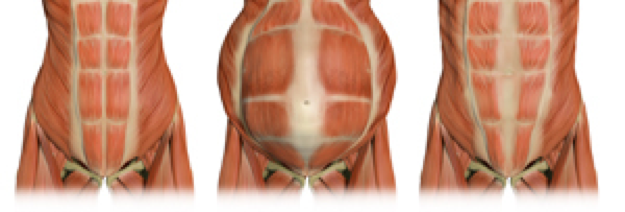
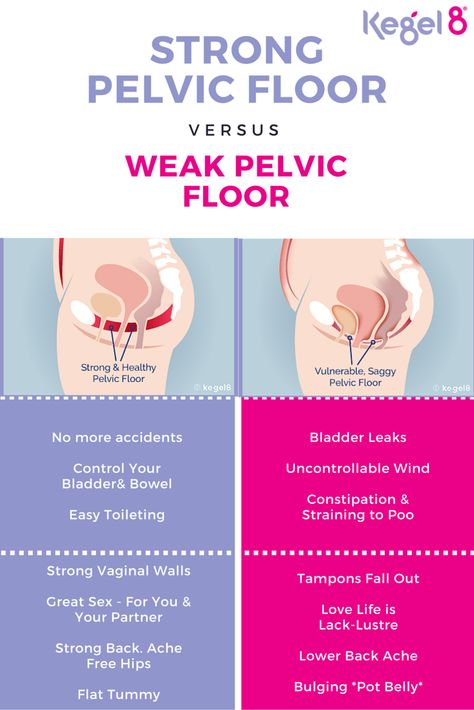
Pelvic rest after miscarriage
7 things you must do after a miscarriage according to a gynaecologist
Listen to this article |
There are many things that can go wrong with a pregnancy and lead to a miscarriage. Just like any other loss, a miscarriage can be very emotionally overwhelming for a woman. In fact, it comes with mental trauma and physical distress.
That’s why it very important to take care of a few things right after a miscarriage to ensure faster recovery for the body and mind. We got in touch with Dr Surabhi Siddharta, a consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist at Motherhood Hospital, to tell you some measures women need to take after a miscarriage for the sake of your health.
1. Rest for a week if you had a miscarriage in your first trimester
Unfortunately, if you were in your first trimester when the miscarriage happen, you need to take rest for at least a week. “To regulate the bleeding it is always advisable to stay at home,” says Dr Siddhartha.
2. You’ll need bed rest if it happened between 6 to 8 weeks
Dr Siddharta suggests that complete bed rest for one-and-a-half months in this case. She also recommends consumption of iron-rich food and multi vitamins for faster recovery.
3. Avoid doing household chores
“Lifting things or doing heavy-duty household tasks might lead to more discomfort, so avoid chores as much as possible,” she warns.
4. Don’t skip medication
According to Dr Siddharta it is very important to take the medication prescribed by your doctor on time and complete the entire course so as to avoid infections.
5. Avoid sexual intercourse
Right after a miscarriage, the uterus is very sensitive therefore she recommends avoiding sexual intercourse completely until the bleeding doesn’t stop. “I recommend a gap of at least six weeks from the miscarriage for sexual intercourse to avoid complications,” Dr Siddhartha says.
6. Don’t douche
“Douching after a miscarriage is a complete no-no. Plus the woman should also avoid using vaginal washes during this time,” she says.
7. No intense workout sessions
This is the time when you should take rest to recover from the physical trauma of a miscarriage. Dr Siddharta says: “Gyming, weight training, HIIT, etc are not recommended right after a miscarriage. If you want to exercise then you can opt for yoga and some breathing techniques. They will also keep you stress free.”
Being in touch with your gynaecologist during this time is important
“Until 20 weeks a miscarriage can happen and you need to be in constant touch with your doctor untill you are fully recovered,” explains Dr Siddhartha. Also, you need to watch out for complications like heavy bleeding, foul smell from your vagina, fever, and severe abdominal pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, rush to the hospital immediately.
If you experience any of these symptoms, rush to the hospital immediately.
