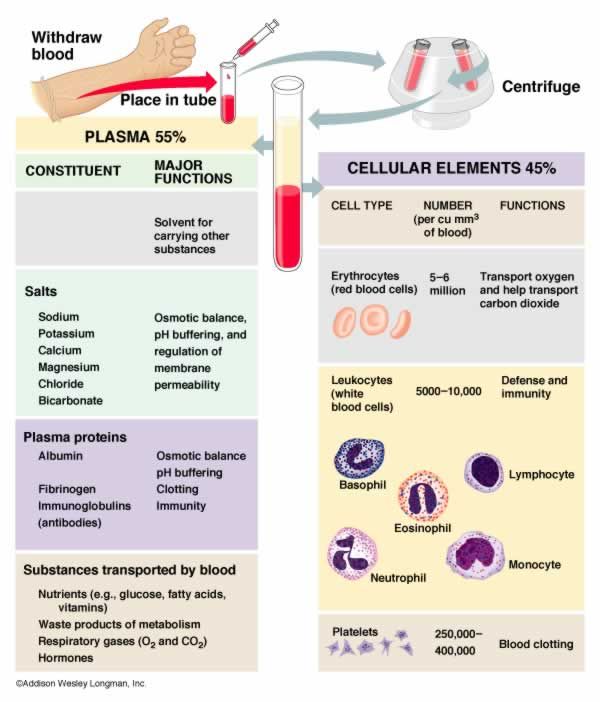
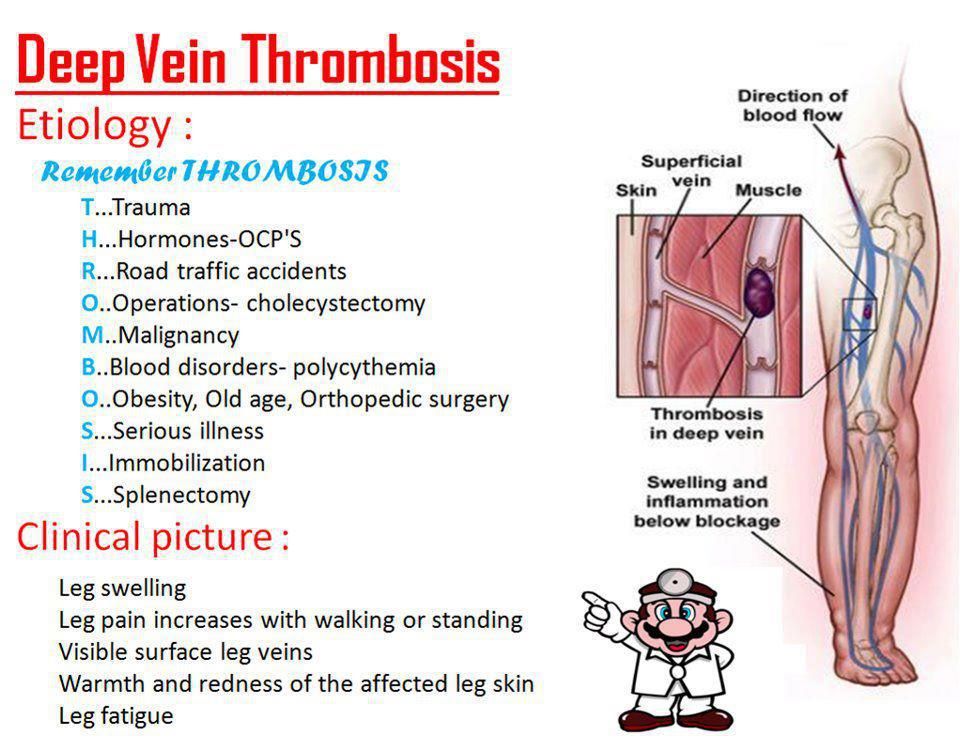
Illness when pregnant
4 Common Pregnancy Complications | Johns Hopkins Medicine
When you find out you’re pregnant, your thoughts and emotions may go into overdrive. You might be as excited about this new person you will bring into the world as you are terrified that something may go wrong.
Most pregnancies progress without incident. But approximately 8 percent of all pregnancies involve complications that, if left untreated, may harm the mother or the baby. While some complications relate to health problems that existed before pregnancy, others occur unexpectedly and are unavoidable.
It can be scary to hear that doctors have diagnosed a complication. You may be worried about your baby’s health and your own health. You may even feel panic that perhaps something you did (or didn’t do) caused this to happen. These feelings are completely normal. It may reassure you to know that nothing you did caused these complications. And beyond that —these complications are treatable. The best thing you can do for you and your baby is to get prenatal care from a provider you trust. With early detection and proper care, you increase the chances of keeping you and your baby healthy.
