Pregnancy pain in left side groin
Pelvic pain in pregnancy - NHS
Some women may develop pelvic pain in pregnancy. This is sometimes called pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain (PGP) or symphysis pubis dysfunction (SPD).
PGP is a collection of uncomfortable symptoms caused by a stiffness of your pelvic joints or the joints moving unevenly at either the back or front of your pelvis.
Symptoms of PGP
PGP is not harmful to your baby, but it can be painful and make it hard to get around.
Women with PGP may feel pain:
- over the pubic bone at the front in the centre, roughly level with your hips
- across 1 or both sides of your lower back
- in the area between your vagina and anus (perineum)
- spreading to your thighs
Some women may feel or hear a clicking or grinding in the pelvic area.
The pain can be worse when you're:
- walking
- going up or down stairs
- standing on 1 leg (for example, when you're getting dressed)
- turning over in bed
- moving your legs apart (for example, when you get out of a car)
Most women with PGP can have a vaginal birth.
Non-urgent advice: Call your midwife or GP if you have pelvic pain and:
- it's hard for you to move around
- it hurts to get out of a car or turn over in bed
- it's painful going up or down stairs
These can be signs of pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain.
Treatments for PGP
Getting diagnosed as early as possible can help keep pain to a minimum and avoid long-term discomfort.
You may be referred to a physiotherapy service that specialises in obstetric pelvic joint problems.
Physiotherapy aims to relieve or ease pain, improve muscle function, and improve your pelvic joint position and stability.
This may include:
- exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor, stomach, back and hip muscles
- equipment, if necessary, such as crutches or pelvic support belts
These problems tend not to get completely better until the baby is born, but treatment from an experienced practitioner can improve the symptoms during pregnancy.
Coping with pelvic pain in pregnancy
Your physiotherapist may recommend a pelvic support belt to help ease your pain, or crutches to help you get around.
It can help to plan your day so you avoid activities that cause you pain. For example, do not go up or down stairs more often than you have to.
For example, do not go up or down stairs more often than you have to.
The Pelvic, Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy (POGP) network also offers this advice:
- be as active as possible within your pain limits, and avoid activities that make the pain worse
- rest when you can
- ask your family, friends or partner, if you have one, to help with everyday activities
- wear flat, supportive shoes
- sit down to get dressed – for example, do not stand on 1 leg when putting on jeans
- keep your knees together when getting in and out of the car – a plastic bag on the seat can help you swivel
- sleep in a comfortable position – for example, on your side with a pillow between your legs
- try different ways of turning over in bed – for example, turning over with your knees together and squeezing your buttocks
- take the stairs 1 at a time, or go upstairs backwards or on your bottom
- if you're using crutches, have a small backpack to carry things in
- if you want to have sex, consider different positions, such as kneeling on all fours
POGP suggests that you avoid:
- standing on 1 leg
- bending and twisting to lift, or carrying a baby on 1 hip
- crossing your legs
- sitting on the floor, or sitting twisted
- sitting or standing for long periods
- lifting heavy weights, such as shopping bags, wet washing or a toddler
- vacuuming
- pushing heavy objects, such as a supermarket trolley
- carrying anything in only 1 hand (try using a small backpack)
The physiotherapist should be able to provide advice on coping with the emotional impact of living with chronic pain, such as using relaxation techniques.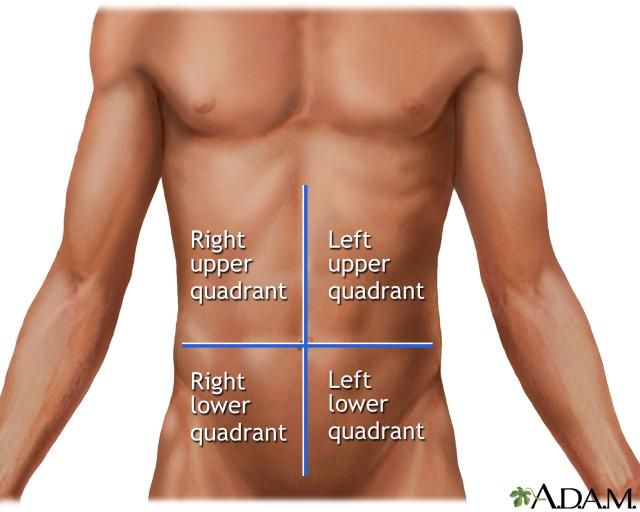 If your pain is causing you considerable distress, then you should let your GP or midwife know. You may require additional treatment.
If your pain is causing you considerable distress, then you should let your GP or midwife know. You may require additional treatment.
Find out more on the Pelvic, Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy (POGP) website.
Labour and birth with pelvic pain
Many women with pelvic pain in pregnancy can have a normal vaginal birth.
Plan ahead and talk about your birth plan with your birth partner and midwife.
Write in your birth plan that you have PGP, so the people supporting you during labour and birth will be aware of your condition.
Think about birth positions that are the most comfortable for you, and write them in your birth plan.
Being in water can take the weight off your joints and allow you to move more easily, so you might want to think about having a water birth. You can discuss this with your midwife.
You can discuss this with your midwife.
Who gets pelvic pain in pregnancy?
It's estimated that PGP affects up to 1 in 5 pregnant women to some degree.
It's not known exactly why pelvic pain affects some women, but it's thought to be linked to a number of issues, including previous damage to the pelvis, pelvic joints moving unevenly, and the weight or position of the baby.
