Normal body temp for a newborn baby
Normal Body Temperature: Babies, Kids, Adults
You may have heard that the “normal” body temperature is 98.6°F (37°C). But this number is only an average. Your body temperature may be slightly higher or lower.
A body temperature reading above or below the average doesn’t automatically mean you’re sick. Several factors can influence your body temperature, including your age, sex, time of day, and activity level.
Read on to learn more about healthy body temperature ranges for babies, kids, adults, and older adults.
Your body’s ability to regulate temperature changes as you get older.
People over the age of 64 generally have more trouble adjusting to sudden changes in temperature as quickly as younger people. In general, older people have more difficulty conserving heat. They’re also more likely to have lower body temperatures.
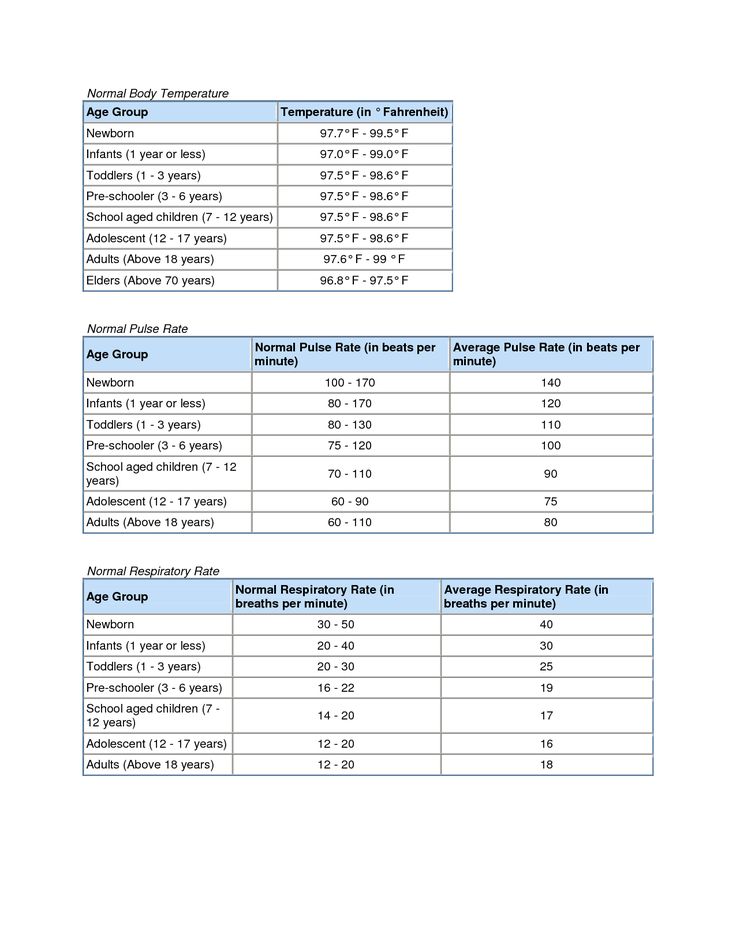
Below are average body temperatures based on age, according to a review of studies and older research:
| Age | Oral | Rectal/Ear | Armpit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–12 months | 95. (36.7–37.3°C) | 96.8–100.3°F (37–37.9°C) | 94.8–98.3°F (36.4–37.3°C) |
| Children | 97.6–99.3°F (36.4–37.4°C) | 98.6–100.3°F (37–37.9°C) | 96.6–98.3°F (35.9–36.83°C) |
| Adults | 96–98°F (35.6–36.7°C) | 97–99°F (36.1–37.2°C) | 95–97°F (35–36.1°C) |
| Adults over age 65 | 93–98.6°F (33.9–37°C) | 94–99.6°F (34.4–37.6°C) | 92–97.6°F (33.3–36.4°C) |
Identifying your normal range can make it easier to know when you have a fever.
Keep in mind that average body temperature varies from person to person. Your body temperature might be up to 1°F (0.6°C) higher or lower than the guidelines above.
There are four different ways to take your or a family member’s temperature. However, the reading can vary from one method to the next.