A Johns Hopkins obstetrician discusses some common pregnancy complications and how they can be managed.
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
What is it? While many pregnant women experience morning sickness (nausea, possibly with vomiting, generally in the morning hours) and other discomforts during pregnancy , women with hyperemesis gravidarum (HG) have morning sickness times 1,000. HG is severe nausea that results in significant weight loss and may require hospitalization. (Though it may not make you feel any better, know that if you have HG, you are in royal company — Her Royal Highness The Duchess of Cambridge, Kate Middleton, suffered from it.)
What are the symptoms? Women with HG have severe nausea and vomiting. The vomiting and reduced appetite leads to weight loss and dehydration. The major difference between HG and normal morning sickness is that HG results in a weight loss of 5 percent or more of your pre-pregnancy weight.
Who is at risk? Doctors do not yet fully understand HG, what causes it or who is more likely to experience it.
Can you prevent it? You cannot prevent HG, but you can take steps to control and manage it during your pregnancy. The most important thing you can do for you and your baby is to get regular prenatal care. HG can lead to not getting enough nutrients, which can be harmful to both you and your baby. However, with proper treatment, there are typically no long-term effects to either mom or child after the pregnancy.
How is it treated? If you have been diagnosed with HG, the priority is ensuring you have enough nutrients to keep you and your baby healthy. For some women, a diet of bland foods and fluids may be enough, while others may need to take medication to help relieve the nausea. In severe cases, you may need to be hospitalized to receive nutrients and fluids via intravenous (IV) line. You may feel down about having to be in the hospital during your pregnancy. But remember that you are just doing what you need to do to protect your and your baby’s health!
But remember that you are just doing what you need to do to protect your and your baby’s health!
Many women start to feel better by the 20th week of pregnancy, while some continue to experience symptoms throughout the entire pregnancy.
What should I ask my doctor? If you’ve had HG in the past, talk to your doctor when you are thinking about getting pregnant again. It’s important to make sure you are physically, emotionally and psychologically ready to begin another pregnancy. If you had severe weight loss or other nutritional deficiencies, you’ll need to talk to your doctor about making sure you are healthy before getting pregnant.
Gestational Diabetes
What is it? Diabetes is a condition that prevents your body from breaking down sugar. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. One of the biggest risks of gestational diabetes is that your baby may grow much larger than normal, a condition called macrosomia. During delivery, a baby’s shoulders can get stuck. If the baby is thought to be too big for a safe vaginal delivery, your doctor will recommend a cesarean section .
During delivery, a baby’s shoulders can get stuck. If the baby is thought to be too big for a safe vaginal delivery, your doctor will recommend a cesarean section .
What are the symptoms? Gestational diabetes has no outward signs or symptoms. Doctors screen for it between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy, or earlier in high-risk women such as those who are overweight or have a history of gestational diabetes.
Who is at risk? Risk factors for gestational diabetes include being overweight or having a history of GDM in previous pregnancies. If you are at high risk, your doctor will screen for GDM earlier than 24 weeks, typically in the first trimester.
Can you prevent it? Losing weight before pregnancy, sticking to a healthy diet and getting regular exercise can lower your risk of developing GDM.
How is it treated? You and your doctor should discuss how you can best control the GDM. Good old diet and exercise seem to be a good place to start. A very high percentage of gestational diabetes can be controlled by diet. Still, some women with GDM will need to take medications (pills or even insulin) to control blood sugar levels.
A very high percentage of gestational diabetes can be controlled by diet. Still, some women with GDM will need to take medications (pills or even insulin) to control blood sugar levels.
Exercise during pregnancy , even just walking 30 minutes a day, is also great for controlling blood sugar. It’s best to do something you enjoy so you’ll stick with it, but you should let your doctor know what type of exercise you are doing.
What should I ask my doctor? If you’ve had GDM, you and your baby are both at risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. So talk to your doctor about steps you can take to reduce that risk.
Placenta Previa
What is it? While you are pregnant, the placenta provides your baby with oxygen and nutrients for proper development. The placenta normally attaches to the upper part of the uterus, but in placenta previa it either totally or partially covers the cervix (which is the opening between the uterus and vagina).
Who is at risk? You may be at higher risk if you have scarring on your uterus from previous pregnancies or from a uterine surgery, or if you have fibroids .
What are the symptoms? The main symptom is vaginal bleeding that is not accompanied by cramping or other pain. Some women, however, do not experience any symptoms. Your doctor will confirm a diagnosis using an ultrasound or physical exam.