Factors that may make a woman more likely to develop PGP include:
- a history of lower back or pelvic girdle pain
- previous injury to the pelvis (for example, from a fall or accident)
- having PGP in a previous pregnancy
- a physically demanding job
- being overweight
Further information
Find support and advice from other women with PGP at the Pelvic Partnership.
Listen to women’s experiences of pain and discomfort in pregnancy, including PGP, on healthtalk.org.
Read more about coping with common health problems in pregnancy, including nausea, heartburn, tiredness and constipation.
Find maternity services or physiotherapy services near you.
Community content from HealthUnlockedGroin pain in pregnancy: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Groin pain is common during pregnancy, and it often becomes more intense as the pregnancy progresses. Ligament pain and vaginal issues are common causes of groin pain during pregnancy.
Groin pain is not an emergency, and it does not usually indicate a problem with the pregnancy. However, it is important to mention all pregnancy symptoms to a doctor or midwife.
In this article, we outline the causes of groin pain during pregnancy, along with their associated symptoms and treatments.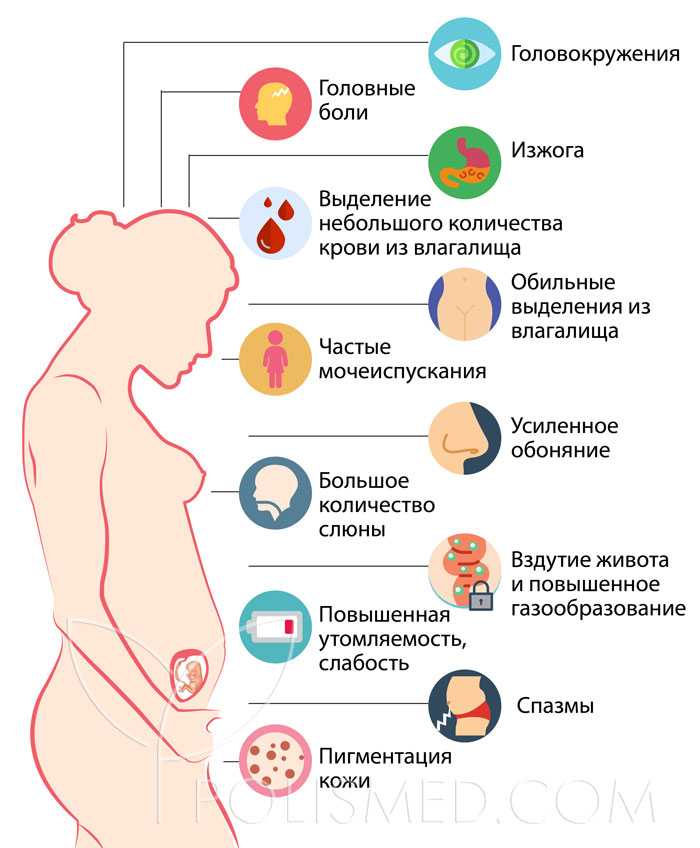 We also provide information on when to see a doctor for this type of pain.
We also provide information on when to see a doctor for this type of pain.
Below are some of the most common causes of groin pain during pregnancy, alongside explanations of their associated symptoms and treatments.
Symphysis pubis dysfunction
The pubic symphysis is a joint that sits between the left and right pubic bones. During pregnancy, the ligaments and muscles that support the joint relax and stretch to accommodate the growing uterus and fetus. This relaxing and stretching causes the pubic symphysis to become unstable, resulting in symphysis pubis dysfunction (SPD).
SPD can cause the following symptoms, which tend to worsen during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy:
- clicking in the hips or pelvis
- muscle spasms or shooting pains in the pelvic area
- sharp, shooting pains in the vagina, perineum, or rectum
- electric shock-like sensations in the vagina or groin area
- pain that radiates from one part of the pelvic area to another
Many women refer to SPD as “lightning crotch” because of the strange electrical sensations they feel.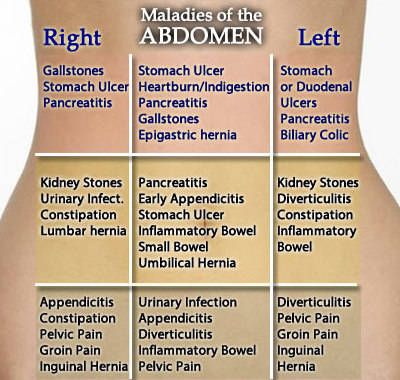 The pain ranges from mild to severe and often gets worse with the following activities:
The pain ranges from mild to severe and often gets worse with the following activities:
- transitioning from sitting to standing
- climbing stairs
- carrying heavy objects
Treatment
SPD is not a medical issue but a temporary pain of pregnancy. It does not indicate that there is anything wrong with the pregnant woman or the developing fetus.
For most women, the symptoms of SPD go away shortly after giving birth. In the meantime, gentle hip stretches and exercises may help alleviate the symptoms.
Some women also find relief using the following treatments:
- acupuncture
- chiropractic massage
- application of heat or ice to the pubic region
Round ligament pain
Round ligaments are tough, fibrous bands of connective tissue in the pelvis that attach to and support the uterus. The growth of the uterus throughout pregnancy causes these ligaments to stretch. This stretching can trigger the following symptoms:
- pain that radiates from the groin to the hips or upper legs
- dull aches in the groin or on either side of the stomach
- spasm-like muscle pain on one or both sides of the stomach
- sharp, sudden, intensely painful aches that last for just a second
Many women notice that the pain is worse during sudden movements, such as changing positions in bed or going from standing to sitting or vice versa.