The chart below shows which method is recommended for each age group:
| Age | Rectal | Temporal (forehead) | Oral | Tympanic (ear) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under 3 months | X | |||
| 3–6 months | X | X | ||
| 6 months–3 years | X | X | X | |
| 4 years–teens | X | X | X | |
| Adults | X | X | X | |
| Older adults | X | X | X |
You may have had your temperature checked under your arm, in the armpit. This method isn’t as accurate and not recommended.
This method isn’t as accurate and not recommended.
German doctor Carl Wunderlich identified the average body temperature of 98.6°F (37°C) during the 19th century. However, many studies have since determined that that isn’t always the case.
A 2019 study found that the average body temperature is 97.86°F (36.59°C). That’s a little lower than initially thought so many years ago.
However, it’s best to take this information with a grain of salt since no single number defines your average body temperature. Instead, it’s best to look at a temperature range that may be higher or lower than the average.
Here are some of the factors that affect body temperature:
- Our bodies tend to warm up throughout the day.
- Older adults have lower body temperatures since our ability to regulate body temperature lessens as we age.
- Younger people have higher body temperatures.
- The level of physical activity affects temperature because the more you move your body, the warmer your core body becomes.
- Hotter and colder weather can also mirror your body temperature — it rises when in a warm environment and lowers in the cold.
- Temperature readings from the armpit are lower than the thermometer read from the mouth.
- Thermometer readings from the mouth are lower than if taken in the ear or rectum.
- Hormone levels can affect body temperature.
- Excess weight can also be associated with lower body temperatures.
A higher-than-normal thermometer reading can be a sign of a fever.
The American College of Critical Care Medicine identifies a temperature of 100.9°F (38.3°C) or higher as a fever. As mentioned previously, the exact reading is dependent upon a few factors. If your temperature’s elevated above the normal range described earlier in the article, you may have a fever.
In general, a reading that’s 2°F (1.1°C) above your normal temperature is usually a sign of a fever.
Fevers can be accompanied by other signs and symptoms, including:
- sweating or feeling flushed
- chills
- aches and pains
- headache
- lack of appetite
- dehydration
- weakness or lack of energy
Our bodies have a built-in temperature control system. This operation raises the body temperature in response to disease and infection that you can sometimes fight without any intervention. With time and rest, your body temperature will likely return to normal without treatment.
This operation raises the body temperature in response to disease and infection that you can sometimes fight without any intervention. With time and rest, your body temperature will likely return to normal without treatment.
When should I call my doctor if I have a fever?
On many occasions, a fever will go away on its own without treatment. However, you’ll want to seek medical advice if you have a fever and any of the following:
- trouble breathing
- skin rash
- persistant cough
- confusion or sleepiness
- unexplained bleeding or bruising
- persistent diarrhea, vomiting, or both
- headache with stiff neck
- feeling unwell
- fever that has lasted for more than 2 days
With babies and younger children, it can be hard to know when to speak with a doctor. Call your pediatrician if:
- your baby is less than 3 months old and has a fever.
- your baby is between 3 months and 3 years old and has a temperature of 102°F (38.
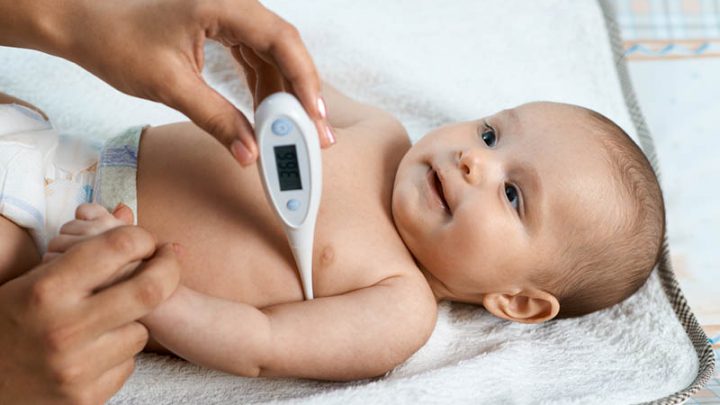 9°C).
9°C). - your child is 3 years or older and has a temperature of 103°F (39.4°C).