Can you prevent it? There’s nothing you can do to prevent placenta previa. However, you can increase your and your baby’s health by getting regular prenatal care. If you are at high risk — because of a previous surgery, C-section or fibroids — make sure to tell your doctor. He or she may want to monitor you more closely during your pregnancy.
How is it treated? Placenta previa may result in bleeding during pregnancy. Some women have no bleeding, some have spotting and others may experience heavy bleeding. If the bleeding is heavy, you may need to stay in the hospital for a period of time. Women with placenta previa will require a C-section to deliver the baby, usually scheduled two to four weeks before their due date.
If the bleeding is heavy, you may need to stay in the hospital for a period of time. Women with placenta previa will require a C-section to deliver the baby, usually scheduled two to four weeks before their due date.
What should I ask my doctor? Always talk to your doctor if you notice any vaginal bleeding at any point during your pregnancy.
Preeclampsia
What is it? Preeclampsia is a condition that causes dangerously high blood pressure. It can be life-threatening if left untreated. Preeclampsia typically happens after 20 weeks of pregnancy, often in women who have no history of high blood pressure.
What are the symptoms? Symptoms of preeclampsia may include severe headache, vision changes and pain under the ribs. However, many women don’t feel symptoms right away. The first alert is usually when a woman comes in for a routine prenatal visit and has high blood pressure. In those cases, your doctor will test for things like kidney and liver function to determine whether it’s preeclampsia or just high blood pressure .
Who is at risk? Risk factors for preeclampsia include having a history of high blood pressure, being obese (having a body mass index, or BMI, greater than 30), age (teenage mothers and those over 40 are at higher risk) and being pregnant with multiples.
Can you prevent it? While you can’t prevent preeclampsia, staying healthy during pregnancy may help. If you have risk factors, experts recommend that you see your obstetrician either before you become pregnant or very early in your pregnancy, so you and your doctor can discuss ways that you can reduce your risk. For example, many women at risk for preeclampsia are prescribed a baby aspirin after the first trimester.
Regular prenatal visits are the best way to control preeclampsia. During those routine visits, your doctor will check your blood pressure. If it’s high, further tests can diagnose the condition so you can start getting the treatment you need.
How is it treated? The condition only goes away once the baby is born, so delivery is the best way to treat preeclampsia. However, delivering the baby too early can put the baby at risk for health problems. The decision about how to treat you will largely depend on how far along the pregnancy is. You may need to be hospitalized so your team can monitor you and your baby closely.
However, delivering the baby too early can put the baby at risk for health problems. The decision about how to treat you will largely depend on how far along the pregnancy is. You may need to be hospitalized so your team can monitor you and your baby closely.
What should I ask my doctor? Your doctor will discuss the risks and benefits of delivering the baby early versus continuing the pregnancy and trying to manage the preeclampsia as long as possible through other methods. After delivery, the condition will go away, but you will be at greater risk for heart disease later in life. Talk to your doctor about what you can do to help reduce and manage those risks.
Pregnancy Complications: The Bottom Line
While these conditions may differ from one another, you may have noticed one common thread: Regular prenatal (even preconception) care is crucial. Women are encouraged to come in for a preconception consult to talk about what they can do to reduce their risks. Being healthy before pregnancy is the best thing you can do for your baby.
Being healthy before pregnancy is the best thing you can do for your baby.
Colds and the Flu | Respiratory Infections During Pregnancy
If you are pregnant, it’s important to take precautions against viral infections. A viral infection is a contagious illness. Most viruses will not hurt your baby. However, some viruses can cause miscarriage or birth defects in your baby. A virus can affect your respiratory tract (breathing) and can cause other symptoms. The flu and the common cold are examples of viral infections. Other examples are:
- chickenpox (varicella)
- fifth disease
- Cytomegalovirus
- rubella (also called German measles)
- Zika virus
Pregnant women can be exposed to people with viral infections. They spread directly through touching, kissing, or sexual activity. You can get them indirectly, through coughing or sneezing. They also spread through contact with infected surfaces, food, and water. This doesn’t mean you will become sick.
Path to improved health
Contact your doctor right away if you are pregnant and exposed to someone who has a viral infection. The doctor will want to know which virus and what type of contact you had. They also may ask about your symptoms.
Here are some questions your doctor may ask you:
- Did you touch or kiss the infected person?
- How long were you in contact with the infected person?
- When did the infected person get sick?
- Did a doctor diagnose the infected person’s illness? Were any tests done?
What if I’m exposed to influenza?
Influenza can be more serious for pregnant women. You may get very sick. However, it hardly ever causes birth defects in the baby. If you are pregnant during flu season (October through March), you should get a flu shot.
What should I do if I’m exposed to chickenpox?