Treatment
Round ligament pain does not indicate an issue with the pregnancy, and it usually goes away shortly after a woman gives birth. In the meantime, some strategies that may help alleviate the pain include:
- bending or flexing the hips before doing anything that tends to cause round ligament pain
- supporting the uterus with the hand before standing, sitting, or coughing
- changing position slowly
- applying a heat pad to the painful area
Vaginal infections
The vagina contains a delicate balance of certain yeasts and bacteria. Vaginal yeast infections occur when there is an overgrowth of yeast inside the vagina. In most cases, there is an overgrowth of a yeast called Candida albicans.
Many factors can cause an overgrowth of yeast in the vagina, including pregnancy. The hormone changes that occur during pregnancy can disrupt the normal pH levels of the vagina, causing yeasts to multiply out of control.
Women who develop a vaginal yeast infection may experience the following symptoms:
- itching and burning in the vagina and vulva
- itching and burning of the perineum or anus
- thick, white vaginal discharge that is usually odorless and resembles cottage cheese
- pain when urinating
- pain when having sex
Treatment
Antifungal medications are the usual treatment for vaginal yeast infections. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take oral antifungal medications. However, it is safe for pregnant women to apply a topical antifungal cream or insert an antifungal suppository into the vagina.
Women who experience the symptoms above during pregnancy should make an appointment with their doctor or midwife. Certain conditions can cause symptoms that mimic those of a vaginal yeast infection. These conditions will require different treatment.
Vaginal dryness
Some women report experiencing vaginal dryness during pregnancy.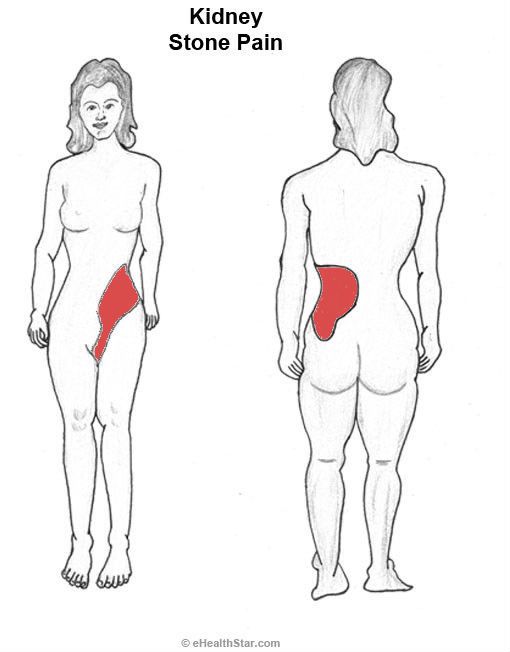 Vaginal dryness can cause the following symptoms:
Vaginal dryness can cause the following symptoms:
- soreness, itchiness, and general discomfort in and around the vagina
- pain or discomfort during sex
- the need to urinate more often than usual
- recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Treatment
Vaginal moisturizers can help alleviate vaginal dryness. These are topical medications that a woman can apply to the inside of the vagina.
Water-based sexual lubricants should help alleviate vaginal dryness during sexual activity. However, a woman should not use estrogen-based lubricants during pregnancy.
If vaginal dryness does not get better with home treatment, a woman should talk to her doctor or midwife for further advice.
Pregnant women should discuss any and all aches and pains with their doctor or midwife.
Groin pain is a common symptom during pregnancy, and it often has a relatively benign and treatable cause. Nonetheless, a woman should see a doctor to rule out more serious underlying medical conditions. A doctor can also provide treatment to help manage the pain and any associated symptoms.
A doctor can also provide treatment to help manage the pain and any associated symptoms.
Anyone who experiences any of the following symptoms during pregnancy should see a doctor as soon as possible:
- severe pain
- worsening pain
- other aches and pains, such as pain in the upper abdomen
If the following symptoms occur during pregnancy, it is important to call a doctor immediately or go to the nearest emergency room:
- painful contractions before the 37th week of pregnancy
- bleeding from the vagina
- fever or chills
- chest pain
Groin pain during pregnancy is common. It is usually the result of normal hormonal and other bodily changes that occur throughout the pregnancy. Nonetheless, a woman should report any aches and pains to her doctor or midwife. It is important to receive the correct diagnosis and any necessary treatment.
Vaginal yeast infections are highly treatable, and a woman can expect to make a full recovery following appropriate treatment. Vaginal dryness should also improve with home treatment. However, if either of these conditions persists, a woman should go back to her doctor for further advice.
Vaginal dryness should also improve with home treatment. However, if either of these conditions persists, a woman should go back to her doctor for further advice.
For most women with SPD or round ligament pain, groin pain goes away shortly after giving birth. However, about 1 in 10 women with SPD experience ongoing pain that requires continued treatment. If the pain persists, a doctor may order diagnostic tests to rule out other underlying health issues, such as hip problems or hypermobility syndrome.