Seek medical care if your baby or child has a fever and:
- has difficulty breathing
- struggles to drink liquids
- is under 3 months old
- has a temperature over 104°F (40°C)
- is shivering for more than 30 minutes
- is inconsolable, especially when touched or moved
- is unable to move an arm or leg as normal
- appears dehydrated by low urine amounts, dry mouth, and no tears with crying
- has pain with urination
- appears very ill
If you feel your child should be seen by a medical professional, then trust your gut and have them checked out.
Hypothermia is a serious condition that occurs when you lose too much body heat. For adults, a body temperature that dips below 95°F (35°C) is a sign of hypothermia.
Most people associate hypothermia with being outside in cold weather for long periods of time. But hypothermia can occur indoors, too.
Babies and older adults are more susceptible. For babies, hypothermia can occur when their body temperature is 97°F (36.1°C) or lower.
Hypothermia can also be a concern in a poorly heated house in winter or an air-conditioned room in summer.
Other signs and symptoms of hypothermia include:
- shivering
- slow, shallow breath
- slurred or mumbled speech
- a weak pulse
- poor coordination or clumsiness
- low energy or sleepiness
- confusion or memory loss
- loss of consciousness
- bright red skin that’s cold to the touch (in babies)
See a doctor if you have a low body temperature with any of the symptoms above.
A fever isn’t usually a cause for concern. The fever goes away with a few days of rest most of the time.
However, seek treatment when your fever climbs too high, lasts too long, or is accompanied by more severe symptoms.
Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms. They might perform or order tests to determine the cause of the fever. Treating the cause of the fever can help your body temperature return to normal.
Treating the cause of the fever can help your body temperature return to normal.
On the other hand, a low body temperature can also cause concern. Hypothermia can be life threatening if left untreated. Seek medical assistance as soon as you notice signs of hypothermia.
Your doctor will use a standard clinical thermometer to diagnose hypothermia and check for physical signs. In addition, they may use a low-reading rectal thermometer if needed.
In some cases, your doctor may order a blood test to confirm the cause of your hypothermia or to check for infection.
In mild cases, hypothermia may be harder to diagnose but easier to treat. Heated blankets and warm fluids can restore heat. Other treatments include blood rewarming and warmed intravenous fluids for more severe cases.
Read this article in Spanish.
Thermoregulation | Definition and Patient Education
Thermoregulation refers to how the body maintains its internal temperature. If your body temperature becomes too cold or hot, it may lead to severe symptoms and even death.
Thermoregulation is a process that allows your body to maintain its core internal temperature. All thermoregulation mechanisms help return your body to homeostasis. This is a state of equilibrium.
A typical internal body temperature falls within a narrow window. The average person has a baseline temperature between 98°F (37°C) and 100°F (37.8°C). Your body has some flexibility with temperature. However, getting to the extremes of body temperature can affect your body’s ability to function.
For example, if your body temperature falls lower than 96°F (35°C) or lower, you have hypothermia. This condition can lead to cardiac arrest, brain damage, or even death.
You can experience heat stroke if your body temperature rises above 104°F (40°C). Heat stroke is considered a medical emergency. If your body temperature rises to high, you can experience brain damage or even death.
Many factors can affect your body’s temperature, such as spending time in cold or hot weather.
Factors that can raise your internal temperature include:
- fever
- exercise
- digestion
Factors that can lower your internal temperature include:
- drug use
- alcohol use
- metabolic conditions, such as an under-functioning thyroid gland
Your hypothalamus is a section of your brain that controls thermoregulation. When the hypothalamus senses your internal temperature becoming too low or high, it sends signals to your muscles, organs, glands, and nervous system. They respond in various ways to help return your temperature to its typical levels.
When your internal temperature changes, sensors in your central nervous system send messages to your hypothalamus. In response, it sends signals to various organs and systems in your body. They respond with a variety of mechanisms.
If your body needs to cool down, these mechanisms include:
- Sweating: Your sweat glands release sweat, which cools your skin as it evaporates.
 This helps lower your internal temperature.
This helps lower your internal temperature. - Vasodilatation: The blood vessels under your skin get wider. This increases blood flow to your skin where it is cooler — away from your warm inner body. This lets your body release heat through heat radiation.
