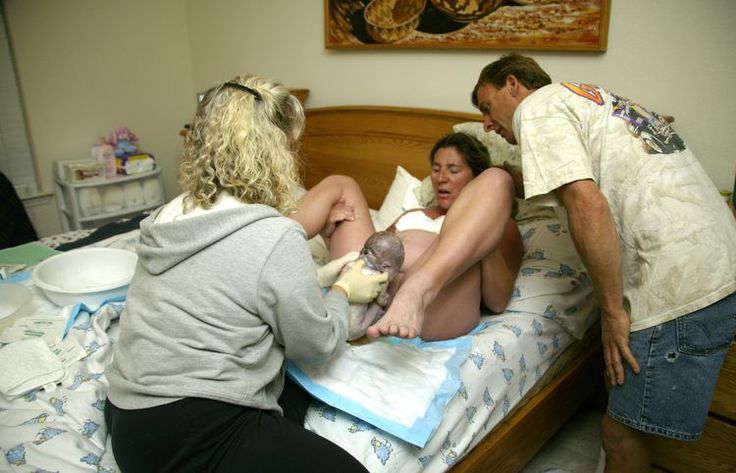
Give birth to placenta
Delivering your placenta | Ready Steady Baby!
The third stage of labour is when your placenta and the bag that held your baby and the amniotic fluid (the membranes) are delivered. You may not know you’re in the third stage (or what’s going on) as you’ll be busy getting to know your baby.
Actively managed or unaided third stage?
In most hospital units, the third stage is 'actively managed' because it is known that women who opt to have this are at less risk of significant blood loss at delivery. However, you may choose a physiological, 'unaided' third stage.
Your midwife can give you more information to help you decide what you’d prefer, and you can put your choice in your birth plan. Your midwife will take your wishes into account.
An actively managed third stage
An actively managed third stage helps to:
- speed up this stage of labour
- reduce your risk of heavy bleeding
During an actively managed third stage:
- you’ll have an injection to reduce the size of your womb
- your midwife will clamp and cut the umbilical cord
- you'll deliver the placenta with or without the help of your midwife
The injection
The injection's given when your baby's being born, and usually when their first shoulder's coming out or just afterwards.
Your midwife will ask if it’s okay to give you the injection and then put it into your thigh or buttock. The injection can sometimes make you feel sick.
Clamping and cutting the umbilical cord
Once your baby's born, the umbilical cord will be:
- clamped (pressed together) to stop the blood flowing
- cut between your baby and the placenta
Once your baby is born, the cord won't usually be clamped until it has stopped pulsating, at least a minute. This ensures your baby receives all the blood from your placenta, which is good for your baby's iron levels.
The cord will be cut immediately if:
- it’s wrapped around your baby’s head and needs to be cut
- your baby needs medical help
Your baby will be kept below the level of your abdomen to make sure that all the blood from the cord has flowed through to them.
Delivering the placenta
As the injection starts to work, it makes your womb reduce in size. This helps the placenta to come away.
This helps the placenta to come away.
At this stage, you may be able to push the placenta out. But it’s more likely your midwife will help deliver it by putting a hand on your tummy to protect your womb and keeping the cord pulled tight. This is called cord traction.
Your placenta will come away, and the blood vessels that were holding on to it will close off as your womb gets smaller. This helps to prevent too much bleeding – although it’s normal to bleed a little.
You may feel the placenta slide down and out between your legs.
An unaided (physiological) third stage
An unaided third stage usually takes longer than an actively managed one. You don’t have an injection or cord traction.
Your body releases the hormone oxytocin when:
- you breastfeed your baby
- your baby lies on your chest with skin-to-skin contact
This helps your womb to tighten and push out the placenta and the membranes. Your baby’s cord is cut when it stops pulsing (usually after your placenta's been delivered).
Possible risks of an unaided third stage
Your midwife will weigh up the possible risks of having an unaided third stage if:
- you've had issues in the first or second stages of your labour (or with a previous birth)
- there’s a high chance you might bleed heavily
You can still choose to do this, but your midwife won't be able to recommend it because an actively managed third stage would be safer for you and your baby.
Complications during the third stage
Possible complication of the third stage include:
- primary postpartum haemorrhage (heavy bleeding)
- issues delivering the placenta if it doesn't come away from the womb
Primary postpartum haemorrhage
Post-partum haemorrhage (PPH) is a complication that can occur during the third stage of labour, after a baby is born.
Losing some blood during childbirth is considered normal. PPH is excessive bleeding from the vagina at any time after the baby's birth, up until 6 weeks afterwards.
More about primary postpartum haemorrhage
Assisted delivery of the placenta
Sometimes the placenta doesn’t come away from your womb. If this happens you'll need assistance to have it taken out. This is usually done with an epidural or spinal anaesthetic.
About 1 in 50 women will need this procedure.