Pain in the side during pregnancy
Pain in the side during pregnancy can be a symptom of many diseases. The abdomen is not a single organ like the heart or the liver. The abdomen is filled with many different organs, tissues, structures. And every organ in the stomach can get sick. First of all, you should pay attention to the sudden sharp pain in the side. This pain may be the first symptom for immediate medical attention . If a sharp sudden pain in the side lasts more than 30 minutes, you should urgently call a doctor or go to the hospital to rule out an urgent surgical pathology.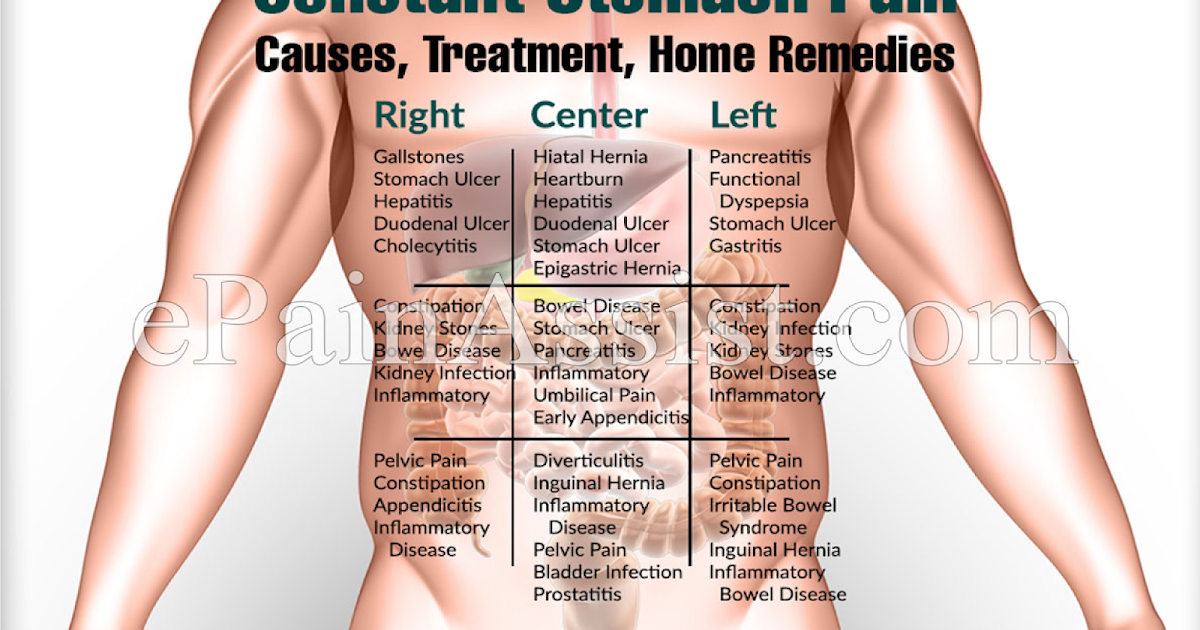
You can fantasize about the diagnosis as much as you like, but only on the way to the hospital. Because if it is, for example, perforation (perforation or hole in the stomach), then it must be sewn up immediately. To figure out for yourself what abdominal pain can mean, you need to know the following. Conventionally, your stomach is divided into four quadrants (or segments) - upper right (right side from above), upper left (left side from above), lower right and lower left (right and left side from below). The localization of any symptom can now be assigned to one of the four quadrants. nine0009
Causes of pain in the side during pregnancy
The left upper quadrant of the abdomen contains the spleen, stomach, pancreas, intestinal loops (as, indeed, everywhere in the abdomen) and the left side of the diaphragm. Pain in the left upper quadrant may be associated with the spleen. The spleen lies very close to the surface of the body. The main job of the spleen is to remove red blood cells from the blood, after their normal life span of 120 days. It captures them, destroys them, after which their components pass into the bone marrow, where new blood cells are formed. nine0009
The main job of the spleen is to remove red blood cells from the blood, after their normal life span of 120 days. It captures them, destroys them, after which their components pass into the bone marrow, where new blood cells are formed. nine0009
In a number of diseases, the spleen enlarges, its capsule is stretched, and this causes pain. Due to the fact that the spleen is located close to the surface of the body, it is prone to rupture. Causes of a ruptured spleen can be trauma and diseases such as infectious mononucleosis. With this disease, the spleen becomes enlarged and soft. And all this increases the likelihood of its rupture. Sometimes an enlarged spleen ruptures on its own. A signal sign of a ruptured spleen, in addition to pain and sensitivity in the corresponding area, is cyanosis of the skin around the navel (due to accumulation of blood). nine0009
Pain in the left side from above during pregnancy can give the stomach. Anything that irritates the stomach lining, causes gastritis (inflammation of the stomach) or functional dyspepsia, can cause pain. More often, this pain is aching in nature, often accompanied by nausea and even vomiting. Antacids prescribed by your doctor will help. In general, only a doctor can tell you exactly what you have. Pain in the stomach can be with peptic ulcer and cancer. After completing a series of laboratory tests and examinations (including endoscopic), the doctor will finally make a diagnosis for you and prescribe the treatment. Pain in the upper left quadrant may be associated with diaphragmatic hernia. In the diaphragm, which separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity, there is a hole through which the esophagus passes on its way to the stomach. nine0009
More often, this pain is aching in nature, often accompanied by nausea and even vomiting. Antacids prescribed by your doctor will help. In general, only a doctor can tell you exactly what you have. Pain in the stomach can be with peptic ulcer and cancer. After completing a series of laboratory tests and examinations (including endoscopic), the doctor will finally make a diagnosis for you and prescribe the treatment. Pain in the upper left quadrant may be associated with diaphragmatic hernia. In the diaphragm, which separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity, there is a hole through which the esophagus passes on its way to the stomach. nine0009
When the muscles that control the size of this opening weaken, the opening enlarges, allowing the upper stomach to exit the abdominal cavity, where it should be, into the chest cavity, where it certainly should be. This condition is called diaphragmatic hernia. More commonly seen in older people. Due to acidic stomach contents, you feel pain in the left upper quadrant. We must not forget that the pain in the left upper quadrant can give the pancreas. After all, it is stretched through the upper abdomen and when the pancreas becomes inflamed, you can feel pain on the right, in the middle and on the left side of the abdomen. Various diseases and toxins can affect the pancreas, including cancer. You should suspect that you have a pancreatic disease if the pain that occurs is very sharp, comes from the inside, is shingling, radiates to the back, is accompanied by fever, nausea, vomiting, and if you also belong to a high risk group for pancreatic disease, that is, you have a gallbladder disorder, you smoke a lot, drink heavily, suffer from diabetes, take diuretics or steroid hormones (the latter are mainly prescribed for asthma, arthritis, cancer, and some chronic diseases). nine0009
We must not forget that the pain in the left upper quadrant can give the pancreas. After all, it is stretched through the upper abdomen and when the pancreas becomes inflamed, you can feel pain on the right, in the middle and on the left side of the abdomen. Various diseases and toxins can affect the pancreas, including cancer. You should suspect that you have a pancreatic disease if the pain that occurs is very sharp, comes from the inside, is shingling, radiates to the back, is accompanied by fever, nausea, vomiting, and if you also belong to a high risk group for pancreatic disease, that is, you have a gallbladder disorder, you smoke a lot, drink heavily, suffer from diabetes, take diuretics or steroid hormones (the latter are mainly prescribed for asthma, arthritis, cancer, and some chronic diseases). nine0009
Pain in the left side from below during pregnancy can be the result of all conditions that cause pain in the right lower region, with the exception of appendicitis.