“Miscarriages are normal these days due to stress and our lifestyle. So even if it happens then you should not worry because, after a couple of months, you can start planning your family again,” she concludes.
How Long to Wait and What to Expect
Physical intimacy may be the last thing on your mind after having a miscarriage. But as you heal both physically and mentally, you’ll likely start to wonder when you can have sex again.
In general, you may get the green light to have sex as soon as 2 weeks after your miscarriage — usually after the bleeding has stopped. But there are some situations that require a longer wait and others that could prompt a visit to your doctor.
And remember, just because your body’s ready doesn’t mean you are ready — and that’s OK. Let’s take a look.
Related: Pregnancy after miscarriage: Answers to your questions
First, the physical details of it — which we know can be hard to process.
After a miscarriage, you may bleed for a period of time as your body clears the uterus. While all this is happening, your cervix dilates wider than normal. When the cervix is more open, the uterus is more prone to infection.
This is why doctors recommend waiting at least 2 weeks after miscarriage to insert anything into the vagina, including tampons, douches, and — yes — anything else that may penetrate.
Up to 20 percent of (known) pregnancies end in miscarriage. This makes loss a relatively common experience. But the actual way a miscarriage happens can be quite individual.
Some people may experience what’s called a missed miscarriage (also medically called a missed abortion, though it’s not elective), where the fetus has died but there are no outward signs. Or other times, a miscarriage may be considered “incomplete” if not all the fetal tissue has passed from the vagina.
In these situations, your doctor may recommend medical intervention — like certain drugs to speed the process along or a dilation and curettage (D and C) procedure. The recommendations to wait to have sex apply here as well, but the specific amount of time may depend on your symptoms and any other unique circumstances.
The recommendations to wait to have sex apply here as well, but the specific amount of time may depend on your symptoms and any other unique circumstances.
Related: Everything you need to know about miscarriage
How long it takes to recover from miscarriage depends on several things.
For example, it may have to do with the development (size) of the fetus. The definition of miscarriage is loss of a pregnancy before week 20. A very early miscarriage or chemical pregnancy may resolve on its own relatively quickly and more closely resemble a late period. A later miscarriage, on the other hand, may require some more physical healing time.
Miscarriages that happen spontaneously and result in all fetal tissue being expelled from the uterus may also resolve more quickly. Missed miscarriages may take longer to start or to complete, requiring surgery and more overall recovery time.
Your doctor may also have different guidelines for you to follow if you’ve experienced an ectopic or molar pregnancy.
In general, it’s a good idea to check in with your doctor regardless of how or when you’ve miscarried. Your specific healing timeline may be different from somebody else’s.
Related: How to tell if you’re having a miscarriage without bleeding
We’ve mentioned that you should wait until the bleeding’s stopped — either after your miscarriage or after your missed or incomplete miscarriage and D and C — to have sex.
Again, how long and how heavy you’ll bleed can be quite individual. It has to do with a number of situations, including whether or not all the tissue has been expelled from the uterus. If you have a complete miscarriage, your bleeding may stop within 1 to 2 weeks. Some experts say it’s not so textbook and that bleeding can last anywhere between just 1 day to 1 month.
With a D and C procedure, bleeding time can also vary. Since surgery aims at removing everything from the uterus, the bleeding may be slightly shorter and last between 1 and 2 weeks. But this may be added onto time you already spent bleeding at the onset of the miscarriage.
Keep in mind that you may need to check in with your doctor if you haven’t stopped bleeding after your miscarriage or D and C. If you’ve retained tissue, you may need more surgical intervention.
Your doctor will likely schedule a follow-up appointment to examine the contents of your uterus via ultrasound and check for any remaining tissue. If tissue remains, it can lead to infection, so it’s important to abstain from sex until your uterus is empty.
Do I need to wait until after my first post-miscarriage period?
Your first menstrual period may come within 4 to 6 weeks after your miscarriage is complete, but you don’t necessarily have to wait — especially if you have a complete miscarriage and you’re feeling ready.
Just keep in mind you can still get pregnant during this time. In fact, fertility may be enhanced after miscarriage, as noted in this 2016 study.