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella virus and is highly contagious. It can be serious during pregnancy. Sometimes, chickenpox can cause birth defects. If you have had chickenpox in the past, it is unlikely you will catch it again. If you have not had chickenpox or if you are not sure, see your doctor. Your doctor will test your blood to see if you are immune.
If you have had chickenpox in the past, it is unlikely you will catch it again. If you have not had chickenpox or if you are not sure, see your doctor. Your doctor will test your blood to see if you are immune.
Many people who don’t remember having chickenpox are immune. If your blood test shows that you are not immune, you can take medicines to make your illness less severe and help protect your baby from chickenpox.
What should I do if I’m exposed to fifth disease?
Fifth disease is a common virus in children. About half of all adults are sensitive to fifth disease and can catch it from children.
Children who have fifth disease often get a rash on their body and have cold-like symptoms. Their cheeks may be red and look like they’ve been slapped or pinched. Adults who get fifth disease do not usually have the “slapped cheek” rash. Adults who contract fifth disease often have very sore joints.
If you get fifth disease early in your pregnancy, you could have a miscarriage. Fifth disease also can cause birth defects in your baby, such as severe anemia. Call your doctor if you are exposed to fifth disease. Your doctor may have you take a blood test to see if you’re immune. You also may need an ultrasound exam to see if the baby has been infected.
Fifth disease also can cause birth defects in your baby, such as severe anemia. Call your doctor if you are exposed to fifth disease. Your doctor may have you take a blood test to see if you’re immune. You also may need an ultrasound exam to see if the baby has been infected.
What if I’m exposed to cytomegalovirus?
Cytomegalovirus usually doesn’t cause any symptoms. This makes it hard to know if you have it. It is the most common infection that can be passed from mother to baby. Cytomegalovirus affects 1 of every 100 pregnant women. It can cause birth defects, such as hearing loss, development disabilities, or even death of the fetus.
It’s important to prevent cytomegalovirus because there is no way to treat it. Women who work in day care centers or a health care setting have the highest risk of getting infected. Pregnant women with these jobs should wash their hands after handling diapers and avoid snuggling or kissing the babies. If you think you’ve been exposed to a person who has cytomegalovirus, see your doctor right away.
What if I’m exposed to rubella?
Since 1969, almost all children have had the rubella vaccine, so it is a rare disease today. At the first prenatal visit, all pregnant women should be tested to see if they are immune to rubella. Women who are not immune should get the vaccine after the baby is born. Talk to your doctor if you are trying to become pregnant. Then you can get the vaccine in advance if you are not immune.
Symptoms of rubella in adults are joint pain and a possible ear infection. The virus can cause severe birth defects or death of the fetus. Talk to your doctor if you have these symptoms or have been exposed.
What if I’m exposed to Zika virus?
The Zika virus is a travel-related virus that can cause birth defects if a woman is exposed during pregnancy. Zika outbreaks have been reported in South America, Central America, and North America. The virus can cause microcephaly (the baby’s head and brain are smaller than normal. This causes an intellectual disability). The infection is transmitted through an infected mosquito bite or is passed to a woman through sexual contact. Women who are pregnant or hope to become pregnant should avoid travel to these regions and use a condom during sex if your partner has traveled to the area. Your doctor will tell you how long you must wait before trying to become pregnant if your partner has been exposed to the virus.
The infection is transmitted through an infected mosquito bite or is passed to a woman through sexual contact. Women who are pregnant or hope to become pregnant should avoid travel to these regions and use a condom during sex if your partner has traveled to the area. Your doctor will tell you how long you must wait before trying to become pregnant if your partner has been exposed to the virus.
Things to consider
Most other viruses do not seem to increase the natural risk for birth defects. This includes viruses such as regular measles, mumps, roseola, mononucleosis (“mono”), and bronchiolitis. In normal pregnancies, the risk of serious birth defects is 2% to 3%.
To protect yourself from all infectious viruses:
- Wash your hands frequently, especially after using the restroom or before a meal.
- Avoid contact with people who are knowingly infected.
- Get a flu shot and other vaccines either before or during pregnancy, as needed.
When to see your doctor
Contact your doctor right away if you have been exposed to an infected person or have symptoms of a virus. They can provide treatment, if possible, and monitor your baby for signs of infection.
They can provide treatment, if possible, and monitor your baby for signs of infection.
Questions to ask your doctor
- How do I know if I’ve been exposed to someone infected with a virus?
- What can I do to prevent exposure?
- How do I know if I’m immune to certain viruses?
- At what point should I get a flu shot?
- Are there any other vaccines I should get before or during pregnancy?
- What should I do once I become exposed to a harmful virus?
Colds during pregnancy: how to treat?
