy may include the following diseases:
• Groin injuries.
• Genital herpes.
• Varicose vein of the great saphenous vein.
• Aneurysm of the femoral artery.
For pain in the groin during pregnancy, seek the help of a gynecologist. You may also need to consult a traumatologist.
Pain in the pubic region during pregnancy
Subscribe to our Instagram! Useful information about pregnancy and childbirth from leading obstetricians and gynecologists in Moscow and foreign experts: https://www.instagram.com/roddompravda/
Tips and opinions from leading child professionals: https://www.instagram.com/emc.child/
The pubic bone is one of the three bones that make up the pelvic bone. Two pubic bones, forming the pubic articulation (symphysis), form the anterior wall of the pelvis. The pubic bone in women with a regular physique has the form of a roller about the thickness of the thumb, which is curved and forms a pubic eminence.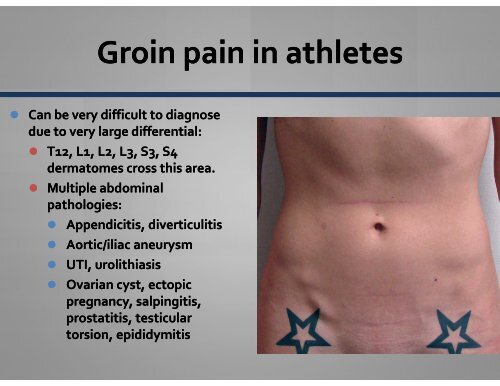 This bone hangs in a kind of arch over the entrance to the vagina. nine0009
This bone hangs in a kind of arch over the entrance to the vagina. nine0009
The main cause of pain in the pubic bone is the divergence and increased mobility of the pubic symphysis. To refer to pathological changes in the pubic symphysis of the pelvis during pregnancy and after childbirth, the following terms are used: symphysiopathy, symphysitis, arthropathy of pregnant women, divergence and rupture of the pubic symphysis, dysfunction of the pubic symphysis. The most commonly used terms are "symphysitis" or "symphysiopathy".
So, symphysiopathy is a disease associated with a pronounced softening of the pubic joint under the influence of the hormone relaxin, which is produced during pregnancy. The process of softening the interosseous joints is natural, it helps the child to pass more easily through the bone pelvis during childbirth. The diagnosis of "symphysiopathy" is made when severe pain appears, the pubic joint swells, greatly stretches, becomes mobile, and the pubic bones diverge excessively.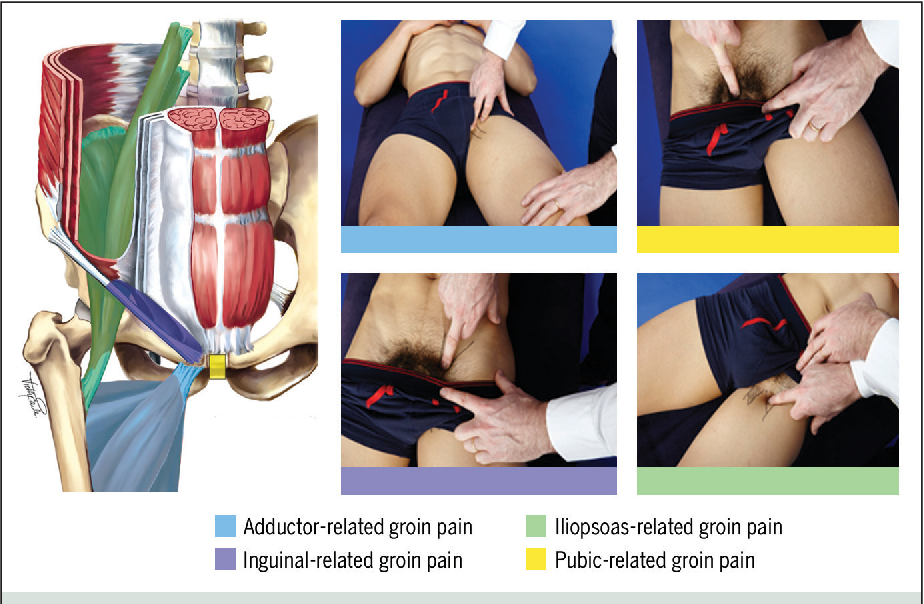 One of the striking, characteristic symptoms of this pathology is that it is impossible to raise the leg in the prone position. In addition to acute pain in the pubis, there are difficulties when walking up the stairs, it becomes difficult to turn from side to side on the bed and get up from the sofa, and the gait changes and becomes like a "duck". According to most doctors, the cause of symphysiopathy is a lack of calcium, an increased concentration of the hormone relaxin, and increased physical activity on the bones of the pelvic region. In addition, the development of symphysiopathy can be provoked by a serious sports injury or a fracture of the pelvic bones. nine0009
One of the striking, characteristic symptoms of this pathology is that it is impossible to raise the leg in the prone position. In addition to acute pain in the pubis, there are difficulties when walking up the stairs, it becomes difficult to turn from side to side on the bed and get up from the sofa, and the gait changes and becomes like a "duck". According to most doctors, the cause of symphysiopathy is a lack of calcium, an increased concentration of the hormone relaxin, and increased physical activity on the bones of the pelvic region. In addition, the development of symphysiopathy can be provoked by a serious sports injury or a fracture of the pelvic bones. nine0009