Related: How long does a miscarriage last?
If you aren’t feeling up to sex after your miscarriage, you most definitely aren’t alone. While physically your body may be recovered and sex may technically be safe, it can take time to heal the emotional wounds of loss.
While physically your body may be recovered and sex may technically be safe, it can take time to heal the emotional wounds of loss.
Give yourself all the time you need.
You may experience a grieving period after your loss. And you might be surprised to know that the level of grief you feel may not have to do with how long your pregnancy lasted. It’s more about how you, as an individual, process your emotions.
Processing things may be easier if you have a solid support network of family and friends or if you consider seeing a therapist to talk through your feelings.
Here’s the thing: Intimacy doesn’t have to equal sex. There are a multitude of other ways to express closeness after pregnancy loss.
You might try:
- hugging
- cuddling
- holding hands
- outercourse (sexual activity without exchange of body fluids)
- massage
- dates
- long talks
Related: Intimacy is so much more than going all the way
As you miscarry, the uterus contracts and you may feel painful cramping.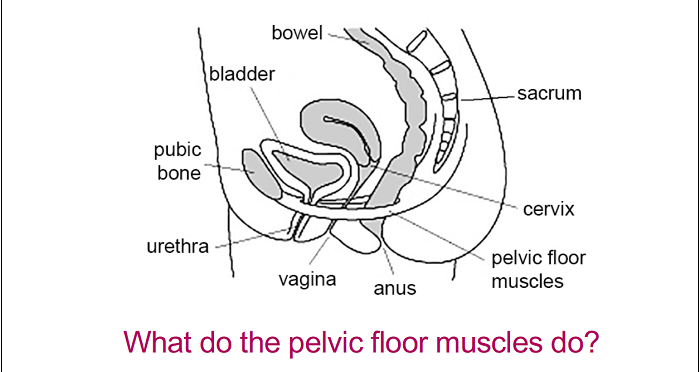 You may also have cramping after your miscarriage that’s similar to the cramping you have during your menstrual periods. Over time, this cramping should subside as the uterus continues to heal.
You may also have cramping after your miscarriage that’s similar to the cramping you have during your menstrual periods. Over time, this cramping should subside as the uterus continues to heal.
Still, you may experience pain or cramping during or after sex, especially in the early days. Keep in mind, though, that pain may be caused by infection or other things that need a doctor’s attention. Other signs of infection include:
- fever
- chills
- unpleasant smelling discharge
You can get pregnant very soon after having a miscarriage — before your first period, even. That’s right! Some people may ovulate as soon as 2 weeks after the miscarriage is complete. If you’re having sex during that time, pregnancy is always a possibility.
If you’re not looking to conceive right away, chat with your doctor about contraceptive methods that are right for you. There’s no right or wrong decision after you’ve had a loss. Take into consideration how you’re feeling both physically and mentally. Talk with your partner about their feelings as well. And give yourself plenty of time to consider your choices.
Talk with your partner about their feelings as well. And give yourself plenty of time to consider your choices.
While you may worry about another loss, only around 1 percent of people experience what’s called recurrent pregnancy loss. Most who get pregnant again will have a healthy pregnancy.
Some other stats, according to the Mayo Clinic:
- After one miscarriage, the risk of another stays at the standard 20 percent.
- After two consecutive losses, it increases to 28 percent.
- After three or more (which is quite rare), however, the risk goes up to about 43 percent.
Related: Late miscarriage: Symptoms and finding support
Make an appointment with your doctor if you experience increased bleeding or if you have pain during or after sex.
Other reasons to see your doctor:
- heavy bleeding (soaking through a thick pad in 1 hour for 2 or more hours)
- large blood clots or tissue passing from the vagina
- fever over 101°F (38.
 3°C) — especially if it persists after taking Tylenol
3°C) — especially if it persists after taking Tylenol - foul-smelling vaginal discharge
Feeling anxious or depressed about sex after miscarriage? You may also want to visit your doctor for a referral to a therapist. Give yourself some grace and understand that you will move past your miscarriage. It may just take time to process.