Any cold or respiratory disease in early pregnancy, during the primary formation of the fetus, can lead to unpredictable consequences and complications. The matter is complicated by the fact that most medications are absolutely contraindicated for use during gestation.
In this regard, the treatment and prevention of colds in pregnant women is an important issue, which should be approached especially responsibly! The main thesis is: be careful with medicines and apply mild preventive measures based on alternative medicine methods to avoid respiratory diseases and flu. nine0003
nine0003
"One for two - immunity"
This is a very fragile system, it is not necessary to interfere in its work, but it is necessary to support and strengthen it. Pregnancy belongs to the category of special, albeit temporary, conditions during which a woman needs additional protection.
This issue will help simple recommendations that are available to everyone:
• During the period of frequent weather changes, it is necessary to dress warmer, paying special attention to footwear. nine0017 • During an epidemic, it is better for a pregnant woman to refrain from being in crowded places - transport, metro, shops and hospitals. If there is an urgent need, to prevent possible infection, a protective respiratory mask should be worn before leaving the house.
• Be especially careful about hygiene after visiting the street and public places. Upon returning home, the first thing to do is wash your hands thoroughly.
Interesting: More than 90% of all acute respiratory infections are caused by viruses, about 10% are bacteria and other pathogens. Accordingly, any soap can be used, not necessarily antibacterial.
• Before going outside, you can lubricate the nasal mucosa with oxolin ointment. Upon returning home, flush the upper respiratory tract with soda solution.
• Rationalization of nutrition and intake of vitamins will strengthen the immune defense. It is especially useful to eat fruits and vegetables that are enriched with vitamins and have not undergone heat treatment. nine0003
Interesting: our grandmothers used to say: in order not to get sick, you need to drink chicken broth! Strange, but until recently, scientists did not attach much importance to this prophylactic. Pulmonologist Stefan Rennard decided to find out if this was true or not. The professor conducted a study and proved that the use of chicken broth affects the mobility of neutrophils, white blood cells that protect the body from infections and activate the immune system.
- Vitamins can be taken using ready-made pharmaceutical multivitamin complexes. Before choosing a drug, you should consult your doctor. nine0035
- Compliance with the regimen and duration of sleep - at least 9 hours a day. The possibility of psychotraumatic situations should be minimized.
- Maintaining cleanliness in the living quarters (ventilation, wet cleaning).
- Air humidification is an important aspect in the prevention of influenza and respiratory diseases. If air conditioners or heaters are used in the house of a pregnant woman, it would be best to purchase a mechanical humidifier. nine0035
Medications for prevention
- Grippferon - a drug in the form of drops for the nose, which provides prevention and treatment of influenza, is not contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women. The medicine stimulates an increase in immunity, has a pronounced antiviral effect that can protect against colds, infections and influenza varieties.

- Ascorbic acid - can be used as a separate source of vitamin C in a synthetic version, with a reduced daily intake from food. Ascorbic acid not only prevents infection, but also fights viruses that have already entered the body of a woman. nine0035
- Viferon - nasal ointment, which is prescribed for the prevention of influenza and respiratory infections during an epidemic. The ointment has protective and immunomodulatory effects, and also allows you to deal with disorders that are already occurring in the body at the time of use. Viferon in the form of a nasal ointment has no contraindications for use in pregnant women at any time, including the first trimester.
- Aquamaris is a natural drug in the form of a nasal spray that allows you to moisturize the nasal mucosa, thereby reducing the risk of influenza viruses entering the nasal cavity. nine0035
I would like to say a few words about such a method of prevention as vaccination. Most often, the expectant mother may be at risk of infection due to the annual influenza epidemic. This disease is dangerous for a pregnant woman precisely because of its complications: pneumonia, bronchitis, otitis media. Influenza in a pregnant woman can also affect the health of the fetus. Most of all, it is dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy, when the tissues and organs of the human embryo are laid and formed. Viral intoxication or drug exposure can lead to pathology of the child's organs. In later pregnancy, there is a risk of infection of the fetus. nine0003
Most often, the expectant mother may be at risk of infection due to the annual influenza epidemic. This disease is dangerous for a pregnant woman precisely because of its complications: pneumonia, bronchitis, otitis media. Influenza in a pregnant woman can also affect the health of the fetus. Most of all, it is dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy, when the tissues and organs of the human embryo are laid and formed. Viral intoxication or drug exposure can lead to pathology of the child's organs. In later pregnancy, there is a risk of infection of the fetus. nine0003
The most dangerous consequence of influenza in a pregnant woman is threatened miscarriage or premature birth!
It is quite natural that expectant mothers often wonder whether or not to vaccinate.