At what stage of pregnancy do they occur?
The disease begins gradually or suddenly during pregnancy, childbirth or after childbirth. Most often, women begin to feel pain in the area of the pubic joint in the third trimester of pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the places of adhesions of the pubic bones, their ligaments and cartilage, soften under the influence of the hormone relaxin. This hormone of pregnancy naturally softens the bony joints, which is necessary to facilitate the passage of the child's bone pelvis and birth canal at the time of childbirth. nine0009
This hormone of pregnancy naturally softens the bony joints, which is necessary to facilitate the passage of the child's bone pelvis and birth canal at the time of childbirth. nine0009
Some women begin to complain of pain in the pelvic bones some time after giving birth. This may be the result of traumatic childbirth (imposition of obstetrical forceps, shoulder dystocia, excessive separation of the hips during childbirth, etc.) or physical exertion (lifting a heavy baby stroller up the stairs, prolonged motion sickness in the arms of a well-fed baby, etc.). It is recommended to limit physical activity, wear an orthopedic bandage, consult a traumatologist. Complaints usually recur after the next pregnancy. In a small proportion of patients, pain persists for a long time. nine0009
When can this be considered the norm, and when not?
Obstetricians-gynecologists do not consider a slight soreness of the pubic joint to be a pathology, but if the pain is acute, restricting the movements of the pregnant woman, accompanied by edema, then we can talk about pathology. Pain can be quite strong and especially manifest itself while walking, turning the body to the right and left in a sitting position and even lying down. In this case, you need to urgently consult a doctor and undergo an ultrasound diagnosis (ultrasound) to determine the size of the divergence of the pubic bones. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is also used, which allows assessing the state of the symphysis, the state of the bone tissue, as well as soft tissues. nine0009
Pain can be quite strong and especially manifest itself while walking, turning the body to the right and left in a sitting position and even lying down. In this case, you need to urgently consult a doctor and undergo an ultrasound diagnosis (ultrasound) to determine the size of the divergence of the pubic bones. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is also used, which allows assessing the state of the symphysis, the state of the bone tissue, as well as soft tissues. nine0009
With ultrasound, the degree of divergence (diastasis) of the pubic bones is determined. The severity of the clinical picture largely depends on the degree of divergence of the pubic bones, and therefore there are three degrees of divergence of the pubic branches: in the first degree - by 6-9 mm, in the second - by 10-20 mm, in the third - more than 20 mm. The severity of the symptoms of the disease varies from mild discomfort to unbearable pain.