Related: What I’ve learned from counseling couples through miscarriage
You may feel pressure to move on from your loss after you’ve stopped bleeding. And to you or your partner, “moving on” may seem to mean having sex. But try reminding yourself that it’s OK to not be OK and that you can take your time.
Even if your miscarriage was early, be sure to give yourself ample room to grieve and to feel all the feelings you have. Sex will come when you’re ready, and that may or may not be right when your body has healed.
When can you get pregnant after a miscarriage - the opinion of geneticists
No matter how scary it sounds, miscarriages are common.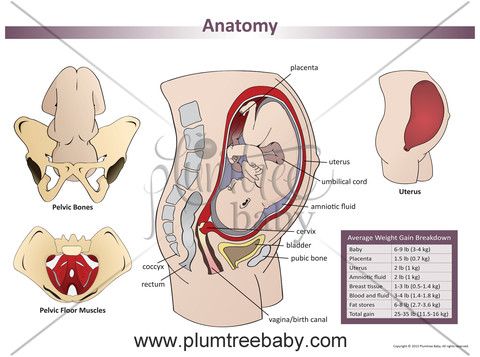 One in four women experience this condition while trying to get pregnant. In most cases, the failed mother does not even know about the irreversible changes that have occurred in her body, since they occur before the conception became known. Couples who know about the misfortune that happened are interested in when it is possible to become pregnant after a miscarriage, and what conditions must be observed in order to endure and give birth to a healthy baby.
One in four women experience this condition while trying to get pregnant. In most cases, the failed mother does not even know about the irreversible changes that have occurred in her body, since they occur before the conception became known. Couples who know about the misfortune that happened are interested in when it is possible to become pregnant after a miscarriage, and what conditions must be observed in order to endure and give birth to a healthy baby.
5 things you should know about miscarriage
Fortunately, many women who experience early and late miscarriages go further in their desire to become a mother. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the facts that confirm the frequency of miscarriage and indicate the normal fertility of a woman in the subsequent period:
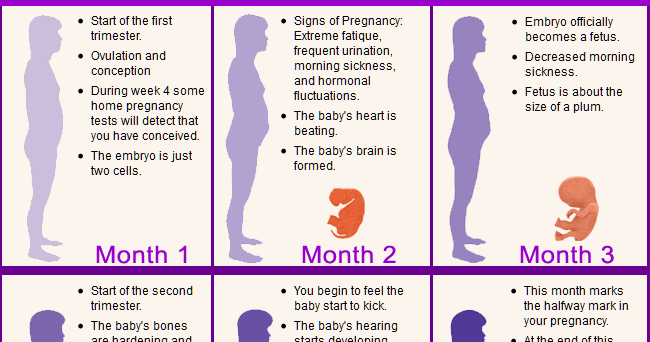
1. Very early miscarriages that occur shortly after implantation of the embryo are called chemical pregnancy. During this period, a woman may not know that she is pregnant;
2. Most miscarriages occur within the first three months after conception. After the 13-week mark and the end of the first trimester, the likelihood of spontaneous abortion decreases;
Most miscarriages occur within the first three months after conception. After the 13-week mark and the end of the first trimester, the likelihood of spontaneous abortion decreases;
3. Miscarriages in the second trimester are rare. This is 1-5% of the number of all pregnancies. If a spontaneous abortion occurred after 20 weeks, it is customary to talk about a stillbirth;
4. Trying to figure out how long it takes to get pregnant after a miscarriage, study all the possible reasons why the misfortune happened. In most situations, it is the result of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. This may be due to the action of the sperm or the egg. The second option is more likely, since the eggs are at rest, maturing in the ovaries for many years, while the sperm is constantly being renewed;
5. More than 85% of women after a late miscarriage can become pregnant again and give birth to healthy children. But many of them are in a difficult psychological state, which can create a real problem for conception. American researchers believe that it is very important to focus on self-soothing techniques, meditation, and learn to act through negative thoughts. The support of loved ones is very important during this period.