Studies have concluded that the use of inactivated ("killed") influenza vaccines does not have a teratogenic effect on the fetus and does not harm the health of a pregnant woman. After consulting with your doctor about such an inoculation, you can come to an optimal solution. nine0073 If an influenza epidemic is inevitable, and the pregnant woman has no contraindications, then the vaccine should be given. If a pregnant woman has a negligible risk of infection, she does not come into contact with a large number of people, or is opposed to vaccination, then you can not do it. According to research, it is known that vaccination of mothers reduces the risk of influenza infection of a born child by 63%. Seasonal influenza prevention is carried out in September, October. Vaccinations for pregnant women are recommended from the second trimester of pregnancy. nine0003
After consulting with your doctor about such an inoculation, you can come to an optimal solution. nine0073 If an influenza epidemic is inevitable, and the pregnant woman has no contraindications, then the vaccine should be given. If a pregnant woman has a negligible risk of infection, she does not come into contact with a large number of people, or is opposed to vaccination, then you can not do it. According to research, it is known that vaccination of mothers reduces the risk of influenza infection of a born child by 63%. Seasonal influenza prevention is carried out in September, October. Vaccinations for pregnant women are recommended from the second trimester of pregnancy. nine0003
In the period of a planned pregnancy, a flu shot is given 1 month before it: the formation of immunity occurs 2-4 weeks. Protection after vaccination lasts about a year.
If infection does occur, action should be taken immediately if at least one symptom of the disease is detected. The health of a pregnant woman and her unborn child depends entirely on her responsibility and respect for her own body.
Proven folk remedies will be used first. Since pregnant women cannot steam their legs, steam their hands, and this will facilitate nasal breathing. Bundle up, put on woolen socks and crawl under the covers: warmth, peace and sleep are good for colds. Do not forget to drink plenty of water - hot green tea with lemon and honey, lime blossom tea, cranberry juice, rosehip broth, dried fruit compote. Ginger in the form of tea also helps, not only with catarrhal symptoms, but with nausea in the morning. nine0003
Various hot milk drinks are also suitable. Honey can be added to milk, and it is best to boil it on onions. It must be emphasized right away that not all herbs for colds during pregnancy can be used. Here is a list of medicinal plants that are contraindicated: aloe, anise, barberry, elecampane (grass and root), sweet clover, oregano, St. John's wort, strawberries (leaves), viburnum (berries), raspberries (leaves), lemon balm, lovage, wormwood, licorice ( root), celandine, sage. Accordingly, preparations containing these plants should not be taken. nine0003
Accordingly, preparations containing these plants should not be taken. nine0003
The use of medicines for colds during pregnancy must be treated with great care!
It is contraindicated to use the following drugs : Pertussin, Tussin plus, Joset, Glycodin, Ascoril, Travisil, Broncholitin, ACC, Grippeks, Codelac, Terpinkod. Do not use lozenges and lozenges for sore throat or cough are also undesirable due to the likelihood of allergic reactions.
Spray Pinosol, judging by the components indicated in the instructions, is not dangerous during pregnancy. However, the essential oils contained in the preparation - pine, peppermint, eucalyptus, thymol, guaiazulene (wormwood oil) - can lead to an allergic reaction with swelling of the nasal mucosa. nine0003
Viferon suppositories are allowed to be used only after 14 weeks from the start of conception. This drug contains recombinant human interferon alpha-2, ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol acetate and has antiviral, immunomodulatory and antiproliferative effects. It is used in the treatment of various infectious and inflammatory diseases in adults and children (including newborns). In the form of an ointment, Viferon is used to treat herpetic lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. The ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days. nine0003
It is used in the treatment of various infectious and inflammatory diseases in adults and children (including newborns). In the form of an ointment, Viferon is used to treat herpetic lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. The ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days. nine0003
The homeopathic preparation Stodal, which includes predominantly herbal ingredients, acts on various types of cough and has an expectorant and bronchodilator effect.
Viburkol - homeopathic suppositories - have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, sedative, antispasmodic action. They are prescribed in the complex therapy of acute respiratory viral infections and other uncomplicated infections (including in newborns), as well as in inflammatory processes of the upper respiratory tract and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. nine0003
So, you can try to eliminate a slight ailment on your own, but there are conditions under which you need to call a doctor at home:
- Prolonged fever;
- Myalgia, fatigue, fatigue, general malaise;
- Difficulty breathing, nasopharyngeal lumps and dry or wet barking cough;
- A pregnant woman is troubled by severe pressing headache.
 nine0035
nine0035
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize the importance of treating chronic diseases before pregnancy, a healthy lifestyle during childbearing and following all doctor's orders.
I wish expectant mothers and their loved ones to try to maintain a good mood: optimists live longer and happier, they are more productive. Remember your victories and pleasant moments more often and everything will be fine!