If this happened when you had a baby before, it would be one of the reasons why your midwife might suggest you have an actively managed third stage.
Translations and alternative formats of this information are available from Public Health Scotland.
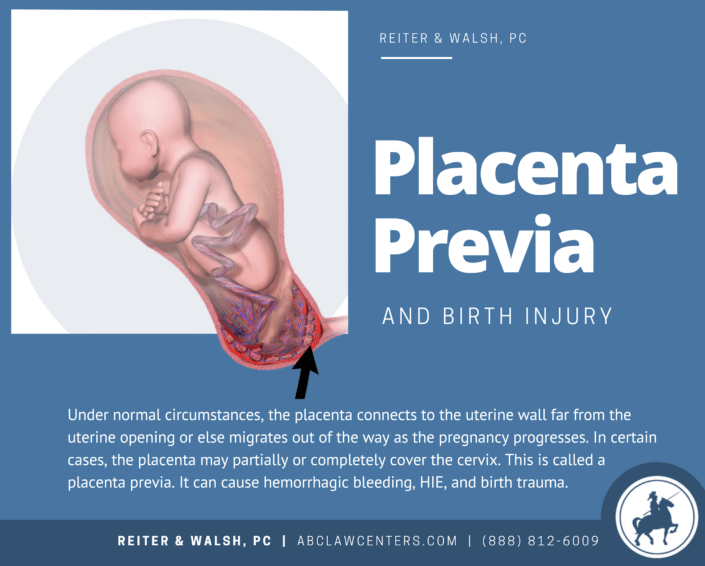
Placenta Delivery: What to Expect
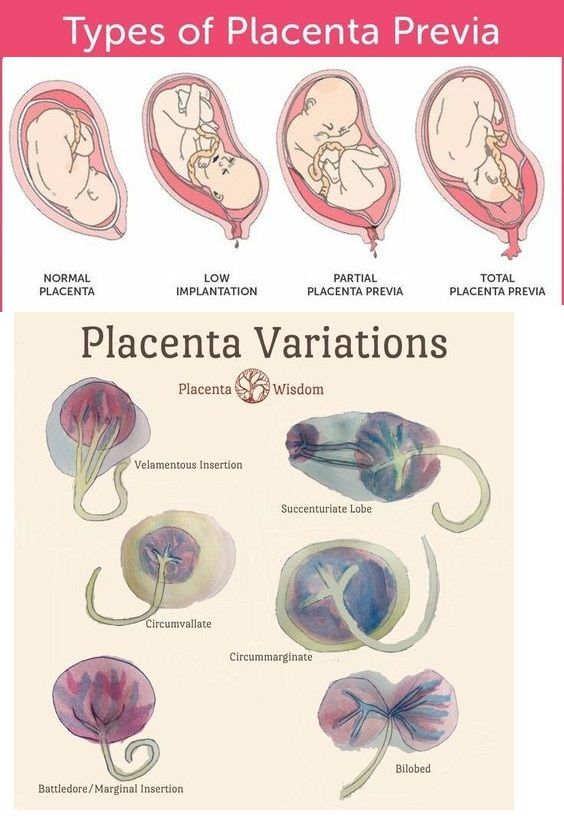
The placenta is a unique organ of pregnancy that nourishes your baby. Typically, it attaches to the top or side of the uterus. The baby is attached to the placenta via the umbilical cord.
After your baby is delivered, the placenta follows. This is the case in most births. But there are some exceptions.
Delivery of the placenta is also known as the third stage of labor.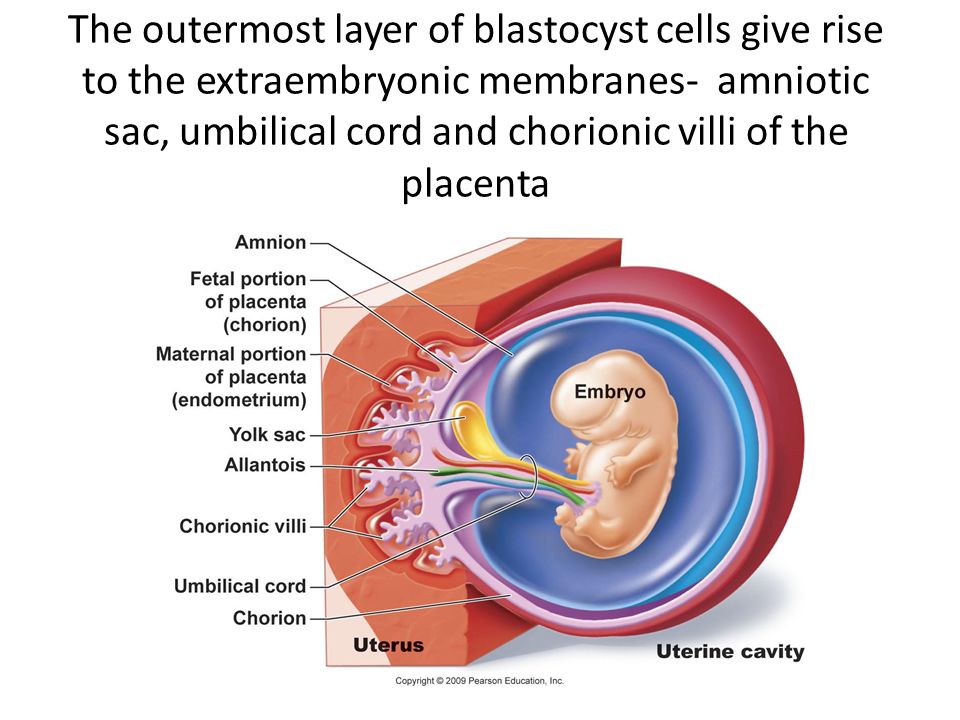 Delivery of the entire placenta is vital to your health after giving birth. Retained placenta can cause bleeding and other unwanted side effects.