American researchers believe that it is very important to focus on self-soothing techniques, meditation, and learn to act through negative thoughts. The support of loved ones is very important during this period.
How long can you get pregnant after a miscarriage, and how long should a woman look after an accident? Each case is unique, and when a woman decides to conceive again depends on many factors. If there was a molar or ectopic pregnancy, when asked when it is possible to become pregnant after a miscarriage, doctors in most situations recommend waiting until the menstrual cycle is restored (at least one period after a miscarriage). But this is not the ultimate truth.
We have prepared for you a list of studies that will help you deal with this problem:
12 working days
Molecular carotping of the Optima Abortion Material
12500 ₽
More
9000 9000
Full sequencing of the abortive material genome Fertus
80000 ₽
Details
21 business days
Karyotype, expert level analysis
5400 ₽
More
When can you get pregnant after a miscarriage - research, experiments, observations
How long should a woman wait to try to conceive again? Recent studies by scientists from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (USA) have shown that by trying to conceive within 3 months after an accident, couples increase the success of their attempts by 71% and subsequently give birth to healthy children.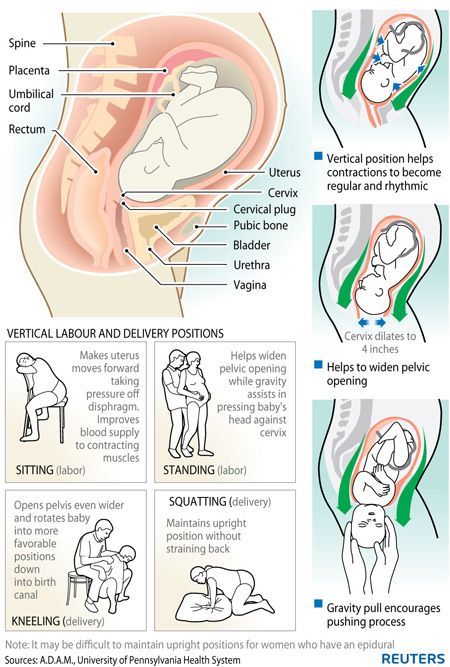 The study, which was based on the conceptual question - is it possible to get pregnant after a miscarriage immediately or should you wait - in the example of 1000 couples, it showed that timing matters.
The study, which was based on the conceptual question - is it possible to get pregnant after a miscarriage immediately or should you wait - in the example of 1000 couples, it showed that timing matters.
765 couples tried to get pregnant in the first 90 days after a miscarriage and in 77% of cases they conceived and gave birth to a healthy baby. For those couples who waited longer than the specified period, only in 23% of cases a child was born. This proves - finding out how much you can get pregnant after a miscarriage, cast aside doubts - try to conceive. Scientists have proven that couples should not wait a certain period. The main thing is the psychological and physiological readiness for pregnancy.
How long before ovulation after a miscarriage
A miscarriage is usually accompanied by bleeding, but this cannot be considered a menstrual period. The discharge of blood is a sign of uterine cleansing. The first period will pass approximately two weeks after the first ovulation. Ovulation can be delayed if there is a high level of pregnancy hormone in the blood. On average, it occurs 14-20 days after the loss of the fetus. It is important not to try to conceive until the hormonal background is restored and the pregnancy hormone is close to zero.
Ovulation can be delayed if there is a high level of pregnancy hormone in the blood. On average, it occurs 14-20 days after the loss of the fetus. It is important not to try to conceive until the hormonal background is restored and the pregnancy hormone is close to zero.
It will not be superfluous to take a pregnancy test and wait until the result is negative. This is the only way to make sure that the uterus does not contain residual effects of a failed pregnancy. In some cases, the uterus may contain foreign tissue, which can lead to fertility problems and cause abnormal bleeding. But if the level of hCG is zero, and the woman feels good, the dilemma of whether it is possible to become pregnant after a miscarriage should not worry her. The answer is obvious - yes.
If a woman has a history of two or three miscarriages in a row, this is called a recurrent miscarriage. In this case, you should contact the services of doctors for a detailed study of the situation in order to prevent its recurrence. If after the examination no serious violations are found, the chances of having healthy offspring are high.