Pain in the right side from above during pregnancy
In this area there are such organs as the liver, gallbladder, part of the intestine, the right part of the diaphragm.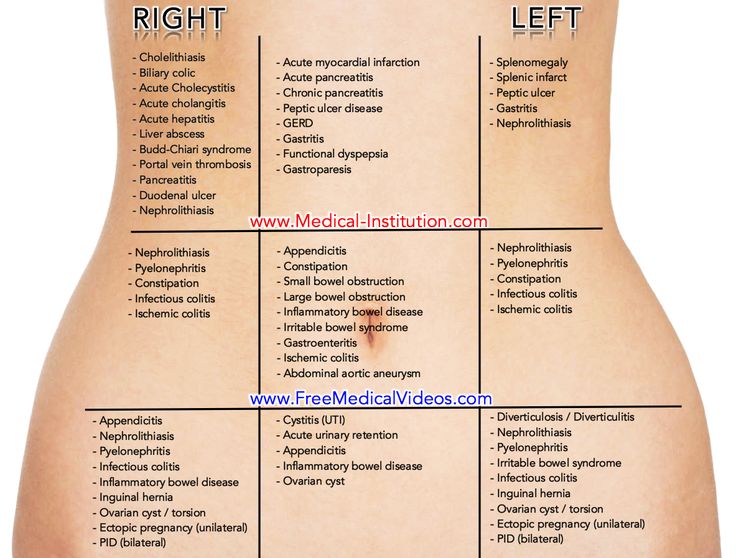 Disease or injury to these organs gives you pain in the upper abdomen. The intensity and severity of pain will depend on what is happening and where. Pain in the right hypochondrium can be with inflammation of the liver (hepatitis). The infectious agents that most often attack the liver are viruses. Hence the so-called viral hepatitis. There are three main types: viral hepatitis A, B, C. People usually get viral hepatitis A after they swallow food or water contaminated with sewage. Hepatitis B is especially common among homosexuals, drug addicts and those who have been in close contact with them. Hepatitis C is almost always transmitted through contaminated blood transfusions, medical needles, and products containing blood. It is especially common among drug addicts. Various chemical agents and drugs can also damage the liver due to their toxicity. This is the so-called toxic hepatitis. The most dangerous nucleus for the liver is alcohol. With regular alcohol abuse, alcoholic hepatitis develops.
Disease or injury to these organs gives you pain in the upper abdomen. The intensity and severity of pain will depend on what is happening and where. Pain in the right hypochondrium can be with inflammation of the liver (hepatitis). The infectious agents that most often attack the liver are viruses. Hence the so-called viral hepatitis. There are three main types: viral hepatitis A, B, C. People usually get viral hepatitis A after they swallow food or water contaminated with sewage. Hepatitis B is especially common among homosexuals, drug addicts and those who have been in close contact with them. Hepatitis C is almost always transmitted through contaminated blood transfusions, medical needles, and products containing blood. It is especially common among drug addicts. Various chemical agents and drugs can also damage the liver due to their toxicity. This is the so-called toxic hepatitis. The most dangerous nucleus for the liver is alcohol. With regular alcohol abuse, alcoholic hepatitis develops. The liver can also suffer from heart failure, when the heart muscle does not pump the blood that comes to the heart well. Part of it stagnates in the lungs and causes respiratory failure, and part stagnates in the liver, stretching it and causing pain. nine0009
The liver can also suffer from heart failure, when the heart muscle does not pump the blood that comes to the heart well. Part of it stagnates in the lungs and causes respiratory failure, and part stagnates in the liver, stretching it and causing pain. nine0009
Pain in the right side from above during pregnancy may be associated with the gallbladder. It should be noted that bile plays an important role in the body. Bile, which is produced in the liver, helps digest food. Excess bile is stored in the gallbladder. And if you have eaten a lot of fatty foods, then you need a lot of bile to absorb fats. Therefore, the gallbladder injects its contents into the intestines. Infection, poor liver function, or gallstones are often responsible for upper right side pain. nine0009
There is also another important organ in the abdomen - the pancreas. The pancreas (or pancreas) is a glandular organ located deep in the abdominal cavity that secretes digestive enzymes, juices, and insulin. The pancreas is extended from right to left. The "head" of the gland is in the upper right quadrant, the "body" crosses the midline of the abdomen, and the "tail" is located in the upper left quadrant. The most common cause of pancreatic pain is inflammation (pancreatitis). The attack of acute pancreatitis has a number of features. First, the attack is extremely painful, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and profuse sweating. The pain radiates straight to the back. It increases in the prone position, and it becomes easier for the patient to sit with an inclination forward. The diagnosis usually requires confirmation by laboratory tests to determine the content of certain enzymes secreted by the damaged gland. nine0009