Delivery of the entire placenta is vital to your health after giving birth. Retained placenta can cause bleeding and other unwanted side effects.
For this reason, a doctor will examine the placenta after delivery to ensure that it is intact. If a piece of placenta is left in the uterus or the placenta doesn’t deliver, there are other steps a doctor can take.
The placenta is an organ shaped like a pancake or disk. It is attached on one side to your uterus and on the other side to the baby’s umbilical cord.
The placenta is responsible for many important functions when it comes to a baby’s growth. This includes producing hormones, such as:
- estrogen
- human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
- progesterone
The placenta has two sides. The parental side is usually dark red in color, while the fetal side is shiny and almost translucent in color. After the baby is born, a doctor will examine the placenta to ensure each side appears as it is expected to.
Some people ask to save their placenta and will boil it to eat it or even dehydrate it and encapsulate it into pills. In fact, some people believe that taking the pills will reduce postpartum depression or postpartum anemia. However, scientific studies have not proven these effects.
Other people plant the placenta in the ground as a symbolic gesture of the connection between life and earth.
Some states and hospitals have rules about saving the placenta, so a pregnant person should always check with the facility they’re delivering at to make sure they can save the placenta.
Placenta delivery after a vaginal birth
In a vaginal delivery, after the baby is born, your uterus will continue to contract. These contractions will move the placenta forward for delivery. They aren’t usually as strong as labor contractions.
However, some doctors may ask you to continue to push, or they may press on your stomach as a means to advance the placenta forward. Usually, placenta delivery is quick, within about 5 minutes after having your baby.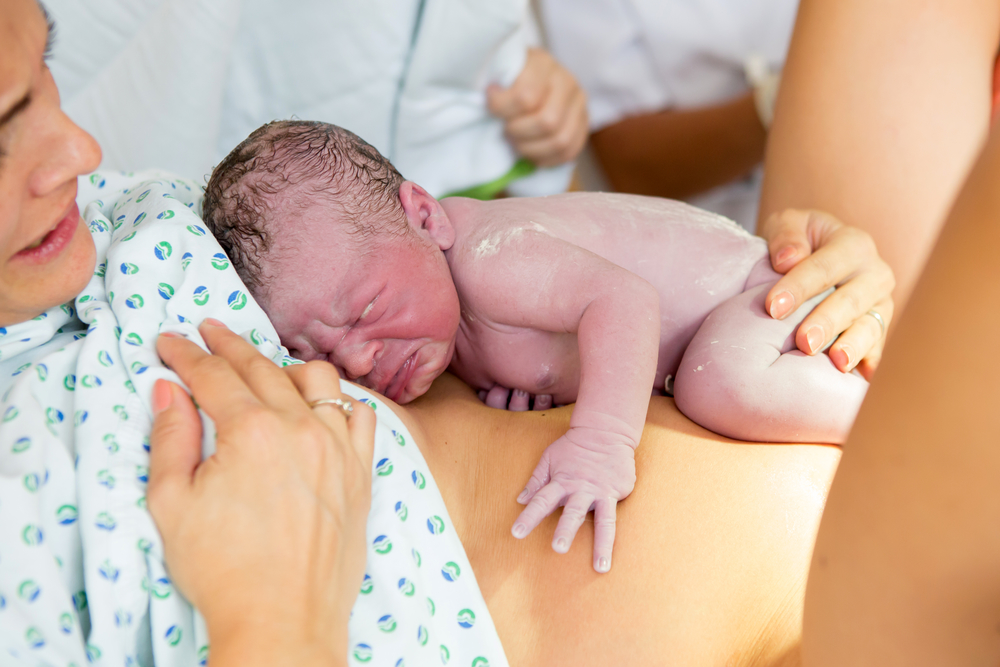 However, it can take longer for some people.
However, it can take longer for some people.