If your body needs to warm up, these mechanisms include:
- Vasoconstriction: The blood vessels under your skin become narrower. This decreases blood flow to your skin, retaining heat near the warm inner body.
- Thermogenesis: Your body’s muscles, organs, and brain produce heat in various ways. For example, muscles can produce heat by shivering.
- Hormonal thermogenesis: Your thyroid gland releases hormones to increase your metabolism. This increases the energy your body creates and the amount of heat it produces.
If your internal temperature drops or rises outside of the typical range, your body will take steps to adjust it.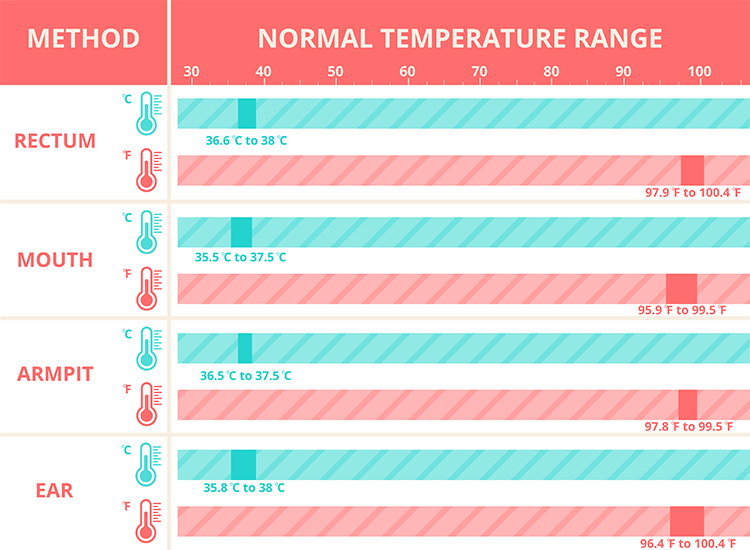 This process is known as thermoregulation. It can help you avoid or recover from potentially dangerous conditions like hypothermia.
This process is known as thermoregulation. It can help you avoid or recover from potentially dangerous conditions like hypothermia.
Normal values of body temperature in children, measurement of the child's body temperature
It is believed that a healthy child should have a body temperature of 36.6 °C. And its increase over 37 degrees is regarded as a sign of illness. But it is not so.
Body temperature depends on age and measurement area. It can increase after physical exertion, emotional arousal and feeding.
Devices and time for measuring body temperature
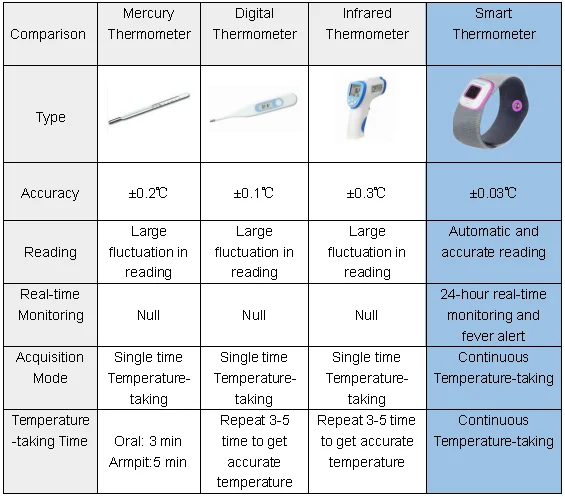
To determine the temperature, the following types of thermometers are used:
-
digital;
-
mercury;
-
infrared.
The optimal time for thermometry is 7-9 am and 17-19 pm. As prescribed by the doctor, the determination of the temperature during the day in children can be performed 3-4 times.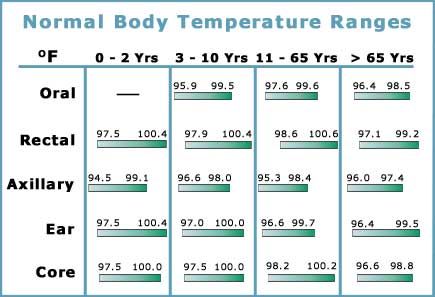
What temperature is considered normal for a child?