The "head" of the gland is in the upper right quadrant, the "body" crosses the midline of the abdomen, and the "tail" is located in the upper left quadrant. The most common cause of pancreatic pain is inflammation (pancreatitis). The attack of acute pancreatitis has a number of features. First, the attack is extremely painful, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and profuse sweating. The pain radiates straight to the back. It increases in the prone position, and it becomes easier for the patient to sit with an inclination forward. The diagnosis usually requires confirmation by laboratory tests to determine the content of certain enzymes secreted by the damaged gland. nine0009
Sometimes pain in the right side from above during pregnancy is caused by a kidney pathology. The kidneys are located on the sides. One kidney on each side of your body, so kidney disease usually causes pain in the corresponding side and back. If the right kidney becomes infected, an abscess forms, or there are stones, then the resulting pain can be felt in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, as well as in the back.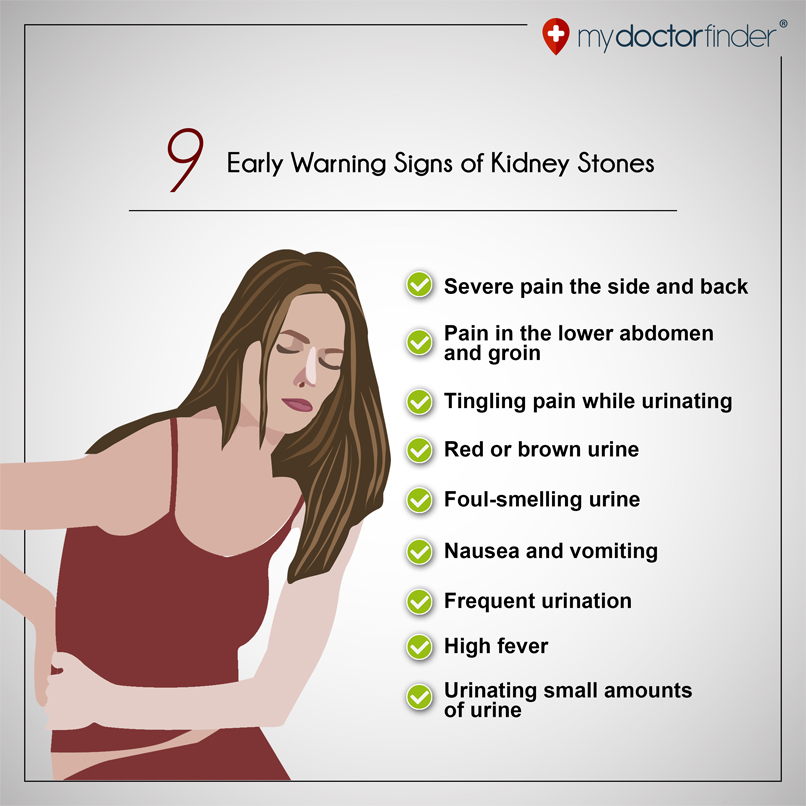 If there was a small stone in the kidney, and it came out of it, and is in the ureter, then the pain comes in waves, it is painful and often radiates to the groin, and in men to the testicle. nine0009
If there was a small stone in the kidney, and it came out of it, and is in the ureter, then the pain comes in waves, it is painful and often radiates to the groin, and in men to the testicle. nine0009
Pain in the right side from below during pregnancy
In the right lower quadrant there is an appendix, an ureter that drains urine from the kidneys to the bladder, fallopian tubes. Any pain in the right side from below should make you think about appendicitis. This diagnosis should not be withdrawn until proven otherwise. If you can point to the location of the pain with one finger, if it lasts for more than 12 hours without easing, if the pain is also localized near the navel, then it is most likely that you have appendicitis. In any case, if you suspect you have appendicitis, see your doctor immediately. And if the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will suggest you an operation. Otherwise, the appendix may fester and burst. And then even a banal appendicitis can lead to death. nine0009
nine0009
Pain in the right side from below during pregnancy, pain may occur during ectopic pregnancy. An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg stays in the fallopian tube instead of going down into the uterus. Pain in this part of the abdomen can occur with sexually transmitted infections (such as gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia).
Ovarian cysts, especially if they rupture, and ovarian tumors can cause similar chronic pain. Pain that worsens with menstruation suggests endometriosis. nine0009
Side pain in late pregnancy.
Pregnant women often notice the appearance of pain, a feeling of heaviness, fullness in the right hypochondrium.
These sensations increase and intensify as the pregnancy progresses. In most of these cases, it turns out that there is dyskinesia of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Biliary dyskinesia is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance, since it contributes to the development of the inflammatory process, stone formation. And vice versa - dyskinesia can be one of the manifestations of cholelithiasis, chronic cholecystitis, anomalies in the development of the biliary tract. nine0009
And vice versa - dyskinesia can be one of the manifestations of cholelithiasis, chronic cholecystitis, anomalies in the development of the biliary tract. nine0009
There are various anatomical, functional and hormonal connections between the biliary system and other digestive organs, they have a significant impact on the activity of this system. So, for example, the intake of food into the stomach not only causes mechanical irritation of the stomach receptors, but often also enhances bile formation and motor activity of the bile ducts.