Often, after you deliver your baby, you’re very focused on seeing them for the first time and may not notice the placenta delivery. However, some people observe an additional gush of blood after delivery that’s usually followed by the placenta.
The placenta is attached to the umbilical cord, which is attached to your baby. Because there aren’t any nerves in the umbilical cord, it doesn’t hurt when the cord is cut.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends in its 2020 guidelines that unless the cord is wrapped around the baby’s neck, it should not be clamped and cut sooner than at least 30 to 60 seconds after birth. This delay improves your baby’s hemoglobin and iron levels, among other benefits.
Placenta delivery after a cesarean
If you deliver via cesarean delivery (also known as C-section), your doctor will physically remove the placenta from your uterus before closing up the incision in the uterus and stomach.
After delivery, your doctor will likely massage the top of your uterus (known as the fundus) to encourage it to contract and start to shrink. If a uterus cannot contract and become firmer, a doctor may give you medication, such as Pitocin, to make the uterus contract.
Breastfeeding or chestfeeding a baby immediately after birth or placing the baby on your skin (known as skin-to-skin contact) can also cause the uterus to contract.
Regardless of how your placenta is delivered, your doctor will inspect it for intactness.
If it appears that a portion of the placenta is missing, your doctor may recommend an ultrasound of the uterus to confirm. Sometimes, excessive bleeding after delivery can indicate that some placenta is still in the uterus.
A birthing person should deliver the placenta within 30 to 60 minutes after having the baby. If the placenta isn’t delivered or doesn’t come out entirely, it’s called retained placenta.
Reasons the placenta may not fully deliver include:
- The cervix has closed and is too small an opening for the placenta to move through.
- The placenta is too tightly attached to the wall of the uterus.
- A portion of the placenta broke off or remained attached during delivery.
Retained placenta is a major concern because the uterus must clamp back down after giving birth. Tightening the uterus helps the blood vessels inside stop bleeding. If the placenta is retained, a person can experience bleeding or infection.
Retained portions of the placenta after delivery can lead to dangerous bleeding and infection. A doctor will typically recommend surgical removal as quickly as possible.
However, sometimes the placenta is so attached to the uterus that it isn’t possible to remove without also removing the uterus (hysterectomy).
A person is at increased risk for retained placenta if they have any of the following:
- previous history of retained placenta
- previous history of cesarean delivery
- history of uterine fibroids
If you are concerned about retained placenta, talk with your doctor prior to delivery. They can discuss your delivery plan with you and notify you when the placenta is delivered.
They can discuss your delivery plan with you and notify you when the placenta is delivered.
The birth process can be an exciting one and one that’s full of emotions. Typically, delivering the placenta isn’t painful.
Often, it occurs so quickly after birth that a new parent may not even notice because they’re so focused on baby (or babies!). But it’s important that the placenta is delivered in its entirety.
If you wish to save your placenta, always notify the facility, doctors, and nurses in advance of delivery to be sure that it can be properly saved or stored.
we conduct a full educational program on fashionable childbirth in Krasnoyarsk
Perhaps in your Instagram feeds you have seen photos of some languid insta-diva, who is photographed in a beautiful interior with flowers in her hair, hugging her perfectly round pregnant belly.
For sure, in the caption to the photo, this diva denies the whole world of evidence-based medicine, telling how she decided to give birth at home under the supervision of a doula, because our ancestors did it, no matter how she never regretted it. And that after giving birth, her baby lay next to her for several hours with an uncut umbilical cord, because it is very useful - and she also read about this on Instagram, only from another, even more popular insta-diva. And that then from this umbilical cord and placenta she will definitely make herself a smoothie, because everyone does it. nine0005
And that after giving birth, her baby lay next to her for several hours with an uncut umbilical cord, because it is very useful - and she also read about this on Instagram, only from another, even more popular insta-diva. And that then from this umbilical cord and placenta she will definitely make herself a smoothie, because everyone does it. nine0005
Before scolding both the insta-diva and world medicine, let's see if there is any sense in all this, and most importantly, is it dangerous? We compiled a complete educational program on fashionable childbirth together with the candidate of medical sciences, deputy chief physician for the medical department of the Krasnoyarsk Interdistrict Clinical Hospital No. 4, obstetrician-gynecologist Evgenia Sivova.