Immediately after the birth of a newborn, the temperature of his body decreases by 1-2 ° C, then within 24 hours it rises to 36-37 ° C. In the first 3 months of a baby's life, its indicators are unstable and depend on external factors: air temperature in the room, sleep, food intake. Normally, these fluctuations do not exceed 0.6 °C per day. For children of the first year of life, a temperature of 37.7 is the norm.
The average body temperature for a child is 37°C. Usually in the morning - 36.3 ° C, and in the evening it can rise to 37.6 ° C.
In what areas can the temperature of children be taken?
Underarm
The temperature measurement time under the arm is 5-10 minutes and depends on the type of device.
In the rectum
It is used in children under 5 years of age and in debilitated patients. For this method, it is desirable to use medical electronic thermometers with a soft tip. It will take 1-1.5 minutes to determine the rectal temperature.
It will take 1-1.5 minutes to determine the rectal temperature.
Oral
The procedure is performed both under the tongue and behind the cheek. Contraindications to the use of this method are: children under 4-5 years old, increased excitability and impaired nasal breathing. The duration of temperature measurement by the oral method is from 10 seconds to 3 minutes.
In the ear
The temperature in the ear is measured with an infrared sensor. The tip of the thermometer is inserted into the ear canal and the result appears on the display.
On forehead
Forehead temperature can be measured with a contact and non-contact thermometer. It will take 3 to 5 seconds to get the result. If the baby is sleeping or excited, then it is more convenient to use a non-contact method for measuring temperature.
Crotch
Mainly used in infants. The measurement time in the inguinal fold is 5 minutes.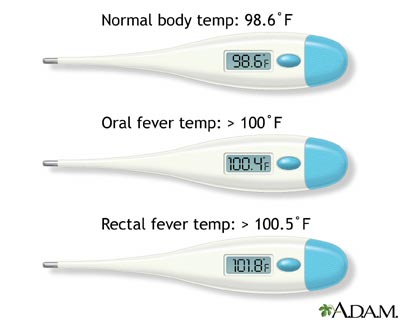 The method is inconvenient because the baby is not easy to keep in one position during this time.
The method is inconvenient because the baby is not easy to keep in one position during this time.
The ranges of normal temperature in children depending on age and measurement area are presented in the following table:
| 0-2 years | 3-10 years | 11-18 years old | |
|---|---|---|---|
| In the armpit | 34.7 - 37.2 | 35.8 - 36.6 | 35.1 - 36.8 |
| On the forehead | 36.7 - 37.5 | 36.7 - 37.5 | 36.5 - 37.4 |
| in the ear | 36.3 - 37.7 | 36.3 - 37.7 | 36.7 - 37.8 |
Temperature in a newborn baby. How to bring down?
When the temperature rises in adults, the algorithm of actions is known. But here we have a newborn baby with a hot forehead - the worries of parents are absolutely understandable: you should be especially courteous with babies.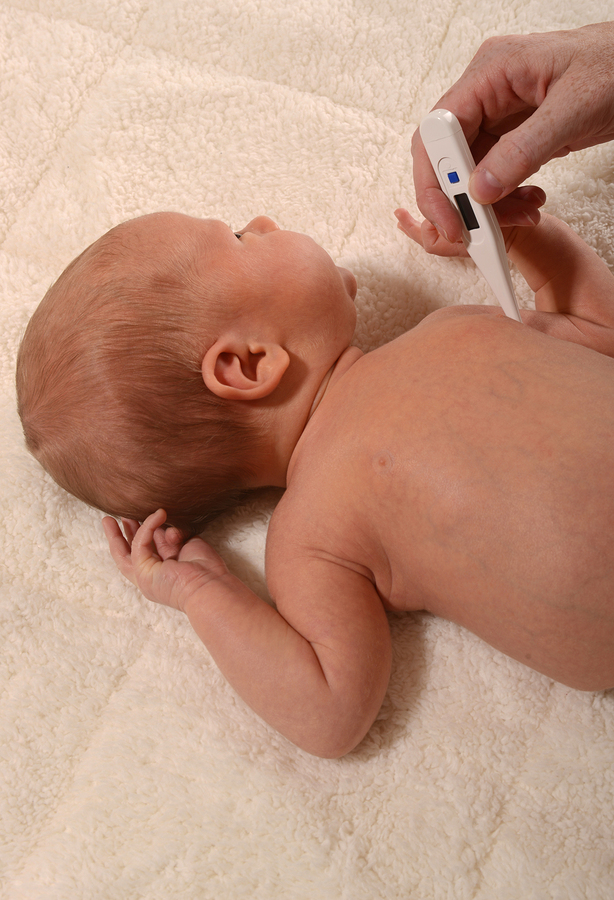 Yes, and such little ones are unable to either say, or show, or make it clear what specifically worries.