The motor function of the gallbladder and bile ducts largely depends on the state of the nervous system: for example, dystonia of the autonomic nervous system can disrupt the coordination of contraction of the muscles of the gallbladder and relaxation of the tone of the sphincters and cause a delay in bile secretion. Psychogenic factors can also play an important role in the occurrence of dyskinesia, since it is often a consequence and one of the clinical manifestations of a general neurosis. nine0009
nine0009
Muscle weakness of the biliary tract is sometimes constitutional (associated with body features) in nature, sometimes provoked by an unbalanced diet or may be the result of a hormonal imbalance.
Pregnant women are characterized by hypomotor (that is, associated with a decrease in motor activity) dysfunction of internal organs caused by a general change in hormonal levels.
A woman's body produces large amounts of progesterone in late pregnancy. The main physiological meaning of the action of progesterone during this period is to relax the uterus, which prevents miscarriage and premature birth. However, other smooth muscle organs, including the gallbladder, also relax "in passing". Hypomotor dyskinesia is based on weak, insufficient emptying of the gallbladder, leading to its stretching and pain. nine0009
The occurrence of dyskinesia can also be associated with purely mechanical causes: the growing uterus presses, "compresses" the organs of the chest cavity, including the liver and gallbladder, as a result, the normal process of bile secretion may be disturbed.
Usually a woman is concerned about dull aching pains in the right hypochondrium (which can spread to the epigastric region), a feeling of heaviness, a feeling of pressure in this area, often accompanied by lack of appetite, nausea, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, belching with air, heartburn, bloating. The pain may increase with the movements of the fetus, depending on its position in the uterus. nine0009
Excessive emotions, nervous exhaustion, and sometimes errors in the diet increase or provoke pain and a feeling of fullness in the hypochondrium. There may be pain in the region of the heart, palpitations, headache, numbness of the limbs, sweating, sleep disturbances - doctors call these symptoms a picture of a vegetative crisis.
Which doctors to contact if there is pain in the side during pregnancy:
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Gastroenterologist
Surgeon
Infectionist
Abdominal pain during pregnancy
Abdominal pain in a pregnant woman can be experienced for various reasons.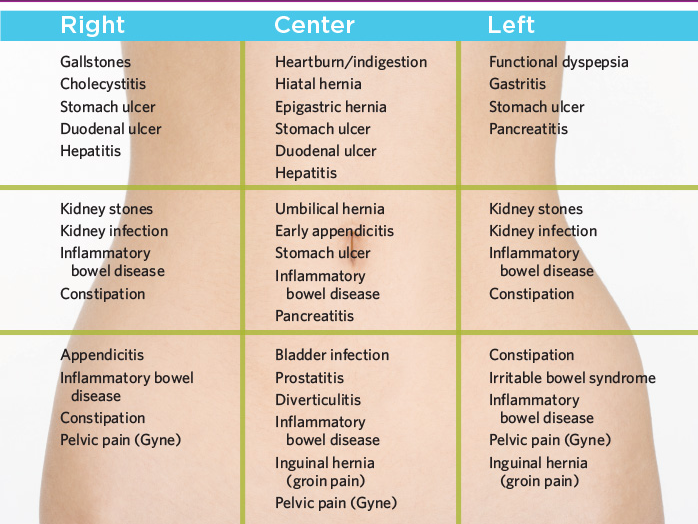 In some cases, this is a natural reaction of the body to changes occurring in the body. In some - an alarming symptom that requires urgent medical intervention.
In some cases, this is a natural reaction of the body to changes occurring in the body. In some - an alarming symptom that requires urgent medical intervention.
Consider the most common causes of abdominal pain in pregnant women.
Fatigue
The most obvious cause of pulling pains in the abdomen, especially in the later stages. Due to the weight of a growing belly, the body gets tired faster, and even habitual physical activity can cause fatigue, shortness of breath and pain. Naturally, this pain goes away during rest. nine0009
Ectopic pregnancy
If the fetal egg is not fixed in the uterus, but outside it, the pregnancy is called ectopic. After 2-3 weeks, the growing embryo begins to damage the surrounding tissues and organs - for example, a rupture of the fallopian tube often occurs. With this dangerous pathology, a woman's life is in danger, urgent hospitalization and surgical intervention are necessary.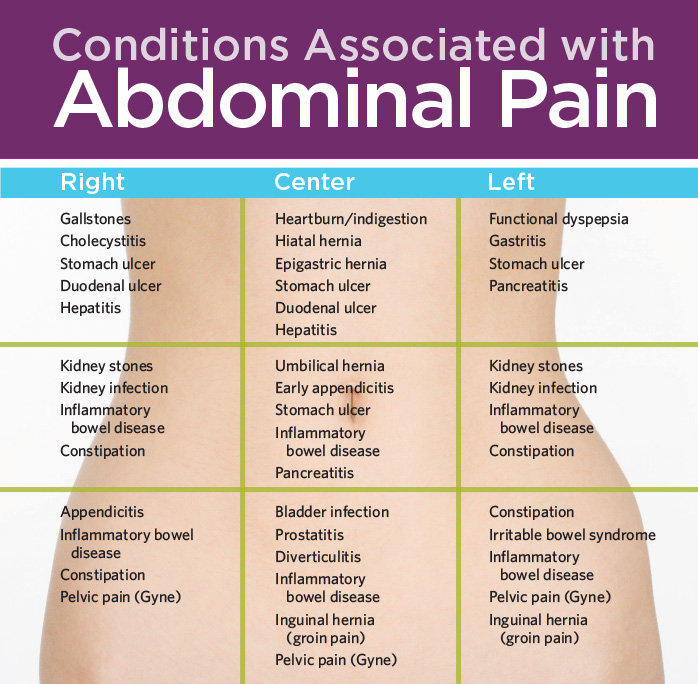 Therefore, it is very important to visit the antenatal clinic, where the doctor will determine whether the fetal egg is fixed in the uterus. nine0009
Therefore, it is very important to visit the antenatal clinic, where the doctor will determine whether the fetal egg is fixed in the uterus. nine0009
Growing pain
As the baby grows in the uterus, the uterus stretches. Most often, a woman does not notice this. But in some cases, the stretching of the uterus is felt and causes pain. Often this happens when the uterus is in hypertonicity. This reason is natural and practically not dangerous.