» 10 DANGEROUS DIAGNOSIS DURING PREGNANCY!
from Down syndrome to heart , from light to the kidneys ...
Without a doubt, the dream of each parent is the picuing in the hands of his healthy child, but everything does not always happen, but it does not always happen. the way we would like. A potential problem can change from feelings of joy and excitement to sadness and anxiety. Fortunately, the latest technologies and the rapid development of medicine are becoming assistants in this situation. The disease of the child that occurs in the womb can now be diagnosed at an early stage through constant examination and observation, as a result of which immediate actions are taken to restore the health of the child. nine0120 Specialist-perinatologist of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Acibadem Maslak Clinic Assoc. Dr. Julia Dede noted: “There is a 3-5 percent chance of developing pathologies during pregnancy. For the detection of which constant surveys and observations are carried out. New generation high resolution ultrasound equipment and obtaining baby DNA from maternal blood sampling are some of the new screening methods.” An innovation that has been successfully practiced in recent years, the method of extracting the DNA of a child from the mother’s blood can be carried out as early as 8 weeks of pregnancy, Dr. Julija Dede added: “A small amount of blood, 20 cc, obtained from the mother, is sufficient to determine the DNA child and risk assessment of Down syndrome at 99 percent.
The disease of the child that occurs in the womb can now be diagnosed at an early stage through constant examination and observation, as a result of which immediate actions are taken to restore the health of the child. nine0120 Specialist-perinatologist of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Acibadem Maslak Clinic Assoc. Dr. Julia Dede noted: “There is a 3-5 percent chance of developing pathologies during pregnancy. For the detection of which constant surveys and observations are carried out. New generation high resolution ultrasound equipment and obtaining baby DNA from maternal blood sampling are some of the new screening methods.” An innovation that has been successfully practiced in recent years, the method of extracting the DNA of a child from the mother’s blood can be carried out as early as 8 weeks of pregnancy, Dr. Julija Dede added: “A small amount of blood, 20 cc, obtained from the mother, is sufficient to determine the DNA child and risk assessment of Down syndrome at 99 percent.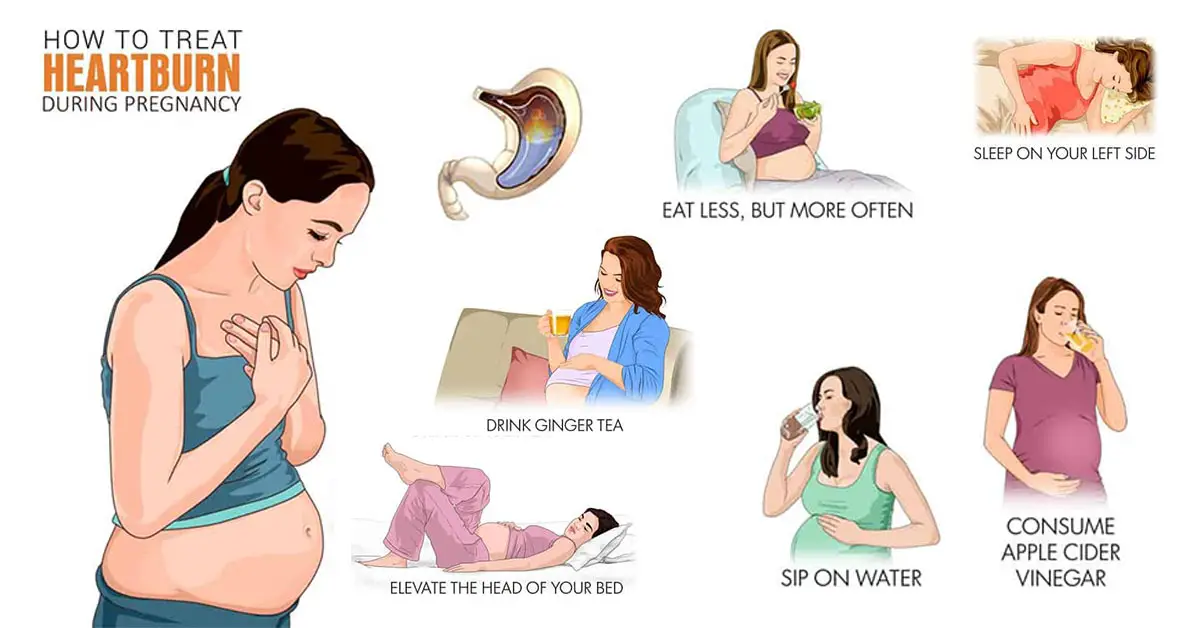 " The doctor explained some of the problems that can be found in the womb and made important warnings and suggestions.