If after the examination no serious violations are found, the chances of having healthy offspring are high.
Treatment - is cleaning required
The main goal of treatment during or after a miscarriage is to prevent bleeding and infection. The earlier the pregnancy, the more likely it is that the body will get rid of the embryonic tissue on its own without the use of additional medical procedures. If this does not happen, the most common method to stop bleeding is cleaning (curettage, curettage, dilatation).
A surgical procedure is often performed after a miscarriage in the first trimester. The doctor dilates the cervix, scrapes or removes the contents. Curettage can be performed by scraping the walls of the uterus with a curette or a suction device (vacuum aspiration). When worried about when you can get pregnant after a miscarriage and curettage, study the information more carefully or ask your doctor a question.
About 50% of women who have a miscarriage do not have a curettage. If a spontaneous abortion occurred before the 10-week period, then the probability of self-cleansing of the uterus is high. If later, most likely the miscarriage will be incomplete, which requires mandatory cleaning. Also, curettage is necessary after an abortion in order to clean the uterine cavity from foreign inclusions. In any case, expectant tactics should be reasonable, you must trust the doctor's opinion.
If a spontaneous abortion occurred before the 10-week period, then the probability of self-cleansing of the uterus is high. If later, most likely the miscarriage will be incomplete, which requires mandatory cleaning. Also, curettage is necessary after an abortion in order to clean the uterine cavity from foreign inclusions. In any case, expectant tactics should be reasonable, you must trust the doctor's opinion.
Risks after curettage
If there is no doubt about when you can get pregnant after a miscarriage, and the terms determined by doctors without cleaning and curettage are the minimum value, then how are things going with curettage? Does the procedure affect conception and can it cause fear of a repeated miscarriage? To figure out when you can get pregnant after a miscarriage and curettage, let's figure out what complications minimally invasive surgery can provoke.
Complications after cleansing
Cleaning, like any surgery, can cause some complications.
In the short term, these are:
- excessive bleeding shortly after surgery;
- uterine perforation;
- trauma of the cervix;
- infectious process and pain in the pelvic region.
In the long term with a history of cleansing, it is possible:
- Development of chronic infection;
- Adhesions (tissue scarring) inside the uterus.
The patient may experience spastic pain after surgery. You can remove them with painkillers recommended by the doctor. You can use drugs based on paracetamol (for example, Panadol) or a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory group (Brufen, Nurofen). Even with cleansing without complications, bleeding is observed for several days after the procedure. This period is different in duration for each woman. If severe bleeding develops, due to which the pad gets wet through every 30-60 minutes, you should immediately consult a doctor.
We have prepared for you a list of studies that will help you deal with this problem:
90 working days
Genome "FERTY" - diagnostics of the genetic causes of infertility in men and women.
75000 ₽
Read more
12 working days
Molecular carotping of the Optima Abortion Material
12500 ₽
more0003
More details
When can you get pregnant after a miscarriage and a purge? Intimacy is available at least two weeks later, after the bleeding stops and the tissues begin to return to normal.
It is imperative to consult a doctor if you develop a fever, have vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor, abdominal and pelvic pains are gaining more intensity, bleeding is increasing. Normally, blood can flow for about two weeks after cleansing with a gradual decrease in the amount of discharge. For several days, a woman's breasts will be particularly sensitive.
Surgical treatment of miscarriage does not carry a greater risk of fertility problems, in most situations it is not necessary to calculate when it is possible to become pregnant after an early miscarriage with a purge or when it is possible to conceive after a late spontaneous abortion with curettage. As soon as the body returns to normal, ovulation and the menstrual cycle are restored, a woman can begin to attempt to conceive a baby if she is emotionally ready for this. The period before conception must be devoted to restoring the body - to organize a healthy meal, use the vitamins recommended by the doctor, give up bad habits, and stabilize the rest and sleep regimen.
As soon as the body returns to normal, ovulation and the menstrual cycle are restored, a woman can begin to attempt to conceive a baby if she is emotionally ready for this. The period before conception must be devoted to restoring the body - to organize a healthy meal, use the vitamins recommended by the doctor, give up bad habits, and stabilize the rest and sleep regimen.