Why Home Birth Can Kill You
— Medically speaking, home births can be planned or unplanned. Speaking of fashion, we probably first of all have in mind a planned home birth, when a woman deliberately decides that she will give birth at home.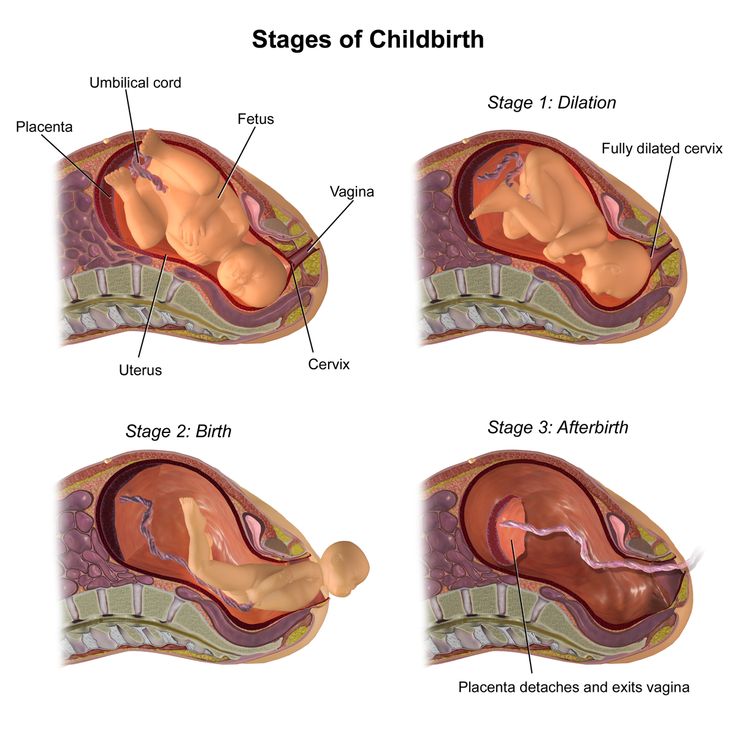 In some foreign countries, this format of childbirth is regulated by law; there is also a midwife or even a family doctor present along with the woman in labor. In Russia, this is not regulated by law in any way, it is not written anywhere how such childbirth should actually take place. nine0007 Home births increase the risk of maternal and infant mortality. During childbirth, unforeseen situations may arise that can be controlled and resolved in a medical organization. If a woman gives birth at home, she is not controlled by anyone, which means that the consequences can be very different.
In some foreign countries, this format of childbirth is regulated by law; there is also a midwife or even a family doctor present along with the woman in labor. In Russia, this is not regulated by law in any way, it is not written anywhere how such childbirth should actually take place. nine0007 Home births increase the risk of maternal and infant mortality. During childbirth, unforeseen situations may arise that can be controlled and resolved in a medical organization. If a woman gives birth at home, she is not controlled by anyone, which means that the consequences can be very different.
What is the danger of such childbirth? Any childbirth can be complicated by bleeding, for example, with placental abruption, blood loss is 2.5 liters or more.
In a medical institution, it is possible to carry out autohemotransfusion (transfusion of one's own blood), at home the situation can be fatal. nine0007 Another danger is acute fetal hypoxia, for example, in the case of umbilical cord entanglement. This situation cannot be foreseen in advance, therefore it is important that a qualified specialist is nearby. Plus, during childbirth, the doctor monitors the fetal heartbeat and, if something goes wrong, will be able to quickly respond. In addition, any childbirth, if there are difficulties, can end with a caesarean section, which is impossible to perform at home.
This situation cannot be foreseen in advance, therefore it is important that a qualified specialist is nearby. Plus, during childbirth, the doctor monitors the fetal heartbeat and, if something goes wrong, will be able to quickly respond. In addition, any childbirth, if there are difficulties, can end with a caesarean section, which is impossible to perform at home.
— Supporters of home births often make an argument: they used to give birth in an open field, and nothing. What can you say about this? nine0005
- In this case, let's take into account that our population is not getting healthier, there is a tendency that the general state of people's health is deteriorating. It is also worthwhile to understand that earlier, after a cesarean section, a woman in labor died, because they only knew how to perform a cerebrosection, the operation technique was unknown. Now, after a caesarean section, women live and enjoy the joy of motherhood.