" The doctor explained some of the problems that can be found in the womb and made important warnings and suggestions.
- Kidney disorders
Kidney disorders may be included in the examination of fetal pathologies. There are many pathologies of the kidneys from small to no kidneys at all and kidneys that are out of place. Although most of the kidney pathologies are not life threatening, they can cause kidney disease in later years. Today, many kidney pathologies can be cured. nine0035
- Lung diseases
Lung diseases are congenital diseases. For example, diseases such as cysts in the lungs, incomplete formation of the lungs, connections of the esophagus with the respiratory tract can develop. These diseases are asymptomatic in the mother and can only be diagnosed by careful ultrasonographic examination. Treatment is carried out after childbirth.
- Heart disease
The 20th week of pregnancy is important for the development of the heart. Therefore, the period from 19to 22 weeks of gestation is ideal for examining fetal pathologies. Many genetic or environmental factors cause cardiac abnormalities. Maternal use of risky diabetes medications during pregnancy, exposure to measles and rubella may be causes. The most common among cardiac pathologies are tetralogy of fallot (“blue” heart disease), transposition of the great vessels of the heart, large holes in the heart, or underdevelopment of one side of the heart due to severe stenosis. Today, many cardiac disorders can be detected during pregnancy. nine0035
Therefore, the period from 19to 22 weeks of gestation is ideal for examining fetal pathologies. Many genetic or environmental factors cause cardiac abnormalities. Maternal use of risky diabetes medications during pregnancy, exposure to measles and rubella may be causes. The most common among cardiac pathologies are tetralogy of fallot (“blue” heart disease), transposition of the great vessels of the heart, large holes in the heart, or underdevelopment of one side of the heart due to severe stenosis. Today, many cardiac disorders can be detected during pregnancy. nine0035
- Cleft lip ( Cleft palate or lip )
The pathology of cleft palate or lip, commonly known as cleft lip, occurs in 1 in 1,000 newborns. The cause of occurrence is still unknown. Drugs taken by the mother during pregnancy, X-rays, consanguineous marriages, some injuries, the use of harmful substances, and trauma during pregnancy can cause this disease. After birth, two plastic surgeries are performed: surgery on the lips in the first months after birth, on the palate - before the end of infancy. nine0035
After birth, two plastic surgeries are performed: surgery on the lips in the first months after birth, on the palate - before the end of infancy. nine0035
- Dwarfism and clubfoot
Problems such as fusion of a child's fingers, more or no limbs, limbs that are too long or too short, can be detected while still in the womb and corrected with surgery and prostheses. Dislocation of the hip, crooked legs, bowed neck, dwarfism, and severe developmental disorders of the limbs and spine are some of the most serious skeletal pathologies.
- Skeletal abnormalities
Skeletal abnormalities in the baby that occur during pregnancy can be detected during a fetal scan, but their causes have not yet been determined. It is believed that they occur due to a vitamin deficiency in the mother. Smoking, alcohol and drug use by the mother during pregnancy can also cause skeletal pathologies, and the influence of genetics is not excluded. In this case, it is necessary to inform the family by the attending physician and take appropriate measures. nine0120
In this case, it is necessary to inform the family by the attending physician and take appropriate measures. nine0120
- Head and brain pathologies
Head and brain pathologies are among the most common pathologies that can be detected at an early stage using ultrasound diagnostics. Some of the most common problems are underdevelopment of the skull, lack of brain tissue, lack of brain tissue, over-expansion of fluid-filled sacs, and underdevelopment of brain tissue. An important part of these pathologies is lost soon after the birth of the child. In this case, depending on the outcome and severity of the disease, the choice is given to the family within the principles of treatment and ethics. nine0120
- Abdominal wall problems
Some types of abdominal wall problems can be treated with surgery after the baby is born. The formation of a hernia on the navel, intestines or other organs of the abdominal cavity (and sometimes even the heart) or the protrusion of the intestines or liver due to the absence of the abdominal wall are the most common types of pathologies of the abdominal cavity.
- Neural tube defect
Non-closure of the tubular structure of the formation of the brain and spinal cord in the womb. Many of the children with neural tube defects do not survive, and the survivors become paralyzed or unable to perform vital functions such as bladder and bowel control. The most obvious cause of the defect is the lack of folic acid in the mother's body, which should be taken before and after pregnancy. nine0035
- Down syndrome
Assoc. . Dr. . Julie Dede explained: “It is not a disease, Down syndrome is a genetic feature that can be detected at an early stage. The potential risk can be determined between the 11th and 14th weeks of pregnancy, with the help of ultrasound, the formation of the nasal bone and the thickness of the child's collar space are determined, and then some parameters taken from the mother's blood are considered.