Compression of internal organs
A growing baby not only stretches the uterus, but also gains weight. In some positions, the uterus presses on adjacent organs, which also causes pain, especially when the child moves. Sometimes it is enough just to move, change the position of the body, so that the squeezed organ is released and the pain is gone. nine0009
Constipation
Due to changes in metabolism, as well as the weight of a growing belly, the intestines may not be active enough to perform their functions, and the pregnant woman suffers from constipation. A mild laxative will help ease the bowel and relieve pain.
A mild laxative will help ease the bowel and relieve pain.
Read in our media center: "What is the luteal phase." Find out why it is so important, what happens to a woman's body during the luteal phase and how it affects the skin.
Appendicitis
Not very often - about 1 in 10,000 pregnancies - the weight of the growing belly leads to inflammation of the appendix. Sometimes this inflammation goes away on its own, the woman does not even have time to understand what is the cause of the pain. But if the inflammation progresses, surgery may be needed. As with any inflammatory process, body temperature rises with appendicitis. In combination with the characteristic pains, the temperature gives a clinical picture that will allow the doctor to make a correct diagnosis.
Training contractions
In the third semester, pregnant women often experience rhythmic contractions of the uterus, which can be quite painful.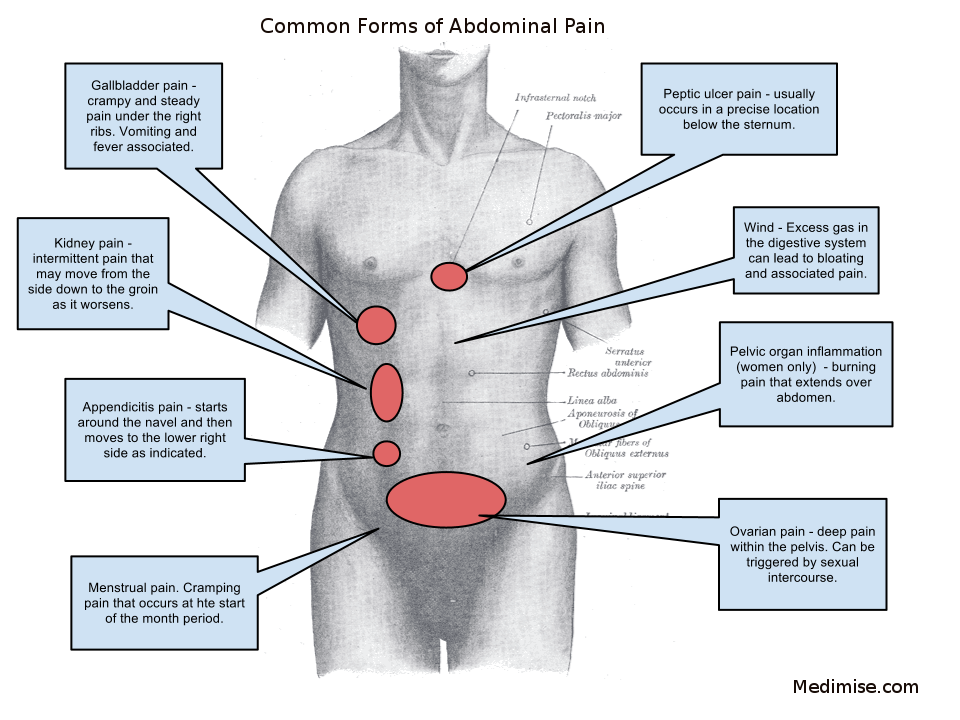 As a rule, they are safe. But if the contractions are strong, frequent and do not stop, you should call an ambulance.
As a rule, they are safe. But if the contractions are strong, frequent and do not stop, you should call an ambulance.
Placental abruption
This is an alarming symptom that is fraught with abortion. For various reasons, the placenta begins to exfoliate from the walls of the uterus. This is fraught with metabolic disorders of the fetus and spontaneous abortion. Usually, a woman notices spotting from the vagina. It is recommended to go to the hospital. nine0009
Miscarriage
Of all the listed causes of abdominal pain, this is one of the most dangerous. Spontaneous abortion can occur at any time, although in the first half it is called autoabortion, and in the later stages - premature birth. The fact that this is the cause of the pain can be recognized by a combination of several signs: pulling pains in the lower abdomen, spotting, preliminary contractions. Without medical assistance, the life of both the fetus and the mother is at risk.