In the end, girls used to give birth at the age of 16-19, and now many women in labor over 35 years old come to us, with increasing age, diseases and the possibility of complications are acquired, so it’s better to give birth to a child under the supervision of doctors, and not on your own.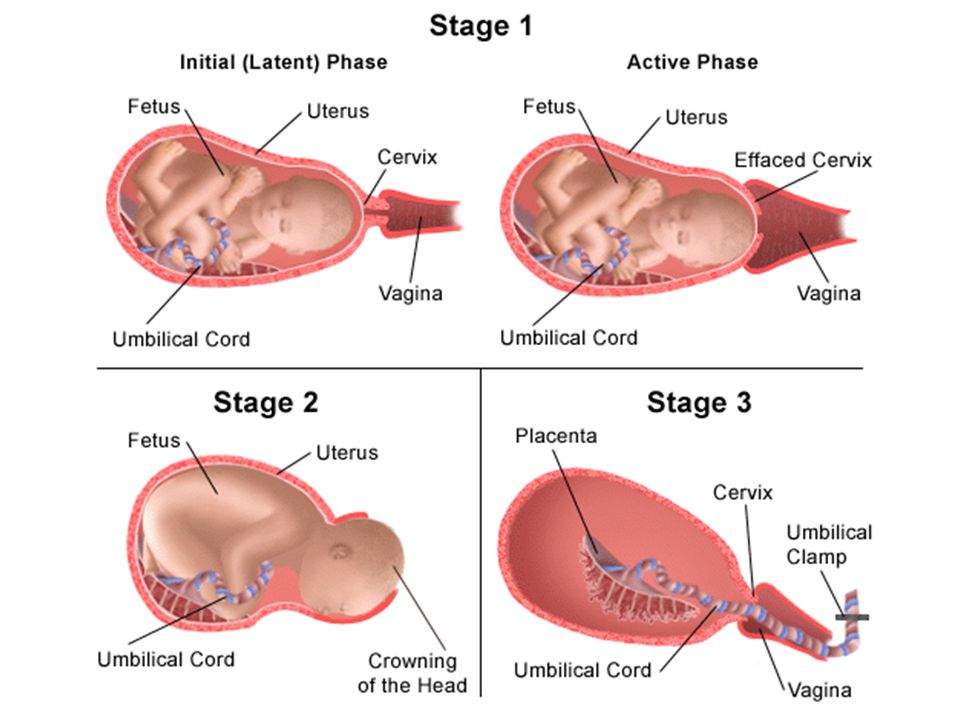 nine0017
nine0017
— What about doulas, the so-called birth assistants? Women sometimes trust them more than doctors.
- Doulas are usually people without medical education, so they cannot prescribe drugs, use medical methods, conduct examinations, that is, the doula does not control anything, does not analyze and does not provide obstetric care. In fact, this is a mother who supports her daughter during pregnancy, or a partner who is nearby during partner childbirth. nine0007 There is an understanding that the concept of "dola" in our reality has been changed, tied to home birth and endowed with the functions of medical support. But within the framework of skilled medical care in the 21st century, what kind of doulas can we talk about? This person will not replace a medical team - a midwife, an obstetrician-gynecologist, a neonatologist. This must be understood.
Tethered all night: what is a lotus birth and is it necessary?
Lotus childbirth is one of the latest fashion trends in childbirth, when after the birth of a child, the umbilical cord is not cut for several hours. Often it is not touched in any way until it falls off on its own. According to supporters of this method, the child's body is better saturated with oxygen and blood. nine0006
Often it is not touched in any way until it falls off on its own. According to supporters of this method, the child's body is better saturated with oxygen and blood. nine0006
— In the umbilical cord, which connects the mother and fetus, there are vessels and arteries, thanks to which blood is exchanged between them. Physiologically, this blood flow ceases after birth, but can persist for a maximum of 20 minutes. Therefore, there is absolutely no point in lying in this position for several hours. It doesn't carry any value.
Perhaps the idea that this is necessary came from somewhat distorted information about a study by American scientists, according to which it makes sense to somewhat delay cutting the umbilical cord - but not for several hours, but for a maximum of 1-3 minutes. It is believed that this time is enough for part of the blood to finish its current and thus saturate the child's blood so that the child's hemoglobin increases. The study also says that within 3-6 months, this helps the child gain weight better. nine0017
nine0017
- It is believed that it is precisely because the umbilical cord is cut immediately that the child turns blue. Therefore, the umbilical cord must be left intact.
- As soon as a child is born, he takes his first breath and his lungs open. He starts to breathe on his own, and that's the whole point. The fact that they can have a bluish color indicates that during childbirth the fetus experiences oxygen starvation, which is completely normal, because during contractions the vessels are pinched, but this is all a physiological process. nine0017
Bon Appetit: Placenta Smoothies and Capsules
- Women eat placenta because they believe it helps with postpartum recovery, increases energy levels, stimulates milk production, and improves hormones. Many also refer to the fact that all animals eat the placenta after childbirth, which means that it is useful.
- The benefits of eating the placenta have not been proven. Now all over the world, studies are being conducted on this subject, but so far they have not given positive results, and there is no point in taking it by itself or drugs made from it. As a rule, studies are conducted as follows: among a very large number of subjects, it is compared whether there was a positive effect from taking placental drugs or not. And if not, then why is all this necessary? But in order to conduct these studies, a lot of time and resources are needed, so this work is still in progress. nine0007 The placenta performs several functions - gas exchange, hormonal and excretory, it is a barrier between the mother and the fetus, helps the fetus grow and protects it from various outside influences, while not protecting it from drugs, alcohol, drugs, nicotine. That is, it, as a temporary organ, works until the moment of childbirth, and after that it no longer exists.
As a rule, studies are conducted as follows: among a very large number of subjects, it is compared whether there was a positive effect from taking placental drugs or not. And if not, then why is all this necessary? But in order to conduct these studies, a lot of time and resources are needed, so this work is still in progress. nine0007 The placenta performs several functions - gas exchange, hormonal and excretory, it is a barrier between the mother and the fetus, helps the fetus grow and protects it from various outside influences, while not protecting it from drugs, alcohol, drugs, nicotine. That is, it, as a temporary organ, works until the moment of childbirth, and after that it no longer exists.