How can pain be relieved? nine0101
There are some recommendations that will help reduce bone pain during pregnancy, if the cause of its occurrence is the divergence of the pubic bones. Be sure to wear a bandage, especially in later pregnancy. The bandage takes on most of the load, thereby releasing pressure from the pubic joint. Limitation of heavy physical exertion is indicated for any manifestations of pain, lying down more often, walking less and being in a sitting position for no longer than 30-40 minutes. In severe cases, before and sometimes after childbirth, a woman may be shown strict bed rest. Moreover, the bed should not be hard and flat. nine0009
Be sure to wear a bandage, especially in later pregnancy. The bandage takes on most of the load, thereby releasing pressure from the pubic joint. Limitation of heavy physical exertion is indicated for any manifestations of pain, lying down more often, walking less and being in a sitting position for no longer than 30-40 minutes. In severe cases, before and sometimes after childbirth, a woman may be shown strict bed rest. Moreover, the bed should not be hard and flat. nine0009
Since the appearance of symphysiopathy is associated not only with a large production of the hormone relaxin, but also with a lack of calcium in the body, the expectant mother is prescribed calcium preparations and complex vitamins for pregnant women, which contain all the necessary vitamins and trace elements in the right amount and proportions. There is evidence that pain is reduced during acupuncture and physiotherapy.
In especially severe cases of symphysiopathy, the pregnant woman is hospitalized.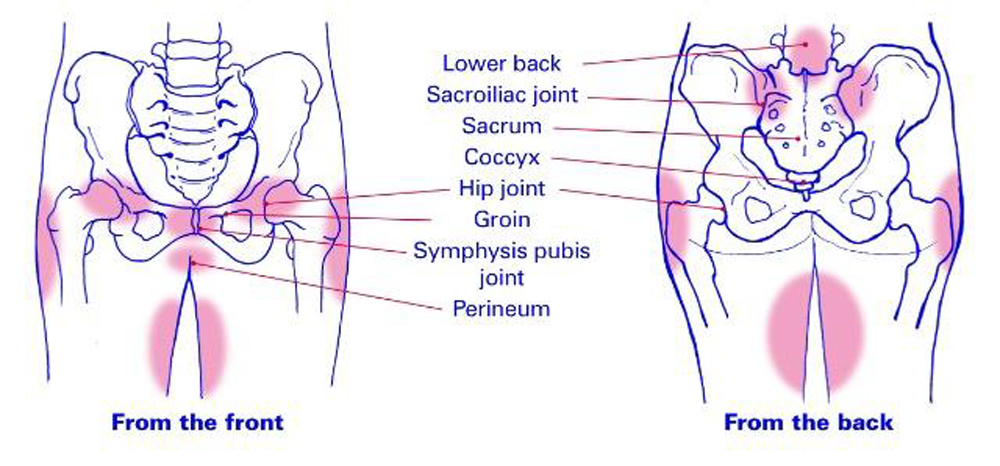 nine0009
nine0009
What is the danger of this condition?
The occurrence of symphysiopathy is due to several reasons. This is a lack of calcium in the body of the future mother, and an excess amount of the hormone relaxin, and the individual structural features of the woman's body, and possible hereditary or acquired problems of the musculoskeletal system.
With an unexpressed clinical picture of the disease, with an expansion of the pubic fissure up to 10 mm, normal pelvic sizes, a small fetus, childbirth can be carried out through the birth canal, avoiding the use of physical force, such as the Christeller maneuver. With a pronounced stretching of the pubic symphysis, pain syndrome, especially with anatomical narrowing of the pelvis, a large fetus, there is a danger of rupture of the pubic symphysis, and the method of choice in this case is caesarean section. This is due to the fact that during natural delivery, the bones can disperse even more and the woman subsequently will not be able to walk at all.