Yes, and such little ones are unable to either say, or show, or make it clear what specifically worries.
In this article, we will figure out what is the normal temperature of a newborn baby and how to measure it correctly, where it comes from and what to do for new moms and dads in general - when to sound the alarm.
What is the normal body temperature of a newborn baby?
The rise in temperature is the main indicator of the functioning of the immune system. And he does not always report the course of an infectious disease! The fact is that the thermoregulation of the body of a newborn is imperfect. It simply reacts to the general temperature of the room in which it is located.
In a child of the first year of life, the body temperature can be 36, and 36.8, and 37, and 37.5. And that's okay.
If the temperature in the room is above 25 degrees, the baby's body temperature can rise to 37. For the generally accepted 36.6 in the room where the small child is, it should not be higher than 22-23 degrees, and the baby should not be very warmly dressed.
What to do when a newborn has a temperature?
The very first thing is to undress the baby. Let it lie quietly for 15 minutes and measure the temperature again.
An increase in body temperature in a newborn baby up to 3 months old is a reason to call a pediatrician ALWAYS.
From 3 months it is reasonable to assess the situation as a whole - look at the general condition of the baby. What can they be?
- If the temperature is around 37 degrees, the child is alert and active, eats well, without unnecessary whims, then it is worth keeping calm.
- If, even at a normal body temperature of 36.8-37, the child is apathetic, refuses to eat and is naughty a lot, or vice versa - he constantly sleeps - it is definitely worth calling a pediatrician. As well as when rising above 38-38.5, even without the slightest cold symptoms (runny nose, cough), or rash (by the way, we already wrote how to treat prickly heat).
 It is better to do this without delay - within the first two days!
It is better to do this without delay - within the first two days! - Pay attention to the trembling of the limbs in the baby (febrile convulsions), or rolling of the eyes at a temperature of 37.5-37.8! This is also a signal for an immediate call to the doctor.
- If the temperature of a newborn child rises, you take certain actions: for example, physical methods of cooling (undressing, airing the room) or giving antipyretics, but within 3-4 hours the temperature does not subside. Call the pediatrician!
- Maintaining an even temperature, for example, 37.5, but for more than 5 days is another reason to consult a doctor.
- Fever above 38-39 degrees. And she always has a reason. There are 2 types of fever: white and red type.
Consider the type of fever
- White type - hot forehead, but cold hands and feet with a marble tint.
 Plus there may be chills. This is the reaction of the nervous system and blood vessels to intoxication. In this situation, it is worth giving an antipyretic, and simply rubbing the arms and legs (massage) - to restore blood supply, relieve spasm from small vessels, due to which the limbs turn pale or turn blue.
Plus there may be chills. This is the reaction of the nervous system and blood vessels to intoxication. In this situation, it is worth giving an antipyretic, and simply rubbing the arms and legs (massage) - to restore blood supply, relieve spasm from small vessels, due to which the limbs turn pale or turn blue. - Red type - the child is all over hot, wet from sweating. It is worth giving an antipyretic, wiping the baby with water, increasing heat transfer - offering more liquid.
!!! Children up to a year old cannot be rubbed with vinegar or alcohol solution, it is dangerous.
How to measure the temperature of a newborn baby?
The most famous thermometers are mercury and electronic. For all their convenience for kids, electronic thermometers are not very reliable.
Modern and safe analogue of a mercury thermometer - Galinstan. It looks the same, but instead of mercury, a mixture of liquid metals, harmless to humans.