The argument that animals eat the placenta cannot be considered justified either, since animals do this not for reasons of benefit, but because the placenta attracts the attention of predators. By eating it, animals protect themselves and their offspring from danger. nine0007 And the production of milk and the restoration of the hormonal background occur after childbirth as a result of other hormonal and physiological processes.
More vitamins: how much dietary supplements do pregnant women need?
— In Instagram, the blogs of the so-called healers, who advise taking a huge amount of dietary supplements, are very common. At the beginning of summer, there was a big scandal with this: the famous Instagram blogger Elena Kornilova prescribed through her blog to women, including pregnant women, a large amount of vitamins from the well-known American site Iherb, some of which contained dangerous elements. Nevertheless, there is an opinion that pregnant women need a lot of vitamins to maintain the health of the body. Is it so? nine0005
- Any medical consultation on Instagram needs to be said categorically "no". The person behind the blog can present themselves as they please, and there is no way you can verify this data. There is also a fashion consultation based on the results of analyzes, but this does not work that way. A doctor does not treat tests, he treats a person, it is necessary to communicate with the patient, to see him.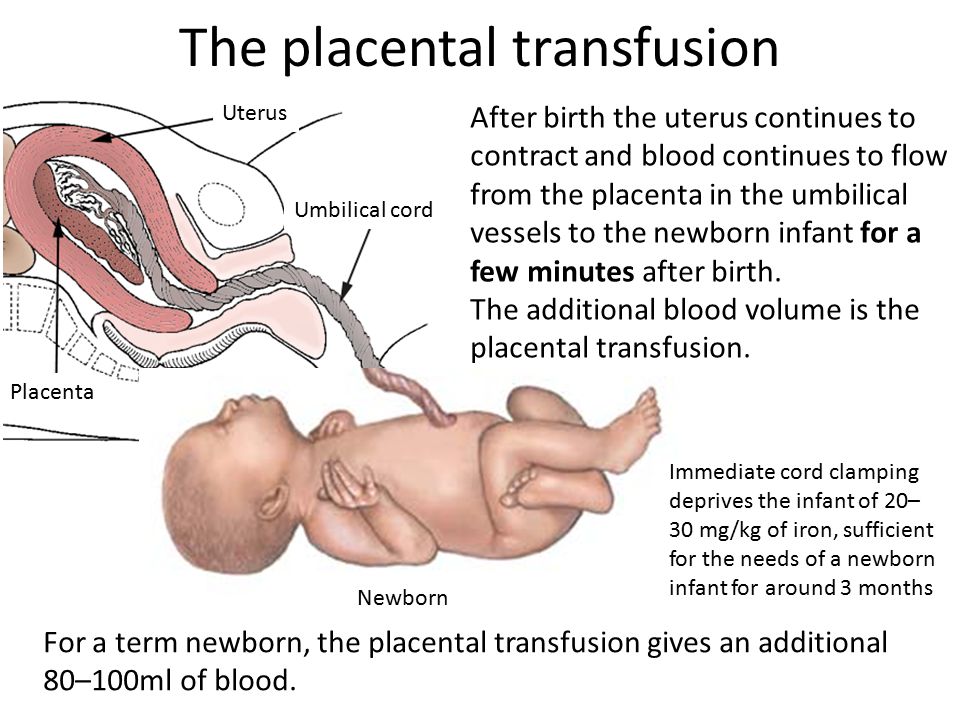 As for drugs for pregnant women, they should be as small as possible. Including vitamins.
As for drugs for pregnant women, they should be as small as possible. Including vitamins.
All over the world, medical research on pregnant women is prohibited, so even on specialized vitamins and medicines it is written that they should be taken with caution by pregnant women. There is the concept of drug safety. nine0007 Almost all pregnant women take folic acid, some drugs are selected individually according to indications, someone takes medications necessary for the treatment of chronic diseases. Take what has been proven to be beneficial, but as prescribed by doctors. Picking something for yourself is dangerous.
https://ngs24.ru/news/more/66199645/
What to do with the placenta? 10 uses
The placenta (baby place, afterbirth, storage) is a unique organ. He only appears on 8-9months to provide the unborn child with oxygen and all the necessary nutrients, but after the third stage of labor becomes unnecessary. What can be done with the placenta after the doctor examined it and said that everything is in order? There are at least 10 options, and each has its supporters.