Treatment and prevention of miscarriage
Miscarriage. Symptoms
Causes of a miscarriage
Questions to ask your doctor about a miscarriage
Diagnosis of a miscarriage
If there is a risk of a miscarriage, your doctor may recommend rest until the bleeding or pain stops. Your doctor may also recommend that you abstain from sports and sexual activity. It is better not to travel, and especially not to travel to places where it is difficult to get emergency medical care.
Thanks to the widespread use of ultrasound, it is much easier these days to know if an embryo has died or not formed at all, and to know for sure that a miscarriage will occur. In this case, there are several options:
Expectant tactics. Before ultrasound was used in early pregnancy, most women had no idea that they were going to have a miscarriage. Some women allow the process to develop naturally. Usually a miscarriage occurs a few weeks after the death of the embryo is established. Unfortunately, this process can take three to four weeks. From an emotional point of view, this can be quite a difficult period.
Conservative treatment for miscarriage. If, after diagnosing a miscarriage, a woman decides to speed up the process, then the removal of the embryonic tissue and placenta from the body can be provoked by taking certain drugs. Some medications are taken by mouth, but your doctor may prescribe intravaginal medications to increase their effectiveness and reduce the risk of side effects such as nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Most likely, a miscarriage will occur at home. The time of action of the drug may vary. You may also need more than one dose of the drug. In 70% of cases, the drug begins to act within a day, and a miscarriage occurs in the next few days or weeks.
You may also need more than one dose of the drug. In 70% of cases, the drug begins to act within a day, and a miscarriage occurs in the next few days or weeks.
Surgical treatment. Another treatment option is vacuum aspiration and curettage. During this procedure, the doctor opens the cervix and, using a special device, gently sucks tissue from the uterus. Sometimes a special metal surgical instrument with a loop at the end (curette) is used to scrape the walls of the uterus after vacuum aspiration. Complications are rare, but the connective tissue of the cervix or the wall of the uterus may be damaged.
In the event of an unavoidable miscarriage, surgery is necessary to stop the bleeding.
Lifestyle and home care
Physical recovery
In most cases, physical recovery after a miscarriage takes a few hours to a few days. It will take 4-6 weeks to return to a normal lifestyle. During this period, if you experience heavy bleeding, fever, chills or severe pain, you should contact your doctor. These signs and symptoms may indicate an infection. For two weeks after a miscarriage, you should not have sex, use tampons, or flush your vagina.
These signs and symptoms may indicate an infection. For two weeks after a miscarriage, you should not have sex, use tampons, or flush your vagina.
Subsequent pregnancy
It is possible to become pregnant during your period immediately after a miscarriage. If you and your partner decide to try for a baby, make sure you are emotionally and physically ready for it. The doctor may recommend to postpone this process until the next menstruation, and maybe even more.
More than three miscarriages in a row should be investigated to determine the underlying causes, such as uterine abnormalities, coagulation problems, or abnormalities at the chromosomal level. In some cases, the doctor will suggest that you get tested after two miscarriages in a row, but two miscarriages still may not have hidden medical reasons. If the cause of miscarriages cannot be determined, do not lose hope. 60-70% of women who have had consecutive miscarriages can become pregnant in the future, even without treatment.
Coping with illness and finding support
Psychological recovery can take much longer than physical recovery. A miscarriage is a painful loss that others will not be able to fully understand. You can experience completely different feelings: from anger to despair. Give yourself time to process this grief and find support from loved ones. Don't blame yourself for what happened. You may not be able to forget all the hopes and dreams you had for this pregnancy, but over time, acceptance will ease the pain. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are experiencing deep sadness or depression.
Prevention
With so many possible causes of miscarriage, there is simply no way to prevent it. It is better to concentrate all your energy on taking care of yourself and your unborn child. Seek medical attention and avoid known risk factors such as smoking and drinking alcohol. In the presence of chronic diseases, you need to consult with your doctor in order to monitor your health.