Eat. This is exactly what female placental mammals do after giving birth, even herbivores. After all, the afterbirth contains many valuable nutrients, and after giving birth in the wild, you need to restore strength as soon as possible in order to be able to run and get food again. nine0017
Women still do this too, especially in parts of Asia. Some experts recommend eating the placenta for the prevention of postpartum depression and anemia. However, in our time, placentophagy has acquired many exotic forms: since it is rather problematic for a civilized person to simply eat a raw afterbirth, as in the wild, the placenta is either heat-treated, like ordinary meat, or smoothies are prepared, or encapsulated. To do this, the placenta must be steam-dried, turned into powder, and then taken in the form of capsules. Of course, only those who have the appropriate technical capabilities resort to such methods. However, you should be aware of the risks: the placenta contains hormones, is not sterile, and may even be infected. nine0017
nine0017
Bury. In our climatic latitudes, the placenta was most often buried in the ground. This could be accompanied by rituals: the placenta was washed, sprinkled with fragrant herbs, spices, put in an embroidered bag (they could cover it with a layer of wet clay and dry it so that it would not become food for wild animals), and only then they put it in a specially prepared hole - under the house, in a wasteland but most often under a tree. If a girl was born, the placenta was buried under a "female" tree - for example, an apple tree. If the family was replenished with a boy, the children's place was buried under a maple or oak tree so that the guy would grow up strong and powerful. Nowadays, the placenta can be buried under the so-called "family tree" to ensure the baby's health and well-being, or they can simply be buried in a flower bed - they say, this is how flowers grow better. nine0017
Bury. In some countries (particularly on the island of Bali), it is customary not just to bury the placenta, but to ritually hide it in a cemetery, believing that it is a living being.
Make a decoration. The placenta looks good in epoxy, so some women order a pendant, bracelet, ring or necklace from their own placenta from jewelers. Such decoration should symbolize the bond between mother and child. nine0017
Dry for memory. Dried placentas are sometimes used in art compositions or sewn into toys.
Sell. Cosmetics made using the placenta - creams, gels, serums, shampoos, etc. are very popular on the market. Especially effective are products with a placenta in anti-aging cosmetology - because in this way you can stimulate the appearance of new cells, as well as activate the production of collagen and elastin, and the skin becomes more elastic. Therefore, some women sell their afterbirth. Although, of course, you won’t earn a lot of money this way. nine0017
Use in homemade skin cream. However, a cream that will help heal the skin, reduce scars and stretch marks, and even heal sore or cracked nipples is even made independently.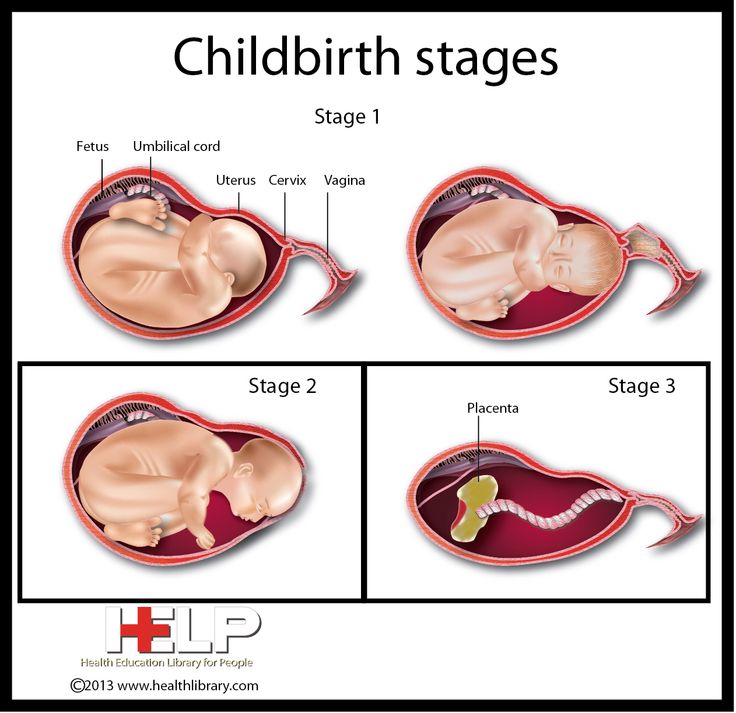 To do this, placenta powder is added to other components.
To do this, placenta powder is added to other components.
Dispose of. In Ukraine, this is the most common scenario for the development of events. Maternity hospitals are guided by a protocol for handling biowaste: after the completion of the third stage of labor, the placenta is examined and sent for freezing in a special chamber. When it is full, the placentas are taken for disposal - more often they are buried, less often they are burned. nine0017
Deposit in the cryobank. Today, the placenta - as well as cord blood - is used to isolate the most valuable mesenchymal stem cells. Even now, stem cells are successfully used for the treatment of various diseases and in cosmetology, this area is rightly called "medicine of the XXI century." Therefore, such a “contribution” can be a very profitable investment in the health of the child and the longevity of the parents. Interestingly, stem cells are obtained from a smaller part of the placenta, from the amnion and chorion, which are genetically related to the child.